化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (7): 3468-3476.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241509
收稿日期:2024-12-25
修回日期:2025-01-31
出版日期:2025-07-25
发布日期:2025-08-13
通讯作者:
王海名
作者简介:杨文毅(1993—),女,硕士,工程师,yangwy@sice-Tsinghua.org
基金资助:
Wenyi YANG1( ), Changfu YOU1,2,3, Haiming WANG1,2(
), Changfu YOU1,2,3, Haiming WANG1,2( )
)
Received:2024-12-25
Revised:2025-01-31
Online:2025-07-25
Published:2025-08-13
Contact:
Haiming WANG
摘要:
通过建立300 MW燃煤机组厂级全流程模型,对比分析了40%~100%额定工况(THA)下3种不同热源驱动的脱硫废水零排放技术的性能,揭示了电厂脱硫废水在热法浓缩过程中的水-能耦合平衡关系。结果表明,当机组负荷降低,负荷偏离额定值越多,热、电负荷差距越大,在40%THA下的热负荷率为45.76%。在3种脱硫废水零排放技术中,两种三效蒸发干燥方式的单位耗热量最低,为0.017 kJ/t,不到高温烟气旁路干燥方式的1/2,节能效果良好,其中三效烟气取热干燥方式利用的是烟气废热,不损失发电量,其锅炉效率和发电效率最高,在100%THA下分别为85.59%和32.25%,在降低能源成本和减少环境污染方面具有更大优势。相关研究可以为合理选择全工况脱硫废水处理技术提供依据。
中图分类号:
杨文毅, 由长福, 王海名. 燃煤机组变负荷运行下的脱硫废水零排放流程模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3468-3476.
Wenyi YANG, Changfu YOU, Haiming WANG. Simulation and analysis of zero discharge of desulphurization wastewater under variable load processes from coal-fired units[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3468-3476.
| 参 数 | 数 值 |
|---|---|
| 连续蒸发量/(t/h) | 1021 |
| 过热蒸汽压力/MPa | 16.7 |
| 再热蒸汽压力/MPa | 3.2 |
| 过热蒸汽温度/℃ | 538 |
| 再热蒸汽温度/℃ | 538 |
| 省煤器出口烟温/℃ | 370 |
| 空气预热器出口烟温/℃ | 208 |
表1 额定工况下主要技术参数
Table 1 Main technical parameters under rated condition
| 参 数 | 数 值 |
|---|---|
| 连续蒸发量/(t/h) | 1021 |
| 过热蒸汽压力/MPa | 16.7 |
| 再热蒸汽压力/MPa | 3.2 |
| 过热蒸汽温度/℃ | 538 |
| 再热蒸汽温度/℃ | 538 |
| 省煤器出口烟温/℃ | 370 |
| 空气预热器出口烟温/℃ | 208 |
| 电负荷率/% | 电负荷/MM | 煤/(kg/h) | 煤耗/(g/(kW·h)) | 比煤耗 | 热负荷率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 298.51 | 113700 | 380.89 | 1.00 | 100 |
| 80 | 238.81 | 92640 | 387.93 | 1.02 | 81.48 |
| 60 | 179.11 | 72104 | 402.58 | 1.06 | 63.42 |
| 40 | 119.40 | 52026 | 435.72 | 1.14 | 45.76 |
表2 热负荷和电负荷的关系
Table 2 Relationship between thermal load and electrical load
| 电负荷率/% | 电负荷/MM | 煤/(kg/h) | 煤耗/(g/(kW·h)) | 比煤耗 | 热负荷率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 298.51 | 113700 | 380.89 | 1.00 | 100 |
| 80 | 238.81 | 92640 | 387.93 | 1.02 | 81.48 |
| 60 | 179.11 | 72104 | 402.58 | 1.06 | 63.42 |
| 40 | 119.40 | 52026 | 435.72 | 1.14 | 45.76 |
| 实际值 | 模拟值 | 相对误差/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 电负荷/MW | 电负荷率/% | 电负荷/MW | 电负荷率/% | |
| 298.51 | 100 | 298.51 | 100.00 | — |
| 238.81 | 80 | 238.14 | 79.78 | 0.27 |
| 179.10 | 60 | 177.49 | 59.46 | 0.90 |
