化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (8): 3353-3365.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230499
曾如宾1,2( ), 沈中杰1,2(
), 沈中杰1,2( ), 梁钦锋1,2, 许建良1,2, 代正华1,2,3, 刘海峰1,2
), 梁钦锋1,2, 许建良1,2, 代正华1,2,3, 刘海峰1,2
收稿日期:2023-05-23
修回日期:2023-07-25
出版日期:2023-08-25
发布日期:2023-10-18
通讯作者:
沈中杰
作者简介:曾如宾(1999—),男,硕士研究生,y82210127@mail.ecust.edu.cn
基金资助:
Rubin ZENG1,2( ), Zhongjie SHEN1,2(
), Zhongjie SHEN1,2( ), Qinfeng LIANG1,2, Jianliang XU1,2, Zhenghua DAI1,2,3, Haifeng LIU1,2
), Qinfeng LIANG1,2, Jianliang XU1,2, Zhenghua DAI1,2,3, Haifeng LIU1,2
Received:2023-05-23
Revised:2023-07-25
Online:2023-08-25
Published:2023-10-18
Contact:
Zhongjie SHEN
摘要:
氧化铁是化工、冶金和能源等领域重要的原料,其在高温下的烧结性对产品性能至关重要。通过分子动力学模拟(MDS)研究了不同温度、粒径与空位缺陷浓度条件下Fe2O3纳米颗粒的烧结机制。结果表明,Fe2O3纳米颗粒粒径由3 nm增加至5 nm,烧结后收缩率由25.0%降低至10.8%,相对颈部宽度由96.6%降低至49.5%。当温度由900 K升高至1300 K,烧结过程原子扩散系数由1.758×10-3 nm2/ps增至4.303×10-3 nm2/ps,增大1.45倍。高温下(1300 K)原子迁移使颗粒部分结构由HCP和BCC结构转变为非晶结构,非晶原子比例为66.7%。含10.0%初始空位缺陷浓度纳米颗粒烧结过程的扩散活化能相比完美晶体(0空位浓度)降低约63.5%,原子迁移性及烧结致密化程度增强。研究结果对氧化铁颗粒高温热处理工艺优化具有指导意义。
中图分类号:
曾如宾, 沈中杰, 梁钦锋, 许建良, 代正华, 刘海峰. 基于分子动力学模拟的Fe2O3纳米颗粒烧结机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365.
Rubin ZENG, Zhongjie SHEN, Qinfeng LIANG, Jianliang XU, Zhenghua DAI, Haifeng LIU. Study of the sintering mechanism of Fe2O3 nanoparticles based on molecular dynamics simulation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365.
| 原子对 | Aij /eV | Bij /Å | Cij /(eV/Å6) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charge | 采用固定电荷值为 | ||
| Fe-O | 62775.704 | 0.165 | 32.055 |
| O-O | 3834.644 | 0.305 | 123.029 |
| Fe-Fe | 2500.943 | 0.029 | 6.383 |
表1 本研究采用的白金汉-库仑势势参数[26]
Table 1 Potential parameters of the Buckingham-Coulomb potential in this study[26]
