CIESC Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (8): 3614-3624.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20200121
• Catalysis, kinetics and reactors • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yin ZHANG( ),Jianjian GUO,Huanjie REN,Juan CHENG,Haitao LI,Jianbing WU,Yongxiang ZHAO(
),Jianjian GUO,Huanjie REN,Juan CHENG,Haitao LI,Jianbing WU,Yongxiang ZHAO( )
)
Received:2020-02-07
Revised:2020-04-01
Online:2020-08-05
Published:2020-08-05
Contact:
Yongxiang ZHAO
通讯作者:
赵永祥
作者简介:张因(1982—),女,博士,副教授,基金资助:CLC Number:
Yin ZHANG, Jianjian GUO, Huanjie REN, Juan CHENG, Haitao LI, Jianbing WU, Yongxiang ZHAO. Effect of intercalation anions on catalytic performance of hydrotalcite-like precursor Ni-Al2O3 catalyst for levulinic acid hydrogenation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(8): 3614-3624.
张因, 郭健健, 任欢杰, 程娟, 李海涛, 武建兵, 赵永祥. 插层阴离子对以类水滑石为前体Ni-Al2O3催化剂催化乙酰丙酸加氢性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(8): 3614-3624.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Sample | Ni/Al molar ratio① | Sample formula② | Theoretical mass loss on thermal decomposition③ /% | Mass loss on thermal decomposition measured by TG④/% | C content⑤/ %(mass) | N content⑤/ %(mass) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiAl-N-LDH | 3.05 | [Ni0.753Al0.247(OH)2]0.247[NO3-]0.247?mH2O | 31.28 | 30.84 | —⑥ | 3.24 |
| NiAl-C-LDH | 3.12 | [Ni0.757Al0.243(OH)2]0.243[CO32-]0.121?mH2O | 25.32 | 25.85 | 1.42 | 0.005 |
Table 1 Composition of NiAl-N-LDH and NiAl-C-LDH
| Sample | Ni/Al molar ratio① | Sample formula② | Theoretical mass loss on thermal decomposition③ /% | Mass loss on thermal decomposition measured by TG④/% | C content⑤/ %(mass) | N content⑤/ %(mass) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiAl-N-LDH | 3.05 | [Ni0.753Al0.247(OH)2]0.247[NO3-]0.247?mH2O | 31.28 | 30.84 | —⑥ | 3.24 |
| NiAl-C-LDH | 3.12 | [Ni0.757Al0.243(OH)2]0.243[CO32-]0.121?mH2O | 25.32 | 25.85 | 1.42 | 0.005 |
| Catalyst | BET specific surface area/ (m2/g) | Pore volume/ (cm3/g) | Average pore diameter/nm | Total acid sites①/(μmol/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiAl-N-R | 92 | 0.18 | 5.4 | 850 |
| NiAl-C-R | 87 | 0.55 | 19.9 | 1320 |
Table 2 Textural parameters of the catalysts
| Catalyst | BET specific surface area/ (m2/g) | Pore volume/ (cm3/g) | Average pore diameter/nm | Total acid sites①/(μmol/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiAl-N-R | 92 | 0.18 | 5.4 | 850 |
| NiAl-C-R | 87 | 0.55 | 19.9 | 1320 |
| Catalysts | Solvent | Conversion of LA/% | Selectivity of GVL/% | Yield of GVL/% | TOFC=O/ min-1① |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiAl-N-R | methanol methanol | 66.6 | 63.2 | 42.1 | 3.45 |
| NiAl-C-R | 86.7 | 82.9 | 71.8 | 4.37 | |
| NiAl-N-R | ethanol ethanol | 62.9 | 60.4 | 37.9 | 3.11 |
| NiAl-C-R | 74.5 | 86.7 | 64.6 | 3.92 | |
| NiAl-N-R | propanol propanol | 54.5 | 61.2 | 33.4 | 2.74 |
| NiAl-C-R | 67.3 | 84.8 | 57.1 | 3.47 | |
