化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (7): 3235-3245.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250426
陈培强1,2( ), 郑群1, 姜玉廷1, 熊春华2, 陈今茂2, 王旭东2, 黄龙2, 阮曼2(
), 郑群1, 姜玉廷1, 熊春华2, 陈今茂2, 王旭东2, 黄龙2, 阮曼2( ), 徐万里2(
), 徐万里2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-22
修回日期:2025-07-01
出版日期:2025-07-25
发布日期:2025-08-13
通讯作者:
阮曼,徐万里
作者简介:陈培强(1994—),男,博士研究生,chenpeiqiang@hrbeu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Peiqiang CHEN1,2( ), Qun ZHENG1, Yuting JIANG1, Chunhua XIONG2, Jinmao CHEN2, Xudong WANG2, Long HUANG2, Man RUAN2(
), Qun ZHENG1, Yuting JIANG1, Chunhua XIONG2, Jinmao CHEN2, Xudong WANG2, Long HUANG2, Man RUAN2( ), Wanli XU2(
), Wanli XU2( )
)
Received:2025-04-22
Revised:2025-07-01
Online:2025-07-25
Published:2025-08-13
Contact:
Man RUAN, Wanli XU
摘要:
海水激活电池输出特性是衡量其实用化的关键指标,而电液流量及电流密度作为其运行过程中的重要参数,对电池输出特性的影响尤为显著。通过构建海水激活电池多物理场耦合模型,系统研究了不同电液流量、电流密度对海水激活电池输出特性(电化学特性、传质特性)的影响。结果表明:适当提高电液流量可以有效降低浓差极化,显著提升电池的输出电压和放电能量。电流密度的增加虽能显著提升功率密度,但同时也会加剧浓差极化与欧姆极化效应,降低电池的能量密度。通过熵权法综合评价发现,电液流量250 ml/min与电流密度600 mA/cm²组合下的综合评价值高达0.808,表明电液流量与电流密度的协同优化可有效提高电池的输出特性,为其实际应用提供可靠的理论依据。
中图分类号:
陈培强, 郑群, 姜玉廷, 熊春华, 陈今茂, 王旭东, 黄龙, 阮曼, 徐万里. 电液流量及电流密度对海水激活电池输出特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3235-3245.
Peiqiang CHEN, Qun ZHENG, Yuting JIANG, Chunhua XIONG, Jinmao CHEN, Xudong WANG, Long HUANG, Man RUAN, Wanli XU. Effects of electrolyte flow rate and current density on the output performance of seawater-activated batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3235-3245.
| 参数 | 数值/mm |
|---|---|
| 阳极长度 | 100 |
| 阳极宽度 | 100 |
| 阳极厚度 | 0.25 |
| 阴极长度 | 100 |
| 阴极宽度 | 100 |
| 阴极厚度 | 1 |
| 阴阳极间隔 | 0.5 |
| 进口直径 | 12 |
| 出口直径 | 12 |
| 进出口处直流道宽度 | 3 |
| 进出口处弧形流道宽度 | 4 |
表1 模型几何参数
Table 1 Geometric parameters of the model
| 参数 | 数值/mm |
|---|---|
| 阳极长度 | 100 |
| 阳极宽度 | 100 |
| 阳极厚度 | 0.25 |
| 阴极长度 | 100 |
| 阴极宽度 | 100 |
| 阴极厚度 | 1 |
| 阴阳极间隔 | 0.5 |
| 进口直径 | 12 |
| 出口直径 | 12 |
| 进出口处直流道宽度 | 3 |
| 进出口处弧形流道宽度 | 4 |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 开路电压/V | 2.06 |
| OH-浓度/(mol/L) | 4 |
| 阴极孔隙率 | 0.56 |
| 电解液密度/(kg/m3) | 1250 |
| 电解液比热容/(J/kg·K) | 4182 |
| 电解液动力黏性系数/(kg/(m·s)) | 0.0025 |
| 压力/Pa | 101325 |
| 运行温度/℃ | 80 |
表2 电化学及动力学参数
Table 2 Electrochemical and kinetic parameters
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 开路电压/V | 2.06 |
| OH-浓度/(mol/L) | 4 |
| 阴极孔隙率 | 0.56 |
| 电解液密度/(kg/m3) | 1250 |
| 电解液比热容/(J/kg·K) | 4182 |
| 电解液动力黏性系数/(kg/(m·s)) | 0.0025 |
| 压力/Pa | 101325 |
| 运行温度/℃ | 80 |
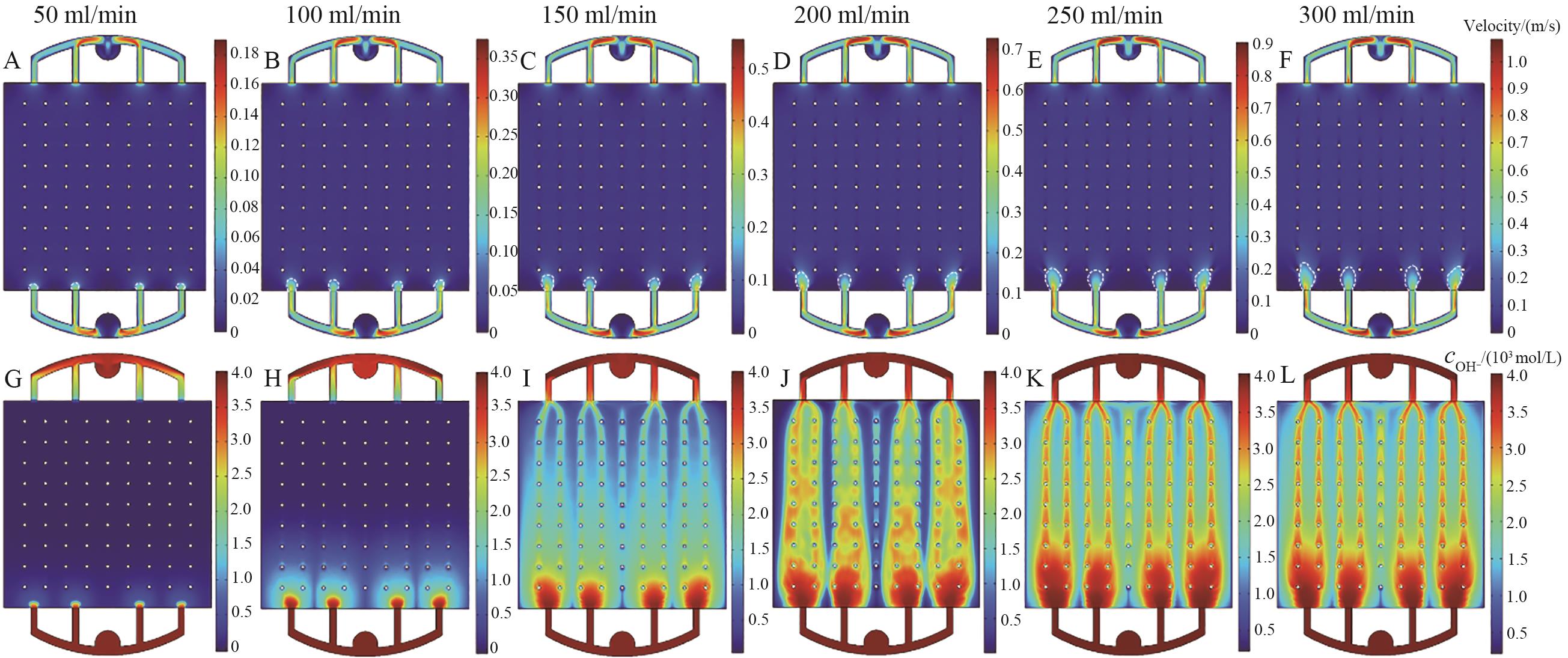
图7 不同流量下的极板间反应区电液速度、离子浓度分布云图
Fig.7 Distribution of electro-hydraulic velocity and ion concentration in the reaction zone between plates at different flow rates
