化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (12): 4563-4575.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240743
吴雨茜1,2,3,4( ), 唐元晖1,2,4, 郭强1, 林亚凯2(
), 唐元晖1,2,4, 郭强1, 林亚凯2( ), 余立新2, 王晓琳2(
), 余立新2, 王晓琳2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-01
修回日期:2024-08-06
出版日期:2024-12-25
发布日期:2025-01-03
通讯作者:
林亚凯,王晓琳
作者简介:吴雨茜(1997—),女,硕士研究生,1863138750@163.com
基金资助:
Yuxi WU1,2,3,4( ), Yuanhui TANG1,2,4, Qiang GUO1, Yakai LIN2(
), Yuanhui TANG1,2,4, Qiang GUO1, Yakai LIN2( ), Lixin YU2, Xiaolin WANG2(
), Lixin YU2, Xiaolin WANG2( )
)
Received:2024-07-01
Revised:2024-08-06
Online:2024-12-25
Published:2025-01-03
Contact:
Yakai LIN, Xiaolin WANG
摘要:
为了探究“吸附-膜”法从盐湖卤水中提锂的可行性,采用NF270纳滤膜对从卤水得到的硫酸型解吸液中的锂镁分离开展了实验研究和“浓缩-渗滤”模拟计算。首先,测定了NF270膜的基本结构和分离特征,初步确定了压力和pH对Li2SO4和MgSO4单盐溶液的体积通量及截留率的影响。其次,探究了NF270膜对Li2SO4/MgSO4混合溶液的分离效果,结果发现中性条件下NF270纳滤膜对
中图分类号:
吴雨茜, 唐元晖, 郭强, 林亚凯, 余立新, 王晓琳. 纳滤膜对硫酸型解吸液锂镁分离的实验研究与模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(12): 4563-4575.
Yuxi WU, Yuanhui TANG, Qiang GUO, Yakai LIN, Lixin YU, Xiaolin WANG. Experimental study and simulation on nanofiltration separation of lithium and magnesium from sulfate desorption solution[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(12): 4563-4575.
| 年份 | 商业化 NF膜型号 | 研究体系 | 主要离子的浓度范围/(mol/L) | 主要结论 | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | DL | 稀释老卤 (Li+、Mg2+、Ca2+、Na+、K+、Cl-、 | Li+:0.052; Mg2+:0.30 | 探究了DL膜分离盐酸型老卤中锂镁的可行性,发现DL膜具有较好的锂镁分离能力,同时能有效分离Cl-和 | [ | |
| 2011 | DK | 模拟卤水 (Li+、Mg2+、Cl-) | Li+:0.014~0.038; Mg2+:0.10~0.20 | 当压力为1.6 MPa时,Li+呈现负截留,且Mg2+的截留率最高,分离因子最高为3.2,说明采用DK膜在中性条件下可以实现高镁锂比盐酸体系模拟卤水的分离 | [ | |
| 2013 | NF90 | 稀释卤水 (Li+、Mg2+、Na+、Cl-) | Li+:0.00087; Mg2+:0.013 | 压力为1.5 MPa时,NF90膜对Mg2+的截留率为100%,对Li+仅为15%,说明NF90膜对于锂镁离子的截留性能与此前的DK体系差异明显 | [ | |
| 2014/2015 | DK、DL、HL、NF270 | 模拟卤水 (Li+、Mg2+、Ca2+、Na+、K+、Cl-) | Li+:0.019~0.046; Mg2+:0.11~0.64 | 对比四种商业化纳滤膜分离盐酸性卤水中锂镁的差异,发现高通量膜(DL、NF270)的分离效果较好;且升高操作压力和降低pH均能够提升NF膜对Mg2+、Li+的选择分离性能,而高镁锂比和升高进料温度不利于分离 | [ | |
| 2014/2019 | DK、NT102、NT103、NT201、NF90、NF270、XN-45 | 模拟卤水 (Li+、Mg2+、Na+、K+、Cl-、 | Li+:0.0016~0.46; Mg2+:0.018~4.9 | NT103、NT201膜对Mg2+的截留性能较高,具有较好的镁锂分离性能;加入一价阳离子Na+、K+和H3BO3均能提升Li+透过率;加入 | [ | |
| 2014/2019/2021 | DK | 稀释老卤/模拟卤水 (Li+、Mg2+、Ca2+、Cl-、 | Li+:0.019~0.18; Mg2+:0.23~2.4 | 镁锂比增加,锂离子截留率更小,但过高镁离子含量会降低镁的截留率;高膜表面切向流速降低浓差极化,有利于镁锂分离 | [ | |
