• •
洪锦波1( ), 陆美杰2, 胡洋2, 袁隆昊1, 刘锋1, 钱飞跃1,2(
), 陆美杰2, 胡洋2, 袁隆昊1, 刘锋1, 钱飞跃1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-07-25
修回日期:2025-10-29
出版日期:2025-10-31
通讯作者:
钱飞跃
作者简介:洪锦波(2000—),男,硕士研究生,hongjinbo0103@163.com
基金资助:
Jinbo HONG1( ), Meijie LU2, Yang HU2, Longhao YUAN1, Feng LIU1, Feiyue QIAN1,2(
), Meijie LU2, Yang HU2, Longhao YUAN1, Feng LIU1, Feiyue QIAN1,2( )
)
Received:2025-07-25
Revised:2025-10-29
Online:2025-10-31
Contact:
Feiyue QIAN
摘要:
近年来,膜曝气生物膜反应器(MABR)因其供氧效率高和运行能耗低的优势,已成为城镇污水处理领域的关键技术方向。有研究表明,MABR中生物膜与活性污泥所构成的复合体系可显著提升生物脱氮效能,但不同污泥形态间菌群的协同机制尚未明确。本研究通过协同调控进水负荷与氮素组成,探究了MABR启动同步硝化反硝化(SND)工艺处理模拟市政污水的可行性,并对反应器处理效能、生物膜生长过程及菌群功能结构展开深入分析。结果表明,当进水碳氮比(COD/TN)为5时,MABR仅运行20天即可实现SND功能。当单位膜面积进水氮负荷提升至3.59 g N·(m2·d)-1时,MABR对COD和TN的去除率分别稳定在89.07 ± 0.57%和88.37 ± 0.36%,其单位膜面积TN去除负荷显著高于文献报道的平均水平(1.89 g N·(m2·d)-1)。由高通量测序和功能基因预测结果可知,在高负荷条件下,生物膜中氨氧化菌(Nitrosomonas属)、亚硝酸盐氧化菌(Nitrospira属)及反硝化菌(如Flavobacterium属等)得到同步富集,而悬浮污泥则以异养菌为主。期间,MABR工艺的单位运行能耗和全流程碳排放强度分别为0.18 kW·h·m-3和0.27 kgCO2eq·m-3,均显著低于活性污泥法。这表明MABR兼具高效生物脱氮与低碳运行特征,拥有良好的应用推广前景。
中图分类号:
洪锦波, 陆美杰, 胡洋, 袁隆昊, 刘锋, 钱飞跃. MABR中泥-膜复合系统的协同脱氮机制与低碳运行特性研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250827.
Jinbo HONG, Meijie LU, Yang HU, Longhao YUAN, Feng LIU, Feiyue QIAN. Study on the synergistic nitrogen removal mechanisms between biofilms and activated sludge and the low-carbon operational characteristics of MABR[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250827.
| 运行阶段 | 运行时间 | 进水氮负荷 NLR(g N·(m2·d)-1) | NH4+-N/NO3--N摩尔比 | 进水有机负荷 OLR(g·(m2·d)-1) | HRT (h) | 管路供气流量 (mL·min-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 第1~19 d | 1.22 ± 0.01 | 1:1 | 6.12 ± 0.02 | 24 | 70 ± 2 |
| Ⅱ | 第20~37 d | 1.62 ± 0.02 | 1:1 | 8.06 ± 0.20 | 18 | 70 ± 2 |
| Ⅲ | 第38~69 d | 2.41 ± 0 .04 | 1:1 | 12.04 ± 0.30 | 12 | 70 ± 2 |
| Ⅳ | 第70~91 d | 3.59 ± 0.05 | 1:1 | 17.84 ± 0.70 | 8 | 70 ± 2 |
| Ⅴ | 第92~150 d | 3.59 ± 0.07 | 3:1 | 17.84 ± 0.70 | 8 | 150 ± 5 |
表1 MABR连续运行的工况条件
Table 1 Operating conditions of the MABR under continuous operation modes
| 运行阶段 | 运行时间 | 进水氮负荷 NLR(g N·(m2·d)-1) | NH4+-N/NO3--N摩尔比 | 进水有机负荷 OLR(g·(m2·d)-1) | HRT (h) | 管路供气流量 (mL·min-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 第1~19 d | 1.22 ± 0.01 | 1:1 | 6.12 ± 0.02 | 24 | 70 ± 2 |
