化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (10): 4808-4819.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20200780
收稿日期:2020-06-19
修回日期:2020-07-23
出版日期:2020-10-05
发布日期:2020-10-05
通讯作者:
樊江莉
作者简介:李晓静(1991—),女,博士研究生,基金资助:
Xiaojing LI( ),Wen SUN,Yao KANG,Jiangli FAN(
),Wen SUN,Yao KANG,Jiangli FAN( ),Xiaojun PENG
),Xiaojun PENG
Received:2020-06-19
Revised:2020-07-23
Online:2020-10-05
Published:2020-10-05
Contact:
Jiangli FAN
摘要:
PEG化的药物递送系统(DDSs)可以通过增强药物的渗透性和滞留性(EPR)效应克服传统化疗的副作用。利用共沉淀法和水热法制备纳米粒子DOX@HAP,进一步通过偶联反应修饰菁染料(Cy),通过铜(I)催化的炔-叠氮化物环加成反应修饰PEG链,构建了纳米制剂DOX@HAP-Cy-PEG。通过透射电子显微镜(TEM)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、粒度分析仪、傅里叶红外光谱仪(FTIR)、X射线光电子能谱仪(XPS)和X射线衍射仪(XRD)对该纳米载药体系的形貌、粒径、物相组成进行表征分析。利用紫外-可见(UV-Vis)分光光度法测定了该纳米材料的药物负载量以及体外药物释放曲线。进一步,利用DOX和Cy双通道荧光成像,监测DDSs在Hela和HepG2细胞中的摄取行为。表明DOX@HAP-Cy-PEG纳米载药体系有望作为一种新型的治疗与示踪一体化的抗癌纳米制剂。
中图分类号:
李晓静, 孙文, 康垚, 樊江莉, 彭孝军. PEG化羟基磷灰石纳米体系的制备及双通道荧光成像[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(10): 4808-4819.
Xiaojing LI, Wen SUN, Yao KANG, Jiangli FAN, Xiaojun PENG. Synthesis of PEGylation hydroxyapatite drug delivery system and its dual channels fluorescence imaging[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(10): 4808-4819.
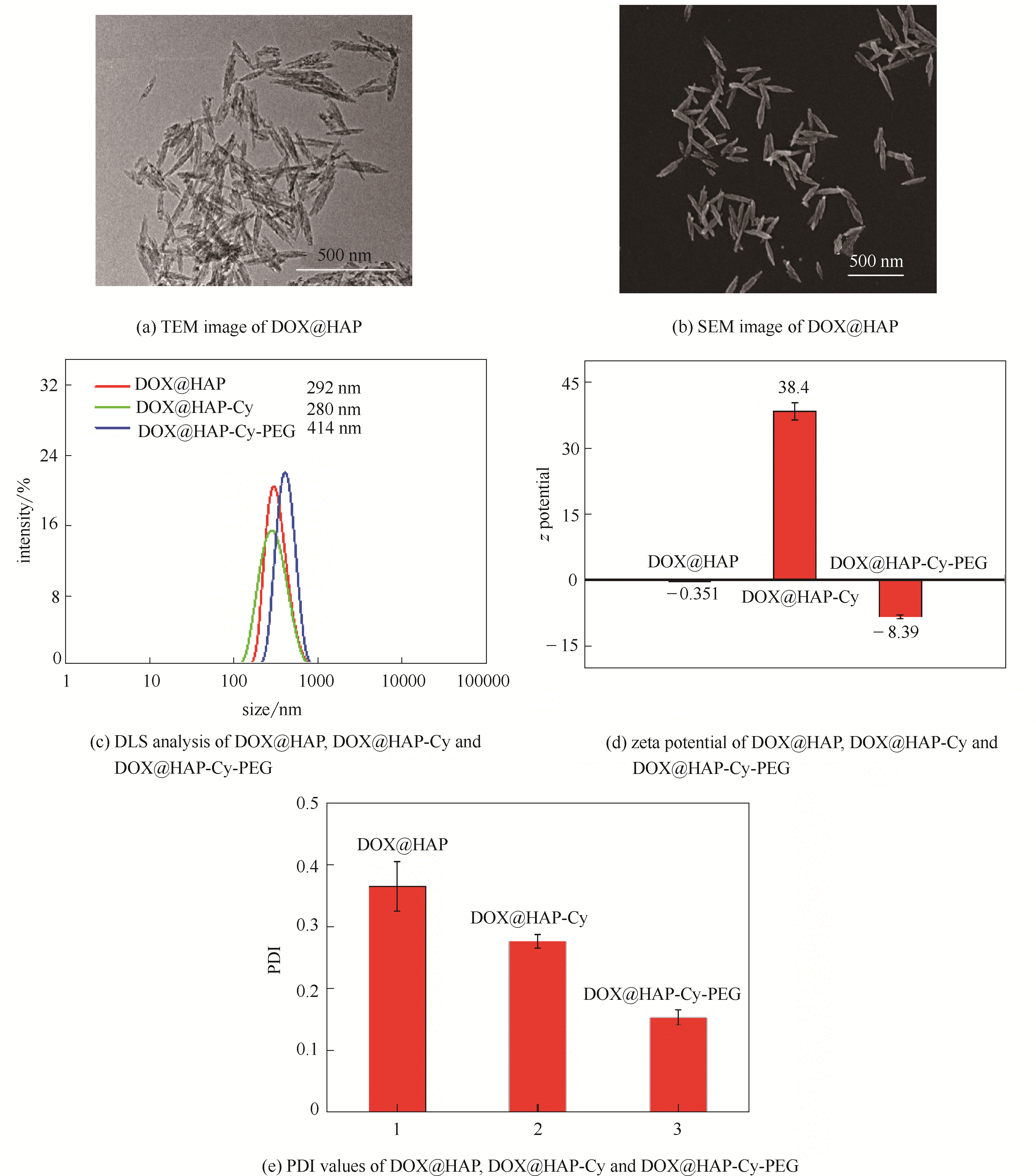
图2 DOX@HAP的TEM(a)和SEM(b)图;DOX@HAP、DOX@HAP-Cy和DOX@HAP-Cy-PEG的DLS图(c),电势电位图(d)和PDI值(e)
Fig.2 TEM (a) and SEM (b) images of DOX@HAP. DLS analysis (c), zeta potential (d) and PDI values (e) of DOX@HAP,DOX@HAP-Cy and DOX@HAP-Cy-PEG
