CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (10): 5277-5289.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250449
• Surface and interface engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xuezhong MA( ), Qingxiang XIE(
), Qingxiang XIE( )
)
Received:2025-04-28
Revised:2025-05-19
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-10-25
Contact:
Xuezhong MA
通讯作者:
马学忠
作者简介:马学忠(1991—),男,博士,副教授,maxz222@163.com基金资助:CLC Number:
Xuezhong MA, Qingxiang XIE. Research on heat transfer enhancing mechanism and cooling performance of herringbone groove on rotor outer sidewall in high-speed contact mechanical seals[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(10): 5277-5289.
马学忠, 谢庆祥. 高速接触式机械密封动环外侧面人字槽强化换热机理与冷却性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(10): 5277-5289.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 端面距l1/mm | 0.1~0.5 |
| 槽间距l2/mm | 0.5 |
| 槽宽l3/mm | 0.5 |
| 动环长度l4/mm | 5.52 |
| 静环长度l5/mm | 5.25 |
| 槽深h1/mm | 0.1~0.5 |
| 进口高度h2/mm | 2 |
| 动环内径d1/mm | 28.9 |
| 动环外径d2/mm | 32.5 |
| 静环外径d3/mm | 34 |
| 密封腔外径d4/mm | 42 |
| 动环旋转速率n/(r/min) | 1800~10000 |
| 槽排数n1 | 1~4 |
| 槽角度α/(°) | 10~25 |
Table 1 Geometric and operational parameters
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 端面距l1/mm | 0.1~0.5 |
| 槽间距l2/mm | 0.5 |
| 槽宽l3/mm | 0.5 |
| 动环长度l4/mm | 5.52 |
| 静环长度l5/mm | 5.25 |
| 槽深h1/mm | 0.1~0.5 |
| 进口高度h2/mm | 2 |
| 动环内径d1/mm | 28.9 |
| 动环外径d2/mm | 32.5 |
| 静环外径d3/mm | 34 |
| 密封腔外径d4/mm | 42 |
| 动环旋转速率n/(r/min) | 1800~10000 |
| 槽排数n1 | 1~4 |
| 槽角度α/(°) | 10~25 |
| 参数名称 | C3H8O2(密封介质) | 碳石墨(静环) | 不锈钢(动环) |
|---|---|---|---|
| k/(W/(m·K)) | 0.29 | 18 | 14 |
| ρ/(kg/m3) | 1018.42 | 1825 | 7900 |
| c/(J/(kg·K)) | 3200 | 419 | 670 |
| μ/(Pa·s) | 0.00705 | — | — |
Table 2 Physical property parameters
| 参数名称 | C3H8O2(密封介质) | 碳石墨(静环) | 不锈钢(动环) |
|---|---|---|---|
| k/(W/(m·K)) | 0.29 | 18 | 14 |
| ρ/(kg/m3) | 1018.42 | 1825 | 7900 |
| c/(J/(kg·K)) | 3200 | 419 | 670 |
| μ/(Pa·s) | 0.00705 | — | — |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| ΔP/MPa | 0.8 |
| B/% | 75 |
| K/% | 50 |
| Psp/MPa | 0.3 |
| f | 0.1 |
Table 3 Related parameters of friction heat
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| ΔP/MPa | 0.8 |
| B/% | 75 |
| K/% | 50 |
| Psp/MPa | 0.3 |
| f | 0.1 |
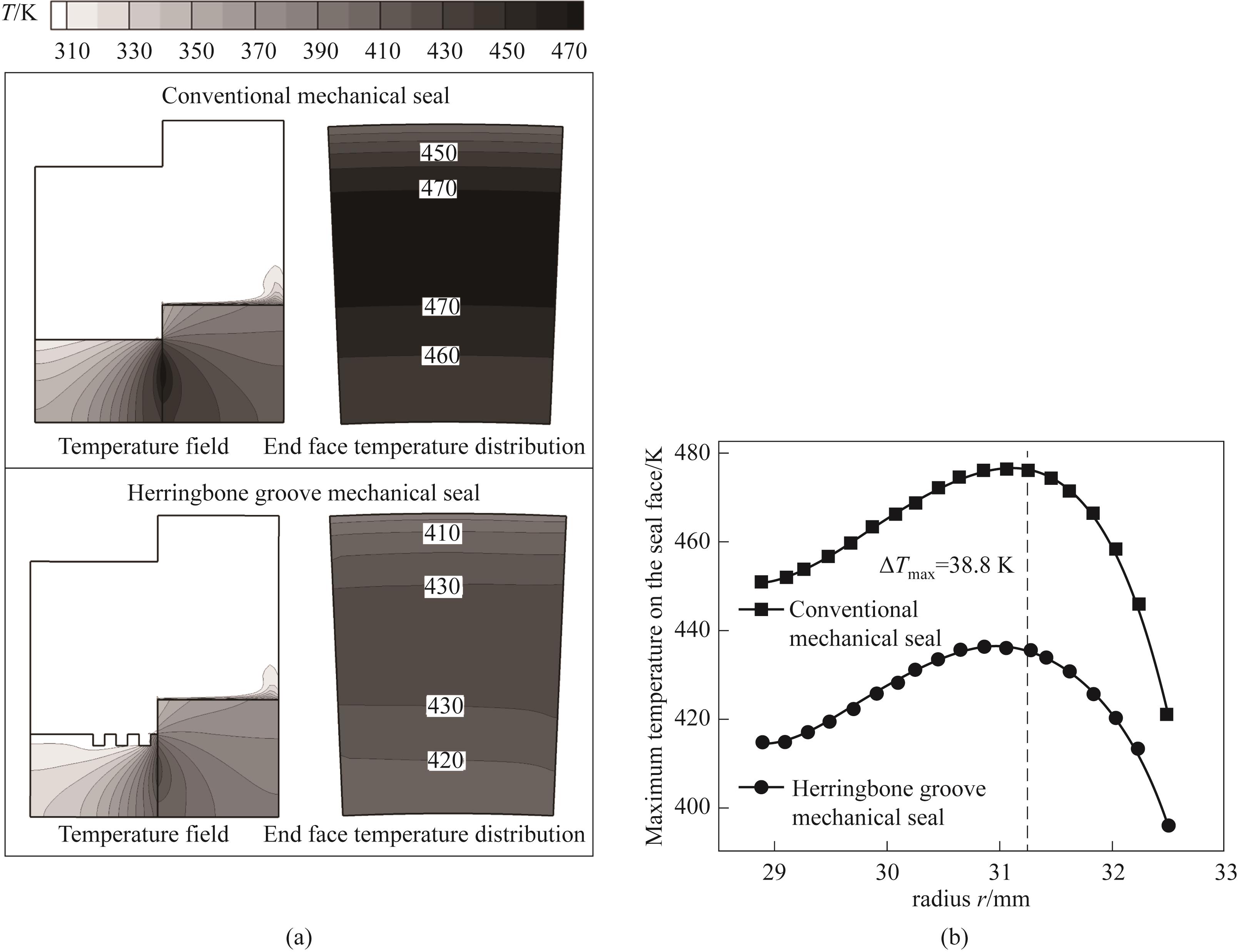
Fig.7 (a) Temperature field distribution of rotating and stationary rings, sealing chamber and sealing end face; (b) Temperature variation curve along the radius on the end face
| [1] | 郑煜, 朱汉华, 任泓吉, 等. 船舶艉轴机械密封温度场与热变形分析[J]. 润滑与密封, 2021, 46(3): 110-118. |
| Zheng Y, Zhu H H, Ren H J, et al. Research on temperature field and thermal deformation of ship's stern shaft mechanical seal[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2021, 46(3): 110-118. | |
| [2] | Zhang G Y, Chen G Z, Zhao W G, et al. An experimental test on a cryogenic high-speed hydrodynamic non-contact mechanical seal[J]. Tribology Letters, 2017, 65(3): 80. |
| [3] | Ma X Z, Xiao X X. Investigation on the influencing mechanism and quantitative evaluation of stirred heat effect in high-speed mechanical seals[J]. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 2025, 67: 105839. |
| [4] | Ha D, Roh T S, Huh H, et al. Development trend of liquid hydrogen-fueled rocket engines (part 2): Core technologies[J]. International Journal of Aeronautical and Space Sciences, 2023, 24(1): 146-165. |
| [5] | Nosaka M. Cryogenic tribology of high-speed bearings and shaft seals in liquid hydrogen[J]. Tribology Online, 2011, 6(2): 133-141. |
