化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (10): 3804-3814.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240371
收稿日期:2024-04-03
修回日期:2024-07-17
出版日期:2024-10-25
发布日期:2024-11-04
通讯作者:
王春英
作者简介:陈贵梅(2001—),女,硕士研究生,2380164332@qq.com
基金资助:
Guimei CHEN( ), Yuyun XIE, Youwei YANG, Yan GAO, Chunying WANG(
), Yuyun XIE, Youwei YANG, Yan GAO, Chunying WANG( )
)
Received:2024-04-03
Revised:2024-07-17
Online:2024-10-25
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
Chunying WANG
摘要:
采用铜铁类普鲁士蓝衍生物(Cu n Fe1-PBAs)活化过一硫酸盐(PMS)降解罗丹明B(RhB),考察铁铜摩尔比、催化剂投加量、PMS与RhB的摩尔比、起始pH和水中常见离子对RhB降解的影响。结果表明:Cu2Fe1-PBAs可以有效活化PMS降解RhB。在RhB浓度为20 mg/L,Cu2Fe1-PBAs用量为0.6 g/L,PMS浓度为0.513 g/L,碱性条件时最有利于RhB降解。
中图分类号:
陈贵梅, 谢雨芸, 杨有威, 高艳, 王春英. 类普鲁士蓝衍生物活化过一硫酸盐降解罗丹明B[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3804-3814.
Guimei CHEN, Yuyun XIE, Youwei YANG, Yan GAO, Chunying WANG. Degradation of rhodamine B by peroxymonosulfate activated by Prussian blue analogue derivatives[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(10): 3804-3814.
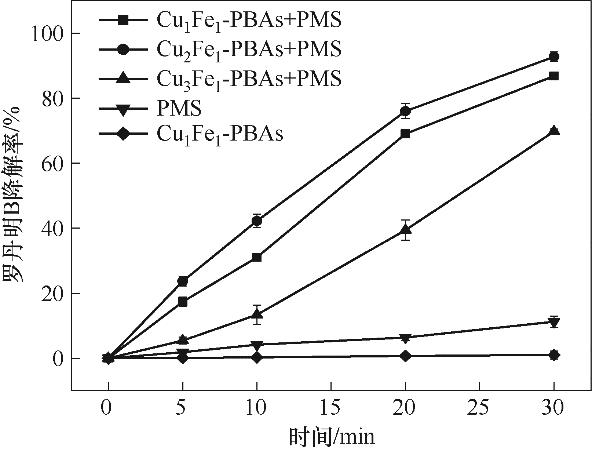
图1 铁铜摩尔比对RhB降解效果的影响(实验条件:[Cu2Fe1-PBAs]0=400 mg/L;[PMS]0=500 mg/L;pH0=5.16;[RhB]0=20 mg/L;反应温度25℃±2℃)
Fig.1 Effect of molar ratio of iron to copper on degradation of RhB(reaction conditions: [Cu2Fe1-PBAs]0=400 mg/L; [PMS]0=500 mg/L; pH0=5.16; [RhB]0=20 mg/L; temperature 25℃±2℃)
| 催化剂 | 催化剂浓度/(mg/L) | 初始浓度/(mg/L) | PMS/(mg/L) | pH | 反应时间/min | 去除率/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu2Fe1-PBAs | 600 | 20.0 | 513 | 5.16 | 30 | 92.72 | 本文 |
| 磁性茶渣炭 | 213 | 40.0 | 302 | 5 | 80 | 98 | [ |
| 紫外线下施氏矿物 | 500 | 4.79 | 307 | — | 45 | 93.7 | [ |
| 黄铁矿 | 1000 | 20 | 307 | 5 | 180 | 99 | [ |
| 铁酸铜 | 100 | 2.39 | 61 | — | 30 | 88.87 | [ |
| 氧化铜纳米颗粒 | 500 | 50 | 614 | 7.5 | 60 | 93.38 | [ |
| 兔粪生物炭 | 600 | 25 | 400 | — | 40 | 98 | [ |
表1 可活化过一硫酸盐降解RhB的实验对比
Table 1 Experiment comparison for the degradation of RhB by activated peroxymonosulfate
| 催化剂 | 催化剂浓度/(mg/L) | 初始浓度/(mg/L) | PMS/(mg/L) | pH | 反应时间/min | 去除率/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu2Fe1-PBAs | 600 | 20.0 | 513 | 5.16 | 30 | 92.72 | 本文 |
