• •
许莉1( ), 王栖2(
), 王栖2( ), 朱启程1, 王钊禹1, 任金翠1(
), 朱启程1, 王钊禹1, 任金翠1( ), 南艳丽1(
), 南艳丽1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-08-12
修回日期:2025-09-30
出版日期:2025-11-18
通讯作者:
任金翠,南艳丽
作者简介:许莉(2001—),女,硕士研究生,xuli@xauat.edu.cn基金资助:
Li XU1( ), Qi WANG2(
), Qi WANG2( ), Qicheng ZHU1, Zhaoyu WANG1, Jincui REN1(
), Qicheng ZHU1, Zhaoyu WANG1, Jincui REN1( ), Yanli NAN1(
), Yanli NAN1( )
)
Received:2025-08-12
Revised:2025-09-30
Online:2025-11-18
Contact:
Jincui REN, Yanli NAN
摘要:
近年来,吸波材料在实际应用环境应用中,如海洋环境、高温条件和潮湿大气等恶劣环境中,极易被腐蚀氧化而失效。为满足复杂应用环境需求,吸波材料必须具备卓越的耐腐蚀性和热稳定性。本研究通过高温碳化工艺成功合成了新型复合材料——碳纳米角限域TiC和MoC纳米颗粒(TiC/MoC@NCNHs)。该复合材料在微波吸收性能上表现优异,并展现出卓越的耐腐蚀性和热稳定性能。碳纳米角因其优异的物理和化学稳定性以及抗渗透性,可作原子级屏障,保护基材免受腐蚀和氧化。MoC的引入增强了TiC/MoC@NCNHs复合材料的磁损耗,改善了阻抗匹配,低密度的TiC提供了显著的导电损耗并减少了复合材料的质量。这种多功能材料可在高温高湿及海洋环境中实现持续性能。TiC/MoC@NCNHs复合材料实现了最低反射损耗-50.89 dB和5.87 GHz的有效吸收带。此外,该复合材料在3.5% NaCl溶液中浸泡30天后仍保持低腐蚀电流,展现出优异的抗腐蚀性能,且在高温处理后仍保持最佳反射损耗,证明其具有优异的热稳定性。
中图分类号:
许莉, 王栖, 朱启程, 王钊禹, 任金翠, 南艳丽. 碳纳米角限域TiC和MoC纳米颗粒的耐腐蚀及吸波性能研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250907.
Li XU, Qi WANG, Qicheng ZHU, Zhaoyu WANG, Jincui REN, Yanli NAN. Corrosion Resistance and Microwave Absorption Properties of TiC and MoC Nanoparticles Confined in Carbon Nanohorns[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250907.
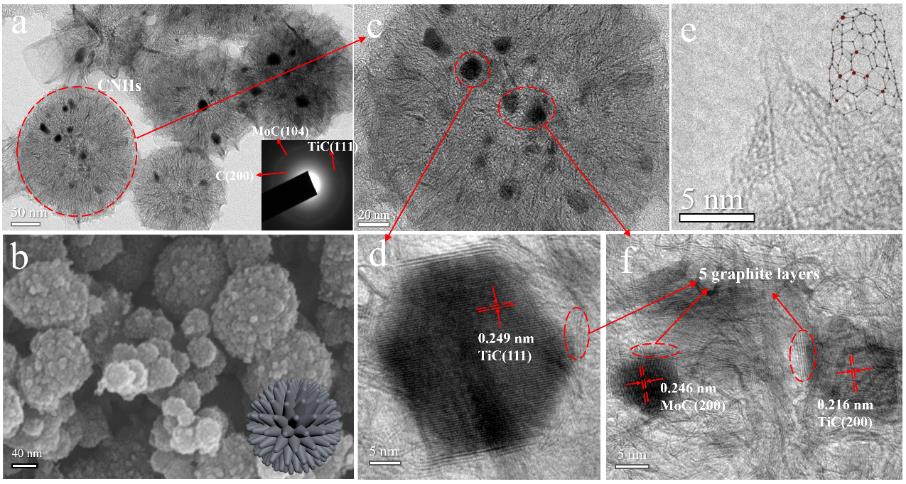
图1 (a) TiC/MoC@NCNHs的透射电子显微镜(TEM)图像(插图为SAED图案),(b) TiC/MoC@NCNHs的扫描电子显微镜(SEM)图像,(b-f) TiC/MoC@NCNHs的高分辨率透射电子显微镜(HRTEM)图像
Fig 1 (a) TEM image of TiC/MoC@NCNHs (inset of the SAED pattern), (b) SEM image of TiC/MoC@NCNHs (b-f) HRTEM images of TiC/MoC@NCNHs

图2 (a) 1-TiC-1-MoC的XPS全谱; (a1-a3) C、Mo和Ti峰的高分辨率光谱;(b) TiC/MoC@NCNHs的XRD图谱;(c) TiC/MoC@NCNHs的拉曼光谱
Fig 2 (a) Wide XPS spectra of 1-TiC-1-MoC. (a1-a3) The high-resolution spectrum of C, Mo and Ti peaks. (b) Raman spectra of TiC/MoC@NCNHs. (c) XRD patterns of TiC/MoC@NCNHs.
