化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (2): 505-519.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20231100
李文俊1( ), 赵中阳1, 倪震2, 周灿2, 郑成航1,2(
), 赵中阳1, 倪震2, 周灿2, 郑成航1,2( ), 高翔1,2
), 高翔1,2
收稿日期:2023-10-26
修回日期:2024-01-09
出版日期:2024-02-25
发布日期:2024-04-10
通讯作者:
郑成航
作者简介:李文俊(1999—),男,硕士,工程师,liwenjun01@zjenergy.com.cn
基金资助:
Wenjun LI1( ), Zhongyang ZHAO1, Zhen NI2, Can ZHOU2, Chenghang ZHENG1,2(
), Zhongyang ZHAO1, Zhen NI2, Can ZHOU2, Chenghang ZHENG1,2( ), Xiang GAO1,2
), Xiang GAO1,2
Received:2023-10-26
Revised:2024-01-09
Online:2024-02-25
Published:2024-04-10
Contact:
Chenghang ZHENG
摘要:
针对燃煤电厂烟气脱硫过程中,高硫煤燃烧产生的高含硫烟气高效脱硫难题,通过计算流体力学(CFD)开展了钙法烟气SO2高效脱除研究,提出了基于塔内筛板构件及喷淋系统优化的多手段耦合增效方法。建立了宏观脱硫塔尺度下涵盖喷淋吸收-筛板鼓泡吸收的SO2多形式吸收脱除耦合模型,获得了浆液下落过程中的pH及SO2吸收速率变化规律,并研究了湍流构件对脱硫塔内的气液混合流动、相内相间传质、浆液内部化学反应等过程的影响机制。探究了筛板对于脱硫塔脱除效率的强化机制,并进一步开展了筛板布置位置优化设计研究。同时,针对脱硫塔喷淋系统开展了优化设计研究,通过对比研究获得了喷淋系统优化后布置方案。基于所提出的脱硫塔多手段耦合增效方法,研究了包括液气比、浆液粒径及入口烟气SO2浓度等不同参数影响下的脱硫塔SO2脱除性能,发现通过塔内筛板构件及喷淋系统优化多手段协同增效后,可实现不同工况下脱硫塔SO2脱除效率提升3%~8%。
中图分类号:
李文俊, 赵中阳, 倪震, 周灿, 郑成航, 高翔. 基于气-液传质强化的湿法烟气脱硫CFD模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 505-519.
Wenjun LI, Zhongyang ZHAO, Zhen NI, Can ZHOU, Chenghang ZHENG, Xiang GAO. CFD numerical simulation of wet flue gas desulfurization:performance improvement based on gas-liquid mass transfer enhancement[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 505-519.
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 塔高/m | 33.7 |
| 吸收塔塔径/m | 16 |
| 气液分布环数量/个 | 3 |
| 喷淋层数量/层 | 4 |
| 喷淋层高度/m | 11.4,13.9,16.4,18.9 |
| 筛板安装高度/m | 9.7 |
| 喷嘴数量/个 | 4×180 |
| 喷嘴喷淋角度/(°) | 120 |
表1 脱硫塔物理模型参数
Table 1 The structure parameters of desulfurization tower
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 塔高/m | 33.7 |
| 吸收塔塔径/m | 16 |
| 气液分布环数量/个 | 3 |
| 喷淋层数量/层 | 4 |
| 喷淋层高度/m | 11.4,13.9,16.4,18.9 |
| 筛板安装高度/m | 9.7 |
| 喷嘴数量/个 | 4×180 |
| 喷嘴喷淋角度/(°) | 120 |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 烟气流量/(m3/h) | 2779200 |
| 烟气入口温度/K | 373.15 |
| 烟气SO2浓度/(mg/m3) | 1680 |
| 浆液流量/(m3/h) | 33750 |
| 浆液粒径/mm | 1.5 |
| 浆液初始pH | 5.5 |
表2 模型参数设置
Table 2 The parameters settings of model
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 烟气流量/(m3/h) | 2779200 |
| 烟气入口温度/K | 373.15 |
| 烟气SO2浓度/(mg/m3) | 1680 |
| 浆液流量/(m3/h) | 33750 |
| 浆液粒径/mm | 1.5 |
| 浆液初始pH | 5.5 |
| 项目 | 边界条件 |
|---|---|
| 连续相 | |
| 脱硫塔入口 | 速度入口 |
| 脱硫塔出口 | 压力出口 |
| 离散相 | |
| 脱硫塔壁面 | 捕捉 |
| 脱硫塔出口及入口 | 逃离 |
| 除雾器 | 捕捉 |
| 气液分配环 | 反射 |
表3 模型边界条件
Table 3 The boundary conditions of model
| 项目 | 边界条件 |
|---|---|
| 连续相 | |
| 脱硫塔入口 | 速度入口 |
| 脱硫塔出口 | 压力出口 |
| 离散相 | |
| 脱硫塔壁面 | 捕捉 |
| 脱硫塔出口及入口 | 逃离 |
| 除雾器 | 捕捉 |
| 气液分配环 | 反射 |
| 工况 | 负荷/MW | 入口SO2浓度/(mg/m3) | 出口SO2浓度/(mg/m3) | 浆液pH | 脱硫 效率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 667 | 1927.22 | 20.26 | 4.62 | 92.43 |
| 2 | 664 | 1838.49 | 20.55 | 4.91 | 94.28 |
| 3 | 663 | 1918.39 | 20.77 | 4.67 | 93.18 |
| 4 | 650 | 1865.04 | 23.02 | 4.97 | 95.13 |
| 5 | 618 | 1870.65 | 19.85 | 5.34 | 97.04 |
| 6 | 612 | 1831.43 | 24.18 | 5.26 | 98.38 |
