化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (6): 2603-2615.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241343
收稿日期:2024-11-22
修回日期:2024-12-30
出版日期:2025-06-25
发布日期:2025-07-09
通讯作者:
郭雪岩
作者简介:包兴(1998—),男,硕士研究生,Bao3356@163.com
Received:2024-11-22
Revised:2024-12-30
Online:2025-06-25
Published:2025-07-09
Contact:
Xueyan GUO
摘要:
为研究不同修饰形状的圆柱颗粒对填充床壁面效应及流动换热特性的影响,采用计算流体力学(CFD)方法,对未修饰的圆柱颗粒及修饰后的单孔圆柱、3孔圆柱、三叶草、3孔三叶草和9孔三叶草6种颗粒填充床进行了数值模拟。分析了径向与轴向空隙率分布、流动特性及流动换热性能。结果表明,圆柱颗粒通过内部开孔或外部开槽修饰均能够改善流体流动均匀性;颗粒内部开孔可以减小壁面附近流量占比,且孔洞数量对近壁面流量的影响不显著,但增加孔洞数量会削弱流体径向流动均匀性,同时提升轴向流动均匀性;圆柱颗粒通过外部开槽为三叶草状后可提升传热系数,但显著增加单位压降,通过内部开孔后传热系数和单位压降均降低;增加孔洞数量能够提升换热性能,但同时会导致压降增加;综合考虑传热效果和流动阻力,混合修饰的9孔三叶草颗粒具备最高的总换热效率,表现出最佳的综合换热性能。
中图分类号:
包兴, 郭雪岩. 圆柱颗粒结构修饰对填充床内流动和换热特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2603-2615.
Xing BAO, Xueyan GUO. Effects of cylindrical particle structure modification on the flow and heat transfer characteristics in packed beds[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2603-2615.
| 颗粒形状 | 颗粒体积 | 孔洞体积 | 孔洞比表面积 | 颗粒个数 | 堆积高度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 圆柱 | 21.2 | — | — | 173 | 40.5 |
| 单孔圆柱 | 14.4 | 6.8 | 2352 | 173 | 40.8 |
| 3孔圆柱 | 14.4 | 6.8 | 4068 | 173 | 40.7 |
| 三叶草 | 14.3 | — | — | 243 | 40.6 |
| 3孔三叶草 | 7.5 | 6.8 | 4068 | 244 | 40.1 |
| 9孔三叶草 | 7.5 | 6.8 | 7049 | 244 | 40.1 |
表1 随机填充床的几何参数
Table 1 Geometrical parameters of randomly packed bed
| 颗粒形状 | 颗粒体积 | 孔洞体积 | 孔洞比表面积 | 颗粒个数 | 堆积高度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 圆柱 | 21.2 | — | — | 173 | 40.5 |
| 单孔圆柱 | 14.4 | 6.8 | 2352 | 173 | 40.8 |
| 3孔圆柱 | 14.4 | 6.8 | 4068 | 173 | 40.7 |
| 三叶草 | 14.3 | — | — | 243 | 40.6 |
| 3孔三叶草 | 7.5 | 6.8 | 4068 | 244 | 40.1 |
| 9孔三叶草 | 7.5 | 6.8 | 7049 | 244 | 40.1 |
| 物质 | 密度/(kg·m-3) | 比热容/ (J·kg-1·K-1) | 动力黏度/ (kg·m-1·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 冷却流体 | 998.2 | 4182 | 0.001003 |
| 固体颗粒 | 2719 | 871 | — |
表2 物性参数
Table 2 Property parameter
| 物质 | 密度/(kg·m-3) | 比热容/ (J·kg-1·K-1) | 动力黏度/ (kg·m-1·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 冷却流体 | 998.2 | 4182 | 0.001003 |
| 固体颗粒 | 2719 | 871 | — |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 基准尺寸/mm | 2.50、2.75、3.00 |
| 面网格尺寸/mm | 基准尺寸×8% |
| 增长率 | 1.2 |
| 边界层数 | 2 |
| 边界层厚度/mm | 基准尺寸×2% |
表3 网格划分控制参数
Table 3 Control parameters for grid generation
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 基准尺寸/mm | 2.50、2.75、3.00 |
| 面网格尺寸/mm | 基准尺寸×8% |
| 增长率 | 1.2 |
| 边界层数 | 2 |
| 边界层厚度/mm | 基准尺寸×2% |
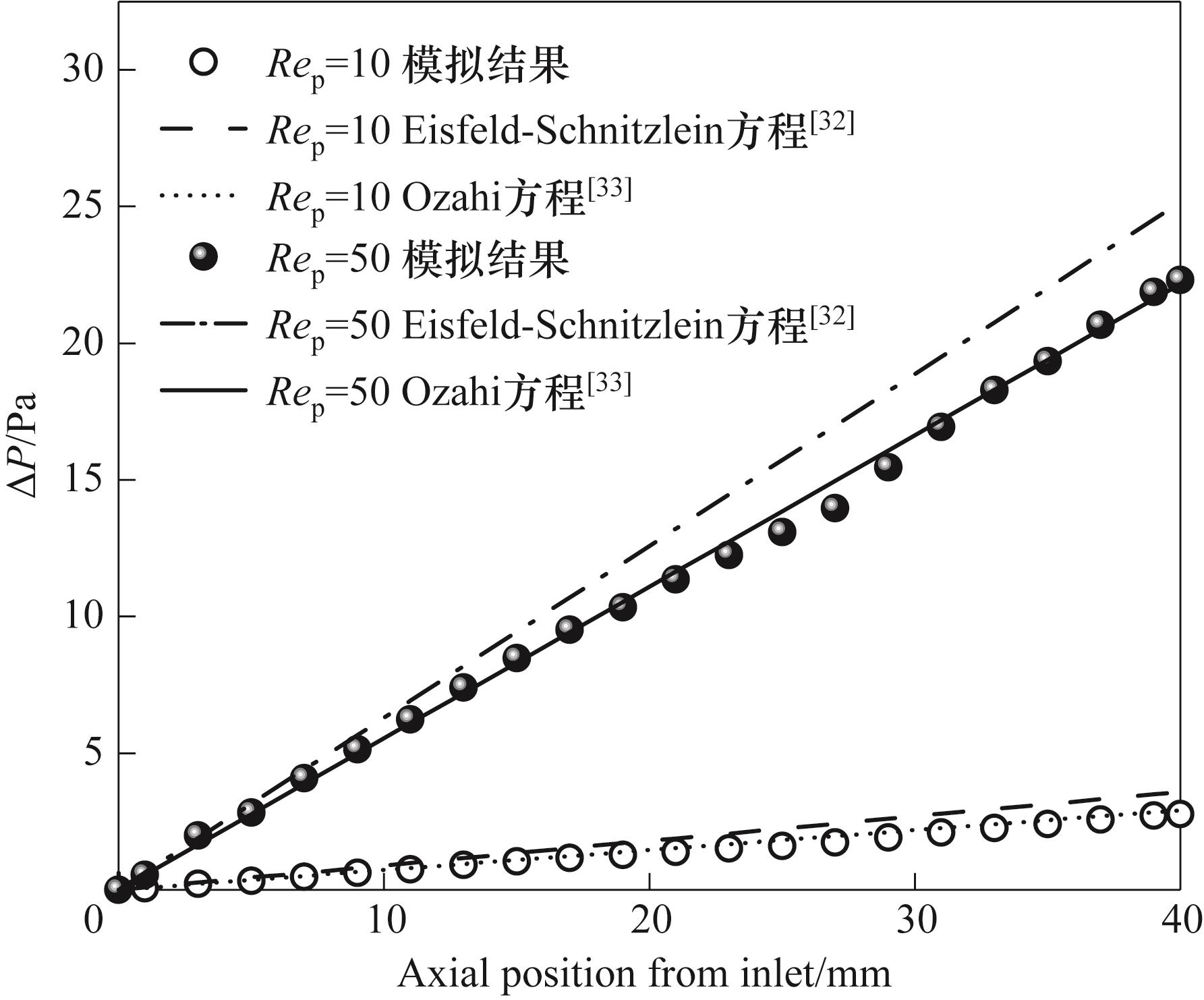
图5 圆柱颗粒填充床轴向压降的CFD模拟结果与关联式计算结果的对比
Fig.5 Comparison of axial pressure drop in cylindrical particle packed bed of CFD simulation results and correlation-based calculations
| [1] | Karthik G M, Buwa V V. Particle-resolved simulations of methane steam reforming in multilayered packed beds[J]. AIChE Journal, 2018, 64(11): 4162-4176. |
| [2] | Wang J Y, Yang J, Sunden B, et al. Hydraulic and heat transfer characteristics in structured packed beds with methane steam reforming reaction for energy storage[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 121: 105109. |
