化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (10): 3623-3638.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240259
王龙龙1,2( ), 秦志峰1,2(
), 秦志峰1,2( ), 班红艳1,2, 李乃珍1,2, 杜朕屹1,2, 于峰2, 翟志强3, 吴琼笑4
), 班红艳1,2, 李乃珍1,2, 杜朕屹1,2, 于峰2, 翟志强3, 吴琼笑4
收稿日期:2024-03-04
修回日期:2024-06-18
出版日期:2024-10-25
发布日期:2024-11-04
通讯作者:
秦志峰
作者简介:王龙龙(1999—),男,硕士研究生, 15383414720@163.com
基金资助:
Longlong WANG1,2( ), Zhifeng QIN1,2(
), Zhifeng QIN1,2( ), Hongyan BAN1,2, Naizhen LI1,2, Zhenyi DU1,2, Feng YU2, Zhiqiang ZHAI3, Qiongxiao WU4
), Hongyan BAN1,2, Naizhen LI1,2, Zhenyi DU1,2, Feng YU2, Zhiqiang ZHAI3, Qiongxiao WU4
Received:2024-03-04
Revised:2024-06-18
Online:2024-10-25
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
Zhifeng QIN
摘要:
探讨了Al2O3载体孔结构对FeMo/Al2O3预加氢脱硫(HDS)催化剂活性和选择性的影响,采用浸渍法制备了一系列具有不同孔结构的FeMo/Al2O3催化剂,并通过微型固定床技术对其在模拟焦炉煤气中COS、CS2、C4H4S和C2H4的HDS活性和选择性进行了系统评价,通过N2吸附-脱附、红外碳硫、XRD、NH3-TPD、H2-TPR、XPS、Raman以及HRTEM等技术对催化剂进行了表征。研究结果表明,Al2O3载体孔结构对催化剂活性相MoS2有显著影响,从而影响加氢脱硫活性和选择性,其中较大孔径的载体更有利于COS和CS2的有效转化,而较小孔径的载体则更倾向于促进C4H4S和C2H4的转化;此外,具有较大孔径的催化剂不仅展现出更低的积炭倾向,还通过提高Mo物种的分散性,有效调控了MoS2片晶的生长尺寸和层数,从而在COS和CS2的加氢脱硫活性上显示了优异性能。研究结果为高效HDS催化剂的设计与开发开辟了新途径。
中图分类号:
王龙龙, 秦志峰, 班红艳, 李乃珍, 杜朕屹, 于峰, 翟志强, 吴琼笑. Al2O3载体孔结构优化:提升FeMo/Al2O3催化剂在焦炉煤气加氢脱硫性能[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3623-3638.
Longlong WANG, Zhifeng QIN, Hongyan BAN, Naizhen LI, Zhenyi DU, Feng YU, Zhiqiang ZHAI, Qiongxiao WU. Optimization of Al2O3 support pore structure: enhancing the hydrodesulfurization performance of FeMo/Al2O3 catalyst in coke oven gas[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(10): 3623-3638.
| 样品 | 孔体积/ (cm3·g-1) | 比表面积/ (m2·g-1) | 平均孔径/nm | 吸水率/ (ml·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a-Al2O3载体 | 0.86 | 246.4 | 12.4 | 129.41 |
| b-Al2O3载体 | 0.78 | 285.8 | 10.2 | 148.91 |
| c-Al2O3载体 | 0.65 | 263.2 | 9.6 | 107.53 |
| d-Al2O3载体 | 0.62 | 214.2 | 8.8 | 116.30 |
| e-Al2O3载体 | 0.49 | 254.7 | 8.2 | 70.33 |
表1 Al2O3载体孔结构参数和吸水率
Table 1 Pore structure parameters and water absorption of the Al2O3 supports
| 样品 | 孔体积/ (cm3·g-1) | 比表面积/ (m2·g-1) | 平均孔径/nm | 吸水率/ (ml·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a-Al2O3载体 | 0.86 | 246.4 | 12.4 | 129.41 |
| b-Al2O3载体 | 0.78 | 285.8 | 10.2 | 148.91 |
| c-Al2O3载体 | 0.65 | 263.2 | 9.6 | 107.53 |
| d-Al2O3载体 | 0.62 | 214.2 | 8.8 | 116.30 |
| e-Al2O3载体 | 0.49 | 254.7 | 8.2 | 70.33 |
| 气体 | 纯度或含量 | 平衡气体 |
|---|---|---|
| 乙烯 | 99.9% | |
| 氮气 | 99.99% | |
| 预硫化气体 | H2S 3% | H2 |
| 含硫反应气体 | COS 170.86 mg·m-3、CS2 130.53 mg·m-3、 C4H4S 18.45 mg·m-3 | H2 |
| 硫化物标气 | H2S 204.95 mg·m-3、COS 222.22 mg·m-3、CH3SH 142.07 mg·m-3、C2H5SH 140.91 mg·m-3、CH3SCH3 146.19 mg·m-3、CS2 224.54 mg·m-3、C4H4S 210.93 mg·m-3、CH3S2CH3 212.46 mg·m-3、C2H5SCH3 209.91 mg·m-3、(C2H5)S 209.42 mg·m-3 | N2 |
表2 实验所用气体组分和纯度
Table 2 Test gas composition and concentration
| 气体 | 纯度或含量 | 平衡气体 |
|---|---|---|
| 乙烯 | 99.9% | |
| 氮气 | 99.99% | |
| 预硫化气体 | H2S 3% | H2 |
| 含硫反应气体 | COS 170.86 mg·m-3、CS2 130.53 mg·m-3、 C4H4S 18.45 mg·m-3 | H2 |
