化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (2): 735-747.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20221423
贾龙菲1,2( ), 付少童2,3, 向星2,3, 张华海2, 张弢1, 王利民2,3(
), 付少童2,3, 向星2,3, 张华海2, 张弢1, 王利民2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2022-10-31
修回日期:2022-12-17
出版日期:2023-02-05
发布日期:2023-03-21
通讯作者:
王利民
作者简介:贾龙菲(1996—),女,硕士研究生,jialongfei@ipe.ac.cn
基金资助:
Longfei JIA1,2( ), Shaotong FU2,3, Xing XIANG2,3, Huahai ZHANG2, Tao ZHANG1, Limin WANG2,3(
), Shaotong FU2,3, Xing XIANG2,3, Huahai ZHANG2, Tao ZHANG1, Limin WANG2,3( )
)
Received:2022-10-31
Revised:2022-12-17
Online:2023-02-05
Published:2023-03-21
Contact:
Limin WANG
摘要:
流化床内部颗粒振动对传递过程有着重要影响。格子Boltzmann方法耦合改进的浸入运动边界法模拟了不同振幅比A/D和频率比k = fe/f0下的单颗粒振动情况,并研究了不同排布和间距的双颗粒振动对传递过程中升阻力系数以及涡脱落频率的影响。结果表明,颗粒Reynolds数Re = 100,单颗粒横向振动时,振幅增大导致锁定区间变大,颗粒锁定区间内的曳力系数大于锁定区间外,有利于传递。单颗粒流向振动,A/D = 1.50时,随振动频率增大,流体流动模式为:2S模式 → 2P模式 → 2P+2S模式 → 混沌。相同振幅下k < 1.25时,颗粒横向振动的曳力系数大于流向振动的曳力系数;k > 1.25时则与之相反。因此,当k < 1.25时,横向振动更有利于传递;k > 1.25时,流向振动更有利于传递。串联双颗粒相互抑制涡的形成使曳力系数减小,不利于传递;相反,并联双颗粒促进传递作用,且在间距H = 3D时效果最佳。以上数值结果为强化传递过程提供了一种思路。
中图分类号:
贾龙菲, 付少童, 向星, 张华海, 张弢, 王利民. 颗粒振动影响动量传递过程的格子Boltzmann方法模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 735-747.
Longfei JIA, Shaotong FU, Xing XIANG, Huahai ZHANG, Tao ZHANG, Limin WANG. Lattice Boltzmann simulations of the effect of particles movement on momentum transfer process[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 735-747.
| 文献 | Re=20 | Re=40 | Re = 100 | Re = 200 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cd | Cd | Cl | Cd | Cl | |
| [ | 2.000 | 1.498 | 1.058±0.001 | — | — | — |
| [ | 2.045 | 1.522 | 1.056 | — | — | — |
| [ | 2.190 | 1.620 | 1.330±0.014 | ±0.298 | 1.172±0.058 | ±0.668 |
| [ | 2.130 | 1.600 | 1.380±0.007 | ±0.300 | 1.290±0.022 | ±0.500 |
| [ | 2.030 | 1.520 | — | — | — | — |
| 本文结果 | 2.152 | 1.600 | 1.375±0.009 | ±0.322 | 1.370±0.045 | ±0.669 |
表1 不同Reynolds数下静止颗粒的曳力系数和升力系数
Table 1 Drag and lift coefficients of the stationary particle at different Reynolds numbers
