化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (5): 1914-1927.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230070
代佳琳1,2( ), 毕唯东3, 雍玉梅1(
), 毕唯东3, 雍玉梅1( ), 陈文强1,2, 莫晗旸1,4, 孙兵5, 杨超1,2(
), 陈文强1,2, 莫晗旸1,4, 孙兵5, 杨超1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2023-02-02
修回日期:2023-04-19
出版日期:2023-05-05
发布日期:2023-06-29
通讯作者:
雍玉梅,杨超
作者简介:代佳琳(1999—),女,硕士研究生,daijialin20@ipe.ac.cn
基金资助:
Jialin DAI1,2( ), Weidong BI3, Yumei YONG1(
), Weidong BI3, Yumei YONG1( ), Wenqiang CHEN1,2, Hanyang MO1,4, Bing SUN5, Chao YANG1,2(
), Wenqiang CHEN1,2, Hanyang MO1,4, Bing SUN5, Chao YANG1,2( )
)
Received:2023-02-02
Revised:2023-04-19
Online:2023-05-05
Published:2023-06-29
Contact:
Yumei YONG, Chao YANG
摘要:
只有掌握基底和相变材料(PCMs)的热物性对换热特性的影响,才能准确描述混合型复合相变材料(CPCMs)储热性能及有效利用CPCMs。基于双分布(DDF)格子Boltzmann模型,验证并模拟了不同基底和PCMs固、液相的比热容和热扩散系数条件下混合型CPCMs的相变换热、流动过程,归纳其对相变速率储热的影响规律。结果表明:PCMs内液体环流的自然对流换热对总的换热过程起到促进作用。基材的比热容越大,相变速率越快,能够获得更大储热量;提高基材热扩散系数有利于提高相变速率。固相PCMs比热容越小,相变速率越快,但固、液相变界面越厚,相变越不稳定,所以如果期望得到更高的相变速率可选择固相小于液相比热容的PCMs,但如果更加看重相变的稳定性优先选择固相大于液相比热容的PCMs。
中图分类号:
代佳琳, 毕唯东, 雍玉梅, 陈文强, 莫晗旸, 孙兵, 杨超. 热物性对混合型CPCMs固液相变特性影响模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1914-1927.
Jialin DAI, Weidong BI, Yumei YONG, Wenqiang CHEN, Hanyang MO, Bing SUN, Chao YANG. Effect of thermophysical properties on the heat transfer characteristics of solid-liquid phase change for composite PCMs[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1914-1927.
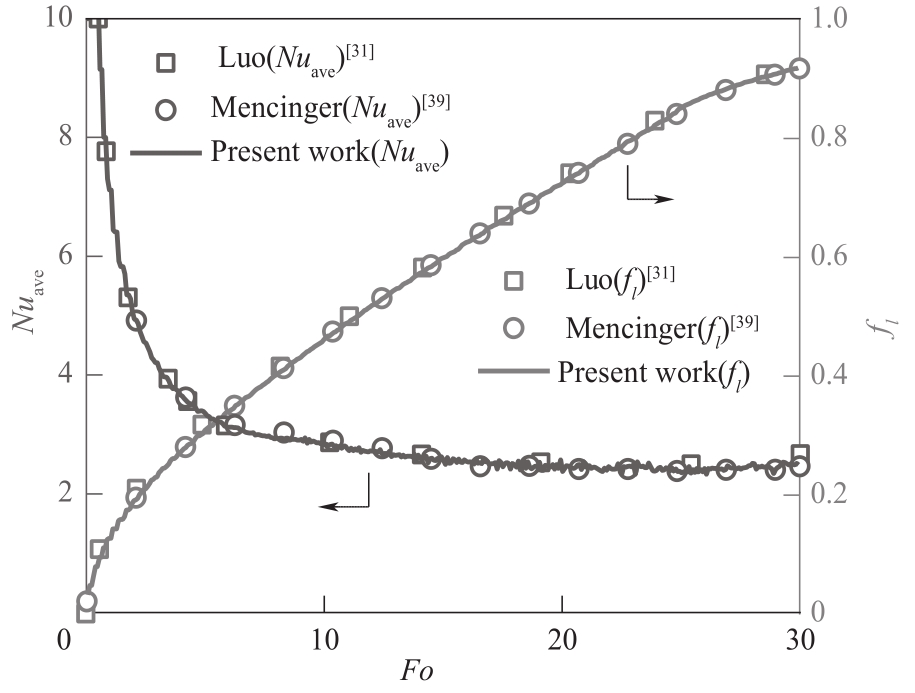
图3 相变模型及程序的验证(Ra=2.5×104,Pr=0.02,St=0.01)
Fig.3 Verification of the correctness of the model and the validity of the code(Ra=2.5×104, Pr=0.02, St=0.01)
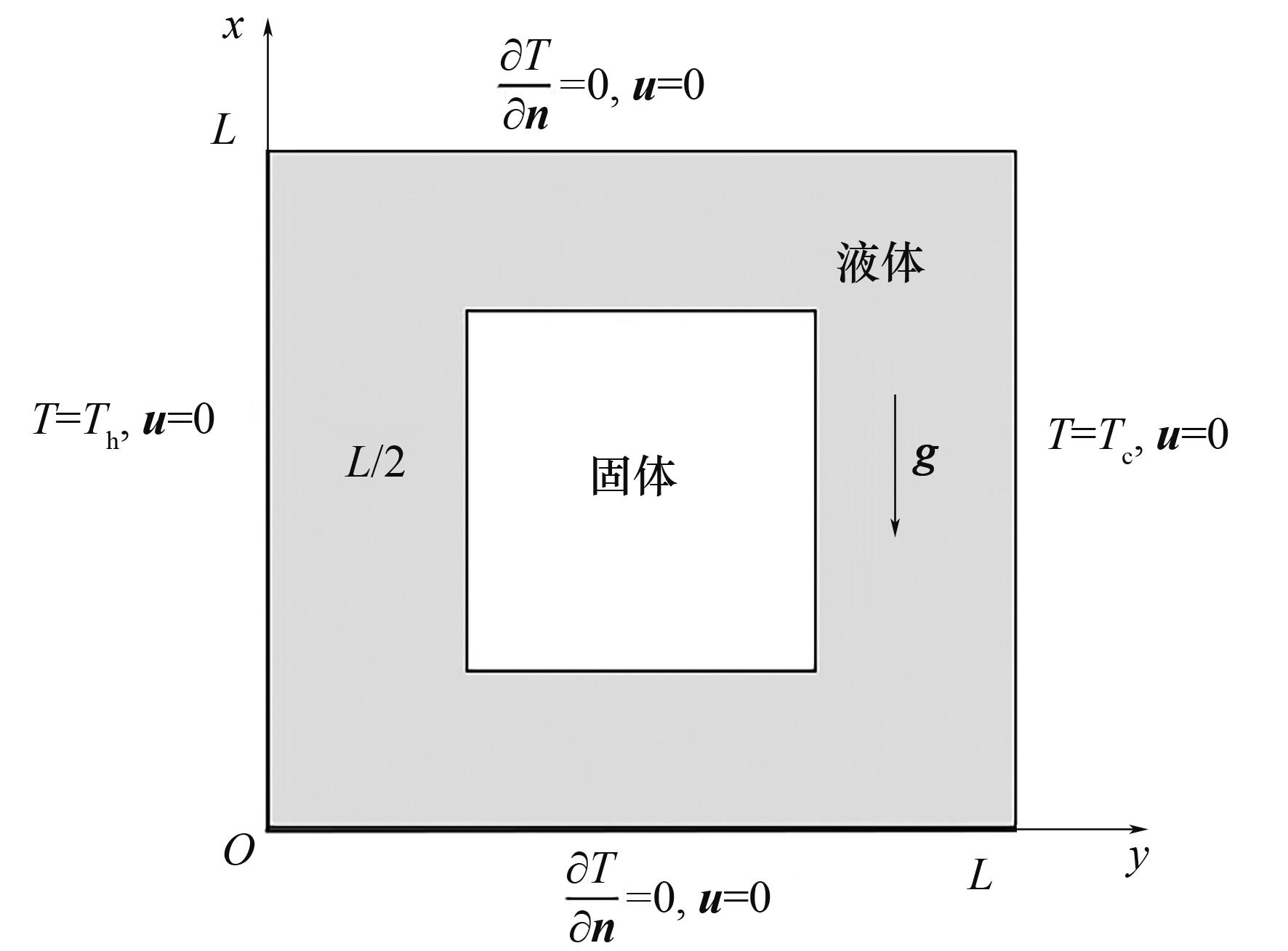
图4 自然对流作用下流固耦合问题计算域选取及边界条件设定示意图(Pr=0.71)
Fig.4 Description of the computing domain and boundary conditions for the fluid-solid coupling problems under natural covection(Pr=0.71)
| Ra | 本文Nuave结果 | 文献Nuave结果 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref.[ | 相对误差/% | Ref.[ | 相对误差/% | ||
