化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (12): 6423-6438.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250844
毛正鑫1,2( ), 申佳昌1,2, 刘梦鑫3, 季延洁3, 王钦宏4, 杨茂华1(
), 申佳昌1,2, 刘梦鑫3, 季延洁3, 王钦宏4, 杨茂华1( ), 邢建民1,2(
), 邢建民1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-07-29
修回日期:2025-10-23
出版日期:2025-12-31
发布日期:2026-01-23
通讯作者:
杨茂华,邢建民
作者简介:毛正鑫(1995—), 男, 博士研究生, maozhengxin@ipe.ac.cn
Zhengxin MAO1,2( ), Jiachang SHEN1,2, Mengxin LIU3, Yanjie JI3, Qinhong WANG4, Maohua YANG1(
), Jiachang SHEN1,2, Mengxin LIU3, Yanjie JI3, Qinhong WANG4, Maohua YANG1( ), Jianmin XING1,2(
), Jianmin XING1,2( )
)
Received:2025-07-29
Revised:2025-10-23
Online:2025-12-31
Published:2026-01-23
Contact:
Maohua YANG, Jianmin XING
摘要:
磷酸糖是重要的生化药物与糖类合成关键中间体。在多酶催化制备糖类物质时,伴随着磷酸糖的生成,磷酸盐(Pi)的浓度逐渐升高,高浓度Pi对酶活性具有抑制作用。因此,Pi的高效去除是实现糖类物质合成技术推广应用的关键。本研究针对磷酸糖/Pi模拟体系,考察了Pi总浓度、pH和溶液组成对分离效率的影响。对比分析了多种纳滤膜,结果表明,在高盐浓度下,纳滤膜NF4和NF7展现出良好的分离选择性能,可以实现磷酸糖与高浓度磷酸盐的高效分离。通过洗滤,Pi的去除率可达到80%以上。采用了DSPM-DE模型对分离机制进行解析,空间位阻和介电排斥是实现溶质分离的关键机制。本研究利用纳滤技术实现了高盐体系中磷酸糖与Pi的高效分离,同时解决了高盐环境对催化体系中酶活性的潜在抑制作用,确保了体系的长期稳定运行,为磷酸糖制备技术的工业应用奠定了基础。
中图分类号:
毛正鑫, 申佳昌, 刘梦鑫, 季延洁, 王钦宏, 杨茂华, 邢建民. 磷酸糖与高浓度磷酸盐的高效纳滤分离[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(12): 6423-6438.
Zhengxin MAO, Jiachang SHEN, Mengxin LIU, Yanjie JI, Qinhong WANG, Maohua YANG, Jianmin XING. Efficient separation of phosphorylated sugars and high-concentration phosphate by nanofiltration[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(12): 6423-6438.
| SOM | MW/(g·mol-1) | pKa | Charge (pH6) | Stokes radius/nm | Diffusion coefficient/(10-10 m2·s-1)③ | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| carbamazepine | 236.27 | 15.96 | 0 | 0.36 | 6.81 | [ |
| dienestrol | 266 | 10.50 | — | 0.47 | 5.21 | [ |
| trimethoprim | 290.32 | 7.16 | 1 | 0.42 | 5.83 | [ |
| ethynyl estradiol | 296 | 10.05 | — | 0.49 | 5.00 | [ |
| perfluoroheptanoic acid | 364.02 | -2.29 | -1 | 0.35 | 7.00 | [ |
| FDP | 340.12 | — | -2① | 0.58② | 4.21 | this work |
表1 SOM的理化性质
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of SOM
| SOM | MW/(g·mol-1) | pKa | Charge (pH6) | Stokes radius/nm | Diffusion coefficient/(10-10 m2·s-1)③ | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| carbamazepine | 236.27 | 15.96 | 0 | 0.36 | 6.81 | [ |
| dienestrol | 266 | 10.50 | — | 0.47 | 5.21 | [ |
| trimethoprim | 290.32 | 7.16 | 1 | 0.42 | 5.83 | [ |
