• •
收稿日期:2025-09-15
修回日期:2025-11-03
出版日期:2025-11-27
通讯作者:
韩晔华
作者简介:刘继坤(1999—),男,博士研究生,liuji_kun@163.com
基金资助:
Jikun LIU( ), Ruoning BAO, Xingying LAN, Chunming XU, Yehua HAN(
), Ruoning BAO, Xingying LAN, Chunming XU, Yehua HAN( )
)
Received:2025-09-15
Revised:2025-11-03
Online:2025-11-27
Contact:
Yehua HAN
摘要:
微纳米气泡(Micro-nano bubbles, MNBs)是指分散于水相、油相或固体基质中,特征尺寸处于微米级至纳米级范围的气泡。与毫米级气泡相比,微纳米气泡具有高比表面积、优异稳定性以及自发产生活性氧(ROS)等独特性质。高比表面积赋予了微纳米气泡体系极高的气-液界面密度,结合其优异稳定性可显著提高气-液传质效率,在化工过程强化、药物靶向输送及土壤修复等领域展现出巨大的应用潜力。微纳米气泡在气-液界面处自发产生的活性氧能够高效降解有机污染物,在废水处理领域展现出显著优势。此类活性氧还可进一步作为绿色合成反应中的活性中间体,在温和条件下实现多种高附加值化学品的高效合成。微纳米气泡从“强化传质”到“界面合成”的跨越,标志着该技术步入全新发展阶段。这一突破为开发清洁、绿色的化学工艺提供了新策略,具有重大的科学与工业价值。
中图分类号:
刘继坤, 包若凝, 蓝兴英, 徐春明, 韩晔华. 微纳米气泡及其气-液界面特性[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251039.
Jikun LIU, Ruoning BAO, Xingying LAN, Chunming XU, Yehua HAN. Micro-nano-bubble technology and its gas-liquid interface characteristics[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251039.
| 制备方法 | 机制和应用 | 优势与劣势 |
|---|---|---|
| 空化 | 机制:在声波或者流体流动作用下,局部压力波动,诱导MNBs生成; 应用:生物成像、药物输送、肿瘤细胞或生物组织的消融、表面清洁、矿物加工以及废水处理等。 | 优势:技术成熟,工艺简单,能耗低,效率高,可持续性和灵活性强; 劣势:超声空化的规模化较差,水力空化易导致堵塞和材料腐蚀。 |
| 气体分散 | 机制:在机械搅拌或者在微孔结构和微流体设备中,将气相分解成更小的尺寸,生成MNBs 应用:功能材料制备、食品加工等。 | 优势:技术成熟,工艺简单,灵活性强; 劣势:能耗高,效率低,生成的气泡尺度有限,制备相对较大的气泡。 |
| 溶剂交换 | 机制:利用两种具有不同气体溶解度的可混溶液体,混合后形成MNBs; 应用:功能材料制备等。 | 优势:技术成熟,工艺简单,能耗低,效率高; 劣势:气泡尺寸控制精度差,难以扩大规模。 |
| 化学反应 | 机制:MNBs通过化学反应产生; 应用:功能材料制备等。 | 优势:技术成熟,工艺简单,能耗低,效率高; 劣势:气泡尺寸控制精度差,难以扩大规模,依赖化学反应体系,可生成的气泡种类有限。 |
| 电解 | 机制:通过电极上的电化学反应生成MNBs; 应用:用于氢气和氧气的制备。 | 优势:技术成熟,工艺简单,可持续性强,气体纯度高; 劣势:巨大的电能消耗,难以扩大规模。 |
表1 MNBs制备方法
Table 1 Methods for MNBs preparation
| 制备方法 | 机制和应用 | 优势与劣势 |
|---|---|---|
| 空化 | 机制:在声波或者流体流动作用下,局部压力波动,诱导MNBs生成; 应用:生物成像、药物输送、肿瘤细胞或生物组织的消融、表面清洁、矿物加工以及废水处理等。 | 优势:技术成熟,工艺简单,能耗低,效率高,可持续性和灵活性强; 劣势:超声空化的规模化较差,水力空化易导致堵塞和材料腐蚀。 |
| 气体分散 | 机制:在机械搅拌或者在微孔结构和微流体设备中,将气相分解成更小的尺寸,生成MNBs 应用:功能材料制备、食品加工等。 | 优势:技术成熟,工艺简单,灵活性强; 劣势:能耗高,效率低,生成的气泡尺度有限,制备相对较大的气泡。 |
| 溶剂交换 | 机制:利用两种具有不同气体溶解度的可混溶液体,混合后形成MNBs; 应用:功能材料制备等。 | 优势:技术成熟,工艺简单,能耗低,效率高; 劣势:气泡尺寸控制精度差,难以扩大规模。 |
| 化学反应 | 机制:MNBs通过化学反应产生; 应用:功能材料制备等。 | 优势:技术成熟,工艺简单,能耗低,效率高; 劣势:气泡尺寸控制精度差,难以扩大规模,依赖化学反应体系,可生成的气泡种类有限。 |
| 电解 | 机制:通过电极上的电化学反应生成MNBs; 应用:用于氢气和氧气的制备。 | 优势:技术成熟,工艺简单,可持续性强,气体纯度高; 劣势:巨大的电能消耗,难以扩大规模。 |
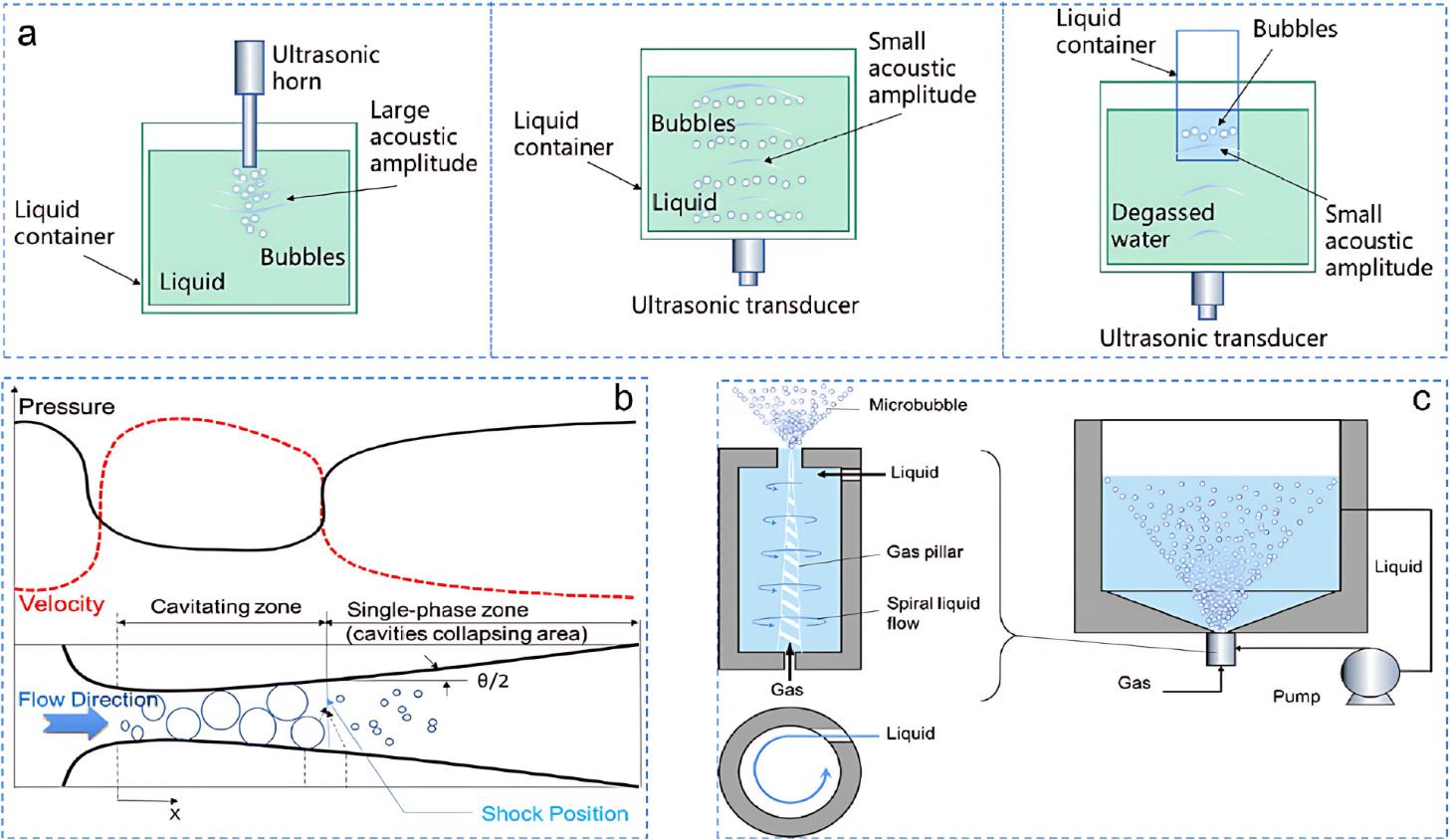
图1 (a)超声空化的三种典型装置[15] (b)文丘里流体动力空化反应器示意图[16] (c)通过轴向流剪切的水动力空化原理图[17]
Fig.1 (a) Three typical setups for ultrasonic cavitation. (b) Schematic of the Venturi Hydrodynamic cavitation reactor. (c) Schematic of Hydrodynamic cavitation via axial flow shearing
| [81] | 李兆军, 杜浩. 我国微细气泡技术发展综述[J]. 过程工程学报, 2017, 17(4): 655-663. |
| Li Z J, Du H. Review of the development of fine bubble technology in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2017, 17(4): 655-663. | |
| [82] | Matsumoto Y, Allen J S, Yoshizawa S, et al. Medical ultrasound with microbubbles[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2005, 29(3): 255-265. |