| 7 | 597 | 1650.07 | 19.79 | 5.29 | 98.80 |
| 8 | 584 | 1426.23 | 13.56 | 5.35 | 99.05 |
| 9 | 576 | 1405.45 | 14.07 | 5.33 | 99.00 |
| 10 | 547 | 1749.27 | 14.31 | 5.36 | 99.18 |
| 11 | 534 | 1494.17 | 13.50 | 5.33 | 99.40 |
| 12 | 512 | 1552.55 | 17.24 | 5.28 | 98.89 |
表4 不同工况下脱硫塔现场测试的脱硫效率
Table 4 Test desulfurization efficiency under different conditions
| 工况 | 负荷/MW | 入口SO2浓度/(mg/m3) | 出口SO2浓度/(mg/m3) | 浆液pH | 脱硫 效率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 667 | 1927.22 | 20.26 | 4.62 | 92.43 |
| 2 | 664 | 1838.49 | 20.55 | 4.91 | 94.28 |
| 3 | 663 | 1918.39 | 20.77 | 4.67 | 93.18 |
| 4 | 650 | 1865.04 | 23.02 | 4.97 | 95.13 |
| 5 | 618 | 1870.65 | 19.85 | 5.34 | 97.04 |
| 6 | 612 | 1831.43 | 24.18 | 5.26 | 98.38 |
| 7 | 597 | 1650.07 | 19.79 | 5.29 | 98.80 |
| 8 | 584 | 1426.23 | 13.56 | 5.35 | 99.05 |
| 9 | 576 | 1405.45 | 14.07 | 5.33 | 99.00 |
| 10 | 547 | 1749.27 | 14.31 | 5.36 | 99.18 |
| 11 | 534 | 1494.17 | 13.50 | 5.33 | 99.40 |
| 12 | 512 | 1552.55 | 17.24 | 5.28 | 98.89 |
筛板安装高度 H/m | 筛板鼓泡区 脱除效率/% | 喷淋吸收区 脱除效率/% | 总脱除效率/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9.0 | 22.4 | 72.4 | 94.8 |
| 9.7 | 31.5 | 64.7 | 96.2 |
| 10.5 | 39.7 | 55.7 | 95.4 |
表5 不同筛板安装高度塔内脱除效果对比
Table 5 Comparison of removal efficiency with different installation heights of sieve plate
筛板安装高度 H/m | 筛板鼓泡区 脱除效率/% | 喷淋吸收区 脱除效率/% | 总脱除效率/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9.0 | 22.4 | 72.4 | 94.8 |
| 9.7 | 31.5 | 64.7 | 96.2 |
| 10.5 | 39.7 | 55.7 | 95.4 |
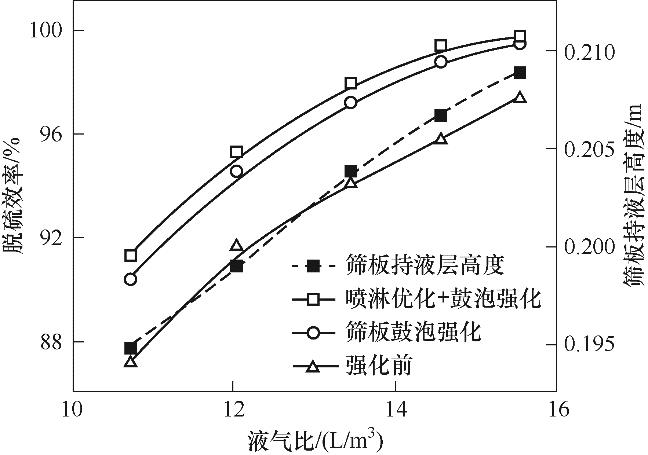
图15 液气比对筛板持液高度及脱除效率的影响(入口SO2浓度3000 mg/m3, d=1.5 mm,H=9.7 m)
Fig.15 The effect of liquid-gas ratio on liquid holding height of sieve plate and removal efficiency
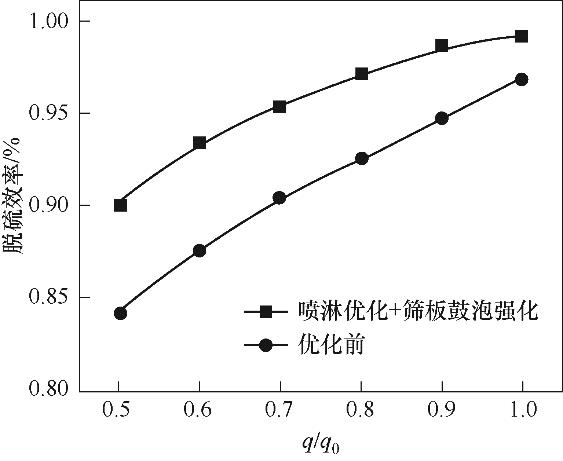
图17 不同烟气流量下脱硫塔性能变化规律(q0=2779200 m3/h,L/G=15.5 L/m3, d=1.5 mm,H=9.7m)
Fig.17 The variation of desulfurization efficiency under different flue gas flow rates
| 1 | 陈阵. 湿法脱硫塔内流场调控与强化传质过程研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2018. |
| Chen Z. Gas-liquid flow pattern controlling and mass transfer enhancement in wet flue gas desulfurization tower[D].Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2018. | |
| 2 | 钟毅. 基于WFGD系统的硫、氮、汞污染物协同脱除的理论与实验研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2008. |
| Zhong Y. Theoretical and experimental study of simultaneous removal of sulfur, nitrogen and mercury pollutant in WFGD system[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2008. | |
| 3 | 李存杰. 湿法烟气SO2高效脱除及SO3协同控制的实验研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017. |
| Li C J. Experimental study on efficient removal of SO2 and synthesis control of SO3 based on wet flue gas desulfurization system[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017. | |
| 4 | Kallinikos L E, Farsari E I, Spartinos D N, et al. Simulation of the operation of an industrial wet flue gas desulfurization system[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2010, 91(12): 1794-1802. |