| ethynyl estradiol | 296 | 10.05 | — | 0.49 | 5.00 | [ |
| perfluoroheptanoic acid | 364.02 | -2.29 | -1 | 0.35 | 7.00 | [ |
| FDP | 340.12 | — | -2① | 0.58② | 4.21 | this work |
| Product model | Material | MWCO/Da | Water flux/(L·m-2·h-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| UE003 | PES | 3500 | 45① |
| UE005 | PES | 5000 | 100① |
| UX003 | — | 3000 | 60① |
| NF2 | PA | 200—300 | 55② |
| NF3 | PA | 300—400 | 70② |
| NF4 | PA | 400—500 | 55② |
| NF7 | PA | 400—700 | 60② |
| NF8 | PA | 800—1000 | 65② |
表2 膜参数
Table 2 Membrane parameters
| Product model | Material | MWCO/Da | Water flux/(L·m-2·h-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| UE003 | PES | 3500 | 45① |
| UE005 | PES | 5000 | 100① |
| UX003 | — | 3000 | 60① |
| NF2 | PA | 200—300 | 55② |
| NF3 | PA | 300—400 | 70② |
| NF4 | PA | 400—500 | 55② |
| NF7 | PA | 400—700 | 60② |
| NF8 | PA | 800—1000 | 65② |
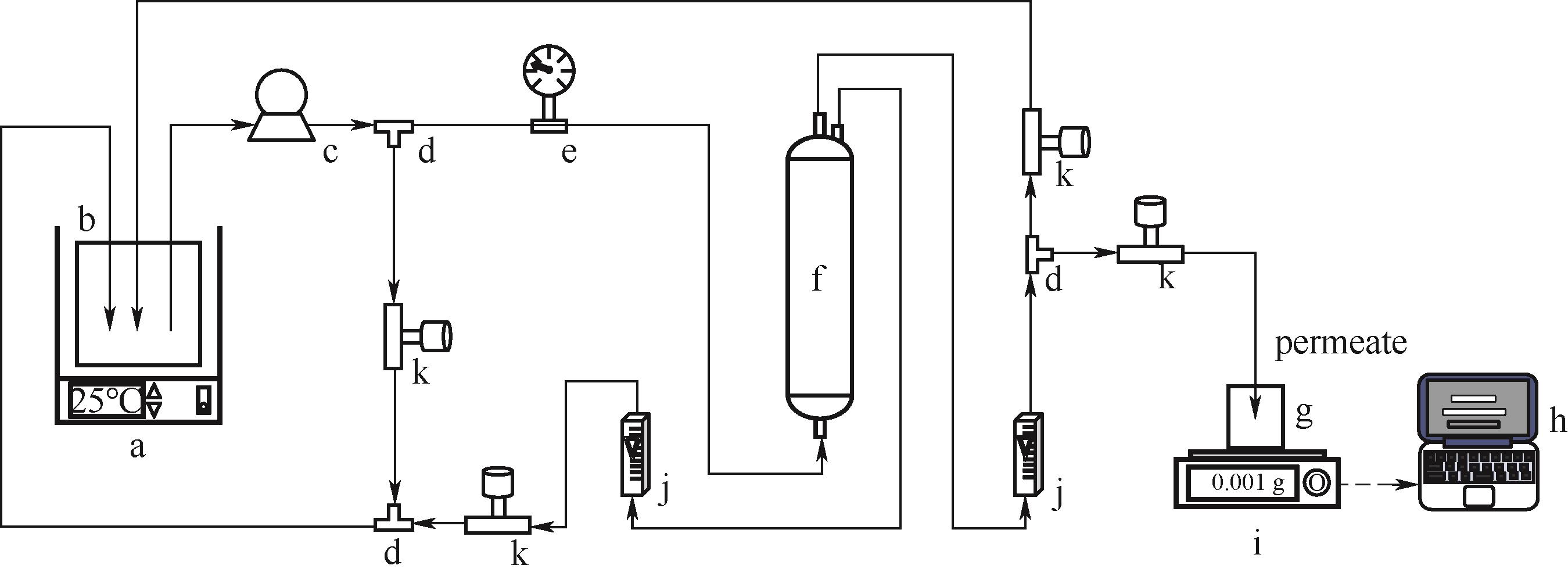
图1 错流洗滤装置示意图a—恒温水浴;b—进料罐;c—隔膜泵;d—三通;e—压力表;f—螺旋缠绕卷式膜组件;g—透过液罐;h—计算机;i—电子天平;j—流量计;k—节流阀
Fig.1 Device diagram of cross-flow diafiltrationa—thermostatic water bath; b—feed tank; c—diaphragm pump; d—three-way; e—pressure gauge; f—spiral-wound membrane module; g—permeate tank; h—computer; i—electronic balance; j—flow meter; k—control valve
| Specie | Stokes radius/nm | Hydrated radius /nm | Hydration free energy/(kJ·mol-1) | Diffusion coefficient/(10-9 m2·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | 0.184 | 0.358 | -365 | 1.177 |
| Cl- | 0.121 | 0.332 | -340 | 2.028 |
| 0.231 | 0.379 | -1080 | 1.062 | |
| 0.256 | 0.302 | -465 | 0.846 | |
| 0.323 | 0.327 | -1089 | 0.690 | |
| — | 0.339 | -2765 | 0.612 |
表3 离子物性参数
Table 3 Physical parameters of ions
| Specie | Stokes radius/nm | Hydrated radius /nm | Hydration free energy/(kJ·mol-1) | Diffusion coefficient/(10-9 m2·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | 0.184 | 0.358 | -365 | 1.177 |
| Cl- | 0.121 | 0.332 | -340 | 2.028 |
| 0.231 | 0.379 | -1080 | 1.062 | |
| 0.256 | 0.302 | -465 | 0.846 | |
| 0.323 | 0.327 | -1089 | 0.690 | |
| — | 0.339 | -2765 | 0.612 |
| No. | Conc. of FDP/ (mmol·L-1) | Conc. of Pi/(mmol·L-1) | Ion strength/(mmol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 18 | 24 |
| 2 | 4 | 36 | 48 |
| 3 | 8 | 72 | 96 |
| 4 | 15 | 135 | 180 |
| 5 | 30 | 270 | 360 |
| 6 | 8 | 216 | 240 |
| 7 | 16 | 192 | 240 |
