CIESC Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (1): 86-104.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20221188
• Reviews and monographs • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hao XIONG( ), Xiaoyu LIANG, Chenxi ZHANG(
), Xiaoyu LIANG, Chenxi ZHANG( ), Haolong BAI, Xiaoyu FAN, Fei WEI(
), Haolong BAI, Xiaoyu FAN, Fei WEI( )
)
Received:2022-08-30
Revised:2023-01-17
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2023-01-05
Contact:
Chenxi ZHANG, Fei WEI
熊昊( ), 梁潇予, 张晨曦(
), 梁潇予, 张晨曦( ), 白浩隆, 范晓宇, 魏飞(
), 白浩隆, 范晓宇, 魏飞( )
)
通讯作者:
张晨曦,魏飞
作者简介:熊昊(1997—),男,博士研究生,xiongh19@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Hao XIONG, Xiaoyu LIANG, Chenxi ZHANG, Haolong BAI, Xiaoyu FAN, Fei WEI. Heavy oil to chemicals: multi-stage downer catalytic pyrolysis[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 86-104.
熊昊, 梁潇予, 张晨曦, 白浩隆, 范晓宇, 魏飞. 重质油直接制化工品:多级逆流下行催化裂解技术[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 86-104.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
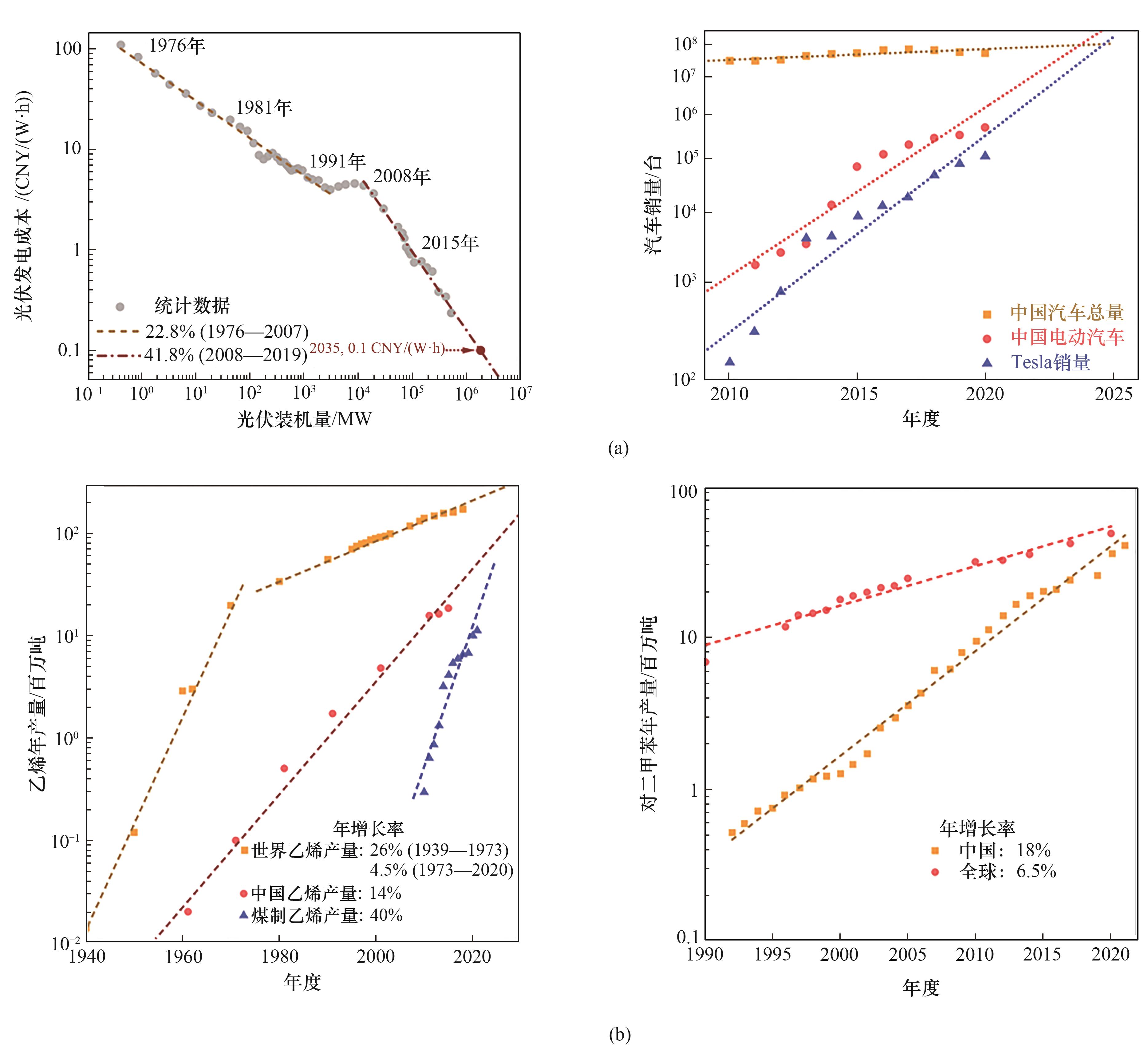
Fig.1 (a) Learning curve of the photovoltaic industry and growing trend of electric vehicles; (b) Growth curves of ethylene and para-xylene production capacity
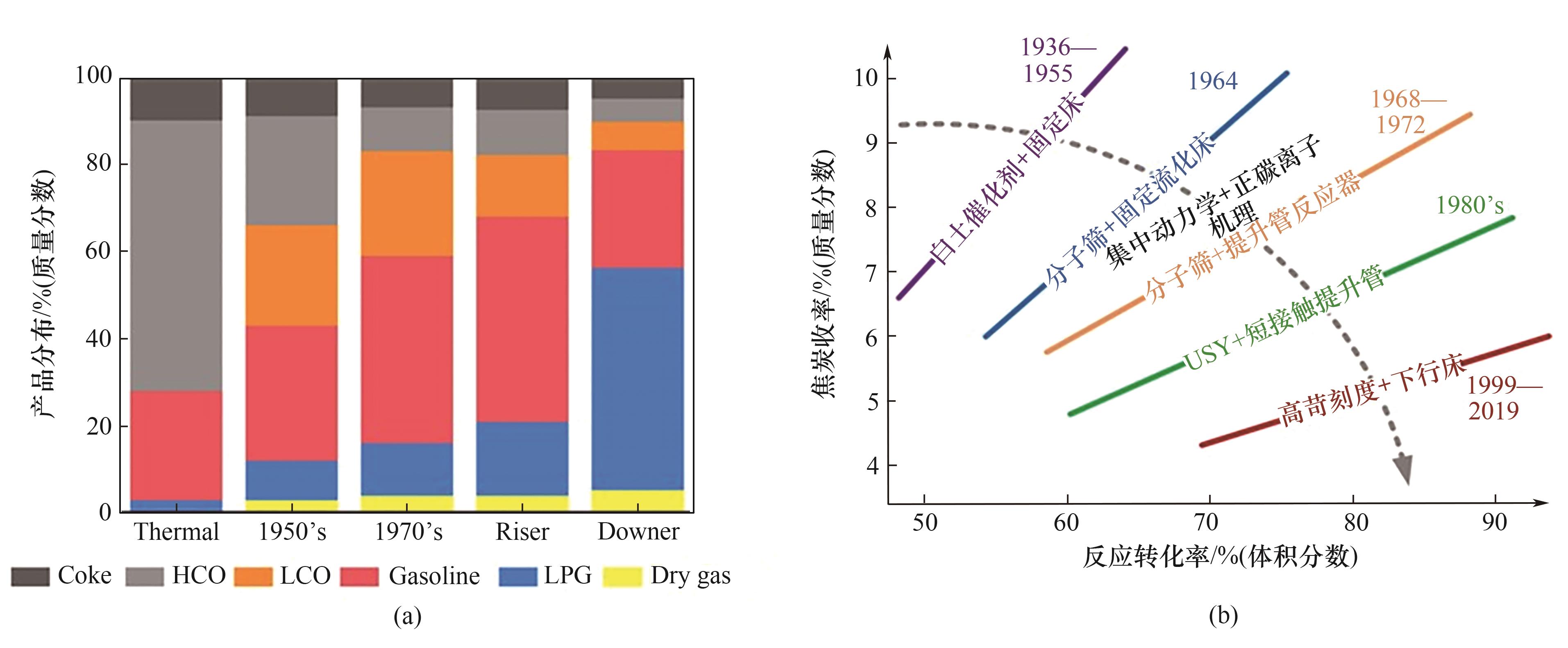
Fig.3 (a) Changes in the product distribution of catalytic cracking with the development of catalyst and reactor technology; (b) Technological development path of catalytic cracking[5]

Fig.10 (a) The residence time distribution in riser and downer; (b) The special inlet of downer without distributor[100]; (c)The fast separator of downer[103]
| 项目 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 密度 | 0.904 g/cm3 |
| 黏度 | |
| 100℃ | 11.13 mm2/s |
| 80℃ | 19.27 mm2/s |
| 残炭 | 3.74% |
| 馏程 | |
| 初馏点 | 281.6℃ |
| 10% | 373.9℃ |
| 30% | 418.0℃ |
| 50% | 464.8℃ |
| 70% | 530.5℃ |
| 金属分析 | |
| Ni | 5.5 μg/g |
| V | 6.7 μg/g |
| Fe | 7.7 μg/g |
| Na | 1.3 μg/g |
| Cu | 0.2 μg/g |
| Ca | 3.2 μg/g |
| 四组分 | |
| 饱和分 | 66.4%(质量分数) |
| 芳香分 | 21.5%(质量分数) |
| 胶质 | 11.1%(质量分数) |
| 沥青质 | 1.0%(质量分数) |
| 元素分析 | |
| C | 86.36%(质量分数) |
| H | 12.81%(质量分数) |
| N | 0.19%(质量分数) |
| S | 0.45%(质量分数) |
Table 1 The feed oil property for downer pilot plant
| 项目 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 密度 | 0.904 g/cm3 |
| 黏度 | |
| 100℃ | 11.13 mm2/s |
| 80℃ | 19.27 mm2/s |
| 残炭 | 3.74% |
| 馏程 | |
| 初馏点 | 281.6℃ |
| 10% | 373.9℃ |
| 30% | 418.0℃ |
| 50% | 464.8℃ |
| 70% | 530.5℃ |
| 金属分析 | |
| Ni | 5.5 μg/g |
| V | 6.7 μg/g |
| Fe | 7.7 μg/g |
| Na | 1.3 μg/g |
| Cu | 0.2 μg/g |
| Ca | 3.2 μg/g |
| 四组分 | |
| 饱和分 | 66.4%(质量分数) |
| 芳香分 | 21.5%(质量分数) |
| 胶质 | 11.1%(质量分数) |
| 沥青质 | 1.0%(质量分数) |
| 元素分析 | |
| C | 86.36%(质量分数) |
| H | 12.81%(质量分数) |
| N | 0.19%(质量分数) |
| S | 0.45%(质量分数) |
| 项目 | 质量指标 | |
|---|---|---|
| LTD-主剂 | LTD-助剂 | |
| 灼烧减量(湿基)/%(质量分数) | <13.0 | <13.0 |
| Na2O | <0.30 | <0.30 |
| 筛分组成 | ||
| 0~20 μm | <3.0 | <3.0 |
| 0~40 μm | <18.0 | <15.0 |
| 0~149 μm | >88.0 | >81.0 |
| APS/μm | 65.0~80.0 | 65.0~80.0 |
| 孔体积/(ml/g) | >0.33 | >0.20 |
| 磨损指数(干基)/%(质量分数) | <2.0 | <3.5 |
| 表观密度/(g/ml) | 0.65~0.75 | 0.60~0.80 |
| 比表面积/(m2/g) | >220 | >80 |
| 微反活性(800℃, 4 h)/% | >75 | >30 |
Table 2 The special catalyst with high activity and selectivity for DCP
| 项目 | 质量指标 | |
|---|---|---|
| LTD-主剂 | LTD-助剂 | |
| 灼烧减量(湿基)/%(质量分数) | <13.0 | <13.0 |
| Na2O | <0.30 | <0.30 |
| 筛分组成 | ||
| 0~20 μm | <3.0 | <3.0 |
| 0~40 μm | <18.0 | <15.0 |
| 0~149 μm | >88.0 | >81.0 |
| APS/μm | 65.0~80.0 | 65.0~80.0 |
| 孔体积/(ml/g) | >0.33 | >0.20 |
| 磨损指数(干基)/%(质量分数) | <2.0 | <3.5 |
| 表观密度/(g/ml) | 0.65~0.75 | 0.60~0.80 |
| 比表面积/(m2/g) | >220 | >80 |
| 微反活性(800℃, 4 h)/% | >75 | >30 |
| 项目 | DCP-Ⅱ | DCP-Ⅰ | 某炼厂提升管 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 反应温度/℃ | 600 | 550 | ~507 |
| 剂油比/(kg/kg) | 30 | 30 | ~8 |
| 停留时间/s | 0.40 | 0.40 | ~2 |
| 产品收率/%(质量分数) | |||