| NiAl-N-R | butanol butanol | 46.7 | 62.3 | 29.1 | 2.39 |
| NiAl-C-R | 58.9 | 85.3 | 50.2 | 3.05 |
Table 3 Catalytic performance of catalysts for the hydrogenation of levulinic acid using different solvents
| Catalysts | Solvent | Conversion of LA/% | Selectivity of GVL/% | Yield of GVL/% | TOFC=O/ min-1① |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiAl-N-R | methanol methanol | 66.6 | 63.2 | 42.1 | 3.45 |
| NiAl-C-R | 86.7 | 82.9 | 71.8 | 4.37 | |
| NiAl-N-R | ethanol ethanol | 62.9 | 60.4 | 37.9 | 3.11 |
| NiAl-C-R | 74.5 | 86.7 | 64.6 | 3.92 | |
| NiAl-N-R | propanol propanol | 54.5 | 61.2 | 33.4 | 2.74 |
| NiAl-C-R | 67.3 | 84.8 | 57.1 | 3.47 | |
| NiAl-N-R | butanol butanol | 46.7 | 62.3 | 29.1 | 2.39 |
| NiAl-C-R | 58.9 | 85.3 | 50.2 | 3.05 |
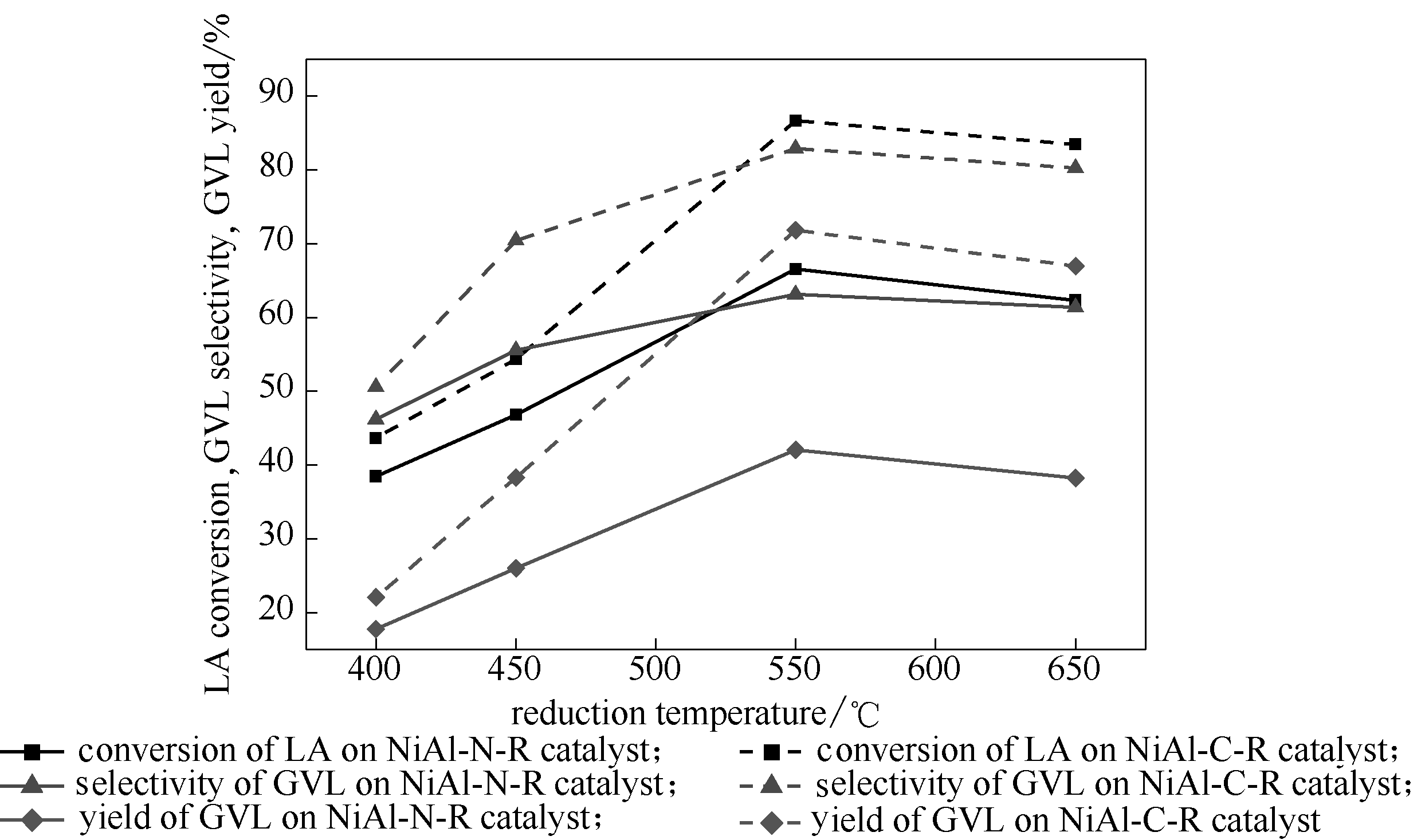
Fig.11 Effect of reduction temperatures on catalytic performance of catalysts (Reaction conditions: LA 1.67 g, catalyst 0.1 g, stirrer 400 r/min, reaction temperature 160℃, hydrogen pressure 4 MPa, methanol 40 ml as solvent, reaction time 1 h)
| Catalyst | Reaction time / h | Conversion of LA / % | Selectivity of GVL / % | Yield of GVL / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiAl-N-R | 0.5 | 47.1 | 56.2 | 26.4 |
| 1.0 | 66.6 | 63.2 | 42.1 | |
| 1.5 | 82.7 | 68.3 | 56.5 | |
| 2.0 | 86.2 | 70.4 | 60.7 | |
| NiAl-C-R | 0.5 | 61.2 | 77.0 | 47.2 |
| 1.0 | 86.7 | 82.7 | 71.8 | |
| 1.5 | 95.9 | 84.8 | 81.3 | |
| 2.0 | 98.3 | 85.1 | 83.7 |
Table 4 Effect of reaction time on catalytic performance of catalysts for hydrogenation of levulinic acid
| Catalyst | Reaction time / h | Conversion of LA / % | Selectivity of GVL / % | Yield of GVL / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiAl-N-R | 0.5 | 47.1 | 56.2 | 26.4 |
| 1.0 | 66.6 | 63.2 | 42.1 | |
| 1.5 | 82.7 | 68.3 | 56.5 | |
| 2.0 | 86.2 | 70.4 | 60.7 | |
| NiAl-C-R | 0.5 | 61.2 | 77.0 | 47.2 |
| 1.0 | 86.7 | 82.7 | 71.8 | |
| 1.5 | 95.9 | 84.8 | 81.3 | |
| 2.0 | 98.3 | 85.1 | 83.7 |
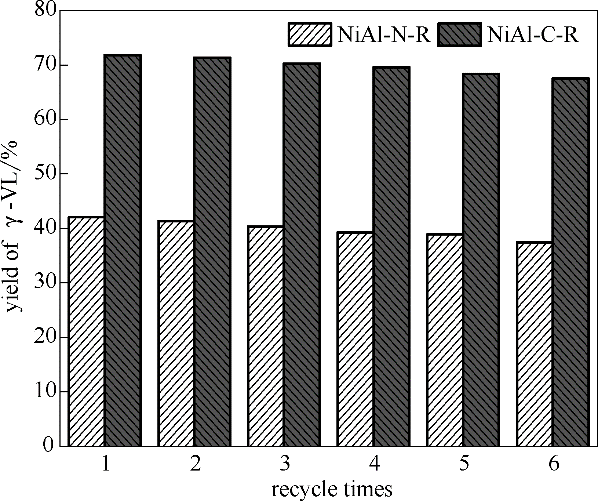
Fig.12 Effect of recycle times on catalytic performance of catalysts (Reaction conditions: LA 1.67 g, catalyst 0.1 g, stirrer 400 r/min, reaction temperature 160℃, hydrogen pressure 4 MPa, methanol 40 ml as solvent, reaction time 1 h)
| 1 | Mehdi H, Fábos V, Tuba R, et al. Integration of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalytic processes for a multi-step conversion of biomass: from sucrose to levulinic acid, γ-valerolactone, 1,4-pentanediol, 2-methyl-tetrahydrofuran, and alkanes[J]. Top. Catal., 2008, 48: 49-54. |
| 2 | 盛栋. 镍基催化剂催化乙酰丙酸制备γ-戊内酯[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2015. |
| Sheng D. Nickel-based catalyst catalyzes the preparation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2015. | |
| 3 | 朱龙云. 负载型Ni催化剂催化乙酰丙酸加氢合成γ-戊内酯的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2015. |
| 4 | Tan J J. Basic research on the application of Ru-based catalysts in aqueous hydrogenation of levulinic acid [D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Institute of Coal Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016. |
