• •
收稿日期:2025-12-11
修回日期:2026-01-09
出版日期:2026-01-14
通讯作者:
许昊翔,程道建
作者简介:陈伟建(2002—),男,硕士研究生,2024210100@buct.edu.cn
基金资助:
Weijian CHEN( ), Haoxiang XU(
), Haoxiang XU( ), Daojian CHENG(
), Daojian CHENG( )
)
Received:2025-12-11
Revised:2026-01-09
Online:2026-01-14
Contact:
Haoxiang XU, Daojian CHENG
摘要:
大型语言模型(LLM)在化学研究中展现出广阔潜力,但面向催化剂研发等专业领域时,其任务表现仍缺乏系统化、多层级的量化评估。为此,本研究以烯烃氢甲酰化催化体系为探针对象,构建涵盖填空、简答、解析与推理四类任务的多层级评估框架,旨在系统比较四种通用大模型(DeepSeek-V3.2-Think、Qwen3、Gemini-3-Pro-Preview、GPT-4o)的基础能力,并探究不同知识增强策略对模型性能的提升效果。首先,在统一任务体系下评估各通用模型的基线表现,筛选出综合性能最优的模型作为后续实验底座;随后,分别接入大知识图谱、小知识图谱、向量相似度检索三种知识增强方法,系统检验其在多类任务中的增益作用。评估采用填空题的正确率与简答、解析、推理题的合规性、准确性、鲁棒性、完整性四维量化指标。结果表明:Gemini-3-Pro-Preview综合表现最佳;引入知识增强策略后,模型性能进一步提升,且不同增强方式在不同任务中呈现差异化优势——知识图谱在复杂推理与机理类任务中表现突出,而向量相似度检索则在信息检索类任务中增益显著。本研究通过系统评测与知识增强实验,为面向专业化工领域的垂类大模型构建与优化提供了方法参考与实证依据,也为化工过程智能化建模与决策支持系统的开发提供了新思路。
中图分类号:
陈伟建, 许昊翔, 程道建. 基于知识增强策略的烯烃氢甲酰化催化剂垂类大模型[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251400.
Weijian CHEN, Haoxiang XU, Daojian CHENG. Knowledge-enhanced strategy based olefin hydroformylation catalyst focused large language model[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251400.
| 序号 | 题型 | 复杂度 | 考察的核心认知能力 | 关键技术挑战与评估侧重 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 填空题 | 低 | 精准检索与对齐 | 细粒度实体识别与参数提取 |
| 2 | 简答题 | 中 | 知识复述与提取 | 上下文理解与事实还原度 |
| 3 | 综合题 | 中高 | 知识关联与逻辑整合 | 多源信息冲突处理与构效关系总结 |
| 4 | 推理题 | 高 | 约束生成与方案外推 | 基于化学原理的方案设计可行性 |
表 1 大语言模型的评估题型分类与技术挑战分解
Table 1 Classification of LLMs evaluation question types and decomposition of technical challenges