| 2019 | NF90和NF270 | 模拟卤水 (Li+、Mg2+、Cl-) | Li+:0.020; Mg2+:0.029~0.12 | 对比了两种纳滤膜的锂镁分离效果,发现高通量NF270膜更好,原料液中镁锂比下降较多 | [ | |
表1 商业NF膜分离盐湖卤水中锂镁的研究工作总结
Table 1 Summary of research work on the separation of lithium and magnesium from brines of salt lakes by commercial NF membranes
| 年份 | 商业化 NF膜型号 | 研究体系 | 主要离子的浓度范围/(mol/L) | 主要结论 | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | DL | 稀释老卤 (Li+、Mg2+、Ca2+、Na+、K+、Cl-、 | Li+:0.052; Mg2+:0.30 | 探究了DL膜分离盐酸型老卤中锂镁的可行性,发现DL膜具有较好的锂镁分离能力,同时能有效分离Cl-和 | [ | |
| 2011 | DK | 模拟卤水 (Li+、Mg2+、Cl-) | Li+:0.014~0.038; Mg2+:0.10~0.20 | 当压力为1.6 MPa时,Li+呈现负截留,且Mg2+的截留率最高,分离因子最高为3.2,说明采用DK膜在中性条件下可以实现高镁锂比盐酸体系模拟卤水的分离 | [ | |
| 2013 | NF90 | 稀释卤水 (Li+、Mg2+、Na+、Cl-) | Li+:0.00087; Mg2+:0.013 | 压力为1.5 MPa时,NF90膜对Mg2+的截留率为100%,对Li+仅为15%,说明NF90膜对于锂镁离子的截留性能与此前的DK体系差异明显 | [ | |
| 2014/2015 | DK、DL、HL、NF270 | 模拟卤水 (Li+、Mg2+、Ca2+、Na+、K+、Cl-) | Li+:0.019~0.046; Mg2+:0.11~0.64 | 对比四种商业化纳滤膜分离盐酸性卤水中锂镁的差异,发现高通量膜(DL、NF270)的分离效果较好;且升高操作压力和降低pH均能够提升NF膜对Mg2+、Li+的选择分离性能,而高镁锂比和升高进料温度不利于分离 | [ | |
| 2014/2019 | DK、NT102、NT103、NT201、NF90、NF270、XN-45 | 模拟卤水 (Li+、Mg2+、Na+、K+、Cl-、 | Li+:0.0016~0.46; Mg2+:0.018~4.9 | NT103、NT201膜对Mg2+的截留性能较高,具有较好的镁锂分离性能;加入一价阳离子Na+、K+和H3BO3均能提升Li+透过率;加入 | [ | |
| 2014/2019/2021 | DK | 稀释老卤/模拟卤水 (Li+、Mg2+、Ca2+、Cl-、 | Li+:0.019~0.18; Mg2+:0.23~2.4 | 镁锂比增加,锂离子截留率更小,但过高镁离子含量会降低镁的截留率;高膜表面切向流速降低浓差极化,有利于镁锂分离 | [ | |
| 2019 | NF90和NF270 | 模拟卤水 (Li+、Mg2+、Cl-) | Li+:0.020; Mg2+:0.029~0.12 | 对比了两种纳滤膜的锂镁分离效果,发现高通量NF270膜更好,原料液中镁锂比下降较多 | [ | |
| 解吸液编号 | Li+/ (mol/L) | Na+/ (mol/L) | K+/(mol/L) | Mg2+/(mol/L) | Ca2+/ (mol/L) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.25 | 0.067 | 0.016 | 0.023 | 0.0014 | 1.20 |
| 2 | 0.18 | 0.072 | 0.022 | 0.032 | 0.0065 | 2.46 |
| 3 | 0.21 | 0.034 | 0.0026 | 0.008 | 0.0016 | 1.42 |
表2 解吸液的主要成分
Table 2 The main components of the desorption solution
| 解吸液编号 | Li+/ (mol/L) | Na+/ (mol/L) | K+/(mol/L) | Mg2+/(mol/L) | Ca2+/ (mol/L) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.25 | 0.067 | 0.016 | 0.023 | 0.0014 | 1.20 |
| 2 | 0.18 | 0.072 | 0.022 | 0.032 | 0.0065 | 2.46 |
| 3 | 0.21 | 0.034 | 0.0026 | 0.008 | 0.0016 | 1.42 |
| 原料液编号 | 原料液中离子浓度/(mol/L) | pH | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | Na+ | K+ | ||
