化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (12): 5605-5614.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20221095
牛卉芳1,2( ), 闫伦靖1,2(
), 闫伦靖1,2( ), 吕鹏3, 张旭峰1,2, 王美君1,2, 孔娇1,2, 鲍卫仁1,2, 常丽萍1,2(
), 吕鹏3, 张旭峰1,2, 王美君1,2, 孔娇1,2, 鲍卫仁1,2, 常丽萍1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-01
修回日期:2022-11-01
出版日期:2022-12-05
发布日期:2023-01-17
通讯作者:
闫伦靖,常丽萍
作者简介:牛卉芳(1996—),女,硕士研究生,1013162598@qq.com
基金资助:
Huifang NIU1,2( ), Lunjing YAN1,2(
), Lunjing YAN1,2( ), Peng LYU3, Xufeng ZHANG1,2, Meijun WANG1,2, Jiao KONG1,2, Weiren BAO1,2, Liping CHANG1,2(
), Peng LYU3, Xufeng ZHANG1,2, Meijun WANG1,2, Jiao KONG1,2, Weiren BAO1,2, Liping CHANG1,2( )
)
Received:2022-08-01
Revised:2022-11-01
Online:2022-12-05
Published:2023-01-17
Contact:
Lunjing YAN, Liping CHANG
摘要:
煤沥青是由多环芳烃组成的复杂混合物,其具有含碳量高的特点,是合成各种功能性碳材料的优质前体之一。以煤焦油沥青为原料、糠醛为交联剂,在硫酸催化作用下反应形成沥青-糠醛凝胶,进而经过常压干燥和碳化处理得到碳气凝胶,探讨了煤焦油沥青与溶剂、交联剂和催化剂的比例对沥青-糠醛凝胶的凝胶化程度以及碳气凝胶微球密度的影响。扫描电镜(SEM)结果显示,碳气凝胶微球的微观结构是由球状颗粒堆积而成;傅里叶红外光谱仪(FTIR)和同步热分析仪(TG)解析了沥青-糠醛凝胶在凝胶过程中的结构演变,及形成机理;CO2活化后,碳气凝胶微球的孔隙结构得到明显改善,并保留了球状颗粒的微观形貌,且颗粒形状规整、表面光滑。
中图分类号:
牛卉芳, 闫伦靖, 吕鹏, 张旭峰, 王美君, 孔娇, 鲍卫仁, 常丽萍. 煤焦油沥青基碳气凝胶微球的制备及分析[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(12): 5605-5614.
Huifang NIU, Lunjing YAN, Peng LYU, Xufeng ZHANG, Meijun WANG, Jiao KONG, Weiren BAO, Liping CHANG. Preparation and analysis of carbon aerogel microspheres based on coal tar pitch[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(12): 5605-5614.
