• •
王飞1( ), 赵世雄1, 卫亮哲1, 鲁香港1, 吕宏洲1(
), 赵世雄1, 卫亮哲1, 鲁香港1, 吕宏洲1( ), 李彩慧1,2
), 李彩慧1,2
收稿日期:2025-10-28
修回日期:2026-01-01
出版日期:2026-01-04
通讯作者:
吕宏洲
作者简介:王飞(1986—),男,博士,副教授,wangfei1859@sxu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Fei WANG1( ), Shixiong ZHAO1, Liangzhe WEI1, Xianggang LU1, Hongzhou LÜ1(
), Shixiong ZHAO1, Liangzhe WEI1, Xianggang LU1, Hongzhou LÜ1( ), Caihui LI1,2
), Caihui LI1,2
Received:2025-10-28
Revised:2026-01-01
Online:2026-01-04
Contact:
Hongzhou Lü
摘要:
焦化废盐成分复杂、有机污染物含量高,其无害化与资源化处理是行业面临的重大挑战。本文系统分析了焦化废盐的理化性质,并通过热重分析对比了其在无氧与有氧条件下的热解/燃烧特性。进一步通过常规热解与微波热解系统对比研究,探究了加热方式、温度对有机物去除效率的影响及微波的选择性活化机制。结果表明,微波热解在550℃下即可实现93%的有机物去除率,效果显著优于常规热解。此外,微波热解技术还展现出降低反应温度、抑制CO₂及有毒芳烃生成、并富集高纯度合成气的综合优势。本研究为焦化废盐的可控热解与资源化利用提供了一条高效、低污染的技术路径,具有重要的科学价值与应用前景。
中图分类号:
王飞, 赵世雄, 卫亮哲, 鲁香港, 吕宏洲, 李彩慧. 微波强化焦化废盐中有机物脱除性能研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251195.
Fei WANG, Shixiong ZHAO, Liangzhe WEI, Xianggang LU, Hongzhou LÜ, Caihui LI. Study on microwave enhanced removal performance of organic matter in coking waste salt[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251195.
| 样品 | 工业分析(%) | 元素分析(%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | A | V | FC* | S | Na | O | CI | C * | Si | Ca | |
| 废盐 | 0.7 | 91.86 | 4.11 | 3.33 | 25.94 | 25.87 | 20.88 | 15.60 | 7.43 | 2.29 | 1.97 |
表1 废盐样品的工业分析和元素分析结果汇总表
Table 1 Summary of industrial analysis and elemental analysis results of waste salt samples
| 样品 | 工业分析(%) | 元素分析(%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | A | V | FC* | S | Na | O | CI | C * | Si | Ca | |
| 废盐 | 0.7 | 91.86 | 4.11 | 3.33 | 25.94 | 25.87 | 20.88 | 15.60 | 7.43 | 2.29 | 1.97 |
| 废盐组分类别 | 可溶解盐(NaCl+ Na₂SO₄) | 不溶物 | 有机物 | 水分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 百分比 | 78% | 13.86% | 7.44% | 0.7% |
表2 焦化废盐各组分的占比
Table 2 The proportion of each component of coking waste salt
| 废盐组分类别 | 可溶解盐(NaCl+ Na₂SO₄) | 不溶物 | 有机物 | 水分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 百分比 | 78% | 13.86% | 7.44% | 0.7% |
| 保留时间 | 名称 | 分子式 | 占比(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9.421 | 苯乙烯 | C8H8 | 3.79 |
| 13.925 | 1-十二烯 | C12H24 | 10.23 |
| 25.251 | 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 | C14H22O | 14.57 |
| 28.285 | 菲 | C14H10 | 4.84 |
| 30.153 | 含氮/硫杂环化合物 | C8H15NOS | 7.18 |
| 31.212 | 氯化苄 | C7H7CI | 22.76 |
| 36.173 | 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯 | C16H22O4 | 15.80 |
| 47.253 | 苯并蒽 | C18H12 | 6.62 |
表3 焦化废盐有机物测定
Table 3 Determination of organic matter in coking waste salt
| 保留时间 | 名称 | 分子式 | 占比(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9.421 | 苯乙烯 | C8H8 | 3.79 |
| 13.925 | 1-十二烯 | C12H24 | 10.23 |
| 25.251 | 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 | C14H22O | 14.57 |