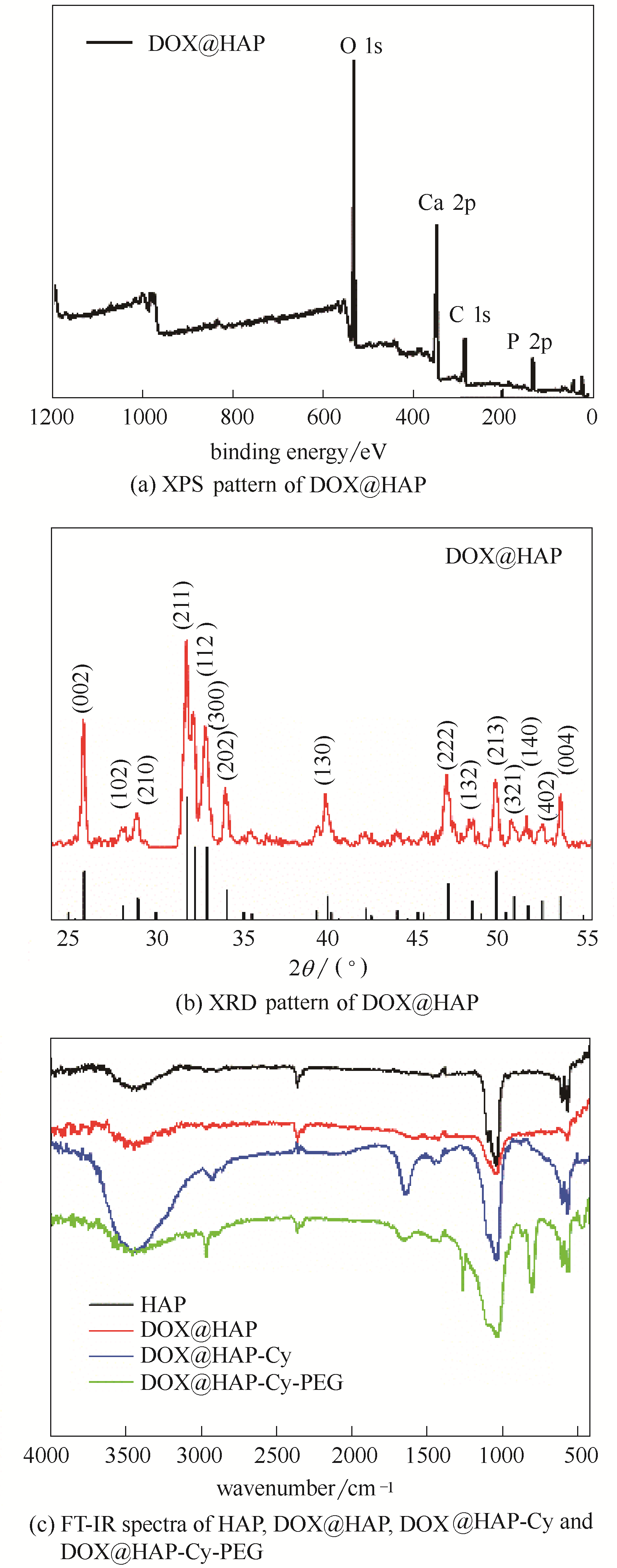
图3 DOX@HAP的XPS(a)和XRD(b)谱图;HAP、DOX@HAP,DOX@HAP-Cy和DOX@HAP-Cy-PEG的FTIR谱图(c)
Fig.3 XPS (a) and XRD (b) patterns of DOX@HAP. FTIR spectra (c) of HAP,DOX@HAP,DOX@HAP-Cy and DOX@HAP-Cy-PEG
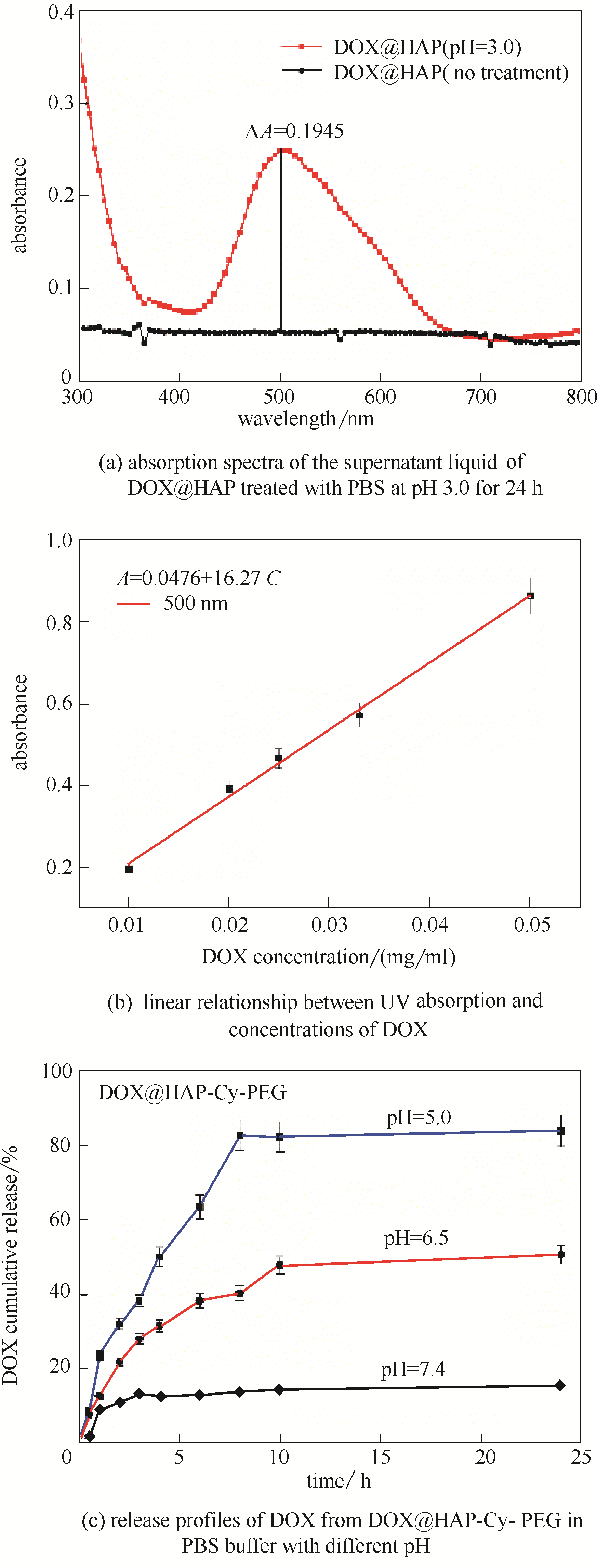
图5 在pH 3.0的 PBS条件下处理DOX@HAP 24 h后,上清液的吸收光谱(a);DOX浓度与吸光度的线性关系(b);在不同pH下,DOX@HAP-Cy-PEG中DOX的药物释放率(c)
Fig.5 The absorption spectra of the supernatant liquid of DOX@HAP treated with PBS at pH 3.0 for 24 h(a). The linear relationship between UV absorption (λab = 500 nm) and concentrations of DOX: (A = 16.27C + 0.0476)(b). Release profiles of DOX from DOX@HAP-Cy-PEG in PBS buffer with different pH (5.0,6.5,7.4) in 24 h(c)
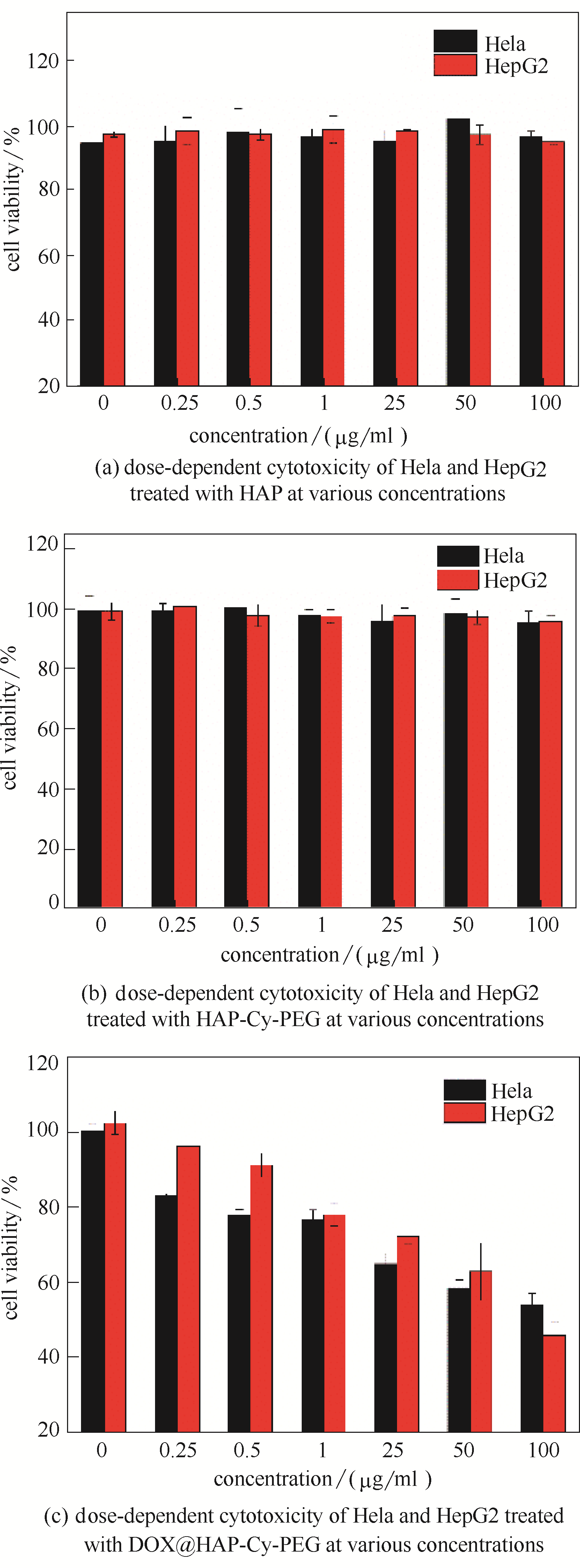
图6 不同浓度下,HAP (a)、HAP-Cy-PEG (b)和DOX@HAP-Cy-PEG (c)对Hela和HepG2细胞的毒性
Fig.6 Dose-dependent cytotoxicity of Hela and HepG2 treated with HAP (a),HAP-Cy-PEG (b) and DOX@HAP-Cy-PEG (c) at various concentrations
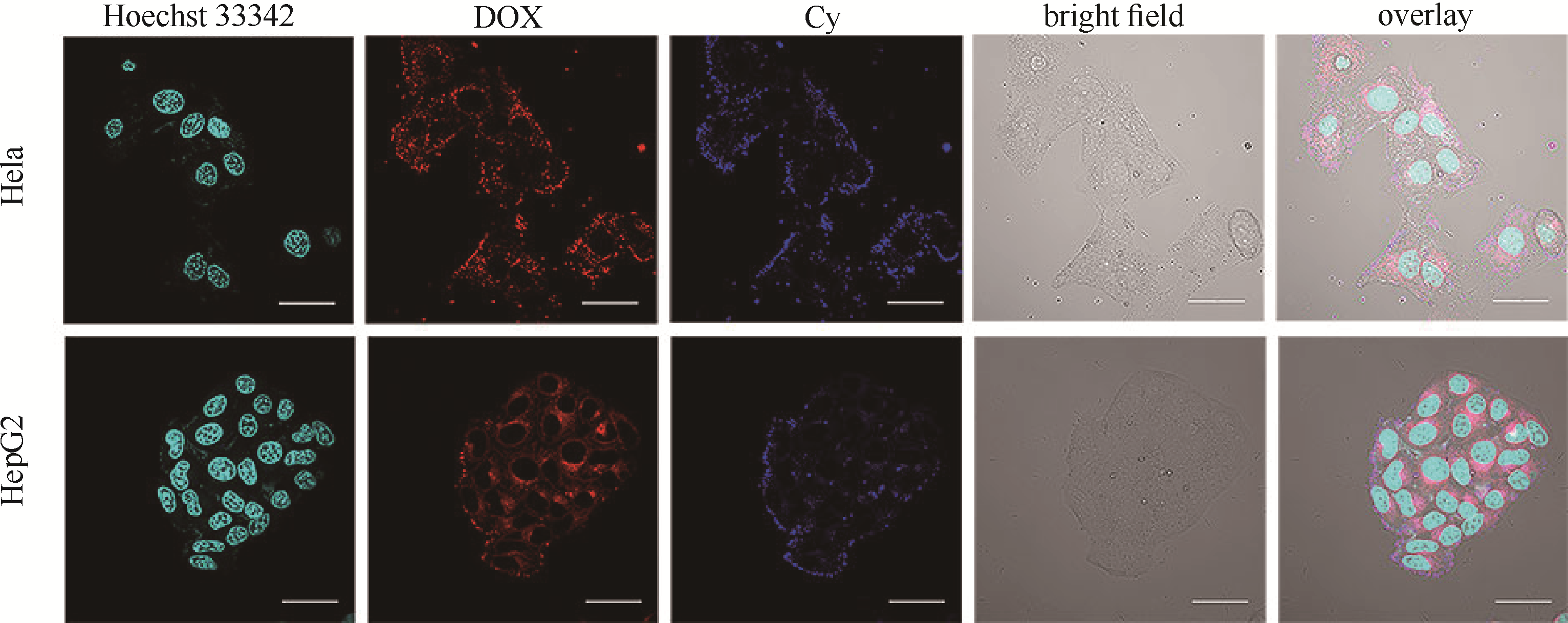
图7 DOX@HAP-Cy-PEG 在Hela和HepG2细胞中孵育4 h后,双通道荧光成像 (标尺: 400 μm)
Fig.7 CLSM images of Hela and HepG2 cells incubated with DOX@HAP-Cy-PEG for 4 h by dual channels fluorescence imaging
| Element | Peak binding energy/eV | Content/%(atom) |
|---|---|---|
| P | 132.75 | 8.96 |
| Ca | 346.88 | 14.6 |
| C | 284.49 | 27.75 |
| O | 530.89 | 48.7 |
表A1 DOX@HAP的XPS元素分析
Table A1 XPS elemental analysis of DOX@HAP
| Element | Peak binding energy/eV | Content/%(atom) |
|---|---|---|
| P | 132.75 | 8.96 |
| Ca | 346.88 | 14.6 |
| C | 284.49 | 27.75 |
| O | 530.89 | 48.7 |