| Ⅱ | 第20~37 d | 1.62 ± 0.02 | 1:1 | 8.06 ± 0.20 | 18 | 70 ± 2 |
| Ⅲ | 第38~69 d | 2.41 ± 0 .04 | 1:1 | 12.04 ± 0.30 | 12 | 70 ± 2 |
| Ⅳ | 第70~91 d | 3.59 ± 0.05 | 1:1 | 17.84 ± 0.70 | 8 | 70 ± 2 |
| Ⅴ | 第92~150 d | 3.59 ± 0.07 | 3:1 | 17.84 ± 0.70 | 8 | 150 ± 5 |
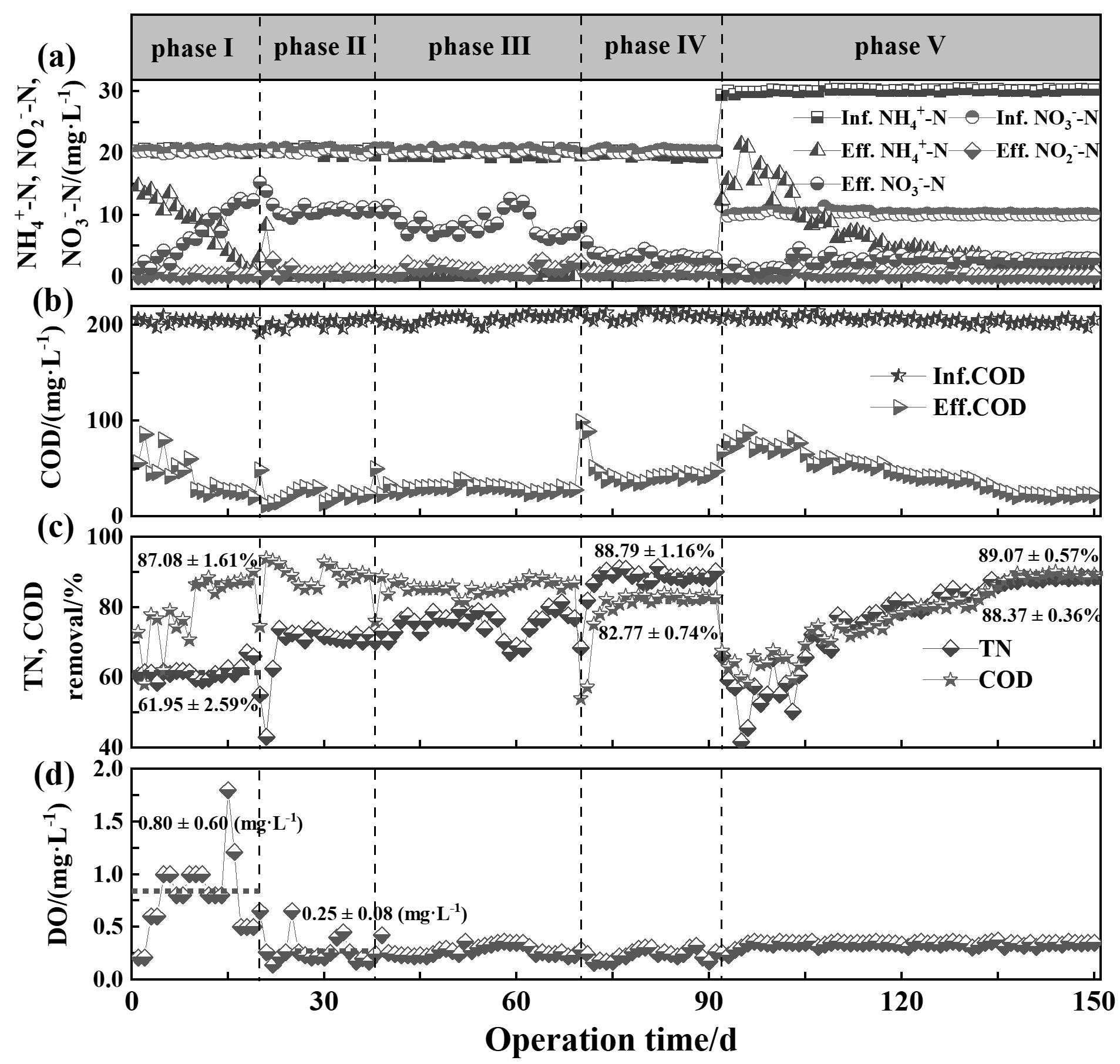
图2 运行期间,MABR进出水中(a)NH4+-N、NO2- -N、NO3—N,(b)COD浓度,(c)TN、COD去除率及(d)DO浓度的变化情况
Fig. 2 Variations in concentrations of (a) NH4+-N, NO2- -N, NO3--N, (b) COD, (c) removal efficiencies of TN and COD, and (d) DO concentrations in the MABR during the operational period
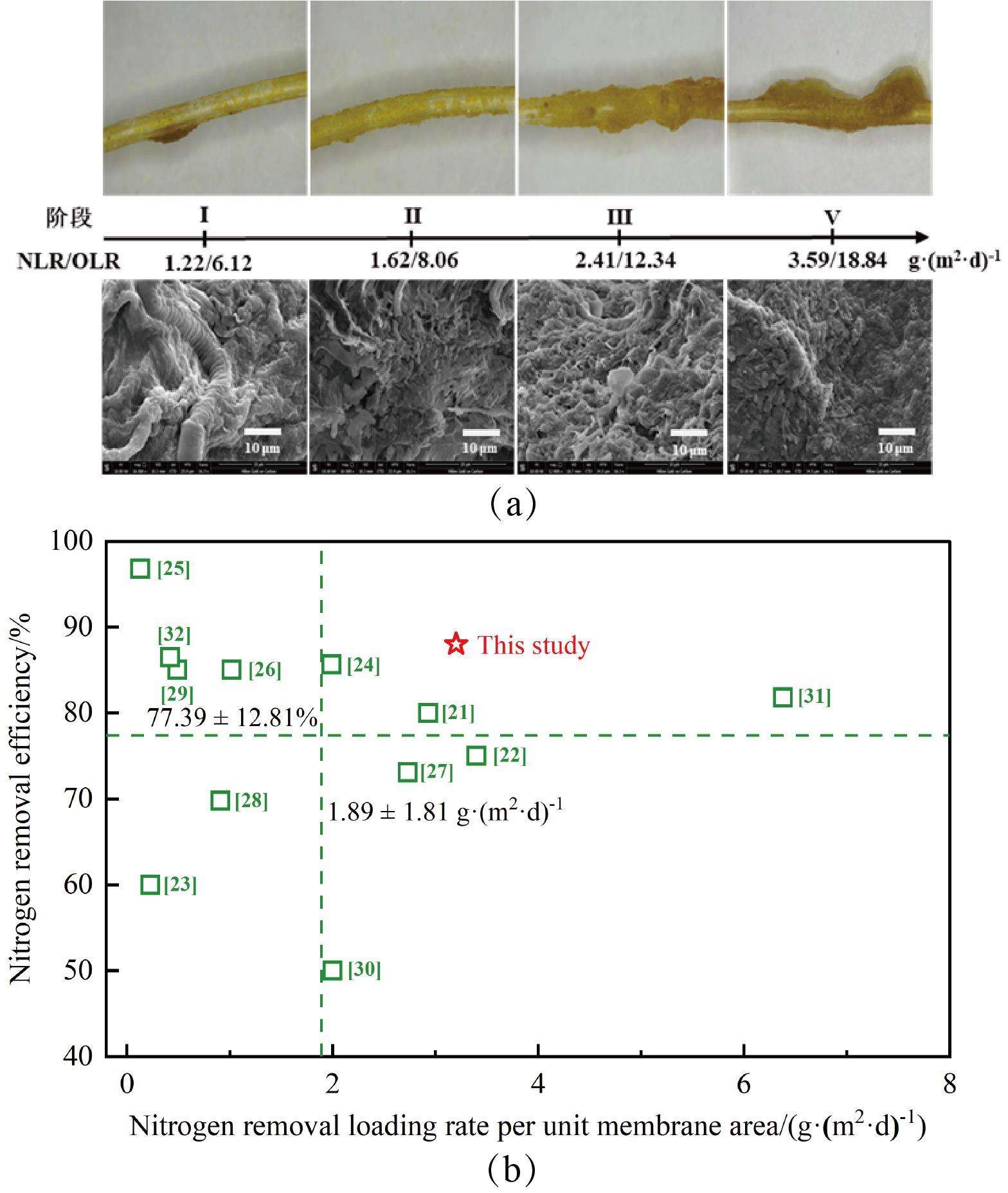
图3(a) PDMS膜表面生物膜的形态变化和(b)本研究中MABR脱氮效能与文献报道结果的对比[21-32]
Fig.3 (a) Morphological evolution of biofilms on the surface of PDMS membranes during operation; (b) Comparison of nitrogen removal efficiency in the MABR with values reported in the literature[21-32]
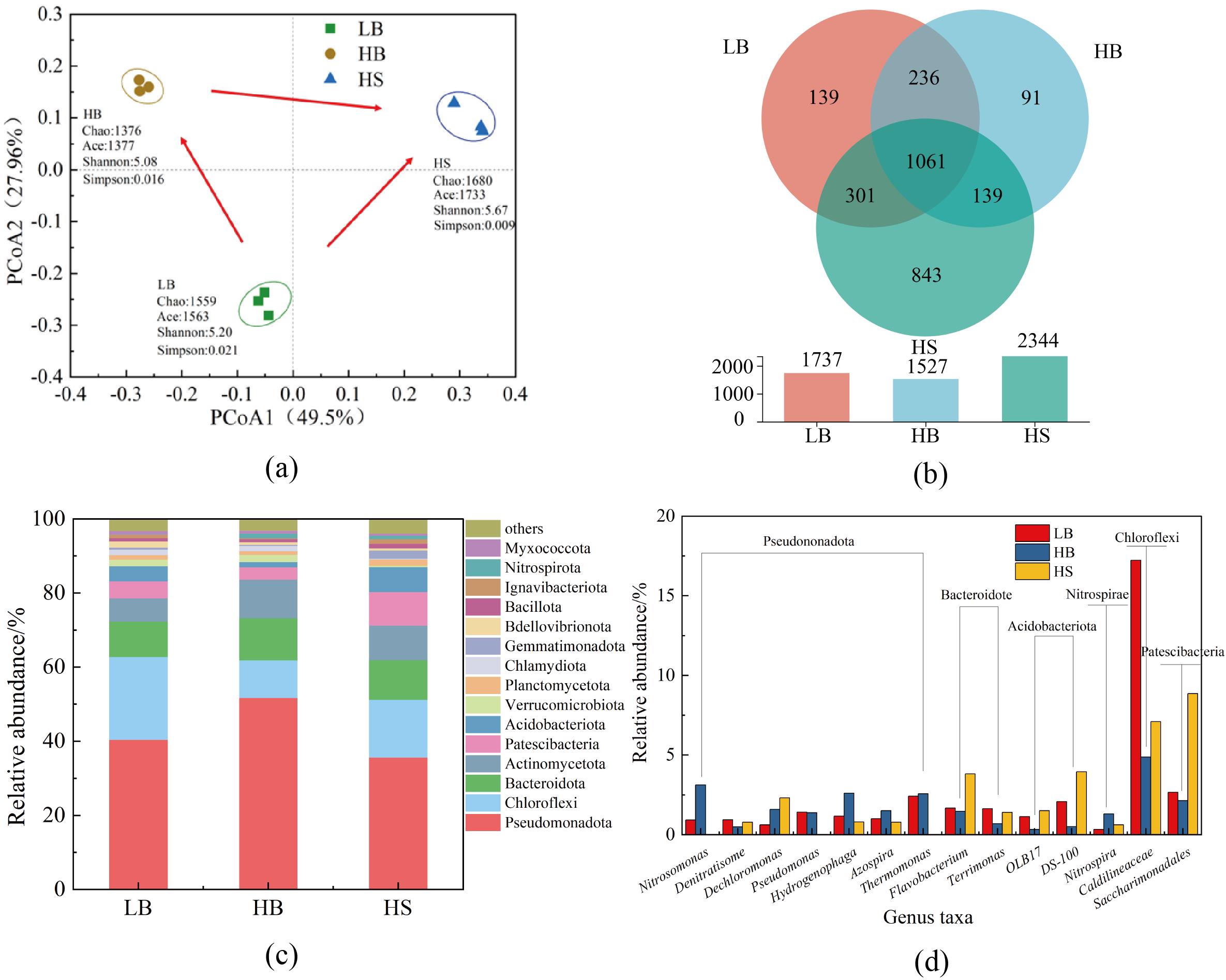
图4 三组微生物样品在OTU水平上的(a)PCoA图和(b)Venn图以及在(c)门和(d)属水平上的菌群结构
Fig.4 (a) PCoA analysis and (b) Venn diagram at the OTU level; Microbial community structure at (c) phylum and (d) genus levels within the three sample groups
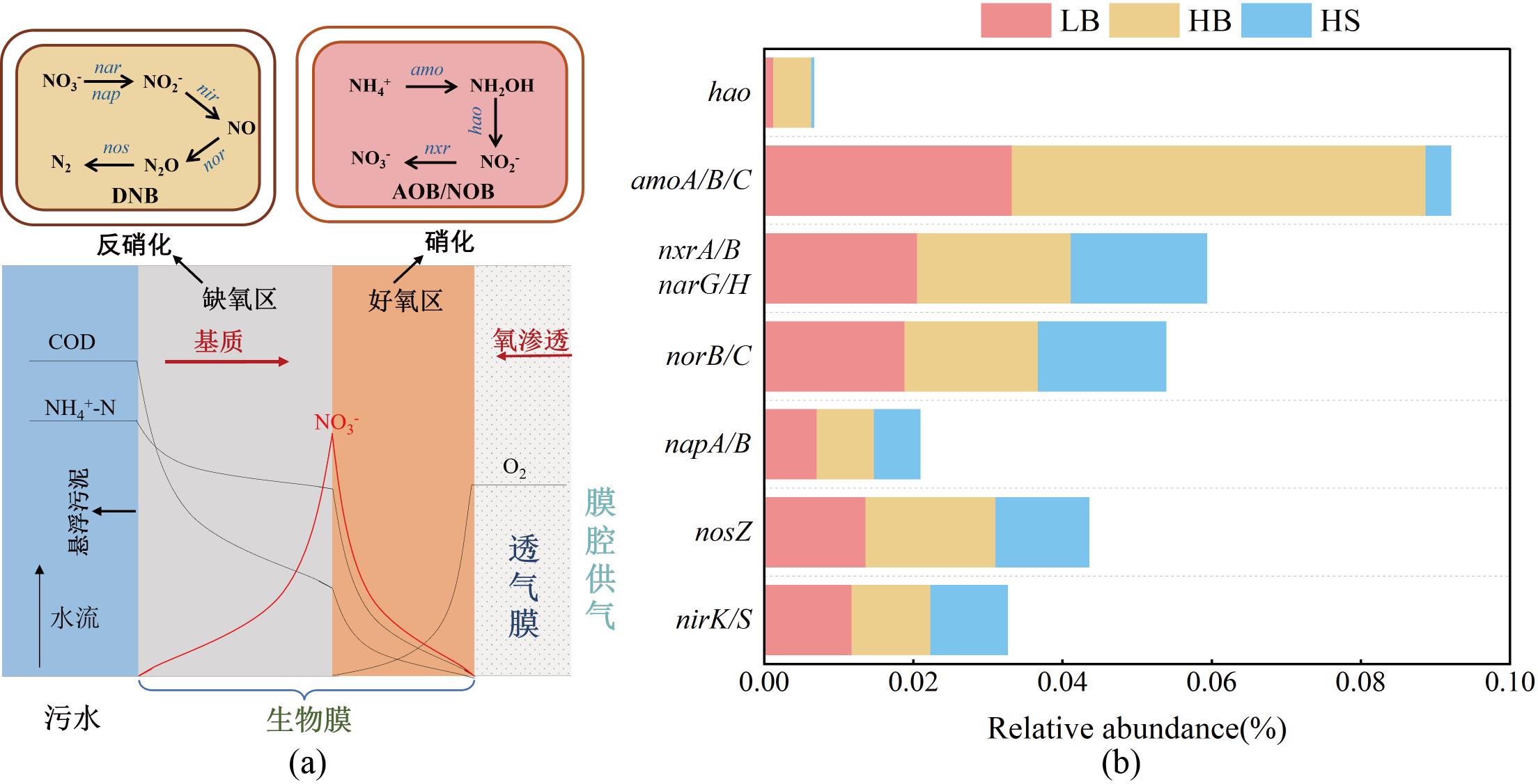
图6 MABR中(a)生物膜驱动SND脱氮的反应机制和(b)PICRUSt对硝化/反硝化功能基因的预测结果
Fig.6 (a) Mechanisms of the SND process for nitrogen removal in MABR; (b) PICRUSt predicted nitrification/denitrification functional genes in the three sample groups
| 工艺类型 | A/A/O工艺 | MABR工艺 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 反应器性能 | 进水COD/TN浓度(mg·L-1) | 270~550 / 35~50 | 210~650 / 32~48 | 200 / 40 |
| 单位膜面积氮负荷(g N·(m2·d)-1) | / | 0.13~4.30 | 3.59 ± 0.07 | |
| 进水TN容积负荷(kg N·(m3·d)-1)1 | 0.05~0.12 | 0.02~0.43 | 0.36 | |
| COD去除率(%) | 85%~95% | 85%~98% | 89.07 ± 0.57% | |
| TN 去除率(%) | 70%~85% | 72%~95% | 88.37 ± 0.36% | |
污水处理 单位能耗药耗 | 运行能耗(kW·h·m-3)2 | 0.20~0.51 | 0.11~0.25 | 0.18 |
| 碳源投加(g·m-3) | 30~150 | / | / | |
全流程 碳排放强度3 (kgCO2eq·m⁻³) | 电力消耗 | 0.24~0.39 | 0.08~0.21 | 0.15 |
| N2O排放 | 0.15~0.47 | 0.02~0.09 | 0.06 | |
| CH4排放 | 0.03~0.07 | 0.01~0.02 | 0.02 | |
| 碳源投加 | 0.12~0.34 | / | / | |
| 剩余污泥处置3 | 0.10~0.23 | 0.02~0.06 | 0.04 | |
| 合 计 | 0.53~1.13 | 0.12~0.30 | 0.27 | |
| 数据来源 | [ | [ | 本研究 | |
表2 A/A/O工艺和MABR反应器处理市政污水的技术参数比较