| 磁性茶渣炭 | 213 | 40.0 | 302 | 5 | 80 | 98 | [ |
| 紫外线下施氏矿物 | 500 | 4.79 | 307 | — | 45 | 93.7 | [ |
| 黄铁矿 | 1000 | 20 | 307 | 5 | 180 | 99 | [ |
| 铁酸铜 | 100 | 2.39 | 61 | — | 30 | 88.87 | [ |
| 氧化铜纳米颗粒 | 500 | 50 | 614 | 7.5 | 60 | 93.38 | [ |
| 兔粪生物炭 | 600 | 25 | 400 | — | 40 | 98 | [ |
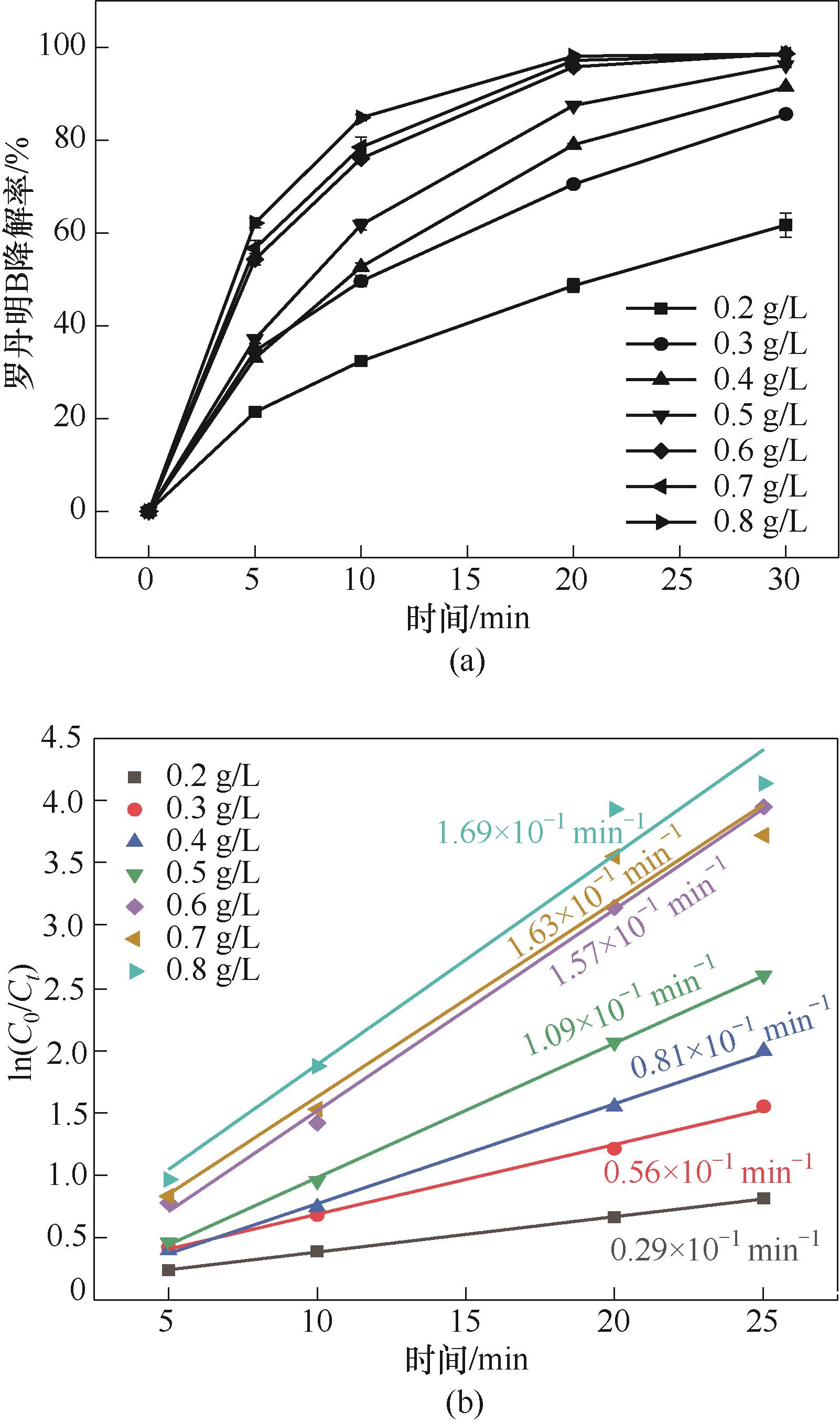
图2 Cu2Fe1-PBAs投加量对RhB降解的影响(a)和一级动力学模拟(b) (实验条件:[PMS]0=500 mg/L;pH0=5.16;[RhB]0=20 mg/L;反应温度25℃±2℃)
Fig.2 Effect of Cu2Fe1-PBAs dosage on RhB degradation (a) and the corresponding curves of pseudo-first order reaction kinetics (b) (reaction conditions: [PMS]0=513 mg/L; pH0=5.16; [RhB]0=20 mg/L; temperature 25℃±2℃)

图3 PMS投加量对RhB降解的影响(a)和一级动力学模拟(b) (实验条件:[Cu2Fe1-PBAs]0=600 mg/L;pH0=5.16;[RhB]0=20 mg/L;反应温度为25℃±2℃)
Fig.3 Effect of PMS Dosage on RhB degradation (a) and the corresponding curves of pseudo-first order reaction kinetics (b)(reaction conditions: [Cu2Fe1-PBAs]0=600 mg/L; pH0=5.16; [RhB]0=20 mg/L; temperature 25℃±2℃)
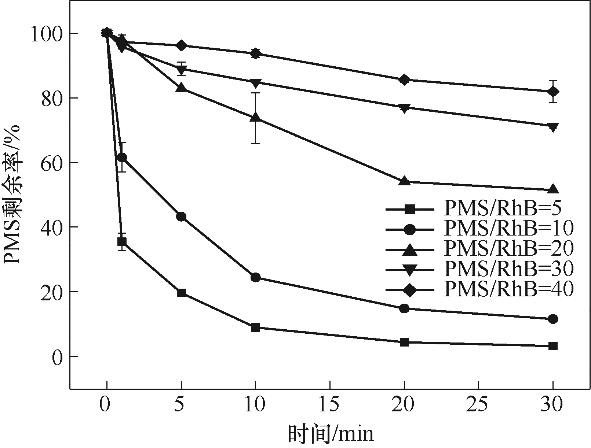
图4 PMS的反应剩余(实验条件:[Cu2Fe1-PBAs]0=600 mg/L;pH0=5.16;[RhB]0=20 mg/L;反应温度25℃±2℃)
Fig.4 Residual degradation of PMS (reaction conditions: [Cu2Fe1-PBAs]0=600 mg/L; pH0=5.16; [RhB]0=20 mg/L; temperature 25℃±2℃)
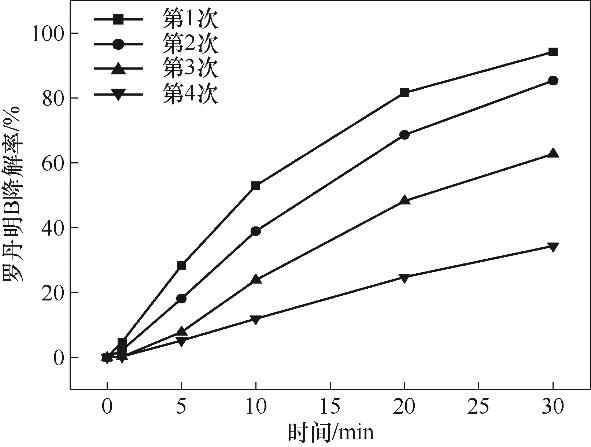
图5 催化剂4次循环催化效果(实验条件:[Cu2Fe1-PBAs]0=600 mg/L;[PMS]0=513 mg/L;pH0=5.16;[RhB]0=20 mg/L;反应温度25℃±2℃)
Fig.5 Catalytic effect of four cycles of catalyst (reaction conditions: [Cu2Fe1-PBAs]0=600 mg/L; [PMS]0=513 mg/L; pH0= 5.16; [RhB]0=20 mg/L; temperature 25℃±2℃)
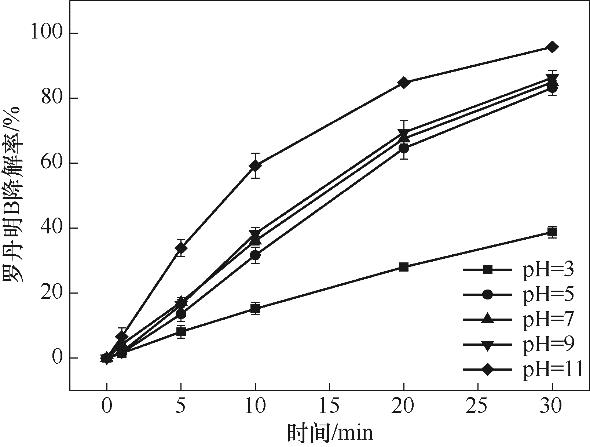
图6 起始pH对RhB降解的影响(实验条件:[Cu2Fe1-PBAs]0= 600 mg/L;[PMS]0=513 mg/L;[RhB]0=20 mg/L;反应温度25℃±2℃)
Fig.6 Effect of initial pH on RhB degradation (reaction conditions: [Cu2Fe1-PBAs]0=600 mg/L; [PMS]0=513 mg/L; [RhB]0=20 mg/L; temperature 25℃±2℃)
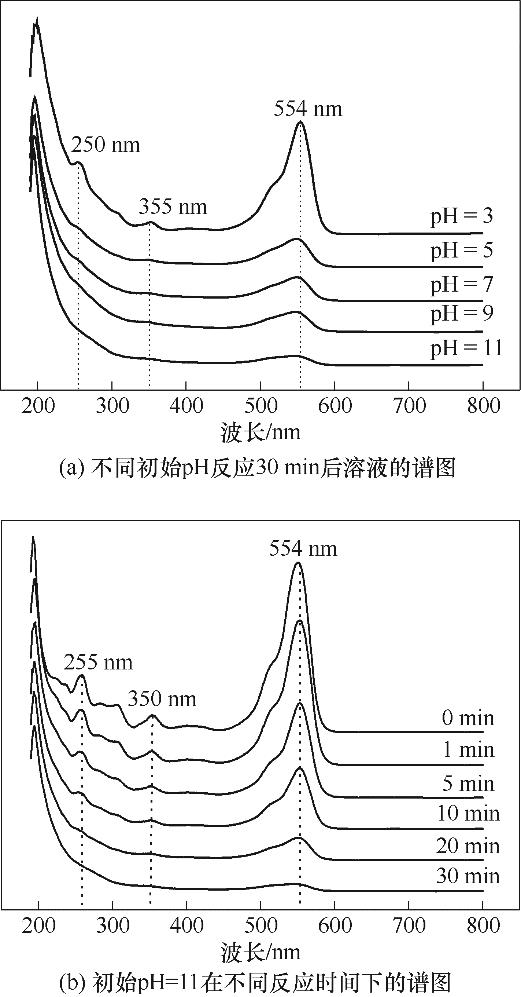
图7 紫外可见光谱(实验条件:[Cu2Fe1-PBAs]0=600 mg/L;[PMS]0=513 mg/L;[RhB]0=20 mg/L;反应温度25℃±2℃)
Fig.7 Ultraviolet-visible spectrum of catalytic degradation of RhB system (reaction conditions: [Cu2Fe1-PBAs]0=600 mg/L; [PMS]0=513 mg/L; [RhB]0=20 mg/L; temperature 25℃±2℃)
