• •
张阳光1( ), 王顺1, 刘杨1, 储金科1, 石慧2, 汤吉海1,3, 崔咪芬1, 乔旭1,3, 夏铭1(
), 王顺1, 刘杨1, 储金科1, 石慧2, 汤吉海1,3, 崔咪芬1, 乔旭1,3, 夏铭1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-11-27
修回日期:2026-01-12
出版日期:2026-01-21
通讯作者:
夏铭
作者简介:张阳光(2001—),男,硕士研究生,18317637815@163.com
基金资助:
Yangguang ZHANG1( ), Shun WANG1, Yang LIU1, Jinke CHU1, Hui SHI2, Jihai TANG1,3, Mifen CUI1, Xu QIAO1,3, Ming XIA1(
), Shun WANG1, Yang LIU1, Jinke CHU1, Hui SHI2, Jihai TANG1,3, Mifen CUI1, Xu QIAO1,3, Ming XIA1( )
)
Received:2025-11-27
Revised:2026-01-12
Online:2026-01-21
Contact:
Ming XIA
摘要:
碳酸二甲酯(DMC)是重要的绿色化工中间体和锂电池电解液溶剂,然而,在DMC生产过程中,DMC与甲醇(MeOH)往往形成共沸体系且存在夹点区域,导致分离难度大,能耗占比高,是制约DMC节能高效生产的关键瓶颈。不同合成工艺如酯交换法、氧化羰基化法、尿素醇解法和二氧化碳直接合成法等所产生的DMC/MeOH混合物组成存在差异,直接影响分离难度、能耗、节能策略及技术适配性,因此亟需开展针对不同进料特性的节能高效分离技术的调研与研究。为此,针对DMC/MeOH共沸体系的节能分离,系统综述了变压精馏、萃取精馏、非均相共沸精馏及膜分离四种技术的基本原理、工艺流程、关键参数、节能方向和应用特性,重点分析了基于不同进料组成的技术适配规律:较低浓度的DMC进料时,萃取精馏展现操作弹性与经济性优势;较高浓度(近共沸组成)的DMC进料时,热集成非均相共沸精馏与变压精馏更具竞争力,精馏-膜耦合技术为节能分离提供重要支撑。展望未来,开发传统精馏耦合低成本绿色材料(膜、离子液体等)的集成工艺,将成为推动DMC节能、低碳和高值化发展的重点研发方向。
中图分类号:
张阳光, 王顺, 刘杨, 储金科, 石慧, 汤吉海, 崔咪芬, 乔旭, 夏铭. 碳酸二甲酯-甲醇共沸体系的节能分离技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251332.
Yangguang ZHANG, Shun WANG, Yang LIU, Jinke CHU, Hui SHI, Jihai TANG, Mifen CUI, Xu QIAO, Ming XIA. Research progress on energy-saving separation of dimethyl carbonate/methanol azeotropic mixture[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251332.
| 项目 | 指标 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 电子级 | 优级 | 一级 | ||
| 碳酸二甲酯,(wt%) | ≥ | 99.99 | 99.9 | 99.5 |
| 甲醇,(wt%) | ≤ | 0.002 | 0.020 | 0.050 |
| 水,(wt%) | ≤ | 0.003 | 0.020 | 0.10 |
| 密度,(ρ)/(g/cm3) | 1.071±0.005 | |||
| 钠,/(μg/mL) | ≤ | 1.0 | ||
| 钾,/(μg/mL) | ≤ | 1.0 | ||
| 铜,/(μg/mL) | ≤ | 1.0 | ||
| 铁,/(μg/mL) | ≤ | 1.0 | ||
| 铅,/(μg/mL) | ≤ | 1.0 | ||
| 锌,/(μg/mL) | ≤ | 1.0 | ||
| 铬,/(μg/mL) | ≤ | 1.0 | ||
| 镍,/(μg/mL) | ≤ | 1.0 | ||
表 1 国标GB/T 33107-2016技术指标
Table 1 Technical Specifications of National Standard GB/T 33107-2016
| 项目 | 指标 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 电子级 | 优级 | 一级 | ||
| 碳酸二甲酯,(wt%) | ≥ | 99.99 | 99.9 | 99.5 |
| 甲醇,(wt%) | ≤ | 0.002 | 0.020 | 0.050 |
| 水,(wt%) | ≤ | 0.003 | 0.020 | 0.10 |
| 密度,(ρ)/(g/cm3) | 1.071±0.005 | |||
| 钠,/(μg/mL) | ≤ | 1.0 | ||
| 钾,/(μg/mL) | ≤ | 1.0 | ||
| 铜,/(μg/mL) | ≤ | 1.0 | ||
| 铁,/(μg/mL) | ≤ | 1.0 | ||
| 铅,/(μg/mL) | ≤ | 1.0 | ||
| 锌,/(μg/mL) | ≤ | 1.0 | ||
| 铬,/(μg/mL) | ≤ | 1.0 | ||
| 镍,/(μg/mL) | ≤ | 1.0 | ||
| 企业名称 | 工艺路线 | 产能(万吨/年) | 合计 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 浙江石化 | EC酯交换法 | 20 | 酯交换法产能64.1万吨/年 |
| 石大胜华 | PC酯交换法 | 12.5 | |
| 铜陵金泰 | PC酯交换法 | 9 | |
| 万华化学 | PC酯交换法 | 8 | |
| 东营海科 | PC酯交换法 | 6 | |
| 维尔斯化工 | PC酯交换法 | 6 | |
| 江苏奥克 | EC酯交换法 | 2.6 | |
| 重庆东能 | 液相羰基化 | 7 | 氧化羰基化法产能18万吨/年 |
| 重庆万盛 | 液相羰基化 | 6 | |
| 安徽红四方 | 气相羰基化 | 5 | |
| 中科惠安 | 尿素醇解 | 5 | 尿素醇解法产能5万吨/年 |
表 2 中国碳酸二甲酯制造商主要工艺路线
Table 2 Main process route of Chinese dimethyl carbonate manufacturers
| 企业名称 | 工艺路线 | 产能(万吨/年) | 合计 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 浙江石化 | EC酯交换法 | 20 | 酯交换法产能64.1万吨/年 |
| 石大胜华 | PC酯交换法 | 12.5 | |
| 铜陵金泰 | PC酯交换法 | 9 | |
| 万华化学 | PC酯交换法 | 8 | |
| 东营海科 | PC酯交换法 | 6 | |
| 维尔斯化工 | PC酯交换法 | 6 | |
| 江苏奥克 | EC酯交换法 | 2.6 | |
| 重庆东能 | 液相羰基化 | 7 | 氧化羰基化法产能18万吨/年 |
| 重庆万盛 | 液相羰基化 | 6 | |
| 安徽红四方 | 气相羰基化 | 5 | |
| 中科惠安 | 尿素醇解 | 5 | 尿素醇解法产能5万吨/年 |
| 进料组成(wt%) | DMC纯度(wt%) | 能耗 | 类型 | 高压塔压力(MPa) | 文献 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMC | MeOH | 净蒸汽单耗 (吨/吨DMC) | 电力 (MW/吨) | ||||
| 30 | 70 | 99.5 | 16.79 | 0 | 高压-低压两塔变压精馏 | 1.32 | [ |
| 5 | 95 | 99.99 | 25.80 | 0 | 常压-加压-常压三塔精馏 (含加压-常压塔热集成) | 1.3 | [ |
| 10.9 | 89.1 | 99.5 | 32.73 | 0 | 完全热集成变压精馏 (低压-高压流程) | 1.2 | [ |
| 33.8 | 66.2 | 99.99 | 5.41 | 0 | 热耦合变压精馏 (高压-低压流程) | 1.5 | [ |
| 30 | 70 | 99.9 | 3.33 | 0.15 | 中间再沸器的热泵辅助 (高压-低压流程) | 0.7 | [ |
| 30 | 70 | 99.9 | 0.54 | 0.84 | 塔底产品闪蒸式热泵精馏 (高压-低压流程) | 0.7 | [ |
| 30 | 70 | 99.9 | 0 | 0.85 | 蒸汽再压缩热泵精馏 (高压-低压流程) | 0.7 | [ |
| 30 | 70 | 99.9 | 0 | 0.84 | 串级换热蒸汽压缩式精馏 (高压-低压流程) | 0.7 | [ |
| 30 | 70 | 99.9 | 2.85 | 0 | 反应变压精馏 | 0.76 | [ |
| 10.89 | 89.91 | 99.5 | 16.95 | 0 | 变压精馏 (高压-低压流程) | 1.2 | [ |
表 3 变压精馏分离效果、单吨产品能耗与操作压力
Table 3 Separation Performance, Energy Consumption and Operating Pressure of Pressure-Swing Distillation
| 进料组成(wt%) | DMC纯度(wt%) | 能耗 | 类型 | 高压塔压力(MPa) | 文献 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMC | MeOH | 净蒸汽单耗 (吨/吨DMC) | 电力 (MW/吨) | ||||
| 30 | 70 | 99.5 | 16.79 | 0 | 高压-低压两塔变压精馏 | 1.32 | [ |
| 5 | 95 | 99.99 | 25.80 | 0 | 常压-加压-常压三塔精馏 (含加压-常压塔热集成) | 1.3 | [ |