| 8 | 24 | 168 | 240 |
| 9 | 32 | 144 | 240 |
| 10 | 48 | 96 | 240 |
表4 模拟高盐体系的组成和浓度
Table 4 Compositions and concentrations of simulated high salinity solution
| No. | Conc. of FDP/ (mmol·L-1) | Conc. of Pi/(mmol·L-1) | Ion strength/(mmol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 18 | 24 |
| 2 | 4 | 36 | 48 |
| 3 | 8 | 72 | 96 |
| 4 | 15 | 135 | 180 |
| 5 | 30 | 270 | 360 |
| 6 | 8 | 216 | 240 |
| 7 | 16 | 192 | 240 |
| 8 | 24 | 168 | 240 |
| 9 | 32 | 144 | 240 |
| 10 | 48 | 96 | 240 |
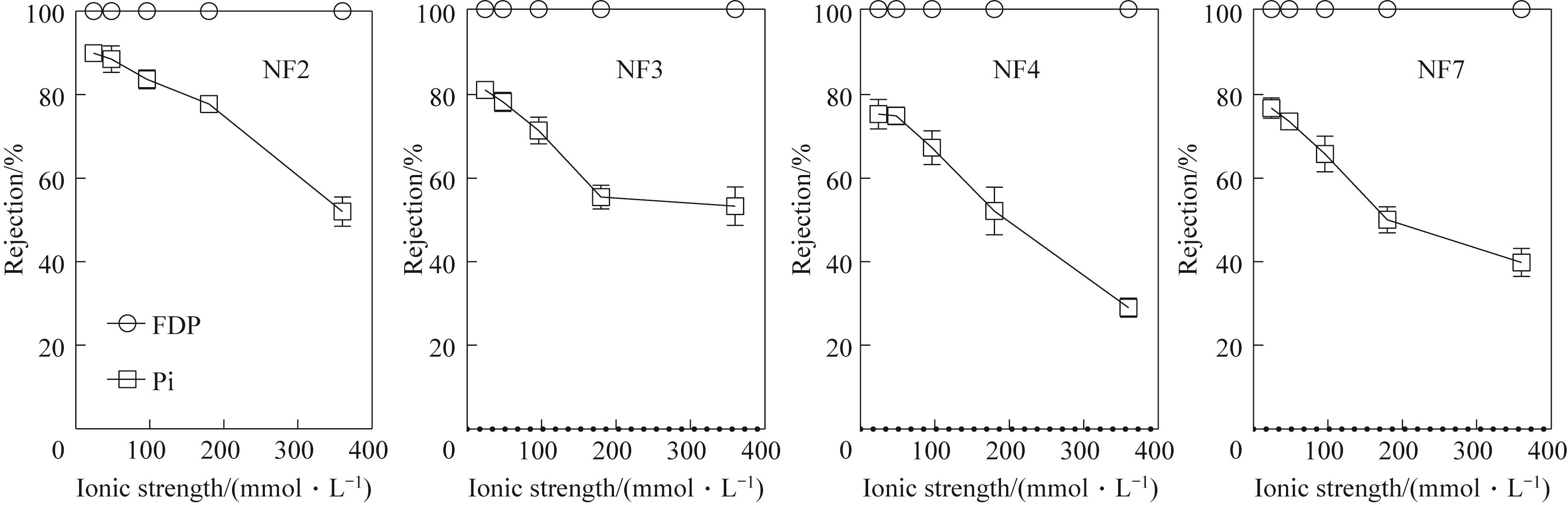
图4 不同离子强度对磷酸糖/Pi截留率的影响(固定FDP的比例)
Fig.4 Effect of different ionic strengths on the rejection of phosphorylated sugars/phosphates (fixed the percentage of FDP)
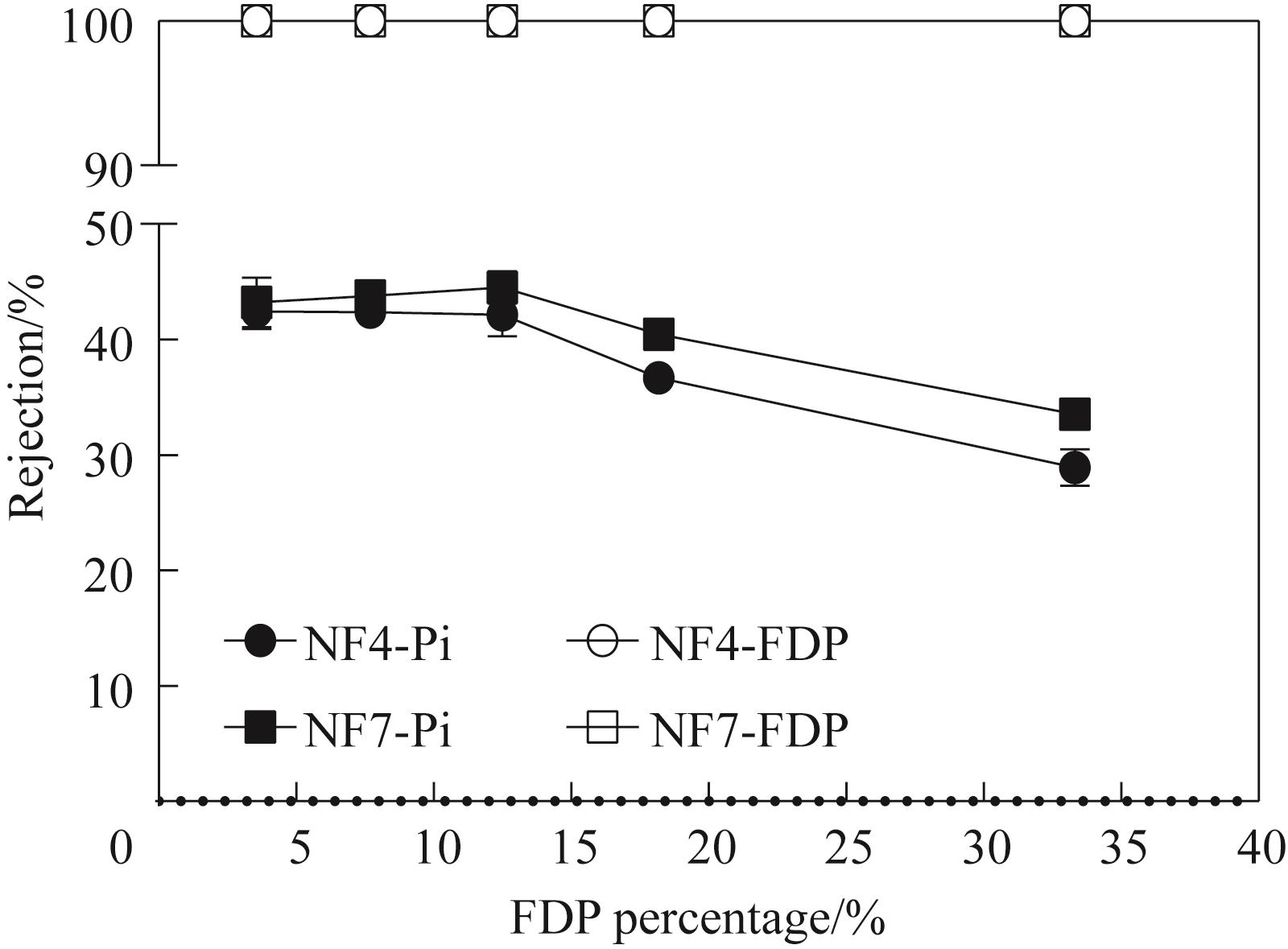
图6 不同磷酸糖比例对磷酸糖/Pi截留率的影响(固定离子强度)
Fig.6 Effect of different percentage of FDP on the rejection of phosphorylated sugars/phosphates (fixed the ionic strengths)
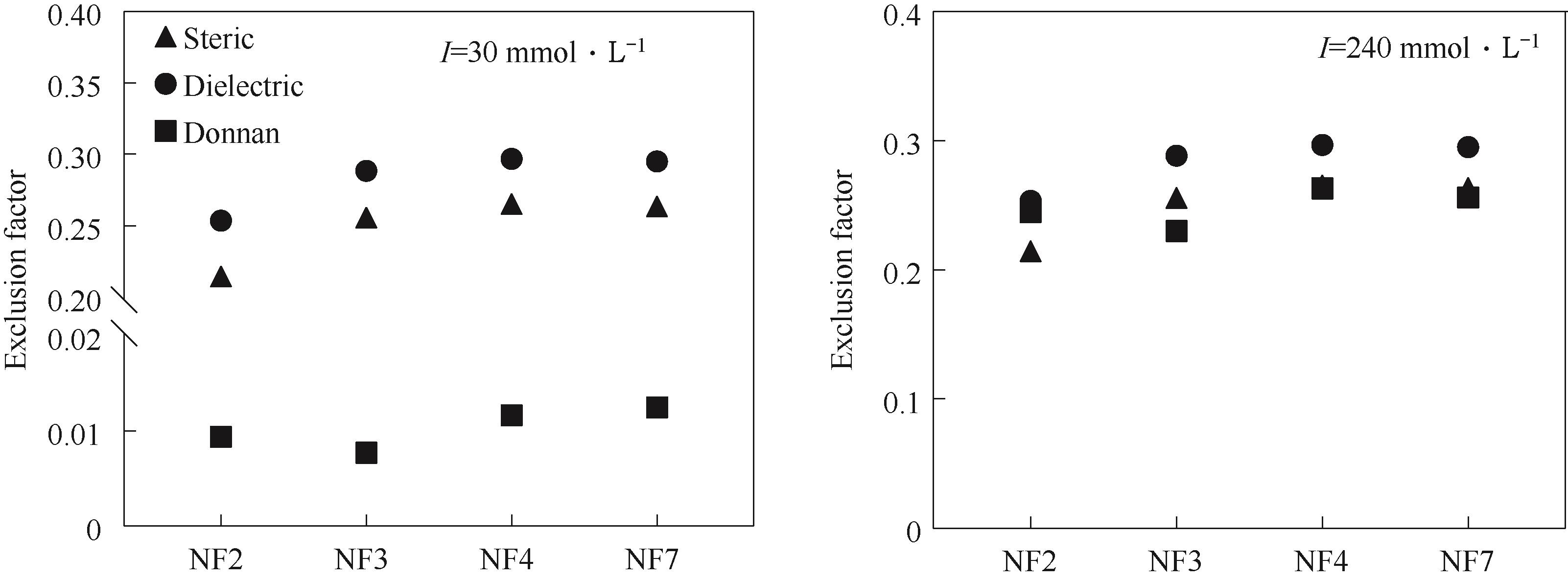
图9 量化空间排斥、介电排斥和Donnan排斥(进料侧)对Pi截留的贡献
Fig.9 Distinction the contribution of steric, dielectric and donnan exclusion (feed side) on phosphates rejection
| Batch | Volume/L | Concentration/(mmol·L-1) | Rejection rate/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pi | Phosphorylated sugars | Pi | Phosphorylated sugars | |||
| 1 | Feed | 0.77 | 89.50 | 28.04 | 66.85 | 100.00 |
| Permeate | 0.53 | 43.10 | ND | |||
| 2 | Feed | 1.00 | 104.16 | 40.05 | 63.15 | 100.00 |
| Permeate | 0.50 | 76.77 | ND | |||
表5 实际体系纳滤测试结果
Table 5 Results of nanofiltration tests in the actual system
| Batch | Volume/L | Concentration/(mmol·L-1) | Rejection rate/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pi | Phosphorylated sugars | Pi | Phosphorylated sugars | |||
| 1 | Feed | 0.77 | 89.50 | 28.04 | 66.85 | 100.00 |
| Permeate | 0.53 | 43.10 | ND | |||
| 2 | Feed | 1.00 | 104.16 | 40.05 | 63.15 | 100.00 |
| Permeate | 0.50 | 76.77 | ND | |||
| [1] | Li Y J, Shi T, Han P P, et al. Thermodynamics-driven production of value-added d-allulose from inexpensive starch by an in vitro enzymatic synthetic biosystem[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2021, 11(9): 5088-5099. |
| [2] | Zhao L T, Ma Z B, Zhang L P, et al. Synthesis of value-added uridine 5'-diphosphate-glucose from sucrose applying an engineered sucrose synthase counteracts the activity-stability trade-off[J]. Food Chemistry, 2025, 464: 141765. |