| 原子对 | Aij /eV | Bij /Å | Cij /(eV/Å6) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charge | 采用固定电荷值为 | ||
| Fe-O | 62775.704 | 0.165 | 32.055 |
| O-O | 3834.644 | 0.305 | 123.029 |
| Fe-Fe | 2500.943 | 0.029 | 6.383 |
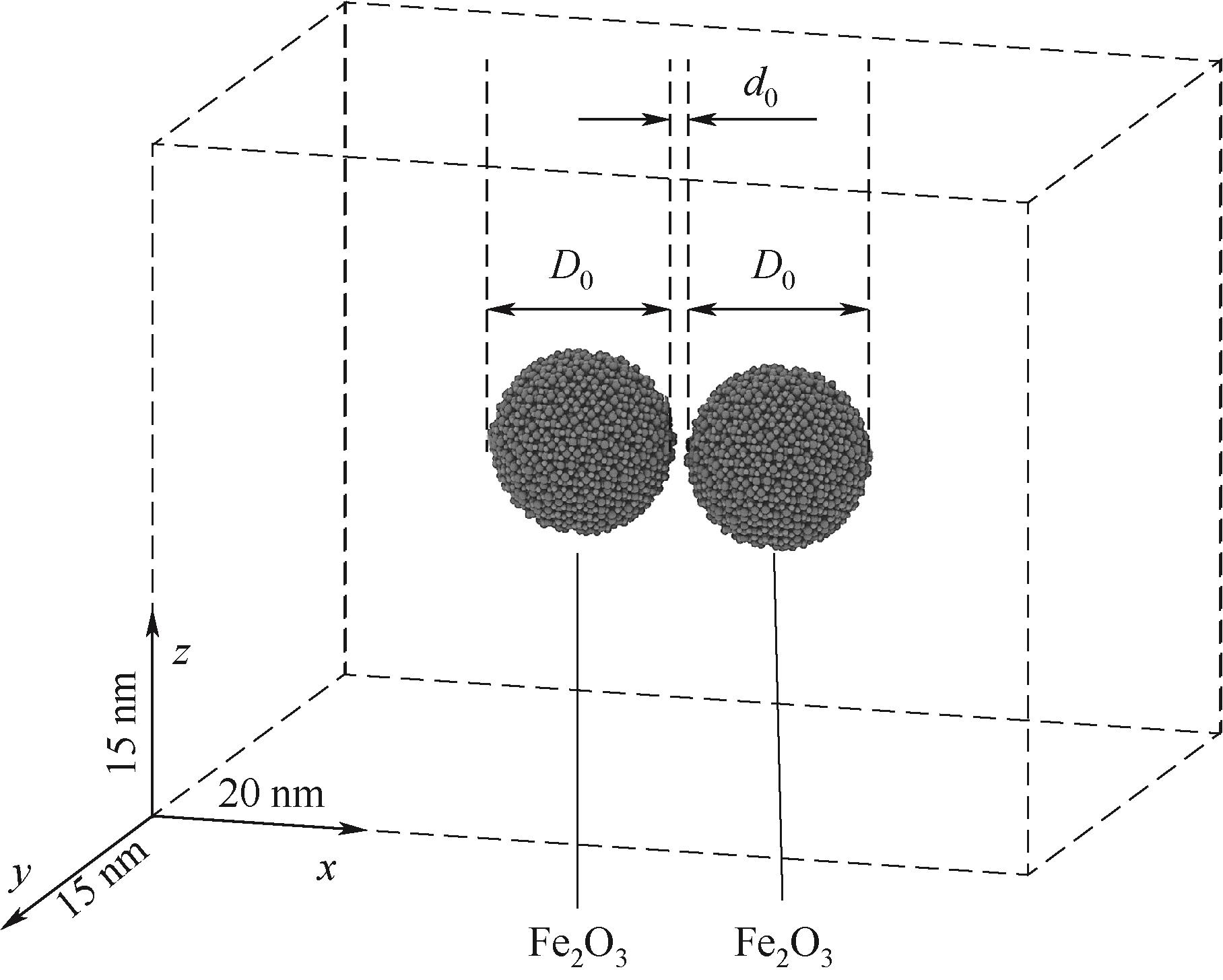
图2 模拟盒(20 nm×15 nm×15 nm)中两个Fe2O3颗粒(直径D0,初始分隔距离d0 =0.4 nm)
Fig.2 Two Fe2O3 nanoparticles (diameter D0) in a simulation box (20 nm × 15 nm × 15 nm) with an initial separation distance d0 = 0.4 nm
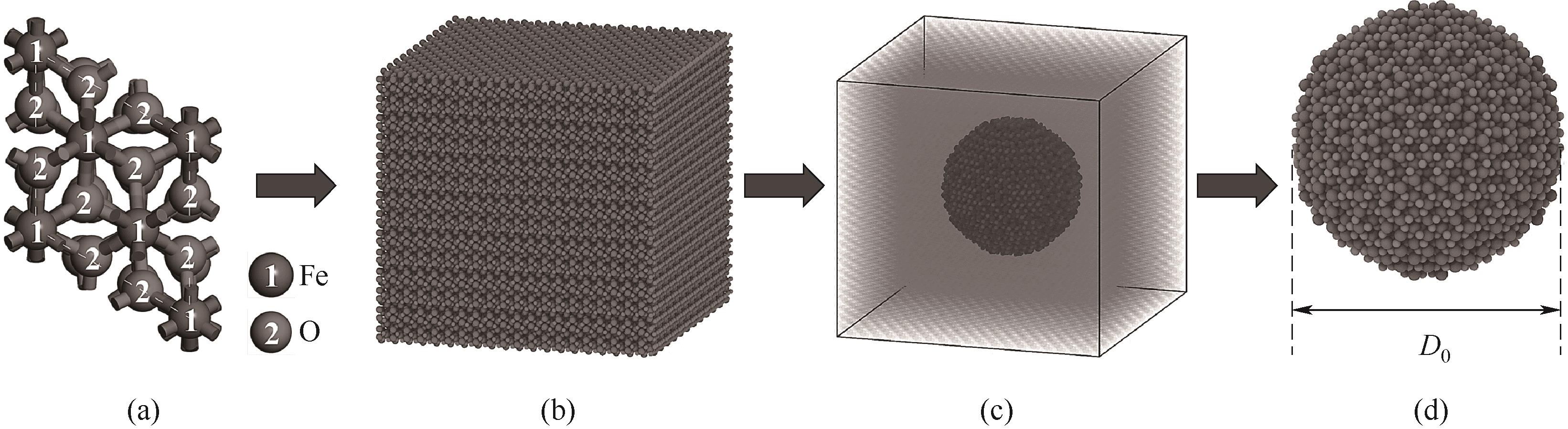
图1 Fe2O3纳米颗粒的建模过程(a)Fe2O3单晶胞;(b)超晶胞;(c)球形切割超晶胞;(d)Fe2O3单颗粒
Fig.1 Modelling process of Fe2O3 nanoparticles(a) Fe2O3 single cell; (b) supercell; (c) spherically cut supercell; (d) Fe2O3 single nanoparticle
| 模拟编号 | 粒径D0/nm | 温度T/K | 空位浓度Cv/% | 原子数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1~6 | 4 | 300、900、1000、1100、1200、1300 | 0 | 6660 |
| 7~11 | 4 | 900、1000、1100、1200、1300 | 10.0 | 5980 |
| 12 | 4 | 1300 | 7.5 | 6150 |
| 13 | 4 | 1300 | 5.0 | 6310 |
| 14 | 4 | 1300 | 2.5 | 6480 |
| 15 | 3 | 1300 | 0 | 2950 |
| 16 | 5 | 1300 | 0 | 13060 |
表2 所有模型初始结构参数配置
Table 2 Configuration of initial structural parameters for all models
| 模拟编号 | 粒径D0/nm | 温度T/K | 空位浓度Cv/% | 原子数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1~6 | 4 | 300、900、1000、1100、1200、1300 | 0 | 6660 |
| 7~11 | 4 | 900、1000、1100、1200、1300 | 10.0 | 5980 |
| 12 | 4 | 1300 | 7.5 | 6150 |
| 13 | 4 | 1300 | 5.0 | 6310 |
| 14 | 4 | 1300 | 2.5 | 6480 |
| 15 | 3 | 1300 | 0 | 2950 |
| 16 | 5 | 1300 | 0 | 13060 |

图7 不同温度纳米颗粒烧结过程(a)收缩率;(b)回转半径;(c)颈部宽度;(d)颈部原子数
Fig.7 Sintering process of nanoparticles under different temperatures(a) shrinkage rate; (b) gyration radius; (c) neck width; (d) number of atoms in the neck