Table 2 Technical comparison between A/A/O process and MABR reactor for municipal wastewater treatment
| 工艺类型 | A/A/O工艺 | MABR工艺 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 反应器性能 | 进水COD/TN浓度(mg·L-1) | 270~550 / 35~50 | 210~650 / 32~48 | 200 / 40 |
| 单位膜面积氮负荷(g N·(m2·d)-1) | / | 0.13~4.30 | 3.59 ± 0.07 | |
| 进水TN容积负荷(kg N·(m3·d)-1)1 | 0.05~0.12 | 0.02~0.43 | 0.36 | |
| COD去除率(%) | 85%~95% | 85%~98% | 89.07 ± 0.57% | |
| TN 去除率(%) | 70%~85% | 72%~95% | 88.37 ± 0.36% | |
污水处理 单位能耗药耗 | 运行能耗(kW·h·m-3)2 | 0.20~0.51 | 0.11~0.25 | 0.18 |
| 碳源投加(g·m-3) | 30~150 | / | / | |
全流程 碳排放强度3 (kgCO2eq·m⁻³) | 电力消耗 | 0.24~0.39 | 0.08~0.21 | 0.15 |
| N2O排放 | 0.15~0.47 | 0.02~0.09 | 0.06 | |
| CH4排放 | 0.03~0.07 | 0.01~0.02 | 0.02 | |
| 碳源投加 | 0.12~0.34 | / | / | |
| 剩余污泥处置3 | 0.10~0.23 | 0.02~0.06 | 0.04 | |
| 合 计 | 0.53~1.13 | 0.12~0.30 | 0.27 | |
| 数据来源 | [ | [ | 本研究 | |
| [1] | Lu L, Guest J S, Peters C A, et al. Wastewater treatment for carbon capture and utilization[J]. Nature Sustainability, 2018, 1(12): 750-758. |
| [2] | Perez-Calleja P, Aybar M, Picioreanu C, et al. Periodic venting of MABR lumen allows high removal rates and high gas-transfer efficiencies[J]. Water Research, 2017, 121: 349-360. |
| [3] | Silveira I T, Cadee K, Bagg W. Startup and initial operation of an MLE-MABR treating municipal wastewater[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2022, 85(4): 1155-1166. |
| [4] | Li J G, Yan W L, Zheng S K, et al. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of impacts of microporous, dense and composite membranes on nitrifier/denitrifier distribution and performance of MABRs[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 505: 159175. |
| [5] | Bunse P, Orschler L, Agrawal S, et al. WITHDRAWN: Membrane Aerated Biofilm Reactors for mainstream partial nitritation/anammox: Experiences using real municipal wastewater[J]. Water Research, 2020, 186: 116351. |
| [6] | Mehrabi S, Houweling D, Dagnew M. Establishing mainstream nitrite shunt process in membrane aerated biofilm reactors: Impact of organic carbon and biofilm scouring intensity[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2020, 37: 101460. |