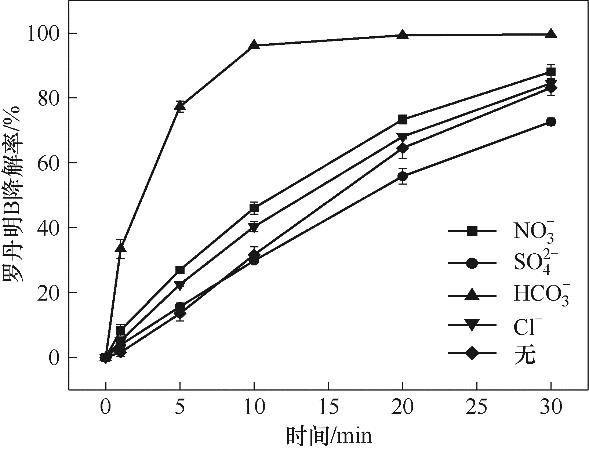
图8 共存阴离子对RhB降解的影响(实验条件:共存阴离子浓度为5 mmol/L;[Cu2Fe1-PBAs]0=600 mg/L;[PMS]0=513 mg/L;pH0=5.16;[RhB]0=20 mg/L;反应温度25℃±2℃)
Fig.8 Effect of co-existing anions on RhB degradation (reaction conditions: coexisting anion 5 mmol/L; [Cu2Fe1-PBAs]0=600 mg/L; [PMS]0=513 mg/L; pH0= 5.16; [RhB]0=20 mg/L; temperature 25℃±2℃)
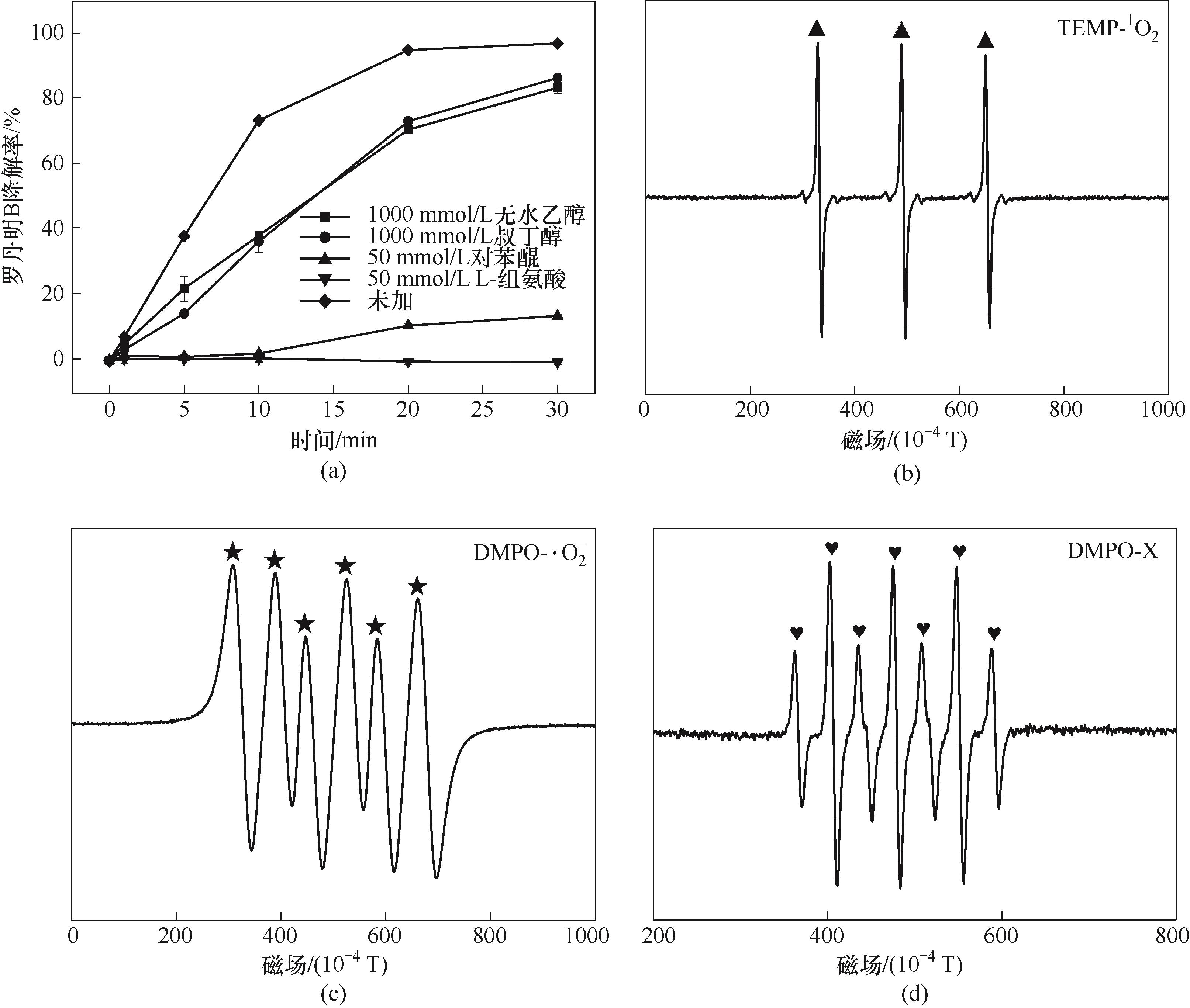
图9 不同活性组分猝灭剂对RhB降解的影响(a); TEMP(b)和DMPO[(c)、(d)]的电子顺磁共振谱(实验条件:[Cu2Fe1-PBAs]0= 600 mg/L;[PMS]0=513 mg/L;pH0=5.16;[RhB]0=20 mg/L;反应温度25℃±2℃)
Fig.9 Effects of different radical scavengers on RhB degradation (a); EPR spectra of TEMP (b) and DMPO [(c),(d)] (reaction conditions: [Cu2Fe1-PBAs]0=600 mg/L; [PMS]0=513 mg/L; pH0=5.16; [RhB]0=20 mg/L; temperature 25℃±2℃)
| 1 | 秦彬, 谷晋川, 殷萍, 等. 染料废水处理技术研究进展[J]. 化工环保, 2021, 41(1): 9-18. |
| Qin B, Gu J C, Yin P, et al. Research progresses on dye wastewater treatment technology[J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2021, 41(1): 9-18. | |
| 2 | 任冬梅, 于清小, 赵阳, 等. 物理法去除废水中罗丹明B研究进展[J]. 渤海大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 41(2): 97-104. |
| Ren D M, Yu Q X, Zhao Y, et al. Research progress of physical method for removing rhodamine B from wastewater[J]. Journal of Bohai University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 41(2): 97-104. | |
| 3 | 王春英, 朱清江, 谷传涛, 等. 稀土Ce3+掺杂Bi2WO6光催化降解罗丹明B的研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(9): 2682-2689. |
| Wang C Y, Zhu Q J, Gu C T, et al. Investigation of rhodamine B photocatalytic degradation by Ce3+ doped Bi2WO6 [J]. China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(9): 2682-2689. | |
| 4 | 赵朦, 李梅, 白毛毛, 等. 高级氧化技术在印染废水处理中的研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2023, 52(6): 1884-1890. |
| Zhao M, Li M, Bai M M, et al. Research progress of advanced oxidation technology in dyeing wastewater treatment[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2023, 52(6): 1884-1890. | |
| 5 | 谷得明, 郭昌胜, 冯启言, 等. 基于硫酸根自由基的高级氧化技术及其在环境治理中的应用[J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(11): 2489-2508. |
