化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (1): 43-53.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20191175
蒲兴群1( ),巨晓洁1,2,谢锐1,2,汪伟1,2,刘壮1,2,褚良银1,2(
),巨晓洁1,2,谢锐1,2,汪伟1,2,刘壮1,2,褚良银1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2019-10-11
修回日期:2019-10-16
出版日期:2020-01-05
发布日期:2020-01-05
通讯作者:
褚良银
作者简介:蒲兴群(1994—),女,博士研究生,基金资助:
Xingqun PU1( ),Xiaojie JU1,2,Rui XIE1,2,Wei WANG1,2,Zhuang LIU1,2,Liangyin CHU1,2(
),Xiaojie JU1,2,Rui XIE1,2,Wei WANG1,2,Zhuang LIU1,2,Liangyin CHU1,2( )
)
Received:2019-10-11
Revised:2019-10-16
Online:2020-01-05
Published:2020-01-05
Contact:
Liangyin CHU
摘要:
阵列微针作为一种新型透皮给药方式,能够避免皮肤角质层的屏障作用,实现亲水性药物和生物大分子药物的高效透皮吸收,具有无痛、微创、高效等优点。聚合物阵列微针的制备材料和制备方法多种多样,其不仅具有其他阵列微针的优点,还具有生物相容性好、安全性高、载药量精确可控及制备成本低廉等优势,是目前研究最为广泛且最具应用前景的一类阵列微针。系统地综述了目前聚合物阵列微针的主要制备方法及其在透皮给药系统中的最新研究进展。
中图分类号:
蒲兴群, 巨晓洁, 谢锐, 汪伟, 刘壮, 褚良银. 聚合物阵列微针及其在透皮给药系统的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(1): 43-53.
Xingqun PU, Xiaojie JU, Rui XIE, Wei WANG, Zhuang LIU, Liangyin CHU. Polymeric microneedle arrays for applications in transdermal drug delivery systems[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(1): 43-53.
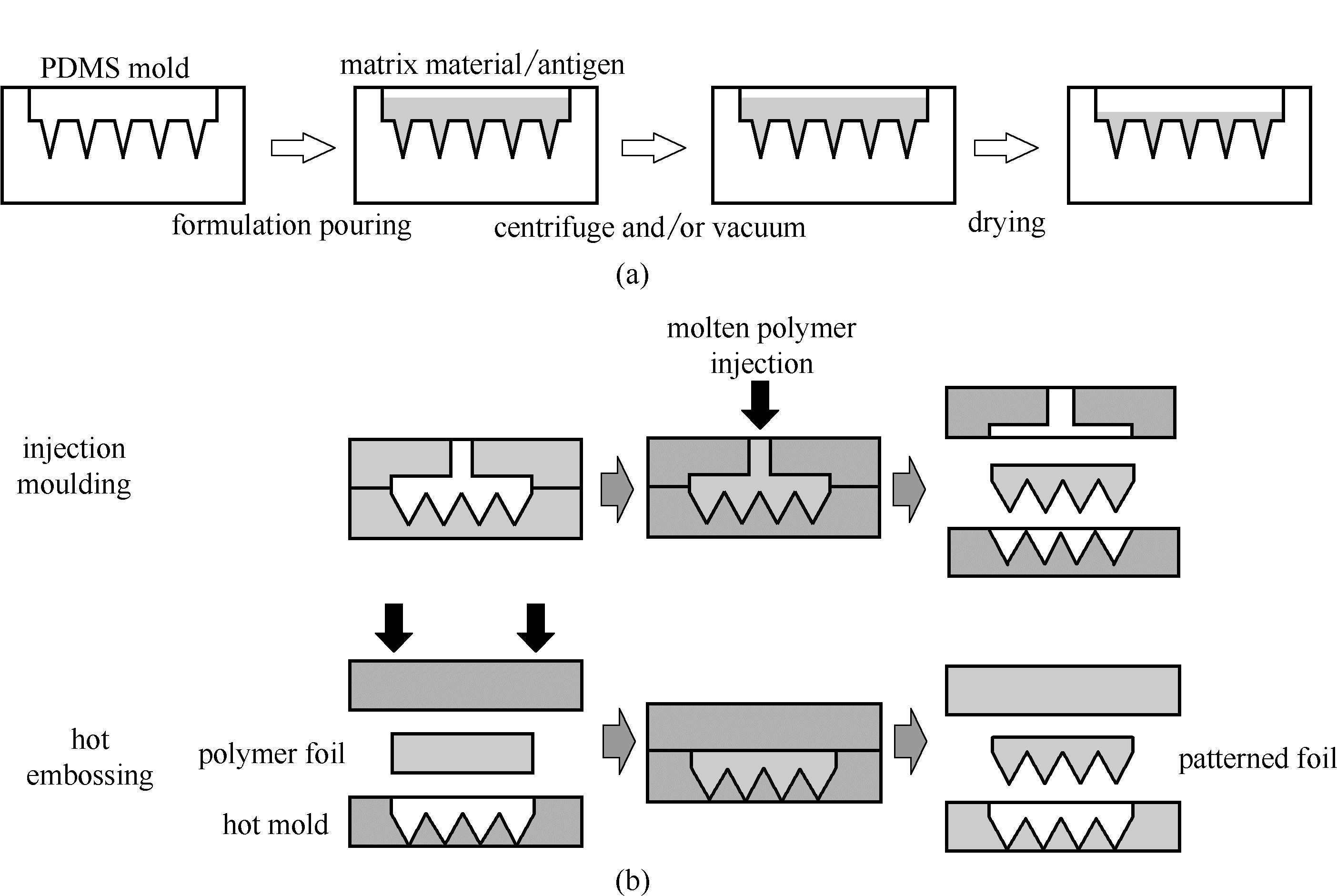
图1 微模板法制备聚合物阵列微针的示意图(a)浇铸法[31]; (b)注塑成型法和热压印法[36]
Fig.1 Schematic illustration of micro-molding methods(a) casting [31]; (b) injection moulding and hot embossing [36]
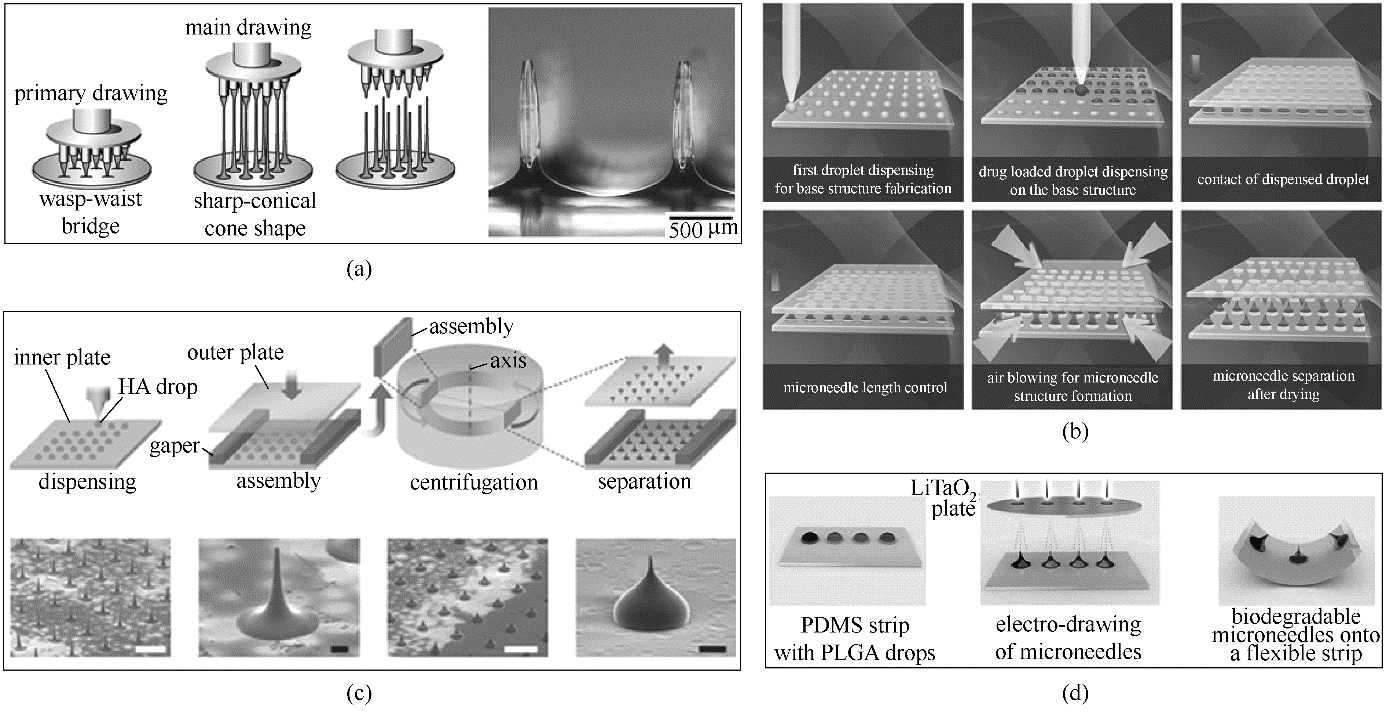
图2 拉伸法制备聚合物阵列微针的示意图(a)立体平板拉伸法[56];(b)液滴吹气法[60];(c)离心拉伸法[61];(d)电性拉伸法[63]
Fig.2 Schematic illustration of drawing techniques(a) drawing lithography [56]; (b) droplet-born air blowing [60]; (c) centrifugal lithography [61]; (d) electro-drawing [63]
| 1 | 刘基, 王媚, 王露, 等. 经皮给药系统研究进展[J]. 现代中医药, 2018, 38(6): 160-163. |
| Liu J, Wang M, Wang L, et al. Research progress in transdermal drug delivery system[J]. Modern Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(6): 160-163. | |
| 2 | 张振波, 房德敏. 微针技术在经皮给药系统的研究进展[J]. 天津药学, 2018, 30(6): 44-47. |
| Zhang Z B, Fang D M. Research progress in transdermal drug delivery system of microneedle technology[J]. Tianjin Pharmacy, 2018, 30(6): 44-47. | |
| 3 | Larrañeta E, McCrudden M T C, Courtenay A J, et al. Microneedles: a new frontier in nanomedicine delivery[J]. Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 33(5): 1055-1073. |
| 4 | 沈瑞雪, 朱壮志, 章俊云, 等. 可溶性微针在经皮给药系统中的开发进展[J]. 世界临床药物, 2017, 38(9): 638-642. |
| Shen R X, Zhu Z Z, Zhang J Y, et al. Dissolving microneedle, a novel transdermal drug delivery system[J]. World Clinical Drugs, 2017, 38(9): 638-642. | |
| 5 | Wang H L, Fan P F, Guo X S, et al. Ultrasound-mediated transdermal drug delivery of fluorescent nanoparticles and hyaluronic acid into porcine skin in vitro[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2016, 25(12): 124314. |
| 6 | Cassagne M, Laurent C, Rodrigues M, et al. Iontophoresis transcorneal delivery technique for transepithelial corneal collagen crosslinking with riboflavin in a rabbit model[J]. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 2016, 57(2): 594-603. |