| 5 | Bond J Q, Alonso D M, Wang D, et al. Integrated catalytic conversion of γ-valerolactone to liquid alkenes for transportation fuels[J]. Science, 2010, 327: 1110-1114. |
| 6 | Serrano-Ruiz J C, Wang D, Dumesic J A. Catalytic upgrading of levulinic acid to 5-nonanone[J]. Green Chem., 2010, 12(4): 574-577. |
| 7 | Contino F, Dagaut P, Dayma G, et al. Combustion and emissions characteristics of valeric biofuels in a compression ignition engine[J]. Journal of Energy Engineering, 2014, 140: 171-175. |
| 8 | Kumar V V, Naresh G, Sudhakar M, et al. An investigation on the influence of support type for Ni catalysed vapour phase hydrogenation of aqueous levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone[J]. RSC Adv., 2016, 6: 9872-9879. |
| 9 | 孙卓文. 肉桂醛与乙酰丙酸选择性加氢的研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2014. |
| Sun Z W. Study on selective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde and levulinic acid [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2014. | |
| 10 | Hengst K, Schubert M, Carvalho H W P, et al. Synthesis of γ-valerolactone by hydrogenation of levulinic acid over supported nickel catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2015, 502: 18-26. |
| 11 | Hengst K, Ligthart D A J M, Doronkin D E, et al. Continuous synthesis of γ-valerolactone in a trickle-bed reactor over supported nickel catalysts[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017, 56: 2680-2689. |
| 12 | Yan K, Chen A. Efficient hydrogenation of biomass-derived furfural and levulinic acid on the facilely synthesized noble-metal-free Cu-Cr catalyst[J]. Energy, 2013, 58: 357-363. |
| 3 | Zhu L Y. Study on supported Ni catalyst for hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2015. |
| 4 | 谭静静. Ru基催化剂在乙酰丙酸水相加氢中的应用基础研究[D]. 太原: 中国科学院山西煤炭化学研究所, 2016. |
| 13 | Yan K, Chen A. Selective hydrogenation of furfural and levulinic acid to biofuels on the ecofriendly Cu-Fe catalyst[J]. Fuel, 2014, 115: 101-108. |
| 14 | Long X, Sun P, Li Z, et al. Magnetic Co/Al2O3 catalyst derived from hydrotalcite for hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2015, 36: 1512-1518. |
| 15 | Gupta S S R, Kantam M L. Selective hydrogenation of levulinic acid into γ-valerolactone over Cu/Ni hydrotalcite-derived catalyst[J]. Catalysis Today, 2017, 8(7): 231-236. |
| 16 | 蒋龙飞. 铜基类水滑石的制备及其催化合成γ-戊内酯的研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2012. |
| Jiang L F. Preparation of copper-based hydrotalcite and study on its catalytic synthesis of γ-valerolactone [D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2012. | |
| 17 | 谢鲜梅. 类水滑石化合物的制备、性能及应用研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2007. |
| Xie X M. Study on preparation, properties and application of hydrotalcite-like compounds [D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2007. | |