| 119.40 | 40 | 115.36 | 38.65 | 3.38 |
表3 电负荷模拟结果
Table 3 The simulation results of electrical load
| 实际值 | 模拟值 | 相对误差/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 电负荷/MW | 电负荷率/% | 电负荷/MW | 电负荷率/% | |
| 298.51 | 100 | 298.51 | 100.00 | — |
| 238.81 | 80 | 238.14 | 79.78 | 0.27 |
| 179.10 | 60 | 177.49 | 59.46 | 0.90 |
| 119.40 | 40 | 115.36 | 38.65 | 3.38 |
| 实际电负荷率/% | 热损失/% | 锅炉效率/% | 发电效率/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q2 | q3 | q4 | q5 | q6 | |||
| 100 | 11.35 | 0.0080 | 4.02 | 0.42 | 0.05 | 84.15 | 32.25 |
| 80 | 11.38 | 0.0080 | 4.06 | 0.53 | 0.05 | 83.98 | 31.58 |
| 60 | 11.49 | 0.0050 | 4.20 | 0.70 | 0.05 | 83.55 | 30.24 |
| 40 | 12.10 | 0.0005 | 4.93 | 1.05 | 0.05 | 81.87 | 27.24 |
表4 变负荷效率模拟结果
Table 4 Simulation results of efficiency on variable load
| 实际电负荷率/% | 热损失/% | 锅炉效率/% | 发电效率/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q2 | q3 | q4 | q5 | q6 | |||
| 100 | 11.35 | 0.0080 | 4.02 | 0.42 | 0.05 | 84.15 | 32.25 |
| 80 | 11.38 | 0.0080 | 4.06 | 0.53 | 0.05 | 83.98 | 31.58 |
| 60 | 11.49 | 0.0050 | 4.20 | 0.70 | 0.05 | 83.55 | 30.24 |
| 40 | 12.10 | 0.0005 | 4.93 | 1.05 | 0.05 | 81.87 | 27.24 |
| 实际电负荷率/% | 烟气量/(m3/h) | 出口烟气SO2含量/(mg/m3) | 脱硫效率/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 1288046 | 1.48 | 99.95 |
| 80 | 1059588 | 1.63 | 99.95 |
| 60 | 855338 | 1.74 | 99.94 |
| 40 | 726902 | 1.41 | 99.94 |
表5 变负荷脱硫模拟结果
Table 5 Simulation results of desulfurization on variable load
| 实际电负荷率/% | 烟气量/(m3/h) | 出口烟气SO2含量/(mg/m3) | 脱硫效率/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 1288046 | 1.48 | 99.95 |
| 80 | 1059588 | 1.63 | 99.95 |
| 60 | 855338 | 1.74 | 99.94 |
| 40 | 726902 | 1.41 | 99.94 |
| 干燥方式 | 实际 电负荷率/% | 锅炉 效率/% | 发电 功率/MW | 发电 效率/% | 高温烟气分流 分数/(mol/mol) | 生蒸汽 流量/(kg/h) | 低压蒸汽分流 分数/(mol/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无干燥 | 100 | 84.15 | 298.51 | 32.25 | — | — | — |
| 80 | 83.98 | 238.14 | 31.58 | — | — | — | |
| 60 | 83.55 | 177.49 | 30.24 | — | — | — | |
| 40 | 81.87 | 115.36 | 27.24 | — | — | — | |
| 旁路烟气 | 100 | 85.48 | 282.83 | 30.56 | 0.285 | — | — |
| 80 | 85.29 | 225.61 | 29.92 | 0.279 | — | — | |
| 60 | 84.81 | 168.15 | 28.65 | 0.261 | — | — | |
| 40 | 82.86 | 109.93 | 25.95 | 0.181 | — | — | |
| 三效烟气 | 100 | 85.59 | 298.51 | 32.25 | — | 20420 | — |
| 80 | 85.41 | 238.14 | 31.58 | — | 16506 | — | |
| 60 | 84.93 | 177.49 | 30.24 | — | 12470 | — | |