| 硫化物标气 | H2S 204.95 mg·m-3、COS 222.22 mg·m-3、CH3SH 142.07 mg·m-3、C2H5SH 140.91 mg·m-3、CH3SCH3 146.19 mg·m-3、CS2 224.54 mg·m-3、C4H4S 210.93 mg·m-3、CH3S2CH3 212.46 mg·m-3、C2H5SCH3 209.91 mg·m-3、(C2H5)S 209.42 mg·m-3 | N2 |
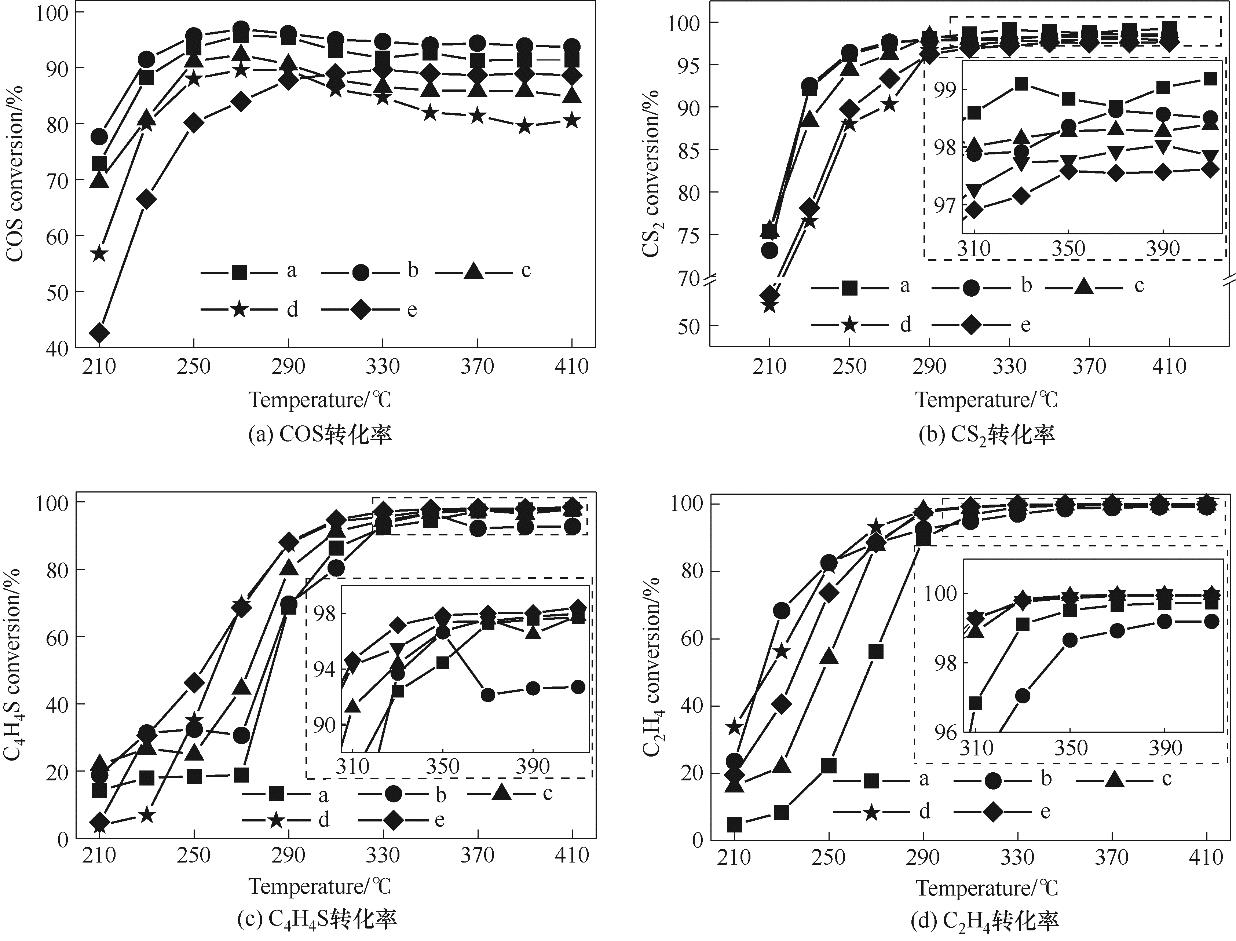
图1 不同孔结构载体FeMo/Al2O3催化剂HDS活性[反应条件:压力1.0 MPa,空速5400 h-1(含硫反应气体与C2H4体积比为5∶1)]a-FeMo/a-Al2O3; b-FeMo/b-Al2O3; c-FeMo/c-Al2O3; d-FeMo/d-Al2O3; e-FeMo/e-Al2O3
Fig.1 HDS performance of FeMo/Al2O3 catalysts of different support pore structures

图2 不同孔结构载体FeMo/Al2O3催化剂加氢产物分布[反应条件:压力1.0 MPa,空速5400 h-1(含硫反应气体与C2H4体积比为5∶1)]
Fig.2 HDS reaction product composition of FeMo/Al2O3 catalyst at different support pore structures
| 催化剂样品 | 比表面积/(m2·g-1) | 孔体积/(cm3·g-1) | 平均孔径/nm | 碳含量/%(质量分数) | 硫含量/%(质量分数) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeMo/a-Al2O3 | 新鲜催化剂 | 226.3 | 0.82 | 13.1 | 0.03 | 0.36 |
| 反应后催化剂 | 210.6 | 0.81 | 13.6 | 0.37 | 3.41 | |
| FeMo/b-Al2O3 | 新鲜催化剂 | 276.1 | 0.72 | 10.7 | 0.03 | 0.20 |
| 反应后催化剂 | 227.2 | 0.65 | 11.1 | 0.48 | 3.08 | |
| FeMo/c-Al2O3 | 新鲜催化剂 | 218.6 | 0.61 | 10.3 | 0.03 | 0.21 |
| 反应后催化剂 | 200.9 | 0.59 | 10.7 | 1.07 | 3.37 | |
| FeMo/d-Al2O3 | 新鲜催化剂 | 207.4 | 0.60 | 10.2 | 0.04 | 0.23 |
| 反应后催化剂 | 170.2 | 0.56 | 10.8 | 1.04 | 3.46 | |
| FeMo/e-Al2O3 | 新鲜催化剂 | 221.8 | 0.45 | 8.6 | 0.02 | 0.21 |
| 反应后催化剂 | 194.3 | 0.41 | 8.9 | 1.06 | 2.87 | |
表3 FeMo/Al2O3催化剂反应前后物理性能
Table 3 Textural properties of the FeMo/Al2O3 catalysts before and after reaction
| 催化剂样品 | 比表面积/(m2·g-1) | 孔体积/(cm3·g-1) | 平均孔径/nm | 碳含量/%(质量分数) | 硫含量/%(质量分数) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeMo/a-Al2O3 | 新鲜催化剂 | 226.3 | 0.82 | 13.1 | 0.03 | 0.36 |
| 反应后催化剂 | 210.6 | 0.81 | 13.6 | 0.37 | 3.41 | |
| FeMo/b-Al2O3 | 新鲜催化剂 | 276.1 | 0.72 | 10.7 | 0.03 | 0.20 |
| 反应后催化剂 | 227.2 | 0.65 | 11.1 | 0.48 | 3.08 | |
| FeMo/c-Al2O3 | 新鲜催化剂 | 218.6 | 0.61 | 10.3 | 0.03 | 0.21 |
| 反应后催化剂 | 200.9 | 0.59 | 10.7 | 1.07 | 3.37 | |
| FeMo/d-Al2O3 | 新鲜催化剂 | 207.4 | 0.60 | 10.2 | 0.04 | 0.23 |
| 反应后催化剂 | 170.2 | 0.56 | 10.8 | 1.04 | 3.46 | |
| FeMo/e-Al2O3 | 新鲜催化剂 | 221.8 | 0.45 | 8.6 | 0.02 | 0.21 |
| 反应后催化剂 | 194.3 | 0.41 | 8.9 | 1.06 | 2.87 | |
| 催化剂 | Mo4+/%① | Mo5+/%① | Mo6+/%① | SMo② | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 229.0 eV | 232.2 eV | 230.5 eV | 233.6 eV | 233.5 eV | 236.2 eV | ||
| FeMo/a-Al2O3 | 29 | 25 | 8 | 1 | 21 | 17 | 54 |
| FeMo/b-Al2O3 | 21 | 25 | 7 | 6 | 20 | 21 | 46 |
| FeMo/c-Al2O3 | 15 | 28 | 4 | 6 | 20 | 17 | 43 |
| FeMo/d-Al2O3 | 15 | 27 | 14 | 4 | 19 | 22 | 42 |
| FeMo/e-Al2O3 | 20 | 19 | 7 | 3 | 30 | 21 | 40 |
表4 反应后催化剂XPS表面元素含量
Table 4 Surface compositions of used catalysts calculated from XPS spectra for Mo and S elements
| 催化剂 | Mo4+/%① | Mo5+/%① | Mo6+/%① | SMo② | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 229.0 eV | 232.2 eV | 230.5 eV | 233.6 eV | 233.5 eV | 236.2 eV | ||
| FeMo/a-Al2O3 | 29 | 25 | 8 | 1 | 21 | 17 | 54 |
| FeMo/b-Al2O3 | 21 | 25 | 7 | 6 | 20 | 21 | 46 |
| FeMo/c-Al2O3 | 15 | 28 | 4 | 6 | 20 | 17 | 43 |
| FeMo/d-Al2O3 | 15 | 27 | 14 | 4 | 19 | 22 | 42 |
| FeMo/e-Al2O3 | 20 | 19 | 7 | 3 | 30 | 21 | 40 |