| [3] | Cai T, Sun H B, Qiao J, et al. Cell-free chemoenzymatic starch synthesis from carbon dioxide[J]. Science, 2021, 373(6562): 1523-1527. |
| [4] | Tian C Y, Yang J G, Liu C, et al. Engineering substrate specificity of HAD phosphatases and multienzyme systems development for the thermodynamic-driven manufacturing sugars[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 3582. |
| [5] | Jung B, Choi J S, Park C M, et al. Tannic acid as a natural organic matter surrogate in ultrafiltration membrane process[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 516, 164132. |
| [6] | Chai Y K, Lam H C, Koo C H, et al. Performance evaluation of polyamide nanofiltration membranes for phosphorus removal process and their stability against strong acid/alkali solution[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2019, 27(8): 1789-1797. |
| [7] | Sun D, Gu B X, Huo H Q, et al. Polyamide modified anion exchange membrane by interfacial polymerization for nitrate and phosphate salt separation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2025, 717: 123640. |
| [8] | 杨丰瑞, 王志. 纳滤用于一价/二价无机盐溶液分离研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 799-813. |
| Yang F R, Wang Z. Progress in separation of monovalent/divalent inorganic salt solutions by nanofiltration[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(2): 799-813. | |
| [9] | Wang J D, Jiang Y X, Tian Z Z, et al. Highly permeable acid-stable poly (sulfonamide-urea) nanofiltration membrane for purifying phosphoric acid[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 362: 131662. |
| [10] | Guo S W, Wan Y H, Chen X R, et al. Loose nanofiltration membrane custom-tailored for resource recovery[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 409: 127376. |
| [11] | Guo X, Zhao B, Li Y, et al. A novel loose nanofiltration membrane prepared using large rigid-contorted diamine monomer for dye purification[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2025, 723: 123928. |
| [12] | Su Y F, Zhang X K, Li H, et al. In-situ incorporation of halloysite nanotubes with 2D zeolitic imidazolate framework-L based membrane for dye/salt separation[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2023, 58: 103-111. |
| [13] | Zhao Y Y, Tong X, Chen Y S. Fit-for-purpose design of nanofiltration membranes for simultaneous nutrient recovery and micropollutant removal[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(5): 3352-3361. |