| 文献 | Re=20 | Re=40 | Re = 100 | Re = 200 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cd | Cd | Cl | Cd | Cl | |
| [ | 2.000 | 1.498 | 1.058±0.001 | — | — | — |
| [ | 2.045 | 1.522 | 1.056 | — | — | — |
| [ | 2.190 | 1.620 | 1.330±0.014 | ±0.298 | 1.172±0.058 | ±0.668 |
| [ | 2.130 | 1.600 | 1.380±0.007 | ±0.300 | 1.290±0.022 | ±0.500 |
| [ | 2.030 | 1.520 | — | — | — | — |
| 本文结果 | 2.152 | 1.600 | 1.375±0.009 | ±0.322 | 1.370±0.045 | ±0.669 |
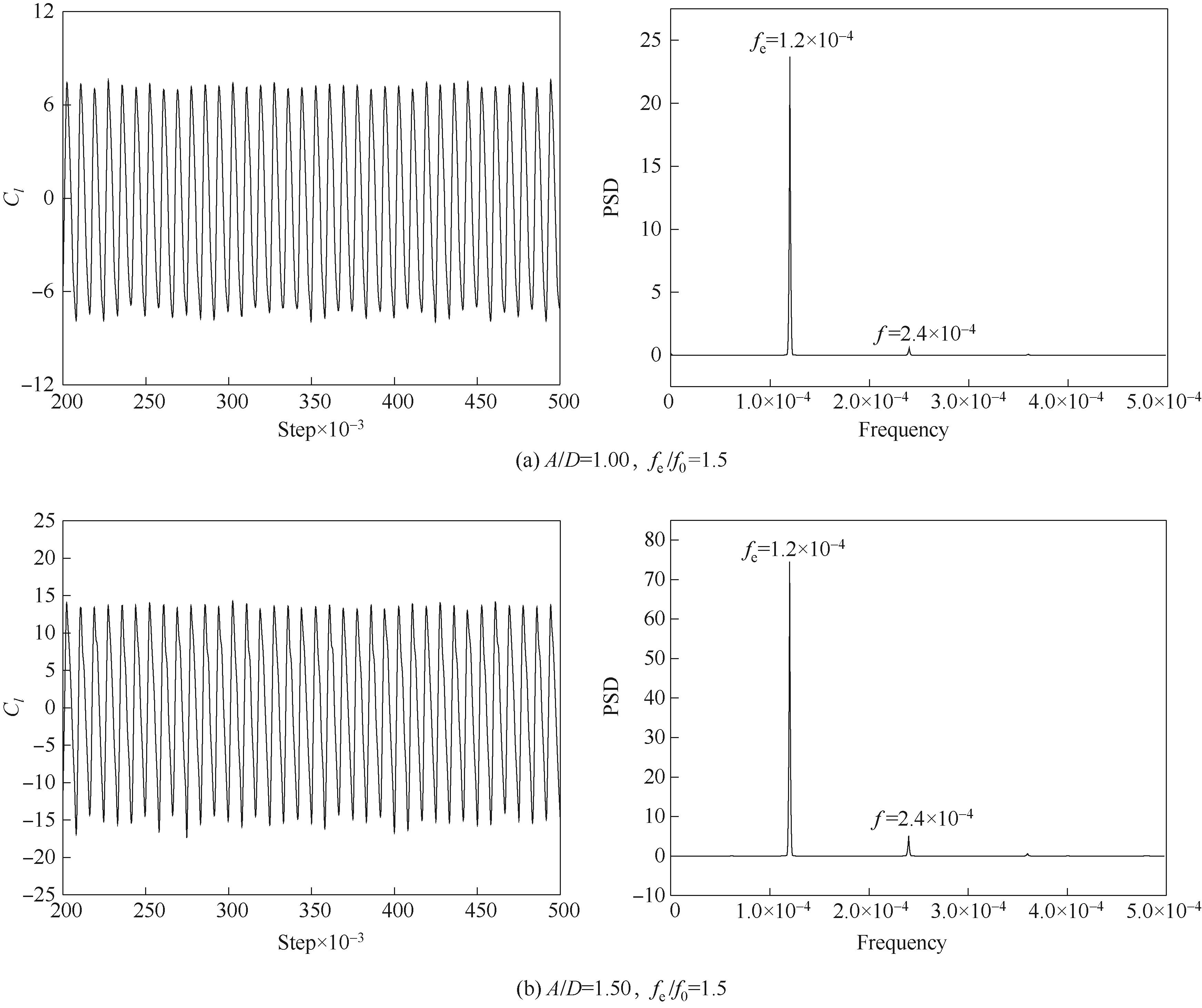
图6 横向振动颗粒升力系数历时曲线及升力系数的能量谱
Fig.6 Time series of the lift coefficients and the power spectra density of lift coefficient of transversely oscillating particle
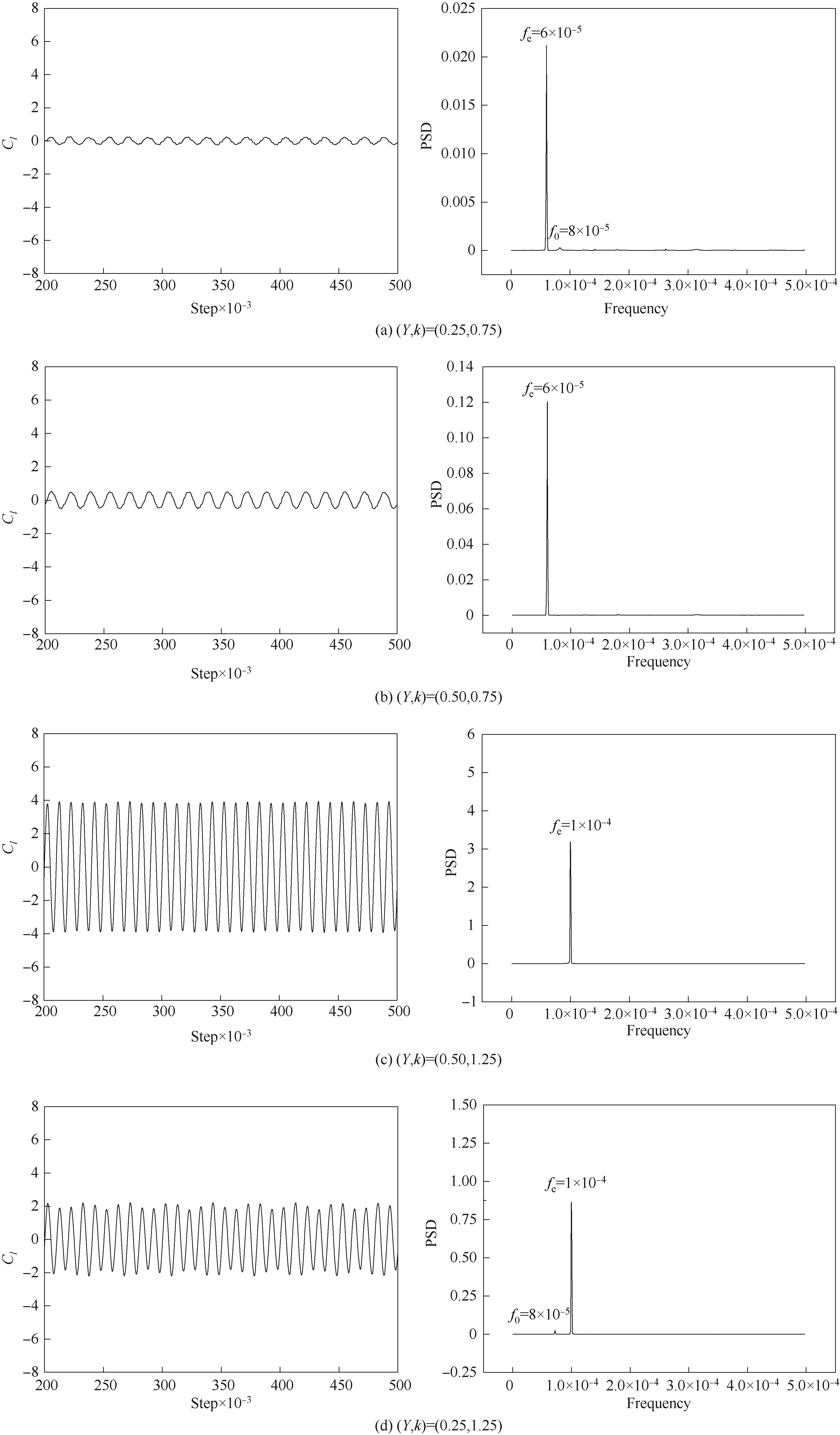
图9 横向振动颗粒不同振幅和频率下升力系数历时曲线以及能量谱
Fig.9 Time series of lift coefficients and the power spectra density at different amplitudes and frequencies for transversely oscillating particle
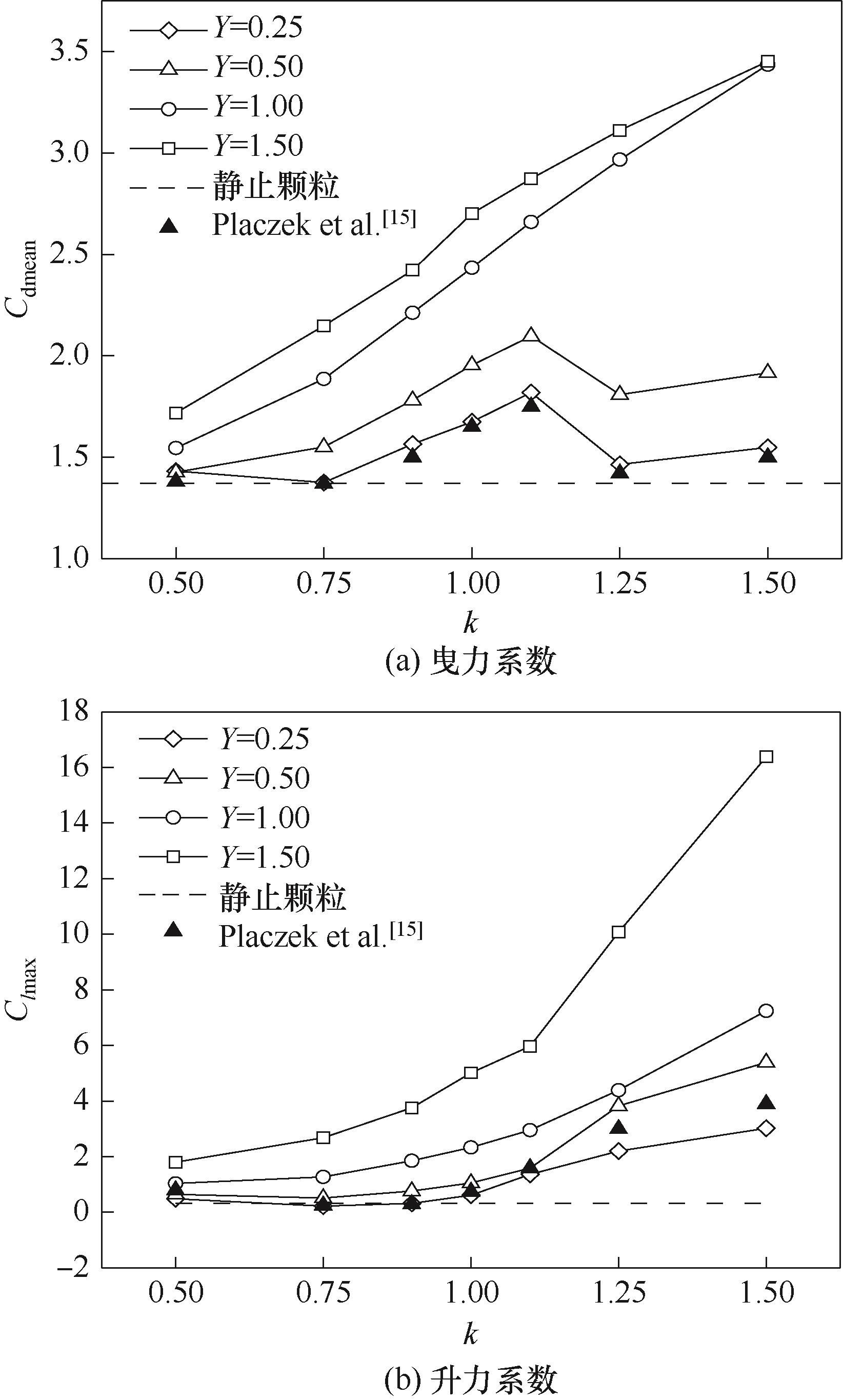
图10 横向振动颗粒曳力系数均值Cdmean和升力系数幅值Clmax随振动频率的变化
Fig.10 Variation of the mean value of drag coefficient Cdmean and the amplitude of lift coefficient Clmax with vibration frequency when particles transversely oscillating
| 1 | Dong L, Zhou E, Cai L, et al. Fluidization characteristics of a pulsing dense-phase gas-solid fluidized bed for high-density separation of fine anthracite[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2016, 30(9): 7180-7186. |
| 2 | Sahu A K, Biswal S K, Reddy P S R, et al. A study on dynamic stability of medium in air dense medium fluidised bed separator[J]. Transactions of Indian Institute of Metals, 2005, 56(1): 103-107. |
| 3 | 唐天琪, 何玉荣.磁场对湿颗粒流化床系统中介尺度结构影响机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2636-2648. |
| Tang T Q, He Y R. Effect of magnetic field on the mesoscale structure evolution process in a wet particle fluidized bed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2636-2648. | |
| 4 | Yu X, Luo Z, Li H, et al. Effect of vibration on the separation efficiency of oil shale in a compound dry separator[J]. Fuel, 2018, 214: 242-253. |