| [7] | Liu H Y, Li L, Ye W J, et al. Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in a hybrid activated sludge-membrane aerated biofilm reactor (H-MABR) for nitrogen removal from low COD/N interflow: a pilot-scale study[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2024, 367: 122038. |
| [8] | Zhao X, Xie Y L, Sun B, et al. Unraveling microbial characteristics of simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and phosphorus removal in a membrane-aerated biofilm reactor[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 239: 117402. |
| [9] | Uri-Carreño N, Nielsen P H, Gernaey K V, et al. Long-term operation assessment of a full-scale membrane-aerated biofilm reactor under Nordic conditions[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 779: 146366. |
| [10] | Nerenberg R. The membrane-biofilm reactor (MBfR) as a counter-diffusional biofilm process[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 2016, 38: 131-136. |
| [11] | Awata T, Oshiki M, Kindaichi T, et al. Physiological characterization of an anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacterium belonging to the "candidatus scalindua" group[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2013, 79(13): 4145-4148. |
| [12] | Qian F Y, Gebreyesus A T, Wang J F, et al. Single-stage autotrophic nitrogen removal process at high loading rate: granular reactor performance, kinetics, and microbial characterization[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(5): 2379-2389. |
| [13] | Gu Y F, Li Y, Li X Y, et al. Energy self-sufficient wastewater treatment plants: feasibilities and challenges[J]. Energy Procedia, 2017, 105: 3741-3751. |
| [14] | Parravicini V, Svardal K, Krampe J. Greenhouse gas emissions from wastewater treatment plants[J]. Energy Procedia, 2016, 97: 246-253. |
| [15] | Xian C F, Gong C, Lu F, et al. The evaluation of greenhouse gas emissions from sewage treatment with urbanization: Understanding the opportunities and challenges for climate change mitigation in China's low-carbon pilot city, Shenzhen[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 855: 158629. |
| [16] | 中国城镇供水排水协会. 城镇水务系统碳核算与减排路径技术指南[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社,2022: 132-138. |