| 1×103 | 1.423 | 1.432 | -0.628 | 1.424 | -0.070 |
| 1×104 | 1.757 | 1.768 | -0.626 | 1.771 | -0.791 |
| 1×105 | 4.234 | 4.308 | -1.718 | 4.324 | -2.081 |
| 1×106 | 8.362 | 8.605 | -2.824 | 8.597 | -2.734 |
表1 自然对流作用下的流固耦合验证结果
Table 1 Verification results of fluid-solid coupling problems under natural covection
| Ra | 本文Nuave结果 | 文献Nuave结果 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref.[ | 相对误差/% | Ref.[ | 相对误差/% | ||
| 1×103 | 1.423 | 1.432 | -0.628 | 1.424 | -0.070 |
| 1×104 | 1.757 | 1.768 | -0.626 | 1.771 | -0.791 |
| 1×105 | 4.234 | 4.308 | -1.718 | 4.324 | -2.081 |
| 1×106 | 8.362 | 8.605 | -2.824 | 8.597 | -2.734 |
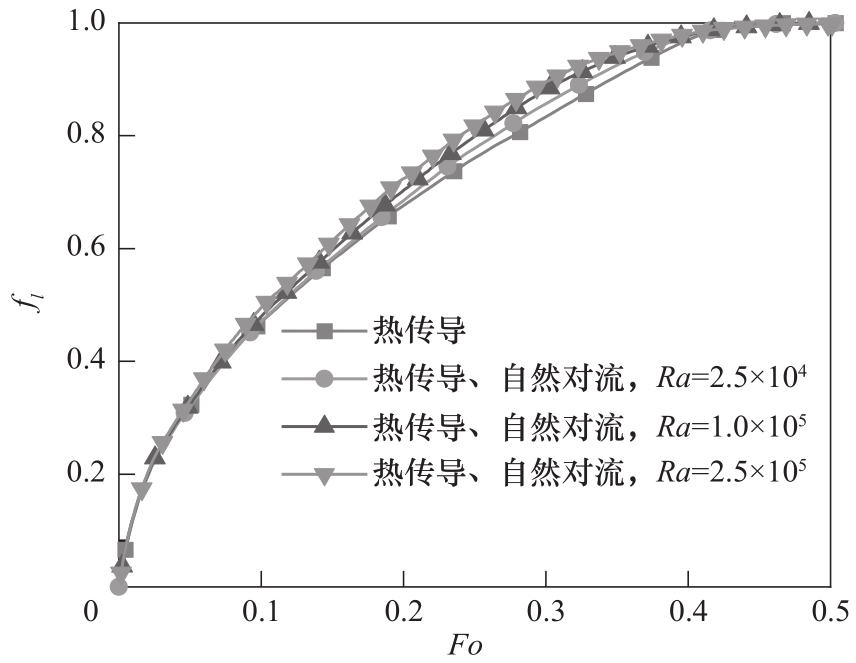
图5 热传导与额外考虑自然对流的不同Ra条件下相变过程中的液相体积分数的对比(Pr=0.1,St=1,Rcp=Rs=Rfcp=Rfs=1)
Fig. 5 Volume fraction of the liquid phase in the process of heat transfer by conduction versus phase change considering natural convection(Pr=0.1, St=1, Rcp=Rs=Rfcp=Rfs=1)
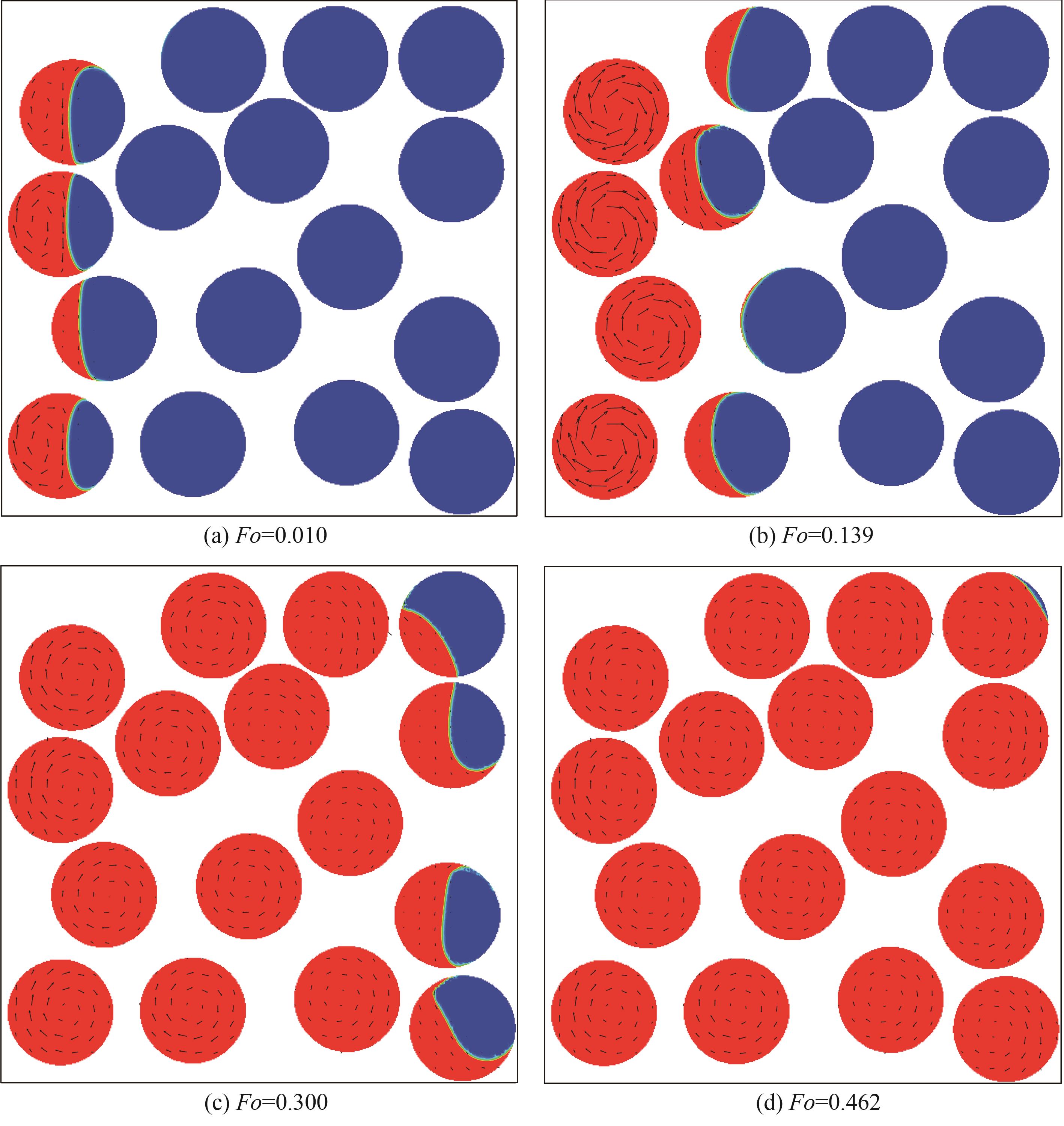
图6 随时间变化CPCMs液相体积分数分布和速度矢量分布(Ra=2.5×104, Pr=0.1, St=1, Rcp=Rs=Rfcp=Rfs=1)
Fig.6 Liquid volume fraction distribution and velocity vector distribution of CPCMs with time(Ra=2.5×104, Pr=0.1, St=1, Rcp=Rs=Rfcp=Rfs=1)
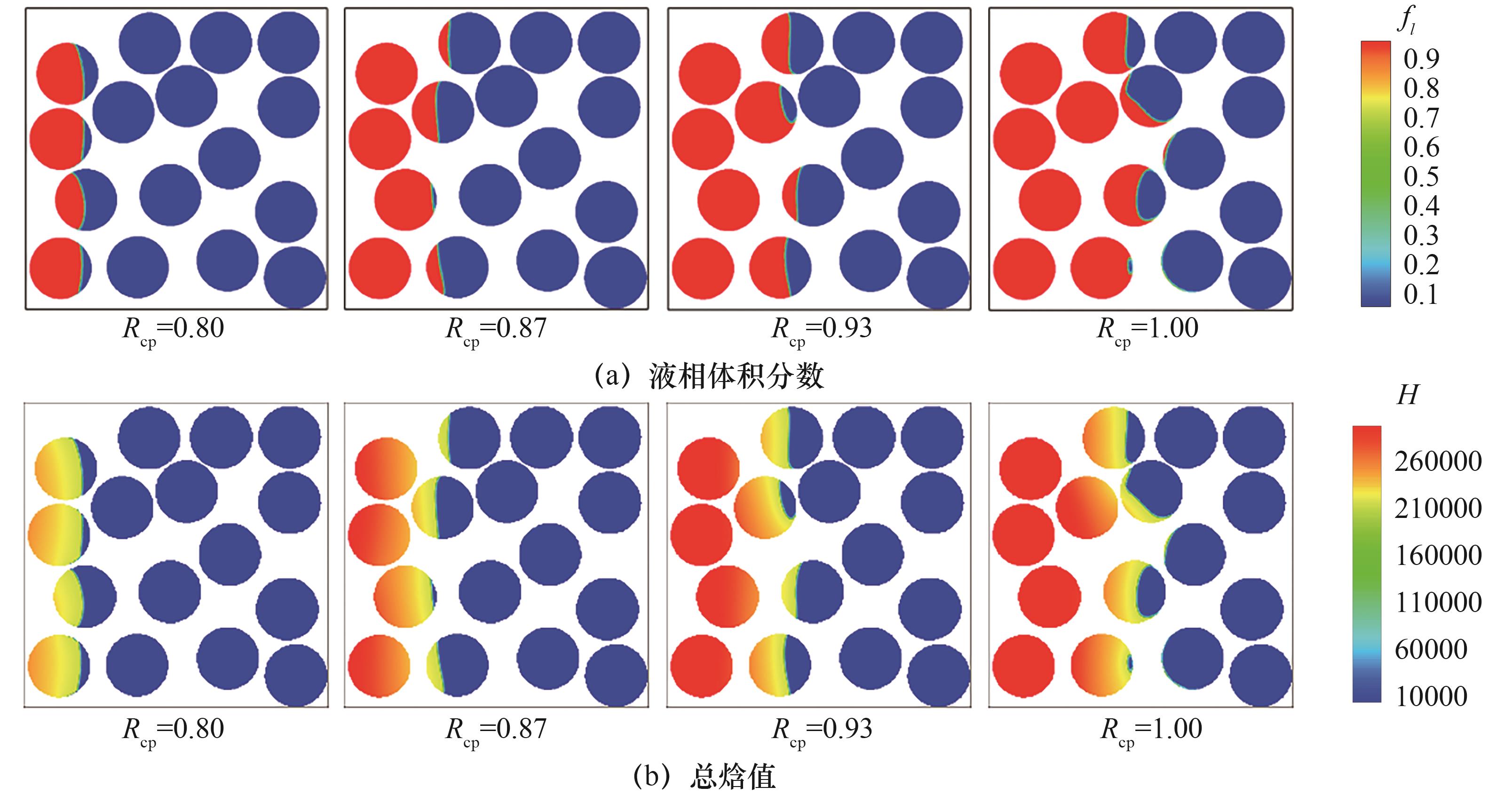
图7 不同基材与PCMs的比热容下液相体积分数和焓值分布(Ra=2.5×104,Pr=0.1,St=1,Rs=Rcp=Rfs=1,Fo=0.1)
Fig.7 Distribution of liquid volume fraction and enthalpy under different specific heat capacities of base and PCMs(Ra=2.5×104, Pr=0.1, St=1, Rs=Rfcp=Rfs=1, Fo=0.1)
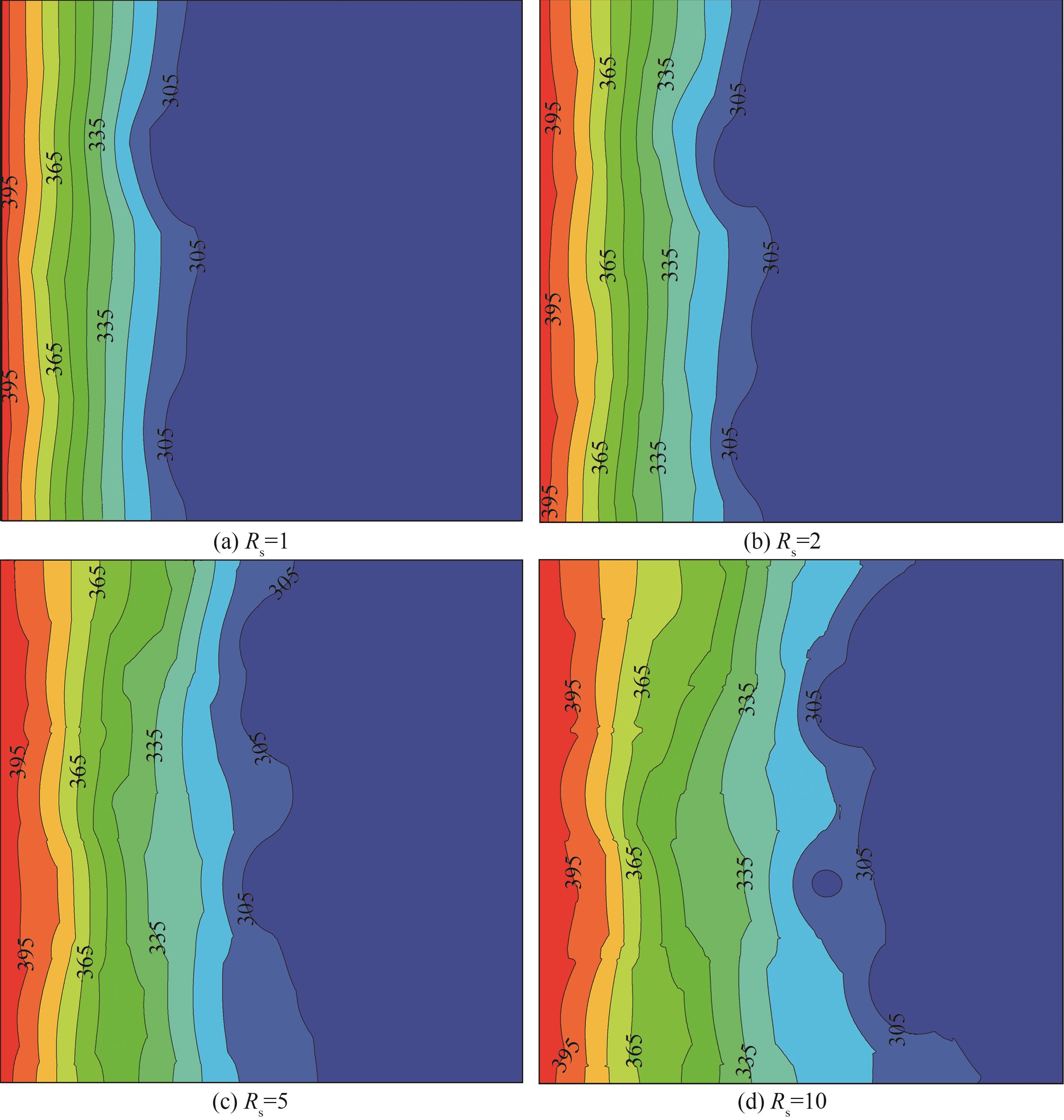
图9 不同基材与PCMs的热扩散系数比下温度分布(Ra=2.5×104,Pr=0.1,St=1,Rcp=Rfcp=Rfs=1,Fo=0.05)
Fig.9 Temperature distribution at different ratios of thermal conductivity coefficient of substrate to PCMs(Ra=2.5×104, Pr=0.1, St=1, Rcp=Rfcp=Rfs=1, Fo=0.05)

图10 不同Rs下平均焓值随Fo的变化(Ra=2.5×104,Pr=0.1,St=1,Rcp=Rfcp=Rfs=1)
Fig.10 Average enthalpy versusFo for different Rs(Ra=2.5×104, Pr=0.1, St=1, Rcp=Rfcp=Rfs=1)
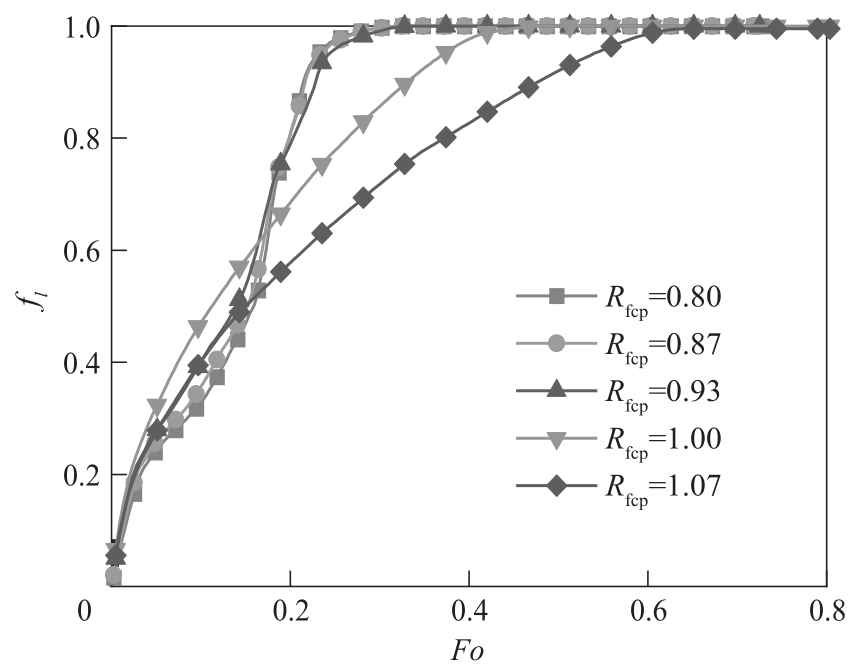
图11 不同固相PCMs比热容下液相体积分数随Fo的变化(Ra=2.5×104,Pr=0.1,St=1,Rs=Rcp=Rfs=1)