| Proximate analysis/%(质量) | Ultimate analysis/%(质量),daf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mad | Ad | Vdaf | C | H | O① | N | S |
| 0.27 | 0.09 | 76.22 | 85.70 | 6.54 | 6.44 | 1.10 | 0.22 |
表1 煤焦油沥青的元素分析与工业分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analyses of coal tar pitch
| Proximate analysis/%(质量) | Ultimate analysis/%(质量),daf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mad | Ad | Vdaf | C | H | O① | N | S |
| 0.27 | 0.09 | 76.22 | 85.70 | 6.54 | 6.44 | 1.10 | 0.22 |
| No. | 煤焦油沥青与交联剂比例/ (g/ml) | 煤焦油沥青与溶剂比例/(g/ml) | 煤焦油沥青与催化剂比例/ (g/ml) | 密度/(g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.9 | 0.06 | 3 | 0.218 |
| 2 | 0.9 | 0.08 | 5 | 0.179 |
| 3 | 0.9 | 0.10 | 8 | 0.231 |
| 4 | 0.9 | 0.12 | 10 | 0.248 |
| 5 | 0.7 | 0.06 | 5 | 0.189 |
| 6 | 0.7 | 0.08 | 3 | 0.224 |
| 7 | 0.7 | 0.10 | 10 | 0.228 |
| 8 | 0.7 | 0.12 | 8 | 0.231 |
| 9 | 0.5 | 0.06 | 8 | 0.165 |
| 10 | 0.5 | 0.08 | 10 | 0.179 |
| 11 | 0.5 | 0.10 | 3 | 0.259 |
| 12 | 0.5 | 0.12 | 5 | 0.262 |
| 13 | 0.3 | 0.06 | 10 | 0.130 |
| 14 | 0.3 | 0.08 | 8 | 0.163 |
| 15 | 0.3 | 0.10 | 5 | 0.207 |
| 16 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 3 | 0.250 |
| K1j | 0.876 | 0.702 | 0.951 | |
| K2j | 0.872 | 0.745 | 0.837 | |
| K3j | 0.865 | 0.925 | 0.790 | |
| K4j | 0.750 | 0.991 | 0.785 | |
| k1j | 0.219 | 0.176 | 0.238 | |
| k2j | 0.218 | 0.186 | 0.209 | |
| k3j | 0.216 | 0.231 | 0.198 | |
| k4j | 0.188 | 0.248 | 0.196 | |
| R | 0.031 | 0.072 | 0.042 |
表2 制备碳气凝胶微球的正交实验
Table 2 Orthogonal test for preparing carbon aerogel microspheres gel
| No. | 煤焦油沥青与交联剂比例/ (g/ml) | 煤焦油沥青与溶剂比例/(g/ml) | 煤焦油沥青与催化剂比例/ (g/ml) | 密度/(g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.9 | 0.06 | 3 | 0.218 |
| 2 | 0.9 | 0.08 | 5 | 0.179 |
| 3 | 0.9 | 0.10 | 8 | 0.231 |
| 4 | 0.9 | 0.12 | 10 | 0.248 |
| 5 | 0.7 | 0.06 | 5 | 0.189 |
| 6 | 0.7 | 0.08 | 3 | 0.224 |
| 7 | 0.7 | 0.10 | 10 | 0.228 |
| 8 | 0.7 | 0.12 | 8 | 0.231 |
| 9 | 0.5 | 0.06 | 8 | 0.165 |
| 10 | 0.5 | 0.08 | 10 | 0.179 |
| 11 | 0.5 | 0.10 | 3 | 0.259 |
| 12 | 0.5 | 0.12 | 5 | 0.262 |
| 13 | 0.3 | 0.06 | 10 | 0.130 |
| 14 | 0.3 | 0.08 | 8 | 0.163 |
| 15 | 0.3 | 0.10 | 5 | 0.207 |
| 16 | 0.3 | 0.12 | 3 | 0.250 |
| K1j | 0.876 | 0.702 | 0.951 | |
| K2j | 0.872 | 0.745 | 0.837 | |
| K3j | 0.865 | 0.925 | 0.790 | |
| K4j | 0.750 | 0.991 | 0.785 | |
| k1j | 0.219 | 0.176 | 0.238 | |