| 1 | Maia A L C, Ferreira C A, Barros A L B, et al. Vincristine-loaded hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as a potential delivery system for bone cancer therapy[J]. J. Drug Target., 2018, 26(7): 592-603. |
| 2 | Kang Y, Sun W, Fan J, et al. Ratiometric real-time monitoring of hydroxyapatite–doxorubicin nanotheranostic agents for on-demand tumor targeted chemotherapy[J]. Mater. Chem. Front., 2018, 2(10): 1791-1798. |
| 3 | Salamanna F, Giavaresi G, Parrilli A, et al. Antiresorptive properties of strontium substituted and alendronate functionalized hydroxyapatite nanocrystals in an ovariectomized rat spinal arthrodesis model[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl., 2019, 95: 355-362. |
| 4 | 康垚, 王素真, 樊江莉, 等. 无机纳米药物载体在肿瘤诊疗中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(1): 128-140. |
| Kang Y, Wang S Z, Fan J L, et al. Progress in inorganic nanomedicine carriers for tumor diagnosis and treatments[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(1): 128-140 | |
| 5 | Jiang F, Wang D P, Ye S, et al. Strontium-substituted, luminescent and mesoporous hydroxyapatite microspheres for sustained drug release[J]. J Mater. Sci. Mater. Med., 2014, 25(2): 391-400. |
| 6 | Xu Y J, Dong L, Lu Y, et al. Magnetic hydroxyapatite nanoworms for magnetic resonance diagnosis of acute hepatic injury[J]. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(3): 1684-1690. |