Fig.11 Liquid volume fraction versusFo for different Rfcp(Ra=2.5×104,Pr=0.1, St=1, Rs=Rcp=Rfs=1)

图12 不同固相PCMs比热容下相分布与焓值分布(Ra=2.5×104,Pr=0.1,St=1,Rs=Rcp=Rfs=1,Fo=0.1)
Fig.12 Phase distribution and enthalpy distribution under different specific heat capacities of solid phase PCMs(Ra=2.5×104, Pr=0.1, St=1, Rs=Rcp=Rfs=1, Fo=0.1)

图13 不同固相PCMs比热容下左壁面的平均Nu随Fo的变化(Ra=2.5×104,Pr=0.1,St=1,Rs=Rcp=Rfs=1)
Fig.13 Average Nu along the left wall versusFo for different Rfcp(Ra=2.5×104, Pr=0.1, St=1, Rs=Rcp=Rfs=1)
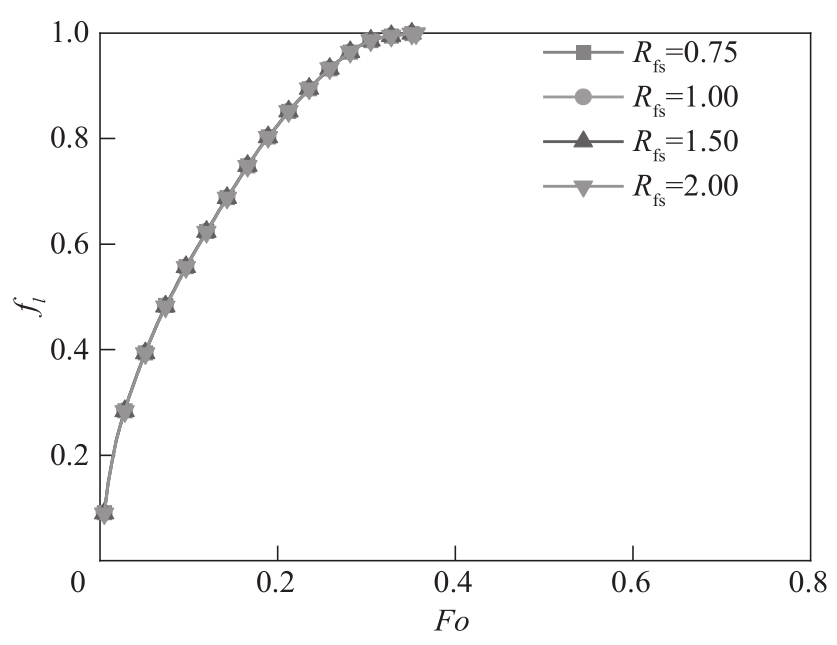
图14 不同固相PCMs热扩散系数下液相体积分数随Fo的变化(Ra=2.5×104,Pr=0.1,St=1,Rs=Rcp=Rfcp=1)
Fig.14 Liquid volume fraction versusFo and Rfs(Ra=2.5×104, Pr=0.1, St=1, Rs=Rcp=Rfcp=1)
| 1 | Oró E, De Gracia A, Castell A, et al. Review on phase change materials (PCMs) for cold thermal energy storage applications[J]. Applied Energy, 2012, 99: 513-533. |
| 2 | 刘亮, 吴爱枝, 黄云, 等. 两类复合无机相变储热材料高温热稳定性和安全性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(S2): 513-320. |
| Liu L, Wu A Z, Huang Y, et al. Research on high temperature thermal stability and safety of two types of composite inorganic phase change thermal storage materials[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(S2): 513-320. | |
| 3 | Banu D, Feldman D, Haghighat F, et al. Energy-storing wallboard: flammability tests[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 1998, 10(2): 98-105. |
| 4 | Huang X, Sun C, Chen Z, et al. Experimental and numerical studies on melting process of phase change materials (PCMs) embedded in open-cells metal foams[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2021, 170: 107151. |
| 5 | 张自仕. 含多孔骨架的储能材料固液相变界面传递机理研究[D]. 济南: 山东建筑大学, 2019. |
| Zhang Z S. Study on solid-liquid interface transfer mechanism of energy storage materials with porous skeleton[D]. Jinan: Shandong Jianzhu University, 2019. | |
| 6 | Gokon N, Nakamura S, Hatamachi T, et al. Steam reforming of methane using double-walled reformer tubes containing high-temperature thermal storage Na2CO3/MgO composites for solar fuel production[J]. Energy, 2014, 68: 773-782. |
