CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (5): 2230-2240.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241125
• Separation engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Peng TAN( ), Xuemei LI, Xiaoqin LIU, Linbing SUN(
), Xuemei LI, Xiaoqin LIU, Linbing SUN( )
)
Received:2024-10-11
Revised:2024-12-13
Online:2025-06-13
Published:2025-05-25
Contact:
Linbing SUN
通讯作者:
孙林兵
作者简介:谈朋(1988—),男,博士,副教授,ptan@njtech.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Peng TAN, Xuemei LI, Xiaoqin LIU, Linbing SUN. Study on magnetically responsive composite materials based on flexible MOFs and their propylene adsorption performance[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2230-2240.
谈朋, 李雪梅, 刘晓勤, 孙林兵. 基于柔性MOFs的磁响应复合材料及其丙烯吸附性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2230-2240.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Vp/(cm3·g-1) | Vmicro/(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPL-1 | 247 | 0.09 | 0.05 |
| MN@CPL-1-1 | 172 | 0.11 | 0.07 |
| MN@CPL-1-2 | 216 | 0.17 | 0.06 |
| MN@CPL-1-3 | 246 | 0.19 | 0.11 |
| MN@CPL-1-4 | 229 | 0.18 | 0.11 |
Table 1 Textural properties of different samples
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Vp/(cm3·g-1) | Vmicro/(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPL-1 | 247 | 0.09 | 0.05 |
| MN@CPL-1-1 | 172 | 0.11 | 0.07 |
| MN@CPL-1-2 | 216 | 0.17 | 0.06 |
| MN@CPL-1-3 | 246 | 0.19 | 0.11 |
| MN@CPL-1-4 | 229 | 0.18 | 0.11 |
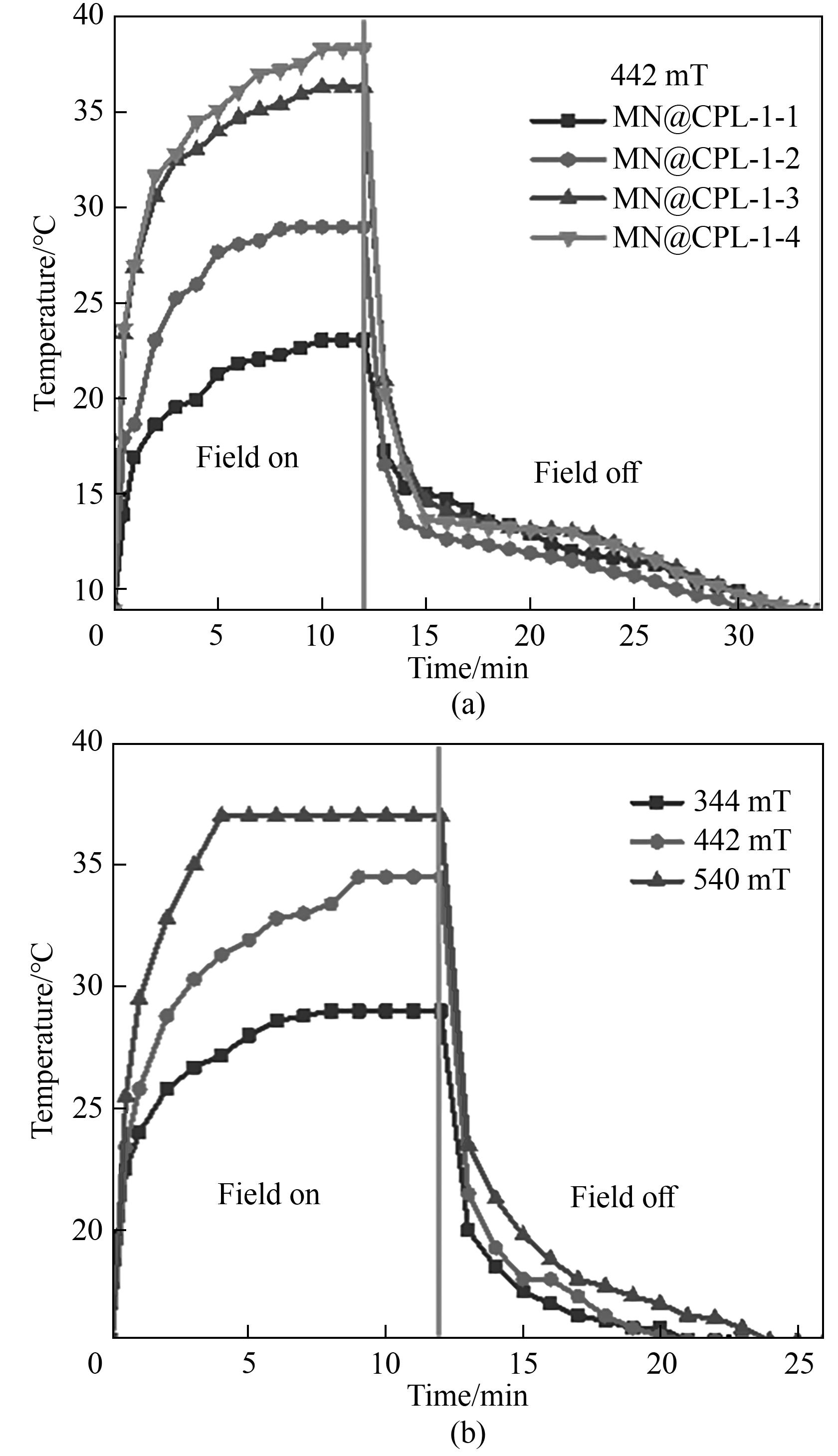
Fig.10 Temperature changes of (a) MN@CPL-1-1, MN@CPL-1-2, MN@CPL-1-3 and MN@CPL-1-4 exposed to the alternating magnetic field of 442 mT and (b) MN@CPL-1-3 exposed to alternating magnetic fields of different intensities
| Sample | Adsorption capacity at 10℃/ (cm3·g-1) | Adsorption capacity at 30℃/ (cm3·g-1) | Working capacity/ (cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPL-1 | 36.8 | 12.0 | 24.8 |
| MN@CPL-1-1 | 32.5 | 10.8 | 21.7 |
| MN@CPL-1-2 | 33.4 | 11.4 | 22.0 |
| MN@CPL-1-3 | 34.0 | 11.5 | 22.5 |
| MN@CPL-1-4 | 28.1 | 10.5 | 17.6 |
Table 2 Saturated adsorption and working capacities of different samples at 10℃ and 30°C
| Sample | Adsorption capacity at 10℃/ (cm3·g-1) | Adsorption capacity at 30℃/ (cm3·g-1) | Working capacity/ (cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPL-1 | 36.8 | 12.0 | 24.8 |
| MN@CPL-1-1 | 32.5 | 10.8 | 21.7 |
| MN@CPL-1-2 | 33.4 | 11.4 | 22.0 |
| MN@CPL-1-3 | 34.0 | 11.5 | 22.5 |
| MN@CPL-1-4 | 28.1 | 10.5 | 17.6 |