| 序号 | 题型 | 复杂度 | 考察的核心认知能力 | 关键技术挑战与评估侧重 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 填空题 | 低 | 精准检索与对齐 | 细粒度实体识别与参数提取 |
| 2 | 简答题 | 中 | 知识复述与提取 | 上下文理解与事实还原度 |
| 3 | 综合题 | 中高 | 知识关联与逻辑整合 | 多源信息冲突处理与构效关系总结 |
| 4 | 推理题 | 高 | 约束生成与方案外推 | 基于化学原理的方案设计可行性 |
| 维度 | 核心问题 | 评估要点 |
|---|---|---|
| 合规性 | 是否严格遵守所有约束条件 | 严格遵循所有指令;无信息越界 |
| 准确性 | 化学逻辑与实验数据是否精确 | 构效关系论证正确;实验参数精确;无事实性幻觉 |
| 鲁棒性 | 结论在不确定性下是否稳定 | 区分事实与推论;能识别知识边界 |
| 完整性 | 关键要素与结构是否涵盖全面 | 无核心信息遗漏;覆盖所有子问题;逻辑结构完整 |
表 2 评估维度定义
Table 2 Definition of evaluation dimensions
| 维度 | 核心问题 | 评估要点 |
|---|---|---|
| 合规性 | 是否严格遵守所有约束条件 | 严格遵循所有指令;无信息越界 |
| 准确性 | 化学逻辑与实验数据是否精确 | 构效关系论证正确;实验参数精确;无事实性幻觉 |
| 鲁棒性 | 结论在不确定性下是否稳定 | 区分事实与推论;能识别知识边界 |
| 完整性 | 关键要素与结构是否涵盖全面 | 无核心信息遗漏;覆盖所有子问题;逻辑结构完整 |
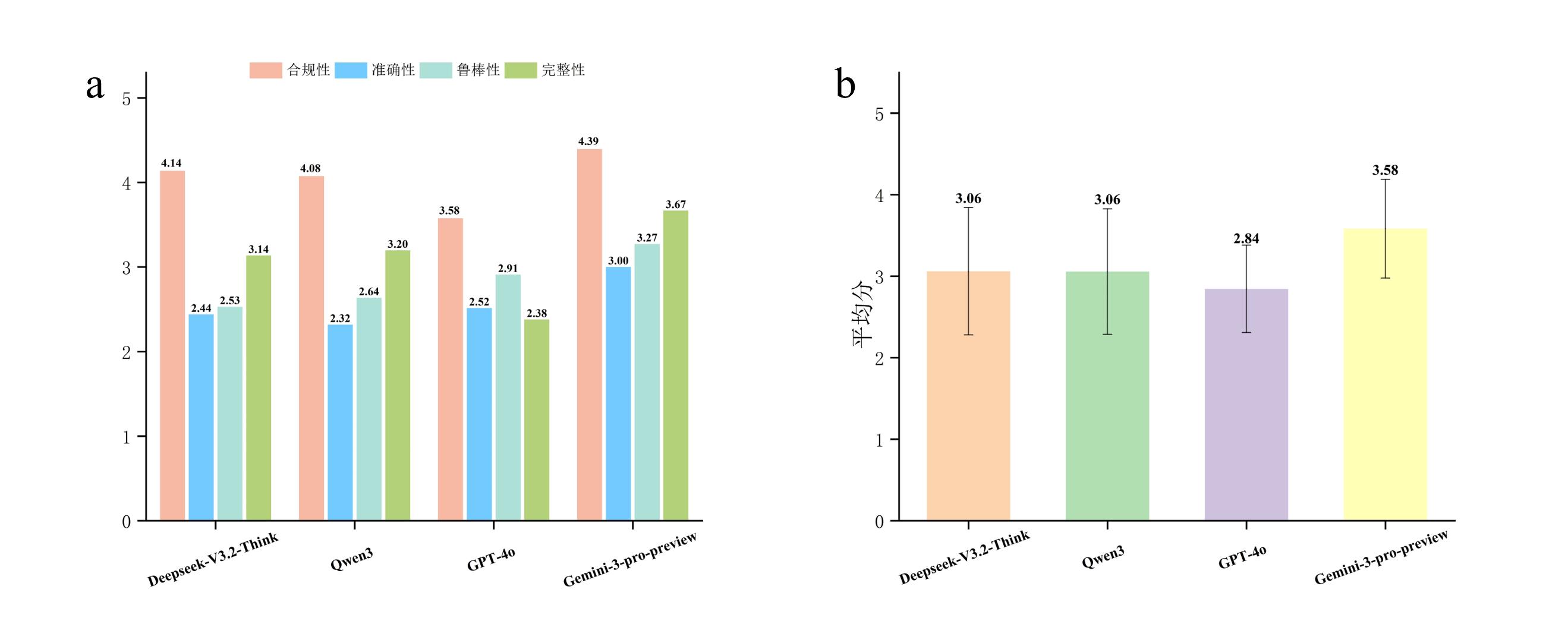
图 2 四个模型在简答题总体性能与各维度性能对比。(a)各维度平均分对比。(b)总体平均分对比
Fig.2 Comparison of overall performance and performance in each dimension of the four models in short-answer questions. (a) Comparison of average scores in each dimension. (b) Comparison of overall average scores
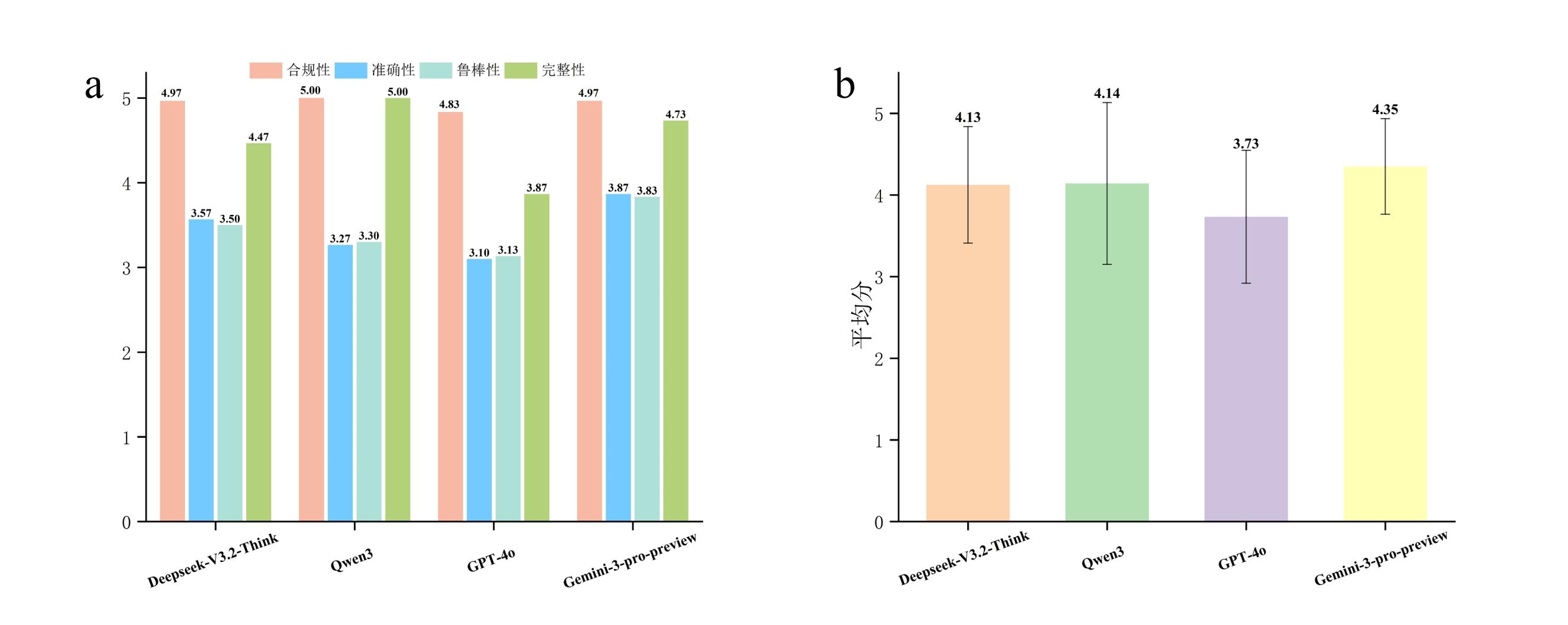
图 3 四个模型在综合题总体性能与各维度性能对比。(a)各维度平均分对比。(b)总体平均分对比
Fig.3 Comparison of the overall performance and performance in each dimension of the four models in the comprehensive questions. (a) Comparison of average scores in each dimension. (b) Comparison of overall average scores
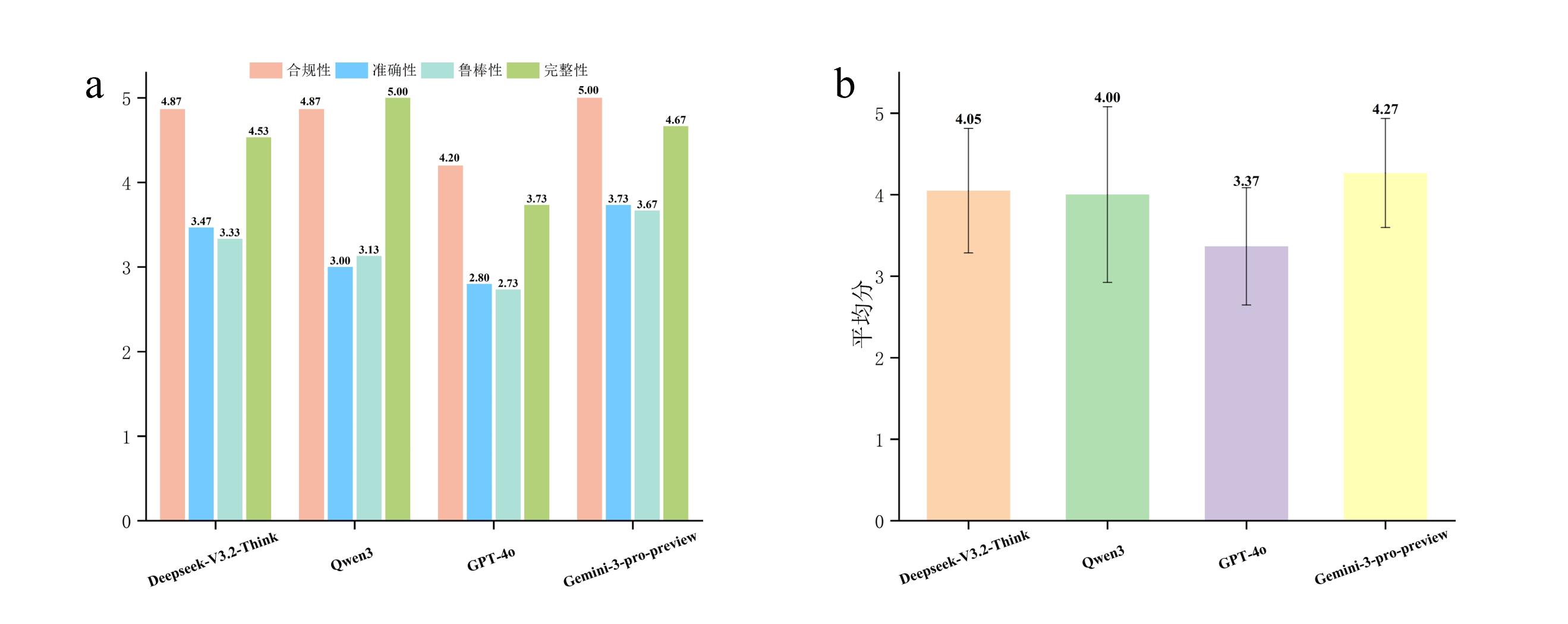
图 4 四个模型在推理题总体性能与各维度性能对比。(a)各维度平均分对比。(b)总体平均分对比