| 7 | 王君雷, 张第玲, 王昆, 等. 碳酸盐/高炉矿渣定型复合相变储热材料的制备与性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(9): 3028-3034. |
| Wang J L, Zhang D L, Wang K, et al. Carbonates/blast furnace slag form-stable phase change materials[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 3028-3034. | |
| 8 | Atinafu D G, Yun B Y, Wi S, et al. A comparative analysis of biochar, activated carbon, expanded graphite, and multi-walled carbon nanotubes with respect to PCM loading and energy-storage capacities[J]. Environmental Research, 2021, 195: 110853. |
| 9 | 杲东彦, 陈振乾, 陈凌海. 开孔泡沫铝内石蜡融化相变过程的可视化实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(S1): 95-100. |
| Gao D Y, Chen Q Z, Chen L H. Visualized experiment of melting of paraffin waxin aluminum foam with open cells[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(S1): 95-100. | |
| 10 | Palazzolo M A, Dourges M-A, Magueresse A, et al. Preparation of lignosulfonate-based carbon foams by pyrolysis and their use in the microencapsulation of a phase change material[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(2): 2453-2461. |
| 11 | Liu Q, Feng X-B, He Y-L, et al. Three-dimensional multiple-relaxation-time lattice Boltzmann models for single-phase and solid-liquid phase-change heat transfer in porous media at the REV scale[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 152: 319-337. |
| 12 | Liu Q, He Y L. Double multiple-relaxation-time lattice Boltzmann model for solid-liquid phase change with natural convection in porous media[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2015, 438: 94-106. |
| 13 | Xu Y, Ren Q L, Zheng Z J, et al. Evaluation and optimization of melting performance for a latent heat thermal energy storage unit partially filled with porous media[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 193: 84-95. |