| Sample | Tl /℃ | Th/℃ | Working capacity/(cm3·g-1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MN@CPL-1-3 | 10 | 30 | 22.50 | This work |
| MAC-4 | 0 | 25 | 13.00 | [ |
| HP-Cu-BTC | 0 | 25 | 6.98 | [ |
| MIL-101 | 20 | 40 | 14.45 | [ |
| ZIF-8 | 0 | 20 | 8.58 | [ |
| Ni-MOF-74 | 25 | 50 | 7.84 | [ |
| 5A | 0 | 20 | 4.14 | [ |
| zeolite 4A | 150 | 185 | 10.30 | [ |
| SG-1 | 20 | 40 | 3.18 | [ |
Table 3 Working capacities of different kinds of C3H6 adsorbents
| Sample | Tl /℃ | Th/℃ | Working capacity/(cm3·g-1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MN@CPL-1-3 | 10 | 30 | 22.50 | This work |
| MAC-4 | 0 | 25 | 13.00 | [ |
| HP-Cu-BTC | 0 | 25 | 6.98 | [ |
| MIL-101 | 20 | 40 | 14.45 | [ |
| ZIF-8 | 0 | 20 | 8.58 | [ |
| Ni-MOF-74 | 25 | 50 | 7.84 | [ |
| 5A | 0 | 20 | 4.14 | [ |
| zeolite 4A | 150 | 185 | 10.30 | [ |
| SG-1 | 20 | 40 | 3.18 | [ |
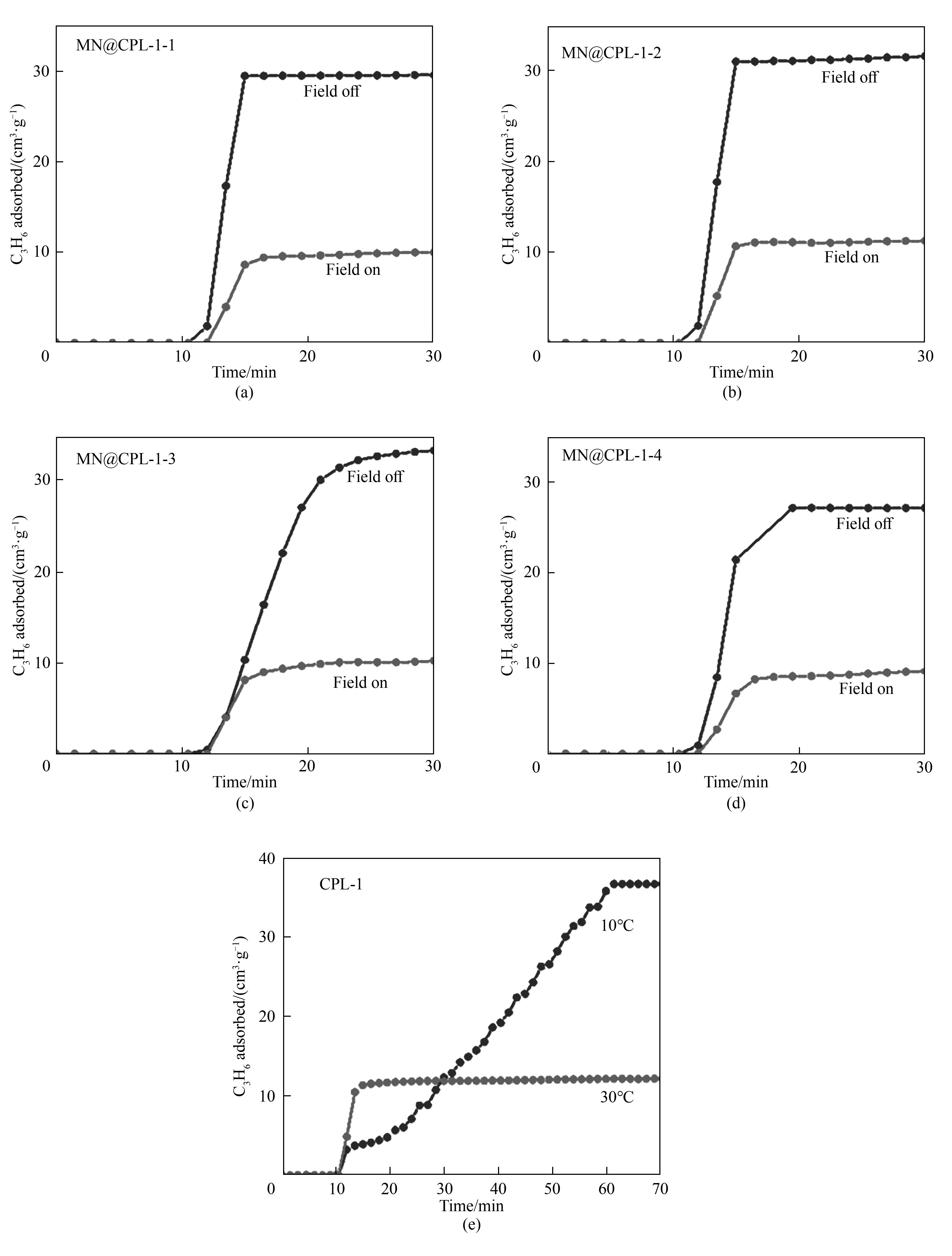
Fig.14 Dynamic adsorption curves of MN@CPL-1-1 (a), MN@CPL-1-2 (b), MN@CPL-1-3 (c), and MN@CPL-1-4 (d) with the alternating magnetic field on and off; (e) Dynamic adsorption curve of CPL-1 at 10 ℃ and 30 ℃
| 1 | Cui J Y, Zhang Z Q, Yang L F, et al. A molecular sieve with ultrafast adsorption kinetics for propylene separation[J]. Science, 2024, 383(6679): 179-183. |
| 2 | Fu H L, Huang J Y, van der Tol J J B, et al. Supramolecular polymers form tactoids through liquid-liquid phase separation[J]. Nature, 2024, 626(8001): 1011-1018. |
| 3 | Mattocks J A, Jung J J, Lin C Y, et al. Enhanced rare-earth separation with a metal-sensitive lanmodulin dimer[J]. Nature, 2023, 618(7963): 87-93. |
| 4 | Mensah M A, Niskanen H, Magalhaes A P, et al. Aberrant phase separation and nucleolar dysfunction in rare genetic diseases[J]. Nature, 2023, 614(7948): 564-571. |
| 5 | Zhang H L, Li A, Li K, et al. Ultrafiltration separation of Am(Ⅵ)-polyoxometalate from lanthanides[J]. Nature, 2023, 616(7957): 482-487. |
| 6 | 任其龙, 杨启炜, 鲍宗必. 中国气体分离领域发展现状和未来挑战[J]. 科学观察, 2023, 18(5): 13-16. |
| Ren Q L, Yang Q W, Bao Z B. Development status and future challenges in the field of gas separation in China[J]. Science Focus, 2023, 18(5): 13-16. | |
| 7 | 张凯博, 沈佳新, 李玉霞, 等. Y沸石中Cu(Ⅰ)的可控构筑及其乙烯/乙烷吸附分离性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1607-1615. |
| Zhang K B, Shen J X, Li Y X, et al. Controllable construction of Cu(Ⅰ) in Y zeolite for adsorptive separation of ethylene/ethane[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1607-1615. | |
| 8 | 郭智芳, 张信伟, 王海洋, 等. 石脑油正异构烷烃吸附分离技术[J]. 当代化工, 2024, 53(7): 1703-1710. |
