• •
高波1( ), 王佳琪1, 刘志亮2, 赵玄烈3, 葛坤1(
), 王佳琪1, 刘志亮2, 赵玄烈3, 葛坤1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-08-07
修回日期:2024-11-11
出版日期:2025-04-21
发布日期:2025-03-28
通讯作者:
葛坤
作者简介:高波(1997—),男,博士研究生,bogao@hrbeu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Bo GAO1( ), Jiaqi WANG1, Zhiliang LIU2, Xuanlie ZHAO3, Kun GE1(
), Jiaqi WANG1, Zhiliang LIU2, Xuanlie ZHAO3, Kun GE1( )
)
Received:2024-08-07
Revised:2024-11-11
Online:2025-04-21
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
Kun GE
摘要:
为系统分析和评估海上风电制氢系统的热力学性能及经济性,构建了一个在热力学方面充分考虑附属设备、在经济学上兼顾海域特殊性的海上风电制氢系统模型。基于该模型,首先进行了参数研究和敏感性分析,以探讨运行参数对系统性能的影响规律;其次,利用我国海域真实风速数据进行了案例研究,模拟并评估了该海域的制氢能力及系统性能。研究结果表明,风速、电解槽运行温度及运行压力的提升均有助于增强制氢系统的运行性能,其中系统性能对风速变化表现出显著敏感性;案例研究显示该海域全年氢气产量为179908 kg,平均能量效率和㶲效率分别为26.6%和54.4%。然而,成本高昂的海上浮体结构使得氢气平准化成本显著上升。此外,该海域在夏季的制氢能力明显不足,特别是6月份的氢气产量最低,仅为10月或11月的15.3%。
中图分类号:
高波, 王佳琪, 刘志亮, 赵玄烈, 葛坤. 海上风电制氢系统建模及热力学与经济学分析[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240904.
Bo GAO, Jiaqi WANG, Zhiliang LIU, Xuanlie ZHAO, Kun GE. Modeling and thermodynamic and economic analysis of offshore wind power-based hydrogen production systems[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240904.
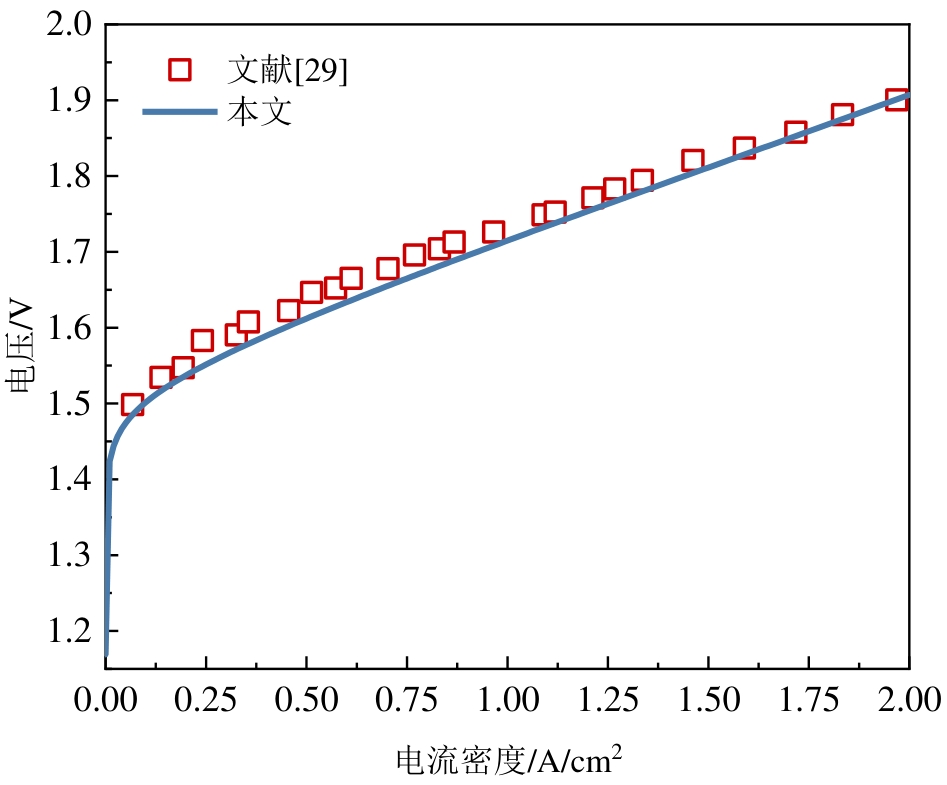
图2 PEM电解槽单元电压特性模拟结果与文献实验数据对比
Fig.2 Comparison between the simulated cell voltage performance of a PEM electrolyzer and the experimental data from the literature
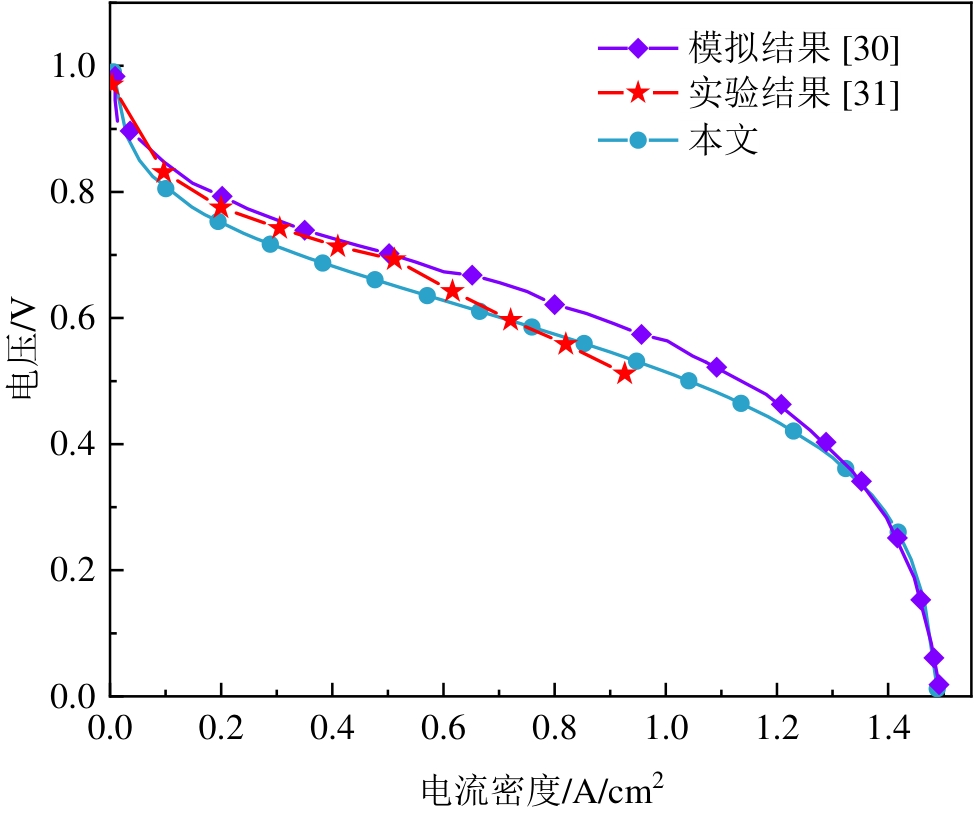
图3 PEM燃料电池模型单电池极化曲线模拟结果与文献结果对比
Fig.3 Comparison between the simulated polarization curve of a single cell in the PEM fuel cell model and the experimental results from the literature
| 参数 | 数值 | 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 风力机切入风速 | 3 m/s | 质子交换膜厚度 | 0.0254 cm |
| 风力机额定功率 | 4 MW | 燃料电池活化面积,Afc | 500 cm2 |
| 风力机额定风速 | 10 m/s | 燃料电池运行压力 | 1.5 bar |
| 风能利用系数,Cp | 0.45 | 用户用电负荷,Wele | 300 kW |
| 风力机效率,ηwp | 0.8 | 蓄电池充电功率,Wbat | 25 kW |
| 风力机叶片半径,Rwp | 155 m | 压缩机等熵效率,ηC | 0.85 |
| PEM电解槽运行温度,Tel | 80℃ | 海水淡化功耗,PRO | 3.0 kWh/kg |
| PEM电解槽运行压力,pel | 1.5 bar | 换热器最小换热温差 | 5℃ |
| 电解槽单元数目,Nel | 800 | 水泵等熵效率,ηC | 0.85 |
| 电解槽活化面积,Ael | 1000 cm2 | 氢气储罐入口温度 | 30℃ |
表1 系统模型基本参数
Table 1 The basic parameters of the system model
| 参数 | 数值 | 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 风力机切入风速 | 3 m/s | 质子交换膜厚度 | 0.0254 cm |
| 风力机额定功率 | 4 MW | 燃料电池活化面积,Afc | 500 cm2 |
| 风力机额定风速 | 10 m/s | 燃料电池运行压力 | 1.5 bar |
| 风能利用系数,Cp | 0.45 | 用户用电负荷,Wele | 300 kW |
| 风力机效率,ηwp | 0.8 | 蓄电池充电功率,Wbat | 25 kW |
| 风力机叶片半径,Rwp | 155 m | 压缩机等熵效率,ηC | 0.85 |
| PEM电解槽运行温度,Tel | 80℃ | 海水淡化功耗,PRO | 3.0 kWh/kg |
| PEM电解槽运行压力,pel | 1.5 bar | 换热器最小换热温差 | 5℃ |