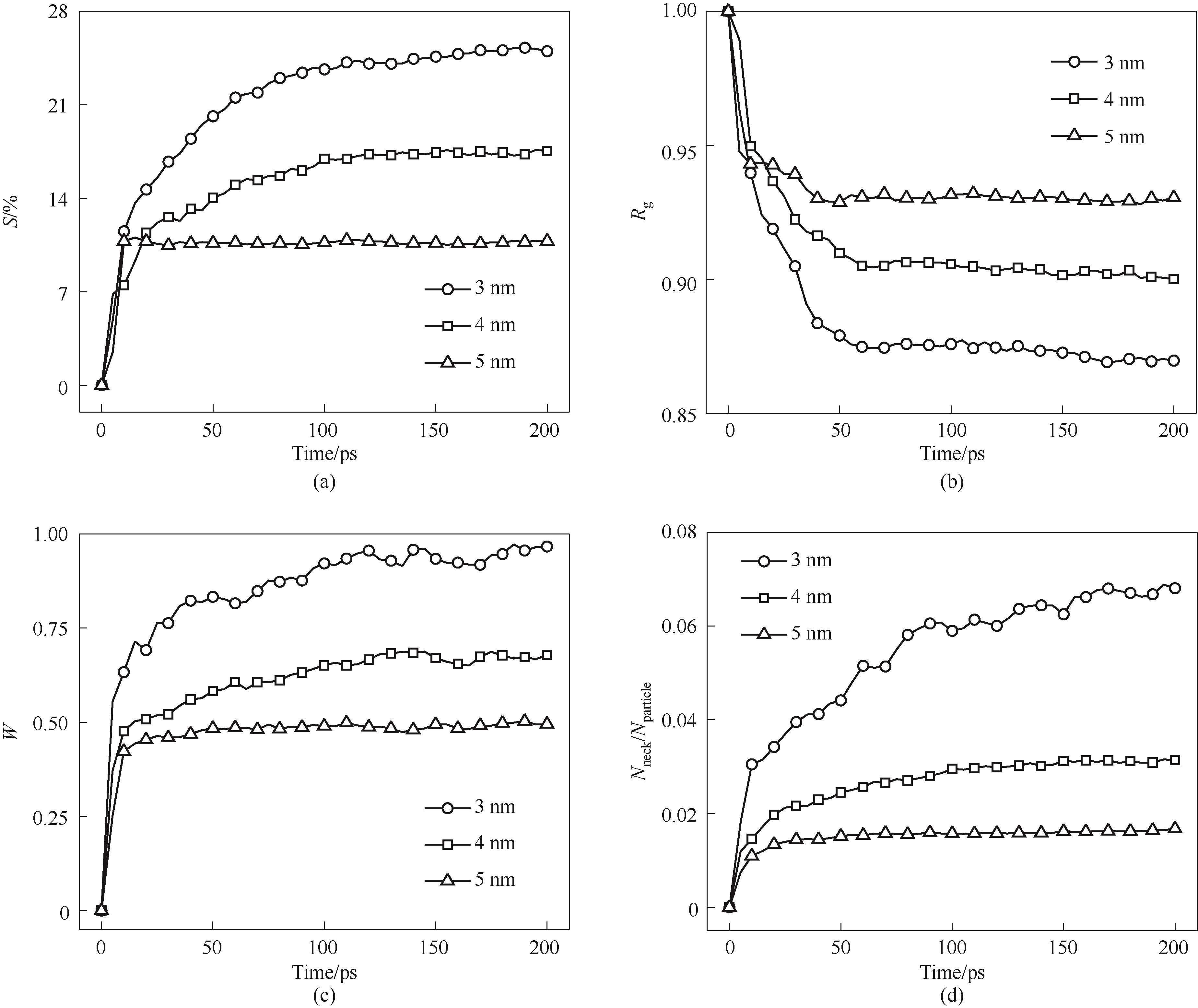
图9 不同粒径纳米颗粒烧结过程(a) 收缩率; (b) 归一化回转半径; (c) 归一化颈部宽度; (d) 颈部原子数/原子总数
Fig.9 Sintering process of nanoparticles with different particle sizes(a) shrinkage rate; (b) normalized gyration radius; (c) normalized neck width; (d) number of atoms in the neck/total number of atoms
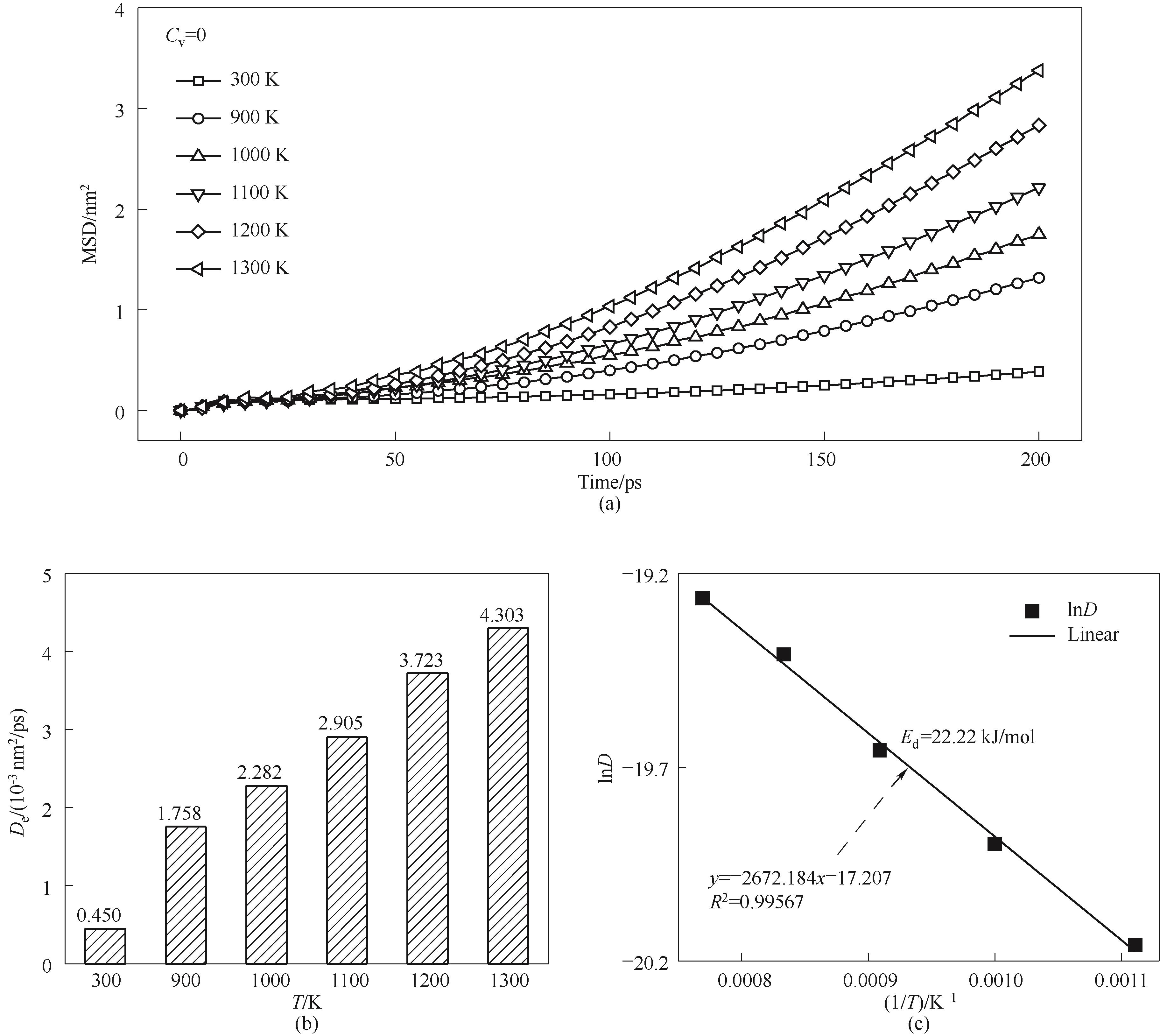
图10 不同温度烧结模拟的原子扩散特性(a)MSD曲线;(b)扩散系数;(c)拟合扩散活化能
Fig.10 Atomic diffusion properties of sintering simulations under different temperatures(a) MSD curves; (b) diffusion coefficient; (c) fitted diffusion activation energy
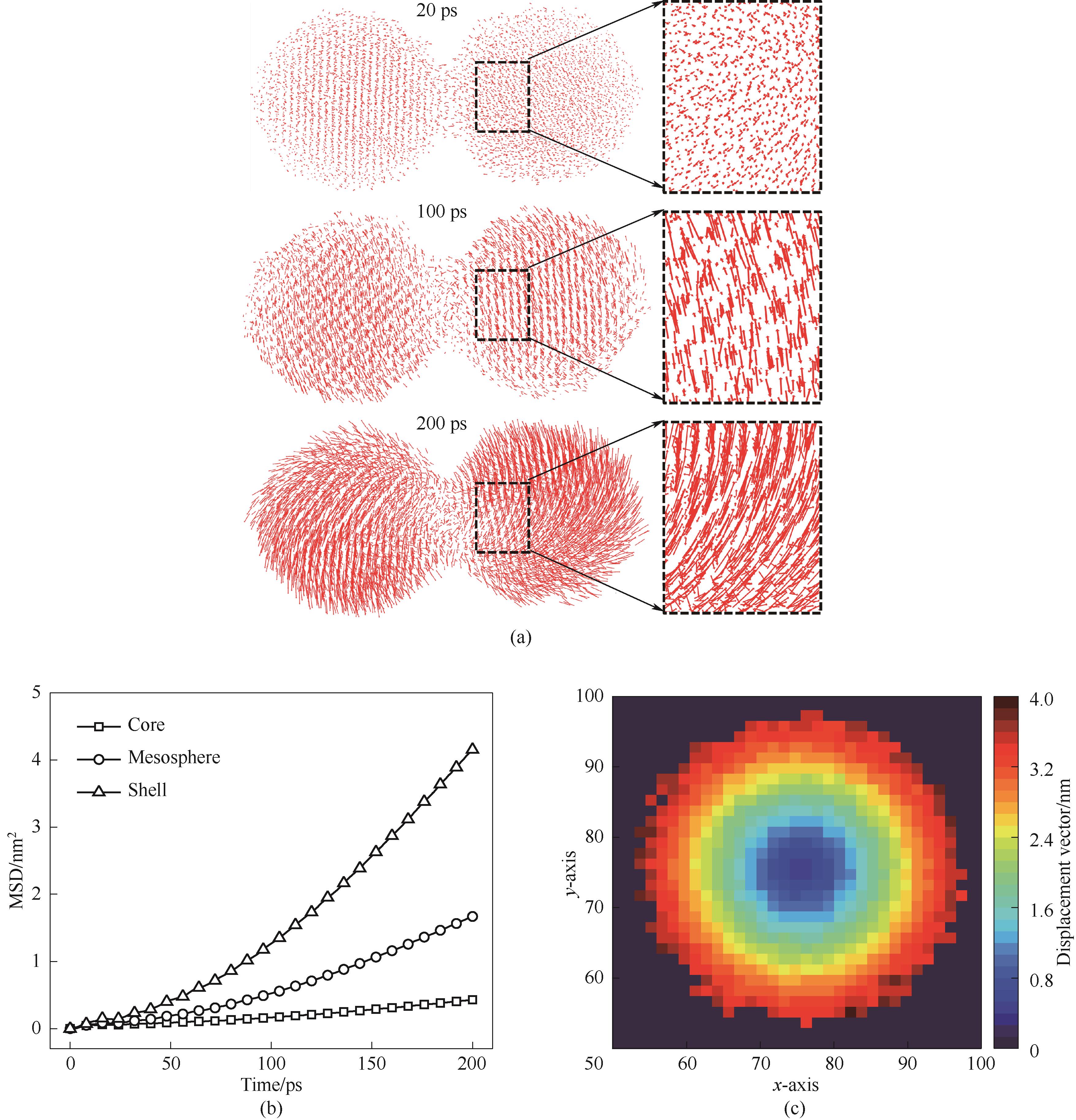
图11 1300 K烧结模拟中的原子迁移特性(a)原子位移矢量;(b)不同层原子MSD;(c)单颗粒原子位移
Fig.11 Atomic migration properties in 1300 K sintering simulations(a) atomic displacement vectors; (b) MSD of different layers of atoms; (c) single particle atomic displacement

图13 1300 K模拟烧结体的晶体结构演变(a)晶体结构变化(蓝色—BCC结构、红色—HCP结构、黄色—无定形结构);(b)不同结构比例变化
Fig.13 Crystal structure evolution of sintered nanoparticles at 1300 K simulation(a) changes in crystal structure (blue — BCC, red — HCP, yellow — amorphous); (b) changes in proportions of different structures
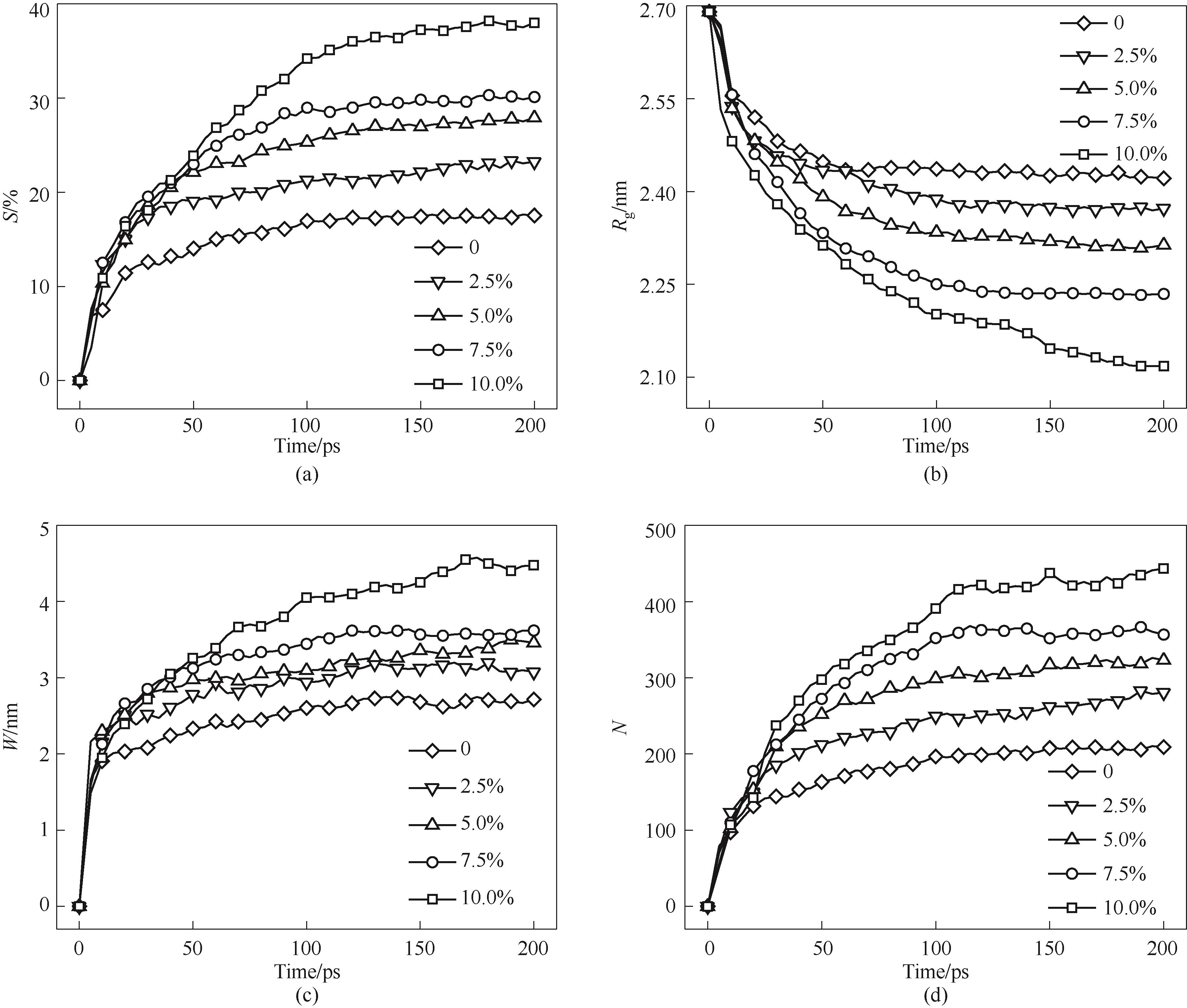
图15 不同空位浓度纳米颗粒烧结过程(a)收缩率;(b)回转半径;(c)颈部宽度;(c)颈部原子数
Fig.15 Sintering process of nanoparticles with different vacancy concentrations(a) shrinkage rate; (b) gyration radius; (c) neck width; (d) number of atoms in the neck
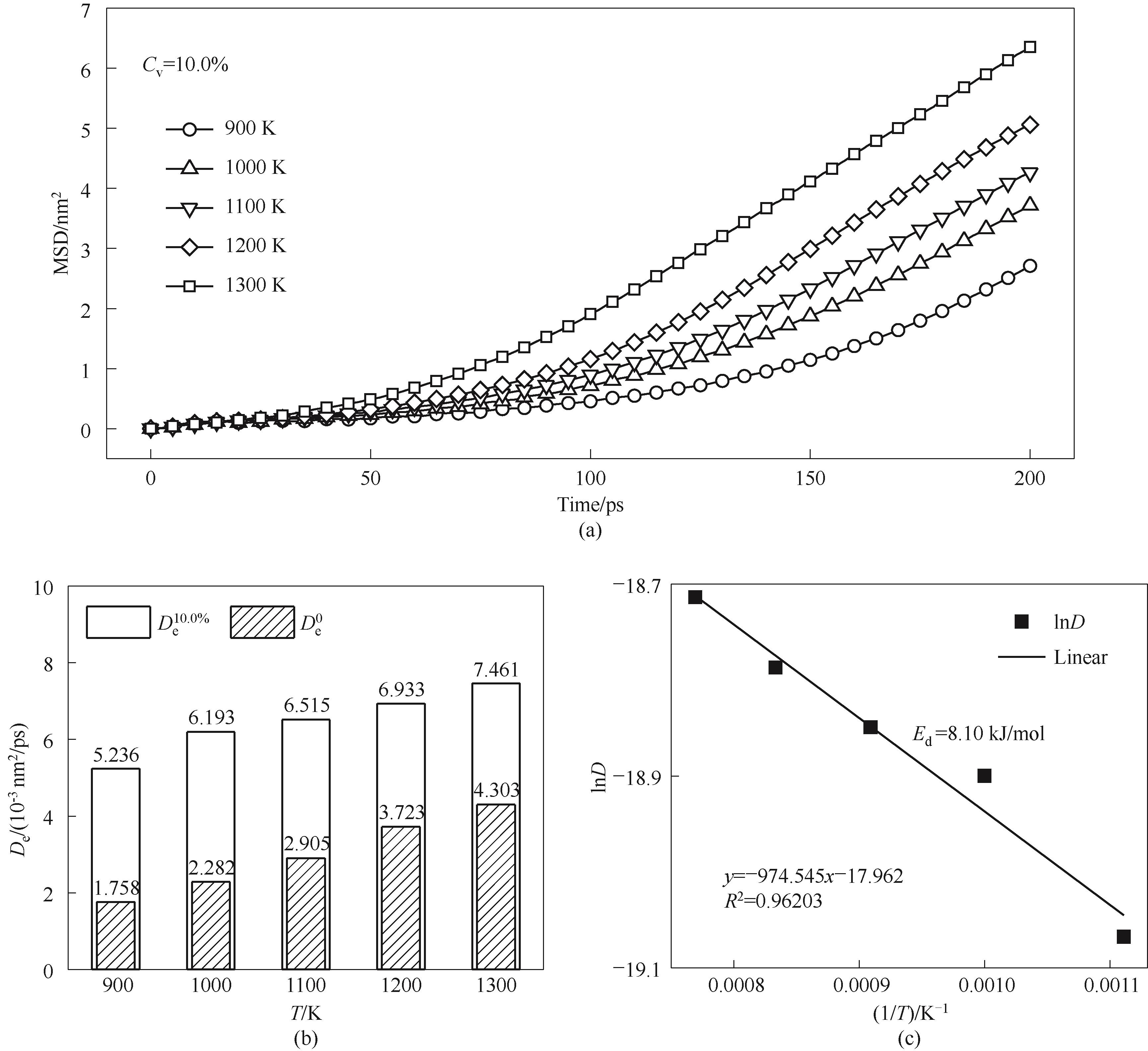
图16 Cv=10.0% 颗粒不同温度烧结的原子扩散特性(a)MSD曲线;(b)扩散系数;(c) 拟合扩散活化能
Fig.16 Atomic diffusion characteristics of Cv=10.0% nanoparticles sintered under different temperatures(a) MSD curves; (b) diffusion coefficients; (c) fitted diffusion activation energy