| k2j | 0.218 | 0.186 | 0.209 | |
| k3j | 0.216 | 0.231 | 0.198 | |
| k4j | 0.188 | 0.248 | 0.196 | |
| R | 0.031 | 0.072 | 0.042 |
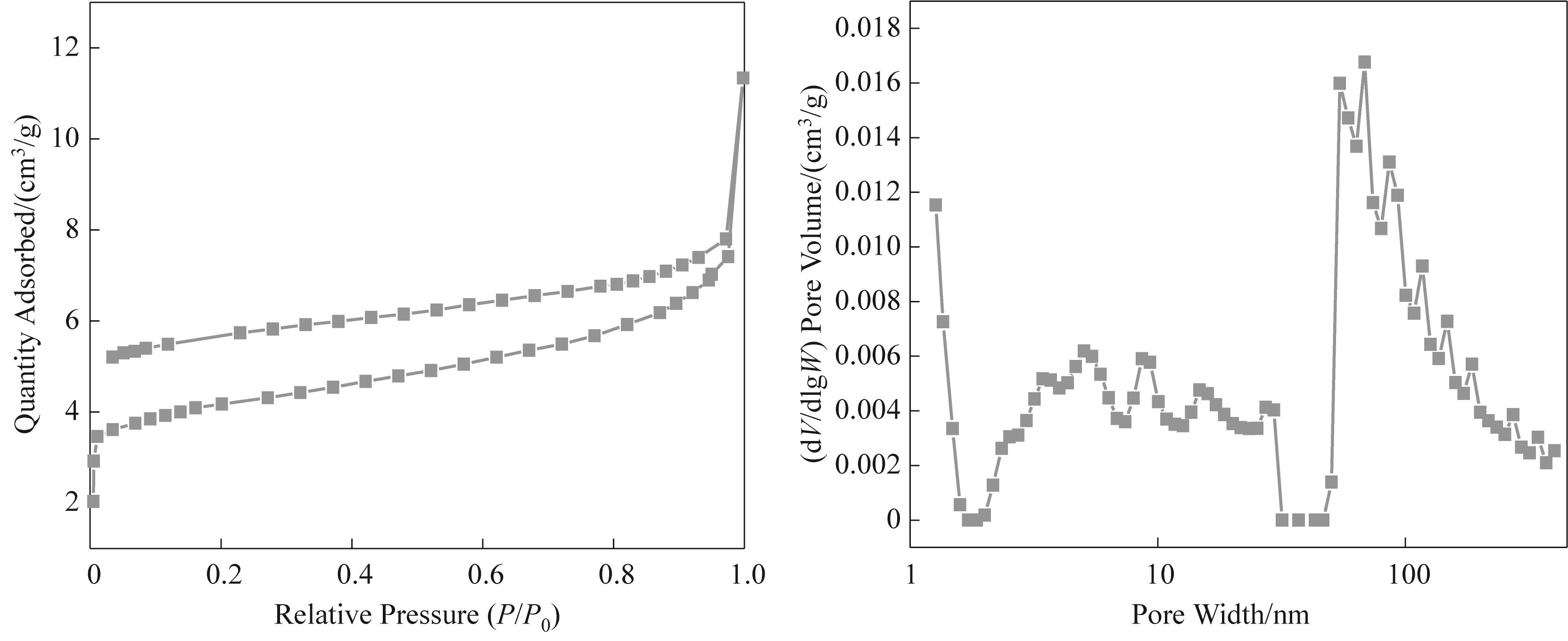
图5 所制备的煤焦油沥青基碳气凝胶微球的N2等温吸脱附曲线和孔径分布
Fig.5 N2 isothermal adsorption and desorption curves and pore size distribution of prepared coal tar pitch based carbon aerogel microspheres
| SBET/(m2/g) | St-plot/ (m2/g) | Vtotal/ (cm3/g) | Vmicro /(cm3/g) | Vmeso/(cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14.98 | 10.22 | 0.02 | 0 | 0.02 |
表3 所制备的煤焦油沥青基碳气凝胶微球的孔结构参数
Table 3 Pore structure parameters of prepared coal tar pitch based carbon aerogel microspheres
| SBET/(m2/g) | St-plot/ (m2/g) | Vtotal/ (cm3/g) | Vmicro /(cm3/g) | Vmeso/(cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14.98 | 10.22 | 0.02 | 0 | 0.02 |

图6 不同活化温度下碳气凝胶微球的N2等温吸脱附曲线和孔径分布
Fig.6 N2 isothermal adsorption and desorption curves and pore size distribution of carbon aerogels microspheres prepared at different activation temperatures
| Sample | SBET/ (m2/g) | St-plot/ (m2/g) | Vtotal/ (cm3/g) | Vmicro/ (cm3/g) | Vmeso/ (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 850-2h | 901 | 886 | 0.34 | 0.33 | 0.01 |
| 900-2h | 1532 | 1412 | 0.61 | 0.54 | 0.07 |
| 950-2h | 2852 | 2581 | 1.37 | 1.09 | 0.28 |
表4 不同活化温度下碳气凝胶微球的孔结构参数
Table 4 Pore structure parameters of carbon aerogels microspheres at different activation temperatures
| Sample | SBET/ (m2/g) | St-plot/ (m2/g) | Vtotal/ (cm3/g) | Vmicro/ (cm3/g) | Vmeso/ (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 850-2h | 901 | 886 | 0.34 | 0.33 | 0.01 |
| 900-2h | 1532 | 1412 | 0.61 | 0.54 | 0.07 |
| 950-2h | 2852 | 2581 | 1.37 | 1.09 | 0.28 |
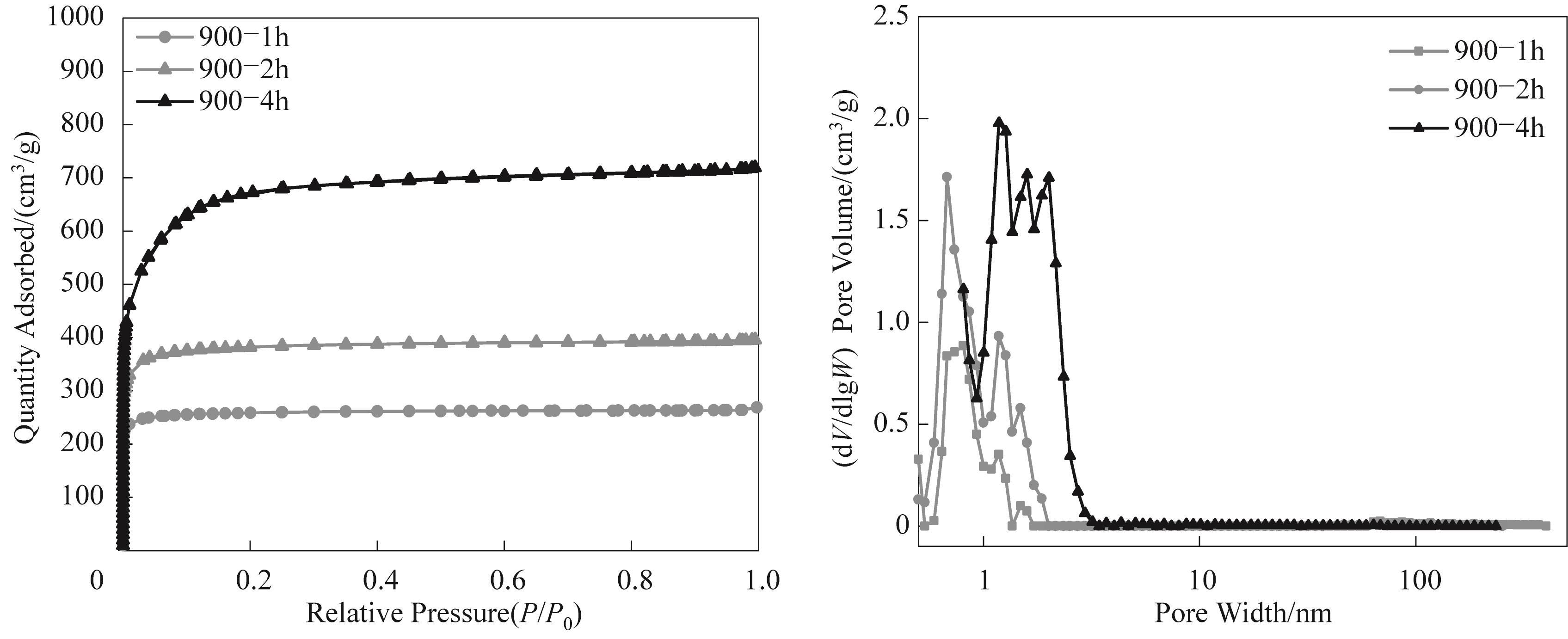
图7 不同活化时间下碳气凝胶微球的N2等温吸脱附曲线和孔径分布
Fig.7 N2 isothermal adsorption and desorption curves and pore size distribution of carbon aerogels microspheres prepared at different activation time
| Sample | SBET/ (m2/g) | St-plot/ (m2/g) | Vtotal/ (cm3/g) | Vmicro/ (cm3/g) | Vmeso/ (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 900-1h | 1051 | 988 | 0.42 | 0.37 | 0.05 |
| 900-2h | 1532 | 1412 | 0.61 | 0.54 | 0.07 |
| 900-4h | 2540 | 1950 | 1.11 | 0.78 | 0.33 |
表5 不同活化时间下碳气凝胶微球的孔结构参数
Table 5 Pore structure parameters of carbon aerogels microspheres with different activation time