| [14] | Yang L Y, Xia C P, Jiang J L, et al. Removal of antibiotics and estrogens by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2024, 461: 132628. |
| [15] | Zhao Y Y, Tong X, Kim J, et al. Capillary-assisted fabrication of thin-film nanocomposite membranes for improved solute–solute separation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(9): 5849-5859. |
| [16] | Novalin S, Kongbangkerd T, Reisinger M, et al. Integration of electrodialysis into an enzymatic synthesis for the separation of phosphate from glucose-1-phosphate[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017, 182: 224-229. |
| [17] | Wang X M, Li B, Zhang T, et al. Performance of nanofiltration membrane in rejecting trace organic compounds: experiment and model prediction[J]. Desalination, 2015, 370: 7-16. |
| [18] | Miyabe K, Isogai R. Estimation of molecular diffusivity in liquid phase systems by the Wilke–Chang equation[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2011, 1218(38): 6639-6645. |
| [19] | Wang R Y, Lin S H. Pore model for nanofiltration: history, theoretical framework, key predictions, limitations, and prospects[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2021, 620: 118809. |
| [20] | Xu S Y, Zheng R Q, Li Z Y, et al. Deciphering the overlooked role of dielectric exclusion in the ion selectivity of nanofiltration membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2025, 733: 124342. |
| [21] | Guo H Y, Gao X Q, Yu K C, et al. Ion adsorption on nanofiltration membrane surface and its effect on rejection of charged solutes: a zeta potential approach[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2023, 326: 124830. |
| [22] | Shen J C, Yang M H, Xing J M. Efficient separation of HEPES and CO2-derived fructose by nanofiltration: optimizing pH for improved separation and proposing a potential mechanism[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 355: 129657. |
| [23] | Luo J Q, Wan Y H. Effect of highly concentrated salt on retention of organic solutes by nanofiltration polymeric membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 372(1/2): 145-153. |
| [24] | Mao Z X, Shen J C, Liu M X, et al. Efficient separation of phosphorylated sugars from multi-enzyme system by ultrafiltration and membrane fouling mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2025, 87: 157-170. |