| 1 | Mishra M, Chun D M. α-Fe2O3 as a photocatalytic material: a review[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2015, 498: 126-141. |
| 2 | Pourmadadi M, Rahmani E, Shamsabadipour A, et al. Role of iron oxide (Fe2O3) nanocomposites in advanced biomedical applications: a state-of-the-art review[J]. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(21): 3873. |
| 3 | Kumar S, Kumar M, Singh A. Synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe2O3, Fe3O4): a brief review[J]. Contemporary Physics, 2021, 62(3): 144-164. |
| 4 | Zeng Y X, Yu M H, Meng Y E, et al. Iron-based supercapacitor electrodes: advances and challenges[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6(24): 1601053. |
| 5 | Qasim M, Ayoub M, Ghazali N A, et al. Recent advances and development of various oxygen carriers for the chemical looping combustion process: a review[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2021, 60(24): 8621-8641. |
| 6 | Fan J J, Qiu G Z, Jiang T, et al. Roasting properties of pellets with iron concentrate of complex mineral composition[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2011, 18(7): 1-7. |
| 7 | Forsmo S P E, Forsmo S E, Samskog P O, et al. Mechanisms in oxidation and sintering of magnetite iron ore green pellets[J]. Powder Technology, 2008, 183(2): 247-259. |
| 8 | Lyngfelt A. Chemical looping combustion: status and development challenges[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2020, 34(8): 9077-9093. |
| 9 | Wang W, Chen X H, Xu R S, et al. Research progress on multiscale structural characteristics and characterization methods of iron ore sinter[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2020, 27(4): 367-379. |