| 催化剂 | 平均堆叠层数 | 平均片晶长度/nm |
|---|---|---|
| FeMo/a-Al2O3 | 2.56 | 4.52 |
| FeMo/b-Al2O3 | 2.75 | 4.72 |
| FeMo/c-Al2O3 | 3.31 | 8.56 |
| FeMo/d-Al2O3 | 5.25 | 9.4 |
| FeMo/e-Al2O3 | 8.28 | 10.88 |
表5 反应后催化剂TEM统计结果
Table 5 TEM statistical results of the used catalysts
| 催化剂 | 平均堆叠层数 | 平均片晶长度/nm |
|---|---|---|
| FeMo/a-Al2O3 | 2.56 | 4.52 |
| FeMo/b-Al2O3 | 2.75 | 4.72 |
| FeMo/c-Al2O3 | 3.31 | 8.56 |
| FeMo/d-Al2O3 | 5.25 | 9.4 |
| FeMo/e-Al2O3 | 8.28 | 10.88 |
| 1 | Moral G, Ortiz-imedio R, Oritz A, et al. Hydrogen recovery from coke oven gas comparative analysis of technical altematives[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2022, 61(18): 6106-6124. |
| 2 | Zhou J B, Guo Y J, Huang Z W, et al. A review and prospects of gas mixture containing hydrogen as vehicle fuel in China[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(56): 29776-29784. |
| 3 | Razzaq R, Li C S, Zhanf S J. Coke oven gas: availability, properties, purification, and utilization in China[J]. Fuel, 2013, 113: 287-299. |
| 4 | Qu Y X, Xu H M, Zhao J F, et al. Conversion and reaction kinetics of coke oven gas over a commercial Fe-Mo/Al2O3 catalyst[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23(2): 293-302. |
| 5 | Al-Degs Y S, El-Sheikh A H, Al Bakain R Z, et al. Conventional and upcoming sulfur-cleaning technologies for petroleum fuel: a review[J]. Energy Technology: Generation,Conversion,Storage,Distribution, 2016, 4(6): 679-699. |
| 6 | Weng X Y, Cao L Y, Zhang G H, et al. Ultradeep hydrodesulfurization of diesel: mechanisms, catalyst design strategies, and challenges[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(49): 21261-21274. |
| 7 | Shafiq I, Shafique S, Akhter P,et al. Recent developments in alumina supported hydrodesulfurization catalysts for the production of sulfur-free refinery products: a technical review[J].Catalysis Reviews, 2022, 64(1): 1-86. |
| 8 | 王艾荣, 虎骁, 史军伟, 等. 焦炉煤气催化加氢转化精脱硫工艺及生产实践[J]. 煤化工, 2016, 44(6): 42-44. |
| Wang A R, Hu X, Shi J W, et al. Catalytic hydrogenation conversion fine desulfurization process of coke oven gas and its production practice[J]. Coal Chemical Industry, 2016, 44(6): 42-44. | |
| 9 | 郭玉峰, 蒋晓娟. 焦炉气净化中的有机硫加氢工艺应用技术[J]. 山西化工, 2017, 37(3): 52-55. |
| Guo Y F, Jiang X J. Application technology of organic sulfur hydrogenation process in purification of coke oven gas[J]. Shanxi Chemical Industry, 2017, 37(3): 52-55. | |
| 10 | 汪佩华, 秦志峰, 吴琼笑, 等. 磷添加方式对NiMo/Al2O3催化剂加氢脱硫性能的影响[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(2): 890-900. |
| Wang P H, Qin Z F, Wu Q X, et al. Effect of phosphorus adding manners on the performance of NiMo/Al2O3 catalyst in hydrodesulfurization[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(2): 890-900. | |
| 11 | 裴学国, 亓栋, 丁卉, 等. T202型催化剂在焦炉气二级加氢脱硫工艺中的应用[J]. 化肥设计, 2011, 49(5): 48-51. |
| Pei X G, Qi D, Ding H, et al. Application for T202 type catalyst in hydrogenation desulphurization process of coking-oven gas in 2 stages[J]. Chemical Fertilizer Design, 2011, 49(5): 48-51. | |