| [83] | Zhang H G, Lyu T, Bi L, et al. Combating hypoxia/anoxia at sediment-water interfaces: a preliminary study of oxygen nanobubble modified clay materials[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 637: 550-560. |
| [84] | Hu L M, Xia Z R. Application of ozone micro-nano-bubbles to groundwater remediation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 342: 446-453. |
| [85] | Xia Z R, Hu L M. Remediation of organics contaminated groundwater by ozone micro-nano bubble[J]. Japanese Geotechnical Society Special Publication, 2016, 2(57): 1978-1981. |
| [86] | Li P, Takahashi M, Chiba K. Degradation of phenol by the collapse of microbubbles[J]. Chemosphere, 2009, 75(10): 1371-1375. |
| [87] | Wang X K, Wang J G, Guo P Q, et al. Chemical effect of swirling jet-induced cavitation: Degradation of rhodamine B in aqueous solution[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2008, 15(4): 357-363. |
| [88] | Wang X K, Zhang Y. Degradation of alachlor in aqueous solution by using hydrodynamic cavitation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 161(1): 202-207. |
| [89] | Kim I, Huang C. Sonochemical degradation of polycyclic aromatic sulfur hydrocarbons (PASHs) in aqueous solutions exemplified by benzothiophene[J]. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, 2005, 28(7): 1107-1118. |
| [90] | Jabesa A, Ghosh P. Removal of diethyl phthalate from water by ozone microbubbles in a pilot plant[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 180: 476-484. |
| [91] | Xing D, Yuan X, Liang C Y, et al. Spontaneous oxidation of I- in water microdroplets and its atmospheric implications[J]. Chemical Communications, 2022, 58(89): 12447-12450. |
| [1] | Wang Y W, Wang T X. Preparation method and application of nanobubbles: a review[J]. Coatings, 2023, 13(9): 1510. |
| [2] | Temesgen T, Bui T T, Han M, et al. Micro and nanobubble technologies as a new horizon for water-treatment techniques: a review[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2017, 246: 40-51. |
| [3] | Agarwal A, Ng W J, Liu Y. Principle and applications of microbubble and nanobubble technology for water treatment[J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 84(9): 1175-1180. |
| [4] | Takahashi M, Chiba K, Li P. Free-radical generation from collapsing microbubbles in the absence of a dynamic stimulus[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2007, 111(6): 1343-1347. |
| [5] | Swart B, Zhao Y B, Khaku M, et al. In situ characterisation of size distribution and rise velocity of microbubbles by high-speed photography[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 225: 115836. |
| [6] | Tesař V. Microbubble smallness limited by conjunctions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 231: 526-536. |
| [7] | Brittle S, Desai P, Ng W C, et al. Minimising microbubble size through oscillation frequency control[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2015, 104: 357-366. |
| [8] | Tesař V. Mechanisms of fluidic microbubble generation Part II: Suppressing the conjunctions[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2014, 116: 849-856. |