| 28.285 | 菲 | C14H10 | 4.84 |
| 30.153 | 含氮/硫杂环化合物 | C8H15NOS | 7.18 |
| 31.212 | 氯化苄 | C7H7CI | 22.76 |
| 36.173 | 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯 | C16H22O4 | 15.80 |
| 47.253 | 苯并蒽 | C18H12 | 6.62 |
| 气氛 | 温度区间 | E (kJ/mol) | ln(A) (min-1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氮气 | 53~118℃ | 445.67 | 1.75 | 0.96505 |
| 214~219℃ | 8.11 | -7.17 | 0.96950 | |
| 558~570℃ | 321.15 | -4.33 | 0.95986 | |
| 736~774℃ | 9503.09 | 11.40 | 0.98114 | |
| 空气 | 53-118℃ | 218.26 | -1.93 | 0.98053 |
| 177-192℃ | 28.72 | -6.19 | 0.99070 | |
| 412-418℃ | 14.37 | -7.99 | 0.97024 | |
| 712-768℃ | 4516.97 | 3.80 | 0.96136 |
表4 焦化废盐热分解反应动力学参数
Table 4 Kinetic parameters of thermal decomposition reaction of coking waste salt
| 气氛 | 温度区间 | E (kJ/mol) | ln(A) (min-1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氮气 | 53~118℃ | 445.67 | 1.75 | 0.96505 |
| 214~219℃ | 8.11 | -7.17 | 0.96950 | |
| 558~570℃ | 321.15 | -4.33 | 0.95986 | |
| 736~774℃ | 9503.09 | 11.40 | 0.98114 | |
| 空气 | 53-118℃ | 218.26 | -1.93 | 0.98053 |
| 177-192℃ | 28.72 | -6.19 | 0.99070 | |
| 412-418℃ | 14.37 | -7.99 | 0.97024 | |
| 712-768℃ | 4516.97 | 3.80 | 0.96136 |
| 保留时间 | 名称 | 分子式 |
|---|---|---|
| 7.728 | 氯苯 | C6H5Cl |
| 9.567 | 吡啶-N-氧化物 | C5H5NO |
| 13.605 | 对二氯苯 | C6H4Cl2 |
| 14.705 | 苯甲醇 | C7H8O |
| 25.696 | 十二醛 | C12H24O |
表5 焦化废盐燃烧新产生有毒有机物测定
Table 5 Determination of new toxic organic compounds produced by coking waste salt combustion
| 保留时间 | 名称 | 分子式 |
|---|---|---|
| 7.728 | 氯苯 | C6H5Cl |
| 9.567 | 吡啶-N-氧化物 | C5H5NO |
| 13.605 | 对二氯苯 | C6H4Cl2 |
| 14.705 | 苯甲醇 | C7H8O |
| 25.696 | 十二醛 | C12H24O |
| 高毒物质 | 有氧燃烧峰面积 | 无氧热解峰面积 | 倍数 | 危害 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氯化苄 | 219166 | 99552 | 2.20 | 皮肤/黏膜强刺激 |
| 甲苯 | 400801 | 191862 | 2.09 | 损害肝肾功能 |
| 壬醛 | 240263 | 118989 | 2.02 | 挥发性刺激物 |
| 苯酚 | 859609 | 794672 | 1.08 | 难降解易累积 |
| 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 | 1172126 | 512422 | 2.29 | 干扰代谢 |
| 邻苯二甲酸酐 | 1669609 | 673437 | 2.48 | 挥发性刺激物 |
表6 焦化废盐燃烧/热解有机残留对比
Table 6 Comparison of organic residues in combustion / pyrolysis of coking waste salt
| 高毒物质 | 有氧燃烧峰面积 | 无氧热解峰面积 | 倍数 | 危害 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氯化苄 | 219166 | 99552 | 2.20 | 皮肤/黏膜强刺激 |
| 甲苯 | 400801 | 191862 | 2.09 | 损害肝肾功能 |
| 壬醛 | 240263 | 118989 | 2.02 | 挥发性刺激物 |
| 苯酚 | 859609 | 794672 | 1.08 | 难降解易累积 |
| 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 | 1172126 | 512422 | 2.29 | 干扰代谢 |
| 邻苯二甲酸酐 | 1669609 | 673437 | 2.48 | 挥发性刺激物 |
| 加热方式 | E (kJ/mol) | ln(A) (min-1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 常规热解 | 4.21 | -3.64 | 0.9832 |
| 微波热解 | 3.55 | -2.56 | 0.9655 |
表7 微波热解与常规热解动力学参数对比