| 10 | Yu Z L, Li C Y, Jing X L, et al. Effects of CO2 atmosphere and K2CO3 addition on the reduction reactivity, oxygen transport capacity, and sintering of CuO and Fe2O3 oxygen carriers in coal direct chemical looping combustion[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2013, 27(5): 2703-2711. |
| 11 | Tian M, Wang C J, Li L, et al. High performance of La-promoted Fe2O3/α-Al2O3 oxygen carrier for chemical looping combustion[J]. AIChE Journal, 2017, 63(7): 2827-2838. |
| 12 | Ma S W, Chen S Y, Zhu M, et al. Enhanced sintering resistance of Fe2O3/CeO2 oxygen carrier for chemical looping hydrogen generation using core-shell structure[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(13): 6491-6504. |
| 13 | 孔令菲, 陈延佩, 王维. 气固流态化中颗粒介尺度结构的动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2486-2495. |
| Kong L F, Chen Y P, Wang W. Dynamic study of mesoscale structures of particles in gas-solid fluidization[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2486-2495. | |
| 14 | 崔文政, 沈照杰, 毛东旭, 等. 纳米流体中纳米颗粒微运动的分子动力学模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(S1): 48-53. |
| Cui W Z, Shen Z J, Mao D X, et al. Micro-movements of nanoparticles in nanofluids: molecular dynamics simulation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(S1): 48-53. | |
| 15 | Zhao H B, Gui J F, Cao J E, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of the microscopic sintering process of CuO nanograins inside an oxygen carrier particle[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2018, 122(44): 25595-25605. |
| 16 | Gu M F, Liu T F, Xiao X Z, et al. Simulation and experimental study of the multisized silver nanoparticles sintering process based on molecular dynamics[J]. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(6): 1030. |