| 5 | Uwaoma R C, Strydom C A, Matjie R H, et al. Influence of density separation of selected South African coal fines on the products obtained during liquefaction using tetralin as a solvent[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(3): 1837-1849. |
| 6 | Derksen J J. Numerical simulation of solids suspension in a stirred tank[J]. AIChE Journal, 2003, 49(11): 2700-2714. |
| 7 | Sbrizzai F, Lavezzo V, Verzicco R, et al. Direct numerical simulation of turbulent particle dispersion in an unbaffled stirred-tank reactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2006, 61(9): 2843-2851. |
| 8 | Ongoren A, Rockwell D. Flow structure from an oscillating cylinder(Part 2): Mode competition in the near wake[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1988, 191: 225-245. |
| 9 | Gómez L C, Milioli F E. Numerical study on the influence of various physical parameters over the gas-solid two-phase flow in the 2D riser of a circulating fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technology, 2003, 132(2/3): 216-225. |
| 10 | 马双忱, 周权, 曹建宗, 等.湿法脱硫系统动态过程建模与仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(8): 3741-3751. |
| Ma S C, Zhou Q, Cao J Z, et al. Modeling and simulation of wet desulfurization system dynamic process[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(8): 3741-3751 | |
| 11 | 任盼锋, 海润泽, 李奇, 等. 流化床液固两相传质过程的模拟研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 1-17. |
| Ren P F, Hai R Z, Li Q, et al. Review of numerical study on liquid-solids two-phase mass transfer process in fluidized bed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(1): 1-17. | |
| 12 | 陈飞国, 葛蔚.耦合粗粒化离散颗粒法和多相物质点法的气固两相流模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2019, 19(4): 651-660. |
| Chen F G, Ge W. Coupling of coarse-grained discrete particle method and particle-in-cell method for simulation of gas-solid flow[J]. Chinese Journal Process Engineering, 2019, 19(4): 651-660. | |
| 13 | Seibert K D, Burns M A. Simulation of structural phenomena in mixed-particle fluidized beds[J]. AIChE Journal, 1998, 44(3): 528-537. |
| 14 | Blackburn H M, Henderson R D. A study of two-dimensional flow past an oscillating cylinder[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1999, 385: 255-286. |
