• •
刘珊珊1( ), 马溪溪1, 杨蔚1, 何金凤1,2, 孙黎1,2, 徐婷婷3, 李传润1,2, 颜海洋1,2(
), 马溪溪1, 杨蔚1, 何金凤1,2, 孙黎1,2, 徐婷婷3, 李传润1,2, 颜海洋1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-12-01
修回日期:2025-12-26
出版日期:2026-01-13
通讯作者:
颜海洋
作者简介:刘珊珊(2001—),女,硕士研究生,lss633068@163.com
基金资助:
Shanshan LIU1( ), Xixi MA1, Wei YANG1, Jinfeng HE1,2, Li SUN1,2, Tingting XU3, Chuanrun LI1,2, Haiyang YAN1,2(
), Xixi MA1, Wei YANG1, Jinfeng HE1,2, Li SUN1,2, Tingting XU3, Chuanrun LI1,2, Haiyang YAN1,2( )
)
Received:2025-12-01
Revised:2025-12-26
Online:2026-01-13
Contact:
Haiyang YAN
摘要:
超滤膜电渗析(EDUF)是基于超滤膜和电渗析分离技术,将孔径筛分和电荷筛分相结合,从而实现溶液中荷电物质与荷电物质、荷电物质与非荷电物质的高效分离与浓缩。目前,该技术在制药、食品、化工和环境等领域展现出广阔的应用前景。本文旨在阐述EDUF技术的分离原理与发展历程,全面综述其在生物制药、中药制药、食品和废水处理等领域的应用进展,并深入探讨EDUF在面向复杂物系分离中的挑战,展望未来在材料改性、过程优化及多技术耦合等方面的发展趋势,以推动EDUF的工业化应用。
中图分类号:
刘珊珊, 马溪溪, 杨蔚, 何金凤, 孙黎, 徐婷婷, 李传润, 颜海洋. 超滤膜电渗析技术的应用、挑战及展望[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251337.
Shanshan LIU, Xixi MA, Wei YANG, Jinfeng HE, Li SUN, Tingting XU, Chuanrun LI, Haiyang YAN. Application, challenges, and prospects of electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes technology[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251337.
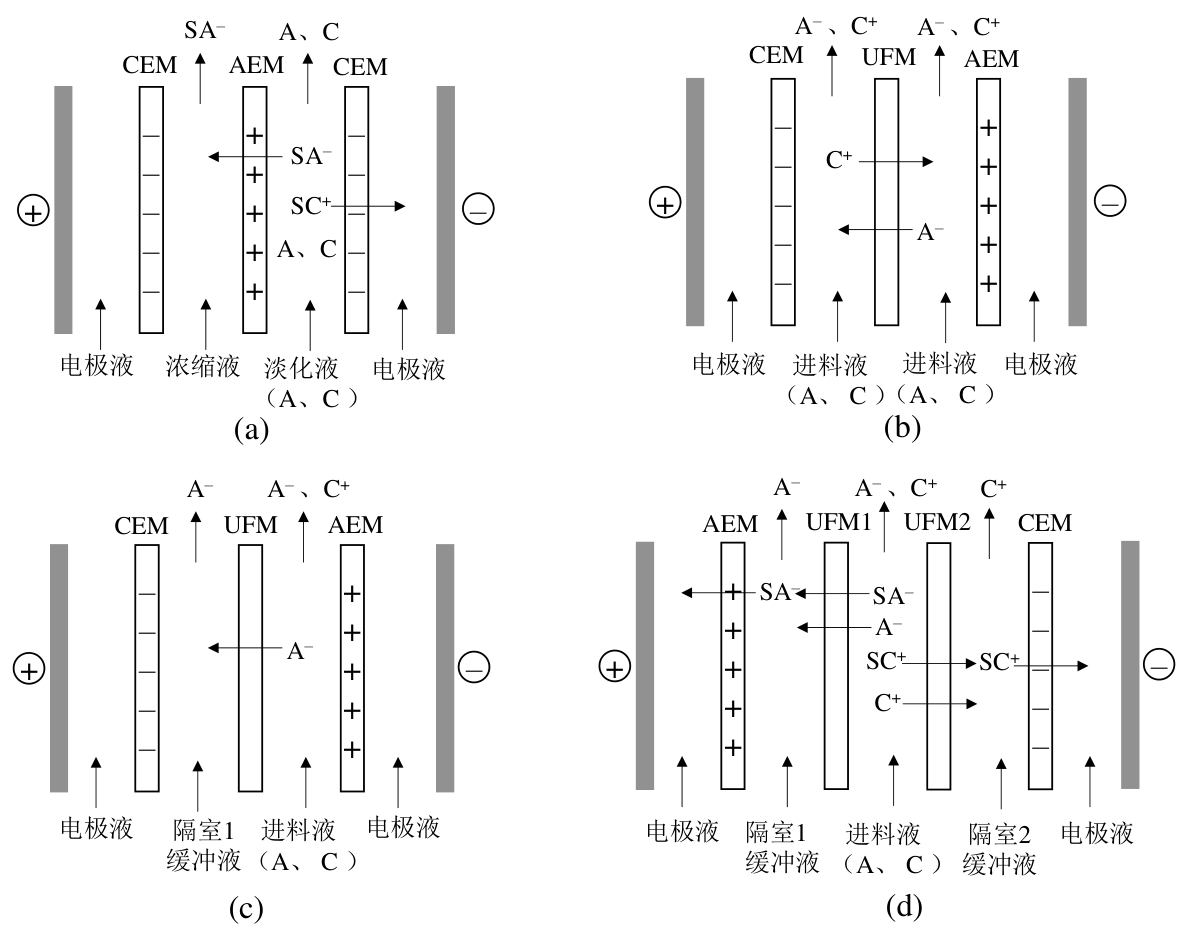
图3 (a) 传统ED分离原理;EDUF的(b)分离和(c)纯化原理[37];(d) EDUF选择性分离原理[40]
Fig.3 (a) Principle of conventional ED separation; (b) separation and (c) purification principles of the EDUF[37]; (d) principle of selective EDUF separation[40]
| 来源 | UFM参数 | 操作条件 | 分离性能 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乳清 | 有效膜面积:10 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:CA | (1) pH=5、9,U=5.5 V (2) pH=5、7、9,U=6 V | 迁移率:7.8~11.9 g/m2·h β-lg 142-148的回收率可达10.8% | [ |
| 乳清 | 有效膜面积:10、40 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:CA | pH=5,E=2.7、5.5、11.0 V/cm | 迁移率:3.1~11.23 g/m2·h 回收率:30%~50% | [ |
| 乳清 | 有效膜面积:10 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:CA | pH=5,U=5.5 V,Qfeed=100~250 mL/min | 迁移率:3.1 g/m2·h | [ |
| 乳清 | 有效膜面积:35 cm2 MWCO:30、100 kDa 膜材料:CA | pH=4.8、6、8,i=3~20 A/m2 | / | [ |
| 乳清 | 有效膜面积:15.6 cm2 MWCO:5 kDa 膜材料: 聚乙烯醇 | E=38.5、77 V/cm | 迁移率:0.4~1.9 g/m2·h | [ |
| 牛血红蛋白 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:纤维素酯 | pH=7,U=8 V | 迁移率:1.99~5.06 g/m2·h | [ |
| 牛血清白蛋白和溶菌酶 | 有效膜面积:35 cm2 MWCO:30 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=10,I=150 mA | / | [ |
| 蛋清溶菌酶 | 有效膜面积:51 cm2 MWCO:100 kDa 膜材料:PVDF | pH=5,U=3、5、8 V,Qfeed =20~65 ml/min | 迁移率:0.07~0.32 g/m2·h 回收率:21.4%~32.2% | [ |
| pH=5~5.5,U=5 V | 迁移率:0.21 g/m2·h 回收率:21.1% | [ | ||
| 雪蟹 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料: PES | pH=3、6、9,U=18 V | 迁移率:1.32~7.13 g/m2·h 回收率:1.2%~9.1% | [ |
| 雪蟹 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:PES、CA | pH=9,E=2 V/cm | 迁移率:2.29~2.62 g/m2·h 回收率:1.5%~10.2% | [ |
| 雪蟹 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:20、50 kDa 膜材料:CA | pH=9,E=2、14 V/cm | 迁移率:0.43~5.40 g/m2·h 回收率:9.7%~43.1% | [ |
| 雪蟹 | 有效膜面积:200 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=9,E=0.9、1.8、2.7、3.6 V/cm | 回收率:0.76%~9.3% | [ |
| 鲑鱼 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=3、6、9,E=14 V/cm | / | [ |
| 鲑鱼 | 有效膜面积:200 cm2 MWCO:5、20、50 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=6,E=6 V/cm | 迁移率:0.01~3.19 g/m2·h 回收率:0.15%~9.2% | [ |
| 鲑鱼 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:50 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=6,E=6 V/cm | / | [ |
| 鲱鱼 | 有效膜面积:200 cm2 MWCO:50 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=7,U=14 V | 迁移率:4.7~5.2 g/m2·h | [ |
表1 EDUF在分离动物多肽中的应用
Table 1 Applications of the EDUF in the separation of animal peptides
| 来源 | UFM参数 | 操作条件 | 分离性能 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乳清 | 有效膜面积:10 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:CA | (1) pH=5、9,U=5.5 V (2) pH=5、7、9,U=6 V | 迁移率:7.8~11.9 g/m2·h β-lg 142-148的回收率可达10.8% | [ |
| 乳清 | 有效膜面积:10、40 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:CA | pH=5,E=2.7、5.5、11.0 V/cm | 迁移率:3.1~11.23 g/m2·h 回收率:30%~50% | [ |
| 乳清 | 有效膜面积:10 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:CA | pH=5,U=5.5 V,Qfeed=100~250 mL/min | 迁移率:3.1 g/m2·h | [ |
| 乳清 | 有效膜面积:35 cm2 MWCO:30、100 kDa 膜材料:CA | pH=4.8、6、8,i=3~20 A/m2 | / | [ |
| 乳清 | 有效膜面积:15.6 cm2 MWCO:5 kDa 膜材料: 聚乙烯醇 | E=38.5、77 V/cm | 迁移率:0.4~1.9 g/m2·h | [ |
| 牛血红蛋白 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:纤维素酯 | pH=7,U=8 V | 迁移率:1.99~5.06 g/m2·h | [ |
| 牛血清白蛋白和溶菌酶 | 有效膜面积:35 cm2 MWCO:30 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=10,I=150 mA | / | [ |
