CIESC Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (2): 709-726.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20201415
• Reviews and monographs • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Jiahe1( ),YUAN Ye1,WANG Ming2,WANG Zhi1(
),YUAN Ye1,WANG Ming2,WANG Zhi1( ),WANG Jixiao1
),WANG Jixiao1
Received:2020-10-10
Revised:2020-12-30
Online:2021-02-05
Published:2021-02-05
Contact:
WANG Zhi
通讯作者:
王志
作者简介:张家赫(1996—),男,硕士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHANG Jiahe, YUAN Ye, WANG Ming, WANG Zhi, WANG Jixiao. Research progress in polymer-metal-organic frameworks[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(2): 709-726.
张家赫, 原野, 王明, 王志, 王纪孝. 聚合物-金属有机框架材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 709-726.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX

Fig.2 Schematic illustration of cross-linking of the organic linkers in MOF (AzM) and subsequent decomposition to obtain polymer gel (PG) (a). Molecular structures of the organic ligand (AzTPDC) and the cross-linkers (b) [52]

Fig.3 DNA functionalization of UiO-66-N3 nanoparticles, using DNA functionalized with dibenzylcyclooctyne (DBCO) (a). Nanoparticle uptake per cell determined by ICP-MS (b)[33]

Fig.9 The strategy described herein to convert a one-dimensional (linear), non-porous, mostly amorphous polymer into a three-dimensional, porous, crystalline polyMOF hybrid material[88]
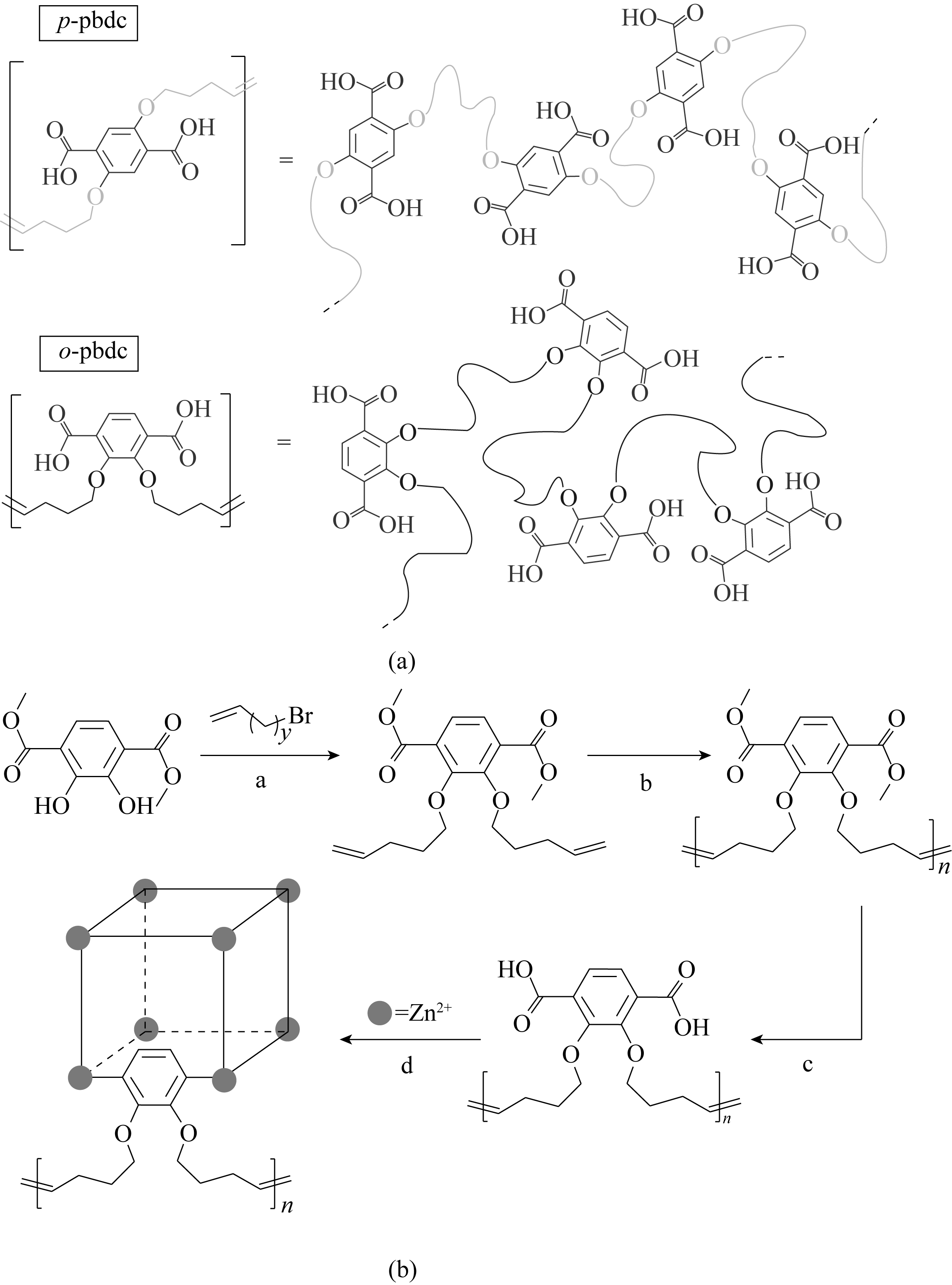
Fig.10 Comparison of para-substituted (top) and ortho-substituted (bottom) polymer ligands (a). Synthesis of o-pbdc-xa-u and subsequent formation of polyIRMOF-1 (b)[91]

Fig.12 In situ synthesis protocol of PEI-g-ZIF-8 nanoparticles (a). Structure illustration of PEI-g-ZIF-8 nanoparticles(only showing some main linkers of Hmim and PEI) (b)[38]
| 混合基质膜 | 掺杂量/%(质量) | 气体分离性能① | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2渗透速率/GPU | CO2/N2分离因子 | |||
| PVAm/ZIF-8/PSf | 13.1 | 600 | 95 | [ |
| PVAm/PEI-g-ZIF-8/PSf | 20 | 1600 | 75 | [ |
Table 1 Comparison of doping amount and gas separation performance of two mixed matrix membranes
| 混合基质膜 | 掺杂量/%(质量) | 气体分离性能① | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2渗透速率/GPU | CO2/N2分离因子 | |||
| PVAm/ZIF-8/PSf | 13.1 | 600 | 95 | [ |
| PVAm/PEI-g-ZIF-8/PSf | 20 | 1600 | 75 | [ |

Fig.13 The main structure of each independent MPF-1 framework (a). The polymer segments of the main MPF-1 framework (b). The structure of PVAmacid (c) [39]

Fig.14 Construction of MMP frameworks using the PDCS process (a). Independent frameworks of MMP-1 and MMP-2 (b). Independent frameworks of MMP-3 and MMP-4 (c)[40]
| 合成方法 | polyMOF材料 | 优点 | 缺点 | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 合成后聚合 | 点击化学法 | polySURMOF | 反应条件温和;催化剂高效稳定;反应速率高,几乎无副产物 | 铜盐作催化剂时后处理烦琐, 不易从产物中去除;环炔与叠氮的反应便于后处理但效率相对较低 | [ |
| UiO-66-N3-DNA-Conjugate | [ | ||||
| MOFs孔道内聚合 | 聚乙烯型polyMOFs | polyMOFs中的聚合物结构可控、分子量分布窄 | 易堵塞孔道,降低孔隙率 | [ | |
| 表面接枝法 | P@MOF | 操作方便,步骤简单;大大提升MOFs表面的聚合物质量分数;有效改善MOFs的机械性与稳定性 | 对侧链的分子量分布及接枝密度的控制难度较大;接枝效率较低;易堵塞MOFs孔道 | [ | |
| terpolymer@ZIF-8@BA | [ | ||||
| PMMA-g-GMA-UiO-66 | [ | ||||
| PMMA@IRMOF-3@MOF-5 | [ | ||||
单晶到单晶 转换 | MOPF | 操作简单且效率较高;能够可逆地合成polyMOFs | 金属与聚合物结合处易断裂,往往制备的polyMOFs的热稳定性和化学稳定性较差 | [ | |
| [Zn(poly-bppcb)(bdc)]n | [84] | ||||
[Zn2(S-poly-bppcb)(obc)2]? 2.5H2O | [86] | ||||
| 直接合成法 | MPF-1 | 合成步骤简单;材料结构可控;有效提升MOFs的稳定性与功能性 | 分离过程烦琐;产率较低 | [ | |