| 40 | 83.03 | 115.36 | 27.24 | — | 7530 | — | |
| 三效蒸汽 | 100 | 84.15 | 297.82 | 32.18 | — | — | 0.0299 |
| 80 | 83.98 | 237.57 | 31.50 | — | — | 0.0298 | |
| 60 | 83.55 | 177.02 | 30.16 | — | — | 0.0296 | |
| 40 | 81.87 | 115.04 | 27.16 | — | — | 0.0260 |
表6 不同干燥方式在变负荷时的效率
Table 6 Efficiency of different drying technologies on variable load
| 干燥方式 | 实际 电负荷率/% | 锅炉 效率/% | 发电 功率/MW | 发电 效率/% | 高温烟气分流 分数/(mol/mol) | 生蒸汽 流量/(kg/h) | 低压蒸汽分流 分数/(mol/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无干燥 | 100 | 84.15 | 298.51 | 32.25 | — | — | — |
| 80 | 83.98 | 238.14 | 31.58 | — | — | — | |
| 60 | 83.55 | 177.49 | 30.24 | — | — | — | |
| 40 | 81.87 | 115.36 | 27.24 | — | — | — | |
| 旁路烟气 | 100 | 85.48 | 282.83 | 30.56 | 0.285 | — | — |
| 80 | 85.29 | 225.61 | 29.92 | 0.279 | — | — | |
| 60 | 84.81 | 168.15 | 28.65 | 0.261 | — | — | |
| 40 | 82.86 | 109.93 | 25.95 | 0.181 | — | — | |
| 三效烟气 | 100 | 85.59 | 298.51 | 32.25 | — | 20420 | — |
| 80 | 85.41 | 238.14 | 31.58 | — | 16506 | — | |
| 60 | 84.93 | 177.49 | 30.24 | — | 12470 | — | |
| 40 | 83.03 | 115.36 | 27.24 | — | 7530 | — | |
| 三效蒸汽 | 100 | 84.15 | 297.82 | 32.18 | — | — | 0.0299 |
| 80 | 83.98 | 237.57 | 31.50 | — | — | 0.0298 | |
| 60 | 83.55 | 177.02 | 30.16 | — | — | 0.0296 | |
| 40 | 81.87 | 115.04 | 27.16 | — | — | 0.0260 |
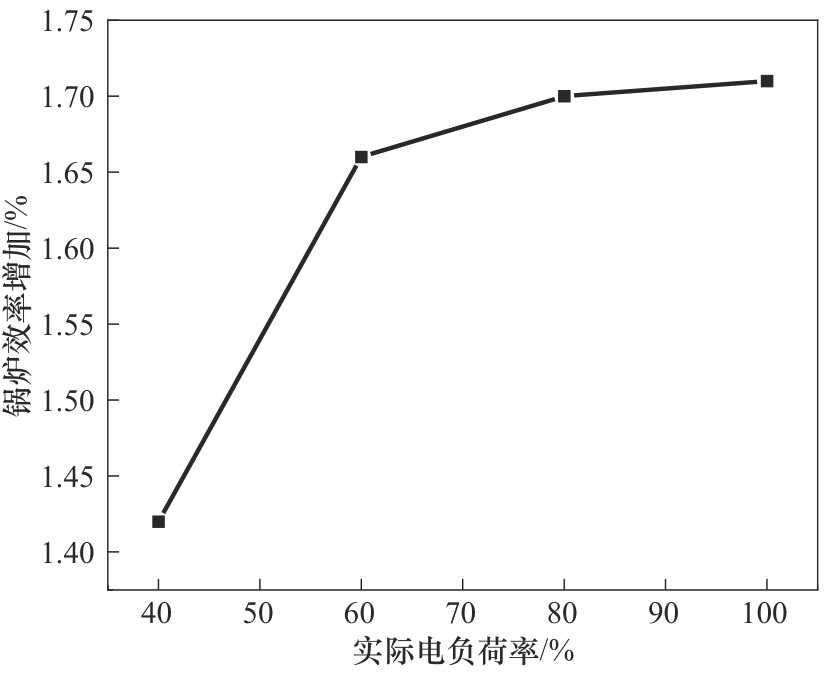
图7 三效烟气干燥方式较不干燥情况下变负荷时锅炉效率的相对变化
Fig.7 Boiler efficiency of triple-effect evaporation technology driven by low-temperature flue gas in relation to without drying technology on variable electrical load rate
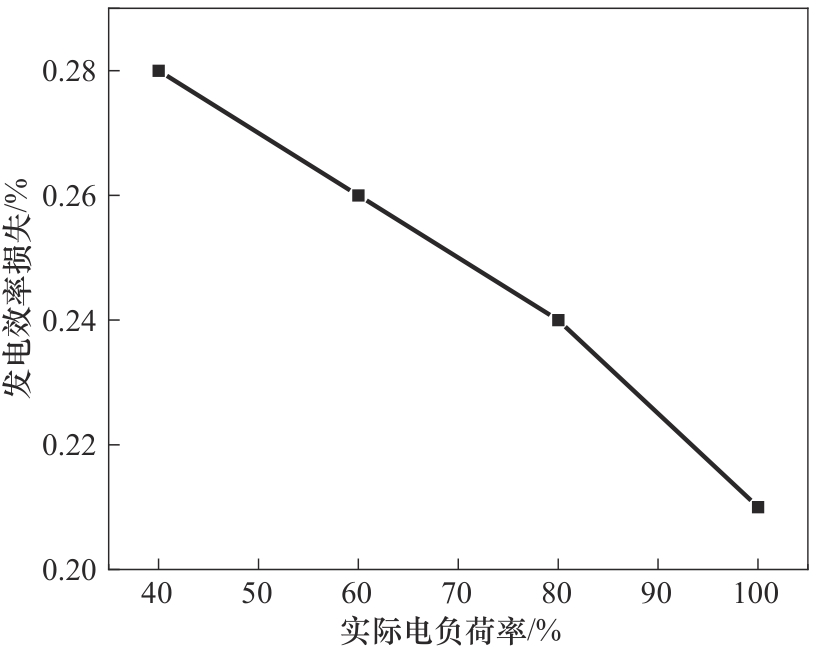
图8 三效蒸汽干燥方式较不干燥情况下变负荷时发电效率的相对变化
Fig.8 Unit efficiency of triple-effect evaporation technology driven by low pressure steam in relation to without drying technology on variable electrical load rate
| 干燥方式 | 实际电负荷率/% | 热源 | 干燥热耗/kW | 回收水量/(t/h) | 单位热耗/(kJ/t) | 凝结水利用方式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 旁路烟气 | 100 | 高温烟气 | 32471 | 54.79 | 0.16 | 被动富集 |
| 80 | 26180 | 44.29 | 0.16 | |||
| 60 | 19678 | 33.54 | 0.16 | |||
| 40 | 11587 | 20.67 | 0.16 | |||
| 三效烟气 | 100 | 低温烟气 | 13351 | 52.64 | 0.07 | 水池回收 |
| 80 | 10792 | 42.61 | 0.07 | |||
| 60 | 8153 | 32.36 | 0.07 | |||
| 40 | 4923 | 20.32 | 0.07 | |||
| 三效蒸汽 | 100 | 低压抽汽 | 13353 | 52.65 | 0.07 | 水池回收 |
| 80 | 10792 | 42.61 | 0.07 | |||
| 60 | 8153 | 32.36 | 0.07 | |||
| 40 | 4935 | 20.22 | 0.07 |
表7 不同干燥方式在变负荷时的脱硫废水干燥情况
