化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (4): 1795-1804.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20221420
尹驰1( ), 张正国1,2,3, 凌子夜1,2, 方晓明1,2(
), 张正国1,2,3, 凌子夜1,2, 方晓明1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-10-28
修回日期:2023-02-27
出版日期:2023-04-05
发布日期:2023-06-02
通讯作者:
方晓明
作者简介:尹驰(1998—),女,硕士研究生,1848981266@qq.com
基金资助:
Chi YIN1( ), Zhengguo ZHANG1,2,3, Ziye LING1,2, Xiaoming FANG1,2(
), Zhengguo ZHANG1,2,3, Ziye LING1,2, Xiaoming FANG1,2( )
)
Received:2022-10-28
Revised:2023-02-27
Online:2023-04-05
Published:2023-06-02
Contact:
Xiaoming FANG
摘要:
含有相变材料的热界面材料(即相变热界面材料)可借助相变材料的吸热来直接缓解高热通量对芯片造成的冲击。将相变胶囊与导热填料复配引入聚合物基料有望获得可靠性好的相变热界面材料。将石蜡@二氧化硅纳米胶囊与碳纤维复配,制备了一系列含不同质量分数碳纤维和纳米相变胶囊的聚二甲基硅氧烷基相变热界面材料样品,测定了它们的相变特性、热导率和硬度,并将它们分别用于模拟芯片散热来评价其应用性能。结果表明,碳纤维含量的增大致使相变热界面材料样品的热导率和硬度上升,而纳米相变胶囊含量的上升带来相变热界面材料的熔化焓上升及硬度下降,从而都对相变热界面材料的散热性能产生影响。石蜡@二氧化硅纳米胶囊和碳纤维的协同作用致使在所有制备的样品中纳米胶囊含量34%(质量)和碳纤维含量9%(质量)的相变热界面材料取得了最佳散热性能。此外,该相变热界面材料还具有优异的热可靠性,因而具备应用前景。
中图分类号:
尹驰, 张正国, 凌子夜, 方晓明. 含石蜡@二氧化硅纳米胶囊和碳纤维的相变热界面材料及其散热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1795-1804.
Chi YIN, Zhengguo ZHANG, Ziye LING, Xiaoming FANG. Combining paraffin@silica nanocapsules with carbon fiber to develop a phase change thermal interface material for efficient heat dissipation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1795-1804.
| 样品 | PA@SiO2/% | CF/% | PDMS/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18Ne-6CF | 18 | 6 | 76 |
| 18Ne-8CF | 18 | 8 | 74 |
| 18Ne-9CF | 18 | 9 | 73 |
| 18Ne-10CF | 18 | 10 | 72 |
| 26Ne-6CF | 26 | 6 | 68 |
| 26Ne-8CF | 26 | 8 | 66 |
| 26Ne-9CF | 26 | 9 | 65 |
| 26Ne-10CF | 26 | 10 | 64 |
| 34Ne-6CF | 34 | 6 | 60 |
| 34Ne-8CF | 34 | 8 | 58 |
| 34Ne-9CF | 34 | 9 | 57 |
| 34Ne-10CF | 34 | 10 | 56 |
表1 PCTIM样品中各组分的质量分数
Table 1 Mass fractions of the components in the PCTIMs
| 样品 | PA@SiO2/% | CF/% | PDMS/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18Ne-6CF | 18 | 6 | 76 |
| 18Ne-8CF | 18 | 8 | 74 |
| 18Ne-9CF | 18 | 9 | 73 |
| 18Ne-10CF | 18 | 10 | 72 |