| 评价指标 | 权重系数 | 方案 | 综合评价值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 功率密度 | 0.3767 | 250~100 | 0.659 |
| 能量密度 | 0.2225 | 250~200 | 0.680 |
| 电解液利用率 | 0.2004 | 250~300 | 0.731 |
| 有效放电容量 | 0.2004 | 250~400 | 0.751 |
| — | — | 250~500 | 0.785 |
| — | — | 250~600 | 0.808 |
| — | — | 250~700 | 0.770 |
| — | — | 250~800 | 0.807 |
| — | — | 250~900 | 0.702 |
| — | — | 250~1000 | 0.409 |
表3 综合评价结果
Table 3 Comprehensive evaluation results
| 评价指标 | 权重系数 | 方案 | 综合评价值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 功率密度 | 0.3767 | 250~100 | 0.659 |
| 能量密度 | 0.2225 | 250~200 | 0.680 |
| 电解液利用率 | 0.2004 | 250~300 | 0.731 |
| 有效放电容量 | 0.2004 | 250~400 | 0.751 |
| — | — | 250~500 | 0.785 |
| — | — | 250~600 | 0.808 |
| — | — | 250~700 | 0.770 |
| — | — | 250~800 | 0.807 |
| — | — | 250~900 | 0.702 |
| — | — | 250~1000 | 0.409 |
| [1] | Arnold S, Wang L, Presser V. Dual-use of seawater batteries for energy storage and water desalination[J]. Small, 2022, 18(43): 2107913. |
| [2] | Chen J L, Sun L, Wang K, et al. Research and applications of rechargeable seawater battery[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 76: 109659. |
| [3] | Zhang D H, Liu X, Li H H, et al. Challenges and strategies for high-energy aqueous electrolyte rechargeable batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(2): 598-616. |
| [4] | Zhou L M, Liu L J, Hao Z M, et al. Opportunities and challenges for aqueous metal-proton batteries[J]. Matter, 2021, 4(4): 1252-1273. |
| [5] | Tian H J, Li Z, Feng G X, et al. Stable, high-performance, dendrite-free, seawater-based aqueous batteries[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 237. |
| [6] | Khezri R, Motlagh S R, Etesami M, et al. Balancing current density and electrolyte flow for improved zinc-air battery cyclability[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 376: 124239. |
| [7] | Trudgeon D P, Loh A, Ullah H, et al. The influence of zinc electrode substrate, electrolyte flow rate and current density on zinc-nickel flow cell performance[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 373: 137890. |
| [8] | Naybour R D. The effect of electrolyte flow on the morphology of zinc electrodeposited from aqueous alkaline solution containing zincate ions[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1969, 116(4): 520. |
| [9] | Despic A R, Diggle J, Bockris J O. Mechanism of the formation of zinc dendrites[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1968, 115(5): 507. |
| [10] | Diggle J W, Despic A R, O'M Bockris J. The mechanism of the dendritic electrocrystallization of zinc[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1969, 116(11): 1503. |