| 蛋清溶菌酶 | 有效膜面积:51 cm2 MWCO:100 kDa 膜材料:PVDF | pH=5,U=3、5、8 V,Qfeed =20~65 ml/min | 迁移率:0.07~0.32 g/m2·h 回收率:21.4%~32.2% | [ |
| pH=5~5.5,U=5 V | 迁移率:0.21 g/m2·h 回收率:21.1% | [ | ||
| 雪蟹 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料: PES | pH=3、6、9,U=18 V | 迁移率:1.32~7.13 g/m2·h 回收率:1.2%~9.1% | [ |
| 雪蟹 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:PES、CA | pH=9,E=2 V/cm | 迁移率:2.29~2.62 g/m2·h 回收率:1.5%~10.2% | [ |
| 雪蟹 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:20、50 kDa 膜材料:CA | pH=9,E=2、14 V/cm | 迁移率:0.43~5.40 g/m2·h 回收率:9.7%~43.1% | [ |
| 雪蟹 | 有效膜面积:200 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=9,E=0.9、1.8、2.7、3.6 V/cm | 回收率:0.76%~9.3% | [ |
| 鲑鱼 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=3、6、9,E=14 V/cm | / | [ |
| 鲑鱼 | 有效膜面积:200 cm2 MWCO:5、20、50 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=6,E=6 V/cm | 迁移率:0.01~3.19 g/m2·h 回收率:0.15%~9.2% | [ |
| 鲑鱼 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:50 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=6,E=6 V/cm | / | [ |
| 鲱鱼 | 有效膜面积:200 cm2 MWCO:50 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=7,U=14 V | 迁移率:4.7~5.2 g/m2·h | [ |
| 来源 | UFM参数 | 操作条件 | 分离性能 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苜蓿 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:10 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=3、9,U=70 V | 迁移率:1.59~7.3 g/m2·h 回收率:18.2% | [ |
| 苜蓿 | 有效膜面积:1200 cm2 MWCO:10 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=3、9,U=70 V | 迁移率:5.3~8.7 g/m2·h 回收率:32% | [ |
| 亚麻籽 | 有效膜面积:200 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:中性 | pH=3,U=6~10 V | 回收率:9.6%~43.3% | [ |
| 亚麻籽 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:20、50 kDa 膜材料:CA | pH=3,E=14 V/cm | 迁移率:1.04~4.70 g/m2·h | [ |
| 亚麻籽 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=3,E=4 V/cm | 迁移率:1.35~1.43 g/m2·h | [ |
| 油菜籽 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:中性 | pH=7,U=20 V | 回收率:28.3%~43.6% | [ |
| 油菜籽 | 有效膜面积:84 cm2 MWCO:3 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=8,U=1.5、3.0 V | 迁移率:0.019~0.060 g/m2·h 去除率:90.3% 保留率:88.8%。 | [ |
| 大豆 | 有效膜面积:1600 cm2 MWCO:10 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=3、6、9,U=8 V | 迁移率:0.097~0.24 g/m2·h 回收率:7%~9% | [ |
| 大豆 | 有效膜面积:200 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=3、6、9,E=3.6 V/cm | 迁移率:1.3~2.4 g/m2·h | [ |
| 大豆 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:100 kDa 膜材料:CA | pH=6,U=50 V | 迁移率:0.3~6.1 g/m2·h | [ |
| 小麦 | 有效膜面积:57 cm2 MWCO:4 kDa 膜材料:PESH | pH=6,U=1~12 V | 回收率:25%~30% | [ |
| pH=6,U=12 V | 回收率:26%~35% | [ | ||
| 藜麦 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:200 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=7,E=20 V/cm | 回收率:1.2%~3.0% | [ |
表2 EDUF在分离植物多肽中的应用
Table 2 Applications of the EDUF in the separation of plant peptides
| 来源 | UFM参数 | 操作条件 | 分离性能 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苜蓿 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:10 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=3、9,U=70 V | 迁移率:1.59~7.3 g/m2·h 回收率:18.2% | [ |
| 苜蓿 | 有效膜面积:1200 cm2 MWCO:10 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=3、9,U=70 V | 迁移率:5.3~8.7 g/m2·h 回收率:32% | [ |
| 亚麻籽 | 有效膜面积:200 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:中性 | pH=3,U=6~10 V | 回收率:9.6%~43.3% | [ |
| 亚麻籽 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:20、50 kDa 膜材料:CA | pH=3,E=14 V/cm | 迁移率:1.04~4.70 g/m2·h | [ |
| 亚麻籽 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=3,E=4 V/cm | 迁移率:1.35~1.43 g/m2·h | [ |
| 油菜籽 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:中性 | pH=7,U=20 V | 回收率:28.3%~43.6% | [ |
| 油菜籽 | 有效膜面积:84 cm2 MWCO:3 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=8,U=1.5、3.0 V | 迁移率:0.019~0.060 g/m2·h 去除率:90.3% 保留率:88.8%。 | [ |
| 大豆 | 有效膜面积:1600 cm2 MWCO:10 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=3、6、9,U=8 V | 迁移率:0.097~0.24 g/m2·h 回收率:7%~9% | [ |
| 大豆 | 有效膜面积:200 cm2 MWCO:20 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=3、6、9,E=3.6 V/cm | 迁移率:1.3~2.4 g/m2·h | [ |
| 大豆 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:100 kDa 膜材料:CA | pH=6,U=50 V | 迁移率:0.3~6.1 g/m2·h | [ |
| 小麦 | 有效膜面积:57 cm2 MWCO:4 kDa 膜材料:PESH | pH=6,U=1~12 V | 回收率:25%~30% | [ |
| pH=6,U=12 V | 回收率:26%~35% | [ | ||
| 藜麦 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:200 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=7,E=20 V/cm | 回收率:1.2%~3.0% | [ |