| 26Ne-6CF | 26 | 6 | 68 |
| 26Ne-8CF | 26 | 8 | 66 |
| 26Ne-9CF | 26 | 9 | 65 |
| 26Ne-10CF | 26 | 10 | 64 |
| 34Ne-6CF | 34 | 6 | 60 |
| 34Ne-8CF | 34 | 8 | 58 |
| 34Ne-9CF | 34 | 9 | 57 |
| 34Ne-10CF | 34 | 10 | 56 |
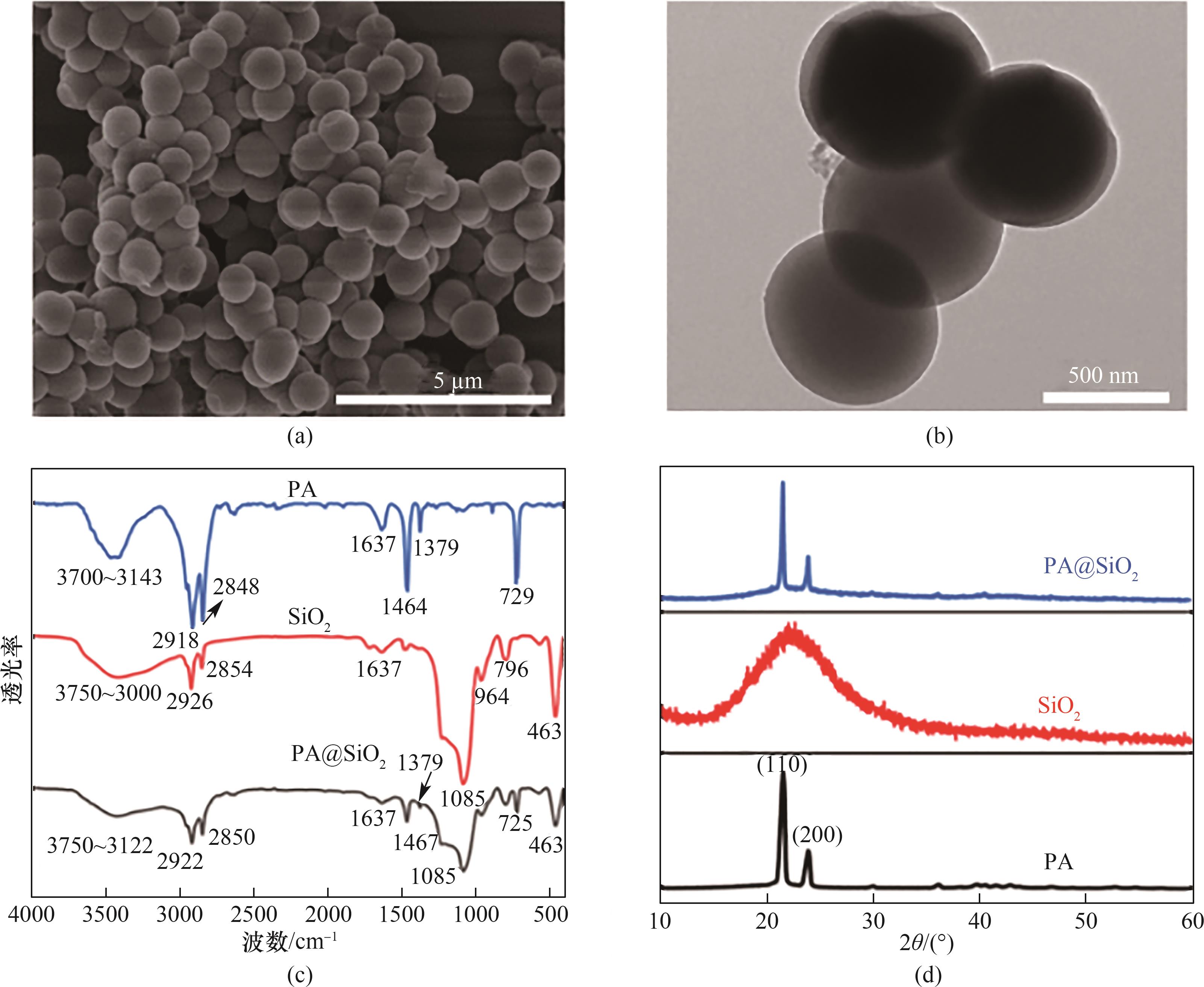
图3 PA@SiO2纳米胶囊的SEM (a)和TEM (b)图像以及PA、SiO2和PA@SiO2纳米胶囊的FT-IR (c)和XRD (d)谱图
Fig.3 SEM (a) and TEM (b) images of PA@SiO2 nanocapsules, together with FT-IR spectra (c) and XRD patterns (d) of PA, SiO2 and PA@SiO2 nanocapsules
| 样品 | Tm/℃ | Tf/℃ | Hm/(J/g) | Hf/(J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA | 69.70 | 71.38 | 192.8 | 180.1 |
| PA@SiO2 | 68.98 | 73.77 | 136.0 | 134.2 |
| PA@SiO2(100th) | 69.15 | 73.79 | 135.0 | 134.1 |
表2 PA以及PA@SiO2纳米胶囊的相变特性
Table 2 Phase change characteristics of PA and PA@SiO2 nanocapsules
| 样品 | Tm/℃ | Tf/℃ | Hm/(J/g) | Hf/(J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA | 69.70 | 71.38 | 192.8 | 180.1 |
| PA@SiO2 | 68.98 | 73.77 | 136.0 | 134.2 |
| PA@SiO2(100th) | 69.15 | 73.79 | 135.0 | 134.1 |
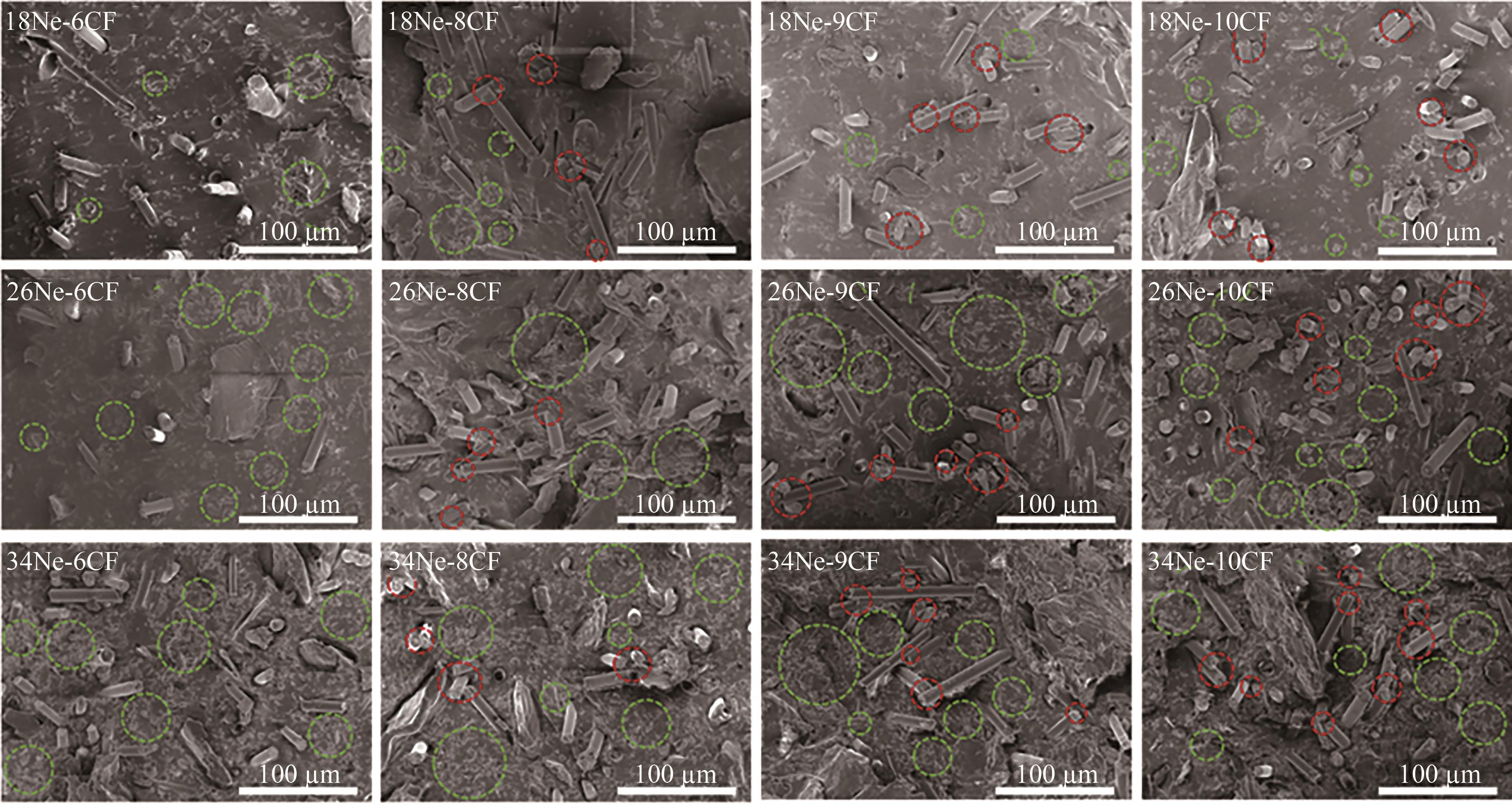
图5 含不同质量分数CF和纳米胶囊的PDMS基PCTIM样品横截面SEM照片
Fig.5 Cross-section SEM images of the PDMS based PCTIM samples containing different mass fractions of CF and PA@SiO2 nanocapsules

图7 含不同质量分数CF和纳米胶囊的PDMS基PCTIM样品的熔化温度(a)、熔化焓(b)、热导率(c)以及硬度(d)
Fig.7 Melting point (a), melting enthalpy (b), thermal conductivity (c) and hardness (d) of the PDMS based PCTIM samples containing different mass fractions of CF and the PA@SiO2 nanocapsules
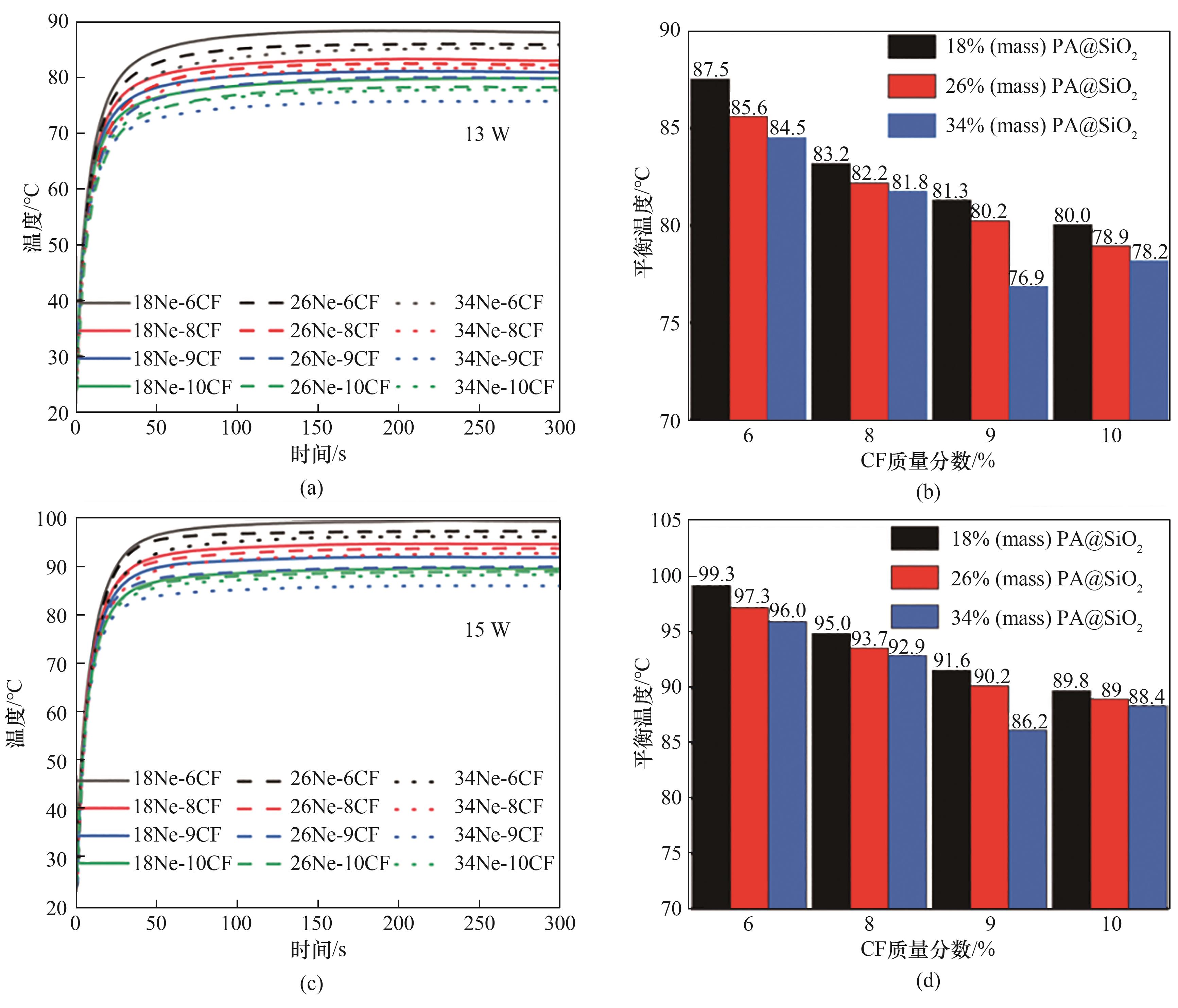
图8 使用含不同质量分数CF和纳米胶囊的PDMS基PCTIM样品时模拟芯片的温升曲线[(a)、(c)]和平衡温度[(b)、(d)]
Fig.8 Temperature rise curves[(a),(c)] and equilibrium temperature [(b),(d)] of the simulative chip when employing the PDMS based PCTIM samples containing different mass fractions of CF and the PA@SiO2 nanocapsules
| 样品 | Tm/℃ | Tf/℃ | Hm/(J/g) | Hf/(J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34Ne-9CF | 72.75 | 74.17 | 45.6 | 44.1 |
| 34Ne-9CF(100th) | 72.62 | 73.77 | 44.6 | 43.2 |