Table 7 Comparison of kinetic parameters between microwave pyrolysis and conventional pyrolysis
| 加热方式 | E (kJ/mol) | ln(A) (min-1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 常规热解 | 4.21 | -3.64 | 0.9832 |
| 微波热解 | 3.55 | -2.56 | 0.9655 |
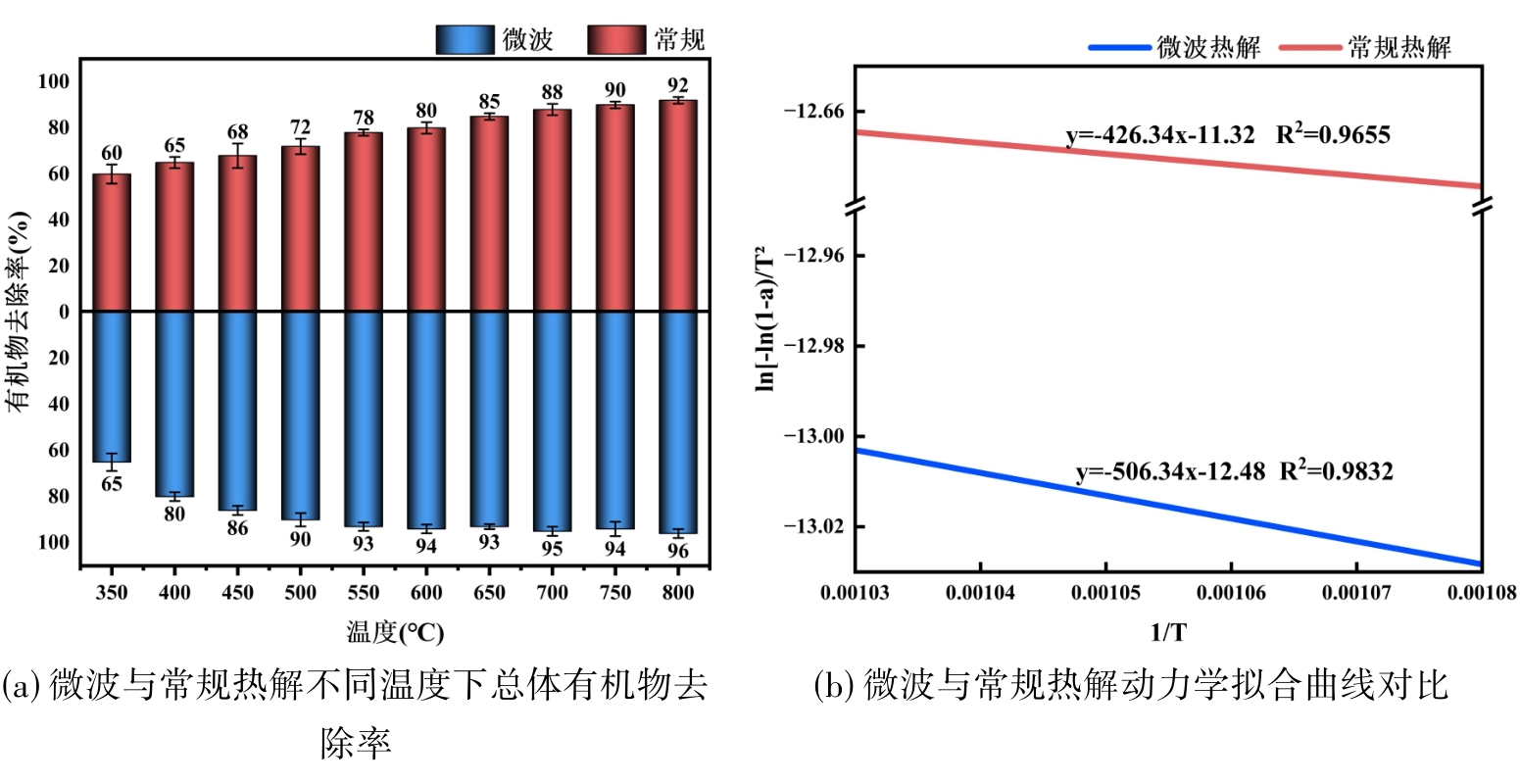
图7 微波与常规热解下不同温度下的有机物去除率及动力学拟合曲线对比
Fig.7 Comparison of organic matter removal rate and kinetic fitting curve at different temperatures under microwave and conventional pyrolysis
| 加热方式 | 加热功率 | 加热时间 | 能耗 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 常规加热 | 1000 W | 35min | 0.58 kWh |
| 微波加热 | 1000 W | 20min | 0.33 kWh |
表8 微波热解与常规热解的参数及能耗对比
Table 8 Comparison of parameters and energy consumption between microwave pyrolysis and conventional pyrolysis
| 加热方式 | 加热功率 | 加热时间 | 能耗 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 常规加热 | 1000 W | 35min | 0.58 kWh |
| 微波加热 | 1000 W | 20min | 0.33 kWh |
| [1] | Guan G Q, Wang R, Wicaksana F, et al. Analysis of membrane distillation crystallization system for high salinity brine treatment with zero discharge using aspen flowsheet simulation[J]. Industrial Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(41): 13405-13413. |
| [2] | 王年禧. 煤化工废盐污染特征分析与利用处置技术效益评价体系研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2025. |
| Wang N X. Analysis of pollution characteristics of waste salt from coal chemical industry and study on technical benefit evaluation system of utilization and disposal[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2025. | |
| [3] | 国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2022. |
| Nbs. China Statistical Yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2022. | |
| [4] | 王丽佳, 顾娅, 郦逸棋, 等. 包装方式对工业废盐填埋过程的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(3): 1023-1028. |
| Wang L J, Gu Y, Li Y Q, et al. Influence of packaging methods on landfill process of industrial waste salt[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(3): 1023-1028. | |
| [5] | 蒋永荣, 胡明成. 硫酸盐废水生物脱硫研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2008, 31(9): 67-71. |
| Jiang Y R, Hu M C. Biological desulfurization of sulfate containing wastewater[J]. Environmental Science Technology, 2008, 31(9): 67-71. | |
| [6] | Zhang B, He J J, Hu C M, et al. Experimental and numerical simulation study on co-incineration of solid and liquid wastes for green production of pesticides[J]. Processes, 2019, 7(10):649. |
| [7] | Yang L, Zhang Z W, Chen A L, et al. Experimental and kinetic study on pyrolysis and combustion characteristics of pesticide waste liquid[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2024, 12(2): 111994.[LinkOut] |
