化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (4): 1655-1667.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230992
收稿日期:2023-09-21
修回日期:2023-12-19
出版日期:2024-04-25
发布日期:2024-06-06
通讯作者:
申威峰
作者简介:文华强(1997—),男,博士研究生,huaqiangwen@cqu.edu.cn基金资助:
Huaqiang WEN( ), Quanhu SUN(
), Quanhu SUN( ), Weifeng SHEN(
), Weifeng SHEN( )
)
Received:2023-09-21
Revised:2023-12-19
Online:2024-04-25
Published:2024-06-06
Contact:
Weifeng SHEN
摘要:
分子定向生成能以超低人力、财力、时间成本高速推动新物质的发现和设计,因此被广泛应用于分离溶剂、反应溶剂、催化剂、功能材料、药物等分子的设计与优化。提出了一种基于分子碎片化学空间的功能驱动分子智能生成框架,以分子的功能指标为生成方向,以分子“骨架-装饰物”集合为基础,以结构碎片的化学空间为搜索范围,推动分子定向生成,深度挖掘具有潜力的新分子结构。通过生成类药性分子的案例演示,该框架能从较小的优异分子集(644)出发,最终生成五倍数量的同等级别优异分子(3158),表明该生成框架能够高效地进化出大量全新且优异的分子。该框架可结合实际化工过程中的功能目标和约束,推动过程尺度的绿色溶剂等全新最优化设计。
中图分类号:
文华强, 孙全虎, 申威峰. 基于分子碎片化学空间的智能分子定向生成框架[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1655-1667.
Huaqiang WEN, Quanhu SUN, Weifeng SHEN. Targeted intelligent molecular generation framework based on fragments chemical space[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1655-1667.
| 筛选项目 | 原始范围 | 最佳值 | 容忍范围 |
|---|---|---|---|
| QED | 0~1 | 1 | 0.8~1 |
| SAscore | 1~10 | 1 | 1~3 |
| SlogP | — | 1.5 | 0~3 |
| IDP | 0~1.5 | 0 | 0~0.8 |
表1 优异分子筛选条件
Table 1 Criteria for screening excellent molecules
| 筛选项目 | 原始范围 | 最佳值 | 容忍范围 |
|---|---|---|---|
| QED | 0~1 | 1 | 0.8~1 |
| SAscore | 1~10 | 1 | 1~3 |
| SlogP | — | 1.5 | 0~3 |
| IDP | 0~1.5 | 0 | 0~0.8 |
| 指纹类别 | 指纹长度 | 学习最大迭代次数 | 学习率 | Neighborhood function | Sigma | 特征初始化算法 | 随机种子 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDKit Topological | 1024 | 1000 | 0.5 | ‘gaussian’ | 3 | 主成分分析降维 | 2023 |
表2 基于Topological分子指纹的SOM聚类网络参数
Table 2 Parameter of SOM clustering network based on Topological molecular fingerprints
| 指纹类别 | 指纹长度 | 学习最大迭代次数 | 学习率 | Neighborhood function | Sigma | 特征初始化算法 | 随机种子 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDKit Topological | 1024 | 1000 | 0.5 | ‘gaussian’ | 3 | 主成分分析降维 | 2023 |
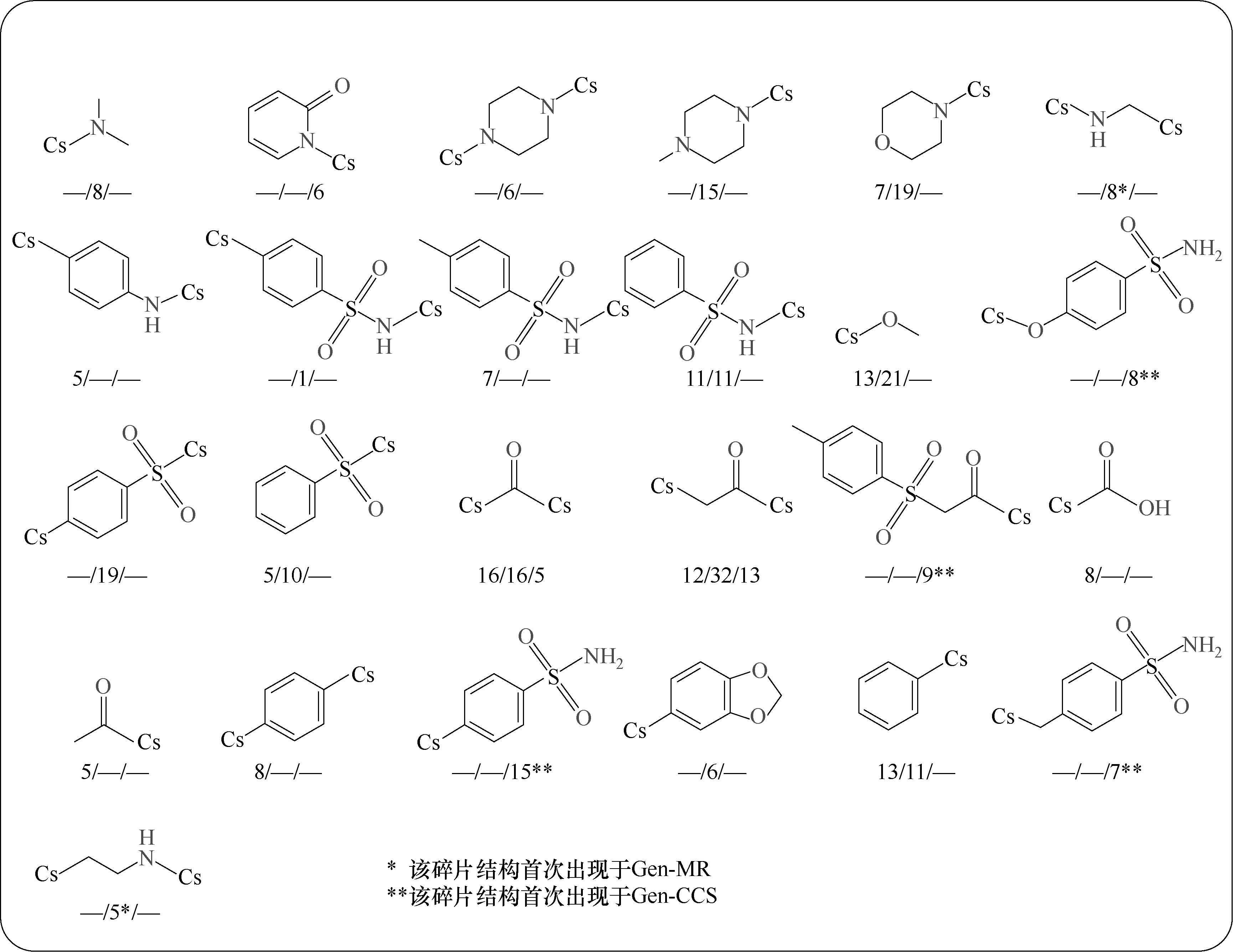
图10 Gen0、Gen-MR和Gen-CSS中的部分优异分子(IDP<0.6)集群碎片结构及其出现频数统计(被展示碎片出现频数不小于5,并以“Gen0中的频数/Gen-MR中的频数/Gen-CSS中的频数”分布展示频数)
Fig.10 Fragment structure and frequency statistics of excellent molecular clusters (IDP <0.6) in Gen0, Gen-MR, and Gen-CSS (the displayed fragment frequency is not less than 5, and it is distributed as “frequency in Gen0/frequency in Gen-MR/frequency in Gen-CSS”)