表3 34Ne-9CF经历100次冷热循环前后的相变特性
Table 3 Phase change characteristics of 34Ne-9CF before and after experiencing 100 heating-cooling cycles
| 样品 | Tm/℃ | Tf/℃ | Hm/(J/g) | Hf/(J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34Ne-9CF | 72.75 | 74.17 | 45.6 | 44.1 |
| 34Ne-9CF(100th) | 72.62 | 73.77 | 44.6 | 43.2 |
| 24 | 陈和生, 孙振亚, 邵景昌. 八种不同来源二氧化硅的红外光谱特征研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2011, 30(4): 934-937. |
| Chen H S, Sun Z Y, Shao J C. Investigation on FT-IR spectroscopy for eight different sources of SiO2 [J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2011, 30(4): 934-937. | |
| 25 | Li B X, Liu T X, Hu L Y, et al. Fabrication and properties of microencapsulated paraffin@SiO2 phase change composite for thermal energy storage[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2013, 1(3): 374-380. |
| 26 | Zhang H Z, Wang X D, Wu D Z. Silica encapsulation of n-octadecane via sol-gel process: a novel microencapsulated phase-change material with enhanced thermal conductivity and performance[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2010, 343(1): 246-255. |
| 27 | Wu J, Chen H, Wu Q, et al. Surface modification of carbon fibers and the selective laser sintering of modified carbon fiber/nylon 12 composite powder[J]. Materials & Design, 2017, 116: 253-260. |
| 28 | Joseph Fortenbaugh R, Lear B J. On-demand curing of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) using the photothermal effect of gold nanoparticles[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(25): 8555-8559. |
| 29 | Kim G M, Lee S J, Kim C L. Assessment of the physical, mechanical, and tribological properties of PDMS thin films based on different curing conditions[J]. Materials, 2021, 14(16): 4489. |
| 30 | Liu Y, Chen T T, Li Y H. Thermal performance investigation of a single medium temperature phase change microcapsule used for wind power absorption and heat storage system[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2020, 44(1): 425-437. |