| 18 | Claudio R, Soria M A, Madeira L M. Effect of interlayer anion on the CO2 capture capacity of hydrotalcite-based sorbents[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 219: 290-302. |
| 19 | Wu X, Du Y L, Liu X Z, et al. Facile synthesis of NiAl-LDHs with tunable establishment of acid-base activity sites[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2018, 211: 72-78. |
| 20 | Oliver M, Frank R, Rainer A, et al. Impact of organic interlayer anions in hydrotalcite precursor on the catalytic activity of hydrotalcite-derived mixed oxides[J]. ChemCatChem, 2010, 2(3): 314-321. |
| 21 | Gupta S A R, Kantam M L. Selective hydrogenation of levulinic acid into γ-valerolactone over Cu/Ni hydrotalcite-derived catalyst[J]. Catalysis Today, 2018, 309: 189-194. |
| 22 | 龙向东, 孙鹏, 李泽龙, 等. 水滑石基磁性Co/Al2O3催化剂在乙酰丙酸加氢制备γ-戊内酯反应中的应用[J]. 催化学报, 2015, 36(9): 1512-1518. |
| Long X D, Sun P, Li Z L, et al. Application of hydrotalcite-based magnetic Co/Al2O3 catalyst in the hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone [J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2015, 36(9): 1512-1518. | |
| 23 | 王杰, 徐亚琳, 张因, 等. 制备方法对Ni-Al2O3催化剂乙酰丙酸加氢性能的影响[J]. 工业催化, 2018, 26: 15-20. |
| Wang J, Xu Y L, Zhang Y, et al. Effect of preparation methods on Ni-Al2O3 catalyst for levulinic acid hydrogenation [J]. Industrial Catalysis, 2018, 26: 15-20. | |
| 24 | 刘洁翔, 张晓光. 阴离子插层镁铝水滑石结构及相互作用的理论研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(6): 761-768. |
| Liu J X, Zhang X G. Theoretical study on the structure and interaction of anion intercalated magnesium aluminum hydrotalcite [J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2013, 41(6): 123-130. | |
| 25 | 罗青松, 李蕾, 王作新, 等. 镁铝水滑石层板与层间阴离子相互作用的理论研究[J]. 无机化学学报, 2001, 17(6): 835-842. |
| Luo Q S, Li L, Wang Z X, et al. Theoretical study on anion interaction between magnesium aluminum hydrotalcite laminates and interlayers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2001, 17(6): 835-842. | |
| 26 | Wu X, Ci C, Du Y, et al. Facile synthesis of NiAl-LDHs with tunable establishment of acid-base activity sites[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2018, 211: 72-78. |
| 27 | Linda M P, Neil B M, Roger H N. The use of hydrotalcite as an anion absorbent[J]. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 1995, 34: 1196-1202. |
| 28 | 李蕾. 类水滑石材料新制备方法及结构与性能的理论研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2002. |
| Li L. A new preparation method of hydrotalcite-like material and theoretical study on structure and performance [D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2002. | |
| 29 | 李海涛, 陈昊然, 张因, 等. 炭包覆氧化铝负载镍催化剂的制备和表征及其催化加氢性能[J]. 催化学报, 2011, 32(1): 127-133. |
| Li H T, Chen H R, Zhang Y, et al. Preparation and characterization of nickel catalyst coated with alumina and its catalytic hydrogenation performance[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2011, 32(1): 127-133. | |
| 30 | 李广燕, 刘长久, 吴华斌, 等. 稀土Nd3+与Cu2+掺杂非晶态纳米Ni(OH)2材料的电化学性能[J]. 化学工程, 2009, 37(12): 55-58. |