| 10.9 | 89.1 | 99.5 | 32.73 | 0 | 完全热集成变压精馏 (低压-高压流程) | 1.2 | [ |
| 33.8 | 66.2 | 99.99 | 5.41 | 0 | 热耦合变压精馏 (高压-低压流程) | 1.5 | [ |
| 30 | 70 | 99.9 | 3.33 | 0.15 | 中间再沸器的热泵辅助 (高压-低压流程) | 0.7 | [ |
| 30 | 70 | 99.9 | 0.54 | 0.84 | 塔底产品闪蒸式热泵精馏 (高压-低压流程) | 0.7 | [ |
| 30 | 70 | 99.9 | 0 | 0.85 | 蒸汽再压缩热泵精馏 (高压-低压流程) | 0.7 | [ |
| 30 | 70 | 99.9 | 0 | 0.84 | 串级换热蒸汽压缩式精馏 (高压-低压流程) | 0.7 | [ |
| 30 | 70 | 99.9 | 2.85 | 0 | 反应变压精馏 | 0.76 | [ |
| 10.89 | 89.91 | 99.5 | 16.95 | 0 | 变压精馏 (高压-低压流程) | 1.2 | [ |
| 进料组成(wt%) | 夹带剂 | DMC纯度 | 净蒸汽单耗(吨/吨DMC) | 类型 | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMC | MeOH | |||||
| 42.8 | 51.9 | 1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑氯盐 | 99.9 wt% | 3.92 | DMC/MeOH/水体系 | [ |
| 33 | 67 | 苯胺 | 99.5 wt% | 3.11 | 萃取精馏 | [ |
| 30 | 70 | 邻二甲苯 | 99.9 wt% | 6.64 | 两塔萃取精馏 | [ |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 二甲基亚砜 | 99.8 wt% | 1.94 | 热集成萃取精馏 (萃取MeOH) | [ |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 水杨酸甲酯 | 99.8 mol% | 3.36 | 两塔萃取精馏 | [ |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 水杨酸甲酯 | 99.8 mol% | 2.24 | 热集成萃取精馏 | [ |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 苯甲酸乙酯 | 99..8 mol% | 5.70 | 两塔萃取精馏 | [ |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 苯甲酸乙酯 | 99.8 mol% | 4.34 | 热集成萃取精馏 | [ |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 苯酚 | 99.8 mol% | 4.70 | 萃取精馏工艺 | [ |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 苯酚 | 99.8 mol% | 3.84 | 热耦合萃取精馏工艺 | [ |
表 4 萃取精馏分离DMC/MeOH体系常用夹带剂、分离效果及单吨产品能耗
Table 4 Commonly Used Extractants and Separation Efficiency in DMC/MeOH Extraction Distillation Systems
| 进料组成(wt%) | 夹带剂 | DMC纯度 | 净蒸汽单耗(吨/吨DMC) | 类型 | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMC | MeOH | |||||
| 42.8 | 51.9 | 1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑氯盐 | 99.9 wt% | 3.92 | DMC/MeOH/水体系 | [ |
| 33 | 67 | 苯胺 | 99.5 wt% | 3.11 | 萃取精馏 | [ |
| 30 | 70 | 邻二甲苯 | 99.9 wt% | 6.64 | 两塔萃取精馏 | [ |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 二甲基亚砜 | 99.8 wt% | 1.94 | 热集成萃取精馏 (萃取MeOH) | [ |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 水杨酸甲酯 | 99.8 mol% | 3.36 | 两塔萃取精馏 | [ |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 水杨酸甲酯 | 99.8 mol% | 2.24 | 热集成萃取精馏 | [ |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 苯甲酸乙酯 | 99..8 mol% | 5.70 | 两塔萃取精馏 | [ |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 苯甲酸乙酯 | 99.8 mol% | 4.34 | 热集成萃取精馏 | [ |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 苯酚 | 99.8 mol% | 4.70 | 萃取精馏工艺 | [ |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 苯酚 | 99.8 mol% | 3.84 | 热耦合萃取精馏工艺 | [ |
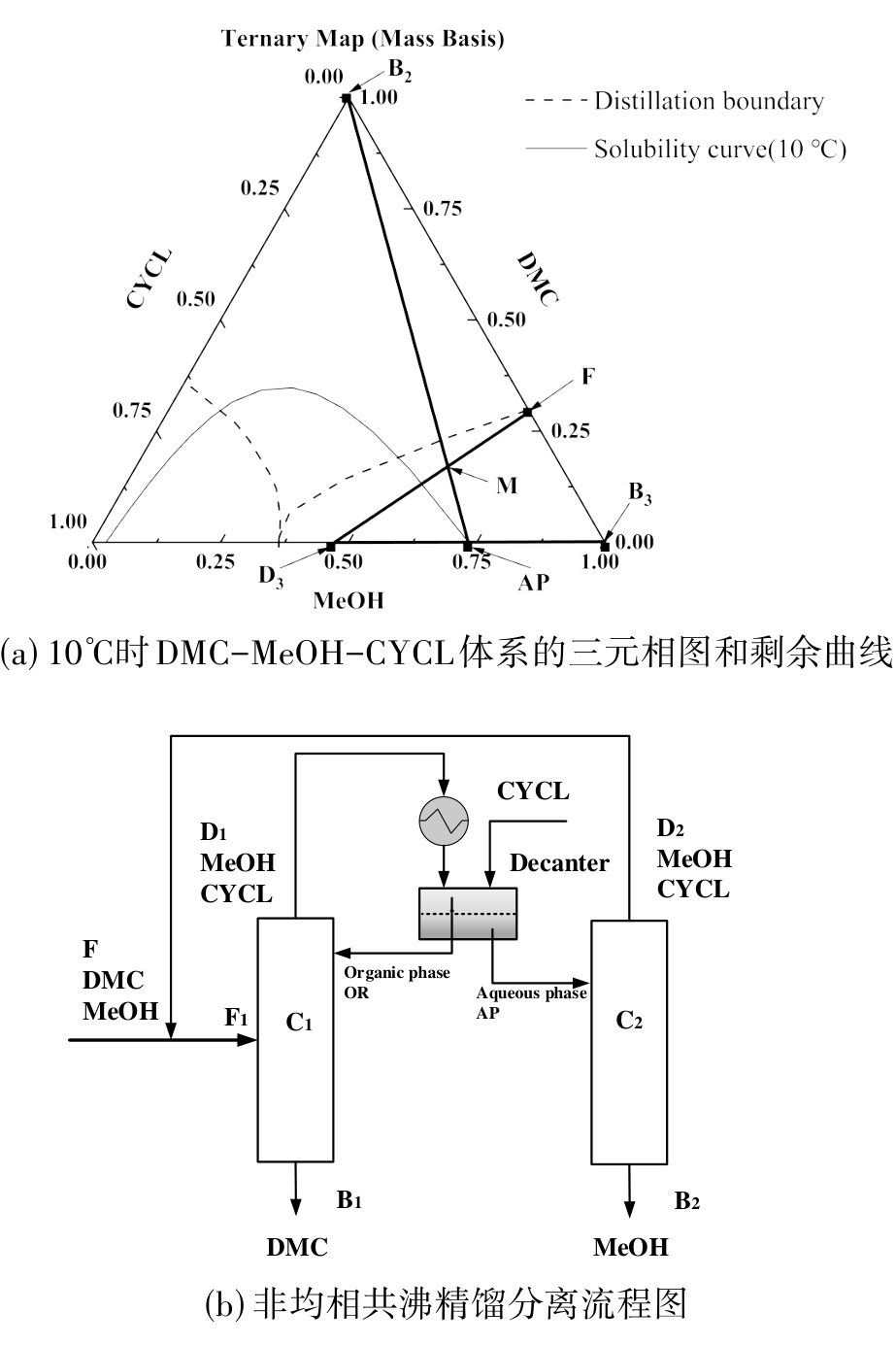
图 4 以CYCL作夹带剂的非均相共沸精馏分离DMC/MeOH体系原理
Fig. 4 Principle of Heterogeneous Azeotropic Distillation for the DMC/MeOH separation with CYCL as light Entrainer
| 进料组成(wt%) | 夹带剂 | DMC纯度(wt%) | 能耗 | 类型 | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMC | MeOH | 蒸汽(吨/吨DMC) | ||||
| 三氯乙烯 | 99.99 | 实验分析、工艺优化 | [ | |||
| 30 | 70 | 正庚烷 | 99.5 | 模型分析、共沸精馏模拟 | [ | |
| 30 | 70 | 正庚烷 | 98.3 | 共沸精馏实验、优化 | [ | |
| 30 | 70 | 正己烷 | 98.7 | 共沸精馏实验、优化 | [ | |
| 30 | 70 | 环己烷 | 99.5 | 共沸精馏实验、优化 | [ | |
| 30 | 70 | 1,2-二氯乙烷 | 99.9 | 共沸精馏实验、优化 | [ | |
| 30 | 70 | 四氯化碳 | 98.8 | 共沸精馏实验、优化 | [ | |
| 30 | 70 | 苯 | 99.6 | 共沸精馏实验、优化 | [ | |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 水 | 99.95 | 2.42 | 热集成双效共沸精馏工艺 | [ |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 环己烷 | 99.9 | 0.82吨低压蒸汽+约73.5吨热水(42~55℃) | 热泵热集成非均相共沸精馏工艺 | [ |
表 5 共沸精馏分离DMC/MeOH共沸体系的各种夹带剂及分离效果
Table 5 Separation Performance in DMC/MeOH Azeotropic Distillation with Various Entrainers
| 进料组成(wt%) | 夹带剂 | DMC纯度(wt%) | 能耗 | 类型 | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMC | MeOH | 蒸汽(吨/吨DMC) | ||||
| 三氯乙烯 | 99.99 | 实验分析、工艺优化 | [ | |||
| 30 | 70 | 正庚烷 | 99.5 | 模型分析、共沸精馏模拟 | [ | |
| 30 | 70 | 正庚烷 | 98.3 | 共沸精馏实验、优化 | [ | |
| 30 | 70 | 正己烷 | 98.7 | 共沸精馏实验、优化 | [ | |
| 30 | 70 | 环己烷 | 99.5 | 共沸精馏实验、优化 | [ | |
| 30 | 70 | 1,2-二氯乙烷 | 99.9 | 共沸精馏实验、优化 | [ | |
| 30 | 70 | 四氯化碳 | 98.8 | 共沸精馏实验、优化 | [ | |
| 30 | 70 | 苯 | 99.6 | 共沸精馏实验、优化 | [ | |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 水 | 99.95 | 2.42 | 热集成双效共沸精馏工艺 | [ |
| 32.6 | 67.3 | 环己烷 | 99.9 | 0.82吨低压蒸汽+约73.5吨热水(42~55℃) | 热泵热集成非均相共沸精馏工艺 | [ |
| 膜材料 | 进料DMC含量/wt% | 膜通量/(g·m-2·h-1) | 优先渗透 | 分离因子 | 选择性 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [C8MIM][NTf2] SILM | 91.83 | 739.8 | DMC | 21.2 | 67 | [ |
| [C8C1Pyrr][NTf2] SILM | 74 | 241 | DMC | 21 | 48.41 | [ |
| PDMS | 30 | 7600 | DMC | 3.2 | [ | |
| MTES-MFI/PDMS | 30 | 11500 | DMC | 3.6 | [ | |