| 7 | Lambricht L, Lopes A, Kos S, et al. Clinical potential of electroporation for gene therapy and DNA vaccine delivery[J]. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery, 2016, 13(2): 295-310. |
| 8 | Pham Q D, Björklund S, Engblom J, et al. Chemical penetration enhancers in stratum corneum-relation between molecular effects and barrier function[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2016, 232: 175-187. |
| 9 | Henry S, McAllister D V, Allen M G, et al. Microfabricated microneedles: a novel approach to transdermal drug delivery[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1998, 87(8): 922-925. |
| 10 | 朱凤, 金凡茂, 赵昱, 等. 微针经皮给药技术研究进展[J]. 中国生化药物杂志, 2016, 36(8): 149-152. |
| Zhu F, Jin F M, Zhao Y, et al. Research progress in transdermal deliver technology of micro needle[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutics, 2016, 36(8): 149-152. | |
| 11 | Hao Y, Li W, Zhou X L, et al. Microneedles-based transdermal drug delivery systems: a review[J]. Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology, 2017, 13(12): 1581-1597. |
| 12 | Vinayakumar K B, Hegde G M, Nayak M M, et al. Fabrication and characterization of gold coated hollow silicon microneedle array for drug delivery[J]. Microelectronic Engineering, 2014, 128: 12-18. |
| 13 | Shin J H, Noh J Y, Kim K H, et al. Effect of zymosan and poly (I: C) adjuvants on responses to microneedle immunization coated with whole inactivated influenza vaccine[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2017, 265: 83-92. |
| 14 | Chong R H E, Gonzalez-Gonzalez E, Lara M F, et al. Gene silencing following siRNA delivery to skin via coated steel microneedles: in vitro and in vivo proof-of-concept[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2013, 166(3): 211-219. |
| 15 | Ruan W, Zhai Y, Yu K, et al. Coated microneedles mediated intradermal delivery of octaarginine/BRAF siRNA nanocomplexes for anti-melanoma treatment[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2018, 553(1/2): 298-309. |
| 16 | Dharadhar S, Majumdar A, Dhoble S, et al. Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery: a systematic review[J]. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 2019, 45(2): 188-201. |
| 17 | Zhang Y, Yu J, Wang J, et al. Thrombin-responsive transcutaneous patch for auto-anticoagulant regulation[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(4): 1604043. |
| 18 | Jeong H R, Kim J Y, Kim S N, et al. Local dermal delivery of cyclosporin A, a hydrophobic and high molecular weight drug, using dissolving microneedles[J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 2018, 127: 237-243. |
| 19 | Kim H G, Gater D L, Kim Y C. Development of transdermal vitamin D3 (VD3) delivery system using combinations of PLGA nanoparticles and microneedles[J]. Drug Delivery and Translational Research, 2018, 8(1): 281-290. |