| 1~4 | 0.19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.7、4.6、3.1、1.7 |
| 5~8 | 0 | 0.093 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.7、4.6、3.1、1.7 |
| 9~12 | 0.14 | 0.023 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.7、4.6、3.1、1.7 |
| 13 | 0.019 | 0.084 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.7 |
| 14 | 0.046 | 0.070 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.7 |
| 15 | 0.14 | 0.023 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.7 |
| 16 | 0.17 | 0.0093 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.7 |
| 17 | 0.25 | 0.023 | 0.0014 | 0.067 | 0.016 | 1.7 |
表3 实验原料液组成
Table 3 The concentrations of the feed solutions
| 原料液编号 | 原料液中离子浓度/(mol/L) | pH | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | Na+ | K+ | ||
| 1~4 | 0.19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.7、4.6、3.1、1.7 |
| 5~8 | 0 | 0.093 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.7、4.6、3.1、1.7 |
| 9~12 | 0.14 | 0.023 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.7、4.6、3.1、1.7 |
| 13 | 0.019 | 0.084 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.7 |
| 14 | 0.046 | 0.070 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.7 |
| 15 | 0.14 | 0.023 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.7 |
| 16 | 0.17 | 0.0093 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.7 |
| 17 | 0.25 | 0.023 | 0.0014 | 0.067 | 0.016 | 1.7 |
| 离子 | Stokes半径/nm | 扩散系数/(10-9 m2/s) |
|---|---|---|
| Li+ | 0.238 | 1.03 |
| K+ | 0.125 | 1.96 |
| Na+ | 0.184 | 1.33 |
| Mg2+ | 0.347 | 0.706 |
| Ca2+ | 0.310 | 0.79 |
| 0.230 | 1.065 |
表4 Stokes半径及扩散系数[22-23]
Table 4 Stokes radius and diffusion coefficients of various ions considered in this study[22-23]
| 离子 | Stokes半径/nm | 扩散系数/(10-9 m2/s) |
|---|---|---|
| Li+ | 0.238 | 1.03 |
| K+ | 0.125 | 1.96 |
| Na+ | 0.184 | 1.33 |
| Mg2+ | 0.347 | 0.706 |
| Ca2+ | 0.310 | 0.79 |
| 0.230 | 1.065 |
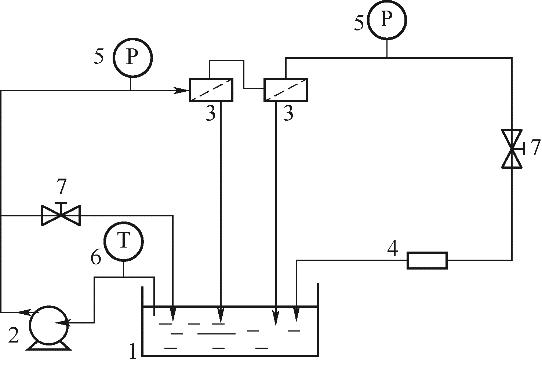
图2 纳滤透过实验装置示意图1—原料槽;2—柱塞泵;3—膜元件;4—流量计;5—压力表;6—温度计;7—阀门
Fig.2 Schematic diagram for the cross-flow NF equipment adopted in the experiments1—raw material tank; 2—plunger pump; 3—membrane; 4—flowmeter; 5—pressure gauge; 6—thermometer; 7—valve