| 来源 | UFM参数 | 操作条件 | 分离性能 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 烟草 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:0.5 kDa 膜材料:纤维素 | pH=5.6~5.8,U=30 V | 回收率:8.6%~28.7% | [ |
| 绿茶 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:1 kDa 膜材料:纤维素酯 | pH=5.6~5.8,i=10 mA/cm2 | 回收率:50% | [ |
| 绿茶 | / | [ | ||
| 蔓越莓汁 | 有效膜面积:10 cm2 MWCO:500 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=2.5,U=30 V | 回收率:34.8%~52.9% | [ |
| pH=2.5,U=30 V | 回收率:19.4% | [ | ||
| 蔓越莓汁 | 有效膜面积:30 cm2 MWCO:500 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=2.6,E=15 V/cm | 回收率:22% | [ |
| 蔓越莓汁 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:3 kDa 膜材料:PS | pH=2.4,U=10 V | 脱酸率:40% | [ |
| 蔓越莓汁 | 有效膜面积:10 cm2 MWCO:250 kDa 膜材料:PVDF | U=30 V | 回收率:26.2%~44.2% | [ |
表3 EDUF在食品中的应用
Table 3 Applications of the EDUF technology in food processing
| 来源 | UFM参数 | 操作条件 | 分离性能 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 烟草 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:0.5 kDa 膜材料:纤维素 | pH=5.6~5.8,U=30 V | 回收率:8.6%~28.7% | [ |
| 绿茶 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:1 kDa 膜材料:纤维素酯 | pH=5.6~5.8,i=10 mA/cm2 | 回收率:50% | [ |
| 绿茶 | / | [ | ||
| 蔓越莓汁 | 有效膜面积:10 cm2 MWCO:500 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=2.5,U=30 V | 回收率:34.8%~52.9% | [ |
| pH=2.5,U=30 V | 回收率:19.4% | [ | ||
| 蔓越莓汁 | 有效膜面积:30 cm2 MWCO:500 kDa 膜材料:PES | pH=2.6,E=15 V/cm | 回收率:22% | [ |
| 蔓越莓汁 | 有效膜面积:100 cm2 MWCO:3 kDa 膜材料:PS | pH=2.4,U=10 V | 脱酸率:40% | [ |
| 蔓越莓汁 | 有效膜面积:10 cm2 MWCO:250 kDa 膜材料:PVDF | U=30 V | 回收率:26.2%~44.2% | [ |
| [1] | 郑龙, 田佳鑫, 张泽鹏, 等. 多肽药物制备工艺研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(7): 3538-3550. |
| Zheng L, Tian J X, Zhang Z P, et al. Progress on pharmaceutical engineering of peptide-based drugs[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(7): 3538-3550. | |
| [2] | Oshima K, Nakamura K, Guo H, et al. Mini-review on application of analytical centrifugation, ultracentrifugation and centrifugal devices to phase equilibria and separation processes[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2022, 558: 113457. |
| [3] | Kurniawan T A, Yap P-S, Chen Z. Techniques for pollutant removal, nutrient recovery, and energy production from landfill leachates: a review[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2025, 23(2): 517-577. |
| [4] | 王梓豪, 闫军营, 王报英, 等. 离子膜分离技术在过程工业减排和流程再造中的应用进展[J]. 中国科学:化学, 2025, 55(9): 2782-2796. |
| Wang Z H, Yan J Y, Wang B Y, et al. Applications of ion-exchange membrane separation techniques in process industries decarbonization and manufacturing reshaping. Scientia Sinica(Chimica), 2025, 55(9): 2782-2796. | |
| [5] | 颜海洋, 汪耀明, 蒋晨啸, 等. 离子膜电渗析在高盐废水"零排放"中的应用、机遇与挑战[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(1): 672-681. |
| Yan H Y, Wang Y M, Jiang C X, et al. Ion exchange membrane electrodialysis for high salinity wastewater "zero liquid discharge": applications, opportunities and challenges[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(1): 672-681. | |
| [6] | 顾天宇, 陈献富, 王思琪, 等. 膜技术在杜仲有效成分分离纯化中的应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(11): 4005-4019. |
| Gu T Y, Chen X F, Wang S Q, et al. Application of membranes for separation and purification of Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 4005-4019. | |
| [7] | Chen Y M L, Wang L C, Del Cerro M, et al. Dialysis opens a new pathway for high-salinity organic wastewater treatment[J]. Nature Water, 2025, 3(1): 49-58. |
| [8] | Zhao C W, Zhang Y J, Jia Y W, et al. Polyamide membranes with nanoscale ordered structures for fast permeation and highly selective ion-ion separation[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 1112. |
| [9] | Wu Y, Lu C H, Hu C Z, et al. Combined Effect of Electrostatic Interaction and Steric Sieving during Ion Transport in Nanochannels[J]. Environmental science & technology, 2025, 59(22): 11377-11388. |
| [10] | Strathmann H. Electrodialysis, a mature technology with a multitude of new applications[J]. Desalination, 2010, 264(3): 268-288. |
| [11] | Uliana A A, Bui N T, Kamcev J, et al. Ion-capture electrodialysis using multifunctional adsorptive membranes[J]. Science, 2021, 372(6539): 296-299. |
| [12] | Boukil A, Suwal S, Chamberland J, et al. Ultrafiltration performance and recovery of bioactive peptides after fractionation of tryptic hydrolysate generated from pressure-treated β-lactoglobulin[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 556: 42-53. |