| Guo Z F, Zhang X W, Wang H Y, et al. Technology of adsorption and separation of n/iso-alkanes in naphtha[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2024, 53(7): 1703-1710. | |
| 9 | Dai H, Yuan X Z, Jiang L B, et al. Recent advances on ZIF-8 composites for adsorption and photocatalytic wastewater pollutant removal: fabrication, applications and perspective[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2021, 441: 213985. |
| 10 | Deutz S, Bardow A. Life-cycle assessment of an industrial direct air capture process based on temperature-vacuum swing adsorption[J]. Nature Energy, 2021, 6: 203-213. |
| 11 | Saheed I O, Oh W D, Suah F B M. Chitosan modifications for adsorption of pollutants—a review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 408: 124889. |
| 12 | Verougstraete B, Gholami M, Gomez-Rueda Y, et al. Advancements and challenges in electric heating for enhanced temperature swing adsorption processes[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 353: 128522. |
| 13 | Li Y C, Delmo E P, Hou G Y, et al. Enhancing local CO2 adsorption by L-histidine incorporation for selective formate production over the wide potential window[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(49): e202313522. |
| 14 | Zhang Z Q, Chen Y L, Chai K G, et al. Temperature-dependent rearrangement of gas molecules in ultramicroporous materials for tunable adsorption of CO2 and C2H2 [J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 3789. |
| 15 | Du X D, Cheng Y G, Liu Z J, et al. CO2 and CH4 adsorption on different rank coals: a thermodynamics study of surface potential, Gibbs free energy change and entropy loss[J]. Fuel, 2021, 283: 118886. |
| 16 | Dang Y X, Tan P, Hu B, et al. Low-energy-consumption temperature swing system for CO2 capture by combining passive radiative cooling and solar heating[J]. Green Energy & Environment, 2024, 9(3): 507-515. |
| 17 | 王丽, 王兴杰, 李浩, 等. 葡萄糖基多孔碳材料对CO2/CH4的分离性能[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(2): 733-740. |
| Wang L, Wang X J, Li H, et al. Separation performance of CO2/CH4 on porous carbons derived from glucose[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(2): 733-740. | |
| 王丽, 王兴杰, 李浩, 等. 葡萄糖基多孔碳材料对CO2/CH4的分离性能[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(2): 733-740. | |
| Wang L, Wang X J, Li H, et al. Separation performance of CO2/CH4 on porous carbons derived from glucose[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(2): 733-740. | |
| 18 | 阎海宇, 付强, 周言, 等. 真空变压吸附捕集烟道气中二氧化碳的模拟、实验及分析[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(6): 2371-2379. |