| [6] | Xiao N, Khonsari M M. Improving thermal performance of mechanical seals via surface texturing[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2015, 229(4): 350-361. |
| [7] | 周宇坤, 彭旭东, 赵文静, 等. 机械密封动环外周表面织构换热机理及结构优化[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2020, 40(4): 538-550. |
| Zhou Y K, Peng X D, Zhao W J, et al. Heat transfer mechanism and optimization of circumferential texture of mechanical seal[J]. Tribology, 2020, 40(4): 538-550. | |
| [8] | 周宇坤. 密封环外周表面织构对机械密封对流换热效应的影响[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2020. |
| Zhou Y K. Effect of the outer circumferential surface texture of the seal ring on the convective heat transfer effect of mechanical seals[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2020. | |
| [9] | 余旻丰, 彭旭东, 孟祥铠, 等. 接触式机械密封外圆周织构强化换热机理研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2023, 34(11): 1268-1279. |
| Yu M F, Peng X D, Meng X K, et al. Research on heat transfer enhancement mechanism of contact mechanical seals with textured circumference surfaces[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 34(11): 1268-1279. | |
| [10] | Yu M F, Peng X D, Meng X K, et al. The influence of cooling medium and cooling channel on heat transfer of textured seal in presence of viscous dissipation[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2024, 107: 109363. |
| [11] | Saha S K, Singh H. Heat transfer analysis of grooved mechanical seal: a numerical study[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2024, 156: 107700. |
| [12] | Ahmed M S, Elsayed K, El-shaer Y, et al. Enhancing heat transfer in various grooved annular for Taylor-Couette-Poiseuille flow[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 250: 123489. |
| [13] | Xiao N, Khonsari M M. Improving bearings thermal and tribological performance with built-In heat pipe[J]. Tribology Letters, 2015, 57(3): 31. |
| [14] | Xie F S, Li Y Z, Ma Y, et al. Cooling behaviors of a novel flow channel in mechanical seals of extreme high-speed rotation for cryogenic rockets[J]. Cryogenics, 2020, 107: 103055. |
| [15] | Khoshvaght-Aliabadi M, Sahamiyan M, Hesampour M, et al. Experimental study on cooling performance of sinusoidal–wavy minichannel heat sink[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 92: 50-61. |
| [16] | Zhang L Y, Duan R J, Che Y, et al. A numerical analysis of fluid flow and heat transfer in wavy and curved wavy channels[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2022, 171: 107248. |
| [17] | Sui Y, Teo C J, Lee P S. Direct numerical simulation of fluid flow and heat transfer in periodic wavy channels with rectangular cross-sections[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2012, 55(1/2/3): 73-88. |
| [18] | Gong L, Kota K, Tao W Q, et al. Parametric numerical study of flow and heat transfer in microchannels with wavy walls[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2011, 133(5): 051702. |
| [19] | Lin L, Zhao J, Lu G, et al. Heat transfer enhancement in microchannel heat sink by wavy channel with changing wavelength/amplitude[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2017, 118: 423-434. |
| [20] | Sui Y, Teo C J, Lee P S, et al. Fluid flow and heat transfer in wavy microchannels[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2010, 53(13/14): 2760-2772. |
| [21] | Sui Y, Lee P S, Teo C J. An experimental study of flow friction and heat transfer in wavy microchannels with rectangular cross section[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2011, 50(12): 2473-2482. |
