化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (11): 4998-5010.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220912
杜智华1( ), 杨娟1,2(
), 杨娟1,2( ), 戴俊1,2, 冷冲冲1, 张鸽1
), 戴俊1,2, 冷冲冲1, 张鸽1
收稿日期:2022-06-29
修回日期:2022-10-07
出版日期:2022-11-05
发布日期:2022-12-06
通讯作者:
杨娟
作者简介:杜智华(1998―),女,硕士研究生,zhihuadu@home.hpu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Zhihua DU1( ), Juan YANG1,2(
), Juan YANG1,2( ), Jun DAI1,2, Chongchong LENG1, Ge ZHANG1
), Jun DAI1,2, Chongchong LENG1, Ge ZHANG1
Received:2022-06-29
Revised:2022-10-07
Online:2022-11-05
Published:2022-12-06
Contact:
Juan YANG
摘要:
以NiCl2·6H2O为镍源,采用水热法首次合成了不同Ni2+取代量的锌钛层状双金属氢氧化物(NiZnTi-LDH),通过X射线衍射、透射电镜、低温氮吸附、X射线光电子能谱与紫外-可见漫反射等测试研究了Ni2+取代对ZnTi-LDH晶相结构、微观形貌、孔结构、表面氧空位与光吸收性能的影响。以NiZnTi-LDH为催化剂,分别考察了模拟太阳光与可见光照射下的NO光氧化消除性能。结果表明:Ni2+部分取代Zn2+可在ZnTi-LDH的能带结构中形成一新的中间能级,产生可见光响应,同时Ni取代可于ZnTi-LDH表面形成氧空位(OV)。可见光照射下,ZnTi-LDH无NO氧化活性,最优催化剂27% NiZnTi-LDH的NO去除率为52.1%,NO x 脱除选择性高达97.4%。模拟太阳光照射下,27% NiZnTi-LDH的NO光氧化去除率为64.8%,是ZnTi-LDH的2.76倍,NO x 脱除选择性可达96.9%,且NO
中图分类号:
杜智华, 杨娟, 戴俊, 冷冲冲, 张鸽. Ni2+取代对ZnTi-LDH选择性光氧化去除NO的性能增强[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 4998-5010.
Zhihua DU, Juan YANG, Jun DAI, Chongchong LENG, Ge ZHANG. Performance enhancement of selective photo-oxidation for NO removal on ZnTi-LDH by Ni2+ substitution[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(11): 4998-5010.