Fig.4 Comparison of the overall performance and performance in each dimension of the four models in the reasoning task. (a) Comparison of average scores in each dimension. (b) Comparison of overall average scores
| 方法 | 准确率 | 平均倒数排名 |
|---|---|---|
| 大知识图谱 | 92.19% | 0.922 |
| 小知识图谱 | 60.94% | 0.63 |
| 相似度匹配 | 82.81% | 0.838 |
| 通用大模型 | 7.81% | 0.094 |
表 3 不同方法在填空题中的准确率和平均倒数排名
Table 3 Accuracy rates and average reciprocal ranks of different methods in fill-in-the-blank questions
| 方法 | 准确率 | 平均倒数排名 |
|---|---|---|
| 大知识图谱 | 92.19% | 0.922 |
| 小知识图谱 | 60.94% | 0.63 |
| 相似度匹配 | 82.81% | 0.838 |
| 通用大模型 | 7.81% | 0.094 |
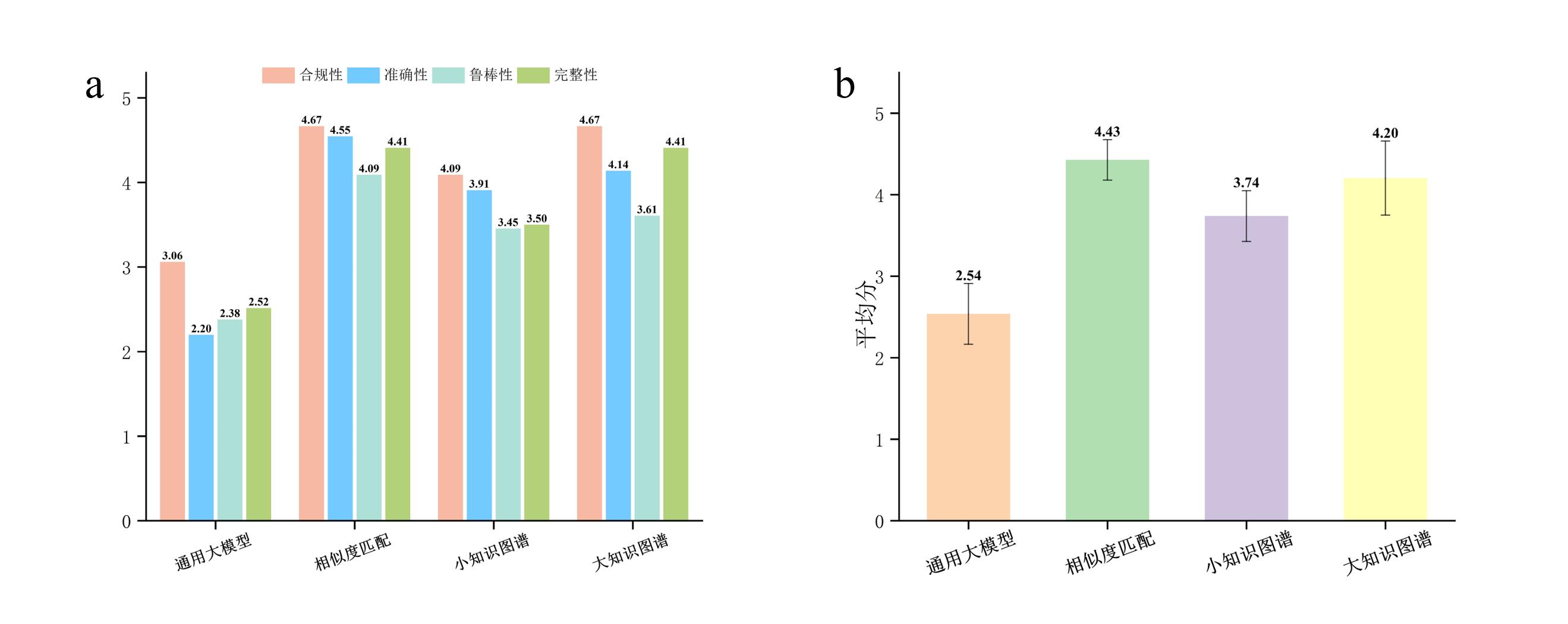
图 6 不同知识增强方法在简答题总体性能与各维度性能对比。(a)各维度平均分对比。(b)总体平均分对比
Fig.6 Comparison of overall performance and performance in each dimension of different knowledge enhancement methods on short answer questions. (a) Comparison of average scores in each dimension. (b) Comparison of overall average scores
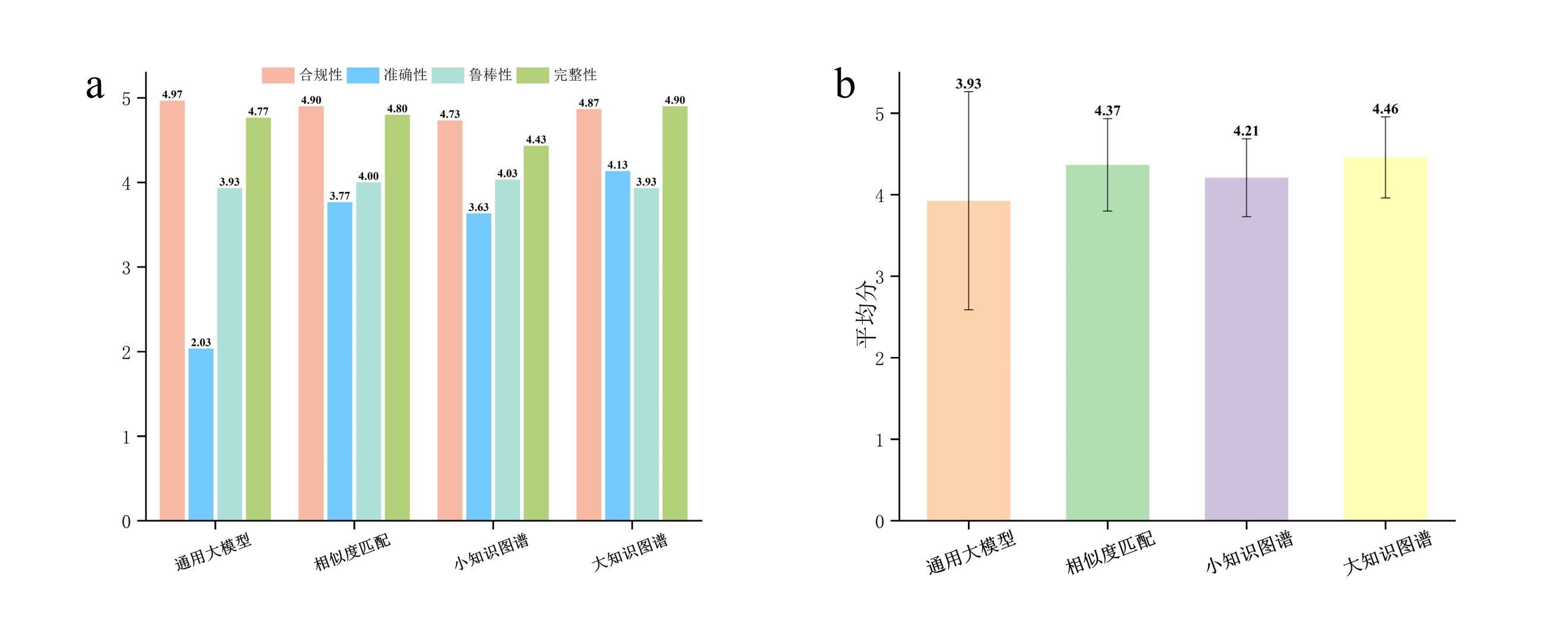
图 7 不同知识增强方法在综合题总体性能与各维度性能对比。(a)各维度平均分对比。(b)总体平均分对比
Fig.7 Comparison of overall performance and performance in each dimension of different knowledge enhancement methods on comprehensive questions. (a) Comparison of average scores in each dimension. (b) Comparison of overall average scores
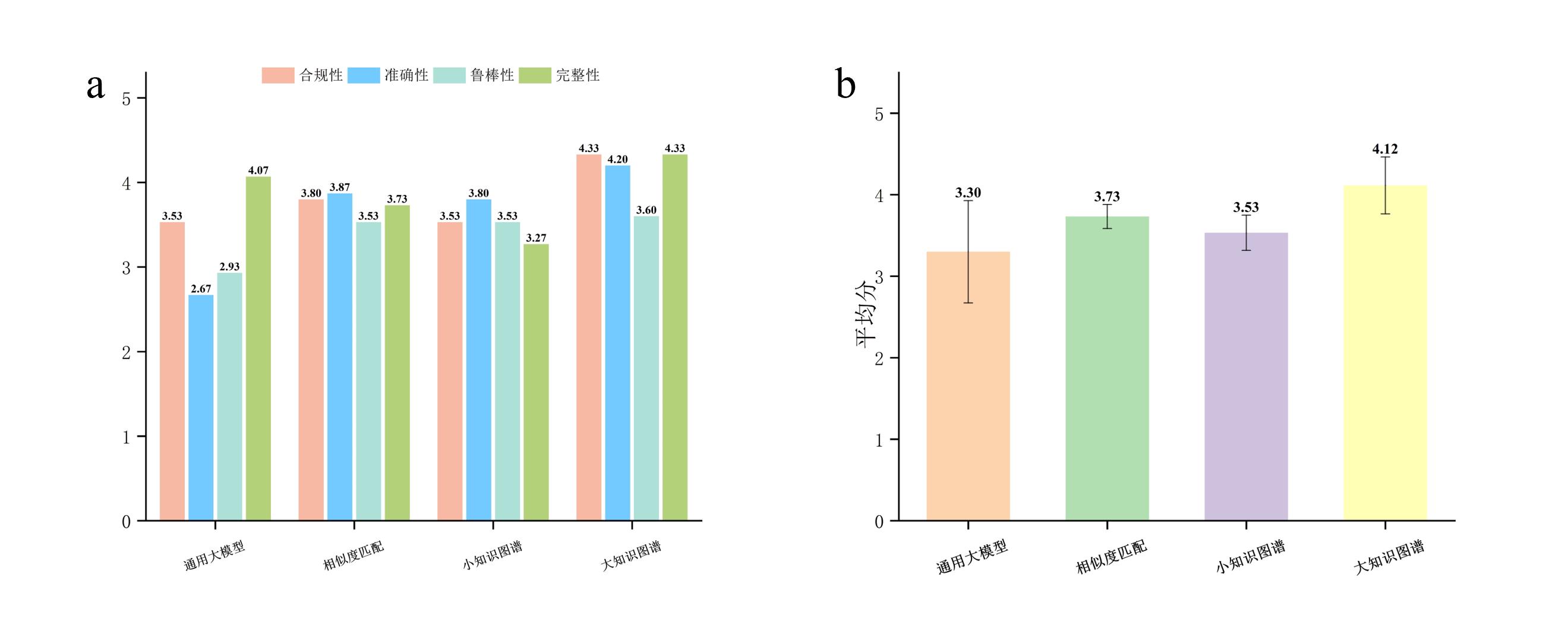
图 8 不同知识增强方法在推理题总体性能与各维度性能对比。(a)各维度平均分对比。(b)总体平均分对比
Fig.8 Comparison of overall performance and performance in each dimension of different knowledge enhancement methods in reasoning questions. (a) Comparison of average scores in each dimension. (b) Comparison of overall average scores