| 17 | Yang H Z, Sun B Y, Zhu Y F, et al. Critical role of surficial activity in the sintering process of TiO2 nanoparticles by molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Powder Technology, 2022, 398: 117071. |
| 18 | Dieckmann R. Point defects and transport in haematite (Fe2O3- ε )[J]. Philosophical Magazine A, 1993, 68(4): 725-745. |
| 19 | Liu Z J, Cheng Q, Li K J, et al. The interaction of nanoparticulate Fe2O3 in the sintering process: a molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 367: 97-104. |
| 20 | Liu Z J, Cheng Q, Wang Y Z, et al. Three-body aggregation of Fe2O3 nanoparticles: a molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2020, 760: 137901. |
| 21 | Khanh B T H L, Hoang V V, Zung H. Structural properties of amorphous Fe2O3 nanoparticles[J]. The European Physical Journal D, 2008, 49(3): 325-332. |
| 22 | Eom N, Messing M E, Johansson J, et al. Sintering mechanism of Core@Shell Metal@Metal oxide nanoparticles[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2021, 125(29): 16220-16227. |
| 23 | Roy S, Prakash A, Sandfeld S. Sintering of alumina nanoparticles: comparison of interatomic potentials, molecular dynamics simulations, and data analysis[J]. Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 2022, 30(6): 065009. |
| 24 | Lewis G V, Catlow C A. Potential models for ionic oxides[J]. Journal of Physics C: Solid State Physics, 1985, 18(6): 1149-1161. |
| 25 | Buesser B, Gröhn A J, Pratsinis S E. Sintering rate and mechanism of TiO2 nanoparticles by molecular dynamics[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Nanomaterials and Interfaces, 2011, 115(22): 11030-11035. |