| Gu D M, Guo C S, Feng Q Y, et al. Sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes and its application in environmental remediation[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(11): 2489-2508. | |
| 6 | 李尚真, 张治宏, 易晓辉, 等. 改性猪粪制生物炭活化过硫酸盐(PS)去除罗丹明B[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(3): 929-939. |
| Li S Z, Zhang Z H, Yi X H, et al. Removal of rhodamine B by modified pig manure made biochar-activated persulfate(PS)[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(3): 929-939. | |
| 7 | 傅晓艳, 鲍建国, 杜江坤, 等. 淀粉稳定化纳米零价铁活化过硫酸盐降解罗丹明B试验研究[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2015, 22(6): 51-56. |
| Fu X Y, Bao J G, Du J K, et al. Degradation of rhodamine B by persulfate activated with starch-stabilized nZVI[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2015, 22(6): 51-56. | |
| 8 | 龚程. 铁钴水滑石活化过一硫酸盐降解罗丹明B的研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2017. |
| Gong C. Study on degradation of rhodamine B by iron-cobalt hydrotalcite activated persulfate[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2017. | |
| 9 | 黄艳, 邢波, 晏伟, 等. 钢渣/氮掺杂改性活性炭复合材料催化过硫酸盐降解罗丹明B[J].工业水处理, 2024(2): 147-156. |
| Huang Y, Xing B, Yan W, et al. Catalytic degradation of rhodamine B by steel slag/nitrogen-doped modified activated carbon composite[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2024(2): 147-156. | |
| 10 | 张磊, 林子雨, 张文静. 紫外强化CuO活化过硫酸盐降解罗丹明B染料废水[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(11): 82-89. |
| Zhang L, Lin Z Y, Zhang W J, et al. Degradation of dyeing wastewater containing rhodamine B by CuO-activated persulfate with UV strengthening[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(11): 82-89. | |
| 11 | 相里鹏, 崔佳丽, 张峰, 等. 磁性生物炭活化过硫酸盐去除水中罗丹明B [J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(4): 1672-1687. |
| Xiangli P, Cui J L, Zhang F, et al. Removal of rhodamine B from aqueous solutions by magnetic biochar activated persulfate[J]. China Environmental Science, 2023, 43(4): 1672-1687. | |
| 12 | 陈于梁, 成先雄, 连军峰, 等. 非均相膨润土@Fe3O4活化PMS降解RhB[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(8): 75-81. |