| 评分 | 合规性 | 准确性 | 鲁棒性 | 完整性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 完全回应题干所有要求,无跑题或信息越界。 | 概念术语完全准确;引用文献真实且与原文高度匹配。 | 主动清晰声明假设与局限;严格区分事实与推论。 | 全面覆盖所有要点;逻辑清晰,结构完整连贯。 |
| 4 | 基本回应核心任务,存在轻微偏离但不影响整体。 | 概念术语基本正确;引用文献基本真实,内容大意相符。 | 对边界条件有基本意识,但声明不够清晰。 | 覆盖大部分核心要点,有个别遗漏;逻辑基本连贯。 |
| 3 | 部分跑题,有关联性弱的段落或论点。 | 概念术语有明显错误;部分引用存疑或与原文有出入。 | 缺乏边界意识,未声明假设;将举例陈述为事实。 | 遗漏关键要点,影响理解;逻辑结构松散。 |
| 2 | 严重跑题,大量内容与题干无关。 | 核心概念严重错误;大部分引用不可靠或与原文严重不符。 | 无边界意识;将推论包装成确凿结论。 | 覆盖极少要点,仅零散回应;缺乏逻辑组织。 |
| 1 | 完全答非所问。 | 概念术语错误百出;引用完全虚构或捏造数据。 | 捏造前提和边界条件;充斥无法验证的断言。 | 内容支离破碎,无法体现基本理解。 |
表A.1 评估评分细则表
Table A.1 Scoring rubric for evaluation
| 评分 | 合规性 | 准确性 | 鲁棒性 | 完整性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 完全回应题干所有要求,无跑题或信息越界。 | 概念术语完全准确;引用文献真实且与原文高度匹配。 | 主动清晰声明假设与局限;严格区分事实与推论。 | 全面覆盖所有要点;逻辑清晰,结构完整连贯。 |
| 4 | 基本回应核心任务,存在轻微偏离但不影响整体。 | 概念术语基本正确;引用文献基本真实,内容大意相符。 | 对边界条件有基本意识,但声明不够清晰。 | 覆盖大部分核心要点,有个别遗漏;逻辑基本连贯。 |
| 3 | 部分跑题,有关联性弱的段落或论点。 | 概念术语有明显错误;部分引用存疑或与原文有出入。 | 缺乏边界意识,未声明假设;将举例陈述为事实。 | 遗漏关键要点,影响理解;逻辑结构松散。 |
| 2 | 严重跑题,大量内容与题干无关。 | 核心概念严重错误;大部分引用不可靠或与原文严重不符。 | 无边界意识;将推论包装成确凿结论。 | 覆盖极少要点,仅零散回应;缺乏逻辑组织。 |
| 1 | 完全答非所问。 | 概念术语错误百出;引用完全虚构或捏造数据。 | 捏造前提和边界条件;充斥无法验证的断言。 | 内容支离破碎,无法体现基本理解。 |
| [4] | Choi J, Kim S, Jung Y. Synthesis-aware materials redesign via large language models[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2025, 147(43): 39113-39122. |