| 5 | Zhu J, Ye S C, Bai J, et al. A concise algorithm for calculating absorption height in spray tower for wet limestone-gypsum flue gas desulfurization[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2015, 129: 15-23. |
| 6 | Brogren C, Karlsson H T. Modeling the absorption of SO2 in a spray scrubber using the penetration theory[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1997, 52(18): 3085-3099. |
| 7 | Uchida S, Koide K, Shindo M. Gas absorption with fast reaction into a slurry containing fine particles[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1975, 30(5/6): 644-646. |
| 8 | Dou B L, Pan W G, Jin Q, et al. Prediction of SO2 removal efficiency for wet flue gas desulfurization[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2009, 50(10): 2547-2553. |
| 9 | 霍旺. 石灰石-石膏湿法脱硫过程的吸收、氧化及结晶机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2009. |
| Huo W. Mechanism research on the absorption, oxidation and crystallization in the process of limestone-gypsum WFGD[D].Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2009. | |
| 10 | Marocco L, Inzoli F. Multiphase Euler–Lagrange CFD simulation applied to wet flue gas desulphurisation technology[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2009, 35(2): 185-194. |
| 11 | Chen Z, Wang H M, Zhuo J K, et al. Experimental and numerical study on effects of deflectors on flow field distribution and desulfurization efficiency in spray towers[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2017, 162: 1-12. |
| 12 | Qu J Y, Qi N N, Zhang K, et al. Wet flue gas desulfurization performance of 330 MW coal-fired power unit based on computational fluid dynamics region identification of flow pattern and transfer process[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2021, 29: 13-26. |
| 13 | 杨国华, 吴迪, 苟远波, 等. 基于气-液传质氨法脱硫喷淋吸收CFD仿真模拟[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(4): 1519-1527. |
| Yang G H, Wu D, Gou Y B, et al. CFD simulation of spray absorption of ammonia-based desulfurization based on gas-liquid mass transfer[J]. China Environmental Science, 2023, 43(4): 1519-1527. | |
| 14 | 韩文雅. 湿式脱硫喷淋塔内部流场的数值模拟[D]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2011. |
| Han W Y. Numerical simulation of flow field in wet desulfurization spray tower[D].Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2011. | |
| 15 | 杨贤平, 赵长遂, 陈晓平, 等. 液体分布环对喷淋塔中烟气流场影响的数值模拟[J]. 南京工程学院学报(自然科学版), 2007, 5(1): 35-40. |
| Yang X P, Zhao C S, Chen X P, et al. Numerical simulation of influence of LDR on flow field in spray scrubber[J]. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 5(1): 35-40. | |
| 16 | Warych J, Szymanowski M. Model of the wet limestone flue gas desulfurization process for cost optimization[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2001, 40(12): 2597-2605. |
| 17 | Gómez A, Fueyo N, Tomás A. Detailed modelling of a flue-gas desulfurisation plant[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2007, 31(11): 1419-1431. |