| Chen Y L, Cheng X X, Lian J F, et al. Heterogeneous bentonite@Fe3O4 activated persulfate to degrade rhodamine B[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 44(8): 75-81. | |
| 13 | Hou M J, Gong S Q, Ji L L, et al. Three-dimensional porous ultrathin carbon networks reinforced PBAs-derived electrocatalysts for efficient oxygen evolution[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 419: 129575. |
| 14 | Zhao C X, Liu B, Li X N, et al. A Co-Fe Prussian blue analogue for efficient Fenton-like catalysis: the effect of high-spin cobalt[J]. Chemical Communications, 2019, 55(50): 7151-7154. |
| 15 | Liu J Y, Li X N, Liu B, et al. Shape-controlled synthesis of metal-organic frameworks with adjustable Fenton-like catalytic activity[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(44): 38051-38056. |
| 16 | 吴永娟, 马青春, 刘博. 磁性茶渣炭的简易制备及其活化过硫酸盐降解罗丹明B的性能[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2022, 49(6): 955-960. |
| Wu Y J, Ma Q C, Liu B. Facile synthesis of magnetic biochar derived from tea residue and its activation of potassium persulfate for degradation of rhodanine B[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2022, 49(6): 955-960. | |
| 17 | 刘慧, 周佳兴, 任鹏飞, 等. 紫外光下施氏矿物活化过硫酸盐降解罗丹明B[J]. 工业水处理, 2022, 42(5): 110-116. |
| Liu H, Zhou J X, Ren P F, et al. Degradation of rhodamine B by schwertmannite activated persulfate under UV light[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2022, 42(5): 110-116. | |
| 18 | 熊玲, 国晓波, 程聪, 等. 黄铁矿活化过硫酸盐降解罗丹明B[J]. 中南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 40(3): 226-230. |
| Xiong L, Guo X B, Cheng C, et al. Degradation of rhodamine B by pyrite-activated persulfate[J]. Journal of South-Central University for Nationalities (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 40(3): 226-230. | |
| 19 | 杨珂, 唐琪, 杨晓丹, 等. 铁酸铜非均相活化过硫酸盐降解罗丹明B[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(9): 3761-3769. |
| Yang K, Tang Q, Yang X D, et al. Degradation of rhodamine B by heterogeneous activation of persulfate with copper ferrate[J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(9): 3761-3769. | |