| 15 | Placzek A, Sigrist J F, Hamdouni A. Numerical simulation of an oscillating cylinder in a cross-flow at low Reynolds number: forced and free oscillations[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2009, 38(1): 80-100. |
| 16 | Ladd A J C. Numerical simulations of particulate suspensions via a discretized Boltzmann equation(Part 1): Theoretical foundation[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1994, 271: 285-309. |
| 17 | Aidun C K, Lu Y, Ding E J. Direct analysis of particulate suspensions with inertia using the discrete Boltzmann equation[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1998, 373: 287-311. |
| 18 | Peskin C S. Numerical analysis of blood flow in the heart[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1977, 25(3): 220-252. |
| 19 | Noble D R, Torczynski J R. A lattice-Boltzmann method for partially saturated computational cells[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics C, 1998, 9(8): 1189-1201. |
| 20 | Xiong Q, Li B, Zhou G, et al. Large-scale DNS of gas-solid flows on Mole-8.5[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2012, 71: 422-430. |
| 21 | 贺睿, 乔崇智, 王利民, 等.运动颗粒对传质过程影响的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2021, 21(2): 125-133. |
| He R, Qiao C Z, Wang L M, et al. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of mass transfer process affected by a moving particle[J]. Chinese Journal Process Engineering, 2021, 21(2): 125-133. | |
| 22 | He X, Zou Q, Luo L S, et al. Analytic solutions of simple flows and analysis of nonslip boundary conditions for the lattice Boltzmann BGK model[J]. Journal of Statistical Physics, 1997, 87(1): 115-136. |
| 23 | 付少童, 贾龙菲, 王利民. 一种改进的浸入运动边界算法[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2022, DOI: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2022.0067 . |
| Fu S T, Jia L F, Wang L M. An improved algorithm for immersed moving boundary[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2022, DOI: 10.7638/kqdlxxb-2022.0067 . | |