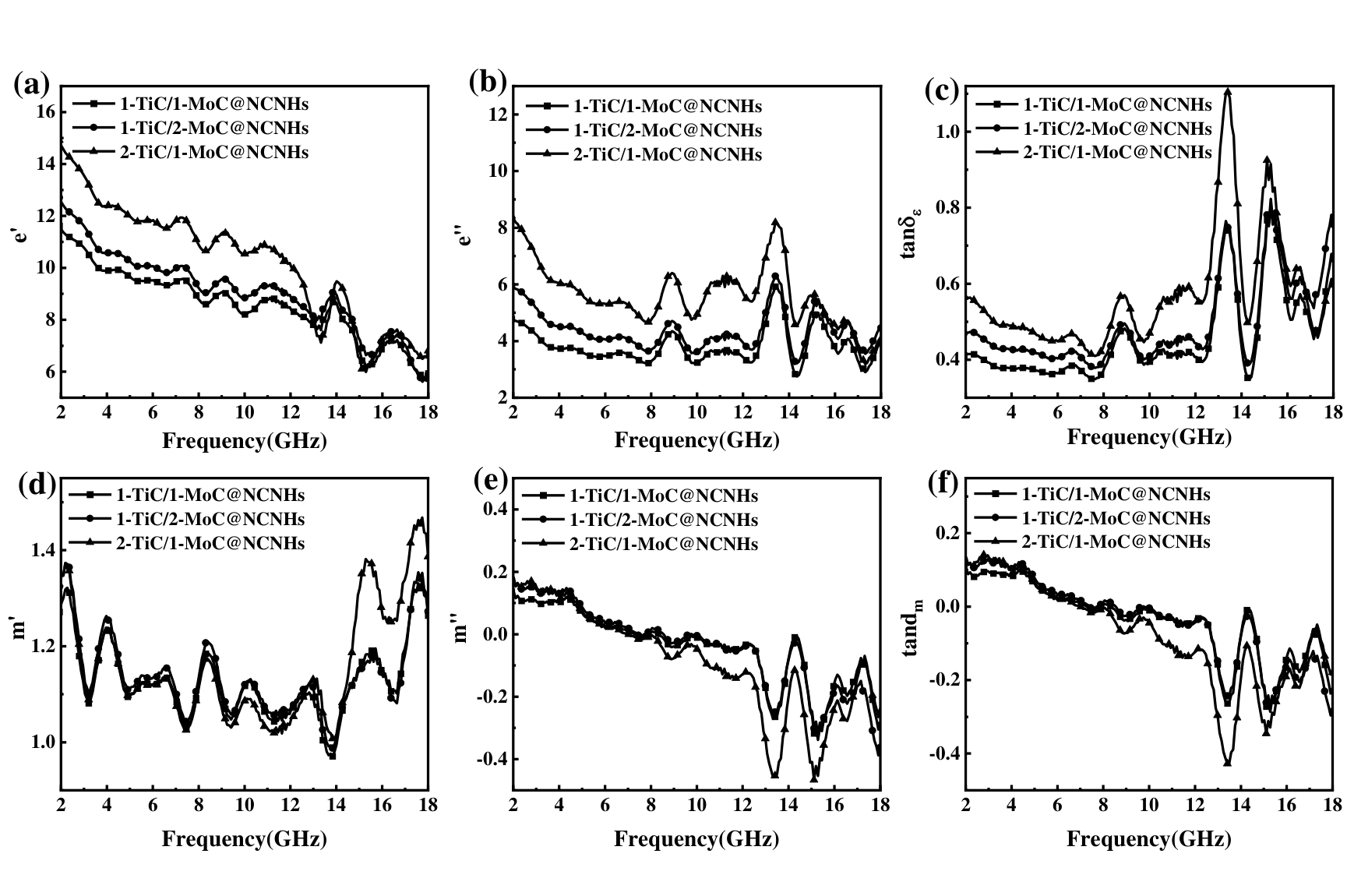
图3 TiC/MoC@NCNHs的电磁参数: (a) 实部介电常数,(b) 虚部介电常数,(c) 介电损耗正切,(d) 实部磁导率,(e) 虚部磁导率,(f) 磁损耗正切
Fig. 3 Electromagnetic parameters of TiC/MoC@NCNHs: (a) real permittivity, (b) imaginary permittivity, (c) dielectric loss tangents, (d) real permeability, (e) imaginary permeability, and (f) magnetic loss tangents.