| China Urban Water Supply and Drainage Association. Technical guidelines for carbon accounting and emission reduction pathways in urban water systems[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2022: 132-138. | |
| [17] | Ghasemi M, Chang S, Sivaloganathan S. Exploring aeration strategies for enhanced simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in membrane aerated bioreactors: a computational approach[J]. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 2024, 86(9): 117. |
| [18] | Ravishankar H, Nemeth A, Massons G, et al. Factors impacting simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in a membrane aerated biofilm reactor (MABR) system treating municipal wastewater[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2022, 10(5): 108120. |
| [19] | Sun Z Y, Li M, Wang G F, et al. Enhanced carbon and nitrogen removal in an integrated anaerobic/anoxic/aerobic-membrane aerated biofilm reactor system[J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(48):28838-28847. |
| [20] | Lu D W, Bai H, Kong F G, et al. Recent advances in membrane aerated biofilm reactors[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2021, 51(7): 649-703. |
| [21] | He H Q, Daigger G T. The hybrid MABR process achieves intensified nitrogen removal while N2O emissions remain low[J]. Water Research, 2023, 244: 120458. |
| [22] | Lakshminarasimman N, Parker W. Long-term monitoring reveals improvements in nitrogen removal and energy efficiency with MABR upgrade at full scale[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2025, 70: 106945. |
| [23] | Li Y, Zhang K S. Pilot scale treatment of polluted surface waters using membrane-aerated biofilm reactor (MABR)[J]. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment, 2018, 32(2): 376-386. |
| [24] | Wu Y, Wu Z D, Chu H L, et al. Comparison study on the performance of two different gas-permeable membranes used in a membrane-aerated biofilm reactor[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 658: 1219-1227. |
| [25] | Zhou Y, Li R, Guo B, et al. Cometabolism accelerated simultaneous ammoxidation and organics mineralization in an oxygen-based membrane biofilm reactor treating greywater under low dissolved oxygen conditions[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 789: 147898. |