| Sample | SBET/ (m2/g) | St-plot/ (m2/g) | Vtotal/ (cm3/g) | Vmicro/ (cm3/g) | Vmeso/ (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 900-1h | 1051 | 988 | 0.42 | 0.37 | 0.05 |
| 900-2h | 1532 | 1412 | 0.61 | 0.54 | 0.07 |
| 900-4h | 2540 | 1950 | 1.11 | 0.78 | 0.33 |
| 1 | 李昭昭, 张琬瑶, 员双刚, 等. 煤沥青基高性能碳材料的研究进展[J]. 广东化工, 2021, 48(8): 133-134. |
| Li Z Z, Zhang W Y, Yuan S G, et al. Research progress of high performance carbon materials from coal tar pitch[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2021, 48(8): 133-134. | |
| 2 | Zang X N, Dong Y, Jian C Y, et al. Upgrading carbonaceous materials: coal, tar, pitch, and beyond[J]. Matter, 2022, 5(2): 430-447. |
| 3 | 王叙春, 李金泽, 李广勇, 等. 气凝胶微球的制备及应用[J]. 物理化学学报, 2017, 33(11): 2141-2152. |
| Wang X C, Li J Z, Li G Y, et al. Fabrication and performance of various aerogel microspheres[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2017, 33(11): 2141-2152. | |
| 4 | Stoycheva I, Tsyntsarski B, Vasileva M, et al. New method for synthesis of carbon foam on the base of mixture of coal tar pitch and furfural without using pressure and stabilization treatment[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2020, 109: 108066. |
| 5 | 王凯, 高超, 李松恩, 等. 煤质沥青基超级活性炭的提质处理及其电化学性能的研究[J]. 新型炭材料, 2018, 33(6): 562-570. |
| Wang K, Gao C, Li S E, et al. Electrochemical performance of high surface area activated carbons derived from coal tar pitch[J]. New Carbon Materials, 2018, 33(6): 562-570. | |
| 6 | Banerjee C, Chandaliya V K, Dash P S, et al. Effect of different parameters on porosity and compressive strength of coal tar pitch derived carbon foam[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2019, 95: 83-90. |
| 7 | Banerjee C, Chandaliya V K, Dash P S. Recent advancement in coal tar pitch-based carbon fiber precursor development and fiber manufacturing process[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2021, 158: 105272. |
| 8 | Wang Z M, Xu Z W, Guan Y F, et al. Preparation of pitch-based activated carbon fibers with high specific surface area and excellent adsorption properties[J].Research on Chemical Intermediates, 2022, 48(4): 1733-1746. |
| 9 | Zhang Z C, Wang Z H, Zhang L J, et al. Study on the co-carbonization behavior of high-temperature coal tar pitch and raffinate oil of low-temperature coal tar[J]. Fuel, 2021, 310(3): 122469. |
| 10 | Lee J H, Park S J. Recent advances in preparations and applications of carbon aerogels: a review[J]. Carbon, 2020, 163: 1-18. |