| [13] | Zhang Y H, Chen T, Chen X F, et al. The application of pressure-driven ceramic-based membrane for the treatment of saline wastewater and desalination–A review[J]. Desalination, 2025, 597: 118327. |
| [14] | Mohammad A W, Ng C Y, Lim Y P, et al. Ultrafiltration in food processing industry: review on application, membrane fouling, and fouling control[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2012, 5(4): 1143-1156. |
| [15] | Rulence A, Perreault V, Thibodeau J, et al. One step purification of active nisin by electrodialysis from a commercial product[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2023, 281: 119134. |
| [16] | 汪耀明, 李为, 徐铜文. 电渗析技术清洁分离纯化肌氨酸[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(8): 3137-3143. |
| Wang Y M, Li W, Xu T W. Electrodialysis for cleaner separation and purification of sarcosine[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(8): 3137-3143. | |
| [17] | Liu S S, Dong Z G, Zhang L L, et al. Efficient separation of alkaloid from extract of traditional Chinese medicine via electrodialysis at over-limiting current density[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2025, 734: 124423. |
| [18] | Richa M, García-Cervilla R, Lobato J, et al. Carboxylic acids selective recovery from wastewater using electrodialysis[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2025, 13(5): 117752. |
| [19] | 苏慧超, 张田明, 吴云奇, 等. 电渗析-超滤耦合技术研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(S2): 1-7. |
| Su H C, Zhang T M, Wu Y Q, et al. Development of electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membrane technology[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2020, 39(S2): 1-7. | |
| [20] | Alavi F, Ciftci O N. Purification and fractionation of bioactive peptides through membrane filtration: a critical and application review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2023, 131: 118-128. |
| [21] | Revellat E, Bazinet L. Production of Anthocyanin-Enriched Juices by Electrodialysis with Filtration Membrane Process: The Influence of Duration on Juice Composition, Process Efficiency, and Membrane Fouling[J]. Foods, 2024, 13(21): 3478. |
| [22] | Dong Z G, Zhou R, Wei Z Q, et al. Electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membrane for efficient isolation of oxymatrine from simulated eluent of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Desalination, 2024, 592: 118058. |
| [23] | Lu H X, Zou W X, Chai P, et al. Feasibility of antibiotic and sulfate ions separation from wastewater using electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membrane[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 112: 3097-3105. |
| [24] | 王湛, 王志, 高学理, 等. 膜分离技术基础[M]. 3版. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2019. |
| Wang Z, Wang Z, Gao X L. Fundamentals of membrane separation technology[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2019. | |
| [25] | Maigrot E, Sabates J. Apparat zur Läuterung von Zuckersäften mittels Elektrizität: Germany, 50443[P]. 1890-10-18. |
| [26] | Schollmeyer G. Reinigung von Zuckersäften durch Elektrodialyse und mit Ozon: Germany, 136670[P]. 1902-07-15. |
| [27] | Michaelis L, Fujita A. The electric phenomenon and ion permeability of membranes. II. Permeability of apple peel [J]. Biochemistry Z, 1925, 158: 28-37. |
| [28] | Wassengger H, Jaeger K. Effecting cation-exchange in removing calcium from hard waters: US2204539[P]. 1940-06-11. |
| [29] | Meyer K H, Straus W. La perméabilité des membranes VI. Sur le passage du courant électrique à travers des membranes sélectives[J]. Helvetica Chimica Acta, 1940, 23(1): 795-800. |
| [30] | Juda W, McRae W A. Coherent ion-exchange gels and membranes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1950, 72(2): 1044. |
| [31] | Loeb S, Sourirajan S. Sea Water Demineralization by Means of an Osmotic Membrane[C]// Saline Water Conversion—II. Washington, DC: American Chemical Society, 1963: 117-132. |
| [32] | 徐玮一, 王征. 超滤膜分离技术在中药生产中的应用[J]. 基层中药杂志, 2002, 16(2): 46. |
| Xu W Y, Wang Z. Application of ultrafiltration membrane separation technology in traditional Chinese medicine production[J]. Primary Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2002, 16(2): 46. | |
| [33] | 王杏娣. 超滤技术的发展及其应用[J]. 今日科技, 1990(9): 5-6. |
| Wang X D. Development and application of ultrafiltration technology[J]. Today Science & Technology, 1990(9): 5-6. | |