| Li G Y, Liu C J, Wu H B, et al. Electrochemical properties of rare earth Nd3+ and Cu2+ doped amorphous nano Ni(OH)2 materials [J]. Chemical Engineering(China), 2009, 37(12): 55-58. | |
| 31 | 王佳. 层状前驱体制备高分散负载型纳米镍基催化剂及其性能的研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2012. |
| Wang J. Study on preparation and performance of highly dispersed supported nano nickel-based catalysts by layered precursors[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2012. | |
| 32 | Sònia A, Danny V, Blaise B, et al. Activated takovite catalysts for partial hydrogenation of ethyne, propyne, and propadiene[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2008, 259(1): 85-95. |
| 33 | Clause O, Goncalves C M, Gazzano M, et al. Synthesis and thermal reactivity of nickel-containing anionic clays[J]. Applied Clay Science, 1993, 8(2): 169-186. |
| 34 | Rebours B, Jean-Baptiste D D L C, Clause O. Decoration of nickel and magnesium oxide crystallites with spinel-type phases[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1995, 116(5): 1707-1717. |
| 35 | Zhu Y F, Kong X, Zhu S H, et al. Construction of Cu/ZrO2/Al2O3 composites for ethanol synthesis: synergies of ternary sites for cascade reaction[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015, 12(15): 551-559. |
| 36 | Federica P, Giovanna G, Robert D, et al. Investigation of acid-base properties of catalysts obtained from layered double hydroxides[J]. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2000, 104(47): 11117-11126. |
| 37 | 张因, 郭健健, 王杰, 等. 以NiAl-NO3-LDH为前驱体制备Ni-Al2O3催化剂及其催化乙酰丙酸加氢性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(8): 1686-1696. |
| Zhang Y, Guo J J, Wang J, et al. Preparation of Ni-Al2O3 catalyst using NiAl-NO3-LDH as precursor and its catalytic performance for hydrogenation of levulinic acid [J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1686-1696. | |
| 38 | Al-shaal M G, Wright W R H, Palkovits R. Exploring the ruthenium catalysed synthesis of γ-valerolactone in alcohols and utilisation of mild solvent-free reaction conditions[J]. Green Chemistry, 2012, 14(5): 1260-1263. |
| 39 | Hengne A M, Rode C V. Cu-ZrO2 nanocomposite catalyst for selective hydrogenation of levulinic acid and its ester to γ-valerolactone[J]. Green Chem., 2012, 14: 1064-1072. |
| [1] | Lihui WANG, Huan LIU, Heyu LI, Xiaobing ZHENG, Yanjun JIANG, Jing GAO. Preparation and application of core-shell hydrophobic magnetic dendritic fibrous organosilica immobilized lipase [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(9): 4861-4871. |
| [2] | Qian ZHANG, Yanhua WANG. Selective hydrogenation of α, β-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones over thermo regulated phase-separable Ir nano catalyst [J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(9): 3396-3403. |
| [3] | Jiacheng TU, Le SANG, Ning AI, Jianhong XU, Jisong ZHANG. Research progress of continuous hydrogenation in organic synthesis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(10): 3859-3868. |