| 20 | Ouyang F, Liu Y J, Chen J, et al. Study on preparation of rabbit manure biochar and activation of peroxymonosulfate for rhodamine B degradation[J]. Water, 2023, 15(11): 2015. |
| 21 | Channab B E, El Ouardi M, Marrane S E, et al. Alginate@ZnCO2O4 for efficient peroxymonosulfate activation towards effective rhodamine B degradation: optimization using response surface methodology[J]. RSC Advances, 2023, 13(29): 20150-20163. |
| 22 | Guo Y X, Yan L G, Li X G, et al. Goethite/biochar-activated peroxymonosulfate enhances tetracycline degradation: inherent roles of radical and non-radical processes[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 783: 147102. |
| 23 | 王雅洁, 龚先河. PMS/Cl-体系中橙黄Ⅱ脱色的影响因素和机理[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2021, 28(1): 219-225, 238. |
| Wang Y J, Gong X H. Effects and mechanism of decolorization of orange Ⅱ in PMS/Cl- system[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2021, 28(1): 219-225, 238. | |
| 24 | 吴瑶. 水稻秸秆生物炭协同过硫酸钠降解水中苯胺和罗丹明B的效果与机制研究[D].南京: 南京农业大学, 2018. |
| Wu Y. Study on the effect and mechanism of rice straw biochar combined with sodium persulfate to degrade aniline and rhodamine B in water[D]. Nangjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| 25 | Chen L Q, Zhang Z H, Wang Y J, et al. Photocatalytic properties and electrochemical characteristic of a novel biomimetic oxygenase enzyme photocatalyst iron(Ⅱ) tetrahydroxymethyl tetra(1,4-dithiin) porphyrazine for the degradation of organic pollutants[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2013, 372: 114-120. |
| 26 | Jiang M D, Lu J H, Ji Y F, et al. Bicarbonate-activated persulfate oxidation of acetaminophen[J]. Water Research, 2017, 116: 324-331. |
| 27 | Cao J Y, Lai L D, Lai B, et al. Degradation of tetracycline by peroxymonosulfate activated with zero-valent iron: performance, intermediates, toxicity and mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 364: 45-56. |