| MOF-801-15%AA | 90 | 3736 | MeOH | 629 | 157 | [ |
| GO-Zn2+ | 90 | 707 | MeOH | 61.9 | [ | |
| PERVAP™1255 | 27.5 | 705 | MeOH | 14.41 | [ | |
| SAPO-34 分子筛 | 10 | 14000-17000 | MeOH | 600-2000 | [ | |
| PEEK-WC | 3.8-96.2 | 78-227 | MeOH | 0.25-13.4 | 0.2-3.5 | [ |
表 6 DMC/MeOH体系分离膜参数
Table 6 Separation Membrane Parameters in DMC/MeOH System
| 膜材料 | 进料DMC含量/wt% | 膜通量/(g·m-2·h-1) | 优先渗透 | 分离因子 | 选择性 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [C8MIM][NTf2] SILM | 91.83 | 739.8 | DMC | 21.2 | 67 | [ |
| [C8C1Pyrr][NTf2] SILM | 74 | 241 | DMC | 21 | 48.41 | [ |
| PDMS | 30 | 7600 | DMC | 3.2 | [ | |
| MTES-MFI/PDMS | 30 | 11500 | DMC | 3.6 | [ | |
| MOF-801-15%AA | 90 | 3736 | MeOH | 629 | 157 | [ |
| GO-Zn2+ | 90 | 707 | MeOH | 61.9 | [ | |
| PERVAP™1255 | 27.5 | 705 | MeOH | 14.41 | [ | |
| SAPO-34 分子筛 | 10 | 14000-17000 | MeOH | 600-2000 | [ | |
| PEEK-WC | 3.8-96.2 | 78-227 | MeOH | 0.25-13.4 | 0.2-3.5 | [ |
| [65] | 李文秀, 连利燕, 张志刚, 等. 萃取精馏分离碳酸二甲酯和甲醇共沸物[J]. 化学工程, 2012, 40(7): 14-17, 25. |
| Li W X, Lian L Y, Zhang Z G, et al. Separation of dimethyl carbonate-methanol mixture by extractive distillation[J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2012, 40(7): 14-17, 25. | |
| [66] | Hsu K Y, Hsiao Y C, Chien I L. Design and control of dimethyl carbonate–methanol separation via extractive distillation in the dimethyl carbonate reactive-distillation process[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2010, 49(2): 735-749. |
| [67] | Matsuda H, Inaba K, Nishihara K, et al. Separation effects of renewable solvent ethyl lactate on the vapor–liquid equilibria of the methanol + dimethyl carbonate azeotropic system[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2017, 62(9): 2944-2952. |
| [68] | Hu C C, Cheng S H. Development of alternative methanol/dimethyl carbonate separation systems by extractive distillation: a holistic approach[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2017, 127: 189-214. |
| [69] | Li K K, Cheng H N, Li X H, et al. Molecular mechanism-based extractant screening and process design for the separation of methanol/dimethyl carbonate azeotrope[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024, 333: 125916. |
| [70] | Zheng M Q, Wang J W. Simulation and optimization of the separation of methanol-dimethyl carbonate azeotrope by extractive dividing wall column[J]. Separations, 2022, 9(8): 189. |
| [71] | Ma X B, Liu X G, Li Z H, et al. Vapor–liquid equilibria for the ternary system methanol + dimethyl carbonate + dimethyl oxalate and constituent binary systems at different temperatures[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2004, 221(1/2): 51-56. |
| [72] | Shen Y Y, Su Z H, Zhao Q, et al. Molecular simulation and optimization of extractive distillation for separation of dimethyl carbonate and methanol[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 158: 181-188. |
| [73] | Guo C, Wang F Q, Xing J F, et al. Thermodynamic and economic comparison of extractive distillation sequences for separating methanol/dimethyl carbonate/water azeotropic mixtures[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 282: 120150. |
| [74] | Guo C, Liu X Y, Wang F Q, et al. Economic analysis and life cycle environmental assessment of imidazolium-based ionic liquids for separation of the methanol/dimethyl carbonate azeotrope[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2023, 11(28): 10482-10495. |
| [75] | Zhang Z G, Xu H H, Zhang Q Q, et al. Separation of methanol + dimethyl carbonate azeotropic mixture using ionic liquids as entrainers[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2017, 435: 98-103. |
| [76] | Cai F F, Wu X Y, Chen C, et al. Isobaric vapor–liquid equilibrium for methanol+dimethyl carbonate+phosphoric-based ionic liquids[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2013, 352: 47-53. |
| [77] | Liu Y, Zhang Y G, Shi H, et al. Energy-saving heterogeneous azeotropic distillation process for the high-purity separation of dimethyl carbonate/methanol azeotrope with cyclohexane as a light entrainer[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2026, 382: 135789. |
| [78] | Li Y, Xia M, Li W S, et al. Process assessment of heterogeneous azeotropic dividing-wall column for ethanol dehydration with cyclohexane as an entrainer: design and control[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55(32): 8784-8801. |
| [79] | Luyben W L. Control of a multiunit heterogeneous azeotropic distillation process[J]. AIChE Journal, 2006, 52(2): 623-637. |