| 7 | Abbasi Aval N, Pirayesh Islamian J, Hatamian M, et al. Doxorubicin loaded large-pore mesoporous hydroxyapatite coated superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for cancer treatment[J]. Int. J. Pharm., 2016, 509(1/2): 159-167. |
| 8 | Govindan B, Swarna Latha B, Nagamony P, et al. Designed synthesis of nanostructured magnetic hydroxyapatite based drug nanocarrier for anti-cancer drug delivery toward the treatment of human epidermoid carcinoma[J]. Nanomaterials, 2017, 7(6): 138-154. |
| 9 | Yang Y H, Liu C H, Liang Y H, et al. Hollow mesoporous hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (hmHANPs) with enhanced drug loading and pH-responsive release properties for intracellular drug delivery[J]. J. Mater. Chem. B, 2013, 1(19): 2447-2450. |
| 10 | Sarkar C, Chowdhuri A R, Kumar A, et al. One pot synthesis of carbon dots decorated carboxymethyl cellulose-hydroxyapatite nanocomposite for drug delivery, tissue engineering and Fe3+ ion sensing[J]. Carbohydr. Polym., 2018, 181: 710-718. |
| 11 | Sun W, Fan J, Wang S, et al. Biodegradable drug-loaded hydroxyapatite nanotherapeutic agent for targeted drug release in tumors[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10(9): 7832-7840. |
| 12 | Xiong H, Du S, Ni J, et al. Mitochondria and nuclei dual-targeted heterogeneous hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for enhancing therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin[J]. Biomaterials, 2016, 94: 70-83. |
| 13 | Pan L, Liu J, He Q, et al. MSN-mediated sequential vascular-to-cell nuclear-targeted drug delivery for efficient tumor regression[J]. Adv. Mater., 2014, 26(39): 6742-6748. |