Table 7 Drying performance of different technologies on variable electrical load rate
| 干燥方式 | 实际电负荷率/% | 热源 | 干燥热耗/kW | 回收水量/(t/h) | 单位热耗/(kJ/t) | 凝结水利用方式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 旁路烟气 | 100 | 高温烟气 | 32471 | 54.79 | 0.16 | 被动富集 |
| 80 | 26180 | 44.29 | 0.16 | |||
| 60 | 19678 | 33.54 | 0.16 | |||
| 40 | 11587 | 20.67 | 0.16 | |||
| 三效烟气 | 100 | 低温烟气 | 13351 | 52.64 | 0.07 | 水池回收 |
| 80 | 10792 | 42.61 | 0.07 | |||
| 60 | 8153 | 32.36 | 0.07 | |||
| 40 | 4923 | 20.32 | 0.07 | |||
| 三效蒸汽 | 100 | 低压抽汽 | 13353 | 52.65 | 0.07 | 水池回收 |
| 80 | 10792 | 42.61 | 0.07 | |||
| 60 | 8153 | 32.36 | 0.07 | |||
| 40 | 4935 | 20.22 | 0.07 |
| [1] | 罗晓明. 300 MW汽轮机变负荷运行热经济性及安全性研究[J]. 汽轮机技术, 2017, 59(5): 385-387, 390. |
| Luo X M. Safety and thermal economic analysis on variable load operation of 300 MW steam turbine[J]. Turbine Technology, 2017, 59(5): 385-387, 390. | |
| [2] | 王伟, 徐婧, 赵翔, 等. 中国煤电机组调峰运行现状分析[J]. 南方能源建设, 2017, 4(1): 18-24. |
| Wang W, Xu J, Zhao X, et al. Analysis on peak load regulation status quo for coal-fired power plants in China[J]. Southern Energy Construction, 2017, 4(1): 18-24. | |
| [3] | Yin J J, Liu M, Zhao Y L, et al. Dynamic performance and control strategy modification for coal-fired power unit under coal quality variation[J]. Energy, 2021, 223: 120077. |
| [4] | 中国电力企业联合会. 2023—2024年度全国电力供需形势分析预测报告[R]. 北京:中国电力企业联合会, 2024. |
| China Electricity Council. Analysis and forecast report of national electricity supply and demand situation in 2023—2024[R]. Beijing: China Electricity Council, 2024. | |
| [5] | 张月雷, 王贵生, 管洪军, 等. 300 MW热电机组凝汽器变工况运行的热经济性模拟研究[J]. 汽轮机技术, 2023, 65(5): 377-381. |
| Zhang Y L, Wang G S, Guan H J, et al. Thermal economy simulation study on the variable condition operation of a 300 MW thermoelectric unit's condenser[J]. Turbine Technology, 2023, 65(5): 377-381. | |
| [6] | 刘国卫. 火电厂300 MW汽轮机组变负荷调峰运行方式[J]. 自动化应用, 2011(7): 13-15. |
| Liu G W. Peak regulation operation mode of 300 MW turbine variable load in thermal power plant[J]. Automation Application, 2011(7): 13-15. | |
| [7] | 刘兴军, 郝俊利. 国产300 MW火电机组调峰方式研究[J]. 内蒙古石油化工, 2011, 37(1): 22-23. |
| Liu X J, Hao J L. Study on peak shaving mode of domestic 300 MW thermal power unit[J]. Inner Mongolia Petrochemical Industry, 2011, 37(1): 22-23. | |
| [8] | 谭俊龙. 火电机组适应电网调频调峰的研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2013. |
