化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (7): 3696-3709.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241250
张海丰1( ), 闫静怡1, 岳玉学2, 张子龙1, 王柏林1(
), 闫静怡1, 岳玉学2, 张子龙1, 王柏林1( ), 李小年2(
), 李小年2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-05
修回日期:2025-02-21
出版日期:2025-07-25
发布日期:2025-08-13
通讯作者:
王柏林,李小年
作者简介:张海丰(1974—),男,博士,教授,zhfeepu@163.com
基金资助:
Haifeng ZHANG1( ), Jingyi YAN1, Yuxue YUE2, Zilong ZHANG1, Bolin WANG1(
), Jingyi YAN1, Yuxue YUE2, Zilong ZHANG1, Bolin WANG1( ), Xiaonian LI2(
), Xiaonian LI2( )
)
Received:2024-11-05
Revised:2025-02-21
Online:2025-07-25
Published:2025-08-13
Contact:
Bolin WANG, Xiaonian LI
摘要:
金属氧化物纳米颗粒改性变压器油因稳定性欠佳,频繁出现绝缘性能下降的现象,表面羟基化对纳米改性变压器油绝缘性能的影响机制仍存在争议。通过溶胶-凝胶法和两步法制备三氧化钨(WO3)纳米改性变压器油。借助X射线光电子能谱(XPS)和傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)等表征分析,证实油中水分子与WO3纳米颗粒表面存在羟基化作用,结合差分电荷密度与Bader电荷计算结果验证了该过程可调控其表面局域电子态结构,优化纳米改性变压器油的绝缘性能(击穿电压可达68.50 kV)。此外,WO3纳米颗粒表面“捕获”电子以及双电层的形成进一步阐释延长弛豫时间对纳米改性变压器油电气性能的优化机理。开展热导率测试并辅以红外热成像分析,揭示了油液中固相纳米颗粒间声子热传导现象,阐明了掺杂WO3纳米颗粒提升体系导热性能的作用机制。本项工作从分子尺度上证实了变压器油体系中羟基化作用对纳米颗粒表面电子排布和重构行为的影响,可为研究纳米改性变压器油的微观机理提供参考。
中图分类号:
张海丰, 闫静怡, 岳玉学, 张子龙, 王柏林, 李小年. WO3纳米颗粒定性表面羟基化重构及其改性变压器油机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3696-3709.
Haifeng ZHANG, Jingyi YAN, Yuxue YUE, Zilong ZHANG, Bolin WANG, Xiaonian LI. Investigation of hydroxylation-induced reconstruction on WO3 surface and the modification mechanism of transformer oil[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3696-3709.
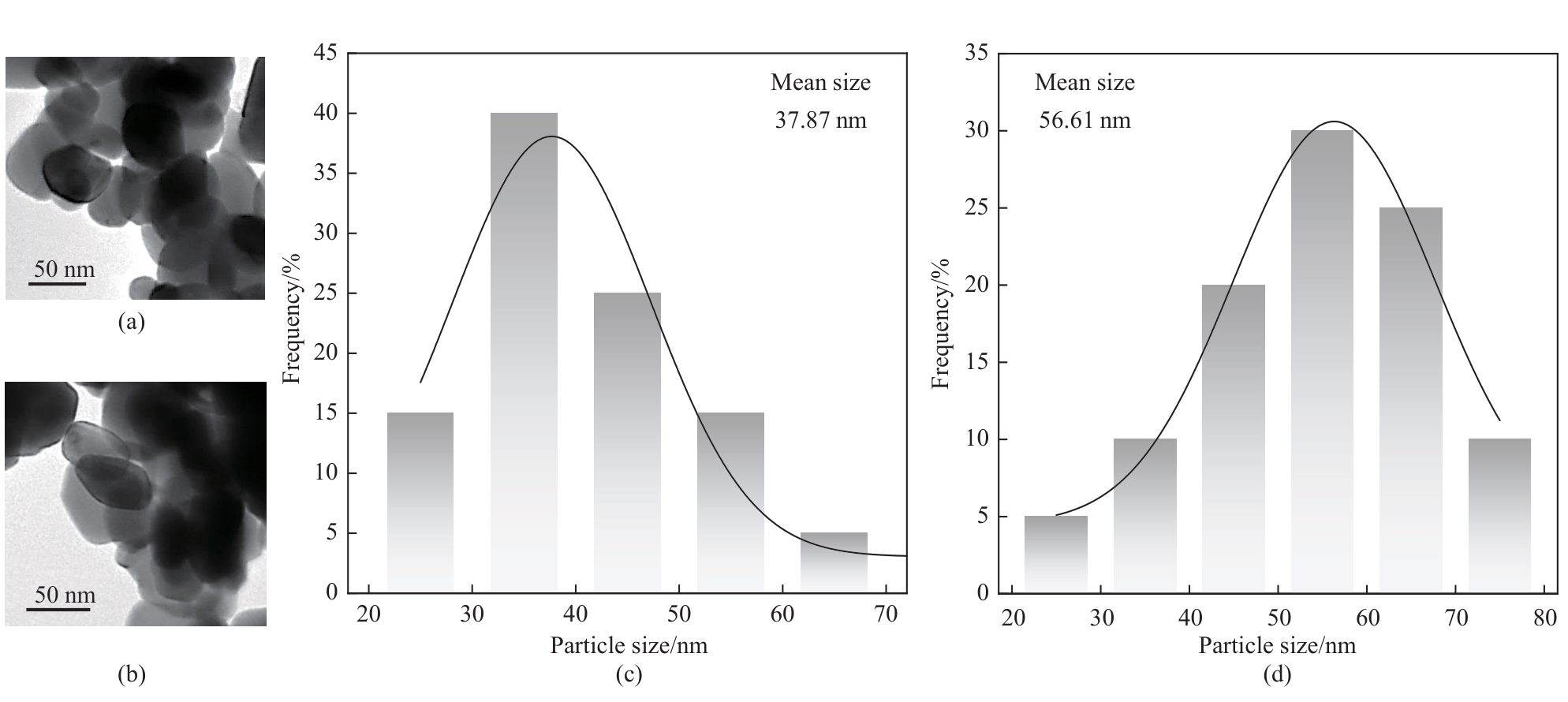
图3 WO3 NPs (a)和WO3/MO NPs (b)的TEM图;WO3 NPs (c)和WO3/MO NPs (d)的粒径分布
Fig.3 TEM images of WO3 NPs (a) and WO3/MO NPs (b); Size distribution of WO3 NPs (c) and WO3/MO NPs (d)
| Structure | Element | Bader charge/e |
|---|---|---|
| H—Oα | W | +2.640 |
| O | -1.172 | |
| H | +0.604 | |
| W—O—H | W | +2.625 |
| O | -1.363 | |
| H | +0.998 |
表1 WO3 NPs表面羟基化后的Bader电荷
Table 1 Bader charge of hydroxylation reconstruction on WO3 NPs surface
| Structure | Element | Bader charge/e |
|---|---|---|
| H—Oα | W | +2.640 |
| O | -1.172 | |
| H | +0.604 | |
| W—O—H | W | +2.625 |
| O | -1.363 | |
| H | +0.998 |
| NFs | BDV at 1%/ kV | BDV at 50%/ kV | BDV at 90%/ kV |
|---|---|---|---|
| MO | 50.49 | 50.52 | 50.55 |
| 1.0WMO | 57.28 | 57.31 | 57.34 |
| 2.5WMO | 65.19 | 65.22 | 65.25 |
| 3.0WMO | 60.29 | 60.33 | 60.36 |
| 5.0WMO | 54.47 | 54.50 | 54.53 |
| 10.0WMO | 45.34 | 45.37 | 45.40 |
表2 不同击穿概率下的交流击穿电压
Table 2 AC breakdown voltage at different breakdown probabilities of nanofluids
| NFs | BDV at 1%/ kV | BDV at 50%/ kV | BDV at 90%/ kV |
|---|---|---|---|
| MO | 50.49 | 50.52 | 50.55 |
| 1.0WMO | 57.28 | 57.31 | 57.34 |