| 14 | Wu J B, Shi C, Chu G C, et al. Near-infrared fluorescence heptamethine carbocyanine dyes mediate imaging and targeted drug delivery for human brain tumor[J]. Biomaterials, 2015, 67: 1-10. |
| 15 | Gorka A P, Nani R R, Zhu J, et al. A near-IR uncaging strategy based on cyanine photochemistry[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(40): 14153-14159. |
| 16 | Nani R R, Gorka A P, Nagaya T, et al. Near-IR light-mediated cleavage of antibody-drug conjugates using cyanine photocages[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54(46): 1-5. |
| 17 | Gorka A P, Yamamoto T, Zhu J, et al. Cyanine photocages enable spatial control of inducible cre-mediated recombination[J]. Chembiochem, 2018, 19(12): 1239-1243. |
| 18 | Ma K, Sai H, Wiesner U. Ultrasmall sub-10 nm near-infrared fluorescent mesoporous silica nanoparticles[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(32): 13180-13183. |
| 19 | Nissinen T, Nakki S, Laakso H, et al. Tailored dual PEGylation of inorganic porous nanocarriers for extremely long blood circulation in vivo[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8(48): 32723-32731. |
| 20 | Zhao L, Yuan W, Ang C Y, et al. Silica-polymer hybrid with self-assembled PEG corona excreted rapidly via a hepatobiliary route[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26(18): 3036-3047. |