| [26] | Campo G, Cerutti A, Zanetti M, et al. Membrane aerated biological reactors (MABRs) to enhance the biological treatment process at a WWTP[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2024, 371: 122921. |
| [27] | Kobayashi M, Agari R, Kigo Y, et al. Efficient oxygen supply and rapid biofilm formation by a new composite polystyrene elastomer membrane for use in a membrane-aerated biofilm reactor[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 183: 108442. |
| [28] | Thant K J W, Anh-Vu N, Yun-Je K, et al. Performance of pilot-scale membrane aerated biofilm reactors integrated with anoxic nano-biotechnological reactor for domestic wastewater treatment[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 319: 137927. |
| [29] | Wang C, Li H Y, Wu B X, et al. A nano-Al2O3 modified polypropylene hollow fiber membrane with enhanced biofilm formation in membrane aerated biofilm reactor application[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2024, 12(3): 112524. |
| [30] | Lakshminarasimman N, Zamanzadeh M, Schraa O, et al. Modeling nitrous oxide emission from full-scale hybrid membrane aerated biofilm reactors (MABR)[J]. Water Research, 2025, 274: 123128. |
| [31] | Wang M J, Tian Y, Tong X, et al. PDMS membranes with bioinspired mineral coatings for the enhancement of microbial adhesion and nitrogen removal performance in MABR system[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2025, 685: 161998. |
| [32] | Zhou Y, Li W J, Hu H J, et al. DOPA/PEI surface-modified poly-4-methyl-1-pentene membranes and application in membrane aeration biofilm reactor[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2025, 77: 114-122. |
| [33] | Duan Y M, Awasthi M K, Yang J F, et al. Bacterial community dynamics and co-occurrence network patterns during different stages of biochar-driven composting[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 384: 129358. |
| [34] | Guo F, Zhang T. Profiling bulking and foaming bacteria in activated sludge by high throughput sequencing[J]. Water Research, 2012, 46(8): 2772-2782. |
| [35] | Xiang T, Liang H, Wang P, et al. Insights into two stable mainstream deammonification process and different microbial community dynamics at ambient temperature[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 331: 125058. |