| 18 | Zhong Y, Gao X, Huo W, et al. A model for performance optimization of wet flue gas desulfurization systems of power plants[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2008, 89(11): 1025-1032. |
| 19 | Tseng C C, Li C J. Eulerian-Eulerian numerical simulation for a flue gas desulfurization tower with perforated sieve trays[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 116: 329-345. |
| 20 | Tseng C C, Li C J. Numerical investigations for the two-phase flow structures and chemical reactions within a tray flue gas desulfurization tower by porous media model[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(5): 2276. |
| 21 | 王鹏辉, 庄黎伟, 张强, 等. 湿法脱硫喷淋塔内文丘里棒层构件流体力学[J]. 华东理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 42(2): 171-179. |
| Wang P H, Zhuang L W, Zhang Q, et al. Flow behavior through Venturi rod banks in WFGD spray tower[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 42(2): 171-179. | |
| 22 | Cui L, Lu, J, Liu L, et al. Simulation study on novel groove separator in a dual‐loop wet flue gas desulfurization spray tower[J]. Asia‐Pacific Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2020, 15(4): e2442. |
| 23 | Li W J, Zhang Y X, Zhao Z Y, et al. Simulation investigation on marine exhaust gas SO2 absorption by seawater scrubbing[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 2022, 72(5): 383-402. |
| 24 | 林军, 王凡, 张凡, 等. 烟气分布器对半干法脱硫塔流场的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2006, 26(2): 129-132. |
| Lin J, Wang F, Zhang F, et al. Influence of flue gas distributor on flow field of semi-dry desulphurization reactor[J]. China Environmental Science, 2006, 26(2): 129-132. | |
| 25 | Li X J, Dong M R, Li S D, et al. A numerical study of the ammonia desulfurization in the spray scattering tower[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 2020, 155: 108069. |
| 26 | 郭瑞堂. 石灰石活性和塔内流场对湿法烟气脱硫效率的影响研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2008. |
| Guo R T. Study on the effects of limestone reactivity and flow field on wet flue gas desulfurization efficiency[D].Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2008. | |
| 27 | 吴其荣, 关越, 周川, 等. 筛板脱硫塔气液流动及运行参数的影响分析[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2019, 45(3): 61-65. |
| Wu Q R, Guan Y, Zhou C, et al. Analysis of multiphase flow and different parameters impact on a sieve-plate desulphurization tower[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2019, 45(3): 61-65. | |
| 28 | Wu Q R, Wu M L, Du Y G, et al. Enhanced efficiency of the sieve tray in a desulfurization spray scrubber[J]. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2022, 10: 918233. |
| 29 | Zhao Z Y, Zhang Y X, Gao W C, et al. Simulation of SO2 absorption and performance enhancement of wet flue gas desulfurization system[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 150: 453-463. |
| 30 | 曲江源, 齐娜娜, 关彦军, 等. 湿法烟气脱硫塔内传递与化学反应过程CFD模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(6): 2117-2128. |