| [8] | Feng L, Tian B H, Zhang L L, et al. Pyrolysis of hydrazine hydrate waste salt: Thermal behaviors and transformation characteristics of organics under aerobic/anaerobic conditions[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 323: 116304. |
| [9] | 陈坚栋. 工业废盐的资源化利用处理方法分析[J]. 当代化工研究, 2022(14): 67-69. |
| Chen J D. Analysis of resource utilization and treatment methods of industrial waste salt[J]. Modern Chemical Research, 2022(14): 67-69. | |
| [10] | 陈齐新, 魏佳. 工业废盐资源化利用典型工艺及前景分析[J]. 节能与环保, 2021(6): 78-80. |
| Chen Q X, Wei J. Typical technology and prospect analysis of industrial waste salt resource utilization[J]. Energy Conservation and Environmental Protection, 2021(6): 78-80. | |
| [11] | 李国骁, 曾永寿. 工业废盐资源化利用及废盐电解使用经验[J]. 中国氯碱, 2021(12): 5-10. |
| Li G X, Zeng Y S. Resource utilization of industrial waste salt and experience of electrolytic use of waste salt[J]. China Chlor-Alkali, 2021(12): 5-10. | |
| [12] | 徐红彬, 张笛, 孙晓岩, 等. 一种洗盐结合非原位氧化的含有机物工业废盐精制处理方法: CN110451530A[P]. 2019-11-15. |
| Xu H B, Zhang D, Sun X Y, et al. A method for refining and processing industrial waste salt containing organic matter by combining salt washing with ex-situ oxidation: CN110451530A[P]. 2019-11-15. | |
| [13] | 崔粲粲, 梁睿, 罗霂, 等. 现代煤化工含盐废水处理技术进展及对策建议[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2016, 22(6): 95-100, 65. |
| Cui C C, Liang R, Luo M, et al. Research progress and suggestion of coal chemical salty waste water treatment technologies[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2016, 22(6): 95-100, 65. | |
| [14] | 赵康合. 多相催化臭氧氧化降解煤化工含盐废水中有机污染物的研究[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2021. |
| Zhao K H. Study on degradation of organic pollutants in salty wastewater from coal chemical industry by heterorgeneous catalytic ozonation[D]. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2021. | |
| [15] | 张旭, 张军, 马宝刚, 等. 电氧化技术资源化处理工业废盐的中试应用[J]. 农药, 2022, 61(8): 573-575, 579. |
| Zhang X, Zhang J, Ma B G, et al. Pilot-scale application of electro-oxidation technology for resource treatment of industrial waste salt[J]. Agrochemicals, 2022, 61(8): 573-575, 579. | |
| [16] | 李强, 戴世金, 郑怡琳, 等. 工业废盐中有机物脱除和资源化技术进展[J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(12): 200-206. |
| Li Q, Dai S J, Zheng Y L, et al. Technical progress of organic matter removal and resource utilization in industrial waste salt[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(12): 200-206. | |
| [17] | 李唯实, 黄泽春, 雷国元, 等. 典型农药废盐热处理过程动力学特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(7): 2691-2698. |
| Li W S, Huang Z C, Lei G Y, et al. Kinetic characteristics of heat treatment process of typical pesticide waste salt[J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(7): 2691-2698. | |
| [18] | 岳培恒. 含有机物结晶盐的热处理试验研究[J]. 煤炭加工与综合利用, 2018(12): 61-65. |