| [22] | Mohammed H A, Gunnasegaran P, Shuaib N H. Numerical simulation of heat transfer enhancement in wavy microchannel heat sink[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2011, 38(1): 63-68. |
| [23] | Mohammed H A, Gunnasegaran P, Shuaib N H. Influence of channel shape on the thermal and hydraulic performance of microchannel heat sink[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2011, 38(4): 474-480. |
| [24] | Zheng Z Y, Fletcher D F, Haynes B S. Laminar heat transfer simulations for periodic zigzag semicircular channels: chaotic advection and geometric effects[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 62: 391-401. |
| [25] | Xie G N, Chen Z Y, Sunden B, et al. Numerical predictions of the flow and thermal performance of water-cooled single-layer and double-layer wavy microchannel heat sinks[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part A: Applications, 2013, 63(3): 201-225. |
| [26] | Xie G N, Chen Z Y, Sunden B, et al. Comparative study of the flow and thermal performance of liquid-cooling parallel-flow and counter-flow double-layer wavy microchannel heat sinks[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part A: Applications, 2013, 64(1): 30-55. |
| [27] | Liu F Y, Li Y F, Yu B, et al. Experimental research on sealing performance of liquid film seal with herringbone-grooved composite textures[J]. Tribology International, 2023, 178: 108005. |
| [28] | Liu F Y, Yu B, Li Y F, et al. Experimental study on lubrication characteristics and leakage inhibition of oil-lubricated seal with herringbone grooves[J]. Tribology International, 2023, 187: 108751. |
| [29] | Luan W L, Liu Y, Wang Y L, et al. Effect of herringbone groove structure parameters on the static performance of gas foil herringbone groove thrust bearings[J]. Tribology International, 2023, 177: 107979. |
| [30] | Xu L S, Wu J H, Yuan X Y, et al. Influence of inlet pressure disturbance on transient performance of liquid oxygen lubricated mechanical seal and rub-impact phenomenon caused by excitation overload[J]. Tribology International, 2023, 178: 108058. |
| [31] | Xu L S, Liu Y Y, Wu J H, et al. Transient dynamic analysis and experimental verification on lubrication regime transition during startup period of non-contacting mechanical seal in liquid oxygen turbopump[J]. Tribology International, 2022, 176: 107932. |
| [32] | Menter F R. Review of the shear-stress transport turbulence model experience from an industrial perspective[J]. International Journal of Computational Fluid Dynamics, 2009, 23(4): 305-316. |
| [33] | Luan Z G, Khonsari M M. Analysis of conjugate heat transfer and turbulent flow in mechanical seals[J]. Tribology International, 2009, 42(5): 762-769. |
| [34] | Merati P, Okita N, Jacobs L. Experimental and computational investigation of flow and thermal behavior of a mechanical seal[J]. Tribology Transactions, 1999, 42(4): 731-738. |
| [1] | Yifei LI, Xinyu DONG, Weishu WANG, Lu LIU, Yifan ZHAO. Numerical study on heat transfer of dry ice sublimation spray cooling on the surface of micro-ribbed plate [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(5): 1830-1842. |
| [2] | GAN Yunhua, WANG Jianqin, LIANG Jialin. Cooling performance of cylindrical battery pack based on thermal management system with heat pipe [J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(5): 1964-1971. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||