| 20 | Donadei A, Kraan H, Ophorst O, et al. Skin delivery of trivalent Sabin inactivated poliovirus vaccine using dissolvable microneedle patches induces neutralizing antibodies[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2019, 311: 96-103. |
| 21 | Ling M H, Chen M C. Dissolving polymer microneedle patches for rapid and efficient transdermal delivery of insulin to diabetic rats[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2013, 9(11): 8952-8961. |
| 22 | Li Y, Liu F, Su C, et al. Biodegradable therapeutic microneedle patch for rapidly antihypertensive treatment[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(34): 30575-30584. |
| 23 | Ali A A, McCrudden C M, McCaffrey J, et al. DNA vaccination for cervical cancer; a novel technology platform of RALA mediated gene delivery via polymeric microneedles[J]. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 2017, 13(3): 921-932. |
| 24 | Wei Z, Zheng S, Wang R, et al. A flexible microneedle array as low-voltage electroporation electrodes for in vivo DNA and siRNA delivery[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2014, 14(20): 4093-4102. |
| 25 | Wang C, Ye Y, Hochu G M, et al. Enhanced cancer immunotherapy by microneedle patch-assisted delivery of anti-PD1 antibody[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(4): 2334-2340. |
| 26 | Ye Y, Wang J, Hu Q, et al. Synergistic transcutaneous immunotherapy enhances antitumor immune responses through delivery of checkpoint inhibitors[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(9): 8956-8963. |
| 27 | Esser E S, Romanyuk A A, Vassilieva E V, et al. Tetanus vaccination with a dissolving microneedle patch confers protective immune responses in pregnancy[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2016, 236: 47-56. |
| 28 | Sullivan S P, Koutsonanos D G, del Pilar Martin M, et al. Dissolving polymer microneedle patches for influenza vaccination[J]. Nature Medicine, 2010, 16(8): 915-920. |
| 29 | Sharma S, Hatware K, Bhadane P, et al. Recent advances in microneedle composites for biomedical applications: advanced drug delivery technologies[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2019, 103: 109717. |
| 30 | Lahiji S F, Jang Y, Ma Y, et al. Effects of dissolving microneedle fabrication parameters on the activity of encapsulated lysozyme[J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2018, 117: 290-296. |
| 31 | Leone M, Mönkäre J, Bouwstra J A, et al. Dissolving microneedle patches for dermal vaccination[J]. Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 34(11): 2223-2240. |
| 32 | Wang Q L, Zhu D D, Chen Y, et al. A fabrication method of microneedle molds with controlled microstructures[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2016, 65: 135-142. |
| 33 | 赵笑, 李欣芳, 张鹏, 等. 聚合物微针介导经皮给药的研究[J]. 化学进展, 2017, 29(12): 1518-1525. |
| Zhao X, Li X F, Zhang P, et al. Research of polymeric microneedles for transdermal drug delivery[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2017, 29(12): 1518-1525. | |