| 2.5WMO | 65.19 | 65.22 | 65.25 |
| 3.0WMO | 60.29 | 60.33 | 60.36 |
| 5.0WMO | 54.47 | 54.50 | 54.53 |
| 10.0WMO | 45.34 | 45.37 | 45.40 |
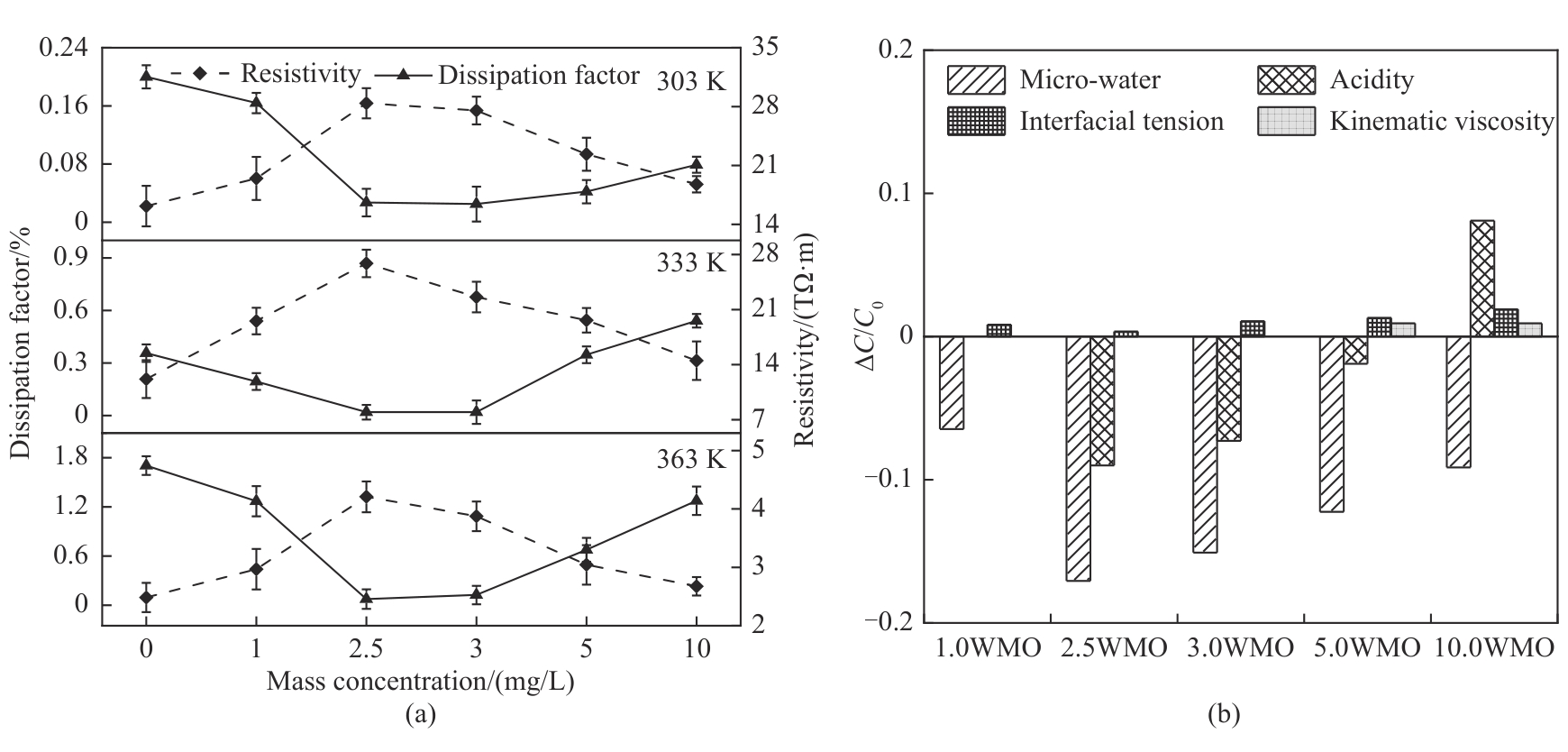
图10 纳米改性变压器油的体积电阻率与介质损耗因数(a)及理化性能数值变化率(b)
Fig.10 The dissipation factor and resistivity (a) and variation rate of physicochemical properties (b) in WO3 NFs
| [1] | Yadav A A, Hunge Y M, Kang S W. Porous nanoplate-like tungsten trioxide/reduced graphene oxide catalyst for sonocatalytic degradation and photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. Surfaces and Interfaces, 2021, 24: 101075. |
| [2] | 赵金龙, 袁杰, 田逢时, 等. 初始油温对变压器油燃烧特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(7): 3379-3386. |
| Zhao J L, Yuan J, Tian F S, et al. Effect of initial fuel temperature on burning characteristics of transformer oil[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(7): 3379-3386. | |
| [3] | Rafiq M, Shafique M, Azam A, et al. Transformer oil-based nanofluid: the application of nanomaterials on thermal, electrical and physicochemical properties of liquid insulation—a review[J]. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 2021, 12(1): 555-576. |
| [4] | Li J H, Zhang X L, Xu B, et al. Nanofluid research and applications: a review[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 127: 105543. |
| [5] | Bhunia M M, Panigrahi K, Das S, et al. Amorphous graphene-transformer oil nanofluids with superior thermal and insulating properties[J]. Carbon, 2018, 139: 1010-1019. |
| [6] | Siddique Z B, Basu S, Basak P. Dielectric behavior of natural ester based mineral oil blend dispersed with TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles as insulating fluid for transformers[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 339: 116825. |
| [7] | Aberoumand S, Jafarimoghaddam A. Tungsten (Ⅲ) oxide (WO3)-silver/transformer oil hybrid nanofluid: preparation, stability, thermal conductivity and dielectric strength[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2018, 57(1): 169-174. |
| [8] | Kadim E J, Ahmad Noorden Z, Adzis Z, et al. Surfactants effects on enhancing electrical performance of nanoparticle-based mineral transformer oil[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2023, 30(4): 1573-1581. |
| [9] | 王威望, 李盛涛, 刘文凤. 聚合物纳米复合电介质的击穿性能[J]. 电工技术学报, 2017, 32(16): 25-36. |
| Wang W W, Li S T, Liu W F. Dielectric breakdown of polymer nanocomposites[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2017, 32(16): 25-36. | |
| [10] | Lv Y Z, Ge Y, Sun Z, et al. Effect of nanoparticle morphology on pre-breakdown and breakdown properties of insulating oil-based nanofluids[J]. Nanomaterials, 2018, 8(7): 476. |