| [4] | WANG Jie, ZHANG Yin, GUO Jianjian, ZHAO Lili, ZHAO Yongxiang. γ-Valerolactone synthesis from levulinic acid hydrogenation over Ni/ZrO2-SiO2 catalyst [J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(8): 3452-3459. |
| [5] | LI Chenyang, FENG Miao, CUI Haifeng, CAO Guiping, LÜ Hui, CHEN Rongqi. Preparation of carbon nanotube catalyst on structure-modified cordierite monolith for polystyrene hydrogenation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(7): 2746-2754. |
| [6] | CHEN Lungang, LIU Yong, DING Mingyue, ZHANG Xinghua, LI Yuping, ZHANG Qi, WANG Tiejun, MA Longlong. Removal of oxygenates in aqueous phase product of F-T process by catalytic hydrogenation over Ru catalyst [J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(11): 4347-4355. |
| [7] | JIANG Nan1,XIE Nan1,QI Wei1,2,3,SU Rongxin1,2,3,HE Zhimin1,2,3. Process intensification of levulinic acid from glucose using sulfuric acid as catalyst [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progree, 2014, 33(11): 2888-2893. |
| [8] | SUN Meijuan1,HUANG Xiaodian1,GUAN Qingqing1,ZHANG Chunyun2,CHAI Xinsheng2,TIAN Senlin1,NING Ping1,GU Junjie1. Degradation behavior of phenol though catalytic hydrogenation in supercritical ethanol [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progree, 2014, 33(07): 1902-1907. |
| [9] | GAO Xueyi,WU Yanwei,WANG Kebing. Preparation of levulinic acid from hydrolysis of Salix psammophila catalyzed by acid and its separation and purification [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progree, 2014, 33(01): 242-246. |
| [10] | SUN Hongzhi,WANG Qian,SONG Mingxiu,Abudoulajiang ? Nasi’er,WANG Fuyan,ZHU Weiqun. Progress in the chemical utilization of carbon dioxide [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progree, 2013, 32(07): 1666-1672. |
| [11] | LIU Tao,LI Lijun,HUANG Wenyi,LIU Liu. Solid superacid catalyst SO42?/ Kaolin for preparation of levulinic acid [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progree, 2013, 32(06): 1300-1306. |
| [12] | DENG Li1,LIAO Bing1,GUO Qingxiang2. Recent progress in selective catalytic conversion of cellulose into key platform molecules [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progree, 2013, 32(02): 245-254. |
| [13] | ZENG Shanshan, LIN Lu, LIU Di, PENG Lincai. Catalytic conversion of glucose to levulinic acid by solid heteropolyacid salts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(12): 3875-3881. |
| [14] | ZHANG Junhua1,GUO Haiguang1,HUAN Changyong1,JIANG Li2,SHEN Qiang1. Preparation of 4,4'-diaminostilbene-2,2'-disulfonic acid by Pt/C catalytic hydrogenation [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progree, 2012, 31(09): 2070-2074. |
| [15] | LIU Tao,LI Lijun,LIU Liu,LI Guo,LI Wei,QIN Gui. Solid superacid catalyst S2O82―/ZrO2-TiO2- Al 2O3 for preparation of levulinic acid [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progree, 2012, 31(09): 1975-1979. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||