| 34 | McGrath M G, Vucen S, Vrdoljak A, et al. Production of dissolvable microneedles using an atomised spray process: effect of microneedle composition on skin penetration[J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 2014, 86(2): 200-211. |
| 35 | Lee J W, Choi S O, Felner E I, et al. Dissolving microneedle patch for transdermal delivery of human growth hormone[J].Small, 2011, 7(4): 531-539. |
| 36 | Larraneta E, Lutton R E M, Woolfson A D, et al. Microneedle arrays as transdermal and intradermal drug delivery systems: materials science, manufacture and commercial development[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: RReports, 2016, 104: 1-32. |
| 37 | Chen M C, Ling M H, Lai K Y, et al. Chitosan microneedle patches for sustained transdermal delivery of macromolecules[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2012, 13(12): 4022-4031. |
| 38 | Meng W, Huang Y, Fu Y, et al. Polymer composites of boron nitride nanotubes and nanosheets[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2014, 2(47): 10049-10061. |
| 39 | Chen J, Qiu Y, Zhang S, et al. Dissolving microneedle-based intradermal delivery of interferon-α-2b[J]. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 2016, 42(6): 890-896. |
| 40 | Di J, Yao S, Ye Y, et al. Stretch-triggered drug delivery from wearable elastomer films containing therapeutic depots[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(9): 9407-9415. |
| 41 | Zheng H, Yin L, Zhang X, et al. Redox sensitive shell and core crosslinked hyaluronic acid nanocarriers for tumor-targeted drug delivery[J]. Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology, 2016, 12(8): 1641-1653. |
| 42 | Gao Y, Sarfraz M K, Clas S D, et al. Hyaluronic acid-tocopherol succinate-based self-assembling micelles for targeted delivery of rifampicin to alveolar macrophages[J]. Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology, 2015, 11(8): 1312-1329. |
| 43 | Yu J, Zhang Y, Ye Y, et al. Microneedle-array patches loaded with hypoxia-sensitive vesicles provide fast glucose-responsive insulin delivery[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2015, 112(27): 8260-8265. |
| 44 | Park Y H, Ha S K, Choi I, et al. Fabrication of degradable carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) microneedle with laser writing and replica molding process for enhancement of transdermal drug delivery[J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2016, 21(1): 110-118. |
| 45 | Xu H, Li X, Kong H, et al. Characterization of the uptake efficiency and cytotoxicity of tetrandrine-loaded poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone)-block-poly (ε-caprolactone)(PVP-b-PCL) nanoparticles in the A549 lung adenocarcinoma cell line[J]. Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology, 2016, 12(8): 1699-1707. |
| 46 | McGrath M G, Vucen S, Vrdoljak A, et al. Production of dissolvable microneedles using an atomised spray process: effect of microneedle composition on skin penetration[J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 2014, 86(2): 200-211. |