| MMPs | [40] | ||||
| HMMP-1 | [102] | ||||
| PEI-g-ZIF-8 | [38] | ||||
| polyIRMOF-1 | [88,93-94,97-98,100] [87,90,94,100] | ||||
polyUiO-66, polyUiO-67,polyUiO-68 | |||||
[Zn2(BME-bdc)2(bpy)]n, [Zn7(bdc)6(H2O)6(bpe)2(NO3)2]n | [89] | ||||
Table 2 Typical polyMOFs synthesized by different methods and their advantages and disadvantages
| 合成方法 | polyMOF材料 | 优点 | 缺点 | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 合成后聚合 | 点击化学法 | polySURMOF | 反应条件温和;催化剂高效稳定;反应速率高,几乎无副产物 | 铜盐作催化剂时后处理烦琐, 不易从产物中去除;环炔与叠氮的反应便于后处理但效率相对较低 | [ |
| UiO-66-N3-DNA-Conjugate | [ | ||||
| MOFs孔道内聚合 | 聚乙烯型polyMOFs | polyMOFs中的聚合物结构可控、分子量分布窄 | 易堵塞孔道,降低孔隙率 | [ | |
| 表面接枝法 | P@MOF | 操作方便,步骤简单;大大提升MOFs表面的聚合物质量分数;有效改善MOFs的机械性与稳定性 | 对侧链的分子量分布及接枝密度的控制难度较大;接枝效率较低;易堵塞MOFs孔道 | [ | |
| terpolymer@ZIF-8@BA | [ | ||||
| PMMA-g-GMA-UiO-66 | [ | ||||
| PMMA@IRMOF-3@MOF-5 | [ | ||||
单晶到单晶 转换 | MOPF | 操作简单且效率较高;能够可逆地合成polyMOFs | 金属与聚合物结合处易断裂,往往制备的polyMOFs的热稳定性和化学稳定性较差 | [ | |
| [Zn(poly-bppcb)(bdc)]n | [84] | ||||
[Zn2(S-poly-bppcb)(obc)2]? 2.5H2O | [86] | ||||
| 直接合成法 | MPF-1 | 合成步骤简单;材料结构可控;有效提升MOFs的稳定性与功能性 | 分离过程烦琐;产率较低 | [ | |
| MMPs | [40] | ||||
| HMMP-1 | [102] | ||||
| PEI-g-ZIF-8 | [38] | ||||
| polyIRMOF-1 | [88,93-94,97-98,100] [87,90,94,100] | ||||
polyUiO-66, polyUiO-67,polyUiO-68 | |||||
[Zn2(BME-bdc)2(bpy)]n, [Zn7(bdc)6(H2O)6(bpe)2(NO3)2]n | [89] | ||||
| 1 | 原野, 王明, 周云琪, 等. 金属有机框架孔径调控进展[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(2): 429-450. |
| Yuan Y, Wang M, Zhou Y Q, et al. Progress in pore size regulation of metal-organic frameworks[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(2): 429-450. | |
| 2 | Kalaj M, Bentz K C, Ayala S, et al. MOF-polymer hybrid materials: from simple composites to tailored architectures[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(16): 8267-8302. |
| 3 | 赵云, 向中华. 微流控制备金属/共价有机框架功能材料研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(6): 2547-2563. |
| Zhao Y, Xiang Z H. Progress of microfluidic synthesis of metal/covalent organic frameworks[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(6): 2547-2563. | |
| 4 | Venna S R, Carreon M A. Metal organic framework membranes for carbon dioxide separation[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2015, 124: 3-19. |
| 5 | Chaoui N, Trunk M, Dawson R, et al. Trends and challenges for microporous polymers[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(11): 3302-3321. |
| 6 | Chen Y, Huang X, Zhang S, et al. Shaping of metal-organic frameworks: from fluid to shaped bodies and robust foams[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(34): 10810-10813. |
| 7 | Schmidt B. Metal-organic frameworks in polymer science: polymerization catalysis, polymerization environment, and hybrid materials[J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2020, 41(1): 1900333-1900361. |
| 8 | Qiu S, Xue M, Zhu G. Metal-organic framework membranes: from synthesis to separation application[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(16): 6116-6140. |
| 9 | Wang Q, Astruc D. State of the art and prospects in metal-organic framework (MOF)-based and MOF-derived nanocatalysis[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(2): 1438-1511. |
| 10 | Chi W S, Kim S J, Lee S J, et al. Enhanced performance of mixed-matrix membranes through a graft copolymer-directed interface and interaction tuning approach[J]. ChemSusChem, 2015, 8(4): 650-658. |