| [34] | Wang D G J. Ultrafiltration and electrodialysis method and apparatus: US3905886[P]. 1975-09-16. |
| [35] | Ahlgren R M. Ultrafiltration and electrodialysis method and apparatus: US4123342[P]. 1978-10-31. |
| [36] | Galier S, Roux-de Balmann H. Study of the mass transfer phenomena involved in an electrophoretic membrane contactor[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2001, 194(1): 117-133. |
| [37] | Galier S, Roux-de Balmann H. Study of biomolecules separation in an electrophoretic membrane contactor[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2004, 241(1): 79-87. |
| [38] | Bazinet L, DeGrandpré Y, Porter A. Electromigration of tobacco polyphenols[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2005, 41(1): 101-107. |
| [39] | Dlask O, Václavíková N. Electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes for peptide separation[J]. Chemical Papers, 2018, 72(2): 261-271. |
| [40] | Poulin J F, Amiot J, Bazinet L. Simultaneous separation of acid and basic bioactive peptides by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membrane[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 2006, 123(3): 314-328. |
| [41] | 倪雅迪, 徐羚欣, 朱钰雅, 等. 中药蛋白资源提取分离及产业化路径展望[J]. 中草药, 2024, 55(8): 2828-2842. |
| Ni Y D, Xu L X, Zhu Y Y, et al. Prospects for extraction, separation, and industrialization of traditional Chinese medicine protein resources[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2024, 55(8): 2828-2842. | |
| [42] | Poulin J F, Amiot J, Bazinet L. Improved peptide fractionation by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membrane: Influence of ultrafiltration membrane stacking and electrical field strength[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2007, 299(1-2): 83-90. |
| [43] | Poulin J F, Amiot J, Bazinet L. Impact of feed solution flow rate on Peptide fractionation by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membrane[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2008, 56(6): 2007-2011. |
| [44] | Galier S, Balmann H R. The electrophoretic membrane contactor: a mass-transfer-based methodology applied to the separation of whey proteins[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2011, 77(2): 237-244. |
| [45] | Wang Q Y, Chen G Q, Kentish S E. Isolation of lactoferrin and immunoglobulins from dairy whey by an electrodialysis with filtration membrane process[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 233: 115987. |
| [46] | Vanhoute M, Firdaous L, Bazinet L, et al. Effect of haem on the fractionation of bovine haemoglobin peptic hydrolysate by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 365(1-2): 16-24. |
| [47] | Chen G Q, Song W J, Qi B K, et al. Separation of protein mixtures by an integrated electro-ultrafiltration–electrodialysis process[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2015, 147: 32-43. |
| [48] | Sun L Q, Lu H X, Wang J Y, et al. Electroseparation of lysozyme from egg white by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membrane[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2023, 317: 123710. |
| [49] | 孙鲁芹, 卢会霞, 王建友. 电渗析/超滤内在耦合过程分离蛋清中溶菌酶[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(5): 2262-2271. |
| Sun L Q, Lu H X, Wang J Y. Separation of lysozyme from egg white by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membrane(EDUF)process[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(5): 2262-2271. | |
| [50] | Doyen A, Beaulieu L, Saucier L, et al. Demonstration of in vitro anticancer properties of peptide fractions from a snow crab by-products hydrolysate after separation by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2011, 78(3): 321-329. |
| [51] | Doyen A, Beaulieu L, Saucier L, et al. Impact of ultrafiltration membrane material on peptide separation from a snow crab byproduct hydrolysate by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2011, 59(5): 1784-1792. |
| [52] | Doyen A, Saucier L, Beaulieu L, et al. Electroseparation of an antibacterial peptide fraction from snow crab by-products hydrolysate by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes[J]. Food Chemistry, 2012, 132(3): 1177-1184. |
| [53] | Doyen A, Roblet C, Beaulieu L, et al. Impact of water splitting phenomenon during electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes on peptide selectivity and migration[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 428: 349-356. |