| 21 | Su Y Y, Teng Z, Yao H, et al. A Multifunctional PB@mSiO2-PEG/DOX nanoplatform for combined photothermal- chemotherapy of tumor[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8(27): 17038-17046. |
| 22 | Ren T B, Xia W J, Dong H Q, et al. Sheddable micelles based on disulfide-linked hybrid PEG-polypeptide copolymer for intracellular drug delivery[J]. Polymer, 2011, 52(16): 3580-3586. |
| 23 | Ni R, Zhu J, Xu Z, et al. A self-assembled pH/enzyme dual-responsive prodrug with PEG deshielding for multidrug-resistant tumor therapy[J]. J. Mater. Chem. B, 2020, 8(6): 1290-1301. |
| 24 | Selli D, Motta S, Di Valentin C. Impact of surface curvature, grafting density and solvent type on the PEGylation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles[J]. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2019, 555: 519-531. |
| 25 | Zhou M, Huang H, Wang D, et al. Light-triggered PEGylation/dePEGylation of the nanocarriers for enhanced tumor penetration [J]. Nano Lett., 2019, 19(6): 3671-3675. |
| 26 | Joh D Y, Zimmers Z, Avlani M, et al. Architectural modification of conformal PEG-bottlebrush coatings minimizes anti-PEG antigenicity while preserving stealth properties[J]. Adv. Healthc. Mater., 2019, 8(8): 1801177-1801190. |
| 27 | Hammarson M, Andersson J, Li S, et al. Molecular AND-logic for dually controlled activation of a DNA-binding spiropyran[J]. Chem. Commun., 2010, 46(38): 7130-7132. |
| 28 | Kumar K, Sagar S, Esau L, et al. Synthesis of novel 1H-1,2,3-triazole tethered C-5 substituted uracil-isatin conjugates and their cytotoxic evaluation[J]. Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2012, 58: 153-159. |