| [11] | Chen B H, Yang J H, Li H X, et al. Electrical properties enhancement of natural ester insulating oil by interfacial interaction between KH550-TiO2 and oil molecules[J]. Surfaces and Interfaces, 2023, 42: 103441. |
| [12] | Warsi A Z, Aziz F, Zulfiqar S, et al. Synthesis, characterization, photocatalysis, and antibacterial study of WO3, MXene and WO3/MXene nanocomposite[J]. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(4): 713. |
| [13] | 谢远航, 娄永, 邓君, 等. La调控WO3介电常数对摩擦纳米发电机输出的影响[J]. 科学通报, 2024, 69(14): 1957-1966. |
| Xie Y H, Lou Y, Deng J, et al. Effects of La-modulated WO3 dielectric constant on the output of a triboelectric nanogenerator[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2024, 69(14): 1957-1966. | |
| [14] | Sima W X, Shi J, Yang Q, et al. Effects of conductivity and permittivity of nanoparticle on transformer oil insulation performance: experiment and theory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2015, 22(1): 380-390. |
| [15] | Sahai A, Goswami N, Kaushik S D, et al. Cu/Cu2O/CuO nanoparticles: novel synthesis by exploding wire technique and extensive characterization[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 390: 974-983. |
| [16] | Tamura H, Mita K, Tanaka A, et al. Mechanism of hydroxylation of metal oxide surfaces[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2001, 243(1): 202-207. |
| [17] | Avramov P V, Kudin K N, Scuseria G E. Single wall carbon nanotubes density of states: comparison of experiment and theory[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2003, 370(5/6): 597-601. |
| [18] | Terohid S A A, Heidari S, Jafari A, et al. Effect of growth time on structural, morphological and electrical properties of tungsten oxide nanowire[J]. Applied Physics A, 2018, 124(8): 567. |
| [19] | Martínez T L M, Muñoz A, Pérez A, et al. The effect of support surface hydroxyls on selective CO methanation with Ru based catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2022, 641: 118678. |
| [20] | Godbole R, Vedpathak A, Godbole V, et al. Tungsten oxide thin films: detection and trapping of hazardous gases[J]. Materials Research Express, 2017, 4(7): 076401. |
| [21] | Shen X F, Garces L J, Ding Y S, et al. Behavior of H2 chemisorption on Ru/TiO2 surface and its application in evaluation of Ru particle sizes compared with TEM and XRD analyses[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2008, 335(2): 187-195. |
| [22] | Hatel R, Baitoul M. Nanostructured tungsten trioxide (WO3): synthesis, structural and morphological investigations[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2019, 1292(1): 012014. |