| 干气 | 5.30 | 3.02 | 4.02 |
| 氢气 | 0.05 | 0.02 | — |
| 甲烷 | 1.19 | 0.41 | 2.16 |
| 乙烷 | 0.45 | 0.21 | — |
| 乙烯 | 3.61 | 2.37 | 1.86 |
| 液化气 | 50.88 | 48.99 | 16.86 |
| 丙烷 | 2.16 | 1.78 | 1.37 |
| 丙烯 | 18.18 | 16.29 | 5.53 |
| 汽油 | 27.00 | 30.60 | 47.1 |
| 柴油 | 6.49 | 6.92 | 14.13 |
| 重油 | 5.30 | 6.03 | 10.32 |
| 焦炭 | 5.00 | 5.41 | 7.43 |
| 损失/%(质量分数) | 0.03 | -0.97 | 0.14 |
| 转化率/%(质量分数) | 88.21 | 87.05 | 75.55 |
Table 3 The comparison between product distribution of riser with DCP
| 项目 | DCP-Ⅱ | DCP-Ⅰ | 某炼厂提升管 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 反应温度/℃ | 600 | 550 | ~507 |
| 剂油比/(kg/kg) | 30 | 30 | ~8 |
| 停留时间/s | 0.40 | 0.40 | ~2 |
| 产品收率/%(质量分数) | |||
| 干气 | 5.30 | 3.02 | 4.02 |
| 氢气 | 0.05 | 0.02 | — |
| 甲烷 | 1.19 | 0.41 | 2.16 |
| 乙烷 | 0.45 | 0.21 | — |
| 乙烯 | 3.61 | 2.37 | 1.86 |
| 液化气 | 50.88 | 48.99 | 16.86 |
| 丙烷 | 2.16 | 1.78 | 1.37 |
| 丙烯 | 18.18 | 16.29 | 5.53 |
| 汽油 | 27.00 | 30.60 | 47.1 |
| 柴油 | 6.49 | 6.92 | 14.13 |
| 重油 | 5.30 | 6.03 | 10.32 |
| 焦炭 | 5.00 | 5.41 | 7.43 |
| 损失/%(质量分数) | 0.03 | -0.97 | 0.14 |
| 转化率/%(质量分数) | 88.21 | 87.05 | 75.55 |
| 项目 | 提升管 | 下行床 | 多级下行床 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 油气+催化剂流向 | 并流向上 | 并流向下 | 气固逆流 |
| 催化剂返混 | 有 | 基本无 | 基本无 |
| 反应推动力 | 小 | 小 | 大 |
| 芳烃竞争吸附 | 有限制 | 有限制 | 基本无 |
| 反应时间/s | 2~5 | < 1 | < 1 |
| 剂油比/(kg/kg) | < 15 | ~ 30 | ~30 |
| 甲烷氢与焦炭 | 高 | 低 | 低 |
| 二次反应 | 强 | 弱 | 弱 |
Table 4 The comparison between riser, single downer and multi-stage downer
| 项目 | 提升管 | 下行床 | 多级下行床 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 油气+催化剂流向 | 并流向上 | 并流向下 | 气固逆流 |
| 催化剂返混 | 有 | 基本无 | 基本无 |
| 反应推动力 | 小 | 小 | 大 |
| 芳烃竞争吸附 | 有限制 | 有限制 | 基本无 |
| 反应时间/s | 2~5 | < 1 | < 1 |
| 剂油比/(kg/kg) | < 15 | ~ 30 | ~30 |
| 甲烷氢与焦炭 | 高 | 低 | 低 |
| 二次反应 | 强 | 弱 | 弱 |
| 项目 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 密度 (20℃) | 0.91 g/cm3 |
| 平均分子量 | 488 |
| 残炭 | 4.13%(质量分数) |
| 元素分析 | |
| C | 86.48%(质量分数) |
| H | 12.98%(质量分数) |
| S | 0.33%(质量分数) |
| N | 0.19%(质量分数) |
| 黏度 | |
| 80℃ | 46.76 mm2/s |
| 100℃ | 24.56 mm2/s |
| 金属含量 | |
| Fe | 3.6μg/g |
| Na | 1.7μg/g |
| Ni | 6.9μg/g |
| V | 2.3μg/g |
| Ca | 1.1μg/g |
| 烃族组成 | |
| 饱和烃 | 62%(质量分数) |
| 芳烃 | 23%(质量分数) |
| 胶质 | 13%(质量分数) |
| 沥青质 | 2%(质量分数) |
| 馏程分析 | |
| 初馏点 | 260℃ |
| 5% | 330℃ |
| 10% | 368℃ |
| 50% | 486℃ |
Table 5 The feed-oil property for MDCPTM
| 项目 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 密度 (20℃) | 0.91 g/cm3 |
| 平均分子量 | 488 |
| 残炭 | 4.13%(质量分数) |
| 元素分析 | |
| C | 86.48%(质量分数) |
| H | 12.98%(质量分数) |
| S | 0.33%(质量分数) |
| N | 0.19%(质量分数) |
| 黏度 | |
| 80℃ | 46.76 mm2/s |
| 100℃ | 24.56 mm2/s |
| 金属含量 | |
| Fe | 3.6μg/g |
| Na | 1.7μg/g |
| Ni | 6.9μg/g |
| V | 2.3μg/g |
| Ca | 1.1μg/g |
| 烃族组成 | |
| 饱和烃 | 62%(质量分数) |
| 芳烃 | 23%(质量分数) |
| 胶质 | 13%(质量分数) |
| 沥青质 | 2%(质量分数) |
| 馏程分析 | |
| 初馏点 | 260℃ |
| 5% | 330℃ |
| 10% | 368℃ |
| 50% | 486℃ |
| 项目 | 反应器形式 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCP | DCP | DCP | MDCPTM | |
| 反应温度/℃ | 550 | 600 | 650 | 620/670 |
| 剂油比/(kg/kg) | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| 停留时间/s | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.3/0.5 |
| 产品分布/%(质量分数) | ||||
| 甲烷氢 | 1.06 | 1.16 | 1.62 | 7.91 |
| 乙烯 | 2.74 | 2.88 | 3.43 | 16.06 |
| 丙烯 | 19.29 | 20.32 | 20.55 | 24.57 |
| 丁烯 | 16.66 | 17.47 | 19.98 | 10.91 |
| 轻质烯烃 | 38.69 | 40.68 | 43.96 | 51.54 |
| 汽油 | 27.84 | 26.93 | 26.19 | 14.27 |
| 汽油芳烃 | 61.47 | 67.11 | 69.58 | 80.78 |
| BTEX | 6.19 | 10.81 | 12.89 | 9.32 |
| 柴油+煤油 | 15.81 | 13.36 | 10.21 | 9.23 |
| 焦炭 | 6.99 | 7.65 | 8.60 | 9.54 |
Table 6 The comparison between product distribution of DCP with MDCPTM
| 项目 | 反应器形式 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCP | DCP | DCP | MDCPTM | |
| 反应温度/℃ | 550 | 600 | 650 | 620/670 |
| 剂油比/(kg/kg) | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| 停留时间/s | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.3/0.5 |