| [25] | Myung S, Wang Y R, Zhang Y P. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase from a hyper-thermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima: characterization, metabolite stability, and its implications[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2010, 45(12): 1882-1887. |
| [26] | Sigurdardottir S B, DuChanois R M, Epsztein R, et al. Energy barriers to anion transport in polyelectrolyte multilayer nanofiltration membranes: role of intra-pore diffusion[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020, 603: 117921. |
| [27] | Epsztein R, Shaulsky E, Qin M H, et al. Activation behavior for ion permeation in ion-exchange membranes: role of ion dehydration in selective transport[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 580: 316-326. |
| [28] | Cevallos-Curva N, Rahman M M, Hailu Kinfu H, et al. Mass transport mechanism of nitrate selective nanofiltration membranes on the basis of the Donnan steric pore model with dielectric exclusion (DSPM-DE) [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 493: 152775. |
| [29] | Geraldes V, Brites Alves A M. Computer program for simulation of mass transport in nanofiltration membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2008, 321(2): 172-182. |
| [30] | Hasted J B, Ritson D M, Collie C H. Dielectric properties of aqueous ionic solutions. Parts Ⅰ and Ⅱ[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1948, 16(1): 1-21. |
| [31] | Zhao Y Y, Tong T Z, Wang X M, et al. Differentiating solutes with precise nanofiltration for next generation environmental separations: a review[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(3): 1359-1376. |
| [32] | Qi T, Chen X F, Lu T D, et al. Enhancing ion separation efficiency: Janus charged nanofiltration membrane fabricated via polyethyleneimine-manipulated interfacial polymerization[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2024, 706: 122930. |
| [33] | Lin J Y, Ye W Y, Baltaru M C, et al. Tight ultrafiltration membranes for enhanced separation of dyes and Na2SO4 during textile wastewater treatment[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016, 514: 217-228. |
| [34] | Epsztein R, DuChanois R M, Ritt C L, et al. Towards single-species selectivity of membranes with subnanometre pores[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2020, 15(6): 426-436. |