| 11 | Sun S J, Yan Q H, Wu M F, et al. Carbon aerogel based materials for secondary batteries[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2021, 30: e00342. |
| 12 | Leila K, Reza G M, Don M J, et al. A comprehensive review on the application of aerogels in CO2-adsorption: materials and characterisation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 412: 128604. |
| 13 | Pekala R W. Organic aerogels from the polycondensation of resorcinol with formaldehyde[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1989, 24(9): 3221-3227. |
| 14 | Long D H, Zhang J, Yang J H, et al. Chemical state of nitrogen in carbon aerogels issued from phenol-melamine-formaldehyde gels[J]. Carbon, 2008, 46(9): 1259-1262. |
| 15 | Guo J, Wu D L, Wang T, et al. P-doped hierarchical porous carbon aerogels derived from phenolic resins for high performance supercapacitor[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 475: 56-66. |
| 16 | Hu H, Zhao Z B, Wan W B, et al. Ultralight and highly compressible graphene aerogels[J]. Advanced Materials (Deerfield Beach, Fla.), 2013, 25(15): 2219-2223. |
| 17 | Wang P, Liu H L, Yuan W J, et al. Carbon nanotubes regulated hollow skeleton carbon aerogel for effective thermal insulation and favorable mechanical behavior[J]. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2022, 101(1): 193-204. |
| 18 | Chen H, Liu D, Shen Z H, et al. Functional biomass carbons with hierarchical porous structure for supercapacitor electrode materials[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 180: 241-251. |
| 19 | Zhang C Y, Lin S, Peng J J, et al. Preparation of highly porous carbon through activation of NH4Cl induced hydrothermal microsphere derivation of glucose[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(11): 6486-6491. |
| 20 | Wu C W, Li P H, Wei Y M, et al. Review on the preparation and application of lignin-based carbon aerogels[J]. RSC Advances, 2022, 12(17): 10755-10765. |
| 21 | Sen S, Singh A, Bera C, et al. Recent developments in biomass derived cellulose aerogel materials for thermal insulation application: a review[J]. Cellulose, 2022, 29(9): 4805-4833. |
| 22 | Pan C, Kazuki M, Wang C Y, et al. Frame-filling structural nanoporous carbon from amphiphilic carbonaceous mixture comprising graphite oxide[J]. Carbon, 2016, 108: 225-233. |