| 11 | Ghalei B, Sakurai K, Kinoshita Y, et al. Enhanced selectivity in mixed matrix membranes for CO2 capture through efficient dispersion of amine-functionalized MOF nanoparticles[J]. Nature Energy, 2017, 2(7): 17086-17095. |
| 12 | Nagata S, Kokado K, Sada K. Metal-organic framework tethering pnipam for ON-OFF controlled release in solution[J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(41): 8614-8617. |
| 13 | Kango S, Kalia S, Celli A, et al. Surface modification of inorganic nanoparticles for development of organic-inorganic nanocomposites—a review[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2013, 38(8): 1232-1261. |
| 14 | Lyu F, Zhang Y, Zare R N, et al. One-pot synthesis of protein-embedded metal-organic frameworks with enhanced biological activities[J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(10): 5761-5765. |
| 15 | Koh K, Wong-Foy A G, Matzger A J. Coordination copolymerization mediated by Zn4O(CO2R)6 metal clusters: a balancing act between statistics and geometry[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(42): 15005-15010. |
| 16 | Le Ouay B, Watanabe C, Mochizuki S, et al. Selective sorting of polymers with different terminal groups using metal-organic frameworks[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 3635-3643. |
| 17 | Kitao T, Bracco S, Comotti A, et al. Confinement of single polysilane chains in coordination nanospaces[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(15): 5231-5238. |
| 18 | Lykourinou V, Chen Y, Wang X S, et al. Immobilization of MP-11 into a mesoporous metal-organic framework, MP-11@mesoMOF: a new platform for enzymatic catalysis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(27): 10382-10385. |
| 19 | Liu S, Zhai L, Li C, et al. Exploring and exploiting dynamic noncovalent chemistry for effective surface modification of nanoscale metal-organic frameworks[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(8): 5404-5412. |
| 20 | Liu H, Zhu H, Zhu S. Reversibly dispersible/collectable metal-organic frameworks prepared by grafting thermally responsive and switchable polymers[J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 2015, 300(2): 191-197. |
| 21 | Dong S, Chen Q, Li W, et al. A dendritic catiomer with an MOF motif for the construction of safe and efficient gene delivery systems[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2017, 5(42): 8322-8329. |
| 22 | Tabatabaii M, Khajeh M, Oveisi A R, et al. Poly(lauryl methacrylate)-grafted amino-functionalized zirconium-terephthalate metal-organic framework: efficient adsorbent for extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water samples[J]. ACS Omega, 2020, 5(21): 12202-12209. |
| 23 | Hou L, Wang L, Zhang N, et al. Polymer brushes on metal-organic frameworks by UV-induced photopolymerization[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2016, 7(37): 5828-5834. |
| 24 | Abánades Lázaro I, Haddad S, Rodrigo-Muñoz J M, et al. Mechanistic investigation into the selective anticancer cytotoxicity and immune system response of surface-functionalized, dichloroacetate-loaded, UiO-66 nanoparticles[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(6): 5255-5268. |
| 25 | Lu Y, Zhu H, Wang W J, et al. Rapid collection and re-dispersion of MOF particles by a simple and versatile method using a thermo-responsive polymer[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(68): 63398-63402. |