| 29 | Kang N Y, Park S J, Ang X W, et al. A macrophage uptaking near-infrared chemical probe CDnir7 for in vivo imaging of inflammation[J]. Chem. Commun., 2014, 50: 6589-6591. |
| 30 | Li B, Lu L, Zhao M, et al. An efficient 1064 nm NIR-II excitation fluorescent molecular dye for deep-tissue high-resolution dynamic bioimaging[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57(25): 7483-7487. |
| 31 | Chen G, Song F, Wang J, et al. FRET spectral unmixing: a ratiometric fluorescent nanoprobe for hypochlorite[J]. Chem. Commun., 2012, 48: 2949-2951. |
| 32 | Sun W, Parowatkin M, Steffen W, et al. Ruthenium-containing block copolymer assemblies: red-light-responsive metallopolymers with tunable nanostructures for enhanced cellular uptake and anticancer phototherapy[J]. Adv. Healthc. Mater., 2016, 5(4): 467-473. |
| 33 | Zhen X, Zhang J, Huang J, et al. Macrotheranostic probe with disease-activated near-infrared fluorescence, photoacoustic, and photothermal signals for imaging-guided therapy[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57(26): 7804-7808. |
| 34 | Ha S W, Park J, Habib M M, et al. Nano-hydroxyapatite stimulation of gene expression requires Fgf receptor, phosphate transporter, and Erk1/2 signaling[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9(45): 39185-39196. |
| 35 | 任欣, 金蜀鄂, 李玉宝, 等. 纳米羟基磷灰石增强聚己内酯/明胶纤维膜的制备及其性能[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(4): 1439-1446. |