| 12 | 王贵. 焦炉煤气脱硫技术进展与分析[J]. 煤化工, 2021, 49(4): 57-61. |
| Wang G. Development and analysis of desulfurization technology of coke oven gas[J]. Coal Chemical Industry, 2021, 49(4): 57-61. | |
| 13 | 朱军利, 张林生, 盛明泽, 等. JT-8型焦炉煤气加氢催化剂失活样品剖析[J]. 工业催化, 2020, 28(9): 45-50. |
| Zhu J L, Zhang L S, Sheng M Z, et al. Analysis of deactivated hydrogenation catalyst JT-8[J]. Industrial Catalysis, 2020, 28(9): 45-50. | |
| 14 | 杨宝刚, 黄成忠, 朱军利. JT-8型加氢催化剂在焦炉煤气制甲醇装置上的工业应用[J]. 工业催化, 2014, 22(8): 628-631. |
| Yang B G, Huang C Z, Zhu J L. Commercial application of JT-8 hydrogenation catalyst in the plant of methanol synthesized from coke oven gas[J]. Industrial Catalysis, 2014, 22(8): 628-631. | |
| 15 | Kraleva E, Spojakina A, Jiratova K, et al. Support effect on the properties of iron-molybdenum hydrodesulfurization catalysts[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2006, 112(3): 203-212. |
| 16 | Puello-Polo E, Brito J L. Effect of the type of precursor and the synthesis method on thiophene hydrodesulfurization activity of activated carbon supported Fe-Mo, Co-Mo and Ni-Mo carbides[J].Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2008, 281(1/2): 85-92. |
| 17 | Yin F K, Yu J L, Dou J X, et al. Sulfidation of Iron-based sorbents supported on activated chars during the desulfurization of coke oven gases: effects of Mo and Ce addition[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(4): 2481-2489. |
| 18 | 韩龙年, 辛靖, 陈禹霏, 等. SEM-EDS组合手段对加氢催化剂失活的分析及应用[J].工业催化, 2023, 31(1): 56-63. |
| Han L N, Xin J, Chen Y F, et al. Analysis and application for deactivation of hydrogenation catalyst by SEM-EDS combination means[J]. Industrial Catalysis, 2023, 31(1): 56-63. | |
| 19 | Zhang D, Liu X M, Liu Y X, et al. Impact of γ-alumina pore structure on structure and performance of Ni-Mo/γ-Al2O3 catalyst for 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene desulfurization[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2021, 310: 110637. |
| 20 | Chen W, Nie H, Long X, et al. Role of pore structure on the activity and stability of sulfide catalyst[J]. Catalysis Today, 2021, 377: 69-81. |
| 21 | Dong Y Y, Xu Y R, Zhang X Q, et al. Synthesis of hierarchically structured alumina support with adjustable nanocrystalline aggregation towards efficient hydrodesulfurization[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2018, 559: 30-39. |
| 22 | 郭蓉, 沈本贤, 方向晨, 等. 载体孔结构对加氢脱硫催化剂催化性能的影响[J].石油学报(石油加工), 2012, 28(5): 724-729. |
| Guo R, Shen B X, Fang X C, et al. Effect of support pore structure on hydrodesulfurization performance of catalyst[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 2012, 28(5): 724-729. | |
| 23 | Wang T H, Fan Y, Wang X L, et al. Selectivity enhancement of CoMoS catalysts supported on tri-modal porous Al2O3 for the hydrodesulfurization of fluid catalytic cracking gasoline[J]. Fuel, 2015, 157(1): 171-176. |
| 24 | Badoga S, Sharma R V, Dalai A K, et al. Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous aluminas with different pore sizes: application in NiMo supported catalyst for hydrotreating of heavy gas oil[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2015, 489: 86-97. |