| Tan J L. Study on thermal power units adapting to frequency regulation and peak regulation of power grid[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2013. | |
| [9] | Agbleze S, Shadle L J, Lima F V. Dynamic modeling and simulation of a subcritical coal-fired power plant under load-following conditions[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2024, 63(25): 11044-11056. |
| [10] | Hoang A T, Nguyen T V, Nguyen B T. The experimental evaluation of energy efficiency and carbonic emission rates for all stable loads of larger-scale (+600 MW) coal-fired power generation units in Vietnam[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(6): 2185. |
| [11] | Chen C, Zhou Z Q, Bollas G M. Dynamic modeling, simulation and optimization of a subcritical steam power plant (Part Ⅰ): Plant model and regulatory control[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 145: 324-334. |
| [12] | Shen H S, Wu Y X, Zhou M M, et al. Large eddy simulation of a 660 MW utility boiler under variable load conditions[J]. Frontiers in Energy, 2021, 15(1): 124-131. |
| [13] | 中华人民共和国国务院. 水污染防治行动计划: 国发[2015]17号[A]. 2015. |
| State Council of the People's Republic of China. Action plan for water pollution control: issued by State Council of the People's Republic of China [2015]No.17[A]. 2015. | |
| [14] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部. 火电厂污染防治可行技术指南: [S]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2017. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China. Guideline on available technologies of pollution prevention and control for thermal power plant: [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2017. | |
| [15] | 韩飞超, 汪旭, 张荣, 等. 石灰石—石膏湿法烟气脱硫废水处理工艺的优化改造[J]. 中国给水排水, 2016, 32(14): 99-102. |
| Han F C, Wang X, Zhang R, et al. Optimized reconstruction of limestone-gypsum wet flue gas desulfurization wastewater treatment process[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2016, 32(14): 99-102. | |
| [16] | Ma S C, Chai J, Chen G D, et al. Research on desulfurization wastewater evaporation: present and future perspectives[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 58: 1143-1151. |
| [17] | 陈程, 陈鑫, 徐凤, 等. 燃煤机组脱硫废水零排放物料-能-水耦合机制及优化[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5800-5809. |
| Chen C, Chen X, Xu F, et al. Matter-energy-water coupling mechanism and optimization for zero discharge of desulfurization wastewater from coal-fired units[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(11): 5800-5809. | |