| 24 | Hassan R. The lift and drag forces on a circular cylinder oscillating in a flowing fluid[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, 1964, 277(1368): 51-75. |
| 25 | Koopmann G H. The vortex wakes of vibrating cylinders at low Reynolds numbers[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1967, 28(3): 501-512. |
| 26 | Biermann D, Herrnstein W H. The interference between struts in various combinations[R]. National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics Collection, 1934. |
| 27 | Williamson C H K. Evolution of a single wake behind a pair of bluff bodies[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1985, 159: 1-18. |
| 28 | Spivack H M. Vortex frequency and flow pattern in the wake of two parallel cylinders at varied spacing normal to an air stream[J]. Journal of the Aeronautical Sciences, 1946, 13(6): 289-301. |
| 29 | Zdravkovich M M. Review of flow interference between two circular cylinders in various arrangements[J]. Journal of Fluid Engineering, 1977: 618-633. |
| 30 | Bhatnagar P L, Gross E P, Krook M. A model for collision processes in gases(Ⅰ): Small amplitude processes in charged and neutral one-component systems[J]. Physical Review, 1954, 94(3): 511-525. |
| 31 | Qian Y H, d'Humières D, Lallemand P. Lattice BGK models for Navier-Stokes equation[J]. Europhysics Letters, 1992, 17(6): 479-484. |
| 32 | Bouzidi M, Firdaouss M, Lallemand P. Momentum transfer of a Boltzmann-lattice fluid with boundaries[J]. Physics of fluids, 2001, 13(11): 3452-3459. |
| 33 | Filippova O, Hänel D. Grid refinement for lattice-BGK models[J]. Journal of computational Physics, 1998, 147(1): 219-228. |
| 34 | Lallemand P, Luo L S. Lattice Boltzmann method for moving boundaries[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2003, 184(2): 406-421. |
| 35 | Zou Q, He X. On pressure and velocity boundary conditions for the lattice Boltzmann BGK model[J]. Physics of Fluids, 1997, 9(6): 1591-1598. |
| 36 | Sumer B M. Hydrodynamics Around Cylindrical Strucures[M]. Singapore: World Scientific, 2006. |