| [80] | Li X, Wang S, Wang Y L, et al. Optimization of decanter temperature in separating partially miscible homoazeotrope to reduce cost and energy consumption[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2019, 94(6): 1998-2008. |
| [81] | Luyben W L. Control of the heterogeneous azeotropic n-butanol/water distillation system[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2008, 22(6): 4249-4258. |
| [82] | Wu Y C, Chien I L. Design and control of heterogeneous azeotropic column system for the separation of pyridine and water[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(23): 10564-10576. |
| [83] | Zhao L, Lyu X Y, Wang W C, et al. Comparison of heterogeneous azeotropic distillation and extractive distillation methods for ternary azeotrope ethanol/toluene/water separation[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2017, 100: 27-37. |
| [84] | Rovaglio M, Doherty M F. Dynamics of heterogeneous azeotropic distillation columns[J]. AIChE Journal, 1990, 36(1): 39-52. |
| [85] | Chien I L, Wang C J, Wong D S H. Dynamics and control of a heterogeneous azeotropic distillation column: conventional control approach[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1999, 38(2): 468-478. |
| [86] | Shi T, Yang A, Jin S M, et al. Comparative optimal design and control of two alternative approaches for separating heterogeneous mixtures isopropyl alcohol-isopropyl acetate-water with four azeotropes[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 225: 1-17. |
| [87] | Luyben W L. Economic optimum design of the heterogeneous azeotropic dehydration of ethanol[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(50): 16427-16432. |
| [88] | 张立庆, 席丹, 徐晓锋. 三氯乙烯恒沸精馏分离甲醇与碳酸二甲酯共沸物[J]. 精细石油化工, 2005, 22(6): 41-43. |
| Zhang L Q, Xi D, Xu X F. Separation of dimethyl carbonate from its azeotrope with methanol using trichloroethylene[J]. Speciality Petrochemicals, 2005, 22(6): 41-43. | |
| [89] | 叶秋云. 甲醇—碳酸二甲酯—正已烷三元体系汽液平衡研究[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2010. |
| Ye Q Y. Study for the vapor-liquid equilibrium of the ternary system methanol-dimethyl carbonate-hexane[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2010. | |
| [90] | 刘立新, 李鲁闽, 刘桂丽, 等. 碳酸二甲酯-甲醇共沸体系分离的模拟与控制[J]. 化工进展, 2017, 36(3): 852-862. |
| Liu L X, Li L M, Liu G L, et al. Comparison of alternative configurations for separation of dimethyl carbonate-methanol mixture: steady state simulation and dynamic control[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2017, 36(3): 852-862. | |
| [91] | 王伟林, 李忠, 郑华艳. 共沸剂对碳酸二甲酯-甲醇分离效率的影响[J]. 精细化工, 2020, 37(8): 1665-1671. |
| Wang W L, Li Z, Zheng H Y. Effect of azeotrope on separation of dimethyl carbonate-methanol[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2020, 37(8): 1665-1671. | |
| [92] | Lyu H, Hu Y X, Zhou T. Dimethyl carbonate/methanol separation by azeotropic distillation with water: an alternative process driven by low-pressure steam[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 355: 129677. |
| [93] | Yin H, Yip A C K. A review on the production and purification of biomass-derived hydrogen using emerging membrane technologies[J]. Catalysts, 2017, 7(10): 297. |
| [94] | Li W Q, Molina-Fernández C, Estager J, et al. Supported ionic liquid membranes for the separation of methanol/dimethyl carbonate mixtures by pervaporation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020, 598: 117790. |
| [95] | 丁坤, 李艳辉, 肖俊江. 膜分离技术的发展及其在工业领域的应用[J]. 上海纺织科技, 2025, 53(7): 13-16. |
| Ding K, Li Y H, Xiao J J. Development of membrane separation technology and its industry application[J]. Shanghai Textile Science & Technology, 2025, 53(7): 13-16. | |
| [96] | Wang S, Li J H, Yu J L, et al. PDMS membrane incorporated by zeolites with tunable pore chemistry for dimethyl carbonate/methanol azeotropic mixture separation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2025, 717: 123593. |
| [1] | Pyo S H, Park J H, Chang T S, et al. Dimethyl carbonate as a green chemical[J]. Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 2017, 5: 61-66. |
| [2] | Cao W R, Cai Z J, Yao X, et al. Digital transformation to help carbon neutrality and green sustainable development based on the metaverse[J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(9): 7132. |
| [3] | 方云进, 肖文德. 绿色工艺的原料: 碳酸二甲酯[J]. 化学通报, 2000, 63(9): 19-25, 7. |
| Fang Y J, Xiao W D. Material of green technology: dimethyl carbonate[J]. Chemistry, 2000, 63(9): 19-25, 7. | |