| 23 | Zeng X H, Wu D C, Fu R W, et al. Preparation and electrochemical properties of pitch-based activated carbon aerogels[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2008, 53(18): 5711-5715. |
| 24 | García-González C A, Camino-Rey M C, Alnaief M, et al. Supercritical drying of aerogels using CO2: effect of extraction time on the end material textural properties[J]. The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 2012, 66: 297-306. |
| 25 | Vazhayal L, Talasila S, Abdul Azeez P M, et al. Mesochanneled hierarchically porous aluminosiloxane aerogel microspheres as a stable support for pH-responsive controlled drug release[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(17): 15564-15574. |
| 26 | Liao S C, Zhai T L, Xia H S. Highly adsorptive graphene aerogel microspheres with center-diverging microchannel structures[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(3): 1068-1077. |
| 27 | Zuo P P, Qu S J, Shen W Z. Asphaltenes: separations, structural analysis and applications[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2019, 34(7): 186-207. |
| 28 | 姚立红, 苏长安, 齐立权, 等. α-呋喃酯的结构与红外光谱特征[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 1999, 19(1): 32-34. |
| Yao L H, Su C G, Qi L Q, et al. The substituent structures and characteristic infrared spectra of α furan esters[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 1999, 19(1): 32-34. | |
| 29 | 贾廷见, 李朋伟, 尚治国, 等. 糠醛分子的拉曼光谱与红外光谱研究[J]. 光散射学报, 2007, 19(1): 1-5. |
| Jia T J, Li P W, Shang Z G, et al. The study on Raman and infrared spectra of furfural molecule[J]. The Journal of Light Scattering, 2007, 19(1): 1-5. | |
| 30 | Wang Z, Yu C H. Preparation and growth characteristics of mesocarbon microbeads[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2013, 750/751/752: 1121-1124. |
| 31 | Rashidi N A, Yusup S. Production of palm kernel shell-based activated carbon by direct physical activation for carbon dioxide adsorption[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(33): 33732-33746. |
| 32 | Zhang G L, Ke Y C, Qin M R, et al. Preparations and tribological properties of COPNA copolymer materials[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2015, 102: 615-624. |