| 产品分布/%(质量分数) | ||||
| 甲烷氢 | 1.06 | 1.16 | 1.62 | 7.91 |
| 乙烯 | 2.74 | 2.88 | 3.43 | 16.06 |
| 丙烯 | 19.29 | 20.32 | 20.55 | 24.57 |
| 丁烯 | 16.66 | 17.47 | 19.98 | 10.91 |
| 轻质烯烃 | 38.69 | 40.68 | 43.96 | 51.54 |
| 汽油 | 27.84 | 26.93 | 26.19 | 14.27 |
| 汽油芳烃 | 61.47 | 67.11 | 69.58 | 80.78 |
| BTEX | 6.19 | 10.81 | 12.89 | 9.32 |
| 柴油+煤油 | 15.81 | 13.36 | 10.21 | 9.23 |
| 焦炭 | 6.99 | 7.65 | 8.60 | 9.54 |
| 1 | 林世雄. 石油炼制工程[M]. 3版. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2000. |
| Lin S X. Petroleum Refining Engineering[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2000. | |
| 2 | Energy Informaion Adminstration U.S.. Petroleum supply annual[R]. Washington: U.S. Energy Information Administration, 2022. |
| 3 | Fahim M A, Alsahhaf T A, Elkilani A. Fundamentals of Petroleum Refining[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2010. |
| 4 | Wojciechowski B W, Corma A. Catalytic Cracking: Catalysts, Chemistry, and Kinetics[M]. New York : Marcel Dekker, 1986. |
| 5 | Vogt E C, Weckhuysen B M. Fluid catalytic cracking: recent developments on the grand old lady of zeolite catalysis[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(20): 7342-7370. |
| 6 | 杨朝合, 陈小博, 李春义, 等. 催化裂化技术面临的挑战与机遇[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 41(6): 171-177. |
| Yang C H, Chen X B, Li C Y, et al. Challenges and opportunities of fluid catalytic cracking technology[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2017, 41(6): 171-177. | |
| 7 | 安超. 全球对二甲苯供需分析与预测[J]. 世界石油工业, 2021, 28(3): 37-43. |
| An C. Analysis and forecast of global p-xylene supply and demand[J]. World Petroleum Industry, 2021, 28(3): 37-43. | |
| 8 | 陈俊武. 催化裂化工艺与工程[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国石化出版社, 2005. |
| Chen J W. Catalytic Cracking Process and Engineering[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: China Petrochemical Press, 2005. | |
| 9 | Wauquier J P, Smith D H. Crude Oil, Petroleum Products, Process Flowsheets[M]. Paris: Editions Technip, 1996. |
| 10 | Cheng W C, Kim G, Peters A W, et al. Environmental fluid catalytic cracking technology[J]. Catalysis Reviews, 1998, 40(1/2): 39-79. |
| 11 | Taufiqurrahmi N, Mohamed A R, Bhatia S. Deactivation and coke combustion studies of nanocrystalline zeolite beta in catalytic cracking of used palm oil[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 163(3): 413-421. |
| 12 | Ibáñez M, Valle B, Bilbao J, et al. Effect of operating conditions on the coke nature and HZSM-5 catalysts deactivation in the transformation of crude bio-oil into hydrocarbons[J]. Catalysis Today, 2012, 195(1): 106-113. |
| 13 | Doronin V P, Lipin P V, Sorokina T P. Effect of process conditions on the composition of products in the conventional and deep catalytic cracking of oil fractions[J]. Catalysis in Industry, 2012, 4(2): 100-104. |
| 14 | Deng R S, Wei F, Jin Y, et al. Experimental study of the deep catalytic cracking process in a downer reactor[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2002, 41(24): 6015-6019. |
| 15 | Fujiyama Y, Al-Tayyar M H, Dean C F, et al. Development of high-severity FCC process: an overview[J]. Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, 2007, 166: 1-12. |
| 16 | Kärger J, Heink W, Pfeifer H, et al. N.M.R. evidence of the existence of surface barriers on zeolite crystallites[J]. Zeolites, 1982, 2(4): 275-278. |
| 17 | Karwacki L, Kox M H F, de Winter D A M, et al. Morphology-dependent zeolite intergrowth structures leading to distinct internal and outer-surface molecular diffusion barriers[J]. Nature Materials, 2009, 8(12): 959-965. |
| 18 | Krishna R. Diffusion in porous crystalline materials[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41(8): 3099-3118. |
| 19 | Kockmann N. History of Distillation[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2014: 1-43. |