| 电解槽单元数目,Nel | 800 | 水泵等熵效率,ηC | 0.85 |
| 电解槽活化面积,Ael | 1000 cm2 | 氢气储罐入口温度 | 30℃ |
| 月份 | 场景一 | 场景二 | 场景三 | 场景四 | 总时长 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
时长 h | 风速 m/s | 时长 h | 风速 m/s | 时长 h | 风速 m/s | 时长 h | ||
| 1 | 613 | 8.16 | 7 | 4.5 | 77 | 3.77 | 47 | 744 |
| 2 | 561 | 8.44 | 4 | 4.5 | 84 | 3.76 | 23 | 672 |
| 3 | 446 | 7.97 | 9 | 4.5 | 152 | 3.75 | 137 | 744 |
| 4 | 367 | 8.59 | 8 | 4.5 | 148 | 3.68 | 197 | 720 |
| 5 | 533 | 7.98 | 9 | 4.5 | 107 | 3.78 | 95 | 744 |
| 6 | 377 | 6.84 | 9 | 4.5 | 134 | 3.70 | 200 | 720 |
| 7 | 401 | 7.62 | 14 | 4.5 | 191 | 3.77 | 138 | 744 |
| 8 | 360 | 7.66 | 11 | 4.5 | 169 | 3.77 | 204 | 744 |
| 9 | 420 | 8.01 | 10 | 4.5 | 155 | 3.73 | 135 | 720 |
| 10 | 619 | 8.72 | 4 | 4.5 | 70 | 3.75 | 51 | 744 |
| 11 | 575 | 8.94 | 8 | 4.5 | 82 | 3.75 | 55 | 720 |
| 12 | 611 | 7.17 | 12 | 4.5 | 97 | 3.79 | 24 | 744 |
| 全年 | 5883 | 8.01 | 105 | 4.5 | 1466 | 3.75 | 1306 | 8760 |
表 2 各月份系统运行处于不同场景的时长及平均风速
Table 2 Duration of system operation in different scenarios and average wind speed in each month
| 月份 | 场景一 | 场景二 | 场景三 | 场景四 | 总时长 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
时长 h | 风速 m/s | 时长 h | 风速 m/s | 时长 h | 风速 m/s | 时长 h | ||
| 1 | 613 | 8.16 | 7 | 4.5 | 77 | 3.77 | 47 | 744 |
| 2 | 561 | 8.44 | 4 | 4.5 | 84 | 3.76 | 23 | 672 |
| 3 | 446 | 7.97 | 9 | 4.5 | 152 | 3.75 | 137 | 744 |
| 4 | 367 | 8.59 | 8 | 4.5 | 148 | 3.68 | 197 | 720 |
| 5 | 533 | 7.98 | 9 | 4.5 | 107 | 3.78 | 95 | 744 |
| 6 | 377 | 6.84 | 9 | 4.5 | 134 | 3.70 | 200 | 720 |
| 7 | 401 | 7.62 | 14 | 4.5 | 191 | 3.77 | 138 | 744 |
| 8 | 360 | 7.66 | 11 | 4.5 | 169 | 3.77 | 204 | 744 |
| 9 | 420 | 8.01 | 10 | 4.5 | 155 | 3.73 | 135 | 720 |
| 10 | 619 | 8.72 | 4 | 4.5 | 70 | 3.75 | 51 | 744 |
| 11 | 575 | 8.94 | 8 | 4.5 | 82 | 3.75 | 55 | 720 |
| 12 | 611 | 7.17 | 12 | 4.5 | 97 | 3.79 | 24 | 744 |
| 全年 | 5883 | 8.01 | 105 | 4.5 | 1466 | 3.75 | 1306 | 8760 |
| 文献 | 制氢系统类型 | 系统输出 | 能量效率 | 㶲效率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [ | 风能 | 氢气、电能、热能、冷能 | 36.1% | 59.5% |
| [ | 风能 | 氢气、电能、热能 | 20.0% | 21.2% |
| [ | 风能、生物质能 | 氢气、电能、热能、冷能 | 25.0% | 41.2% |
| [ | 太阳能 | 氢气、电能、淡水 | 38.5% | 35.6% |
| 本文 | 风能 | 氢气、电能 | 26.6% | 54.4% |
表 3 本研究与其他可再生能源制氢系统相关研究中系统效率的对比
Table 3 Comparison of system efficiency between this study and related research on hydrogen production systems from renewable energy sources
| 文献 | 制氢系统类型 | 系统输出 | 能量效率 | 㶲效率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [ | 风能 | 氢气、电能、热能、冷能 | 36.1% | 59.5% |
| [ | 风能 | 氢气、电能、热能 | 20.0% | 21.2% |
| [ | 风能、生物质能 | 氢气、电能、热能、冷能 | 25.0% | 41.2% |
| [ | 太阳能 | 氢气、电能、淡水 | 38.5% | 35.6% |