| [9] | Achar J C, Nam G, Jung J, et al. Microbubble ozonation of the antioxidant butylated hydroxytoluene: Degradation kinetics and toxicity reduction[J]. Environmental Research, 2020, 186: 109496. |
| [10] | Seddon J R T, Lohse D, Ducker W A, et al. A deliberation on nanobubbles at surfaces and in bulk[J]. ChemPhysChem, 2012, 13(8): 2179-2187. |
| [11] | Luo J, Xu W L, Li R. Collapse of cavitation bubbles near air bubbles[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2020, 32(5): 929-941. |
| [12] | Kim J Y, Song M G, Kim J D. Zeta potential of nanobubbles generated by ultrasonication in aqueous alkyl polyglycoside solutions[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2000, 223(2): 285-291. |
| [13] | Oeffinger B E, Wheatley M A. Development and characterization of a nano-scale contrast agent[J]. Ultrasonics, 2004, 42(1): 343-347. |
| [14] | Nazari S, Hassanzadeh A, He Y Q, et al. Recent developments in generation, detection and application of nanobubbles in flotation[J]. Minerals, 2022, 12(4): 462. |
| [15] | Yasui K, Tuziuti T, Iida Y. Dependence of the characteristics of bubbles on types of sonochemical reactors[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2005, 12(1): 43-51. |
| [16] | Jia J G, Zhu Z X, Chen H, et al. Full life circle of micro-nano bubbles: Generation, characterization and applications[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 471: 144621. |
| [17] | Li H Z, Hu L M, Xia Z R. Impact of groundwater salinity on bioremediation enhanced by micro-nano bubbles[J]. Materials, 2013, 6(9): 3676-3687. |
| [18] | Daryabor M, Ahmadi A, Zilouei H. Solvent extraction of cadmium and zinc from sulphate solutions: Comparison of mechanical agitation and ultrasonic irradiation[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2017, 34: 931-937. |
| [19] | Shams M, Dehghani M H, Nabizadeh R, et al. Adsorption of phosphorus from aqueous solution by cubic zeolitic imidazolate framework-8: Modeling, mechanical agitation versus sonication[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2016, 224: 151-157. |
| [20] | Hettiarachchi K, Talu E, Longo M L, et al. On-chip generation of microbubbles as a practical technology for manufacturing contrast agents for ultrasonic imaging[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2007, 7(4): 463-468. |
| [21] | Pancholi K P, Farook U, Moaleji R, et al. Novel methods for preparing phospholipid coated microbubbles[J]. European Biophysics Journal, 2008, 37(4): 515-520. |
| [22] | Dollet B, van Hoeve W, Raven J P, et al. Role of the channel geometry on the bubble pinch-off in flow-focusing devices[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100(3): 034504. |
| [23] | Sattari A, Hanafizadeh P, Hoorfar M. Multiphase flow in microfluidics: From droplets and bubbles to the encapsulated structures[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 282: 102208. |