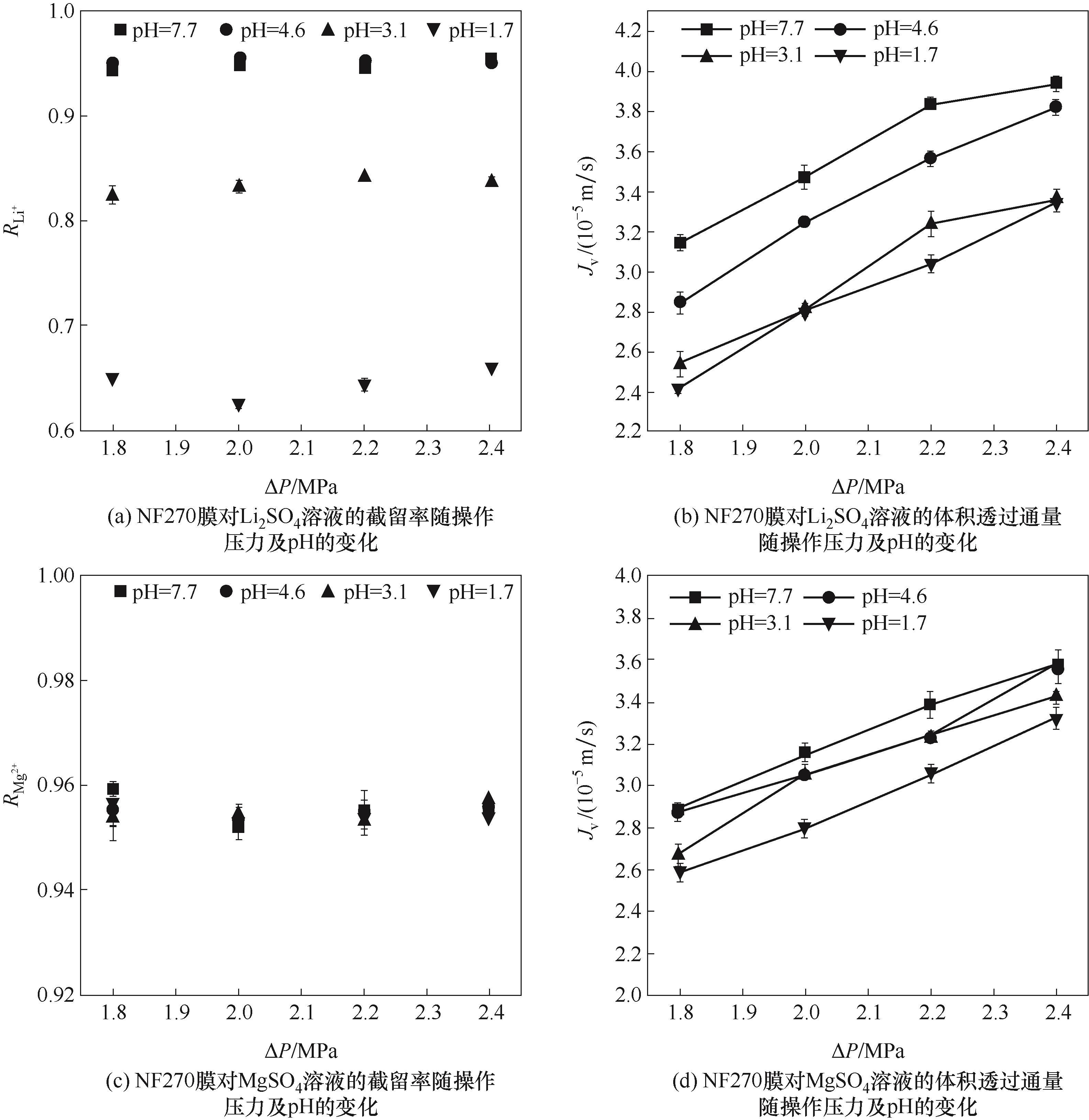
图4 pH和操作压力对NF270膜对Li2SO4/MgSO4溶液的分离和透过性能的影响
Fig.4 The effects of pH and operating pressure on the separation and permeation performance of the NF270 membrane for Li₂SO₄/MgSO₄ solutions
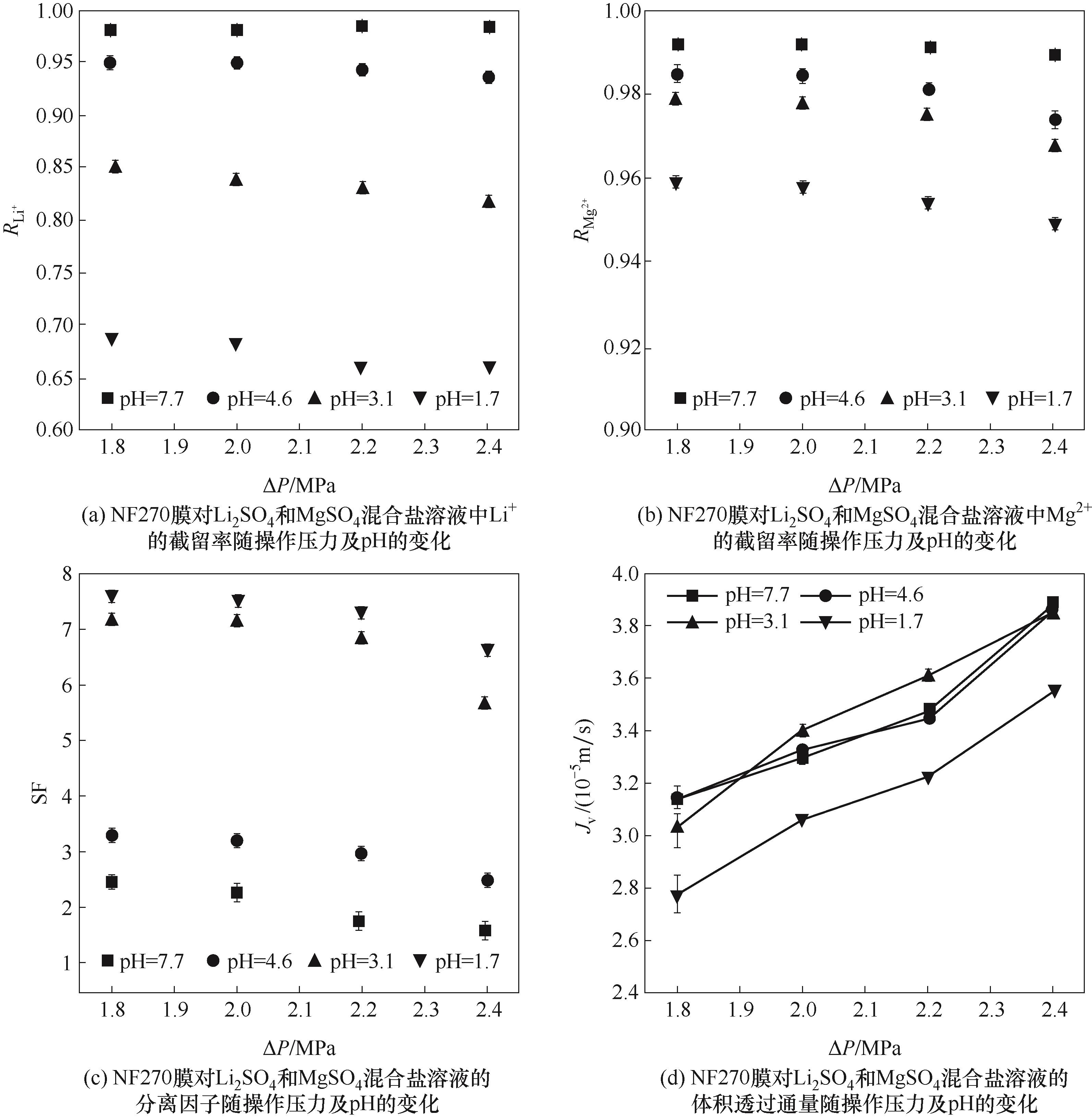
图5 pH和操作压力对NF270膜对Li2SO4和MgSO4混合盐溶液的分离和透过性能的影响
Fig.5 The effects of pH and operating pressure on the separation and permeation performance of the NF270 membrane for Li2SO4/MgSO4 mixed solutions
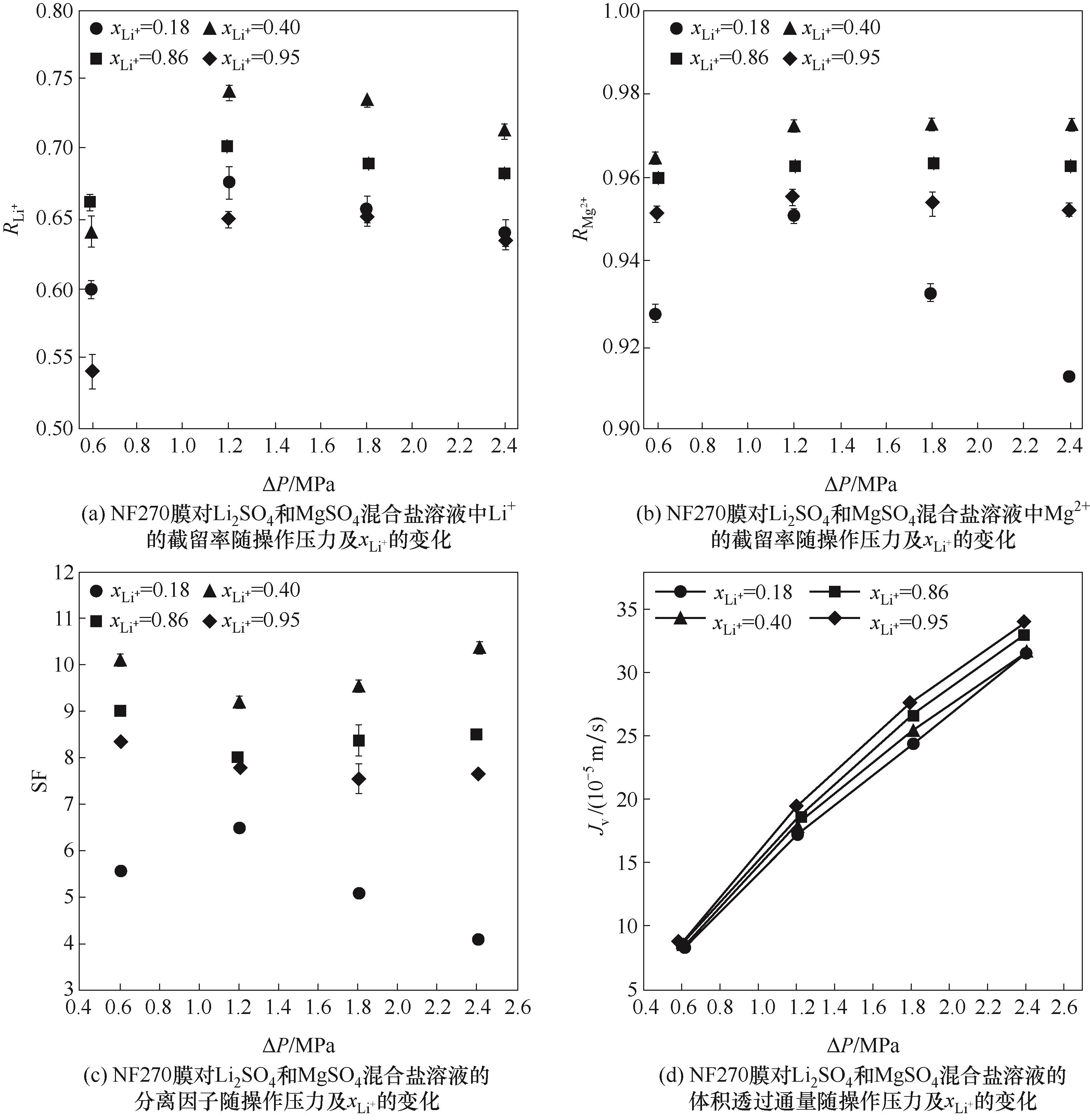
图6 xLi+和操作压力对NF270膜对硫酸型混合盐溶液的分离和透过性能的影响
Fig.6 The effects of xLi+ and operating pressure on the separation and permeation performance of the NF270 membrane for Li2SO4/MgSO4 mixed solutions
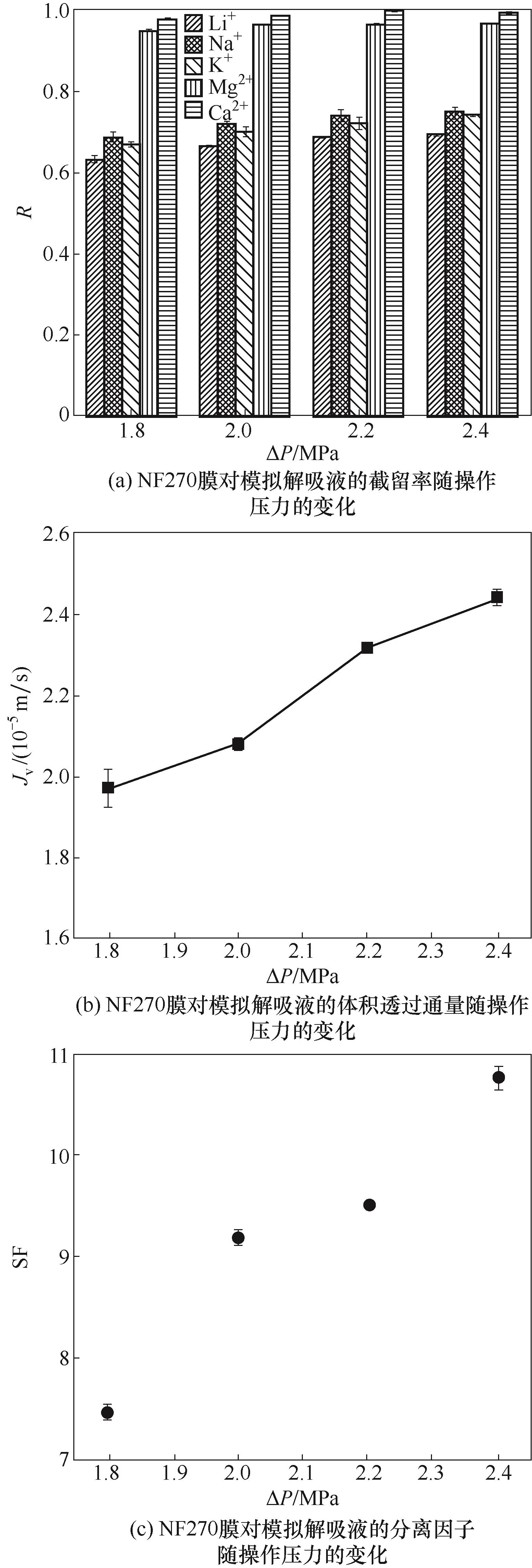
图7 不同操作压力下NF270膜对模拟解吸液的分离和渗透性能
Fig.7 Separation and permeation performance of the NF270 membrane for simulated desorption solution under different operating pressures
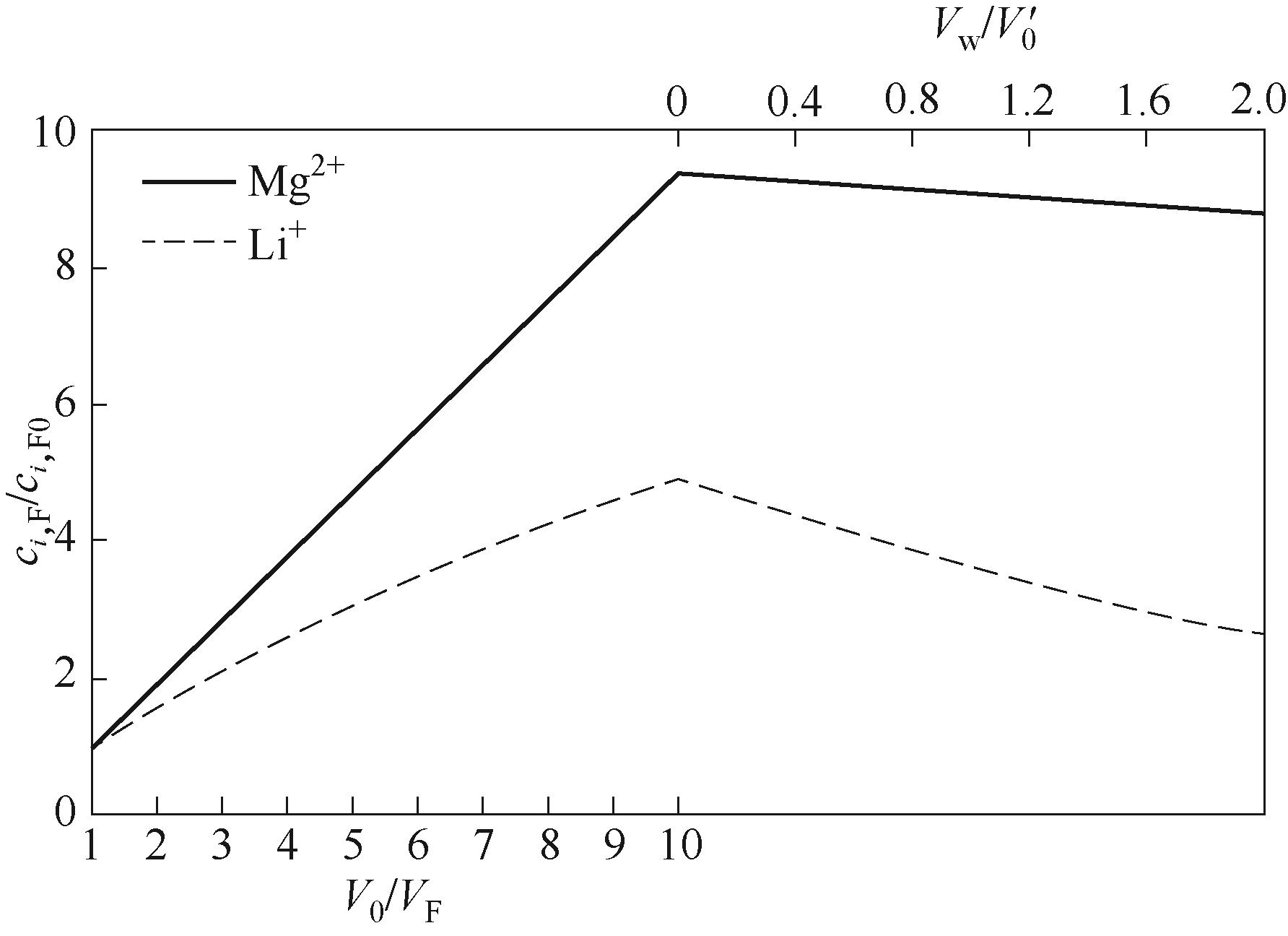
图8 预浓缩-连续恒容渗滤过程料液中Mg2+和Li+浓度比随浓缩倍数(V0/VF)与水消耗量(Vw/V0′)的变化
Fig.8 Relationship between the concentration ratio of Mg2+and Li+ in the feed solution during preconcentration-continuous constant volume percolation with the concentration factor (V0/VF ) and the water consumption (Vw/V0′) during the percolation process
| 渗滤过程 | 水消耗量 | 料液 | 透过液 | Li+回收率/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 体积 | c(Mg2+)/ (mol/L) | c(Li+)/ (mol/L) | 体积 | c(Mg2+)/ (mol/L) | c(Li+)/ (mol/L) | |||
| 初始 | — | V0 | 0.023 | 0.25 | — | — | — | — |
| 预浓缩后 | 0 | (1/10)V0 | 0.21 | 1.22 | (9/10)V0 | 0.0017 | 0.14 | 50 |
| 连续恒容渗滤后 | 1/5V0 | (1/10)V0 | 0.20 | 0.66 | (11/10)V0 | 0.0025 | 0.17 | 75 |
表5 整个渗滤过程中的水消耗量、料液及透过液的体积、盐浓度和锂离子回收率变化
Table 5 Variations of water consumption, volume,concentration of feed and permeate and the yield of lithium during the whole concentrationinfiltration process
| 渗滤过程 | 水消耗量 | 料液 | 透过液 | Li+回收率/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 体积 | c(Mg2+)/ (mol/L) | c(Li+)/ (mol/L) | 体积 | c(Mg2+)/ (mol/L) | c(Li+)/ (mol/L) | |||
| 初始 | — | V0 | 0.023 | 0.25 | — | — | — | — |
| 预浓缩后 | 0 | (1/10)V0 | 0.21 | 1.22 | (9/10)V0 | 0.0017 | 0.14 | 50 |
| 连续恒容渗滤后 | 1/5V0 | (1/10)V0 | 0.20 | 0.66 | (11/10)V0 | 0.0025 | 0.17 | 75 |