| 本文 | 风能 | 氢气、电能 | 26.6% | 54.4% |
| 1 | Egeland-Eriksen T, Jensen J F, Ulleberg Ø, et al. Simulating offshore hydrogen production via PEM electrolysis using real power production data from a 2.3 MW floating offshore wind turbine[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(74): 28712-28732. |
| 2 | 邱一苇, 吉旭, 朱文聪, 等. 面向新能源规模化消纳的绿氢化工技术研究现状与关键支撑技术展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43(18): 6934-6955. |
| Qiu Y W, Ji X, Zhu W C, et al. Research status of green hydrogen-based chemical engineering technology and prospect of key supporting technologies for large-scale utilization of new energies[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(18): 6934-6955.. | |
| 3 | 姜波, 丁杰, 方舣洲, 等. 涠洲岛海洋风能和波浪能资源评估[J]. 太阳能学报, 2023, 44(10): 461-466. |
| Jiang B, Ding J, Fang Y Z, et al. Offshore wind energy and wave energy resource valuation in Weizhou island[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2023, 44(10): 461-466. | |
| 4 | Jang D, Kim K, Kim KH, et al. Techno-economic analysis and Monte Carlo simulation for green hydrogen production using offshore wind power plant[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 263: 115695. |
| 5 | d'Amore-Domenech R, Leo T J. Sustainable hydrogen production from offshore marine renewable farms: techno-energetic insight on seawater electrolysis technologies[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 7(9): 8006-8022. |
| 6 | Ishaq H, Dincer I, Naterer G F. Performance investigation of an integrated wind energy system for co-generation of power and hydrogen[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(19): 9153-9164. |
| 7 | Cai D S, Acen C, Hu Y H, et al. Cost and thermodynamic analysis of wind-hydrogen production via multi-energy systems[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2024, 306: 118286. |
| 8 | 张焱, 郝振波, 朱振涛, 等. 海上风能岸上制氢的经济可行性分析[J]. 电力建设, 2023, 44(3): 148-154. |
| Zhang Y, Hao Z B, Zhu Z T, et al. Economic feasibility analysis of onshore hydrogen production using offshore wind power[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2023, 44(3): 148-154. | |
| 9 | Nasser M, Megahed T F, Ookawara S, et al. Performance evaluation of PV panels/wind turbines hybrid system for green hydrogen generation and storage: Energy, exergy, economic, and enviroeconomic[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 267: 115870. |
| 10 | Nasser M, Hassan H. Techno-enviro-economic analysis of hydrogen production via low and high temperature electrolyzers powered by PV/Wind turbines/Waste heat[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2023, 278: 116693. |