| 37 | Fornberg B. A numerical study of steady viscous flow past a circular cylinder[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1980, 98(4): 819-855. |
| 38 | Dennis S C R, Chang G Z. Numerical solutions for steady flow past a circular cylinder at Reynolds numbers up to 100[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1970, 42(3): 471-489. |
| 39 | Calhoun D. A Cartesian grid method for solving the two-dimensional streamfunction-vorticity equations in irregular regions[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2002, 176(2): 231-275. |
| 40 | Russell D, Wang Z J. A Cartesian grid method for modeling multiple moving objects in 2D incompressible viscous flow[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2003, 191(1): 177-205. |
| 41 | Ye T, Mittal R, Udaykumar H S, et al. An accurate Cartesian grid method for viscous incompressible flows with complex immersed boundaries[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1999, 156(2): 209-240. |
| 42 | 龚帅, 郭照立.横向振荡圆柱绕流的格子Boltzmann方法模拟[J]. 力学学报, 2011, 43(5): 809-818. |
| Gong S, Guo Z L. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of the flow around a circular cylinder oscillating transversely [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2011, 43(5): 809-818. | |
| 43 | 龚帅, 郭照立.流向振荡圆柱绕流的格子Boltzmann方法模拟[J]. 力学学报, 2011, 43(1): 11-17. |
| Gong S, Guo Z L. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of the flow around a circular cylinder oscillating streamwisely [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2011, 43(1): 11-17. | |
| 44 | Haussmann M, Hafen N, Raichle F, et al. Galilean invariance study on different lattice Boltzmann fluid-solid interface approaches for vortex-induced vibrations[J]. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 2020, 80(5): 671-691. |
| 45 | Williamson C H K, Roshko A. Vortex formation in the wake of an oscillating cylinder[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 1988, 2(4): 355-381. |