| Yan H Y, Fu Q, Zhou Y, et al. Simulation, experimentation and analyzation of vacuum pressure swing adsorption process for CO2 capture from dry flue gas[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(6): 2371-2379. | |
| 19 | Gu C, Tan P, Jiang T Y, et al. Solar-radiation-induced adsorption/desorption system for carbon dioxide capture[J]. Cell Reports Physical Science, 2022, 3: 101122. |
| 20 | Jacobs J H, Deering C E, Sui R H, et al. Degradation of desiccants in temperature swing adsorption processes: the temperature dependent degradation of zeolites 4A, 13X and silica gels[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 451: 139049. |
| 21 | Zanco S E, Ambrosetti M, Groppi G, et al. Heat transfer intensification with packed open-cell foams in TSA processes for CO2 capture[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 430: 131000. |
| 22 | Huang G S, Huang C, Tao Y L, et al. Localized heating driven selective growth of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) in wood: a novel synthetic strategy for significantly enhancing MOF loadings in wood[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 564: 150325. |
| 23 | Tao Y L, Li Q Q, Wu Q N, et al. Embedding metal foam into metal-organic framework monoliths for triggering a highly efficient release of adsorbed atmospheric water by localized eddy current heating[J]. Materials Horizons, 2021, 8(5): 1439-1445. |
| 24 | Li X M, Tan P, Sun Z, et al. Magnetic MOFs with flexibility for efficient magnetic-induced swing adsorption[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024, 348: 127723. |
| 25 | De Belder M, Morais A F, De Vos N, et al. Performance of ferrite nanoparticles in inductive heating swing adsorption (IHSA): how tailoring material properties can circumvent the design limitations of a system[J]. Materials Horizons, 2024, 11(17): 4144-4149. |
| 26 | Bellusci M, Masi A, Albino M, et al. Fe3O4@HKUST-1 magnetic composites by mechanochemical route for induction triggered release of carbon dioxide[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2021, 328: 111458. |
| 27 | Maity R, Gholami M, Peter S A, et al. Strategic fast induction heating to combat hysteresis barriers in a flexible MOF for rapid CO2 desorption in biogas upgrading[J]. Small, 2023, 19(29): 2302893. |
| 28 | Schoukens M, Sharma R, Laha P, et al. Enhancing desorption performance of a compressible hybrid structured adsorbent via localized magnetic induction heating[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2024, 11(19): 2400105. |