| 31 | Wei J M, Liao M Z, Ma A J, et al. Enhanced thermal conductivity of polydimethylsiloxane composites with carbon fiber[J]. Composites Communications, 2020, 17: 141-146. |
| 32 | Kim I H, Sim H W, Hong H H, et al. Effect of filler size on thermal properties of paraffin/silver nanoparticle composites[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2019, 36(6): 1004-1012. |
| 33 | Wang W Y, Ma X, Sun D X, et al. Achieving electrical insulation, high thermal conductivity and high fracture toughness in polyamide 6/carbon nanofiber composites through the interfacial welding effect of elastomer[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2020, 128: 105671. |
| 34 | Uetani K, Ata S, Tomonoh S, et al. Elastomeric thermal interface materials with high through-plane thermal conductivity from carbon fiber fillers vertically aligned by electrostatic flocking[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(33): 5857-5862. |
| 35 | Liu H B, Su X Q, Fu R L, et al. The flexible film of SCF/BN/PDMS composites with high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation[J]. Composites Communications, 2021, 23: 100573. |
| 1 | Moore A L, Shi L. Emerging challenges and materials for thermal management of electronics[J]. Materials Today, 2014, 17(4): 163-174. |
| 2 | Schelling P K, Shi L, Goodson K E. Managing heat for electronics[J]. Materials Today, 2005, 8(6): 30-35. |
| 3 | Mallik S, Ekere N, Best C, et al. Investigation of thermal management materials for automotive electronic control units[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2011, 31(2/3): 355-362. |
| 4 | Hansson J, Nilsson T M J, Ye L L, et al. Novel nanostructured thermal interface materials: a review[J]. International Materials Reviews, 2018, 63(1): 22-45. |
| 5 | Razeeb K M, Dalton E, Cross G L W, et al. Present and future thermal interface materials for electronic devices[J]. International Materials Reviews, 2018, 63(1): 1-21. |