| [4] | Tundo P, Musolino M, Aricò F. The reactions of dimethyl carbonate and its derivatives[J]. Green Chemistry, 2018, 20(1): 28-85. |
| [5] | Ono Y. Catalysis in the production and reactions of dimethyl carbonate, an environmentally benign building block[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 1997, 155(2): 133-166. |
| [6] | Wang S J, Yu C C, Huang H P. Plant-wide design and control of DMC synthesis process via reactive distillation and thermally coupled extractive distillation[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2010, 34(3): 361-373. |
| [7] | Aresta M, Galatola M. Life cycle analysis applied to the assessment of the environmental impact of alternative synthetic processes. The dimethylcarbonate case: part 1[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 1999, 7(3): 181-193. |
| [8] | 王锦玉, 张宗飞, 刘佳, 等. 碳酸二甲酯的生产技术及市场分析[J]. 化肥设计, 2021, 59(5): 1-5, 45. |
| Wang J Y, Zhang Z F, Liu J, et al. Production technologiesand market analysis of dimethyl carbonate[J]. Chemical Fertilizer Design, 2021, 59(5): 1-5, 45. | |
| [9] | 张建海. 碳酸二甲酯生产工艺及节能过程研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛科技大学, 2020. |
| Zhang J H. Study on production process and energy saving process of dimethyl carbonate[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Science and Technology, 2020. | |
| [97] | Chen L, Mo B Y, Yin J, et al. Modulator regulated Zr-MOF membrane for organic azeotropic separation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2025, 723: 123933. |
| [98] | Liu S, Liu G Z, Zhao B J, et al. Methanol/dimethyl carbonate separation using graphene oxide membrane via cationic control of molecular transport channels[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2022, 650: 120457. |
| [99] | Won W, Feng X S, Lawless D. Separation of dimethyl carbonate/methanol/water mixtures by pervaporation using crosslinked chitosan membranes[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2003, 31(2): 129-140. |
| [100] | Holtbruegge J, Wierschem M, Steinruecken S, et al. Experimental investigation, modeling and scale-up of hydrophilic vapor permeation membranes: Separation of azeotropic dimethyl carbonate/methanol mixtures[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2013, 118: 862-878. |
| [101] | Wang M Q, Li M, Chang N, et al. Vapor separation of methanol-dimethyl carbonate mixture on SAPO-34 zeolite membrane[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 565: 311-321. |
| [102] | Li W Q, Galiano F, Estager J, et al. Sorption and pervaporation study of methanol/dimethyl carbonate mixture with poly(etheretherketone) (PEEK-WC) membrane[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 567: 303-310. |
| [103] | 朱建良, 张珂, 李乐易, 等. 甲醇氧化羰基化合成碳酸二甲酯铜系催化剂研究进展[J]. 南京工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 43(4): 420-424, 479. |
| Zhu J L, Zhang K, Li Y Y, et al. Research progress of copper-based catalysts for oxidative carbonylation of methanol to dimethyl carbonate[J]. Journal of Nanjing Tech University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 43(4): 420-424, 479. | |
| [104] | 刘芃 卢永祥, 刘波. 液相法甲醇氧化羰基化合成DMC的工艺条件研究[J]. 煤化工, 1998(1): 36-39. |
| Liu P, Lu Y X, Liu B. Study on technological parameter of dmc synthesis through liquid phase methanol oxidativecarbonylation[J]. Coal Chemical Industry, 1998(1): 36-39. | |
| [105] | Marciniak A A, Alves O C, Appel L G, et al. Synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from CO2 and methanol over CeO2: Role of copper as dopant and the use of methyl trichloroacetate as dehydrating agent[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2019, 371: 88-95. |
| [10] | 窦雅利. 电池级碳酸二甲酯提纯节能新工艺研究[D]. 福州: 福州大学, 2018. |
| Dou Y L. Research on new technology of battery-grade dimethyl carbonate purification[D]. Fuzhou: Fuzhou University, 2018. | |
| [11] | 刘亚利, 吴娇杨, 李泓. 锂离子电池基础科学问题(Ⅸ): 非水液体电解质材料[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2014, 3(3): 262-282. |
| Liu Y L, Wu J Y, Li H. Fundamental scientific aspects of lithium ion batteries (Ⅸ): Nonaqueous electrolyte materials[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2014, 3(3): 262-282. | |
| [12] | 王永苗. 甲醇和固体光气合成碳酸二甲酯反应的研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2007. |
| Wang Y M. Study of dimethyl carbonate synthesis by methanol and triphosgene[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2007. | |
| [13] | Yan M, Shen Y Y, Wang S, et al. Green separation of azeotropes in dimethyl carbonate synthesis by transesterification[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2024, 202: 114687. |