| 1 | Sanchez-Lengeling B, Aspuru-Guzik A. Inverse molecular design using machine learning: generative models for matter engineering[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6400): 360-365. |
| 2 | Chen H M, Engkvist O, Wang Y H, et al. The rise of deep learning in drug discovery[J]. Drug Discovery Today, 2018, 23(6): 1241-1250. |
| 3 | Butler K T, Davies D W, Cartwright H, et al. Machine learning for molecular and materials science[J]. Nature, 2018, 559(7715): 547-555. |
| 4 | Lu S H, Zhou Q H, Ouyang Y X, et al. Accelerated discovery of stable lead-free hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites via machine learning[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 3405. |
| 5 | Pretel E J, López P A, Bottini S B, et al. Computer-aided molecular design of solvents for separation processes[J]. AIChE Journal, 1994, 40(8): 1349-1360. |
| 6 | Scheffczyk J, Fleitmann L, Schwarz A, et al. COSMO-CAMD: a framework for optimization-based computer-aided molecular design using COSMO-RS[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 159: 84-92. |
| 7 | 赵红庆, 刘奇磊, 张磊, 等. 考虑选择性和反应速率的多目标制药反应溶剂设计[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(3): 1465-1472. |
| Zhao H Q, Liu Q L, Zhang L, et al. Multi-objective solvent design considering selectivity and reaction rate for pharmaceutical reactions[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(3): 1465-1472. | |
| 8 | Gani R, Nielsen B, Fredenslund A. A group contribution approach to computer-aided molecular design[J]. AIChE Journal, 1991, 37(9): 1318-1332. |
| 9 | 张学岗, 张军保, 宋静, 等. 基于MGASA的计算机辅助分子设计[J]. 化工进展, 2008, 27(12): 2019-2024. |
| Zhang X G, Zhang J B, Song J, et al. Computer aided molecular design based on MGASA[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2008, 27(12): 2019-2024. | |
| 10 | von Lilienfeld O A, Müller K R, Tkatchenko A. Exploring chemical compound space with quantum-based machine learning[J]. Nature Reviews Chemistry, 2020, 4(7): 347-358. |
| 11 | Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735-1780. |
| 12 | Kingma D P, Welling M. Auto-encoding variational bayes[EB/OL]. 2014, . |
| 13 | Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, et al. Generative adversarial networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2020, 63(11): 139-144. |
| 14 | Kusner M J, Paige B, Hernández-Lobato J M. Grammar variational autoencoder[C]//Precup D, Teh Y W. Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney, Australia, 2017: 1945-1954. |