| 20 | Greensfelder B S, Voge H H, Good G M. Catalytic and thermal cracking of pure hydrocarbons: mechanisms of reaction[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 1949, 41(11): 2573-2584. |
| 21 | Miale J, Chen N Y, Weisz P. Catalysis by crystalline aluminosilicates (Ⅳ): Attainable catalytic cracking rate constants, and superactivity[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1966, 6(2): 278-287. |
| 22 | Houdry E, Burt W F, Pew A, et al. The houdry process[J]. Oil and Gas Journal, Engineering and Operating Section, 1938, 37: 40-45. |
| 23 | Avidan A A, Shinnar R. Development of catalytic cracking technology. A lesson in chemical reactor design[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1990, 29(6): 931-942. |
| 24 | Eigenberger G, Ruppel W. Catalytic fixed-bed reactors[M]// Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Berlin: Wiley-VCH, 2000. |
| 25 | 张执刚, 谢朝钢, 施至诚, 等. 催化热裂解制取乙烯和丙烯的工艺研究[J]. 石油炼制与化工, 2001(5): 21-24. |
| Zhang Z G, Xie C G, Shi Z C, et al. Study on catalytic pyrolysis process for ethylene and propylene production[J]. Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals, 2001(5): 21-24. | |
| 26 | Magee J, Dolbear G. Catalytic cracking[M]// Petroleum Catalysis in Nontechnical Language. Tulsa: PennWell Publishing Company, 1998: 53-93. |
| 27 | Ward J W. Hydrocracking processes and catalysts[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 1993, 35(1/2): 55-85. |
| 28 | Kunii D, Levenspiel O. Fluidization Engineering[M]. 2nd ed. Boston: Butterworths, 1991. |
| 29 | Wei J, Norman E. Lie algebraic solution of linear differential equations[J]. Journal of Mathematical Physics, 1963, 4: 575-581. |
| 30 | Weekman Jr V W, Nace D M. Kinetics of catalytic cracking selectivity in fixed, moving, and fluid bed reactors [J]. AIChE Journal, 1970, 16(3): 397-404. |
| 31 | Olah G A, Tolgyesi W S, Kuhn S J, et al. Stable carbonium ions. IV. 1a Secondary and tertiary alkyl and aralkyl oxocarbonium hexafluoroantimonates. Formation and identification of the trimethylcarbonium ion by decarbonylation of the tert-butyl oxocarbonium ion[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1963, 85(9): 1328-1334. |
| 32 | Theologos K N, Markatos N C. Advanced modeling of fluid catalytic cracking riser-type reactors[J]. AIChE Journal, 1993, 39(6): 1007-1017. |
| 33 | Degnan T F, Chitnis G K, Schipper P H. History of ZSM-5 fluid catalytic cracking additive development at Mobil[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2000, 35/36: 245-252. |
| 34 | Gholami Z, Gholami F, Tišler Z, et al. A review on production of light olefins via fluid catalytic cracking[J]. Energies, 2021, 14(4): 1089. |
| 35 | Biswas J, Maxwell I E. Recent process- and catalyst-related developments in fluid catalytic cracking[J]. Applied Catalysis, 1990, 63(1): 197-258. |
| 36 | Meng X H, Gao J S, Li L, et al. Advances in catalytic pyrolysis of hydrocarbons[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology, 2004, 22(9/10): 1327-1341. |
| 37 | Ino T, Fujiyama Y, Redhwi H, et al. A new FCC process upgrades gasoline and maximizes propylene[J]. Catalagram, 2004, 94: 45-49. |
| 38 | Eng C, Heidenreich S, Swart S, et al. Clean fuels and petrochemicals at SASOL via SUPERFLEXTM [C]//18th World Petroleum Congress. Johannesburg: OnePetro, 2005. |
| 39 | Yarulina I, Chowdhury A D, Meirer F, et al. Recent trends and fundamental insights in the methanol-to-hydrocarbons process[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2018, 1(6): 398-411. |
| 40 | Tian P, Wei Y X, Ye M, et al. Methanol to olefins (MTO): from fundamentals to commercialization[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(3): 1922-1938. |
| 41 | Chen Y J, Zhou H Q, Zhu J, et al. Direct synthesis of a fluidizable SAPO-34 catalyst for a fluidized dimethyl ether-to-olefins process[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2008, 124(3): 297-303. |