| 25 | Yuan P, Liu J X, Li Y T, et al. Effect of pore diameter and structure of mesoporous sieve supported catalysts on hydrodesulfurization performance[J].Chemical Engineering Science, 2014, 111: 381-389. |
| 26 | 李乃珍, 孙瑞洁, 秦志峰, 等. 焦炉煤气常量含碳气氛对加氢脱硫催化剂活性、选择性和积炭的影响[J].化工进展, 2023, 42(2): 783-793. |
| Li N Z, Sun R J, Qin Z F,et al. Effects of constant carbon atmosphere on the activity, selectivity and coking of catalysts in hydrodesulfurization of coke oven gas[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(2):783-793. | |
| 27 | 穆福军, 隋宝宽, 刘文洁, 等. 渣油加氢处理催化剂失活研究[J]. 石油化工, 2022, 51(9): 1044-1051. |
| Mu F J, Sui B K, Liu W J, et al. Study on deactivation of residue hydrotreating catalyst[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 2022, 51(9): 1044-1051. | |
| 28 | 李硕, 刘熠斌, 冯翔, 等. MoS2基催化剂加氢脱硫反应活性相和作用机理研究进展[J].化工进展, 2019, 38(2):867-875. |
| Li S, Liu Y B, Feng X, et al. Research progress in active phase structure and reaction mechanism of MoS2-based catalysts for hydrodesulfurization[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(2): 867-875. | |
| 29 | Zhang D, Xue L J, Xu Y Q, et al. Adsorption of 4, 6-dimethyldibenzothiophene and collidine over MoO3/γ-Al2O3 catalysts with different pore structures[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2017, 493: 218-227. |
| 30 | Singh S B, De M. Room temperature adsorptive removal of thiophene over zinc oxide-based adsorbents[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2018, 27(6): 2661-2667. |
| 31 | Frilund C, Simell P, Kaisalo N, et al. Desulfurization of biomass syngas using ZnO-based adsorbents: long-term hydrogen sulfide breakthrough experiments[J]. Energy & Fuels: an American Chemical Society Journal, 2020, 34(3): 3316-3325. |
| 32 | Buttrill S E. Ion-molecule reactions of hydrogen sulfide with ethylene and acetylene[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1970, 92(12): 3560-3564. |
| 33 | 袁礼, 王学谦, 李翔, 等. 催化脱除钢铁副产煤气中COS和H2S的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(10): 5147-5161. |
| Yuan L, Wang X Q, Li X, et al. Research advances on catalytic removal COS and H2S from by-product gas in iron and steel industry[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(10): 5147-5161. | |
| 34 | 张海鹰, 王旭珍, 郑军, 等. 高温煤气中羰基硫的加氢脱除研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2008, 37(8): 943-947. |
| Zhang H Y, Wang X Z, Zheng J, et al. Research progress of hydrodesulfurization of carbonyl sulfide in hot coal gas[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2008, 37(8): 943-947. | |
| 35 | 王成, 邵春宇, 姚劲, 等. 二硫化碳对Ni/Al2O3加氢催化剂中毒机理的研究[J]. 当代化工, 2019, 48(11): 2445-2448. |
| Wang C, Shao C Y, Yao J, et al. Study on the mechanism of Ni/ Al2O3 catalyst poisoning caused by CS2 [J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2019, 48(11): 2445-2448. | |
| 36 | 于沛, 柯明, 刘强,等. CoMo/γ-Al2O3选择性加氢脱硫催化剂上硫醇的生成反应[J]. 石油化工, 2016, 45(6): 691-696. |