| 15 | Grisoni F, Moret M, Lingwood R, et al. Bidirectional molecule generation with recurrent neural networks[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2020, 60(3): 1175-1183. |
| 16 | Gómez-Bombarelli R, Wei J N, Duvenaud D, et al. Automatic chemical design using a data-driven continuous representation of molecules[J]. ACS Central Science, 2018, 4(2): 268-276. |
| 17 | Sánchez-Lengeling B, Outeiral C, Guimaraes G, et al. Optimizing distributions over molecular space. An objective-reinforced generative adversarial network for inverse-design chemistry(ORGANIC)[EB/OL]. Cambridge: Cambridge Open Engage, 2017, . |
| 18 | Jin W G, Barzilay R, Jaakkola T. Junction tree variational autoencoder for molecular graph generation[EB/OL]. 2018, . |
| 19 | Bagal V, Aggarwal R, Vinod P K, et al. MolGPT: molecular generation using a transformer-decoder model[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2022, 62(9): 2064-2076. |
| 20 | Barredo Arrieta A, Díaz-Rodríguez N, Del Ser J, et al. Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI): concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 58: 82-115. |
| 21 | Degen J, Wegscheid-Gerlach C, Zaliani A, et al. On the art of compiling and using ‘drug-like’ chemical fragment spaces[J]. ChemMedChem, 2008, 3(10): 1503-1507. |
| 22 | Kim S, Thiessen P A, Bolton E E, et al. PubChem substance and compound databases[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, 44(D1): D1202-D1213. |
| 23 | Kohonen T. Self-organized formation of topologically correct feature maps[J]. Biological Cybernetics, 1982, 43(1): 59-69. |
| 24 | Gaulton A, Bellis L J, Bento A P, et al. ChEMBL: a large-scale bioactivity database for drug discovery[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, 40(D1): D1100-D1107. |
| 25 | SMILES Weininger D., a chemical language and information system( 1): Introduction to methodology and encoding rules[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences, 1988, 28(1): 31-36. |
| 26 | Nilakantan R, Bauman N, Dixon J S, et al. Topological torsion: a new molecular descriptor for SAR applications. Comparison with other descriptors[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences, 1987, 27(2): 82-85. |
| 27 | Durant J L, Leland B A, Henry D R, et al. Reoptimization of MDL keys for use in drug discovery[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences, 2002, 42(6): 1273-1280. |
| 28 | Landrum G. RDKit: open-source cheminformatics software (version 2021.09.1)[CP/OL]. [2023-06-15]. . |