| [14] | Wang J Q, Sun J, Cheng W G, et al. Synthesis of dimethyl carbonate catalyzed by carboxylic functionalized imidazolium salt via transesterification reaction[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2012, 2(3): 600-605. |
| [15] | Pandey S, Srivastava V C, Kumar V. Comparative thermodynamic analysis of CO2 based dimethyl carbonate synthesis routes[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2021, 99(2): 467-478. |
| [16] | Zhao T S, Han Y Z, Sun Y H. Novel reaction route for dimethyl carbonate synthesis from CO2 and methanol[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2000, 62(2/3): 187-194. |
| [17] | Petrescu L, Iurian C A. Green dimethyl carbonate production feasibility based on technical and environmental considerations[J]. Fuel, 2025, 399: 135663. |
| [18] | 吴子锋, 王红娟, 王浩帆, 等. 电合成碳酸二甲酯的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2025, 44(9): 5033-5042. |
| Wu Z F, Wang H J, Wang H F, et al. Progress on electrosynthesis of dimethyl carbonate[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2025, 44(9): 5033-5042. | |
| [19] | 郑惠, 米多. 国内碳酸二甲酯生产及市场分析预测[J]. 化学工业, 2023, 41(3): 60-65. |
| Zheng H, Mi D. Domestic production, market analysis and prediction of dimethyl carbonate[J]. Chemical Industry, 2023, 41(3): 60-65. | |
| [20] | Deng W J, Shi L, Yao J, et al. A review on transesterification of propylene carbonate and methanol for dimethyl carbonate synthesis[J]. Carbon Resources Conversion, 2019, 2(3): 198-212. |
| [21] | Fang Y J, Xiao W D. Experimental and modeling studies on a homogeneous reactive distillation system for dimethyl carbonate synthesis by transesterification[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2004, 34(1/2/3): 255-263. |
| [22] | Kumar P, Srivastava V C, Mishra I M. Dimethyl carbonate synthesis by transesterification of propylene carbonate with methanol: Comparative assessment of Ce-M (M=Co, Fe, Cu and Zn) catalysts[J]. Renewable Energy, 2016, 88: 457-464. |
| [23] | Xia M, Zhao W, Qi X X, et al. Kinetic insights into energy-saving and low-carbon reactive distillation processes for the transesterification to dimethyl carbonate[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 356: 129745. |
| [24] | Fukuoka S, Fukawa I, Adachi T, et al. Industrialization and expansion of green sustainable chemical process: a review of non-phosgene polycarbonate from CO2 [J]. Organic Process Research & Development, 2019, 23(2): 145-169. |
| [25] | Yamamoto Y. Vapor phase carbonylation reactions using methyl nitrite over Pd catalysts[J]. Catalysis Surveys from Asia, 2010, 14(3): 103-110. |
| [26] | Raab V, Merz M, Sundermeyer J. Ligand effects in the copper catalyzed aerobic oxidative carbonylation of methanol to dimethyl carbonate (DMC)[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2001, 175(1/2): 51-63. |
| [27] | Itoh H, Watanabe Y, Mori K, et al. Synthesis of dimethyl carbonate by vapor phase oxidative carbonylation of methanol[J]. Green Chemistry, 2003, 5(5): 558-562. |
| [28] | Shi K, Huang S Y, Zhang Z Y, et al. Novel fabrication of copper oxides on AC and its enhanced catalytic performance on oxidative carbonylation of methanol[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2017, 28(1): 70-74. |
| [29] | Guo R, Wu S Q, Chen J S, et al. Construction of mesopores and skeleton Si–Al rearrangement to design Pd-based catalysts for dimethyl carbonate synthesis[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2025, 13(12): 4823-4832. |
| [30] | Adelieti S, Wu S Q, Wu X H, et al. Effect of gel alkalinity on the catalytic properties of PdCu/NaY zeolites for methyl nitrite carbonylation to dimethyl carbonate[J]. Helvetica Chimica Acta, 2025, 108(6): e202500015. |
| [31] | Raza A, Ikram M, Guo S, et al. Green synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from CO2 and methanol: new strategies and industrial perspective[J]. Advanced Sustainable Systems, 2022, 6(8): 2200087. |
| [32] | Wang H, Lu B, Wang X G, et al. Highly selective synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from urea and methanol catalyzed by ionic liquids[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2009, 90(10): 1198-1201. |
| [33] | 张树峰. 尿素醇解法合成碳酸二甲酯工艺研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2015. |
| Zhang S F. Study on synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from urea and methanol[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2015. | |