| 29 | Zeng H, Xie M, Wang T, et al. Orthogonal-array dynamic molecular sieving of propylene/propane mixtures[J]. Nature, 2021, 595(7868): 542-548. |
| 30 | Deng Y H, Cai Y, Sun Z K, et al. Multifunctional mesoporous composite microspheres with well-designed nanostructure: a highly integrated catalyst system[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(24): 8466-8473. |
| 31 | Wang G D, Li Y Z, Krishna R, et al. Scalable synthesis of robust MOF for challenging ethylene purification and propylene recovery with record productivity[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(15): e202319978. |
| 32 | Yang P, Li Y X, Liang W B, et al. Prediction of adsorption isotherms of C3H6/C3H8 on hierarchical porous HP-Cu-BTC[J]. Journal of the Indian Chemical Society, 2022, 99(9): 100657. |
| 33 | Su W, Zhang A, Sun Y, et al. Adsorption properties of C2H4 and C3H6 on 11 adsorbents[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2017, 62(1): 417-421. |
| 34 | Chen D L, Shang H, Zhu W D, et al. Transient breakthroughs of CO2/CH4 and C3H6/C3H8 mixtures in fixed beds packed with Ni-MOF-74[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2014, 117: 407-415. |
| 35 | Patiño-Iglesias M E, Aguilar-Armenta G, Jiménez-López A, et al. Kinetics of the total and reversible adsorption of propylene and propane on zeolite 4A (CECA) at different temperatures[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2004, 237(1/2/3): 73-77. |
| [1] | Yaohui ZHANG, Yujie BAN, Weishen YANG. Vapor-phase synthesis and post-synthetic modification of metal-organic framework membranes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2070-2086. |
| [2] | Yanan YANG, Shengran CHANG, Songlin XUE, Jianming PAN, Weihong XING. Progress of research on photo- and electric-driven to promote uranium and lithium extraction from seawater [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 1927-1942. |
| [3] | Zibo YANG, Youfa WANG, Hansong YUE, Shuangjie YUAN, Fujiang GENG, Qingqing LI, De AO, Bin LI, Mao YE, Zhenjie GU, Zhihua QIAO. Recent progress of MOF glasses based gas separation membrane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2158-2168. |
| [4] | Di ZHU, Shoujian GAO, Wangxi FANG, Jian JIN. Construction of PES membranes with sponge-like pores and stable super-hydrophilicity through vapor-induced phase separation for oil-in-water emulsion separation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2397-2409. |