| [18] | 安雪峰, 刘广建, 陈海平. 燃煤电厂脱硫废水热法零排放系统设计及分析[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2022, 28(6): 175-183. |
| An X F, Liu G J, Chen H P. Design and analysis of thermal zero discharge for flue gas desulfurization wastewater of coal-fired power plants[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2022, 28(6): 175-183. | |
| [19] | 王仁雷, 王丰吉, 戴瑜, 等. 300 MW机组脱硫废水旁路蒸发干燥系统性能试验研究[J]. 工业用水与废水, 2021, 52(3): 23-26. |
| Wang R L, Wang F J, Dai Y, et al. Performance test of bypass evaporation drying system for desulfurization wastewater from 300 MW unit[J]. Industrial Water & Wastewater, 2021, 52(3): 23-26. | |
| [20] | 刘锋瑞. 脱硫废水低温高效蒸发浓缩技术研究[D]. 太原: 山西大学, 2023. |
| Liu F R. Study on low temperature and high efficiency evaporation concentration technology of desulfurization wastewater[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi University, 2023. | |
| [21] | 吴伟. 脱硫废水喷雾干燥在电厂的实际应用[J]. 上海节能, 2021(9): 1033-1037. |
| Wu W. Practical application of flue gas drying device for desulfurization waste water at power plant[J]. Shanghai Energy Conservation, 2021(9): 1033-1037. | |
| [22] | 冉初萌. 烟气余热蒸发浓缩干燥技术在电厂脱硫废水零排放中的应用[J]. 机电信息, 2020(35): 75-77. |
| Ran C M. Application of evaporation, concentration and drying technology of flue gas waste heat in zero discharge of desulfurization wastewater in power plant[J]. Mechanical and Electrical Information, 2020(35): 75-77. | |
| [23] | 侯致福, 魏晓仪, 邢树涛, 等. 300 MW机组低温余热闪蒸脱硫废水零排放技术应用研究[J]. 华电技术, 2020, 42(3): 31-36. |
| Hou Z F, Wei X Y, Xing S T, et al. Research on low-temperature waste heat flash evaporation technology applied in desulfurization wastewater zero discharge of 300 MW units[J]. Huadian Technology, 2020, 42(3): 31-36. | |
| [24] | 杨文毅, 由长福, 王海名. 燃煤机组脱硫废水零排放技术分析[J/OL]. 现代化工, . |
| Yang W Y, You C F, Wang H M. Technology analysis of zero discharge of desulfurization wastewater from coal-fired power plants[J/OL]. Modern Chemical Industry, . | |
| [25] | 樊泉桂. 锅炉原理[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2013. |
| Fan Q G. Boiler Principle[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2013. | |
| [26] | 刘福国, 郭新根, 王守恩. 一种快速确定火力发电机组煤耗特性曲线的方法: 109934493B[P]. 2020-12-22. |
| Liu G F, Guo X G, Wang S E. The invention relates to a method for quickly determining the coal consumption characteristic curve of a thermal generator set: 109934493B[P]. 2020-12-22. | |