| [23] | 彭梦琦, 张涛, 李茂胜, 等. 光谱分频水基ZnO纳米流体制备及其热电性能调控[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(12): 5027-5037. |
| Peng M Q, Zhang T, Li M S, et al. Study on preparation and thermoelectric regulation performance of water-ZnO nanofluids for spectral-beam splitting[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(12): 5027-5037. | |
| [24] | Yue T, Han H S, Sun W, et al. Low-pH mediated goethite precipitation and nickel loss in nickel hydrometallurgy[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2016, 165: 238-243. |
| [25] | 刘娟丽, 吴蓉, 祖一丹, 等. 采用Rietveld精修, 谢乐公式以及Williamson-Hall法分析不同煅烧温度TiO2的晶粒尺寸[J]. 化工管理, 2023(13): 151-155. |
| Liu J L, Wu R, Zu Y D, et al. Crystalline size of TiO2 at calcination temperature with by rietveld ref inement, Debye-Scherrer and Williamson-Hall method[J]. Chemical Engineering Management, 2023(13): 151-155. | |
| [26] | Atahar A, Mafy N N, Rahman M M, et al. Aggregation of urea in water: dynamic light scattering analyses[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019, 294: 111612. |
| [27] | Dhanola A, Garg H C. Experimental analysis of the efficacy of vegetable oil-based nanolubricants for improving journal-bearing performance[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2021, 235(9): 1974-1991. |
| [28] | Chong S K, Dee C F, Rahman S A. Single reactor deposition of silicon/tungsten oxide core-shell heterostructure nanowires with controllable structure and optical properties[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(3): 2346-2353. |
| [29] | Aldrees A, Khan H, Alzahrani A, et al. Synthesis and characterization of tungsten trioxide (WO3) as photocatalyst against wastewater pollutants[J]. Applied Water Science, 2023, 13(7): 156. |
| [30] | Zhang Z L, Zuo F M, Cai T Z, et al. Modification of insulating oils and oil-based titanium dioxide nanofluids for transformers: a review[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2023, 25(34): 22565-22582. |
| [31] | 梁瑜, 赵彤, 赵斌彬, 等. WO3对Pt/α-Al2O3催化萘深度加氢的促进作用[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5643-5652. |
| Liang Y, Zhao T, Zhao B B, et al. Promotion of WO3 species on Pt/α-Al2O3 for the deep hydrogenation of naphthalene[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(11): 5643-5652. | |
| [32] | 王龙飞, 张亚平, 郭婉秋, 等. WO3/TiO2-ZrO2脱硝催化剂制备及其NH3活化机理[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(10): 3903-3910. |
| Wang L F, Zhang Y P, Guo W Q, et al. Preparation of WO3/TiO2-ZrO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction and mechanism of NH3 activation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(10): 3903-3910. | |
| [33] | Wang Z J, Zhong R, Lai T, et al. Preparation of UV-curable nano-WO3 coating and its infrared shielding properties[J]. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(21): 3920. |