| 42 | Zeeshan N, 汤效平, 朱杰, 等. 不同结构SAPO-34催化剂上1-己烯催化裂解制丙烯[J]. 催化学报, 2009, 30(10): 1049-1057. |
| Zeeshan N, Tang X P, Zhu J, et al. Catalytic cracking of 1- hexene to propylene over SAPO-34 catalysts with different structures[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2009, 30(10): 1049-1057. | |
| 43 | 汤效平, 周华群, 魏飞, 等. 催化裂解多产丙烯过程热力学分析[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2008, 24(1): 22-27. |
| Tang X P, Zhou H Q, Wei F, et al. Thermodynamic analysis of propylene-enhancing FCC process[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 2008, 24(1): 22-27. | |
| 44 | Zhou J, Fan W, Wang Y D, et al. The essential mass transfer step in hierarchical/nano zeolite: surface diffusion[J]. National Science Review, 2020, 7(11): 1630-1632. |
| 45 | Fasano M, Humplik T, Bevilacqua A, et al. Interplay between hydrophilicity and surface barriers on water transport in zeolite membranes[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 12762. |
| 46 | Shen B Y, Wang H Q, Xiong H, et al. Atomic imaging of zeolite-confined single molecules by electron microscopy[J]. Nature, 2022, 607(7920): 703-707. |
| 47 | Kärger J, Pfeifer H. N.M.R. self-diffusion studies in zeolite science and technology[J]. Zeolites, 1987, 7(2): 90-107. |
| 48 | Keil F J, Krishna R, Coppens M O. Modeling of diffusion in zeolites[J]. Reviews in Chemical Engineering, 2000, 16(2): 71-197. |
| 49 | Cai D L, Ma Y H, Hou Y L, et al. Establishing a discrete Ising model for zeolite deactivation: inspiration from the game of Go[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2017, 7(12): 2440-2444. |
| 50 | Saravanan C, Jousse F, Auerbach S M. Ising model of diffusion in molecular sieves[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1998, 80(26): 5754-5757. |
| 51 | Chai Y C, Dai W L, Wu G J, et al. Confinement in a zeolite and zeolite catalysis[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2021, 54(13): 2894-2904. |
| 52 | Sastre G, Corma A. The confinement effect in zeolites[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2009, 305(1/2): 3-7. |
| 53 | Cai D L, Xiong H, Zhang C X, et al. Transport phenomena in zeolites in view of graph theory and pseudo-phase transition[J]. Small, 2020, 16(15): e1901979. |
| 54 | Cai D L, Hou Y L, Zhang C X, et al. Analyzing transfer properties of zeolites using small-world networks[J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(35): 16431-16433. |
| 55 | Li Y, Yu J H. New stories of zeolite structures: their descriptions, determinations, predictions, and evaluations[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(14): 7268-7316. |
| 56 | Watts D J, Strogatz S H. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks[J]. Nature, 1998, 393(6684): 440-442. |
| 57 | Wang N, Hou Y L, Sun W J, et al. Modulation of b-axis thickness within MFI zeolite: correlation with variation of product diffusion and coke distribution in the methanol-to-hydrocarbons conversion[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 243: 721-733. |
| 58 | Barbera K, Bonino F, Bordiga S, et al. Structure-deactivation relationship for ZSM-5 catalysts governed by framework defects[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2011, 280(2): 196-205. |
| 59 | Aerts A, Kirschhock C E A, Martens J A. Methods for in situ spectroscopic probing of the synthesis of a zeolite[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2010, 39(12): 4626-4642. |
| 60 | Wang W, Hunger M. Reactivity of surface alkoxy species on acidic zeolite catalysts[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2008, 41(8): 895-904. |
| 61 | Knops-Gerrits P P, De Vos D E, Feijen E J P, et al. Raman spectroscopy on zeolites[J]. Microporous Materials, 1997, 8(1/2): 3-17. |
| 62 | Coudurier G, Naccache C, Vedrine J C. Uses of I.R. spectroscopy in identifying ZSM zeolite structure[J]. Chemical Communications, 1982(24): 1413. |