| [24] | Huang J, Yao Z H. Influencing factors and size prediction of bubbles formed by flow focusing in a cross-channel[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2022, 248: 117228. |
| [25] | Zhan Q C, Shi X Q, Fan D, et al. Solvent mixing generating air bubbles as a template for polydopamine nanobowl fabrication: Underlying mechanism, nanomotor assembly and application in cancer treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 404: 126443. |
| [26] | Qiu J, Zou Z L, Wang S, et al. Formation and stability of bulk nanobubbles generated by ethanol–water exchange[J]. ChemPhysChem, 2017, 18(10): 1345-1350. |
| [27] | Tang J, Bai X, Huang H L, et al. Templating synthesis of oxime/amidoxime functionalized hollow nanospheres by air bubbles generated from "Ouzo-Like" effect for fast and massive uranium uptake[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2023, 306: 122463. |
| [28] | Bai X, Liu J X, Xu Y H, et al. CO2 Pickering emulsion in water templated hollow porous sorbents for fast and highly selective uranium extraction[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 387: 124096. |
| [29] | Bai X, Wang Y, Li H, et al. Stalagmites in karst cave inspired construction: lotus root-type adsorbent with porous surface derived from CO2-in-water Pickering emulsion for selective and ultrafast uranium extraction[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 419: 126398. |
| [30] | Zhu P W, Wang Y, Bai X, et al. CO2-in-Water Pickering Emulsion-Assisted Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly of Raspberry-like sorbent microbeads for uranium adsorption[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 279: 119710. |
| [31] | Xia Z R, Hu L M. Treatment of organics contaminated wastewater by ozone micro-nano-bubbles[J]. Water, 2019, 11(1): 55. |
| [32] | Xu Q Y, Nakajima M, Ichikawa S, et al. A comparative study of microbubble generation by mechanical agitation and sonication[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 2008, 9(4): 489-494. |
| [33] | Li Y F, Yang G Q, Yu S L, et al. In-situ investigation and modeling of electrochemical reactions with simultaneous oxygen and hydrogen microbubble evolutions in water electrolysis[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(52): 28283-28293. |
| [34] | Chen Q J, Zhao J, Deng X L, et al. Single-entity electrochemistry of nano- and microbubbles in electrolytic gas evolution[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2022, 13(26): 6153-6163. |
| [35] | Xu Q, Liang L, Nie T F, et al. Effect of electrolyte pH on oxygen bubble behavior in photoelectrochemical water splitting[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2023, 127(11): 5308-5320. |
| [36] | Lu J S, Huang X J, Zhang Z Q, et al. Co-coagulation of micro-nano bubbles (MNBs) for enhanced drinking water treatment: a study on the efficiency and mechanism of a novel cleaning process[J]. Water Research, 2022, 226: 119245. |