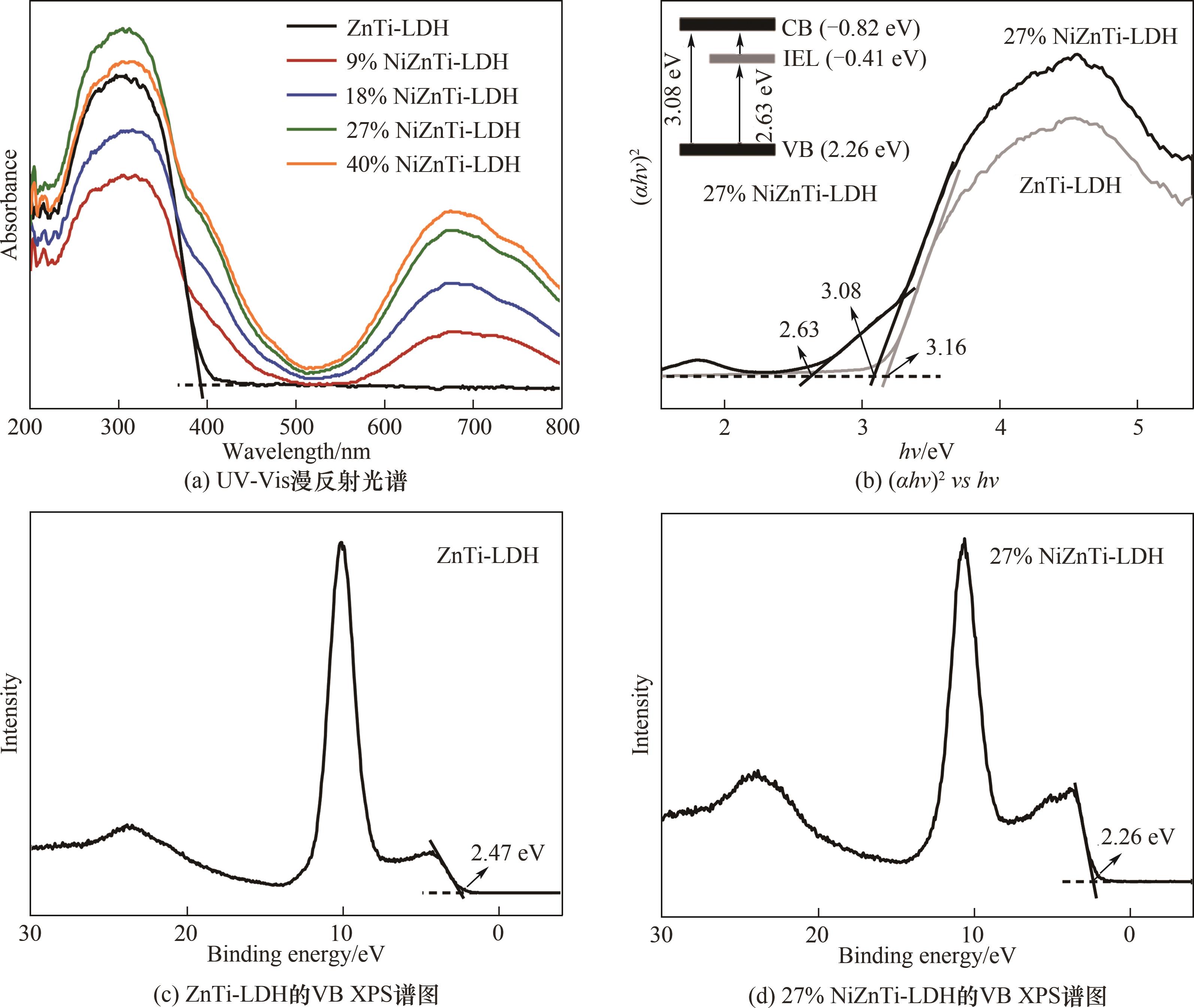
图6 NiZnTi-LDH样品的UV-Vis DRS光谱,ZnTi-LDH与27% NiZnTi-LDH样品的(αhν)2对hν曲线及其XPS价带谱
Fig.6 UV-Vis DRS spectra of NiZnTi-LDH samples, (αhν)2vshν curves and valence band XPS spectra of ZnTi-LDH and 27% NiZnTi-LDH sample
| Sample | Ni/(Ni + Zn)① | 比表面积/(m2/g) | 孔体积/(cm3/g) | NOrem/SBET② |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnTi-LDH | 0 | 103 | 0.311 | 0.228 |
| 9% NiZnTi-LDH | 8.90% | 116 | 0.283 | 0.338 |
| 18% NiZnTi -LDH | 17.86% | 131 | 0.302 | 0.404 |
| 27% NiZnTi -LDH | 26.81% | 146 | 0.330 | 0.445 |
| 40% NiZnTi -LDH | 39.73% | 156 | 0.368 | 0.371 |