| Ren X, Jin S E, Li Y B, et al. Preparation and performance of nano-hydroxyapatite reinforced polycaprolactone/gelatin fibrous membrane for guided tissue regeneration[J]. Chem. Ind. & Eng. Pro., 2020, 39(4): 1439-1446. |
| [1] | 欧阳李科, 笪国进, 田鹏飞, 陈天元, 徐晶, 韩一帆. 羟基磷灰石负载钯催化剂用于H2和O2直接合成H2O2的动力学[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(1): 152-159. |
| [2] | 莫冬传,邹冠生,丁楠,吕树申. 双通道平板型环路热管的传热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(S1): 114-118. |
| [3] | 沈 娟,金 波,蒋琪英,胡亚敏,钟国清,霍冀川. 羟基磷灰石/合成高分子复合材料的制备方法、性能及其应用研究进展 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2011, 30(8): 1749-. |
| [4] | 杨庆, 王洁欣, 郭奋, 邵磊, 陈建峰. 微通道反应-水热晶化法制备羟基磷灰石纳米粉体 [J]. 化工学报, 2010, 61(1): 235-242. |
| [5] | 汪学军,宋国君,楼 涛,彭文娟. 聚乳酸/纳米羟基磷灰石复合纳米纤维支架的制备与表征 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2009, 28(4): 669-. |
| [6] | 李 洋;冉 旭;苟 立;冉均国. 微波合成掺锶羟基磷灰石 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2007, 26(10): 1466-. |
| [7] | 吕彩霞,姚子华. 羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖复合材料研究进展 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2006, 25(7): 755-. |
| [8] | 李俊杰,姚 晖,陈亦平,柏金根,马军阳,姚康德 . 微纳米羟基磷灰石及其复合材料研究进展 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2006, 25(6): 651-. |
| [9] | 刘海峰, 李伟锋, 陈谋志, 秦军, 许建良, 曹显奎, 于遵宏. 大液气质量流量比双通道气流式喷嘴雾化滴径 [J]. 化工学报, 2005, 56(8): 1462-1466. |
| [10] | 殷钢; 李琛; 詹劲; 袁乃驹; 刘铮. 羟基磷灰石电色谱中电渗流动与分离过程特性 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2001, 52(8): 666-672. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号