| [5] | Jinyue WANG, Enze XIE, Hanze MA, Sheng YUAN, Guangwei HE, Zhongyi JIANG. Monoatomic layer separation membrane: progress and prospect [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 1943-1959. |
| [6] | Yanqiu LU, Yang DI, Wenbo SHI, Congcong YIN, Yong WANG. Research progress of smart responsive membranes based on novel porous organic polymers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2101-2118. |
| [7] | Hao QI, Yujie WANG, Shenhui LI, Qi ZOU, Yiqun LIU, Zhiping ZHAO. Molecular simulation study on adsorption and diffusion of C3H6 and C3H8 on Co/Zn-ZIFs [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2313-2326. |
| [8] | Chunhui TAO, Yinhui LI, Yu FU, Ran DUAN, Zeyi ZHAO, Yufeng TANG, Gang ZHANG, Heping MA. Selective adsorption and purification of low-concentration Kr gas using various adsorbents [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2358-2366. |
| [9] | Haofan ZHAO, Haojie REN, Zongkai LIU, Guanying DONG, Yatao ZHANG. Research progress of MOFs glass membranes in gas separation applications [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2042-2054. |
| [10] | Yue ZHANG, Jiaxin LIU, Jing MA, Yi LIU. Recent progress on metal-organic framework membranes towards uranium separation from seawater [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2087-2100. |
| [11] | Ruijie MA, Zixuan HUANG, Xueqian GUAN, Guangjin CHEN, Bei LIU. Efficient ethane and methane separation using ZIF-8/DMPU slurry [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2262-2269. |
| [12] | Bingbing GAO, Nuo XU, Yunxiang BAI, Chunfang ZHANG, Yongqiang YANG, Liangliang DONG. Polymeric membranes for helium separation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2119-2135. |
| [13] | Liao HE, Jun LI, Mengshu GAO, Dongyang LIU, Yuhao ZHANG, Liang ZHAO, Jinsen GAO, Chunming XU. Research progress on aromatic hydrocarbons separation from petroleum hydrocarbons [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 1909-1926. |
| [14] | Zehai XU, Chao LIU, Guoliang ZHANG. Hydrophobic pervaporation membranes on polymer substrate for solvent recovery [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2055-2069. |
| [15] | Zhichao XU, Zhendong YU, Haofeng WU, Peiwen WU, Hongxiang WU, Yanhong CHAO, Wenshuai ZHU, Zhichang LIU, Chunming XU. Preparation of acid-rich 13X molecular sieve and its ultra-deep adsorption removal of mercaptan in biodiesel [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2198-2208. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||