| [5] | Ma Q Y, Zhou Y H, Li J F. Automated retrosynthesis planning of macromolecules using large language models and knowledge graphs[J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2025: e2500065. |
| [6] | Fu F, Li Q Q, Wang F R, et al. Synergizing a knowledge graph and large language model for relay catalysis pathway recommendation[J]. National Science Review, 2025, 12(8): nwaf271. |
| [7] | Chen Z Y, Xie F K, Wan M, et al. MatChat: a large language model and application service platform for materials science[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2023, 32(11): 118104. |
| [8] | Chithrananda S, Grand G, Ramsundar B. ChemBERTa: large-scale self-supervised pretraining for molecular property prediction[EB/OL]. 2020: arXiv: 2010.09885. |
| [9] | Zhang D, Liu W, Tan Q, et al. ChemLLM: a chemical large language model[EB/OL]. 2024: arXiv: 2402.06852. |
| [10] | Weininger D. SMILES, a chemical language and information system. 1. Introduction to methodology and encoding rules[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences, 1988, 28(1): 31-36. |
| [11] | Krenn M, Häse F, Nigam A, et al. Self-referencing embedded strings (SELFIES): a 100% robust molecular string representation[J]. Machine Learning: Science and Technology, 2020, 1(4): 045024. |
| [12] | Hastedt F, Bailey R M, Hellgardt K, et al. Investigating the reliability and interpretability of machine learning frameworks for chemical retrosynthesis[J]. Digital Discovery, 2024, 3(6): 1194-1212. |