| [35] | 李燕, 王敏, 赵有璟, 等. 纳滤膜对高镁锂比盐湖卤水镁锂分离性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(6): 3130-3139. |
| Li Y, Wang M, Zhao Y J, et al. Study on separation of magnesium and lithium from salt lake brine with high magnesium-to-lithium mass ratio by nanofiltration membrane[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(6): 3130-3139. | |
| [36] | Liu W K, Wang X M, Li D Y, et al. Dominant mechanism of nanofiltration for chloride/sulfate ion separation in high salinity solutions: the quantification of pore size-influenced dielectric exclusion[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2025, 59(11): 5848-5855. |
| [37] | Bruni L, Bandini S. The role of the electrolyte on the mechanism of charge formation in polyamide nanofiltration membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2008, 308(1/2): 136-151. |
| [38] | Zhu Y Z, Gui L L, Wang R Y, et al. Regulation of molecular transport in polymer membranes with voltage-controlled pore size at the angstrom scale[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 2373. |
| [39] | Zhou W Z, Chen J, Dai R B, et al. Selective removal of organic matters from high-salinity chemical industrial wastewater: ultrafiltration or nanofiltration?[J]. Water Research, 2025, 282: 123762. |
| [40] | Han L, Tian J, Liu C, et al. Influence of pH and NaCl concentration on boron rejection during nanofiltration[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 261: 118248. |
| [41] | Hoek E M V, Elimelech M. Cake-enhanced concentration polarization: a new fouling mechanism for salt-rejecting membranes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(24): 5581-5588. |
| [42] | Shefer I, Peer-Haim O, Leifman O, et al. Enthalpic and entropic selectivity of water and small ions in polyamide membranes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(21): 14863-14875. |
| [43] | Liu L L, Lin S H, Xu X Y, et al. Preference of negatively charged membranes in magnesium and lithium separation by nanofiltration[J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16: 5731. |
| [44] | Pérez-González A, Ibáñez R, Gómez P, et al. Nanofiltration separation of polyvalent and monovalent anions in desalination brines[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 473: 16-27. |