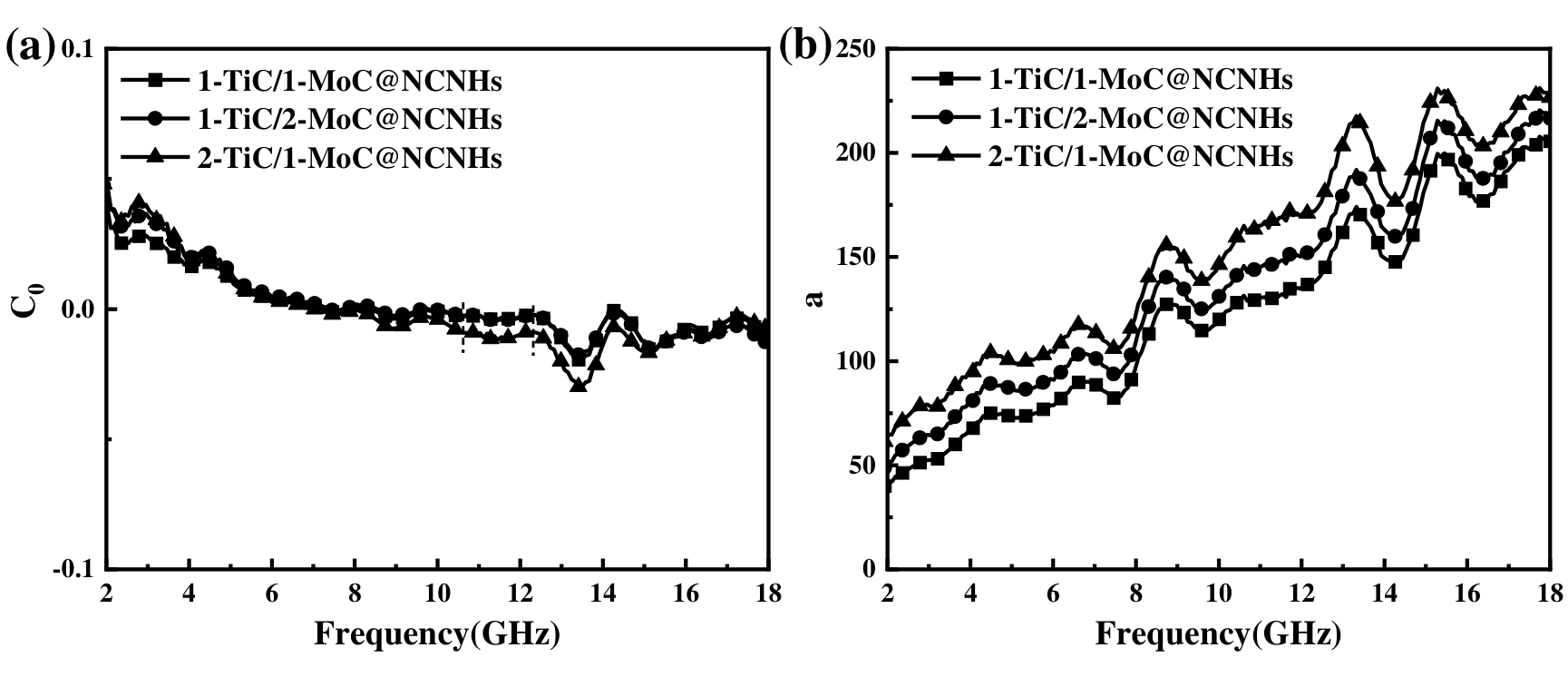
图5 (a) TiC/MoC@NCNHs的涡流损耗C0,(b) TiC/MoC@NCNHs的衰减常数α
Fig 5 (a) Frequency dependences of C0 for TiC/MoC@NCNHs, (b) Attenuation constant α of TiC/MoC@NCNHs.