| [13] | Xu Z W, Jain S, Kankanhalli M. Hallucination is inevitable: an innate limitation of large language models[EB/OL]. 2024: arXiv: 2401.11817. |
| [14] | Mirza A, Alampara N, Kunchapu S, et al. A framework for evaluating the chemical knowledge and reasoning abilities of large language models against the expertise of chemists[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2025, 17(7): 1027-1034. |
| [15] | Bran A M, Cox S, Schilter O, et al. Augmenting large language models with chemistry tools[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2024, 6(5): 525-535. |
| [16] | Bai X F, He S, Li Y, et al. Construction of a knowledge graph for framework material enabled by large language models and its application[J]. npj Computational Materials, 2025, 11: 51. |
| [17] | Lewis P, Perez E, Piktus A, et al. Retrieval-augmented generation for knowledge-intensive NLP tasks[EB/OL]. 2020: arXiv: 2005.11401. |
| [18] | Liu B Y, Huang N, Wang Y, et al. Regioselectivity regulation of styrene hydroformylation over Rh-based Phosphides: Combination of DFT calculations and kinetic studies[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 441: 136101. |
| [19] | 孙嘉辰, 张晓昕, 张涛, 等. 非均相Rh基烯烃氢甲酰化反应催化剂研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2025, 54(8): 2170-2175. |
| Sun J C, Zhang X X, Zhang T, et al. Recent development towards heterogeneous hydroformylation of alkenes by Rh-based catalysts[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2025, 54(8): 2170-2175. | |