| 6 | Zhang Y Y, Ma J, Wei N, et al. Recent progress in the development of thermal interface materials: a review[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics:PCCP, 2021, 23(2): 753-776. |
| 7 | 陈鑫, 刘凌云, 陶马冠宇, 等. 用于电机散热的定形复合相变材料研究[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(19): 32-38. |
| Chen X, Liu L Y, Tao M G Y, et al. Study of composite phase change materials for heat dissipation of motor[J]. Materials Reports, 2022, 36(19): 32-38. | |
| 8 | de Bock H P, Huitink D, Shamberger P, et al. A system to package perspective on transient thermal management of electronics[J]. Journal of Electronic Packaging, 2020, 142(4): 041111. |
| 9 | Sharma A, Tyagi V V, Chen C R, et al. Review on thermal energy storage with phase change materials and applications[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2009, 13(2): 318-345. |
| 10 | Farid M M, Khudhair A M, Ali K Razack S, et al. A review on phase change energy storage: materials and applications[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2004, 45(9/10): 1597-1615. |
| 11 | Chandra D, Chellappa R, Chien W M. Thermodynamic assessment of binary solid-state thermal storage materials[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2005, 66(2/3/4): 235-240. |
| 12 | 蔡楚玥, 方晓明, 凌子夜, 等. 相变热界面材料导热增强及定形改善的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(9): 4907-4917. |
| Cai C Y, Fang X M, Ling Z Y, et al. Research progress on thermal conductivity enhancement and form stability improvement of phase change thermal interface materials[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(9): 4907-4917. | |
| 13 | Rauch B. Understanding the performance characteristics of phase-change thermal interface materials[C]//ITHERM 2000. The Seventh Intersociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronic Systems (Cat. No. 00CH37069). Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2002: 42-47. |
| 14 | He X Q, Zhang L, Li C Z. PEG-based polyurethane/paraffin@SiO2/boron nitride phase change composite with efficient thermal conductive pathways and superior mechanical property[J]. Composites Communications, 2021, 25: 100609. |