| 11 | Rezaei M, Khalilpour K R, Mohamed M A. Co-production of electricity and hydrogen from wind: A comprehensive scenario-based techno-economic analysis[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(35): 18242-18256. |
| 12 | Han B, Steen S M, Mo J K, et al. Electrochemical performance modeling of a proton exchange membrane electrolyzer cell for hydrogen energy[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(22): 7006-7016. |
| 13 | Mohebali Nejadian M, Ahmadi P, Houshfar E. Comparative optimization study of three novel integrated hydrogen production systems with SOEC, PEM, and alkaline electrolyzer[J]. Fuel, 2023, 336: 126835. |
| 14 | Abdin Z, Webb C J, Gray E M. Modelling and simulation of a proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolyser cell[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(39): 13243-13257. |
| 15 | Liu L T, Zhai R R, Hu Y D. Performance evaluation of wind-solar-hydrogen system for renewable energy generation and green hydrogen generation and storage: energy, exergy, economic, and enviroeconomic[J]. Energy, 2023, 276: 127386. |
| 16 | 刘秀龙, 曹泷, 徐进良, 等. ORC驱动RO海水淡化不同能量回收方式性能分析[J]. 动力工程学报, 2018, 38(4): 329-336. |
| Liu X L, Cao S, Xu J L, et al. Performance analysis of an ORC-RO desalination system with different energy recovery methods[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2018, 38(4): 329-336. | |
| 17 | 楚帅, 葛维春, 李音璇, 等. 含海水淡化负荷的可再生能源消纳技术研究综述[J]. 智慧电力, 2021, 49(11): 14-23. |
| Chu S, Ge W C, Li Y X, et al. Review on renewable energy integration technology with seawater desalination load[J]. Smart Power, 2021, 49(11): 14-23. | |
| 18 | Ma Y G, Morozyuk T, Liu M, et al. Optimal integration of recompression supercritical CO2 Brayton cycle with main compression intercooling in solar power tower system based on exergoeconomic approach[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 242: 1134-1154. |
| 19 | Qi X R, Kochan O, Ma Z J, et al. Energy, exergy, exergoeconomic and exergoenvironmental analyses of a hybrid renewable energy system with hydrogen fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 52: 617-634. |
| 20 | Shokri A, Sanavi Fard M. Techno-economic assessment of water desalination: Future outlooks and challenges[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2023, 169: 564-578. |
| 21 | Sadeghi S, Ghandehariun S, Naterer G F. Exergoeconomic and multi-objective optimization of a solar thermochemical hydrogen production plant with heat recovery[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2020, 225: 113441. |