| Yue P H. Experimental study on heat treatment of crystalline salt containing organic matter[J]. Coal Processing and Comprehensive Utilization, 2018(12): 61-65. | |
| [19] | 王利超, 王志良, 马堂文, 等. 模拟氯化钠盐渣的高温处理[J]. 化工环保, 2014, 34(5): 419-422. |
| Wang L C, Wang Z L, Ma T W, et al. High temperature treatment of simulated sodium chloride salt residue[J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2014, 34(5): 419-422. | |
| [20] | Yang Y, Zhang Y Q, Omairey E, et al. Intermediate pyrolysis of organic fraction of municipal solid waste and rheological study of the pyrolysis oil for potential use as bio-bitumen[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 187: 390-399. |
| [21] | Zhao Z W, Qin W N, Long J, et al. The removal of organic impurities from industrial waste salt by pyrolysis[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2023, 30(8): 21671-21682. |
| [22] | 蒋正兴, 袁梦霞, 丁雅倩, 等. 一种微波热力脱附及氧化处理废盐的方法和系统: CN113843264A[P]. 2021-12-28. |
| Jiang Z X, Yuan M X, Ding Y Q, et al. A method and system for the treatment of waste salt by microwave thermal desorption and oxidation: CN113843264A[P]. 2021-12-28. | |
| [23] | Su G C, Ong H C, Cheah M Y, et al. Microwave-assisted pyrolysis technology for bioenergy recovery: Mechanism, performance, and prospect[J]. Fuel, 2022, 326: 124983. |
| [24] | Nizamuddin S, Baloch H A, Siddiqui M T H, et al. An overview of microwave hydrothermal carbonization and microwave pyrolysis of biomass[J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 2018, 17(4): 813-837. |
| [25] | Haeldermans T, Claesen J, Maggen J, et al. Microwave assisted and conventional pyrolysis of MDF–Characterization of the produced biochars[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2019, 138: 218-230. |
| [26] | Ren L, Wang F, Cheng F Q, et al. Mechanisms of gas generation from conventional and microwave pyrolysis of coal slime[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 452: 139388. |
| [27] | 张丁超,安兴璇,杜昭,等.废塑料微波热解研究进展[J].化工环保, 2025, 45(06): 749-760. |
| Zhang D C, An X X, Du Z, et al. Research progress on microwave pyrolysis of waste plastics[J]. Chemical Industry and Environmental Protection, 2025, 45(06): 749-760. | |
| [28] | Li W S, Xu Y, Lei G Y, et al. Thermal treatment characteristics and applicability of typical pesticide waste salts [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 31 (10): 1779-1786. |
| [29] | Ding Y M, Zhang J, He Q Z, et al. The application and validity of various reaction kinetic models on woody biomass pyrolysis[J]. Energy, 2019, 179: 784-791. |
| [30] | 金婷, 朱廷钰, 叶猛, 等. 循环流化床烧结烟气脱硫灰理化性能研究[J]. 北京化工大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 37(6): 35-40. |