| Yu P, Ke M, Liu Q, et al. Production of mercaptan in selective hydrodesulfurization over CoMo/γ-Al2O3 catalyst[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 2016, 45(6): 691-696. | |
| 37 | Shi Y, Wang G, Mei J L, et al. The influence of pore structure and acidity on the hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene over NiMo-supported catalysts[J].ACS Omega, 2020, 5(25):15576-15585. |
| 38 | 于秋莹, 王永林, 袁胜华, 等. 球形氧化铝载体结构优化[J]. 当代化工, 2024, 53(5):1086-1089. |
| Yu Q Y, Wang Y L, Yuan S H, et al. Optimization of spherical alumina support structure[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2024, 53(5):1086-1089. | |
| 39 | 郑金玉, 罗一斌, 舒兴田. 孔结构与酸性质对多孔氧化铝材料催化性能的影响研究[J]. 石油炼制与化工, 2018, 49(12): 27-33. |
| Zheng J Y, Luo Y B, Shu X T. Effect of pore structure and acidic property on catalytic properties of porous alumina materials[J]. Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals, 2018, 49(12): 27-33. | |
| 40 | Guo X M, Song M N, Zhao X, et al. Effect of fluoride promoter on the catalytic activity of NiWF/γ-Al2O3 for hydrodenitrogenation and hydrodesulfurization of coal tar[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2016, 44(11): 1326-1333. |
| 41 | Hao L, Xiong G, Liu L P, et al. Preparation of highly dispersed desulfurization catalysts and their catalytic performance in hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2016, 37(3): 412-419. |
| 42 | Sui B K, Wang G, Yuan S H, et al. Macroporous Al2O3 with three-dimensionally interconnected structure: catalytic performance of hydrodemetallization for residue oil[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2021, 49(8): 1201-1207. |
| 43 | Peng C, Guo R, Feng X, et al. Tailoring the structure of Co-Mo/mesoporous γ-Al2O3 catalysts by adding multi-hydroxyl compound: a 3000 kt/a industrial-scale diesel ultra-deep hydrodesulfurization study[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 377: 119706. |
| 44 | Liu T B, Sun P L, Zhu H H, et al. The effect of hydroxyl and metal synergetic structures on the FCC diesel hydrotreating performance of NiMo/Al2O3 catalysts[J]. Fuel, 2024, 356: 129487. |
| 45 | Zhang Y, Zhou K D, Zhang L F, et al. Synthesis of mesoporous γ-Al2O3 by using cellulose nanofiber as template for hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene[J]. Fuel, 2019, 253: 431-440. |
| 46 | Song S T, Zhou X F, Duan A J, et al. Synthesis of mesoporous silica material with ultra-large pore sizes and the HDS performance of dibenzothiophene[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2016, 226: 510-521. |
| 47 | Liu B S, Jiang L, Sun H, et al. XPS, XAES, and TG/DTA characterization of deposited carbon in methane dehydroaromatization over Ga-Mo/ZSM-5 catalyst[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2007, 253(11): 5092-5100. |
| 48 | Montesinos-Castellanos A, Zepeda T A, Pawelec B, et al. Preparation, characterization, and performance of alumina-supported nanostructured Mo-phosphide systems[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2007, 19(23): 5627-5636. |