| 26 | Erlebach A, Kurland H D, Grabow J, et al. Structure evolution of nanoparticulate Fe2O3 [J]. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(7): 2960-2969. |
| 27 | Hirel P. Atomsk: a tool for manipulating and converting atomic data files[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2015, 197: 212-219. |
| 28 | Plimpton S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1995, 117(1): 1-19. |
| 29 | Stukowski A. Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO—the open visualization tool[J]. Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 2010, 18(1): 015012. |
| 30 | Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K. VMD: visual molecular dynamics[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics, 1996, 14(1): 33-38. |
| 31 | Tian X K, Lin S C, Yan J, et al. Sintering mechanism of calcium oxide/calcium carbonate during thermochemical heat storage process[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 428: 131229. |
| 32 | Stukowski A. Structure identification methods for atomistic simulations of crystalline materials[J]. Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 2012, 20(4): 045021. |
| 33 | Vollath D, Fischer F D, Holec D. Surface energy of nanoparticles-influence of particle size and structure[J]. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology, 2018, 9: 2265-2276. |
| 34 | Babalola B J, Ayodele O O, Olubambi P A. Sintering of nanocrystalline materials: sintering parameters[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(3): e14070. |
| [1] | 张永泉, 玄伟伟. 碱金属/(FeO+CaO+MgO)对硅酸盐灰熔渣结构和黏度的影响机理[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1764-1771. |
| [2] | 刘万强,杨帆,袁华,张远达,易平贵,周虎. 醇类有机物热传导的分子动力学模拟及微观机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(11): 5159-5168. |