| [36] | Lu H J, Chandran K, Stensel D. Microbial ecology of denitrification in biological wastewater treatment[J]. Water Research, 2014, 64: 237-254. |
| [37] | Karanasios K A, Vasiliadou I A, Pavlou S, et al. Hydrogenotrophic denitrification of potable water: a review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 180(1/2/3): 20-37. |
| [38] | Zhao W H, Bi X J, Peng Y Z, et al. Research advances of the phosphorus-accumulating organisms of Candidatus Accumulibacter, Dechloromonas and Tetrasphaera: Metabolic mechanisms, applications and influencing factors[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 307: 135675. |
| [39] | Zhou M Y, Han Y, Zhuo Y, et al. Bioinduced phosphorus precipitation in granular sludge undergoing denitrifying biological phosphorus removal: Phosphorus recovery from sewage as hydroxyapatite[J]. Water Research, 2025, 281: 123590. |
| [40] | Deng Y L, Ruan Y J, Ma B, et al. Multi-omics analysis reveals niche and fitness differences in typical denitrification microbial aggregations[J]. Environment International, 2019, 132: 105085. |
| [41] | Yan F, Wang S Q, Huang Z H, et al. Microbial ecological responses of partial nitritation/anammox granular sludge to real water matrices and its potential application[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 226: 115701. |
| [42] | Zhu S M, Zhang L P, Ye Z Y, et al. Denitrification performance and bacterial ecological network of a reactor using biodegradable poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) as an electron donor for nitrate removal from aquaculture wastewater[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 857: 159637. |
| [43] | Corsino S F, Torregrossa M. Achieving complete nitrification below the washout SRT with hybrid membrane aerated biofilm reactor (MABR) treating municipal wastewater[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2022, 10(1): 106983. |
| [44] | Tong Y D, Liao X W, He Y Y, et al. Mitigating greenhouse gas emissions from municipal wastewater treatment in China[J]. Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, 2024, 20: 100341. |