| [92] | Jin S H, Zhu C H, Zhang J Z, et al. Single-electron-mediated redox processes at the air-water interface of water microdroplets[J]. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2024, 54(1): 59-72. |
| [93] | Xing D, Meng Y F, Yuan X, et al. Capture of hydroxyl radicals by hydronium cations in water microdroplets[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(33): e202207587. |
| [94] | Gong K, Meng Y F, Zare R N, et al. Molecular mechanism for converting carbon dioxide surrounding water microdroplets containing 1, 2, 3-triazole to formic acid[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(12): 8576-8584. |
| [95] | Chen H, Wang R J, Xu J H, et al. Spontaneous reduction by one electron on water microdroplets facilitates direct carboxylation with CO2 [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(4): 2647-2652. |
| [96] | Bose S, Mofidfar M, Zare R N. Direct conversion of N2 and air to nitric acid in gas–water microbubbles[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(40): 27964-27971. |
| [97] | Li J, Xu J H, Song Q Y, et al. Methane C(sp3)–H bond activation by water microbubbles[J]. Chemical Science, 2024, 15(41): 17026-17031. |
| [98] | Bose S, Mehrgardi M A, Zare R N. Selective photochemical conversion of carbon dioxide to formic acid at gas–water interface of microbubbles[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2025, 147(31): 27449-27457. |
| [37] | Asakuma Y, Munenaga T, Nakata R. Observation of bubble formation in water during microwave irradiation by dynamic light scattering[J]. Heat and Mass Transfer, 2016, 52(9): 1833-1840. |
| [38] | Hassan P A, Rana S, Verma G. Making sense of Brownian motion: colloid characterization by dynamic light scattering[J]. Langmuir, 2015, 31(1): 3-12. |
| [39] | Hao R, Fan Y S, Howard M D, et al. Imaging nanobubble nucleation and hydrogen spillover during electrocatalytic water splitting[J]. PNAS, 2018, 115(23): 5878-5883. |
| [40] | Karpitschka S, Dietrich E, Seddon J R T, et al. Nonintrusive optical visualization of surface nanobubbles[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2012, 109(6): 066102. |
| [41] | Midtvedt D, Eklund F, Olsén E, et al. Size and refractive index determination of subwavelength particles and air bubbles by holographic nanoparticle tracking analysis[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 92(2): 1908-1915. |
| [42] | Zhang W, Wang J F, Li B, et al. Experimental investigation on bubble coalescence regimes under non-uniform electric field[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 417: 127982. |
| [43] | Tanimura Y, Yoshida K, Watanabe Y. A study on cleaning ability of oscillating bubbles driven by low-frequency ultrasound[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 49(7S): 07HE20. |
| [44] | Oh S H, Kim J M. Generation and stability of bulk nanobubbles[J]. Langmuir, 2017, 33(15): 3818-3823. |
| [45] | Ohgaki K, Khanh N Q, Joden Y, et al. Physicochemical approach to nanobubble solutions[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2010, 65(3): 1296-1300. |