| [54] | Roblet C, Akhtar M J, Mikhaylin S, et al. Enhancement of glucose uptake in muscular cell by peptide fractions separated by electrodialysis with filtration membrane from salmon frame protein hydrolysate[J]. Journal of Functional Foods, 2016, 22: 337-346. |
| [55] | Henaux L, Thibodeau J, Pilon G, et al. How charge and triple size-selective membrane separation of peptides from salmon protein hydrolysate orientate their biological response on glucose uptake[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(8): 1939. |
| [56] | Henaux L, Pereira K D, Thibodeau J, et al. Glucoregulatory and anti-inflammatory activities of peptide fractions separated by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes from salmon protein hydrolysate and identification of four novel glucoregulatory peptides[J]. Membranes, 2021, 11(7): 528. |
| [57] | Thibodeau J, Benoit N, Perreault V, et al. Scale-up and long-term study of electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membrane for the separation of a herring milt hydrolysate[J]. Membranes, 2021, 11(8): 558. |
| [58] | Madureira A R, Pereira C I, Gomes A M P, et al. Bovine whey proteins–Overview on their main biological properties[J]. Food Research International, 2007, 40(10): 1197-1211. |
| [59] | Halim N R A, Yusof H M, Sarbon N M. Functional and bioactive properties of fish protein hydolysates and peptides: A comprehensive review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2016, 51: 24-33. |
| [60] | Wang W Q, Liu Z C, Liu Y J, et al. Plant polypeptides: a review on extraction, isolation, bioactivities and prospects[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2022, 207: 169-178. |
| [61] | He R, Girgih A T, Rozoy E, et al. Selective separation and concentration of antihypertensive peptides from rapeseed protein hydrolysate by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes[J]. Food Chemistry, 2016, 197: 1008-1014. |
| [62] | Firdaous L, Dhulster P, Amiot J, et al. Concentration and selective separation of bioactive peptides from an alfalfa white protein hydrolysate by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2009, 329(1-2): 60-67. |
| [63] | Firdaous L, Dhulster P, Amiot J, et al. Investigation of the large-scale bioseparation of an antihypertensive peptide from alfalfa white protein hydrolysate by an electromembrane process[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 355(1-2): 175-181. |
| [64] | Udenigwe C C, Adebiyi A P, Doyen A, et al. Low molecular weight flaxseed protein-derived arginine-containing peptides reduced blood pressure of spontaneously hypertensive rats faster than amino acid form of arginine and native flaxseed protein[J]. Food Chemistry, 2012, 132(1): 468-475. |
| [65] | Doyen A, Udenigwe C C, Mitchell P L, et al. Anti-diabetic and antihypertensive activities of two flaxseed protein hydrolysate fractions revealed following their simultaneous separation by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes[J]. Food Chemistry, 2014, 145: 66-76. |
| [66] | Cecile Urbain Marie G, Perreault V, Henaux L, et al. Impact of a high hydrostatic pressure pretreatment on the separation of bioactive peptides from flaxseed protein hydrolysates by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 211: 242-251. |
| [67] | Ayan K, Boom R M, Nikiforidis C V. Electrophoretic removal of sinapic acid from rapeseed protein extract[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 357: 130215. |
| [68] | Langevin M E, Roblet C, Moresoli C, et al. Comparative application of pressure- and electrically-driven membrane processes for isolation of bioactive peptides from soy protein hydrolysate[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012, 403-404: 15-24. |
| [69] | Roblet C, Doyen A, Amiot J, et al. Impact of pH on ultrafiltration membrane selectivity during electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membrane (EDUF) purification of soy peptides from a complex matrix[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 435: 207-217. |
| [70] | Roblet C, Doyen A, Amiot J, et al. Enhancement of glucose uptake in muscular cell by soybean charged peptides isolated by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes (EDUF): Activation of the AMPK pathway[J]. Food Chemistry, 2014, 147: 124-130. |
| [71] | Giesler L, Linke D, Rabe S, et al. Hydrolysis of wheat gluten by combining peptidases of flammulina velutipes and electrodialysis[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2013, 61(36): 8641-8649. |