| 1 | Alessia A, Alessandro B, Maria V G, et al. Challenges for sustainable lithium supply: a critical review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 300: 126954. |
| 2 | 杨卉芃, 柳林, 丁国峰. 全球锂矿资源现状及发展趋势[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2019(5): 26-40. |
| Yang H P, Liu L, Ding G F. Present situation and development trend of lithium resources in the world[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(5): 26-40. | |
| 3 | Wang X L, Tsuru T, Togoh M, et al. Evaluation of pore structure and electrical properties of nanofiltration membranes[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 1995, 28(2): 186-192. |
| 4 | Fridman-Bishop N, Nir O, Lahav O, et al. Predicting the rejection of major seawater ions by spiral-wound nanofiltration membranes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(14): 8631-8638. |
| 5 | 周久龙, 树银雪. 我国盐湖卤水提锂产业化现状及发展建议[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2023, 52(1): 57-62. |
| Zhou J L, Shu Y X. Industrialization status and development proposal of lithium extraction from salt lake brine in China[J]. Industrial Minerals & Processing, 2023, 52(1): 57-62. | |
| 6 | 乜贞, 伍倩, 丁涛, 等. 中国盐湖卤水提锂产业化技术研究进展[J]. 无机盐工业, 2022, 54(10): 1-12. |
| Nie Z, Wu Q, Ding T, et al. Research progress on industrialization technology of lithium extraction from salt lake brine in China[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(10): 1-12. | |
| 7 | 靳佳奇, 李岩, 林森. 盐湖卤水吸附提锂技术研究进展[J]. 化学工程, 2023, 51(5): 20-25. |
| Jin J Q, Li Y, Lin S. Research progress of lithium extraction from salt lake brine by adsorption[J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2023, 51(5): 20-25. | |
| 8 | Wen X M, Ma P H, Zhu C L, et al. Preliminary study on recovering lithium chloride from lithium-containing waters by nanofiltration[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2006, 49(3): 230-236. |
| 9 | Yang G, Shi H, Liu W Q, et al. Investigation of Mg2+/Li+ separation by nanofiltration[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2011, 19(4): 586-591. |
| 10 | Somrani A, Hamzaoui A H, Pontie M. Study on lithium separation from salt lake brines by nanofiltration (NF) and low pressure reverse osmosis (LPRO)[J]. Desalination, 2013, 317: 184-192. |
| 11 | 计超. 纳滤分离镁锂过程研究[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2014. |