| [46] | Zhou L M, Wang X Y, Shin H J, et al. Ultrahigh density of gas molecules confined in surface nanobubbles in ambient water[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(12): 5583-5593. |
| [47] | Ke S, Xiao W, Quan N N, et al. Formation and stability of bulk nanobubbles in different solutions[J]. Langmuir, 2019, 35(15): 5250-5256. |
| [48] | Popov E, He L L, Dominguez-Ontiveros E, et al. Detection of vapor nanobubbles by small angle neutron scattering (SANS)[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2018, 112(15): 153704. |
| [49] | Zhou L M, Wang S, Zhang L J, et al. Generation and stability of bulk nanobubbles: a review and perspective[J]. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 2021, 53: 101439. |
| [50] | Wei W, Chu F J, Chen G R, et al. Prebiotic formation of peptides through bubbling and arc plasma[J]. Chemistry – A European Journal, 2024, 30(42): e202401809. |
| [51] | Song X X, Wan Y Y, Yang Q, et al. Electrode fouling by gas bubbles enables catalyst-free hydrogen peroxide synthesis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2025, 147(26): 22864-22872. |
| [52] | Jia M Y, Farid M U, Kharraz J A, et al. Nanobubbles in water and wastewater treatment systems: Small bubbles making big difference[J]. Water Research, 2023, 245: 120613. |
| [53] | Zhang X H, Maeda N, Craig V S J. Physical properties of nanobubbles on hydrophobic surfaces in water and aqueous solutions[J]. Langmuir, 2006, 22(11): 5025-5035. |
| [54] | Zhang Z H, Wang S M, Cheng L N, et al. Micro-nano-bubble technology and its applications in food industry: a critical review[J]. Food Reviews International, 2023, 39(7): 4213-4235. |
| [55] | Sakr M, Mohamed M M, Maraqa M A, et al. A critical review of the recent developments in micro–nano bubbles applications for domestic and industrial wastewater treatment[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2022, 61(8): 6591-6612. |
| [56] | Li H Z, Hu L M, Song D J, et al. Characteristics of micro-nano bubbles and potential application in groundwater bioremediation[J]. Water Environment Research, 2014, 86(9): 844-851. |
| [57] | Li H Z, Hu L M, Song D J, et al. Subsurface transport behavior of micro-nano bubbles and potential applications for groundwater remediation[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2014, 11(1): 473-486. |
| [58] | Wang T Z, Yang C, Sun P Z, et al. Generation mechanism of hydroxyl free radicals in micro–nanobubbles water and its prospect in drinking water[J]. Processes, 2024, 12(4): 683. |
| [59] | Shen D S, Xie Z M, Shentu J, et al. Enhanced oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons by ozone micro-nano bubble water: Mechanism and influencing factors[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(3): 110281. |
| [60] | Jin N, Zhang F H, Cui Y, et al. Environment-friendly surface cleaning using micro-nano bubbles[J]. Particuology, 2022, 66: 1-9. |
| [61] | Tan K A, Mohan Y, Liew K J, et al. Development of an effective cleaning method for metallic parts using microbubbles[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 261: 121076. |