表1 Ni2+与二价金属(Ni2++Zn2+)的实测摩尔比,NiZnTi-LDH样品的BET比表面积、孔体积,及比表面积归一化的NO去除率(NOrem/SBET)
Table 1 Actual molar ratios of Ni2+ to divalent metal (Ni2++Zn2+), BET surface area, pore volume of NiZnTi-LDH samples and NO removal normalized by specific surface area (NOrem/SBET)
| Sample | Ni/(Ni + Zn)① | 比表面积/(m2/g) | 孔体积/(cm3/g) | NOrem/SBET② |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnTi-LDH | 0 | 103 | 0.311 | 0.228 |
| 9% NiZnTi-LDH | 8.90% | 116 | 0.283 | 0.338 |
| 18% NiZnTi -LDH | 17.86% | 131 | 0.302 | 0.404 |
| 27% NiZnTi -LDH | 26.81% | 146 | 0.330 | 0.445 |
| 40% NiZnTi -LDH | 39.73% | 156 | 0.368 | 0.371 |
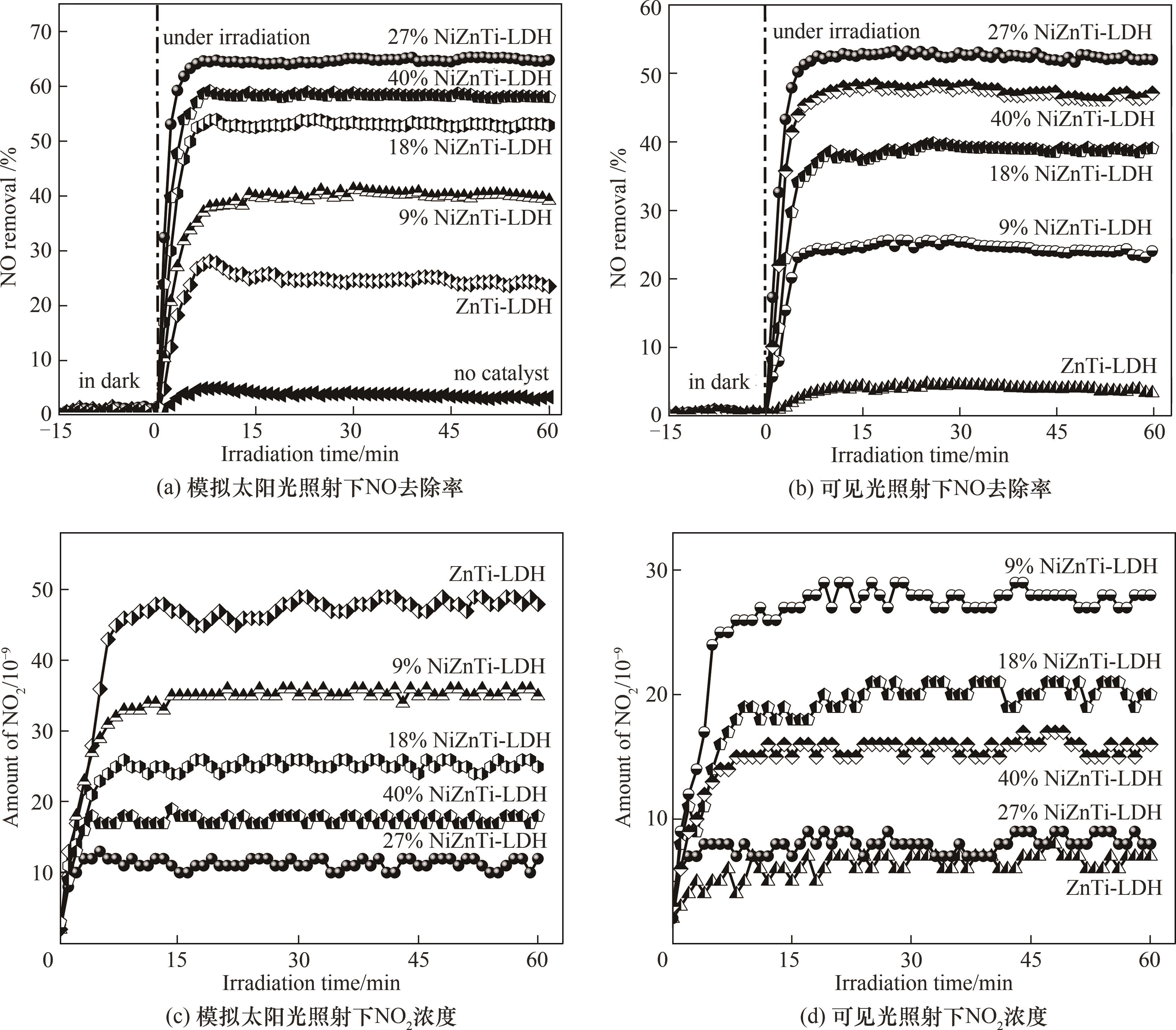
图8 模拟太阳光与可见光照射下不同光催化剂的NO去除率和有毒NO2的生成