| Ji C. Study on separation of magnesium and lithium by nanofiltration[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2014. | |
| 12 | Sun S Y, Cai L J, Nie X Y, et al. Separation of magnesium and lithium from brine using a desal nanofiltration membrane[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2015, 7: 210-217. |
| 13 | Bi Q Y, Zhang Z Q, Zhao C Y, et al. Study on the recovery of lithium from high Mg2+/Li+ ratio brine by nanofiltration[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2014, 70(10): 1690-1694. |
| 14 | 成琪. 纳滤膜法用于硫酸镁亚型盐湖卤水锂的分离与富集[D]. 西宁: 青海大学, 2019. |
| Cheng Q. Separation and enrichment of lithium in salt lake brine of magnesium sulfate subtype by nanofiltration membrane method[D]. Xining: Qinghai University, 2019. | |
| 15 | 康为清, 时历杰, 赵有璟, 等. 纳滤法用于盐湖卤水镁锂分离的初步实验[J]. 无机盐工业, 2014, 46(12): 22-24. |
| Kang W Q, Shi L J, Zhao Y J, et al. Preliminary test of separation of Mg2+/Li+ in salt lake brine by nanofiltration[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2014, 46(12): 22-24. | |
| 16 | Li Y, Zhao Y J, Wang H Y, et al. The application of nanofiltration membrane for recovering lithium from salt lake brine[J]. Desalination, 2019, 468: 114081. |
| 17 | 李燕, 王敏, 赵有璟, 等. 纳滤膜对高镁锂比盐湖卤水镁锂分离性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(6): 3130-3139. |
| Li Y, Wang M, Zhao Y J, et al. Study on separation of magnesium and lithium from salt lake brine with high magnesium-to-lithium mass ratio by nanofiltration membrane[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(6): 3130-3139. | |
| 18 | Pramanik B K, Asif M B, Kentish S, et al. Lithium enrichment from a simulated salt lake brine using an integrated nanofiltration-membrane distillation process[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2019, 7(5): 103395. |
| 19 | 燕志琴. 高浓一二价盐溶液的纳滤膜分离性能研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2016. |
| Yang Z Q. Research on separation performance of mono- and divalent salt solution with high concentration by nanofiltration membrane[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2016. | |
| 20 | 徐萍, 钱晓明, 郭昌盛, 等. 用于盐湖卤水镁锂分离的纳滤技术研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(3): 410-417. |