| [11] | Khazaeli A, Vatani A, Tahouni N, et al. Numerical investigation and thermodynamic analysis of the effect of electrolyte flow rate on performance of all vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 293: 599-612. |
| [12] | Abdelghani-Idrissi S, Dubouis N, Grimaud A, et al. Effect of electrolyte flow on a gas evolution electrode[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11: 4677. |
| [13] | Maruthi Prasanna M, Jayanti S. Effect of electrolyte circulation rate in flow-through mode on the performance of vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 582: 233536. |
| [14] | Ito Y, Nyce M, Plivelich R, et al. Zinc morphology in zinc-nickel flow assisted batteries and impact on performance[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(4): 2340-2345. |
| [15] | Wang T, Fu J H, Zheng M L, et al. Dynamic control strategy for the electrolyte flow rate of vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 227: 613-623. |
| [16] | Wang R Y, Kirk D W, Zhang G X. Effects of deposition conditions on the morphology of zinc deposits from alkaline zincate solutions[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2006, 153(5): C357. |
| [17] | Sharifi B, Mojtahedi M, Goodarzi M, et al. Effect of alkaline electrolysis conditions on current efficiency and morphology of zinc powder[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 99(1/2): 72-76. |
| [18] | Dam A P, Franz T, Papakonstantinou G, et al. Catalyst dissolution in PEM water electrolysis: influence of time, current density and iridium ion transport in single-pass and recirculation water flow modes[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy, 2025, 365: 124946. |
| [19] | Zarei-Jelyani M, Loghavi M M, Babaiee M, et al. The significance of charge and discharge current densities in the performance of vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2023, 443: 141922. |
| [20] | Pismenskaya N, Gorobchenko A, Solonchenko K, et al. Effect of current density on anion-exchange membrane scaling during electrodialysis of phosphate-containing solution: experimental study and predictive simulation[J]. Desalination, 2025, 600: 118487. |
| [21] | Qiu C S, He G, Shi W K, et al. The polarization characteristics of lithium-ion batteries under cyclic charge and discharge[J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2019, 23(6): 1887-1902. |
| [22] | Dong N, Zhang F L, Pan H L. Towards the practical application of Zn metal anodes for mild aqueous rechargeable Zn batteries[J]. Chemical Science, 2022, 13(28): 8243-8252. |
| [23] | Chen P Q, Zheng Q. Investigation on flow field optimization of seawater activated battery based on flow channel structure design[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 84: 110798. |