| [34] | Plakhova T V, Romanchuk A Y, Butorin S M, et al. Towards the surface hydroxyl species in CeO2 nanoparticles[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(39): 18142-18149. |
| [35] | 张宏亮, 黄宁, 刘鹏, 等. 含水率对环氧浸渍纸低频介电弛豫过程的影响研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2025, 40(1): 312-324. |
| Zhang H L, Huang N, Liu P, et al. Effect of water content on low frequency dielectric relaxation of epoxy resin impregnated paper[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2025, 40(1): 312-324. | |
| [36] | 黄青丹, 莫文雄, 宋浩永. 植物油纸绝缘加速热老化特性研究[J]. 电工技术, 2018(2): 72-74, 76. |
| Huang Q D, Mo W X, Song H Y. Study on accelerated thermal aging characteristics of plant oil-paper insulation[J]. Electric Engineering, 2018(2): 72-74, 76. | |
| [37] | Thiviyanathan V A, Ker P J, Leong Y S, et al. Power transformer insulation system: a review on the reactions, fault detection, challenges and future prospects[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2022, 61(10): 7697-7713. |
| [38] | Tuok L P, Elkady M, Zkria A, et al. Experimental investigation of copper oxide nanofluids for enhanced oil recovery in the presence of cationic surfactant using a microfluidic model[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 488: 151011. |
| [39] | 缪金, 董明, 吴雪舟, 等. 纳米改性变压器油研究进展[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2013, 33(9): 146-154. |
| Miao J, Dong M, Wu X Z, et al. Reviews on transformer oil-based nanofluids[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2013, 33(9): 146-154. | |
| [40] | Xu F, Wang H X, Xing S Q, et al. Seeking optimized transformer oil-based nanofluids by investigation of the modification mechanism of nano-dielectrics[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2020, 8(22): 7336-7343. |
| [41] | Duzkaya H, Beroual A. Statistical analysis of AC dielectric strength of natural ester-based ZnO nanofluids[J]. Energies, 2021, 14(1): 99. |
| [42] | 张荣伦, 吴佳穗, 管紫璇, 等. 基于弛豫时间分布函数的油纸绝缘老化状态研究[J]. 绝缘材料, 2024, 57(8): 82-91. |
| Zhang R L, Wu J S, Guan Z X, et al. Research on ageing state of oil-paper insulation based on relaxation time distribution function[J]. Insulating Materials, 2024, 57(8): 82-91. | |
| [43] | 胡一卓, 董明, 谢佳成, 等. 空间电荷引起的油纸绝缘低频弛豫现象研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40(6): 2026-2038. |
| Hu Y Z, Dong M, Xie J C, et al. Study of low frequency domain relaxation of oil-paper insulation caused by space charge[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(6): 2026-2038. | |