| [3] | Kim S G, Addad Y, Liu M L, et al. Computational investigation into heat transfer coefficients of randomly packed pebbles in flowing FLiBe[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 145: 118769. |
| [4] | Wang M H, Bu S S, Zhou B, et al. Pore-scale simulation on flow and heat transfer characteristics in packed beds with internal heat sources at low Reynolds numbers[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2023, 213: 124325. |
| [5] | 黄志国, 孙志高. 纳米相变微胶囊在蓄热结构化填充床中的应用模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(10): 4109-4128. |
| Huang Z G, Sun Z G. Simulation of the application of nano-scale phase change microcapsules for thermal storage in structured packed bed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(10): 4109-4128. | |
| [6] | Li C, Li Q, Ding Y L. Investigation on the thermal performance of a high temperature packed bed thermal energy storage system containing carbonate salt based composite phase change materials[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 247: 374-388. |
| [7] | 郭雪岩. CFD方法在固定床反应器传热研究中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2008, 59(8): 1914-1922. |
| Guo X Y. CFD modeling of heat transfer in fixed bed reactors[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2008, 59(8): 1914-1922. | |
| [8] | 郭雪岩, 晁东海, 柴辉生, 等. 小直径比固定床壁效应的CFD分析[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(1): 103-108. |
| Guo X Y, Chao D H, Chai H S, et al. CFD analysis of wall effects in packed beds with small tube-to-sphere diameter ratio[J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(1): 103-108. | |
| [9] | Dong Y, Sosna B, Korup O, et al. Investigation of radial heat transfer in a fixed-bed reactor: CFD simulations and profile measurements[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 317: 204-214. |
| [10] | Guo X Y, Zhu Z P. CFD based modeling on chemical looping combustion in a packed bed reactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2015, 138: 303-314. |
| [11] | Huo G P, Guo X Y. Numerical analyses of heterogeneous CLC reaction and transport processes in large oxygen carrier particles[J]. Processes, 2021, 9(1): 125. |
| [12] | 郭雪岩, 戴韧, 王宏光. 基于Chimera网格的固定床反应器内局部流动模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2008, 59(9): 2214-2219. |
| Guo X Y, Dai R, Wang H G. 3D numerical simulation on Chimera grid for local flows in fixed-bed reactors[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2008, 59(9): 2214-2219. | |
| [13] | Tiftikci A, Catalbas S S, Polat E, et al. Investigation of natural convection heat transfer of self-heating packed beds[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2023, 142: 106642. |
| [14] | Wang J Y, Yang J, Sunden B, et al. Numerical study of flow inhomogeneity and heat transfer enhancement in structured packed beds[J]. Thermal Science, 2020, 24(6 Part A): 3533-3542. |