| 63 | Palomino G T, Bordiga S, Zecchina A, et al. XRD, XAS, and IR characterization of copper-exchanged Y zeolite[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2000, 104(36): 8641-8651. |
| 64 | Cha W, Jeong N C, Song S, et al. Core-shell strain structure of zeolite microcrystals[J]. Nature Materials, 2013, 12(8): 729-734. |
| 65 | Stavitski E, Kox M, Swart I, et al. In situ synchrotron-based IR microspectroscopy to study catalytic reactions in zeolite crystals[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2008, 120(19): 3599-3603. |
| 66 | Vjunov A, Fulton J L, Huthwelker T, et al. Quantitatively probing the Al distribution in zeolites[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(23): 8296-8306. |
| 67 | Karwacki L, Stavitski E, Kox M H F, et al. Intergrowth structure of zeolite crystals as determined by optical and fluorescence microscopy of the template-removal process[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2007, 46(38): 7228-7231. |
| 68 | Ristanović Z, Kerssens M M, Kubarev A V, et al. High-resolution single-molecule fluorescence imaging of zeolite aggregates within real-life fluid catalytic cracking particles[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2015, 127(6): 1856-1860. |
| 69 | Ristanović Z, Hofmann J P, De Cremer G, et al. Quantitative 3D fluorescence imaging of single catalytic turnovers reveals spatiotemporal gradients in reactivity of zeolite H-ZSM-5 crystals upon steaming[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(20): 6559-6568. |
| 70 | Kärger J, Binder T, Chmelik C, et al. Microimaging of transient guest profiles to monitor mass transfer in nanoporous materials[J]. Nature Materials, 2014, 13(4): 333-343. |
| 71 | Saint Remi J C, Lauerer A, Chmelik C, et al. The role of crystal diversity in understanding mass transfer in nanoporous materials[J]. Nature Materials, 2016, 15(4): 401-406. |
| 72 | Chmelka B F, Pearson J G, Liu S B, et al. NMR study of the distribution of aromatic molecules in NaY zeolite[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1991, 95(1): 303-310. |
| 73 | Hong U, Kärger J, Kramer R, et al. PFG N.M.R. study of diffusion anisotropy in oriented ZSM-5 type zeolite crystallites[J]. Zeolites, 1991, 11(8): 816-821. |
| 74 | Li S H, Zheng A M, Su Y C, et al. Brønsted/Lewis acid synergy in dealuminated HY zeolite: a combined solid-state NMR and theoretical calculation study[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(36): 11161-11171. |
| 75 | Ma D, Deng F, Fu R Q, et al. MAS NMR studies on the dealumination of zeolite MCM-22[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2001, 105(9): 1770-1779. |
| 76 | Fraissard J, Ito T. 129Xe N.M.R. study of adsorbed xenon: a new method for studying zeolites and metal-zeolites[J]. Zeolites, 1988, 8(5): 350-361. |
| 77 | Haw J F, Richardson B R, Oshiro I S, et al. Reactions of propene on zeolite HY catalyst studied by in situ variable temperature solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1989, 111(6): 2052-2058. |
| 78 | de Vience S J, Pham L M, Lovchinsky I, et al. Nanoscale NMR spectroscopy and imaging of multiple nuclear species[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2015, 10(2): 129-134. |
| 79 | Ruska E. The development of the electron microscope and of electron microscopy[J]. Bioscience Reports, 1987, 7(8): 607-629. |
| 80 | Egerton R F. Analytical electron microscopy[M]//Physical Principles of Electron Microscopy. Boston, MA: Springer US, 2005: 155-175. |
| 81 | Chen Q L, Dwyer C, Sheng G, et al. Imaging beam-sensitive materials by electron microscopy[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(16): e1907619. |
| 82 | Lazić I, Bosch E G T, Lazar S. Phase contrast STEM for thin samples: integrated differential phase contrast[J]. Ultramicroscopy, 2016, 160: 265-280. |