| 26 | Abánades Lázaro I, Haddad S, Sacca S, et al. Selective surface pegylation of UiO-66 nanoparticles for enhanced stability, cell uptake, and pH-responsive drug delivery[J]. Chem, 2017, 2(4): 561-578. |
| 27 | Giménez-Marqués M, Bellido E, Berthelot T, et al. Graftfast surface engineering to improve MOF nanoparticles furtiveness[J]. Small, 2018, 14(40): 1801900-1801911. |
| 28 | Zhao D, Tan S, Yuan D, et al. Surface functionalization of porous coordination nanocages via click chemistry and their application in drug delivery[J]. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(1): 90-93. |
| 29 | Zhu Q L, Xu Q. Metal-organic framework composites[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(16): 5468-5512. |
| 30 | Bentz K C, Cohen S M. Supramolecular metallopolymers: from linear materials to infinite networks[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(46): 14992-15001. |
| 31 | Giliopoulos D, Zamboulis A, Giannakoudakis D, et al. Polymer/metal organic framework (MOF) nanocomposites for biomedical applications[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(1):185-213. |
| 32 | Saleem S, Sajid M S, Hussain D, et al. Highly porous terpolymer-ZIF-8@BA MOF composite for identification of mono- and multi-glycosylated peptides/proteins using MS-based bottom-up approach[J]. Microchimica Acta, 2020, 187(10): 555-564. |
| 33 | Morris W, Briley W E, Auyeung E, et al. Nucleic acid-metal organic framework (MOF) nanoparticle conjugates[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(20): 7261-7264. |
| 34 | Goetjen T A, Liu J, Wu Y, et al. Metal-organic framework (MOF) materials as polymerization catalysts: a review and recent advances[J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(72): 10409-10418. |
| 35 | Xie K, Fu Q, He Y, et al. Synthesis of well dispersed polymer grafted metal-organic framework nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(85): 15566-15569. |
| 36 | Lee H C, Antonietti M, Schmidt B V K J. A Cu(Ⅱ) metal-organic framework as a recyclable catalyst for ARGET ATRP[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2016, 7(47): 7199-7203. |
| 37 | Molavi H, Shojaei A, Mousavi S A. Improving mixed-matrix membrane performance via PMMA grafting from functionalized NH2-UiO-66[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(6): 2775-2791. |
| 38 | Gao Y Q, Qiao Z H, Zhao S, et al. In situ synthesis of polymer grafted ZIFs and application in mixed matrix membrane for CO2 separation[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(7): 3151-3161. |
| 39 | Qiao Z H, Sheng M L, Wang J X, et al. Metal-induced polymer framework membrane with high performance for CO2 separation[J]. AIChE Journal, 2019, 65(1): 239-249. |
| 40 | Qiao Z H, Zhao S, Sheng M L, et al. Metal-induced ordered microporous polymers for fabricating large-area gas separation membranes[J]. Nature Materials, 2019, 18(2): 163-168. |
| 41 | Cohen S M. The postsynthetic renaissance in porous solids[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(8): 2855-2863. |
| 42 | Zhang Y, Feng X, Li H, et al. Photoinduced postsynthetic polymerization of a metal-organic framework toward a flexible stand-alone membrane[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(14): 4259-4263. |