| 14 | Yang J L, Yang L J, Xu C, et al. Numerical analysis on thermal behavior of solid-liquid phase change within copper foam with varying porosity[J]. International Journal of Heat & Mass Transfer, 2015, 84: 1008-1018. |
| 15 | Beckermann C, Viskanta R. Natural convection solid/liquid phase change in porous media[J]. International Journal of Heat & Mass Transfer, 1988, 31(1): 35-46. |
| 16 | Gong X Z, Mujumdar A S. Finite-element analysis of cyclic heat transfer in a shell-and-tube latent heat energy storage exchanger[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 1997, 17(6): 583-591. |
| 17 | Cornubert R, d'Humières D, Levermore D. A Knudsen layer theory for lattice gases[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1991, 47(1): 241-259. |
| 18 | Ziegler D P. Boundary conditions for lattice Boltzmann simulations[J]. Journal of Statistical Physics, 1993, 71(5): 1171-1177. |
| 19 | Ginzbourg I, Adler P M. Boundary flow condition analysis for the three-dimensional lattice Boltzmann model[J]. Journal de Physique Ⅱ, 1994, 4(2): 191-214. |
| 20 | He X Y, Zou Q S, Luo L S, et al. Analytic solutions of simple flows and analysis of nonslip boundary conditions for the lattice Boltzmann BGK model[J]. Journal of Statistical Physics, 1997, 87(1): 115-136. |
| 21 | Pan C X, Luo L S, Miller C T. An evaluation of lattice Boltzmann schemes for porous medium flow simulation[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2006, 35(8): 898-909. |
| 22 | de Fabritiis G, Mancini A, Mansutti D, et al. Mesoscopic models of liquid/solid phase transitions[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics C, 1998, 09(8): 1405-1415. |
| 23 | Miller W, Succi S, Mansutti D. Lattice Boltzmann model for anisotropic liquid-solid phase transition[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2001, 86(16): 3578-3581. |
| 24 | Jiaung W S, Ho J R, Kuo C P. Lattice Boltzmann method for the heat conduction problem with phase change[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part B: Fundamentals, 2001, 39(2): 167-187. |