| [15] | 吴江权, 杨剑, 周浪, 等. 不同圆球复合无序堆积床内流动传热数值分析[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(S1): 111-116. |
| Wu J Q, Yang J, Zhou L, et al. Numerical analysis of fluid flow and heat transfer in various composite packed beds[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(S1): 111-116. | |
| [16] | 曹兴, 于恒, 刘宇飞, 等. 小管径/粒径比有序填充床流动传热性能及场协同分析[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2019, 33(6): 1386-1393. |
| Cao X, Yu H, Liu Y F, et al. Flow and heat transfer performance and field synergy analysis of structured packed beds with low tube-to-particle diameter ratios[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2019, 33(6): 1386-1393. | |
| [17] | Kumar P, Saha S K, Sharma A. Experimental and CFD-DEM study on local packing distribution and thermofluidic analysis of binary packed bed[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2023, 282: 119372. |
| [18] | Shen C L, Li M C, Ji J, et al. Effect of packing structure evolution on the flow characteristics in a binary composite packed bed based on DEM-CFD method[J]. Processes, 2023, 11(3): 732. |
| [19] | Moghaddam E M, Foumeny E A, Stankiewicz A I, et al. Heat transfer from wall to dense packing structures of spheres, cylinders and Raschig rings[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 407: 127994. |
| [20] | Pashchenko D. Pressure drop in the thermochemical recuperators filled with the catalysts of various shapes: a combined experimental and numerical investigation[J]. Energy, 2019, 166: 462-470. |
| [21] | 霍官平, 郭雪岩. 不同径高比柱状载氧体固定床CLC非均相反应及共轭传递过程的数值分析[J]. 动力工程学报, 2023, 43(6): 663-669. |
| Huo G P, Guo X Y. Numerical analyses of heterogeneous reaction and conjugate transport processes in fixed-bed CLC with columnar oxygen carriers of various diameter-to-height ratios[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2023, 43(6): 663-669. | |
| [22] | Karthik G M, Buwa V V. A computational approach for the selection of optimal catalyst shape for solid-catalysed gas-phase reactions[J]. Reaction Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 5(1): 163-182. |
| [23] | Partopour B, Dixon A G. Effect of particle shape on methanol partial oxidation in a fixed bed using CFD reactor modeling[J]. AIChE Journal, 2020, 66(5): e16904. |
| [24] | Zhang S Z, Zhu Z X, Xin F, et al. Effect of particle shape on catalyst deactivation during 2-butene and isobutane alkylation of liquid phase in fixed-bed reactor using particle-resolved CFD simulation[J]. China Petroleum Processing & Petrochemical Technology, 2022, 24(4): 139-150. |
| [25] | Shi Y, Chen H, Chen W Y, et al. Effects of particle shape and packing style on ethylene oxidation reaction using particle-resolved CFD simulation[J]. Particuology, 2023, 82: 87-97. |
| [26] | Liu X L, Qin B, Zhang Q F, et al. Optimizing catalyst supports at single catalyst pellet and packed bed reactor levels: a comparison study[J]. AIChE Journal, 2021, 67(8): e17163. |
| [27] | 贺逸健, 刘祥坤, 施尧, 等. 乙烷氧化脱氢制乙烯催化剂颗粒外形设计[J]. 化工进展, DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2024-0704 . |