| 83 | Lazic I, Bosch E G T, Lazar S, et al. Integrated differential phase contrast (iDPC)-direct phase imaging in STEM for thin samples[J]. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 2016, 22(S3): 36-37. |
| 84 | Yücelen E, Lazić I, Bosch E G T. Phase contrast scanning transmission electron microscopy imaging of light and heavy atoms at the limit of contrast and resolution[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 2676. |
| 85 | Liu L M, Wang N, Zhu C Z, et al. Direct imaging of atomically dispersed molybdenum that enables location of aluminum in the framework of zeolite ZSM-5[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2020, 59(2): 819-825. |
| 86 | Shen B Y, Chen X, Cai D L, et al. Atomic spatial and temporal imaging of local structures and light elements inside zeolite frameworks[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(4): e1906103. |
| 87 | Shen B Y, Chen X, Shen K, et al. Imaging the node-linker coordination in the bulk and local structures of metal-organic frameworks[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 2692. |
| 88 | Shen B Y, Chen X, Fan X Y, et al. Resolving atomic SAPO-34/18 intergrowth architectures for methanol conversion by identifying light atoms and bonds[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 2212. |
| 89 | Shen B Y, Chen X, Wang H Q, et al. A single-molecule van der Waals compass[J]. Nature, 2021, 592(7855): 541-544. |
| 90 | Arslan M T, Tian G, Ali B, et al. Highly selective conversion of CO2 or CO into precursors for kerosene-based aviation fuel via an aldol-aromatic mechanism[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(3): 2023-2033. |
| 91 | Wang N, Li J, Sun W J, et al. Rational design of zinc/zeolite catalyst: selective formation of p-xylene from methanol to aromatics reaction[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2022, 61(10): e202114786. |
| 92 | Xiong H, Liu Z Q, Chen X, et al. In situ imaging of the sorption-induced subcell topological flexibility of a rigid zeolite framework[J]. Science, 2022, 376(6592): 491-496. |
| 93 | Lan X, Shi X, Zhang Y, et al. Solids back-mixing behavior and effect of the mesoscale structure in CFB risers[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(34): 11888-11896. |
| 94 | Mahmoudi S, Seville J P K, Baeyens J. The residence time distribution and mixing of the gas phase in the riser of a circulating fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technology, 2010, 203(2): 322-330. |
| 95 | Das A K, Baudrez E, Marin G B, et al. Three-dimensional simulation of a fluid catalytic cracking riser reactor[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2003, 42(12): 2602-2617. |
| 96 | Cheng Y, Wu C N, Zhu J X, et al. Downer reactor: from fundamental study to industrial application[J]. Powder Technology, 2008, 183(3): 364-384. |
| 97 | 郭慕孙, 李洪钟. 流态化手册[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008. |
| Guo M S, Li H Z. Handbook of Fluidization[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008. | |
| 98 | Deng R, Wei F, Jin Y, et al. Downer catalytic pyrolysis (DCP): a novel process for light olefins production[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2002, 25(7): 711. |
| 99 | Parthasarathi R S, Alabduljabbar S S. HS-FCC high-severity fluidized catalytic cracking: a newcomer to the FCC family[J]. Applied Petrochemical Research, 2014, 4(4): 441-444. |
| 100 | 金涌, 魏飞, 程易, 等. 气固并流折叠式快速流化床反应装置: 1265937A[P]. 2000-09-13. |
| Jin Y, Wei F, Cheng Y, et al. Gas and solid parallel- flow folding type quick fluidized-bed reactor: 1265937A[P]. 2000-09-13. | |
| 101 | Johnson A R, Gartside R J, Ross J L, et al. Low residence time catalytic cracking process: US5976355A[P]. 1999-11-02. |
| 102 | 祁春鸣, 俞青, 金涌, 等. 气-固并流下行惯性分离装置的研究[J]. 石油炼制与化工, 1989(12): 51-56. |