| [27] | 陈宝明. 660 MW循环流化床燃煤电站热力系统优化及提效研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2020. |
| Chen B M. Study on thermal system optimization and efficiency improvement of 660 MW circulating fluidized bed coal-fired power station[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2020. | |
| [28] | 江成林. 循环流化床锅炉建模及效率计算[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2016. |
| Jiang C L. Modeling and efficiency calculation of circulating fluidized bed boiler[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2016. | |
| [29] | 张燕平, 叶涛. 热力发电厂[M]. 6版. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2020. |
| Zhang Y P, Ye T. Thermal Power Plant[M]. 6th ed. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2020. | |
| [30] | 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 火电厂大气污染物排放标准: [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2012. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Emission standard of air pollutants for thermal power plants: [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2012. |
| [1] | 陈程, 陈鑫, 徐凤, 吴斌, 李元媛, 陆规. 燃煤机组脱硫废水零排放物料-能-水耦合机制及优化[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5800-5809. |
| [2] | 羊城, 王可心, 邵之江, 黄晓津. HTR-PM大范围变负荷的MA自适应优化算法[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(6): 2211-2220. |
| [3] | 马双忱, 范紫瑄, 万忠诚, 陈嘉宁, 张净瑞, 马采妮. 高盐水条件下亚硫酸盐氧化特性实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(5): 1964-1972. |
| [4] | 戚春萍, 武文粉, 王晨晔, 李会泉. 燃煤电厂废旧SCR脱硝催化剂中TiO2载体的回收与再利用[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(11): 4239-4248. |
| [5] | 刘勇, 赵汶, 刘瑞, 杨林军. 化学团聚促进电除尘脱除PM2.5的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(9): 3609-3616. |
| [6] | 李卜义,王建友. 浓海水处理及综合利用技术的新进展[J]. 化工进展, 2014, 33(11): 3067-3074. |
| [7] | 高岩, 栾涛, 彭吉伟, 吕涛. 燃煤电厂真实烟气条件下SCR催化剂脱硝性能[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(7): 2611-2618. |
| [8] | 张彩珠,王春燕,陈 珊,魏顺安 . 亚临界燃煤电厂的用能分析[J]. 化工进展, 2013, 32(06): 1278-1282. |
| [9] | 王愉晨1,池勇志1,苏润西1,孙 涛2,杨和义2,苑宏英1,姜远光1,费学宁1. 浓盐水零排放技术的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2013, 32(06): 1423-1428. |
| [10] | 张正江,曾国强,邵之江,王可心,陈曦. 过程系统变负荷下的数据校正与参数估计方法[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(6): 1780-1789. |
| [11] | 马学虎,兰 忠,王四芳,李 璐. 海水淡化浓盐水排放对环境的影响与零排放技术研究进展 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2011, 30(1): 233-. |
| [12] | 郑剑铭, 周劲松, 何胜, 骆仲泱. 燃煤电厂汞排放对周边环境的影响 [J]. 化工学报, 2009, 60(12): 3104-3111. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号