| He Y J, Liu X K, Shi Y, et al. Catalyst particle shape design for ethane oxidative dehydrogenation to ethylene[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2024-0704 . | |
| [28] | Partopour B, Dixon A G. An integrated workflow for resolved-particle packed bed models with complex particle shapes[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 322: 258-272. |
| [29] | Wehinger G D, Fütterer C, Kraume M. Contact modifications for CFD simulations of fixed-bed reactors: cylindrical particles[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017, 56(1): 87-99. |
| [30] | Huo G P, Guo X Y. Is monolithic configuration superior to random packing in a fixed bed reactor for CLC like processes?[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 2023, 194: 109581. |
| [31] | Caulkin R, Jia X, Xu C, et al. Simulations of structures in packed columns and validation by X-ray tomography[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(1): 202-213. |
| [32] | Eisfeld B, Schnitzlein K. The influence of confining walls on the pressure drop in packed beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2001, 56(14): 4321-4329. |
| [33] | Ozahi E, Gundogdu M Y, Carpinlioglu M Ö. A modification on Ergun's correlation for use in cylindrical packed beds with non-spherical particles[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2008, 19(4): 369-381. |
| [34] | 汪健生, 张辉鹏, 刘雪玲, 等. 多孔介质结构对储层内流动和换热特性的影响[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(8): 4212-4220. |
| Wang J S, Zhang H P, Liu X L, et al. Analysis of flow and heat transfer characteristics in porous media reservoir[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(8): 4212-4220. |
| [1] | 于宏鑫, 王宁波, 郭焱华, 邵双全. 动态蓄冰系统的板式换热器流动换热模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 106-113. |
| [2] | 吴馨, 龚建英, 李祥宇, 王宇涛, 杨小龙, 蒋震. 超声波激励疏水表面液滴运动的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 133-139. |
| [3] | 燕子腾, 詹飞龙, 丁国良. 空调用套管式分流器结构设计及分流效果验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 152-159. |
| [4] | 密晓光, 孙国刚, 程昊, 张晓慧. 印刷电路板式天然气冷却器性能仿真模型和验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 426-434. |
| [5] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [6] | 任现超, 谷雅秀, 段少斌, 贾文竹, 李汉林. 翅片式椭圆套管蒸发式冷凝器传热传质性能实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 75-83. |
| [7] | 张文锋, 郭玮, 张新玉, 曹昊敏, 丁国良. 铝管铝翅片换热器模型开发及软件实现[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 84-92. |
| [8] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [9] | 袁琳慧, 王瑜. 单服务器浸没射流式液冷系统散热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 160-169. |
| [10] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [11] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [12] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [13] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [14] | 孙云龙, 徐肖肖, 黄永方, 郭纪超, 陈卫卫. 水平光滑管内CO2流动沸腾的非绝热可视化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 230-236. |
| [15] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号