| [3] | 郑禾, 杨盛江, 郑永超, 崔燕, 郭旋, 钟近艺, 周健. 尿素和二甲基亚砜诱导DhaA变性的分子动力学模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(11): 4337-4345. |
| [4] | 张晋玮, 成洪业, 陈立芳, 漆志文. [BMIM]HSO4离子液体腐蚀性的实验与分子模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(2): 808-814. |
| [5] | 徐上, 赵伶玲, 蔡庄立, 陈超. 二维氮化铝材料传热性能的模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(9): 3321-3327. |
| [6] | 南怡伶, 孔宪, 李继鹏, 卢滇楠. 纳米狭缝中水流动非平衡分子动力学模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(5): 1786-1793. |
| [7] | 冯志明, 李微微, 李雪, 赵阳, 谢晓峰, 柴春鹏, 罗运军. 不同羧酸根含量对双官能团聚降冰片烯质子交换膜性能影响的分子动力学模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(S1): 253-259. |
| [8] | 单晨旭, 曹绪龙, 祝仰文, 刘坤, 曲广淼, 吕鹏飞, 薛春龙, 丁伟. 辛基酚聚氧乙烯醚磺酸盐界面行为的分子动力学模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(4): 1416-1423. |
| [9] | 钱建华, 潘晓娜, 张强, 刘琳. 2,5-二芳基-1,3,4-噻二唑衍生物的合成及缓蚀性能[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(7): 2737-2748. |
| [10] | 高宁, 王一超, 刘育红. 丙炔基双酚A醚硼聚合物热解过程的ReaxFF分子动力学模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(4): 1557-1564. |
| [11] | 刘琳, 潘晓娜, 张强, 钱建华. 噻二唑衍生物分子结构与其缓蚀性能的关系[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(10): 4039-4048. |
| [12] | 吴刚, 郝宁眉, 陈银娟, 米思奇, 贾晓林, 胡松青. 新型油酸咪唑啉缓蚀剂的合成及其性能评价[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(4): 1485-1492. |
| [13] | 周勤丽,孟 枭,徐 刚,杨立荣. 基于化学修饰法探讨脂肪酶对手性伯醇的识别机理[J]. 化工进展, 2013, 32(11): 2695-2700. |
| [14] | 邱福生1,2,任力1,2,王家鸣1,2,刘卅1,2,郑志雯1,2,方立明1,2,王迎军1,2. 分子动力学模拟预测壳聚糖的玻璃化转变温度[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(7): 2285-2289. |
| [15] | 岳雅娟, 刘清芝, 伍联营, 胡仰栋. 有机分子在聚乙烯膜中扩散过程的分子动力学模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(1): 109-113. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号