图6 (a1-a2) 1-TiC-1-MoC的RL值和阻抗匹配Z图, (b1-b2) 1-TiC-2-MoC的RL值和阻抗匹配Z图,(c1-c2) 2-TiC-1-MoC的RL值和阻抗匹配Z图
Fig 6 (a1-a2) The RL values and impedance matching Z of 1-TiC-1-MoC. (b1-b2) The RL values and impedance matching Z of 1-TiC-2-MoC. (c1-c2) The RL values and impedance matching Z of 2-TiC-1-MoC.

图7 (a) 热处理后TiC/MoC@NCNHs的XRD谱图,(b) 热处理后1-TiC-1-MoC的XPS谱图,(c) 1-TiC-1-MoC-450℃的RL值,(d) 1-TiC-2-MoC-450℃的RL值,(e) 2-TiC-1-MoC-450℃的RL值。
Fig 7 (a) XRD patterns of heat-treated TiC/MoC@NCNHs. (b) XPS patterns of heat-treated 1-TiC-1-MoC (c) The RL values of 1-TiC-1-MoC-450℃. (d) The RL values of 1-TiC-2-MoC-450℃. (e) The RL values of 2-TiC-1-MoC-450℃.

图8 TiC/MoC@NCNHs复合材料、裸露的Q235钢和纯EP在3.5% NaCl溶液中浸泡30天后的电化学特性表征:(a)Bode图,(b)动极化曲线,(c)TiC/MoC@NCNHs可能的耐腐蚀机制示意图。
Fig 8 Electrochemical characterization of the TiC/MoC@NCNHs composites, bare Q235 and pure EP after the immersion in a 3.5 wt% NaCl solution for 30 days (a) Bode plots, (b) Potentiodynamic polarization curves, (c)Schematic illustration of the possible corrosion protection mechanism for the TiC/MoC@NCNHs
| [1] | Lu P P, Xue F, Xin L, et al. Anticorrosion coating with heterogeneous assembly of nanofillers modulated by a magnetic field[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(5): 7538-7551. |
| [2] | Yan X, Liu F, Guo J H, et al. Excellent electrically insulated, thermal-oxidation resistant and corrosion resistant flaky-FeSiAl/BN core–shell composites for high-performance microwave absorption in harsh environments[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2023, 175: 107778. |
| [3] | Zhang Y F, Zhang L, Tang L F, et al. S-NiSe/HG nanocomposites with balanced dielectric loss encapsulated in room-temperature self-healing polyurethane for microwave absorption and corrosion protection[J]. ACS Nano, 2024, 18(11): 8411-8422. |
| [4] | Wang Y Y, Zhou Z H, Zhu J L, et al. Low-temperature carbonized carbon nanotube/cellulose aerogel for efficient microwave absorption[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2021, 220: 108985. |
| [5] | Gao T, Zhang Z Y, Li Y X, et al. Solid-state reaction induced defects in multi-walled carbon nanotubes for improving microwave absorption properties[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 108: 37-45. |
| [6] | Wu Q L, Wang J, Jin H H, et al. Facile synthesis of co-embedded porous spherical carbon composites derived from Co3O4/ZIF-8 compounds for broadband microwave absorption[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2020, 195: 108206. |
| [7] | Zhong B, Liu W, Yu Y L, et al. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of graphite nanoflakes by coating hexagonal boron nitride nanocrystals[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 420: 858-867. |
| [8] | Prasai D, Tuberquia J C, Harl R R, et al. Graphene: corrosion-inhibiting coating[J]. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(2): 1102-1108. |
| [9] | Zhu S Q, Gao Y, Zhou H R, et al. Expanded graphite/Co@C composites with dual functions of corrosion resistance and microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 23: 3557-3569. |
| [10] | Li S Z, Xie T W, Ma L, et al. Ni3Fe@N-doped carbon nanotubes 3D network induced by nanoconfined symmetry breaking for high-performance microwave absorption, corrosion protection, and pollutant purification[J]. Carbon, 2023, 213: 118302. |
| [11] | Lu S Q, Xie Z P, Zhang D, et al. Facile constructing core-shell F–CIP@O/N-SWCNHs composites for high-performance microwave absorption and anti-corrosion[J]. Carbon, 2024, 230: 119632. |
| [12] | Peng H Y, Zhang D, Xie Z P, et al. Recent advances in structural design of carbon/magnetic composites and their electromagnetic wave absorption applications[J]. Small, 2025, 21(8): 2408570. |
| [13] | Liu Y C, Xie Z P, Lu S Q, et al. Regulating the vacancies of nitrogen-doped carbon nanohorns for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2024, 53(27): 11454-11463. |
| [14] | Xu Y H, Zhu Y J, Liu Y H, et al. Electrochemical performance of porous carbon/tin composite anodes for sodium-ion and lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2013, 3(1): 128-133. |