| 33 | Wu M B, Shi Y Y, Li S B, et al. Synthesis and characterization of condensed polynuclear aromatic resin derived from ethylene tar[J]. China Petroleum Processing & Petrochemical Technology, 2012, 14(4): 42-47. |
| 34 | Zhang X W, Meng Y C, Fan B L, et al. Preparation of mesophase pitch from refined coal tar pitch using naphthalene-based mesophase pitch as nucleating agent[J]. Fuel, 2019, 243: 390-397. |
| 35 | Li L, lin X C, He J, et al. Preparation of mesocarbon microbeads from coal tar pitch with blending of biomass tar pitch[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2021, 155: 105039. |
| [1] | 刘杰, 吴立盛, 李锦锦, 罗正鸿, 周寅宁. 含乙烯基胺酯键聚醚类可逆交联聚合物的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3051-3057. |
| [2] | 刘璇, 马溢昌, 张秋根, 刘庆林. 富勒烯交联季铵化聚苯醚阴离子交换膜的制备[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(7): 3849-3855. |
| [3] | 袁旭东,贾磊,周到,赵盼盼,吴俊峰,王汝金. 微通道临界热通量的基础理论与提升技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(4): 1796-1814. |
| [4] | 岳航勃, 郑萍璇, 郑煜如, 邝柳尹, 张银, 李梁君, 郭建维. 棉籽蛋白/剑麻纤维复合材料加工、界面与性能[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(3): 1751-1760. |
| [5] | 肖覃, 曾旭, 黄健涵, 刘又年. 富氧功能化超交联树脂的合成及其对苯胺的吸附[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(3): 1742-1750. |
| [6] | 孙晶晶, 贾丽娜, 林波, 王艳, 龚俊波. 药物-药物共晶的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 828-840. |
| [7] | 邹树平, 姜镇涛, 王志才, 柳志强, 郑裕国. 环氧化物水解酶交联细胞聚集体催化合成(R)-环氧氯丙烷[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(9): 4238-4245. |
| [8] | 田叶顺,任文,王国袖,孙爽,周萍,王文龙,宋占龙,赵希强. 微波加热CO2活化法制备生物质活性炭及其脱硫性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(12): 5774-5784. |
| [9] | 涂卓恒,史名珍,张效敏,吴有庭,胡兴邦. 环氧氯丙烷与离子液体的交联过程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(11): 4971-4980. |
| [10] | 张淑芬. 中国染料工业现状与发展趋势[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(10): 3704-3711. |
| [11] | 姜玉良, 刘元伟, 韩波, 阮慧敏, 沈江南, 高从堦. PEI交联的PECH/nylon复合阴离子交换膜的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(6): 2744-2752. |
| [12] | 李立欣, 张斯, 王冬, 马放. 真菌菌丝球研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(6): 2364-2372. |
| [13] | 尹春华, 马烨炜, 赵志敏, 张海洋, 闫海. 新型层状交联酶聚集体的制备条件优化与性质研究[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(12): 5192-5198. |
| [14] | 张双正, 陈国, 苏鹏飞. 磁响应交联糖化酶聚集体的制备及催化特性[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(7): 2763-2770. |
| [15] | 赵世鹏, 冯宗财, 袁爽, 宋秀美, 梁楚欣, 刘芳. 乙二胺丙酰化交联壳聚糖微球对甲基橙的吸附性能[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(3): 1253-1261. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号