| 28 | Zhang G C, Yang X Y, Wu Z X, et al. Fe-Mn bimetallic oxide-enabled facile cleaning of microfiltration ceramic membranes for effluent organic matter fouling mitigation via activation of oxone[J]. ACS ES&T Water, 2022, 2(7): 1234-1246. |
| 29 | Santamarina J C, Klein K A, Wang Y H, et al. Specific surface: determination and relevance[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2002, 39(1): 233-241. |
| 30 | Zhang S Q, Yang X, Liu L, et al. Adsorption behavior of selective recognition functionalized biochar to Cd(Ⅱ) in wastewater[J]. Materials, 2018, 11(2): 299. |
| 31 | 任洁青, 王朝旭, 张峰, 等. 改性稻壳生物炭对水中Cd2+的吸附性能研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2021, 37(1): 73-79. |
| Ren J Q, Wang C X, Zhang F, et al. Adsorption of Cd2+ from aqueous solution by modified rice husk-derived biochars[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2021, 37(1): 73-79. | |
| 32 | Habibi M H, Parhizkar H J. FTIR and UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy studies of the wet chemical (WC) route synthesized nano-structure CoFe2O4 from CoCl2 and FeCl3 [J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2014, 127: 102-106. |
| 33 | Wu Z D, Wang X M, Yao J, et al. Synthesis of polyethyleneimine modified CoFe2O4-loaded porous biochar for selective adsorption properties towards dyes and exploration of interaction mechanisms[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 277: 119474. |
| 34 | Liu F, Zhou H Y, Pan Z C, et al. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole by cobalt-nickel powder composite catalyst coupled with peroxymonosulfate: performance, degradation pathways and mechanistic consideration[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 400: 123322. |
| 35 | Cagnetta G, Huang J, Lu M N, et al. Defect engineered oxides for enhanced mechanochemical destruction of halogenated organic pollutants[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 184: 879-883. |
| 36 | Yang Y W, Guo C S, Zeng Y T, et al. Peroxymonosulfate activation by CuFe-Prussian blue analogues for the degradation of bisphenol S: effect, mechanism, and pathway[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 311: 138748. |