| [15] | HUANG X, QI X, BOEY F, et al. Graphene-based composites[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012,2(41): 666-686. |
| [16] | Nan Y L, Zhang Z H, Wang Z Y, et al. Controllable synthesis of Mo3C2 encapsulated by N-doped carbon microspheres to achieve highly efficient microwave absorption at full wavebands: from lemon-like to fig-like morphologies[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2022, 61(16): 6281-6294. |
| [17] | Wang W L, Sun G X, Sun X N, et al. Electromagnetic microwave absorption property of MoC synthesized via a facile solid-state reaction method[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2021, 32(19): 24351-24362. |
| [18] | Wu Z C, Jin C, Yang Z Q, et al. Integrating hierarchical interfacial polarization in yeast-derived Mo2C/C nanoflower/microsphere nanoarchitecture for boosting microwave absorption performance[J]. Carbon, 2022, 189: 530-538. |
| [19] | Izadi-Najafabadi A, Yamada T, Futaba D N, et al. High-power supercapacitor electrodes from single-walled carbon nanohorn/nanotube composite[J]. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(2): 811-819. |
| [20] | Kadambi S B, Pramoda K, Ramamurty U, et al. Carbon-nanohorn-reinforced polymer matrix composites: synergetic benefits in mechanical properties[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(31): 17016-17022. |
| [21] | Eijiro Miyako T D. Photothermic regulation of gene expression triggered by laser-induced carbon nanohorns[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(19): 7523-7528. |
| [22] | Nan Y L, Lei L M, Zhang Z H, et al. Superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance of TiC nanoparticles embedded into nitrogen‐doping carbon nanohorns in one-step synthesis[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2024, 175: 112761. |
| [23] | Nan Y L, Zhang Z H, He Y Y, et al. Optimized nanopores opened on N-doped carbon nanohorns filled with Fe/Fe2O3 nanoparticles as advanced electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2021, 60(21): 16529-16537. |
| [24] | Sahoo P, Saini L, Dixit A. Microwave-absorbing materials for stealth application: a holistic overview[J]. Oxford Open Materials Science, 2023, 3(1): itac012. |
| [25] | Yu J Y, Yu H T, Gao J, et al. Synthesis and electrochemical activities of TiC/C core-shell nanocrystals[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 693: 500-509. |
| [26] | Jung H J, Kim Y J, Han J H, et al. Thermal-treatment-induced enhancement in effective surface area of single-walled carbon nanohorns for supercapacitor application[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(49): 25877-25883. |
| [27] | Li Z J, Lin H, Ding S Q, et al. Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances of Fe3O4@C decorated walnut shell-derived porous carbon[J]. Carbon, 2020, 167: 148-159. |
| [28] | Li X P, Deng Z M, Li Y, et al. Controllable synthesis of hollow microspheres with Fe@Carbon dual-shells for broad bandwidth microwave absorption[J]. Carbon, 2019, 147: 172-181. |
| [29] | Liu P B, Li Y R, Xu H X, et al. Hierarchical Fe-Co@TiO2 with incoherent heterointerfaces and gradient magnetic domains for electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. ACS Nano, 2024, 18(1): 560-570. |
| [30] | Kong L, Yin X W, Yuan X Y, et al. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of graphene modified with carbon nanotube/poly(dimethyl siloxane) composites[J]. Carbon, 2014, 73: 185-193. |
| [31] | Zhao B, Fan B B, Shao G, et al. Facile synthesis of novel heterostructure based on SnO2 nanorods grown on submicron Ni walnut with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption capabilities[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(33): 18815-18823. |
| [32] | Jian X, Tian W, Li J Y, et al. High-temperature oxidation-resistant ZrN0.4B0.6/SiC nanohybrid for enhanced microwave absorption[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(17): 15869-15880. |
| [33] | Qiao M T, Wei D, He X W, et al. Novel yolk–shell Fe3O4@void@SiO2@PPy nanochains toward microwave absorption application[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2021, 56(2): 1312-1327. |