| [45] | Zeng S Y, Chen X, Dong X, et al. Efficiency assessment of urban wastewater treatment plants in China: Considering greenhouse gas emissions[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2017, 120: 157-165. |
| [46] | Li Y M, Gu H, Zhao G Y, et al. Carbon accounting of A2O process based on carbon footprint in a full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plant[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2023, 55: 104162. |
| [47] | 张超男, 潘杨, 刘佳音. 膜曝气生物反应器综述[J]. 工业水处理, 2021, 41(9):43-49. |
| Zhang C N, Pan Y, Liu J Y. Review of membrane aerated biofilm reactors[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2021, 41(9): 43-49. | |
| [48] | Zhuang J L, Ai W, Wang Q H, et al. Sludge reflux promotes biofilm formation in upflow membrane aerated biofilm reactor for partial nitritation: insight from computational fluid dynamics stimulation and experiments[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2025, 437: 133077. |
| [1] | 黄珊, 陆勇泽, 朱光灿, 孔赟. 耦合生物阴极SND的MLMB -MFC的构建与运行[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(4): 1772-1780. |
| [2] | 巩有奎, 彭永臻. 运行方式对SBBR亚硝酸型同步脱氮及N2O释放的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(6): 2289-2297. |
| [3] | 巩有奎, 任丽芳, 彭永臻. 不同DO下SBBR亚硝酸型同步脱氮及N2O释放特性[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(4): 1550-1558. |
| [4] | 巩有奎, 赵强, 彭永臻. 不同C/N下SBBR脱氮过程N2O释放及胞外多聚物变化[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(12): 4847-4855. |
| [5] | 巩有奎, 彭永臻. 曝气强度对SBBR同步生物脱氮及N2O释放影响[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(11): 4410-4419. |
| [6] | 李忠明, 王淑莹, 苗蕾, 曹天昊, 张为堂, 刘文龙, 彭永臻. 单级SBR厌氧/好氧/缺氧处理中期垃圾渗滤液深度脱氮[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(2): 746-752. |
| [7] | 胡家玮, 李军, 卞伟, 郑林雪, 王盟. 城市污水连续流A/O系统富氧条件下脱氮特征[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(10): 4071-4077. |
| [8] | 巩有奎, 王赛, 彭永臻, 王淑莹. 生活污水不同生物脱氮过程中N2O产量及控制 [J]. 化工学报, 2010, 61(5): 1286-1292. |
| [9] | 张万友1,张兰河1,2,3,杨 涛1,张海丰1. 不同有机碳源对SBR工艺同步硝化反硝化影响 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2010, 29(12): 2395-. |
| [10] | 高大文;彭永臻;王淑莹. 高氮豆制品废水的亚硝酸型同步硝化反硝化生物脱氮工艺 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2005, 56(4): 699-704. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号