| 47 | Nguyen H X, Bozorg B D, Kim Y, et al. Poly (vinyl alcohol) microneedles: fabrication, characterization, and application for transdermal drug delivery of doxorubicin[J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 2018, 129: 88-103. |
| 48 | Yang S, Feng Y, Zhang L, et al. A scalable fabrication process of polymer microneedles[J]. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2012, 7: 1415-1422. |
| 49 | Tanpichai S, Oksman K. Crosslinked poly (vinyl alcohol) composite films with cellulose nanocrystals: mechanical and thermal properties[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2018, 135(3): 45710. |
| 50 | DeMuth P C, Li A V, Abbink P, et al. Vaccine delivery with microneedle skin patches in nonhuman primates[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(12): 1082-1085. |
| 51 | Chen M C, Wang K W, Chen D H, et al. Remotely triggered release of small molecules from LaB6@ SiO2-loaded polycaprolactone microneedles[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2015, 13: 344-353. |
| 52 | Xin L, Cao J Q, Liu C, et al. Evaluation of rMETase-loaded stealth PLGA/liposomes modified with anti-CAGE scFV for treatment of gastric carcinoma[J]. Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology, 2015, 11(7): 1153-1161. |
| 53 | Han M, Kim D K, Kang S H, et al. Improvement in antigen-delivery using fabrication of a grooves-embedded microneedle array[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2009, 137(1): 274-280. |
| 54 | Sammoura F, Kang J J, Heo Y M, et al. Polymeric microneedle fabrication using a microinjection molding technique[J]. Microsystem Technologies, 2007, 13(5/6): 517-522. |
| 55 | Worgull M, Kolew A, Heilig M, et al. Hot embossing of high performance polymers[J]. Microsystem Technologies, 2011, 17(4): 585-592. |
| 56 | Lee K, Lee C Y, Jung H. Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug administration prepared by stepwise controlled drawing of maltose[J]. Biomaterials, 2011, 32(11): 3134-3140. |
| 57 | Lee K, Lee H C, Lee D S, et al. Drawing lithography: three-dimensional fabrication of an ultrahigh-aspect-ratio microneedle[J]. Advanced Materials, 2010, 22(4): 483-486. |
| 58 | Zhang J, Wang Y, Jin J Y, et al. Use of drawing lithography-fabricated polyglycolic acid microneedles for transdermal delivery of itraconazole to a human basal cell carcinoma model regenerated on mice[J]. Journal of Metals, 2016, 68(4): 1128-1133. |
| 59 | Lee K, Jung H. Drawing lithography for microneedles: a review of fundamentals and biomedical applications[J]. Biomaterials, 2012, 33(30): 7309-7326. |
| 60 | Kim J D, Kim M, Yang H, et al. Droplet-born air blowing: novel dissolving microneedle fabrication[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2013, 170(3): 430-436. |
| 61 | Huh I, Kim S, Yang H, et al. Effects of two droplet-based dissolving microneedle manufacturing methods on the activity of encapsulated epidermal growth factor and ascorbic acid[J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2018, 114: 285-292. |