| 43 | Xu R, Wang Z, Wang M, et al. High nanoparticles loadings mixed matrix membranes via chemical bridging-crosslinking for CO2 separation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 573: 455-464. |
| 44 | Marti A M, Venna S R, Roth E A, et al. Simple fabrication method for mixed matrix membranes with in situ MOF growth for gas separation[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(29): 24784-24790. |
| 45 | Yao B J, Jiang W L, Dong Y, et al. Post-synthetic polymerization of UiO-66-NH2 nanoparticles and polyurethane oligomer toward stand-alone membranes for dye removal and separation[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2016, 22(30): 10565-10571. |
| 46 | Qin A, Lam J W Y, Tang B Z. Click polymerization[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2010, 39(7): 2522-2544. |
| 47 | Tajima K, Aida T. Controlled polymerizations with constrained geometries[J]. Chemical Communications, 2000, 24: 2399-2412. |
| 48 | Sun W, Liu W, Wu Z, et al. Chemical surface modification of polymeric biomaterials for biomedical applications[J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 2020, 41(8): 1900430-1900456. |
| 49 | Decker C, Nguyen T V T, Decker D, et al. UV-radiation curing of acrylate/epoxide systems[J]. Polymer, 2001, 42(13): 5531-5541. |
| 50 | Döhler D, Michael P, Binder W H. CUAAC-based click chemistry in self-healing polymers[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2017, 50(10): 2610-2620. |
| 51 | Goto Y, Sato H, Shinkai S, et al.“Clickable” metal-organic framework[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130(44): 14354-14355. |
| 52 | Ishiwata T, Furukawa Y, Sugikawa K, et al. Transformation of metal-organic framework to polymer gel by cross-linking the organic ligands preorganized in metal-organic framework[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(14): 5427-5432. |
| 53 | Tsotsalas M, Liu J, Tettmann B, et al. Fabrication of highly uniform gel coatings by the conversion of surface-anchored metal-organic frameworks[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(1): 8-11. |
| 54 | Uemura T, Ono Y, Kitagawa K, et al. Radical polymerization of vinyl monomers in porous coordination polymers: nanochannel size effects on reactivity, molecular weight, and stereostructure[J]. Macromolecules, 2008, 41(1): 87-94. |
| 55 | Uemura T, Ono Y, Hijikata Y, et al. Functionalization of coordination nanochannels for controlling tacticity in radical vinyl polymerization[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(13): 4917-4924. |
| 56 | Uemura T, Uchida N, Higuchi M, et al. Effects of unsaturated metal sites on radical vinyl polymerization in coordination nanochannels[J]. Macromolecules, 2011, 44(8): 2693-2697. |
| 57 | Takashi U, Yukari O, Susumu K. Radical copolymerizations of vinyl monomers in a porous coordination polymer[J]. Chemistry Letters, 2008, 37(6): 616-617. |
| 58 | Uemura T, Mochizuki S, Kitagawa S. Radical copolymerization mediated by unsaturated metal sites in coordination nanochannels[J]. ACS Macro Letters, 2015, 4(7): 788-791. |
| 59 | Uemura T, Kaseda T, Sasaki Y, et al. Mixing of immiscible polymers using nanoporous coordination templates[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6(1): 7473-7481. |
| 60 | Uemura T, Kaseda T, Kitagawa S. Controlled synthesis of anisotropic polymer particles templated by porous coordination polymers[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2013, 25(18): 3772-3776. |