| Qi C M, Yu Q, Jin Y, et al. A novel inertial separator for gas-solid suspension in concurrent downflow[J]. Petrol Process, 1989(12): 51-56. | |
| 103 | 魏飞, 金涌, 钱震, 等. 附壁切割式气固快速分离装置: 1267564A[P]. 2000-09-27. |
| Wei F, Jin Y, Qian Z, et al. Wall-attached cutting type fast gas-solid separator: 1267564A[P]. 2000-09-27. |
| [1] | Ruitao SONG, Pai WANG, Yunpeng WANG, Minxia LI, Chaobin DANG, Zhenguo CHEN, Huan TONG, Jiaqi ZHOU. Numerical simulation of flow boiling heat transfer in pipe arrays of carbon dioxide direct evaporation ice field [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 96-103. |
| [2] | Yue YANG, Dan ZHANG, Jugan ZHENG, Maoping TU, Qingzhong YANG. Experimental study on flash and mixing evaporation of aqueous NaCl solution [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3279-3291. |
| [3] | Ming DONG, Jinliang XU, Guanglin LIU. Molecular dynamics study on heterogeneous characteristics of supercritical water [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2836-2847. |
| [4] | Kuikui HAN, Xianglong TAN, Jinzhi LI, Ting YANG, Chun ZHANG, Yongfen ZHANG, Hongquan LIU, Zhongwei YU, Xuehong GU. Four-channel hollow fiber MFI zeolite membrane for the separation of xylene isomers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2468-2476. |
| [5] | Zhihang ZHENG, Junnan MA, Zihan YAN, Chunxi LU. Study on the pressure pulsation characteristics in jet influence zone of riser [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2335-2350. |
| [6] | Caihong LIN, Li WANG, Yu WU, Peng LIU, Jiangfeng YANG, Jinping LI. Effect of alkali cations in zeolites on adsorption and separation of CO2/N2O [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2013-2021. |
| [7] | Xinya LI, Lei XING, Minghu JIANG, Lixin ZHAO. Research on performance of downhole oil-water separation hydrocyclone enhanced by inverted cone gas injection [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1134-1144. |
| [8] | Shaohang YAN, Tianwei LAI, Yanwu WANG, Yu HOU, Shuangtao CHEN. Visual experimental study on cavitation of R134a in micro clearance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1054-1061. |
| [9] | Chenghao ZHANG, Jing LUO, Jisong ZHANG. Advances in continuous aerobic oxidation based on nitroxyl radical catalyst in microreactors [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 511-524. |
| [10] | Yuen BAI, Binrui ZHANG, Dongyang LIU, Liang ZHAO, Jinsen GAO, Chunming XU. Influence of synergistic effect of acid properties and pore structure of ZSM-5 zeolite on the catalytic cracking performance of pentene [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 438-448. |
| [11] | Xiaoping GUAN, Ning YANG. Multiphase drag and population balance models based on mesoscale stability condition [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2427-2437. |
| [12] | Mengxi LIU, Yiping FAN, Zihan YAN, Xiuying YAO, Chunxi LU. Regulation and industrial application of gas jet hydrodynamic behavior in a feedstock injection zone of a riser [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2496-2513. |
| [13] | Tienan LI, Bidan ZHAO, Peng ZHAO, Yongmin ZHANG, Junwu WANG. CFD-DEM simulation of the force acting on immersed baffles during the start-up stage of a gas-solid fluidized bed [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2649-2661. |
| [14] | Xiaoqiang FAN, Zhengliang HUANG, Jingyuan SUN, Jingdai WANG, Xiaofei WANG, Xiaobo HU, Guodong HAN, Yongrong YANG, Wenqing WU. Development of cloudy gas-liquid fluidized bed ethylene polymerization process and high performance products [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2742-2747. |
| [15] | Wenjie LAN, Xiaojie HU, Dizong CAI. Determination of interaction force between droplet and solid surface using droplet probe [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(3): 1119-1126. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||