| 62 | Yang H, Kim S, Kang G, et al. Centrifugal lithography: self-shaping of polymer microstructures encapsulating biopharmaceutics by centrifuging polymer drops[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2017, 6(19): 1700326. |
| 63 | Vecchione R, Coppola S, Esposito E, et al. Electro-drawn drug-loaded biodegradable polymer microneedles as a viable route to hypodermic injection[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2014, 24(23): 3515-3523. |
| 64 | Anderson K B, Lockwood S Y, Martin R S, et al. A 3D printed fluidic device that enables integrated features[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 85(12): 5622-5626. |
| 65 | 杨雅丽, 童想柳, 边琼, 等. 3D 打印技术在透皮领域的研究进展[J]. 中国医药工业杂志, 2018, 49(11): 1492-1499. |
| Yang Y L, Tong X L, Bian Q, et al. Research advances of 3D printing technology in tandermal drug delivery system[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceuticals, 2018, 49(11): 1492-1499. | |
| 66 | Johnson A R, Caudill C L, Tumbleston J R, et al. Single-step fabrication of computationally designed microneedles by continuous liquid interface production[J]. Public Library of Science One, 2016, 11(9): e0162518. |
| 67 | Bhatnagar S, Bankar N G, Kulkarni M V, et al. Dissolvable microneedle patch containing doxorubicin and docetaxel is effective in 4T1 xenografted breast cancer mouse model[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2019, 556: 263-275. |
| 68 | Pei P, Yang F, Liu J, et al. Composite-dissolving microneedle patches for chemotherapy and photothermal therapy in superficial tumor treatment[J]. Biomaterials Science, 2018, 6(6): 1414-1423. |
| 69 | Hao Y, Chen Y W, Lei M Y, et al. Near-infrared responsive PEGylated gold nanorod and doxorubicin loaded dissolvable hyaluronic acid microneedles for human epidermoid cancer therapy[J]. Advanced Therapeutics, 2018, 1(2): 1800008. |
| 70 | Zhao X, Li X, Zhang P, et al. Tip-loaded fast-dissolving microneedle patches for photodynamic therapy of subcutaneous tumor[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2018, 286: 201-209. |
| 71 | Pan J, Ruan W, Qin M, et al. Intradermal delivery of STAT3 siRNA to treat melanoma via dissolving microneedles[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 1117. |
| 72 | GhavamiNejad A, Li J, Lu B, et al. Glucose-responsive composite microneedle patch for hypoglycemia-triggered delivery of native glucagon[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(30): 1901051. |
| 73 | Liu S, Jin M, Quan Y, et al. The development and characteristics of novel microneedle arrays fabricated from hyaluronic acid, and their application in the transdermal delivery of insulin[J]. Journal of Controlled Release, 2012, 161(3): 933-941. |
| 74 | Yu W, Jiang G, Zhang Y, et al. Polymer microneedles fabricated from alginate and hyaluronate for transdermal delivery of insulin[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2017, 80: 187-196. |