| [34] | Shukla K, Srivastava V C. Synthesis of organic carbonates from alcoholysis of urea: a review[J]. Catalysis Reviews, 2017, 59(1): 1-43. |
| [35] | 耍芬芬, 吕云辰, 朱止阳, 等. 碳酸二甲酯技术进展及市场分析[J]. 山东化工, 2025, 54(2): 107-109, 112. |
| Shua F F, Lyu Y C, Zhu Z Y, et al. Technological progress and market analysis of dimethyl carbonate[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2025, 54(2): 107-109, 112. | |
| [36] | Saada R, Kellici S, Heil T, et al. Greener synthesis of dimethyl carbonate using a novel ceria–zirconia oxide/graphene nanocomposite catalyst[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015, 168-169: 353-362. |
| [37] | Bai Z L, Huang T T, Qi L X, et al. (311) high-index facet of CeO2 effectively promotes the synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from CO2 and methanol[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2025, 17(25): 36784-36795. |
| [38] | Guan X S, Wang X K, Zhang X C, et al. Boosting CO2 fixation into dimethyl carbonate via multiple active sites constituted by VO-Ce-O vacancy clusters on single-unit-cell CeO2 nano-sheets[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2025, 64(33): e202423958. |
| [39] | Kang L, Zhang J Y, Wang S P. Surface-dependent role of oxygen vacancies in dimethyl carbonate synthesis from CO2 and methanol over CeO2 catalysts[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2025, 17(10): 16132-16144. |
| [40] | Dong L, Yuan Y Y, Zhu S J, et al. Promoting effect of Fe modification on the direct synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from CO2 and methanol over Fe–Ce binary oxide[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2025, 49(25): 10616-10631. |
| [41] | Daniel C, Schuurman Y, Farrusseng D. Surface effect of nano-sized cerium-zirconium oxides for the catalytic conversion of methanol and CO2 into dimethyl carbonate[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2021, 394: 486-494. |
| [42] | Wang D, Shi F, Wang L T. A review of catalysts for synthesis of dimethyl carbonate[J]. Catalysts, 2024, 14(4): 259. |
| [43] | Zhou S J, Xu E Z, Liu K L, et al. Regulation of surface oxygen vacancies on Ce-based catalysts for dimethyl carbonate direct synthesis from CO2 and CH3OH[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2024, 63(44): 18783-18790. |
| [44] | Santos B A V, Pereira C S M, Silva V M T M, et al. Kinetic study for the direct synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from methanol and CO2 over CeO2 at high pressure conditions[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2013, 455: 219-226. |
| [45] | Santos B A V, Silva V M T M, Loureiro J M, et al. Review for the direct synthesis of dimethyl carbonate[J]. ChemBioEng Reviews, 2014, 1(5): 214-229. |
| [46] | Mi Y Y, Xue Y Y, Yan Y Q, et al. Promoting intermediate stabilization and coupling for dimethyl carbonate electrosynthesis[J]. Small, 2025, 21(19): e2501780. |
| [47] | Yu Y T, Liu X H, Zhang W, et al. Electrosynthesis of dimethyl carbonate from methanol and carbon monoxide under mild conditions[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(21): 6901-6907. |
| [48] | Wade J, Merriman R W. CIV.: Influence of water on the boiling point of ethyl alcohol at pressures above and below the atmospheric pressure[J]. J Chem Soc, Trans, 1911, 99: 997-1011. |
| [49] | Luyben W L. Design and control of a pressure-swing distillation process with vapor recompression[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 2018, 123: 174-184. |
| [50] | 何康. 碳酸二甲酯—甲醇共沸体系分离的模拟与控制研究[D]. 东营: 中国石油大学(华东), 2015. |
| He K. Design and control of dimethyl carbonate-methanol separation[D]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum (Huadong), 2015. | |
| [51] | Luo H P, Xiao W D, Zhu K H. Isobaric vapor–liquid equilibria of alkyl carbonates with alcohols[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2000, 175(1/2): 91-105. |
| [52] | 李春山, 张香平, 张锁江, 等. 加压-常压精馏分离甲醇-碳酸二甲酯的相平衡和流程模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2003, 3(5): 453-458. |
| Li C S, Zhang X P, Zhang S J, et al. Vapor-liquid equilibria and process simulation for separation of dimethyl carbonate and methanol azeotropic system[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2003, 3(5): 453-458. | |
| [53] | 毕利君, 钱宏义, 欧进永, 等. 常压-加压-常压三塔流程分离甲醇和碳酸二甲酯[J]. 山东化工, 2019, 48(8): 155-156, 160. |
| Bi L J, Qian H Y, Ou J Y, et al. Separation of methanol and dimethyl carbonate with atmospheric-pressurized-atmospheric three-column process[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2019, 48(8): 155-156, 160. | |