| [72] | Giesler L, Linke D, Berger R G. Factors limiting the enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat gluten[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2014, 62(20): 4762-4768. |
| [73] | González-Muñoz A, Valle M, Aluko R E, et al. Production of antihypertensive and antidiabetic peptide fractions from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness, 2022, 11(6): 1650-1659. |
| [74] | Graf B L, Rojas-Silva P, Rojo L E, et al. Innovations in Health Value and Functional Food Development of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.)[J]. Comprehensive reviews in food science and food safety, 2015, 14(4): 431-445. |
| [75] | 宋宏臣, 王建明, 郭立玮. 基于中药"非药效共性高分子物质"分子结构解析的膜材料设计与膜过程优化机制及方法探索[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2019, 44(18): 4060-4066. |
| Song H C, Wang J M, Guo L W. Study on mechanism and method of membrane preparation and membrane process optimization based on molecular structure analysis of noneffective common macromolecules[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2019, 44(18): 4060-4066. | |
| [76] | 董治国, 周容, 何金凤, 等. 膜分离技术在中药绿色制造中的应用与展望[J]. 中草药, 2024, 55(12): 4225-4234. |
| Dong Z G, Zhou R, He J F, et al. Application and prospect of membrane separation technology in green manufacturing of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2024, 55(12): 4225-4234. | |
| [77] | 徐丽, 张浅, 李益群, 等. 基于膜材料性质的中药化学成分透膜规律研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2019, 50(8): 1785-1794. |
| Xu L, Zhang Q, Li Y Q, et al. Research progress on membrane permeation regularity of chemical composition in Chinese materia medica based on membrane performance[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2019, 50(8): 1785-1794. | |
| [78] | Aider M, Brunet S, Bazinet L. Electroseparation of chitosan oligomers by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membrane (EDUF) and impact on electrodialytic parameters[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2008, 309(1-2): 222-232. |
| [79] | Aider M, Brunet S, Bazinet L. Effect of solution flow velocity and electric field strength on chitosan oligomer electromigration kinetics and their separation in an electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membrane (EDUF) system[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2009, 69(1): 63-70. |
| [80] | Labbé D, Araya-Farias M, Tremblay A, et al. Electromigration feasibility of green tea catechins[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2005, 254(1-2): 101-109. |
| [81] | Labbé D, Bazinet L. Effect of membrane type on cation migration during green tea electromigration and equivalent mass transported calculation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2006, 275(1-2): 220-228. |
| [82] | Bazinet L, Cossec C, Gaudreau H, et al. Production of a phenolic antioxidant enriched cranberry juice by electrodialysis with filtration membrane[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2009, 57(21): 10245-10251. |
| [83] | Bazinet L, Brianceau S, Dubé P, et al. Evolution of cranberry juice physico-chemical parameters during phenolic antioxidant enrichment by electrodialysis with filtration membrane[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2012, 87: 31-39. |
| [84] | Husson E, Araya-Farias M, Desjardins Y, et al. Selective anthocyanins enrichment of cranberry juice by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes stacked[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 2013, 17: 153-162. |
| [85] | Serre E, Rozoy E, Pedneault K, et al. Deacidification of cranberry juice by electrodialysis: Impact of membrane types and configurations on acid migration and juice physicochemical characteristics[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2016, 163: 228-237. |
| [86] | Tamersit S, Bouhidel K E, Zidani Z. Investigation of electrodialysis anti-fouling configuration for desalting and treating tannery unhairing wastewater: Feasibility of by-products recovery and water recycling[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 207: 334-340. |
| [87] | Meng J Z, Shi L, Wang S, et al. Membrane fouling during nutrient recovery from digestate using electrodialysis: Impacts of the molecular size of dissolved organic matter[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2023, 685: 121974. |
| [88] | Malmali M, Askegaard J, Sardari K, et al. Evaluation of ultrafiltration membranes for treating poultry processing wastewater[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2018, 22: 218-226. |