| 25 | Chakraborty S, Chatterjee D. An enthalpy-based hybrid lattice-Boltzmann method for modelling solid-liquid phase transition in the presence of convective transport[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2007, 592: 155-175. |
| 26 | Chatterjee D, Chakraborty S. An enthalpy-based lattice Boltzmann model for diffusion dominated solid-liquid phase transformation[J]. Physics Letters A, 2005, 341(1/2/3/4): 320-330. |
| 27 | Chatterjee D, Chakraborty S. An enthalpy-source based lattice Boltzmann model for conduction dominated phase change of pure substances[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2008, 47(5): 552-559. |
| 28 | Chatterjee D. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of incompressible transport phenomena in macroscopic solidification processes[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part B: Fundamentals, 2010, 58(1): 55-72. |
| 29 | Chatterjee D, Chakraborty S. A hybrid lattice Boltzmann model for solid-liquid phase transition in presence of fluid flow[J]. Physics Letters A, 2006, 351(4/5): 359-367. |
| 30 | Chatterjee D. An enthalpy-based thermal lattice Boltzmann model for non-isothermal systems[J]. Europhysics Letters, 2009, 86(1): 14004. |
| 31 | Luo K, Yao F J, Yi H L, et al. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of convection melting in complex heat storage systems filled with phase change materials[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2015, 86: 238-250. |
| 32 | Li X Y, Ma T, Liu J, et al. Pore-scale investigation of gravity effects on phase change heat transfer characteristics using lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 222: 92-103. |
| 33 | 杲东彦. 基于格子Boltzmann方法的泡沫金属内固液相变传热过程的研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2011. |
| Gao D Y. Study on the effect of thermal properties of porous skeleton on solid-liquid phase change based on LBM[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2011. | |