| Jin T, Zhu T Y, Ye M, et al. Physical and chemical properties of circulating fluidized bed sintering flue gas desulfurization ash[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 37(6): 35-40. | |
| [31] | Cao Y, Xiang H J, Yan Y H, et al. Catalyst design for microwave-enhanced hydrogen production: Comparative performance across diverse feedstocks[J]. Catalysis Today, 2026, 461: 115523. |
| [32] | Xi S B, Wei X L, Ding J, et al. The removal of organic contaminants from industrial waste salts by pyrolysis and potential use for energy storage[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 425: 138931. |
| [33] | Agboola O S, Bello O S. Enhanced adsorption of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions using functionalized banana stalk[J]. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 2022, 12(12): 5463-5478. |
| [34] | Kim S Y, Park S H, Kim D W, et al. Ecological effects of benzyl chloride on different Korean aquatic indigenous species using an artificial stream mesocosm simulating a chemical spill[J]. Toxics, 2021, 9(12): 347. |
| [35] | Khurshid S, Anjum M, Nawaz R, et al. Di-butyl phthalates (DBP) in the environment: health risks and advances in treatment technologies[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2025, 47(9): 371. |
| [36] | Gao H N, Wang Y C, Liang X F, et al. Long-term exposure to 2, 4-di-tert-butylphenol impairs zebrafish fecundity and affects offspring development[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2025, 492: 138108. |
| [37] | Babić S, Ćurković L, Ljubas D, et al. TiO2 assisted photocatalytic degradation of macrolide antibiotics[J]. Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 2017, 6: 34-41. |
| [38] | Perono G A, Tomy T, Loudon K, et al. Sulfur-containing heterocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons alter estrogen metabolism and cause DNA damage and apoptosis in granulosa cells[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2025, 26(16): 8004. |
| [39] | 孔娇. 两种低阶煤中有机质的逐级解离及分析[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2016. |
| Kong J. Dissociation and composition characterizationof organic matter in two low-rank coals[D]. Xu Zhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2016. | |
| [40] | Vainio P J, Vahlberg T, Liesivuori J. Citizen scientist lepidopterists exposed to potential carcinogens[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2016, 91: 1-7. |
| [41] | Taheri-Shakib J, Shekarifard A, Naderi H. The influence of electromagnetic waves on the gas condensate characterisation: Experimental evaluation[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 166: 568-576. |
| [42] | 李昕皓. 微波加速有机反应的本质研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2016. |