| 61 | Furukawa Y, Ishiwata T, Sugikawa K, et al. Nano- and microsized cubic gel particles from cyclodextrin metal-organic frameworks[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(42): 10566-10569. |
| 62 | Distefano G, Suzuki H, Tsujimoto M, et al. Highly ordered alignment of a vinyl polymer by host-guest cross-polymerization[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2013, 5(4): 335-341. |
| 63 | Mochizuki S, Ogiwara N, Takayanagi M, et al. Sequence-regulated copolymerization based on periodic covalent positioning of monomers along one-dimensional nanochannels[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 329-335. |
| 64 | Uemura T, Kitagawa K, Horike S, et al. Radical polymerisation of styrene in porous coordination polymers[J]. Chemical Communications, 2005, 48: 5968-5970. |
| 65 | Uemura T, Horike S, Kitagawa K, et al. Conformation and molecular dynamics of single polystyrene chain confined in coordination nanospace[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130(21): 6781-6788. |
| 66 | Gamage N D H, McDonald K A, Matzger A J. MOF-5-polystyrene: direct production from monomer, improved hydrolytic stability, and unique guest adsorption[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(39): 12099-12103. |
| 67 | Uemura T, Uchida N, Asano A, et al. Highly photoconducting π-stacked polymer accommodated in coordination nanochannels[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(20): 8360-8363. |
| 68 | Bai L, Wang P, Bose P, et al. Macroscopic architecture of charge transfer-induced molecular recognition from electron-rich polymer interpenetrated porous frameworks[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(9): 5056-5060. |
| 69 | Matyjaszewski K, Xia J. Atom transfer radical polymerization[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2001, 101(9): 2921-2990. |
| 70 | 何鹏鹏, 赵颂, 毛晨岳, 等. 耐溶剂复合纳滤膜的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 727-747. |
| He P P, Zhao S, Mao C Y, et al. Research progress of solvent-resistant composite nanofiltration membrane[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(2): 727-747. | |
| 71 | 潘祖仁. 高分子化学[M]. 5版. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2011: 243. |
| Pan Z R. Polymer Chemistry[M]. 5th ed. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2011: 243. | |
| 72 | Hansson S, Trouillet V, Tischer T, et al. Grafting efficiency of synthetic polymers onto biomaterials: a comparative study of grafting-from versus grafting-to[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2013, 14(1): 64-74. |
| 73 | Bentz K C, Ejaz M, Arencibia S, et al. Hollow amphiphilic crosslinked nanocapsules from sacrificial silica nanoparticle templates and their application as dispersants for oil spill remediation[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2017, 8(34): 5129-5138. |
| 74 | Bentz K C, Savin D A. Chain dispersity effects on brush properties of surface-grafted polycaprolactone-modified silica nanoparticles: Unique scaling behavior in the concentrated polymer brush regime[J]. Macromolecules, 2017, 50(14): 5565-5573. |
| 75 | McDonald K A, Feldblyum J I, Koh K, et al. Polymer@MOF@MOF: “grafting from” atom transfer radical polymerization for the synthesis of hybrid porous solids[J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(60): 11994-11996. |