| 75 | Chen M C, Ling M H, Kusuma S J. Poly-γ-glutamic acid microneedles with a supporting structure design as a potential tool for transdermal delivery of insulin[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2015, 24: 106-116. |
| 76 | Ye Y, Yu J, Wang C, et al. Microneedles integrated with pancreatic cells and synthetic glucose-signal amplifiers for smart insulin delivery[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(16): 3115-3121. |
| 77 | Hu X, Yu J, Qian C, et al. H2O2-responsive vesicles integrated with transcutaneous patches for glucose-mediated insulin delivery[J]. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(1): 613-620. |
| 78 | Yu J, Qian C, Zhang Y, et al. Hypoxia and H2O2 dual-sensitive vesicles for enhanced glucose-responsive insulin delivery[J]. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(2): 733-739. |
| 79 | Tong Z, Zhou J, Zhong J, et al. Glucose-and H2O2-responsive polymeric vesicles integrated with microneedle patches for glucose-sensitive transcutaneous delivery of insulin in diabetic rats[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(23): 20014-20024. |
| 80 | Zhang Y, Wang J, Yu J, et al. Bioresponsive microneedles with a sheath structure for H2O2 and pH cascade-triggered insulin delivery[J]. Small, 2018, 14(14): 1704181. |
| 81 | Nagao K, Ginhoux F, Leitner W W, et al. Murine epidermal Langerhans cells and langerin-expressing dermal dendritic cells are unrelated and exhibit distinct functions[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2009, 106(9): 3312-3317. |
| 82 | Pearton M, Pirri D, Kang S M, et al. Host responses in human skin after conventional intradermal injection or microneedle administration of virus-like-particle influenza vaccine[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2013, 2(10): 1401-1410. |
| 83 | Moon S, Wang Y, Edens C, et al. Dose sparing and enhanced immunogenicity of inactivated rotavirus vaccine administered by skin vaccination using a microneedle patch[J]. Vaccine, 2013, 31(34): 3396-3402. |
| 84 | Liao J F, Lee J C, Lin C K, et al. Self-assembly DNA polyplex vaccine inside dissolving microneedles for high-potency intradermal vaccination[J]. Theranostics, 2017, 7(10): 2593-2605. |
| 85 | Chen Y H, Lai K Y, Chiu Y H, et al. Implantable microneedles with an immune-boosting function for effective intradermal influenza vaccination[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2019, 97: 230-238. |
| 86 | Tang J, Wang J, Huang K, et al. Cardiac cell-integrated microneedle patch for treating myocardial infarction[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(11): eaat9365. |
| 87 | Zhang Y, Liu Q, Yu J, et al. Locally induced adipose tissue browning by microneedle patch for obesity treatment[J]. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(9): 9223-9230. |
| [1] | 谭畯坤, 刘玉东, 耿世超, 陈兵, 童明伟. 真空探针冷冻和复温性能实验测试及数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(4): 1440-1449. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号