| Xu P, Qian X M, Guo C S, et al. Nanofiltration technology used for separation of magnesium and lithium from salt lake brine: a survey[J]. Materials Reports, 2019, 33(3): 410-417. | |
| 21 | Gao L, Wang H Y, Zhang Y, et al. Nanofiltration membrane characterization and application: extracting lithium in lepidolite leaching solution[J]. Membranes, 2020, 10(8): 178. |
| 22 | King H W. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2002. |
| 23 | Nightingale E R Jr. Phenomenological theory of ion solvation. Effective radii of hydrated ions[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1959, 63(9): 1381-1387. |
| 24 | Mohammad A W, Teow Y H, Ang W L, et al. Nanofiltration membranes review: recent advances and future prospects[J]. Desalination, 2015, 356: 226-254. |
| 25 | Su B W, Duan X J, Dou M W, et al. Charge characteristics of nanofiltration membrane by streaming potential method[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 396/397/398: 547-551. |
| 26 | 姚红娟. 纳滤膜法染料水溶液的脱盐浓缩及其过程模拟[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2003. |
| Yao H J. Desalination and concentration of aqueous aqueous solution by nanofiltration membrane and its process simulation[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2003. | |
| 27 | 计超, 张杰, 张志君, 等. DK纳滤膜对高镁锂比卤水的分离性能研究[J]. 膜科学与技术, 2014, 34(3): 79-85. |
| Ji C, Zhang J, Zhang Z J, et al. Separation properties of magnesium and lithium from brine with high Mg2+/Li+ ratio by DK nanofiltration membrane[J]. Membrane Science and Technology, 2014, 34(3): 79-85. | |
| 28 | Park H M, Takaba H, Lee Y T. Preparation and characterization of TFC NF membrane with improved acid resistance behavior[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020, 616: 118620. |
| 29 | Gao S L, Qin Z X, Wang B F, et al. Lithium recovery from the spent lithium-ion batteries by commercial acid-resistant nanofiltration membranes: a comparative study[J]. Desalination, 2024, 572: 117142. |
| 30 | Luo J Q, Wan Y H. Effects of pH and salt on nanofiltration—a critical review[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 438: 18-28. |
| 31 | Jun B M, Cho J, Jang A, et al. Charge characteristics (surface charge vs. zeta potential) of membrane surfaces to assess the salt rejection behavior of nanofiltration membranes[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 247: 117026. |