| 15 | Deng H, Yang W B, Cai T Y, et al. Phase-change composites silicone rubber/paraffin@SiO2 microcapsules with different core/shell ratio for thermal management[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2021, 45(12): 18033-18047. |
| 16 | Wu W L, Chen Z. A novel phase-change composites based on silicone rubber containing energy-storage microcapsules[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2018, 133(3): 1365-1370. |
| 17 | Zhou Y C, Li S S, Zhao Y, et al. Compatible paraffin@SiO2 microcapsules/polydimethylsiloxane composites with heat storage capacity and enhanced thermal conductivity for thermal management[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2022, 218: 109192. |
| 18 | Peng G J, Hu Y H, Dou G J, et al. Enhanced mechanical properties of epoxy composites embedded with MF/TiO2 hybrid shell microcapsules containing n-octadecane[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2022, 110: 414-423. |
| 19 | Liao H H, Guo S W, Liu Y, et al. Form-stable phase change composites with high thermal conductivity and adjustable thermal management capacity[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2021, 221: 110881. |
| 20 | Şahan N, Paksoy H. Determining influences of SiO2 encapsulation on thermal energy storage properties of different phase change materials[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2017, 159: 1-7. |
| 21 | Zhang D F, Cai T Y, Li Y J, et al. Paraffin@silica microencapsulated phase change materials with improved anti-leakage properties[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2022, 7(40): e202202930. |
| 22 | Kang L, Ren L C, Niu H Y, et al. Paraffin@SiO2 microcapsules-based phase change composites with enhanced thermal conductivity for passive battery cooling[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2022, 230: 109756. |