| 29 | Ertl P, Schuffenhauer A. Estimation of synthetic accessibility score of drug-like molecules based on molecular complexity and fragment contributions[J]. Journal of Cheminformatics, 2009, 1(1): 8. |
| 30 | Bickerton G R, Paolini G V, Besnard J, et al. Quantifying the chemical beauty of drugs[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2012, 4(2): 90-98. |
| 31 | Wildman S A, Crippen G M. Prediction of physicochemical parameters by atomic contributions[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences, 1999, 39(5): 868-873. |
| 32 | Hughes J D, Blagg J, Price D A, et al. Physiochemical drug properties associated with in vivo toxicological outcomes[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2008, 18(17): 4872-4875. |
| [1] | 温凯杰, 郭力, 夏诏杰, 陈建华. 一种耦合CFD与深度学习的气固快速模拟方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3775-3785. |
| [2] | 齐书平, 王文龙, 张磊, 都健. 基于深度学习的金属离子-有机配体配位稳定常数的预测[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(12): 5461-5468. |
| [3] | 谢昊源, 黄群星, 林晓青, 李晓东, 严建华. 基于图像深度学习的垃圾热值预测研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(5): 2773-2782. |
| [4] | 陈忠圣, 朱梅玉, 贺彦林, 徐圆, 朱群雄. 基于分位数回归CGAN的虚拟样本生成方法及其过程建模应用[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(3): 1529-1538. |
| [5] | 于程远, 吴金奎, 周利, 吉旭, 戴一阳, 党亚固. 基于深度学习预测有机光伏电池能量转换效率[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(3): 1487-1495. |
| [6] | 王晓慧, 王延江, 邓晓刚, 张政. 基于加权深度支持向量数据描述的工业过程故障检测[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5707-5716. |
| [7] | 尹林子, 关羽吟, 蒋朝辉, 许雪梅. 基于k-means++的高炉铁水硅含量数据优选方法[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(8): 3661-3670. |
| [8] | 田璐瑶, 王梓豪, 粟杨, 文华强, 申威峰. 基于深度学习的溶剂定量构效关系建模研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(10): 4462-4472. |
| [9] | 黄正梁, 王超, 李少硕, 杨遥, 孙婧元, 王靖岱, 阳永荣. 基于深度学习的气液固三相反应器图像分析方法及应用[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(1): 274-282. |
| [10] | 顾恒昌, 牟鹏, 李建伟. 基于交叉迭代BLSTM网络的乙烯裂解炉建模[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(2): 548-555. |
| [11] | 董顺, 李益国, 孙栓柱, 刘西陲, 沈炯. 基于状态空间主成分分析网络的故障检测方法[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(8): 3528-3536. |
| [12] | 王康成, 尚超, 柯文思, 江永亨, 黄德先. 化工过程深度神经网络软测量的结构与参数自动调整方法[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(3): 900-906. |
| [13] | 王功明, 李文静, 乔俊飞. 基于PLSR自适应深度信念网络的出水总磷预测[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(5): 1987-1997. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号