| 22 | Khan M A, Young C, Mackinnon C, et al. The Techno- Economics of Hydrogen Compression[J]. Transition Accelerator Technical Briefs, 2021, 1(1): 1-36. |
| 23 | Shakibi H, Assareh E, Chitsaz A, et al. Exergoeconomic and optimization study of a solar and wind-driven plant employing machine learning approaches; a case study of Las Vegas city[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 385: 135529. |
| 24 | Zhang S G, Li K Y, Zhu P F, et al. An efficient hydrogen production process using solar thermo-electrochemical water-splitting cycle and its techno-economic analyses and multi-objective optimization[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 266: 115859. |
| 25 | 张生安, 刘桂莲. 高效太阳能电解水制氢系统及其性能的多目标优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1260-1274. |
| Zhang S A, Liu G L. Multi-objective optimization of high-efficiency solar water electrolysis hydrogen production system and its performance[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1260-1274. | |
| 26 | Sutar S V, Nirukhe A B, Yadav G D. Hydrogen production using hybrid six-step copper-chlorine thermochemical cycle: Energy and exergy analyses[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 49: 1478-1489. |
| 27 | Zhao X Y, Chen H, Zheng Q W, et al. Thermo-economic analysis of a novel hydrogen production system using medical waste and biogas with zero carbon emission[J]. Energy, 2023, 265: 126333. |
| 28 | Mehrenjani J R, Gharehghani A, Nasrabadi A M, et al. Design, modeling and optimization of a renewable-based system for power generation and hydrogen production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(31): 14225-14242. |
| 29 | Debe M K, Hendricks S M, Vernstrom G D, et al. Initial performance and durability of ultra-low loaded NSTF electrodes for PEM electrolyzers[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2012, 159(6): K165-K176. |
| 30 | Tu Z K, Zhang H N, Luo Z P, et al. Evaluation of 5 kW proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack operated at 95℃ under ambient pressure[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 222: 277-281. |
| 31 | Zhao P, Wang J F, Gao L, et al. Parametric analysis of a hybrid power system using organic Rankine cycle to recover waste heat from proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(4): 3382-3391. |
| 32 | 王辉东, 姚海燕, 郭强, 等. 质子交换膜电解水制氢系统建模与仿真[J]. 南通大学学报(自然科学版), 2024 (5): 1-10. |
| Wang H D, Yao H Y, Guo Qet al. Modeling and simulation of proton exchange membrane electrolyzer system[J]. Journal of Nantong University (Natural Science Edition), 2024 (5): 1-10. | |