| 37 | Yamashita T, Hayes P. Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2008, 254(8): 2441-2449. |
| 38 | Wang S X, Tian J Y, Wang Q, et al. Development of CuO coated ceramic hollow fiber membrane for peroxymonosulfate activation: a highly efficient singlet oxygen-dominated oxidation process for bisphenol a degradation[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 256: 117783. |
| 39 | Guo R N, Chen Y, Nengzi L C, et al. In situ preparation of carbon-based Cu-Fe oxide nanoparticles from CuFe Prussian blue analogues for the photo-assisted heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate activation process to remove lomefloxacin[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 398: 125556. |
| 40 | Niu L J, Zhang G M, Xian G, et al. Tetracycline degradation by persulfate activated with magnetic γ - F e 2 O 3 / C e O 2 catalyst: performance, activation mechanism and degradation pathway[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 259: 118156. |
| [1] | 李瑞康, 何盈盈, 卢维鹏, 王园园, 丁皓东, 骆勇名. 电化学强化钴基阴极活化过一硫酸盐的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2207-2216. |
| [2] | 韩雪, 高生旺, 王国英, 夏训峰. 铈掺杂强化碳纳米管活化过一硫酸盐实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(4): 1743-1753. |
| [3] | 王柯晴, 徐劼, 沈芷璇, 陈家斌, 吴玮. LaCoO3钙钛矿活化过一硫酸盐降解萘普生[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(3): 1326-1334. |
| [4] | 尹飞, 王翠, 童少平. rGO-Fe3O4活化过硫酸盐处理酸性红73[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(1): 207-213. |
| [5] | 周伟, 赵海谦, 高继慧, 吴少华. 添加剂改性Fenton体系中Fe2+再生过程及机制的对比[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(10): 4413-4421. |
| [6] | 赵琳, 高晗, 韦冰心, 王亭杰, 金涌. 颜料二氧化钛光催化特性评价[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(7): 2453-2461. |
| [7] | 刘 潘1,3,郭晓宁2,南 昊2,刘 红2,李圣楠1. 炉渣制光催化剂催化降解罗丹明B的机理 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2010, 29(6): 1075-. |
| [8] | 丘永樑;陈洪龄;徐南平. 水热法制备CdS/TiO2及其光活性 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2005, 56(7): 1338-1342. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号