| [24] | Sun J, Jiang H R, Zhang B W, et al. Towards uniform distributions of reactants via the aligned electrode design for vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 259: 114198. |
| [25] | Zhu S, Pelton R H, Collver K. Mechanistic modelling of fluid permeation through compressible fiber beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1995, 50(22): 3557-3572. |
| [26] | Newman J, Balsara N P. Electrochemical Systems[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2021. |
| [27] | Tjaden B, Cooper S J, Brett D J, et al. On the origin and application of the Bruggeman correlation for analysing transport phenomena in electrochemical systems[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2016, 12: 44-51. |
| [28] | Torabi F, Aliakbar A. A single-domain formulation for modeling and simulation of zinc-silver oxide batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2012, 159(12): A1986-A1992. |
| [29] | He X H, Li Z, Wang Y K, et al. A high-purity AgO cathode active material for high-performance aqueous AgO-Al batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 551: 232151. |
| [30] | Chen P Q, Xiong C H, Zheng Q, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental investigation on the optimization of flow-guided structures for high-performance aqueous AgO-Al batteries[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2024, 235: 126167. |
| [1] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [2] | 任现超, 谷雅秀, 段少斌, 贾文竹, 李汉林. 翅片式椭圆套管蒸发式冷凝器传热传质性能实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 75-83. |
| [3] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [4] | 沙鑫权, 胡然, 丁磊, 蒋珍华, 吴亦农. 空间用单机两级有阀线性压缩机研制及测试[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 114-122. |
| [5] | 孙浩然, 吴成云, 王艳蒙, 孙静楠, 胡仞与, 段钟弟. 热对流影响下液滴蒸发特性模型与实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 123-132. |
| [6] | 苏伟, 赵大海, 金旭, 刘忠彦, 李静, 张小松. 吸湿液滴与混合润湿性表面协同抑霜特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 140-151. |
| [7] | 燕子腾, 詹飞龙, 丁国良. 空调用套管式分流器结构设计及分流效果验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 152-159. |
| [8] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [9] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [10] | 黄博, 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. 薄膜型LNG船液货舱温度场计算分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 195-204. |
| [11] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [12] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [13] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [14] | 石一帆, 柯钢, 陈浩, 黄孝胜, 叶芳, 李成娇, 郭航. 大型高低温环境实验室温度控制仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 268-280. |
| [15] | 孔繁臣, 张硕, 唐明生, 邹慧明, 胡舟航, 田长青. 二氧化碳直线压缩机气体轴承模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 281-288. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号