| [44] | Hwang J G, Zahn M, O’Sullivan F M, et al. Effects of nanoparticle charging on streamer development in transformer oil-based nanofluids[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 107(1): 014310. |
| [45] | Gowtham B, Balasubramani V, Ramanathan S, et al. Dielectric relaxation, electrical conductivity measurements, electric modulus and impedance analysis of WO3 nanostructures[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 888: 161490. |
| [46] | 陈亚琦, 黄铁铁, 金桂, 等. 水热法合成的六方晶相WO3伏安特性的研究[J]. 电子元件与材料, 2013, 32(6): 31-33. |
| Chen Y Q, Huang T T, Jin G, et al. Study on the I-V characteristics of hexagonal tungsten trioxide synthesized by hydrothermal method[J]. Electronic Components and Materials, 2013, 32(6): 31-33. | |
| [47] | Coelho M F, Rivas M A, Vilão G, et al. Permittivity and electrical conductivity of copper oxide nanofluid (12 nm) in water at different temperatures[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2019, 132: 164-173. |
| [48] | Guo Z K, Ren X, Li L J, et al. Hierarchical porous electrode impedance model based on diffusion dynamics and the electrode morphology and prediction of electric double-layer structures[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2023, 6(1): 508-518. |
| [49] | Rashed A K, Mansour D E A, Rezk A, et al. Developing a novel optical sensor for condition assessment of aged mineral oil based on carbon dots[J]. Measurement, 2024, 225: 113956. |
| [50] | 邹阳, 蔡金锭. 油纸绝缘变压器时域极化谱特性实验分析[J]. 电工技术学报, 2015, 30(12): 307-313. |
| Zou Y, Cai J D. Experimental analysis on time-domain polarization spectrum of oil-paper insulation transformer[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2015, 30(12): 307-313. | |
| [51] | Samy A M, Ibrahim M E, Abd-Elhady A M, et al. On electric field distortion for breakdown mechanism of nanofilled transformer oil[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2020, 117: 105632. |
| [52] | Dhar P, Katiyar A, Maganti L S, et al. Superior dielectric breakdown strength of graphene and carbon nanotube infused nano-oils[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2016, 23(2): 943-956. |
| [53] | Liu X H, Xi S B, Kim H, et al. Restructuring highly electron-deficient metal-metal oxides for boosting stability in acidic oxygen evolution reaction[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 5676. |
| [54] | Zhang C R, Wang Y, Yan Z M, et al. Interplay between nanoparticles and water on dielectric properties of nanofluids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2019, 26(5): 1456-1462. |
| [55] | Zhang C R, Wang Y, Yan Z M, et al. Effect of the coexistence of Al2O3 nanoparticles and water on transformer oil electrical performance[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 10189-10195. |