| 49 | Jaroszewska K, Masalska A, Marek D, et al. Effect of support composition on the activity of Pt and PtMo catalysts in the conversion of n-hexadecane[J]. Catalysis Today, 2014, 223:76-86. |
| 50 | Wang J M, Song Z, Han M X, et al. Molybdenum-based catalysts supported on alumina for direct dehydrogenation of isobutane[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2021, 511: 111746. |
| 51 | Venezia A M, La Parola V, Deganello G, et al. Influence of the preparation method on the thiophene HDS activity of silica supported CoMo catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2002, 229(1/2): 261-271. |
| 52 | Xiao C K, Xia Z S, Chi K B, et al. Titanium-modified TUD-1 mesoporous catalysts for the hydrotreating of FCC diesel[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(8): 8210-8219. |
| 53 | Wang B W, Hu Z Y, Liu S H, et al. Effect of sulphidation temperature on the performance of NiO-MoO3/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for sulphur-resistant methanation[J]. RSC Adv., 2014, 4(99): 56174-56182. |
| 54 | Arun N, Maley J, Chen N, et al. NiMo nitride supported on γ-Al2O3 for hydrodeoxygenation of oleic acid: novel characterization and activity study[J]. Catalysis Today, 2017, 291: 153-159. |
| 55 | Mestl G, Srinivasan T K K. Raman spectroscopy of monolayer-type catalysts: supported molybdenum oxides[J]. Catalysis Reviews, 1998, 40(4): 451-570. |
| 56 | Usman, Yamamoto T, Kubota T, et al. Effect of phosphorus addition on the active sites of a Co-Mo/Al2O3 catalyst for the hydrodesulfurization of thiophene[J].Applied Catalysis A: General, 2007, 328(2): 219-225. |
| 57 | Koizumi N, Urabe Y, Inamura K, et al. Investigation of carbonaceous compounds deposited on NiMo catalyst used for ultra-deep hydrodesulfurization of gas oil by means of temperature-programmed oxidation and Raman spectroscopy[J]. Catalysis Today, 2005, 106(1/2/3/4): 211-218. |
| 58 | Xu Q, Jia G Q, Zhang J, et al. Surface phase composition of iron molybdate catalysts studied by UV Raman spectroscopy[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112(25): 9387-9393. |
| 59 | 徐军科, 羌宁. 反应器材质对Ni-Co双金属催化剂上沼气重整制氢性能与积炭的影响[J]. 天然气化工(C1化学与化工), 2021, 46(4): 52-57, 69. |
| Xu J K, Qiang N. Effect of reactor material on performance and carbon deposition of biogas reforming for hydrogen production over Ni-Co bimetallic catalyst[J]. Natural Gas Chemical Industry, 2021, 46(4): 52-57, 69. | |
| 60 | Said S, Abdelrahman A A. Atomic layer deposition of MoO3 on mesoporous γ-Al2O3 prepared by sol-gel method as efficient catalyst for oxidative desulfurization of refractory dibenzothiophene compound[J]. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2020, 95(2): 308-320. |
| 61 | 范峰, 凌凤香, 王少军, 等. 氧化铝表面碱性与钼金属负载研究[J]. 石油化工, 2020, 49(11):1043-1048. |
| Fan F, Ling F X, Wang S J, et al. Study on surface alkalinity of alumina and molybdenum metal loading[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 2020, 49(11):1043-1048. | |