| 32 | Wang D X, Su M, Yu Z Y, et al. Separation performance of a nanofiltration membrane influenced by species and concentration of ions[J]. Desalination, 2005, 175(2): 219-225. |
| 33 | Silva V, Geraldes V, A M Brites Alves, et al. Multi-ionic nanofiltration of highly concentrated salt mixtures in the seawater range[J]. Desalination, 2011, 277(1/2/3): 29-39. |
| [1] | 吕阳光, 左培培, 杨正金, 徐铜文. 三嗪框架聚合物膜用于有机纳滤甲醇/正己烷分离[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1598-1606. |
| [2] | 周国莉, 韩项珂, 武文佳, 王景涛, 张毛娃, 李凤丽. 异质结构g-C3N4@AM层状膜构筑及纳滤性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 941-950. |
| [3] | 张后虎, 吴晓莉, 陈冲冲, 陈静静, 王景涛. CD-MOF二维层状膜制备及混合溶剂精准分离研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4539-4550. |
| [4] | 李燕, 王敏, 赵有璟, 王怀有, 杨红军, 祝增虎. 纳滤膜对高镁锂比盐湖卤水镁锂分离性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(6): 3130-3139. |
| [5] | 刘嘉玮, 郝雨峰, 苏延磊. 石墨烯量子点纳滤膜的仿生修饰及稳定性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(6): 3390-3398. |
| [6] | 冉瑾,黄强,艾新宇,吴玉莹,张朋朋,窦焰. Zn-BTC/MoS2复合二维膜构筑及有机溶剂纳滤性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(4): 2148-2155. |
| [7] | 陆至彬, 谢星, 鲁思达, 何畅, 张冰剑, 陈清林. 基于代理模型的含盐废水多级纳滤系统的过程优化设计[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(3): 1400-1408. |
| [8] | 何鹏鹏, 赵颂, 毛晨岳, 王志, 王纪孝. 耐溶剂复合纳滤膜的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 727-747. |
| [9] | 杨丰瑞, 王志, 燕方正, 韩向磊, 王纪孝. 纳滤用于一价/二价无机盐溶液分离研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 799-813. |
| [10] | 刘宁, 褚昌辉, 王乾, 孙世鹏. 用于混合一价盐分离的纳滤膜的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 578-588. |
| [11] | 汪菊, 牛淑锋, 费莹, 漆虹. GO/Al2O3复合纳滤膜的制备及其稳定性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(6): 2795-2803. |
| [12] | 徐燕青, 李文飞, 吴梦瑶, 沈江南. 用于喷墨印花染料纯化的自组装GO/TiO2复合纳滤膜的制备[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(3): 1352-1361. |
| [13] | 刘丽雪, 张少峰, 赵长伟, 宝乐尔呼, 俞灵, 王军. β-环糊精为水相单体的复合纳滤膜制备及染料截留性能[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(2): 889-898. |
| [14] | 徐颜军, 徐泽海, 孟琴, 沈冲, 侯蕊, 张国亮. 新型还原氧化石墨烯/氮化碳复合纳滤膜制备及其性能[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(9): 3565-3572. |
| [15] | 唐元晖, 扈阳, 燕至琴, 李春玉. 高浓度含盐草甘膦溶液的纳滤分离实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(7): 2574-2583. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号