| [54] | 卫红梅, 马秀峰, 王栋. 热集成变压分离碳酸二甲酯-甲醇过程模拟[J]. 化学工程, 2023, 51(2): 78-82. |
| Wei H M, Ma X F, Wang D. Process simulation of dimethyl carbonate-methanol separation via heat-integrated pressure swing distillation[J]. Chemical Engineering, 2023, 51(2): 78-82. | |
| [55] | 高海见, 严诚磊, 阎笠. 碳酸二甲酯-甲醇变压精馏工艺及热耦合研究[J]. 现代化工, 2022, 42(S2): 365-369. |
| Gao H J, Yan C L, Yan L. Study on dimethyl carbonate-methanol pressure-swing distillation process and thermal coupling[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2022, 42(S2): 365-369. | |
| [56] | 林子昕, 田伟, 安维中. 热泵辅助变压精馏分离碳酸二甲酯/甲醇工艺及系统模拟优化[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(11): 5722-5730. |
| Lin Z X, Tian W, An W Z. Separation of dimethyl carbonate/methanol via heat pump assisted pressure swing distillation process and system simulation optimization[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(11): 5722-5730. | |
| [57] | An R, Chen S X, Li H, et al. Energy-saving reactive pressure-swing distillation process for separation of methanol - dimethyl carbonate azeotrope via reacting with propylene oxide[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 292: 120889. |
| [58] | Xia M, Shi H, Niu C C, et al. The importance of pressure-sensitive pinch/azeotrope feature on economic distillation design[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 250: 116753. |
| [59] | Wei H M, Wang F, Zhang J L, et al. Design and control of dimethyl carbonate–methanol separation via pressure-swing distillation[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(33): 11463-11478. |
| [60] | You C X, Zhou C, Shi H, et al. Energy-saving extractive distillation system using o-xylene as an entrainer for the high-purity separation of dimethyl carbonate/methanol azeotrope[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024, 350: 127893. |
| [61] | Matsuda H, Takahara H, Fujino S, et al. Selection of entrainers for the separation of the binary azeotropic system methanol+dimethyl carbonate by extractive distillation[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2011, 310(1/2): 166-181. |
| [62] | Foucher E R, Doherty M F, Malone M F. Automatic screening of entrainers for homogeneous azeotropic distillation[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1991, 30(4): 760-772. |
| [63] | Laroche L, Andersen H W, Morari M, et al. Homogeneous azeotropic distillation: Comparing entrainers[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1991, 69(6): 1302-1319. |
| [64] | Rodríguez-Donis I, Gerbaud V, Joulia X. Entrainer selection rules for the separation of azeotropic and close-boiling-temperature mixtures by homogeneous batch distillation process[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2001, 40(12): 2729-2741. |
| [1] | 臧子晴, 李修真, 谈莹莹, 刘晓庆. 分凝器对两级分离自复叠制冷循环特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 17-25. |
| [2] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [3] | 黄博, 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. 薄膜型LNG船液货舱温度场计算分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 195-204. |
| [4] | 裴星亮, 叶翠平, 裴赢丽, 李文英. 碱改性MIL-53(Cr)选择性吸附分离二甲苯异构体[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 258-267. |
| [5] | 李银龙, 刘国强, 晏刚. 分馏与闪蒸分离耦合自复叠制冷循环性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 26-35. |
| [6] | 李文龙, 常程, 吴小林, 姬忠礼. 油水聚结过滤材料中的液体分布特性及过程压降演化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4850-4861. |
| [7] | 王钰, 冯英楠, 王涛, 赵之平. 原位生长构筑纳米复合纳滤膜:膜制备与应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4723-4736. |
| [8] | 张建民, 何美贵, 贾万鑫, 赵静, 金万勤. 聚氧化乙烯/冠醚共混膜及其二氧化碳分离性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4862-4871. |
| [9] | 郭旭, 贾继宁, 姚克俭. 基于优化CNN-BiLSTM神经网络的间歇精馏过程建模[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4613-4629. |
| [10] | 王杰, 林渠成, 张先明. 基于分解算法的混合气体多级膜分离系统全局优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4670-4682. |
| [11] | 黄正宗, 刘科成, 李泽方, 曾平生, 刘永富, 闫红杰, 刘柳. 锌精馏炉砖砌式换热室数值模拟与场协同优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4425-4439. |
| [12] | 陈治宏, 吴佳伟, 楼小玲, 贠军贤. 化学品生物制造过程机器学习的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3789-3804. |
| [13] | 张荟钦, 赵泓竣, 付正军, 庄力, 董凯, 贾添智, 曹雪丽, 孙世鹏. 纳滤膜在离子型稀土浸出液提浓中的应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4095-4107. |
| [14] | 王珺仪, 夏章讯, 景粉宁, 王素力. 基于重整气的高温聚合物电解质膜燃料电池电化学阻抗谱弛豫时间分布研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3509-3520. |
| [15] | 丁宏鑫, 干文翔, 赵雍洋, 贾润泽, 康子祺, 赵玉隆, 向勇. X65钢焊接接头在超临界CO2相及富H2O相中的腐蚀机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3426-3435. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号