| [62] | Jia W H, Ren S L, Hu B. Effect of water chemistry on zeta potential of air bubbles[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2013, 8(4): 5828-5837. |
| [63] | Takahashi M. ζ potential of microbubbles in aqueous solutions: electrical properties of the Gas-Water interface[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2005, 109(46): 21858-21864. |
| [64] | Ushikubo F Y, Furukawa T, Nakagawa R, et al. Evidence of the existence and the stability of nano-bubbles in water[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2010, 361(1): 31-37. |
| [65] | Nosaka Y, Nosaka A Y. Generation and detection of reactive oxygen species in photocatalysis[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(17): 11302-11336. |
| [66] | Liu S, Oshita S, Kawabata S, et al. Identification of ROS produced by nanobubbles and their positive and negative effects on vegetable seed germination[J]. Langmuir, 2016, 32(43): 11295-11302. |
| [67] | Takahashi M, Shirai Y, Sugawa S. Free-radical generation from bulk nanobubbles in aqueous electrolyte solutions: ESR spin-trap observation of microbubble-treated water[J]. Langmuir, 2021, 37(16): 5005-5011. |
| [68] | Takahashi M, Chiba K, Li P. Formation of hydroxyl radicals by collapsing ozone microbubbles under strongly acidic conditions[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2007, 111(39): 11443-11446. |
| [69] | Nami-Ana S F, Mehrgardi M A, Mofidfar M, et al. Sustained regeneration of hydrogen peroxide at the water–gas interface of electrogenerated microbubbles on an electrode surface[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(46): 31945-31949. |
| [70] | Takahashi M, Ishikawa H, Asano T, et al. Effect of microbubbles on ozonized water for photoresist removal[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(23): 12578-12583. |
| [71] | Fan W, An W G, Huo M X, et al. Solubilization and stabilization for prolonged reactivity of ozone using micro-nano bubbles and ozone-saturated solvent: a promising enhancement for ozonation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 238: 116484. |
| [72] | Zeng W, Jia C, Luo H X, et al. Microbubble-dominated mass transfer intensification in the process of ammonia-based flue gas desulfurization[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(44): 19781-19792. |
| [73] | Wang X Y, Zhu Y L, Shuai Y, et al. Bubble size "bimodal" distribution enhances mixing and mass transfer in slurry bubbling column reactor[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2024, 63(16): 7401-7414. |
| [74] | Yao Z P, Chen C X, Wang T, et al. Effects of gas distributor on hydrodynamics in gas–liquid bubble column by visual experiments and CFD simulations[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 504: 158476. |
| [75] | 田洪舟, 杨高东, 杨国强, 等. 微界面强化重油浆态床低压加氢的传质基础[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(11): 4927-4935. |