| [20] | Gillum M, Ariyaratne G K P A, Tawny C, et al. Recent advances in heterogeneous hydroformylation at metal–oxide interfaces[J]. Molecules, 2025, 30(20): 4078. |
| [21] | Samanta P, Canivet J. MOF-supported heterogeneous catalysts for hydroformylation reactions: a minireview[J]. ChemCatChem, 2024, 16(7): e202301435. |
| [22] | Wang T, Wang W L, Lyu Y, et al. Porous Rh/BINAP polymers as efficient heterogeneous catalysts for asymmetric hydroformylation of styrene: Enhanced enantioselectivity realized by flexible chiral nanopockets[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2017, 38(4): 691-698. |
| [23] | Breit B, Breuninger D. Desymmetrizing hydroformylation with the aid of a planar chiral catalyst-directing group[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(33): 10244-10245. |
| [24] | Zhu Y X, Zhang Y C, He D Y, et al. Rhodium-catalyzed asymmetric reductive hydroformylation of α-substituted enamides[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(48): 33249-33257. |
| [25] | Sandmann S, Hegselmann S, Fujarski M, et al. Benchmark evaluation of DeepSeek large language models in clinical decision-making[J]. Nature Medicine, 2025, 31(8): 2546-2549. |
| [26] | DeepSeek-AI, Liu A X, Mei A X, et al. DeepSeek- V3.2: pushing the frontier of open large language models[EB/OL]. 2025: arXiv: 2512.02556. |
| [27] | Yang A, Li A F, Yang B S, et al. Qwen3 technical report[EB/OL]. 2025: arXiv: 2505.09388. |
| [28] | OpenAI,:, Hurst A, et al. GPT-4o system card[EB/OL]. 2024: arXiv: 2410.21276. |