| [34] | Yuan H R, Yan F, Li C Y, et al. Nickel nanoparticle encapsulated in few-layer nitrogen-doped graphene supported by nitrogen-doped graphite sheets as a high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing material[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(1): 1399-1407. |
| [35] | Xiang Z, Huang C, Song Y M, et al. Rational construction of hierarchical accordion-like Ni@porous carbon nanocomposites derived from metal-organic frameworks with enhanced microwave absorption[J]. Carbon, 2020, 167: 364-377. |
| [36] | Wang J W, Wang B B, Wang Z, et al. Synthesis of 3D flower-like ZnO/ZnCo2O4 composites with the heterogeneous interface for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 586: 479-490. |
| [37] | Zhao Z H, Kou K C, Wu H J. 2-Methylimidazole-mediated hierarchical Co3O4/N-doped carbon/short-carbon-fiber composite as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorber[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 574: 1-10. |
| [38] | Wen F S, Yi H B, Qiao L, et al. Analyses on double resonance behavior in microwave magnetic permeability of multiwalled carbon nanotube composites containing Ni catalyst[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(4): 042507. |
| [39] | Hua A, Wei F, Pan D S, et al. Wide-band microwave absorption by in situ tailoring morphology and optimized N-doping in nano-SiC[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 111(22): 223105. |
| [40] | Cui X Q, Liang X H, Chen J B, et al. Customized unique core-shell Fe2N@N-doped carbon with tunable void space for microwave response[J]. Carbon, 2020, 156: 49-57. |
| [41] | Wu N D, Liu X G, Or S W. Core/shell-structured nickel/nitrogen-doped onion-like carbon nanocapsules with improved electromagnetic wave absorption properties[J]. AIP Advances, 2016, 6(5): 056206. |
| [42] | Hou T Q, Jia Z R, Wang B B, et al. Metal-organic framework-derived NiSe2-CoSe2@C/Ti3C2T x composites as electromagnetic wave absorbers[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 422: 130079. |
| [43] | Wang J P, Wang J, Xu R X, et al. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of epoxy composites reinforced with Fe50Ni50-functionalized graphene[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 653: 14-21. |
| [44] | Chuai D, Liu X F, Yu R H, et al. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of flake-shaped FePCB metallic glass/graphene composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2016, 89: 33-39. |
| [45] | Hou T Q, Jia Z R, Wang B B, et al. MXene-based accordion 2D hybrid structure with Co9S8/C/Ti3C2T x as efficient electromagnetic wave absorber[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 414: 128875. |
| [46] | Xie Z P, Liu Y C, Lu S Q, et al. One-step rapid achieving O-SWCNHs@SiO2 core–shell heterostructures with tunable electromagnetic absorption performance via arc plasma[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 489: 151311. |
| [47] | Peng H Y, Xie Z P, Lu S Q, et al. Dual-functionality composites of polyaniline-coated oxidized carbon nanohorns: Efficient wave absorption and enhanced corrosion resistance[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2025, 36(6): 110818. |
| [48] | Tian W, Zhang X Z, Guo Y, et al. Hybrid silica-carbon bilayers anchoring on FeSiAl surface with bifunctions of enhanced anti-corrosion and microwave absorption[J]. Carbon, 2021, 173: 185-193. |
| [1] | 胡兴枝, 张皓焱, 庄境坤, 范雨晴, 张开银, 向军. 嵌有超小CeO2纳米粒子的碳纳米纤维的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3584-3596. |
| [2] | 汤进, 林斌, 毕松, 苏正安, 侯根良, 刘朝辉, 李浩, 林阳阳. 轻薄炭黑涂层的制备及其微波吸收性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(11): 4469-4477. |
| [3] | 贾海鹏,苏勋家,侯根良,郭锋,刘朝辉,梅冰. 石墨烯/聚合物纳米复合材料制备与微波吸收性能研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(6): 1663-1668. |
| [4] | 王万福1,李 果2,雍兴跃2,刘 鹏1,张晓飞1,王际东2. 油泥微波程序升温热转化[J]. CIESC Journal, 2011, 30(10): 2310-. |
| [5] | 邹正, 宣爱国, 吴元欣, 何俊, 何佳. 铜铁尾矿制酸烧渣制备纳米Fe/SiO2核壳复合粒子的微波吸收性能 [J]. 化工学报, 2009, 60(5): 1322-1326. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号