| 34 | 宋林泉, 陈宝明, 郜凯凯. 基于LBM的多孔骨架热物性对固液相变的影响研究[J]. 山东建筑大学学报, 2017, 32(4): 356-364. |
| Song L Q, Chen B M, Gao K K. Research on the influence of solid liquid phase change in porous skeleton media based on LBM method[J]. Journal of Shandong Jianzhu University, 2017, 32(4): 356-364. | |
| 35 | Dardis O, McCloskey J. Lattice Boltzmann scheme with real numbered solid density for the simulation of flow in porous media[J]. Physical Review E, 1998, 57(4): 4834-4837. |
| 36 | Luo L S, Liao W, Chen X W, et al. Numerics of the lattice Boltzmann method: effects of collision models on the lattice Boltzmann simulations[J]. Physical Review E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2011, 83(5Pt2): 056710. |
| 37 | Lallemand P, Luo L S. Lattice Boltzmann method for moving boundaries[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2003, 184(2): 406-421. |
| 38 | Huang R Z, Wu H Y, Cheng P. A new lattice Boltzmann model for solid-liquid phase change[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 59: 295-301. |
| 39 | Mencinger J. Numerical simulation of melting in two-dimensional cavity using adaptive grid[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2004, 198(1): 243-264. |
| 40 | Gallivan M A, Noble D R, Georgiadis J G, et al. An evaluation of the bounce-back boundary condition for lattice Boltzmann simulations[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 1997, 25(3): 249-263. |
| 41 | House J M, Beckermann C, Smith T F. Effect of a centered conducting body on natural convection heat transfer in an enclosure[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part A: Applications, 1990, 18(2): 213-225. |
| 42 | Das M K, Reddy K S K. Conjugate natural convection heat transfer in an inclined square cavity containing a conducting block[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2006, 49(25): 4987-5000. |
| 43 | 林琦. 微胶囊悬浮液双尺度建模及管内换热特性研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2019. |