| 23 | Fang G Y, Chen Z, Li H. Synthesis and properties of microencapsulated paraffin composites with SiO2 shell as thermal energy storage materials[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 163(1/2): 154-159. |
| [1] | 李靖, 沈聪浩, 郭大亮, 李静, 沙力争, 童欣. 木质素基碳纤维复合材料在储能元件中的应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2322-2334. |
| [2] | 罗伟莉, 王雯雯, 潘权稳, 葛天舒, 王如竹. 基于活性碳纤维毡复合吸附剂的储热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(S1): 554-559. |
| [3] | 赵玉海, 罗英武. 可逆失活自由基界面聚合[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 653-668. |
| [4] | 王艳芳,毛恒,蔡玮玮,张傲率,徐李昊,赵之平. ZIF-L/PDMS混合基质膜蒸气渗透耦合发酵强化乙醇生产效率的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(10): 5226-5236. |
| [5] | 刘燕青, 胡听听, 鲁落义, 王维, 邹昀, 童张法. PDMS/ZSM-5膜的制备及渗透汽化分离水中乙酸正丁酯和乙酸乙酯[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(2): 843-853. |
| [6] | 殷金英,韩江月,祁彩辉. 碳纤维结构排布对其辐射特性影响的分析[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(S2): 356-362. |
| [7] | 牟春霞, 张时雨, 邹昀, 刘香君, 董颜箔, 崔学民, 童张法. 疏水SiO2填充PDMS膜分离水中乙酸正丁酯的性能[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(6): 2407-2414. |
| [8] | 金震, 范宏. 长支链型PDMS-g-PE共聚物的制备及其增塑润滑作用[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(2): 672-678. |
| [9] | 孙军, 黄延强, 张涛. 纳米碳纤维/碳毡负载碳化钨和碳氮化钨的肼分解性能[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(8): 2976-2981. |
| [10] | 胡玉东, 刘锦辉, 王海东, 张兴. 拉曼方法同时测量单根碳纤维热物性和对流传热系数[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(S1): 251-257. |
| [11] | 潘彬, 孙丹, 刘伟凤, 叶遥立, 郭剑, 成少安. 碳纤维阳极构造对微生物燃料电池性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(8): 3250-3254. |
| [12] | 隋志军, 李平, 周静红, 朱贻安, De Chen, 周兴贵. 纳米碳纤维的微观结构调控与催化作用[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(1): 22-31. |
| [13] | 韩小龙, 张杏梅, 马晓迅, 李继定. 碳纳米管填充PDMS膜的渗透汽化性能[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(1): 271-278. |
| [14] | 李金亮, 田艳红, 张学军, 李晨, 胡琪. 甲基丙烯酸羟乙酯改性水性聚氨酯的合成与应用[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(6): 2257-2263. |
| [15] | 蔡卫滨, 朴香兰, 李继定, 朱慎林. 不同交联剂对PDMS/PVDF纳滤膜溶剂回收性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(2): 581-589. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号