| [29] | 于婷, 刘英琦, 王恒飞, 等. 基于大语言模型的乏燃料后处理脉冲柱萃取过程预测[J]. 化工学报, 2025. |
| Yu T, Liu Y Q, Wang H F, et al. Prediction of the pulse column extraction process for spent fuel reprocessing based on large language models [J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2025. | |
| [30] | Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[EB/OL]. 2017: arXiv: 1706.03762. |
| [1] | Walls B W, Linic S. Use of large language models for extracting and analyzing data from heterogeneous catalysis literature[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2025, 15(17): 14751-14763. |
| [2] | Kang Y, Lee W, Bae T, et al. Harnessing large language models to collect and analyze metal–organic framework property data set[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2025, 147(5): 3943-3958. |
| [3] | Dagdelen J, Dunn A, Lee S, et al. Structured information extraction from scientific text with large language models[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15: 1418. |
| [1] | 文华强, 孙全虎, 申威峰. 基于分子碎片化学空间的智能分子定向生成框架[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1655-1667. |
| [2] | 阮见, 李双, 温正慧. 自动化与智能化在流动化学中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(11): 4120-4140. |
| [3] | 应雨轩, 林晓青, 吴昂键, 李晓东. 生活垃圾智慧焚烧的研究现状及展望[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 886-900. |
| [4] | 秦磊, 俞杰, 宁小钰, 孙文涛, 李春. 合成生物系统构建与绿色生物“智”造[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(9): 3979-3994. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号