| [89] | Przybylski R, Bazinet L, Firdaous L, et al. Electroseparation of slaughterhouse by-product: antimicrobial peptide enrichment by pH modification[J]. Membranes, 2020, 10(5): 90. |
| [90] | Przybylski R, Bazinet L, Firdaous L, et al. Harnessing slaughterhouse by-products: From wastes to high-added value natural food preservative[J]. Food Chemistry, 2020, 304: 125448. |
| [91] | Adaile-Pérez V M, Thibodeau J, Ortiz-Basurto R I, et al. Enhanced antihypertensive chicken by-product hydrolysate fraction after its separation by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membrane (EDUF)[J]. Food Research International, 2025, 202: 115595. |
| [92] | Nikonenko V V, Vasil'eva V I, Akberova E M, et al. Competition between diffusion and electroconvection at an ion-selective surface in intensive current regimes[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2016, 235: 233-246. |
| [93] | Langevin M E, Bazinet L. Ion-exchange membrane fouling by peptides: a phenomenon governed by electrostatic interactions[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 369(1-2): 359-366. |
| [94] | Suwal S, Doyen A, Bazinet L. Characterization of protein, peptide and amino acid fouling on ion-exchange and filtration membranes: Review of current and recently developed methods[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 496: 267-283. |
| [95] | Suwal S, Roblet C, Amiot J, et al. Presence of free amino acids in protein hydrolysate during electroseparation of peptides: Impact on system efficiency and membrane physicochemical properties[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2015, 147: 227-236. |
| [96] | Persico M, Mikhaylin S, Doyen A, et al. How peptide physicochemical and structural characteristics affect anion-exchange membranes fouling by a tryptic whey protein hydrolysate[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016, 520: 914-923. |
| [97] | Dou Y C, Dong X C, Ma Y C, et al. Hollow fiber ultrafiltration membranes of poly(biphenyl-trifluoroacetone)[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2022, 659: 120779. |
| [98] | Tan L, Gong L, Wang S Y, et al. Superhydrophilic sub-1-nm porous membrane with electroneutral surface for nonselective transport of small organic molecules[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(34): 38778-38787. |
| [99] | Yao Y Y, Mu J J, Li Y, et al. Rechargeable Multifunctional Anti-Bacterial AEMs for Electrodialysis: Improving Anti-Biological Performance via Synergistic Antibacterial Mechanism[J]. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(30): 2303588. |
| [1] | 臧子晴, 李修真, 谈莹莹, 刘晓庆. 分凝器对两级分离自复叠制冷循环特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 17-25. |
| [2] | 裴星亮, 叶翠平, 裴赢丽, 李文英. 碱改性MIL-53(Cr)选择性吸附分离二甲苯异构体[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 258-267. |
| [3] | 李银龙, 刘国强, 晏刚. 分馏与闪蒸分离耦合自复叠制冷循环性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 26-35. |
| [4] | 李文龙, 常程, 吴小林, 姬忠礼. 油水聚结过滤材料中的液体分布特性及过程压降演化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4850-4861. |
| [5] | 张建民, 何美贵, 贾万鑫, 赵静, 金万勤. 聚氧化乙烯/冠醚共混膜及其二氧化碳分离性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4862-4871. |
| [6] | 郭旭, 贾继宁, 姚克俭. 基于优化CNN-BiLSTM神经网络的间歇精馏过程建模[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4613-4629. |
| [7] | 王杰, 林渠成, 张先明. 基于分解算法的混合气体多级膜分离系统全局优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4670-4682. |
| [8] | 陈治宏, 吴佳伟, 楼小玲, 贠军贤. 化学品生物制造过程机器学习的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3789-3804. |
| [9] | 周运桃, 崔丽凤, 张杰, 于富红, 李新刚, 田野. Ga2O3调控CuCeO催化CO2加氢制甲醇的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4042-4051. |
| [10] | 杨敏, 段新伟, 吴俊宏, 米杰, 王建成, 武蒙蒙. Sm2O3/γ-Al2O3催化剂的COS催化水解性能及失活机制[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4061-4070. |
| [11] | 张荟钦, 赵泓竣, 付正军, 庄力, 董凯, 贾添智, 曹雪丽, 孙世鹏. 纳滤膜在离子型稀土浸出液提浓中的应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4095-4107. |
| [12] | 蒋明虎, 汪帆, 邢雷, 赵立新, 李新亚, 陈丁玮. 井下含气对油水分离管柱流场特性及性能影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3361-3372. |
| [13] | 高照, 吴熙, 夏丹, 张霖宙. 石油加工分子管理平台热力学及分离单元模块开发[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3212-3225. |
| [14] | 高凤凤, 程慧峰, 杨博, 郝晓刚. 电驱动NiFeMn LDH/CNTs/PVDF膜电极选择性提取钨酸根离子[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3350-3360. |
| [15] | 梁碧麟, 余倩, 贾思琦, 李芳, 李其明. Ni-MOF-74金属有机框架膜的结构调变及气体分离性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2714-2721. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号