| 76 | Mendes R F, Paz F A A. Transforming metal-organic frameworks into functional materials[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2015, 2(6): 495-509. |
| 77 | He W W, Li S L, Lan Y Q. Liquid-free single-crystal to single-crystal transformations in coordination polymers[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2018, 5(2): 279-300. |
| 78 | Marti-Rujas J. Thermal reactivity in metal organic materials (MOMs): from single-crystal-to-single-crystal reactions and beyond[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(24): 4088-4114. |
| 79 | Lässig D, Lincke J, Gerhardt R, et al. Solid-state syntheses of coordination polymers by thermal conversion of molecular building blocks and polymeric precursors[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2012, 51(11): 6180-6189. |
| 80 | Ou Y C, Zhi D S, Liu W T, et al. Single-crystal-to-single-crystal transformation from 1D staggered-sculls chains to 3D NbO-type metal-organic framework through [2+2] photodimerization[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2012, 18(24): 7357-7361. |
| 81 | Medishetty R, Koh L L, Kole G K, et al. Solid-state structural transformations from 2D interdigitated layers to 3D interpenetrated structures[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 2011, 50(46): 10949-10952. |
| 82 | Medishetty R, Tandiana R, Koh L L, et al. Assembly of 3D coordination polymers from 2D sheets by [2+2] cycloaddition reaction[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 20(5): 1231-1236. |
| 83 | Xie M H, Yang X L, Wu C D. From 2D to 3D: a single-crystal-to-single-crystal photochemical framework transformation and phenylmethanol oxidation catalytic activity[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2011, 17(41): 11424-11427. |
| 84 | Park I H, Chanthapally A, Zhang Z, et al. Metal-organic organopolymeric hybrid framework by reversible 2+2 cycloaddition reaction[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(2): 414-419. |
| 85 | Park I H, Chanthapally A, Lee H H, et al. Solid-state conversion of a MOF to a metal-organo polymeric framework (MOPF) via [2+2] cycloaddition reaction[J]. Chemical Communications, 2014, 50(28): 3665-3667. |
| 86 | Park I H, Medishetty R, Lee H H, et al. Formation of a syndiotactic organic polymer inside a MOF by a [2+2] photo-polymerization reaction[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(25): 7313-7317. |
| 87 | Schukraft G E M, Ayala S, Dick B L, et al. Isoreticular expansion of polyMOFs achieves high surface area materials[J]. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(77): 10684-10687. |
| 88 | Zhang Z, Nguyen H T, Miller S A, et al. PolyMOFs: a class of interconvertible polymer-metal-organic-framework hybrid materials[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(21): 6152-6157. |
| 89 | Zhang Z, Ha Thi Hoang N, Miller S A, et al. Polymer-metal-organic frameworks (PolyMOFs) as water tolerant materials for selective carbon dioxide separations[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(3): 920-925. |
| 90 | Ayala S, Zhang Z J, Cohen S M. Hierarchical structure and porosity in UiO-66 polyMOFs[J]. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(21): 3058-3061. |
| 91 | Palomba J M, Ayala S J, Cohen S M. PolyMOF formation from kinked polymer ligands via ortho-substitution[J]. Israel Journal of Chemistry, 2018, 58(9/10): 1123-1126. |