| 62 | Meng D J, Wang B W, Yu W X, et al. Effect of citric acid on MoO3/Al2O3 catalysts for sulfur-resistant methanation[J]. Catalysts, 2017, 7(5): 151. |
| 63 | Wang B W, Meng D J, Wang W H, et al. Effect of citric acid addition on MoO3/CeO2-Al2O3 catalyst for sulfur-resistant methanation[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2016, 44(12): 1479-1484. |
| 64 | Wang X L, Zhao Z, Chen Z T, et al. Effect of synthesis temperature on structure-activity-relationship over NiMo/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for the hydrodesulfurization of DBT and 4,6-DMDBT[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2017, 161: 52-61. |
| 65 | Cao Z K, Duan A J, Zhao Z, et al. A simple two-step method to synthesize the well-ordered mesoporous composite Ti-FDU-12 and its application in the hydrodesulfurization of DBT and 4,6-DMDBT[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(46): 19738-19749. |
| 66 | Daage M, Chianelli R R. Structure-function relations in molybdenum sulfide catalysts: the “rim-edge” model[J].Journal of Catalysis, 1994, 149(2): 414-427. |
| [1] | 丁禹, 杨昌泽, 李军, 孙会东, 商辉. 原子尺度钼系加氢脱硫催化剂的研究进展与展望[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1735-1749. |
| [2] | 潘越, 刘相洋, 黄奕晨, 李江涛, 邱丽, 李瑞丰, 李莎, 闫晓亮. Ni/Al2O3与ZnO距离对含硫菲加氢性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3548-3556. |
| [3] | 杨光, 程鑫, 王峥, 王晔, 张良俊, 吴静怡. 微纳多孔结构中稀薄气体流动渗透率的解析型预测模型[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 2895-2901. |
| [4] | 郑喜, 王涛, 任永胜, 赵珍珍, 王雪琪, 赵之平. 聚间苯二甲酰间苯二胺平板膜的制备及其性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4707-4721. |
| [5] | 隋宝宽, 施尧, 林见阳, 刘文洁, 袁胜华, 耿新国, 段学志. 焙烧气氛和孔结构对加氢脱金属催化剂性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 993-1000. |
| [6] | 王晓波,赵青山,程智年,张浩然,胡涵,王路海,吴明铂. 高性能碳基储能材料的设计、合成与应用[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(6): 2660-2677. |
| [7] | 陈亮, 赵帆, 闫广精, 王春波. H2O和SO2对CFB内石灰石同时煅烧/硫化反应中煅烧动力学的协同作用[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(9): 3859-3868. |
| [8] | 马卫园, 张东. 磷酸镁多孔材料的制备及其在结构超级电容器的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(10): 4438-4448. |
| [9] | 岳源源, 郑晓桂, 康颖, 白正帅, 袁珮, 朱海波, 鲍晓军. 基于镁铝水滑石的Mo/Al2O3-MgO催化剂制备及其加氢脱硫性能[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(1): 405-413. |
| [10] | 陈超, 杨修春, 刘巍. 有机-无机杂化钙钛矿太阳能电池的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(3): 811-820. |
| [11] | 郭凤, 余剑, Tran Tuyet-Suong, 李长明, 许光文. 溶胶-凝胶原位合成钒钨钛催化剂及NH3-SCR性能[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(10): 3747-3754. |
| [12] | 庄嘉豪, 靳国静, 古芳娜, 贾丽华, 苏发兵. 一锅法制备高活性高稳定性Ni-Nd-Al三元有序介孔甲烷化催化剂[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(10): 3823-3831. |
| [13] | 张伟清, 郭文光, 储丽丽, 孔令朋, 靳广洲. 钼酸铵与LaHY固相反应机理[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(8): 3380-3386. |
| [14] | 汪怀远, 肖博, 王池嘉, 程小双, 蒋凤. 静电纺丝法制备氧化钛-氧化石墨复合载体的加氢脱硫性能[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(7): 2514-2520. |
| [15] | 李阳, 朱玉雯, 高继慧, 孙飞, 雷鸣. 活性焦孔结构演变规律及对脱硫性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(3): 1126-1132. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号