| [45] | Schaep J, Vandecasteele C, Mohammad A W, et al. Analysis of the salt retention of nanofiltration membranes using the donnan-steric partitioning pore model[J]. Separation Science and Technology, 1999, 34(15): 3009-3030. |
| [46] | Wang W, Liu M X, You C, et al. ATP-free biosynthesis of a high-energy phosphate metabolite fructose 1,6-diphosphate by in vitro metabolic engineering[J]. Metabolic Engineering, 2017, 42: 168-174. |
| [47] | Luo J Q, Guo S W, Wu Y Y, et al. Separation of sucrose and reducing sugar in cane molasses by nanofiltration[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2018, 11(5): 913-925. |
| [1] | 臧子晴, 李修真, 谈莹莹, 刘晓庆. 分凝器对两级分离自复叠制冷循环特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 17-25. |
| [2] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [3] | 黄博, 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. 薄膜型LNG船液货舱温度场计算分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 195-204. |
| [4] | 裴星亮, 叶翠平, 裴赢丽, 李文英. 碱改性MIL-53(Cr)选择性吸附分离二甲苯异构体[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 258-267. |
| [5] | 李银龙, 刘国强, 晏刚. 分馏与闪蒸分离耦合自复叠制冷循环性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 26-35. |
| [6] | 李文龙, 常程, 吴小林, 姬忠礼. 油水聚结过滤材料中的液体分布特性及过程压降演化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4850-4861. |
| [7] | 王钰, 冯英楠, 王涛, 赵之平. 原位生长构筑纳米复合纳滤膜:膜制备与应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4723-4736. |
| [8] | 张建民, 何美贵, 贾万鑫, 赵静, 金万勤. 聚氧化乙烯/冠醚共混膜及其二氧化碳分离性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4862-4871. |
| [9] | 郭旭, 贾继宁, 姚克俭. 基于优化CNN-BiLSTM神经网络的间歇精馏过程建模[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4613-4629. |
| [10] | 王杰, 林渠成, 张先明. 基于分解算法的混合气体多级膜分离系统全局优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4670-4682. |
| [11] | 陈治宏, 吴佳伟, 楼小玲, 贠军贤. 化学品生物制造过程机器学习的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3789-3804. |
| [12] | 张荟钦, 赵泓竣, 付正军, 庄力, 董凯, 贾添智, 曹雪丽, 孙世鹏. 纳滤膜在离子型稀土浸出液提浓中的应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4095-4107. |
| [13] | 孙国庆, 李海波, 丁志阳, 郭文辉, 徐浩, 赵艳侠. 硅基负极材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3197-3211. |
| [14] | 高凤凤, 程慧峰, 杨博, 郝晓刚. 电驱动NiFeMn LDH/CNTs/PVDF膜电极选择性提取钨酸根离子[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3350-3360. |
| [15] | 蒋明虎, 汪帆, 邢雷, 赵立新, 李新亚, 陈丁玮. 井下含气对油水分离管柱流场特性及性能影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3361-3372. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号