| 92 | Mileo P G M, Yuan S, Ayala S, et al. Structure of the polymer backbones in polyMOF materials[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(24): 10863-10868. |
| 93 | Yazaki K, Takahashi M, Miyajima N, et al. Construction of a polyMOF using a polymer ligand bearing the benzenedicarboxylic acid moiety in the side chain[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 44(14): 5182-5185. |
| 94 | 赵小燕, 单国荣. RAFT聚合制备PMPS-b-PNIPAM嵌段共聚物及温敏性纳米粒子[J].化工学报, 2019, 70(10): 4080-4088. |
| Zhao X Y, Shan G R. PMPS-b-PNIPAM copolymers synthesized by RAFT polymerization and their thermo-responsive nanoparticles[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(10): 4080-4088. | |
| 95 | Bates C M, Bates F S. 50th anniversary perspective: block polymers—pure potential[J]. Macromolecules, 2017, 50(1): 3-22. |
| 96 | Jain S, Bates F S. On the origins of morphological complexity in block copolymer surfactants[J]. Science, 2003, 300(5618): 460-464. |
| 97 | Macleod M J, Johnson J A. Block co-polymofs: assembly of polymer-polyMOF hybrids via iterative exponential growth and “click” chemistry[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2017, 8(31): 4488-4493. |
| 98 | Gu Y W, Huang M J, Zhang W X, et al. PolyMOF nanoparticles: Dual roles of a multivalent polyMOF ligand in size control and surface functionalization[J]. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2019, 58(46): 16676-16681. |
| 99 | Kaye S S, Dailly A, Yaghi O M, et al. Impact of preparation and handling on the hydrogen storage properties of Zn4O(1,4-benzenedicarboxylate)3 (MOF-5)[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(46): 14176-14177. |
| 100 | Ayala S, Bentz K C, Cohen S M. Block co-polyMOFs: morphology control of polymer-MOF hybrid materials[J]. Chemical Science, 2019, 10(6): 1746-1753. |
| 101 | Zhao S, Cao X, Ma Z, et al. Mixed-matrix membranes for CO2/N2 separation comprising a poly(vinylamine) matrix and metal-organic frameworks[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015, 54(18): 5139-5148. |
| 102 | Yuan Y, Qiao Z H, Xu J Y, et al. Mixed matrix membranes for CO2 separations by incorporating microporous polymer framework fillers with amine-rich nanochannels[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2021, 620: 118923. |
| 103 | Kitao T, Uemura T. Polymers in metal-organic frameworks: from nanostructured chain assemblies to new functional materials[J]. Chemistry Letters, 2020, 49(6): 624-632. |
| [1] | ZHANG Meijia, WU Dengfeng, XU Haoxiang, CHENG Daojian. Research progress of Pd-based catalysts for DSHP from hydrogen and oxygen [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(1): 292-303. |
| [2] | DENG Jialin1,SHANG Xiaoqin1,2,LIU Rufeng1,LIU Peng1,2,WU Lunfu3,LI Zehua1,WU Mi1. Preparation and surface properties of cassava starch-based dodecylycoside [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progree, 2014, 33(07): 1880-1883. |
| [3] | DA Guojin, OUYANG Like, XU Jing, HAN Yifan. Pyridine modified Pd/SiO2 catalyst for direct synthesis of H2O2 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(2): 561-567. |
| [4] | GUAN Yongchuan,LI Wei,ZHANG Jinli. Research progress in the green synthesis process of hydrogen peroxide [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progree, 2012, 31(08): 1641-1646. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||