| 33 | 张岑, 魏华, 庄妍, 等. 海上风电制氢经济评价模型及关键影响参数[J]. 天然气工业, 2023, 43(2): 146-154. |
| Zhang C, Wei H, Zhuang Y, et al. Economic evaluation model of offshore wind to hydrogen and its key influence parameters[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2023, 43(2): 146-154. | |
| 34 | Salehmin M N I, Husaini T, Goh J, et al. High-pressure PEM water electrolyser: A review on challenges and mitigation strategies towards green and low-cost hydrogen production[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 268: 115985. |
| 35 | Shabani M J, Babaelahi M. Innovative solar-baased multi-generation system for sustainable power generation, desalination, hydrogen production, and refrigeration in a novel configuration[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 59: 1115-1131. |
| [1] | 张赵雪, 李正宇, 崔文慧, 王倩, 王志平, 龚领会. 基于液氖液氮梯级蓄冷的液氢储能中冷能回收利用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, (): 1-11. |
| [2] | 郭磊磊, 吴震, 杨福胜, 张早校. 基于流通式金属氢化物反应器的氢高效分离提纯实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(12): 4576-4586. |
| [3] | 卓红英, 赵忠正, 沈铮, 杨小峰, 黄延强. 正-仲氢催化转化研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(11): 3883-3895. |
| [4] | 王军锋, 张俊杰, 张伟, 王家乐, 双舒炎, 张亚栋. 液相放电等离子体分解甲醇制氢:电极配置的优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3277-3286. |
| [5] | 王倩倩, 李冰, 郑伟波, 崔国民, 赵兵涛, 明平文. 氢燃料电池局部动态特征三维模型[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2812-2820. |
| [6] | 吕方明, 包志铭, 王博文, 焦魁. 气体扩散层侵入流道对燃料电池水管理影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2929-2938. |
| [7] | 豆少军, 郝亮. PEMFC催化层耦合气体电荷传输过程的介观模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 3002-3010. |
| [8] | 王金山, 王世学, 朱禹. 冷却表面温差对高温质子交换膜燃料电池性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 2026-2035. |
| [9] | 范以薇, 刘威, 李盈盈, 王培霞, 张吉松. 有机液体储氢中全氢化乙基咔唑催化脱氢研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1198-1208. |
| [10] | 钱志广, 樊越, 王世学, 岳利可, 王金山, 朱禹. 吹扫条件对PEMFC阻抗弛豫现象和低温启动的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1286-1293. |
| [11] | 郑克晴, 孙亚, 闫阳天, 李丽, 杨钧. 一种热电协同增强的固体氧化物燃料电池新型连接件的数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(12): 5572-5580. |
| [12] | 厉劲风, 方凯, 许好好, 李鑫坤, 谢军龙, 陈建业. 大空间液氢射流泄漏扩散特性[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5177-5185. |
| [13] | 龚翔, 李林森, 姜召. PdCo/SiO2双金属催化剂用于杂环储氢载体的高效脱氢[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4448-4460. |
| [14] | 周云龙, 林东尧, 叶校源, 孙博. 常见离子对玉米秸秆为牺牲剂的光催化制氢影响[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 722-729. |
| [15] | 王振华,蒋军成,尤飞,李刚,庄陈浩,赵耀鹏,倪磊,潘勇,李丹. 高压氢气储运设施泄漏喷射火过程预测模型及其验证[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(10): 5412-5423. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号