| Qu J Y, Qi N N, Guan Y J, et al. CFD simulation of transfer and chemical reaction process in wet flue gas desulfurization tower[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(6): 2117-2128. | |
| 31 | Qu J Y, Qi N N, Li Z, et al. Mass transfer process intensification for SO2 absorption in a commercial-scale wet flue gas desulfurization scrubber[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing- Process Intensification, 2021, 166: 108478. |
| 32 | Guo H, Zhou S, Shreka M, et al. A numerical investigation on the optimization of uneven flow in a marine de-SO x scrubber[J]. Processes, 2020, 8(7): 862. |
| 33 | Neveux T, Le Moullec Y. Wet industrial flue gas desulfurization unit: model development and validation on industrial data[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(12): 7579-7592. |
| 34 | Marocco L. Modeling of the fluid dynamics and SO2 absorption in a gas-liquid reactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 162(1): 217-226. |
| 35 | Morsi S A, Alexander A J. An investigation of particle trajectories in two-phase flow systems[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1972, 55: 193-208. |
| 36 | Xu Z P, Afacan A, Chuang K T. Efficiency of dual flow trays in distillation[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1994, 72(4): 607-613. |
| [1] | 詹小斌, 王会彬, 蒋亚龙, 史铁林. 声共振混合器高黏度流体混合的功耗特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 531-542. |
| [2] | 麻雪怡, 刘克勤, 胡激江, 姚臻. POE溶液聚合反应器内混合与反应过程的CFD研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 322-337. |
| [3] | 余洋, 罗祎青, 魏荣辉, 张文慧, 袁希钢. 考虑节点中断风险的弹性供应链设计方法[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 338-353. |
| [4] | 张思雨, 殷勇高, 贾鹏琦, 叶威. 双U型地埋管群跨季节蓄热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 295-301. |
| [5] | 黄琮琪, 吴一梅, 陈建业, 邵双全. 碱性电解水制氢装置热管理系统仿真研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 320-328. |
| [6] | 金正浩, 封立杰, 李舒宏. 氨水溶液交叉型再吸收式热泵的能量及 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. |
| [7] | 肖明堃, 杨光, 黄永华, 吴静怡. 浸没孔液氧气泡动力学数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 87-95. |
| [8] | 米泽豪, 花儿. 基于DFT和COSMO-RS理论研究多元胺型离子液体吸收SO2气体[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3681-3696. |
| [9] | 温凯杰, 郭力, 夏诏杰, 陈建华. 一种耦合CFD与深度学习的气固快速模拟方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3775-3785. |
| [10] | 陈哲文, 魏俊杰, 张玉明. 超临界水煤气化耦合SOFC发电系统集成及其能量转化机制[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3888-3902. |
| [11] | 齐聪, 丁子, 余杰, 汤茂清, 梁林. 基于选择吸收纳米薄膜的太阳能温差发电特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3921-3930. |
| [12] | 邢雷, 苗春雨, 蒋明虎, 赵立新, 李新亚. 井下微型气液旋流分离器优化设计与性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3394-3406. |
| [13] | 张瑞航, 曹潘, 杨锋, 李昆, 肖朋, 邓春, 刘蓓, 孙长宇, 陈光进. ZIF-8纳米流体天然气乙烷回收工艺的产品纯度关键影响因素分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3386-3393. |
| [14] | 胡兴枝, 张皓焱, 庄境坤, 范雨晴, 张开银, 向军. 嵌有超小CeO2纳米粒子的碳纳米纤维的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3584-3596. |
| [15] | 岳林静, 廖艺涵, 薛源, 李雪洁, 李玉星, 刘翠伟. 凹坑缺陷对厚孔板喉部空化流动特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3292-3308. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号