| Tian H Z, Yang G D, Yang G Q, et al. Mass transfer basis of low-pressure hydrogenation for heavy oil in microinterface-intensified slurry-bed reactor[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(11): 4927-4935. | |
| [76] | 吴梦思, 田洪舟, 丁方园, 等. 微界面强化柴油加氢脱硫过程的模拟计算研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 2022, 58(4): 706-712. |
| Wu M S, Tian H Z, Ding F Y, et al. Simulation study on micro-interface intensified diesel hydrodesulfurization process[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Science), 2022, 58(4): 706-712. | |
| [77] | Janajreh I, ElSamad T, Noorul Hussain M. Intensification of transesterification via sonication numerical simulation and sensitivity study[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 185: 2151-2159. |
| [78] | 张晓国, 谢清峰, 李思, 等. 喷气燃料FITS加氢技术的工业应用[J]. 炼油技术与工程, 2017(9): 21-24. |
| Zhang X G, Xie Q F, Li S, et al. Commercial application of FITS hydrotreating technology for jet fuel[J]. Petroleum Refinery Engineering, 2017(9): 21-24. | |
| [79] | 谢清峰, 夏登刚, 姚峰, 等. 重整生成油全馏分FITS加氢脱烯烃技术的应用[J]. 炼油技术与工程, 2016, 46(1): 7-12. |
| Xie Q F, Xia D G, Yao F, et al. Application of FITS hydrogenation process for olefin removal of full fraction of reformate[J]. Petroleum Refinery Engineering, 2016, 46(1): 7-12. | |
| [80] | Li H, Zhang Y, Shu H, et al. Highlights in ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-mediated gene/drug delivery strategy for treatment of malignancies[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2022, 613: 121412. |
| [1] | 王御风, 罗小雪, 范鸿亮, 吴白婧, 李存璞, 魏子栋. 耦合电解水制氢的绿色有机电合成——电极界面调控策略综述[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3753-3771. |
| [2] | 李文俊, 赵中阳, 倪震, 周灿, 郑成航, 高翔. 基于气-液传质强化的湿法烟气脱硫CFD模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 505-519. |
| [3] | 张家琳, 徐大为, 高越, 李新刚. 泡沫镍负载CeO2改性CuO催化剂的碳烟燃烧性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 312-321. |
| [4] | 王婵, 肖国锡, 郭小雪, 徐人威, 岳源源, 鲍晓军. 基于介尺度结构解聚-重组装的Beta分子筛的绿色合成及应用[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2690-2697. |
| [5] | 刘华, 彭佳杰, 余凯, 倪毅, 王芳, 潘权稳, 葛天舒, 王如竹. 活性氧化铝基质新型复合吸附剂的制备和储热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(7): 3354-3361. |
| [6] | 李春曦, 张硕, 薛全喜, 叶学民. 基于抛物线形气-液界面的超疏水微通道减阻特性[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(10): 4126-4134. |
| [7] | 赵清华, 全学军, 程治良, 晏云鹏. 水力喷射-空气旋流器用于湿法烟气脱硫及其传质机理[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(11): 3993-4000. |
| [8] | 赵清华, 全学军, 程治良, 白薇扬. 水力喷射-空气旋流器中气液传质特性及其机理[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(10): 3652-3657. |
| [9] | 李 维1,韩大超1,张 红1,马 超2,蓝兴旺2,张雪平2. 压缩热再生干燥器活性氧化铝固体吸附剂的除湿性能[J]. 化工进展, 2013, 32(10): 2316-2318. |
| [10] | 王小梅,王家喜,张留成. 聚氨酯绿色合成工艺初探 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2009, 28(9): 1605-. |
| [11] | 石晓鹏,梅 华,沈 健. Ni2O3催化剂的制备及其催化NaClO分解产生活性氧的性能 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2009, 28(6): 962-. |
| [12] | 张 婷,俞树荣,冯辉霞,王 毅. 复合吸附脱硫剂的制备及其脱除SO2实验 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2009, 28(1): 159-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号