| Lin Q. Two-scale modeling of microcapsule suspension and study on heat transfer characteristics in tube[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2019. |
| [1] | 宋嘉豪, 王文. 斯特林发动机与高温热管耦合运行特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 287-294. |
| [2] | 张思雨, 殷勇高, 贾鹏琦, 叶威. 双U型地埋管群跨季节蓄热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 295-301. |
| [3] | 叶展羽, 山訸, 徐震原. 用于太阳能蒸发的折纸式蒸发器性能仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 132-140. |
| [4] | 张双星, 刘舫辰, 张义飞, 杜文静. R-134a脉动热管相变蓄放热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 165-171. |
| [5] | 张义飞, 刘舫辰, 张双星, 杜文静. 超临界二氧化碳用印刷电路板式换热器性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. |
| [6] | 王志国, 薛孟, 董芋双, 张田震, 秦晓凯, 韩强. 基于裂隙粗糙性表征方法的地热岩体热流耦合数值模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 223-234. |
| [7] | 江河, 袁俊飞, 王林, 邢谷雨. 均流腔结构对微细通道内相变流动特性影响的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 235-244. |
| [8] | 吴延鹏, 刘乾隆, 田东民, 陈凤君. 相变材料与热管耦合的电子器件热管理研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 25-31. |
| [9] | 何松, 刘乔迈, 谢广烁, 王斯民, 肖娟. 高浓度水煤浆管道气膜减阻两相流模拟及代理辅助优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3766-3774. |
| [10] | 邢雷, 苗春雨, 蒋明虎, 赵立新, 李新亚. 井下微型气液旋流分离器优化设计与性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3394-3406. |
| [11] | 程小松, 殷勇高, 车春文. 不同工质在溶液除湿真空再生系统中的性能对比[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3494-3501. |
| [12] | 刘文竹, 云和明, 王宝雪, 胡明哲, 仲崇龙. 基于场协同和 耗散的微通道拓扑优化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3329-3341. 耗散的微通道拓扑优化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3329-3341. |
| [13] | 胡兴枝, 张皓焱, 庄境坤, 范雨晴, 张开银, 向军. 嵌有超小CeO2纳米粒子的碳纳米纤维的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3584-3596. |
| [14] | 洪瑞, 袁宝强, 杜文静. 垂直上升管内超临界二氧化碳传热恶化机理分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3309-3319. |
| [15] | 韩晨, 司徒友珉, 朱斌, 许建良, 郭晓镭, 刘海峰. 协同处理废液的多喷嘴粉煤气化炉内反应流动研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3266-3278. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号