| 46 | Singh S P, Mittal S. Vortex-induced oscillations at low Reynolds numbers: hysteresis and vortex-shedding modes[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2005, 20(8): 1085-1104. |
| 47 | Kumar S, Navrose, Mittal S. Lock-in in forced vibration of a circular cylinder[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2016, 28(11): 113605. |
| [1] | 代佳琳, 毕唯东, 雍玉梅, 陈文强, 莫晗旸, 孙兵, 杨超. 热物性对混合型CPCMs固液相变特性影响模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1914-1927. |
| [2] | 刘学文, 李金京, 全晓军, 熊伟. 单个固体颗粒促进薄液膜破裂的格子Boltzmann研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(7): 3091-3097. |
| [3] | 周毓佳, 赵陈儒, 薄涵亮. 气泡曳力系数模型分区研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(S2): 108-116. |
| [4] | 王鑫, 杨斌鑫. 耦合格子Boltzmann的聚合物结晶相场方法[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(S2): 193-199. |
| [5] | 李斌, 张尚彬, 张磊, 滕昭钰, 王佑天. 基于LBM-DEM的鼓泡床内气泡-颗粒动力学数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(9): 3843-3850. |
| [6] | 刘冰冰, 王明雨, 高洪涛, 张少君. 高气液密度比的传热相变复合模型[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(8): 3418-3427. |
| [7] | 林琦, 王树刚, 王继红, 宋双林. 球形胶囊内约束熔化过程的LBM模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(6): 2373-2379. |
| [8] | 杨晨, 何航行. 气液两相分离的免方程多尺度模拟方法[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(6): 2031-2040. |
| [9] | 阚安康, 康利云, 曹丹, 王冲. 基于Lattice-Boltzmann方法的纳米颗粒多孔介质导热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(11): 4412-4417. |
| [10] | 李超, 吴慧英, 黄荣宗. 电场作用下液滴分裂动力学行为的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(8): 2882-2888. |
| [11] | 付宇航, 赵述芳, 王文坦, 金涌, 程易. 多相/多组分LBM模型及其在微流体领域的应用[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(7): 2535-2543. |
| [12] | 王帅, 刘国栋, 赵飞翔, 张清红, 陆慧林. 循环流化床中颗粒聚团特性的模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(6): 2027-2033. |
| [13] | 朱卫兵, 王猛, 陈宏, 韩丁, 刘建文. 多孔介质内流体流动的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(S1): 33-40. |
| [14] | 付博, 袁希钢, 张会书, 余国琮. 伴有Rayleigh对流的气液传质理论[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(S1): 21-25. |
| [15] | 孙涛, 李维仲, 杨柏丞, 祝普庆. 气泡群上升过程相互作用的格子 Boltzmann三维数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(5): 1586-1591. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号