| [56] | Malta G, Kondrat S A, Freakley S J, et al. Deactivation of a single-site gold-on-carbon acetylene hydrochlorination catalyst: an X-ray absorption and inelastic neutron scattering study[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(9): 8493-8505. |
| [57] | Wang J, Yang X, Klemeš J J, et al. A review on nanofluid stability: preparation and application[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2023, 188: 113854. |
| [58] | 慕江勇, 崔继峰, 陈小刚, 等. 微通道中一类生物流体在高Zeta势下的电渗流及传热特性[J]. 物理学报, 2024, 73(6): 161-172. |
| Mu J Y, Cui J F, Chen X G, et al. Electroosmotic flow and heat transfer characteristics of a class of biofluids in microchannels at high Zeta potential[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2024, 73(6): 161-172. | |
| [59] | 仇磊, 陈鼎, 朱莉莉, 等. 氧化石墨烯作为润滑油添加剂的分散稳定性[J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(16): 2638-2643. |
| Qiu L, Chen D, Zhu L L, et al. Dispersion stability of graphene oxide as lubricant additive[J]. Materials Reports, 2019, 33(16): 2638-2643. | |
| [60] | Nabil M F, Azmi W H, Hamid K A, et al. Experimental investigation of heat transfer and friction factor of TiO2-SiO2 nanofluids in water: ethylene glycol mixture[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 124: 1361-1369. |
| [61] | Gulzar O, Qayoum A, Gupta R. Experimental study on thermal conductivity of mono and hybrid Al2O3-TiO2 nanofluids for concentrating solar collectors[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2021, 45(3): 4370-4384. |
| [62] | Zhang H F, Zhang Z L, Yan J Y, et al. Revealing the intrinsic correlation between Cu scales and free radical chain reactions in the regulation of catalytic behaviour[J]. Molecules, 2024, 29(19): 4690. |
| [63] | Das S, Bandyopadhyay K, Ghosh M M. A study on thermal conductivity and stability of nanofluids containing chemically synthesized nanoparticles for advanced thermal applications[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2018, 27(8): 3994-4004. |
| [64] | Liu Y Z, Xu Y, Duan W H. Berry phase and topological effects of phonons[J]. National Science Review, 2018, 5(3): 314-316. |
| [65] | Oresta P, Micali F, De Risi A. Undulatory theory of phonons on the nanofluid thermal conduction[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2023, 183: 107853. |
| [1] | 刘向东, 王超, 陈永平. 基于红外热成像的脉动热管运行及传热特性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(4): 1129-1135. |
| [2] | 李红智, 罗毓珊, 王海军, 陈听宽, 熊伟, 李晨飞. 圆弧型与X型开缝翅片空气侧流动与传热特性可视化试验 [J]. 化工学报, 2008, 59(8): 1936-1941. |
| [3] | 张 锋,耿 皎,赵贤广,王志祥,张志炳. 红外热像法研究降膜流动 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2006, 25(10): 1188-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号