| Li X H.Origin of the acceleration of organic reactions under microwave irradiation. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2016. | |
| [43] | Li H, Liu J H, Li X G, et al. Microwave-induced polar/nonpolar mixture separation performance in a film evaporation process[J]. AIChE Journal, 2019, 65(2): 745-754.[LinkOut] |
| [44] | 吴成强, 施雅琪, 温慧娟, 等. 某工业废盐中有机物去除及盐纯化研究[J]. 浙江工业大学学报, 2025, 53(3): 339-345. |
| Wu C Q, Shi Y Q, Wen H J, et al. Study on organic matter removal and salt purification from an industrial waste salt[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology, 2025, 53(3): 339-345. | |
| [45] | Lee C S, Adam M, Robinson J P, et al. Highly efficient and rapid dechlorination of polyvinyl chloride via microwave pyrolysis[J]. Philosophical Transactions. Series A, Mathematical, Physical, and Engineering Sciences, 2025, 383(2297): 20240064. |
| [46] | Kiralan S S, Erdogdu F, Tekin A. Reducing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) formation in olive pomace oil using microwave pre-heating of olive pomace[J]. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, 2017, 119(1): 1600241. |
| [47] | Xu Q, Peng W C, Ling C M, et al. An experimental analysis of soybean straw combustion on both CO and NOX emission characteristics in a tubular furnace[J]. Energies, 2020, 13(7): 1587. |
| [48] | Kocbek E, Garcia H A, Hooijmans C M, et al. Microwave treatment of municipal sewage sludge: Evaluation of the drying performance and energy demand of a pilot-scale microwave drying system[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 742: 140541. |
| [49] | 曾昭文, 郑成, 毛桃嫣, 等. 微波在化工过程中的研究及应用进展[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(S1): 1-14. |
| Zeng Z W, Zheng C, Mao T Y, et al. Research and application progress of microwave in chemical engineering processes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70 (S1): 1-14. | |
| [50] | 刘兴鹏, 严丹丹. 化学反应体系中电磁脉冲的频谱变化[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(S1): 177-181. |
| Liu X P, Yan D D. Spectral changes of electromagnetic pulses in chemical reaction systems[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70 (S1): 177-181. |
| [1] | 吴雷, 刘姣, 李长聪, 周军, 叶干, 刘田田, 朱瑞玉, 张秋利, 宋永辉. 低阶粉煤催化微波热解制备含碳纳米管的高附加值改性兰炭末[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3956-3967. |
| [2] | 赵希强, 张健, 孙爽, 王文龙, 毛岩鹏, 孙静, 刘景龙, 宋占龙. 生物质炭改性微球去除化工废水中无机磷的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2158-2173. |
| [3] | 张贺东, 高作鹏, 敖文雅, 付洁, 冉春梅, 毛笑, 康秦豪, 刘洋, 刘广青, 陈晓春, 代建军. 基于移动床的印染污泥微波热解及固相产物的表征与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(6): 2510-2518. |
| [4] | 王万福1,李 果2,雍兴跃2,刘 鹏1,张晓飞1,王际东2. 油泥微波程序升温热转化[J]. CIESC Journal, 2011, 30(10): 2310-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号