Fig.8 NO removal percentage and toxic NO2 generation on different photocatalysts under simulated solar light and visible light irradiation respectively
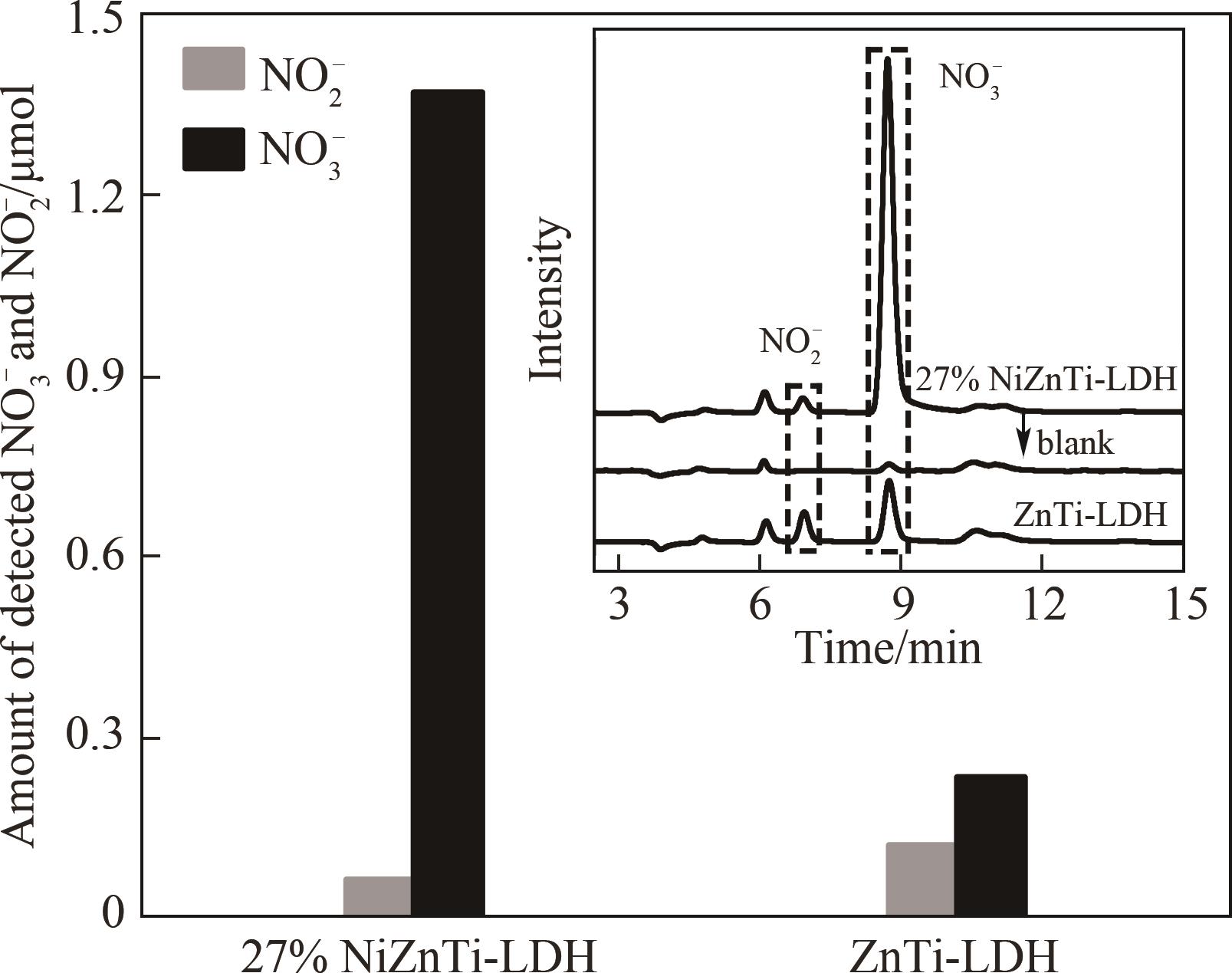
图9 27% NiZnTi-LDH与ZnTi-LDH光氧化去除NO的NO3-与NO2-产生量(插图为催化剂淋洗液的离子色谱图)
Fig. 9 Production amount of NO2- and NO3- during photo-oxidation NO removal over 27% NiZnTi-LDH and ZnTi-LDH respectively (inset is ion chromatography spectra of catalyst eluent)
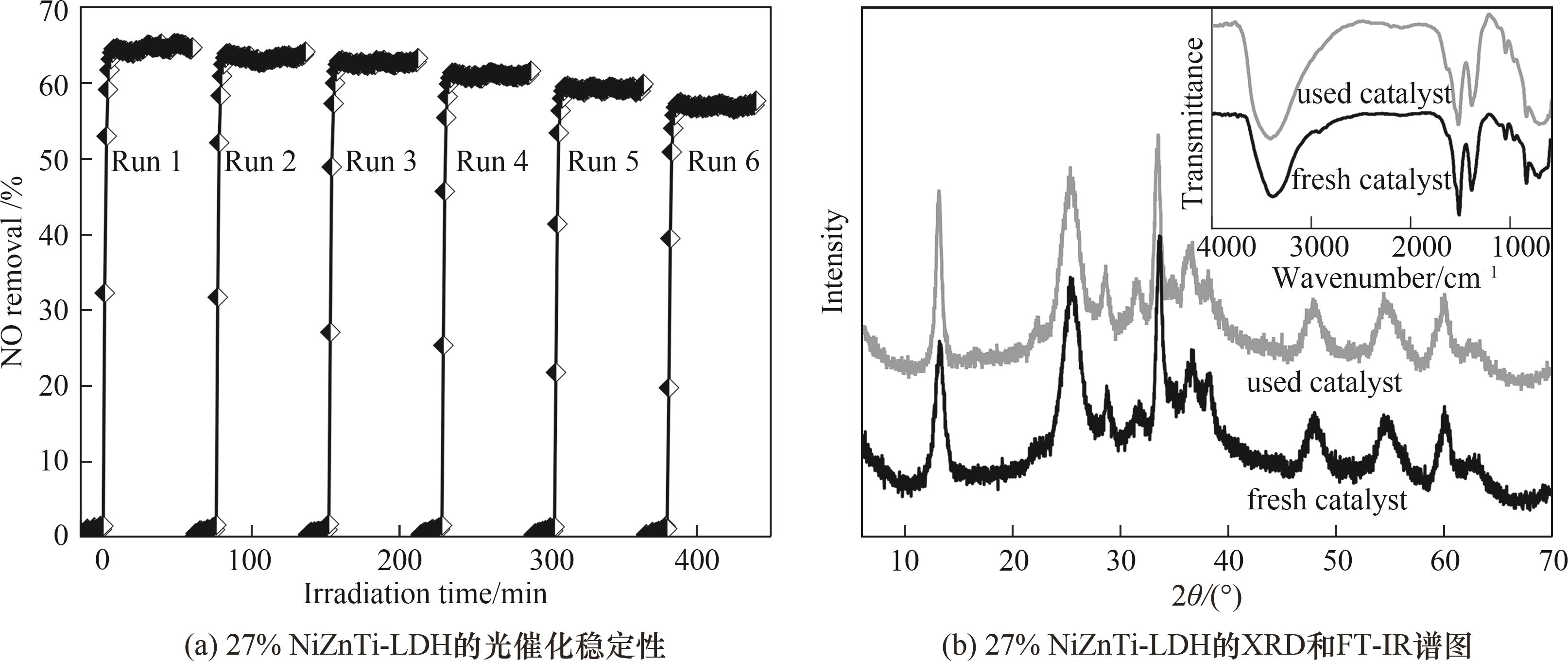
图10 27% NiZnTi-LDH光氧化消除NO的循环稳定性和6次循环实验后催化剂的XRD谱图与红外光谱
Fig.10 Cycling stability of 27% NiZnTi-LDH for photo-oxidative removal of NO, XRD and IR spectra of the catalyst after 6 cycles
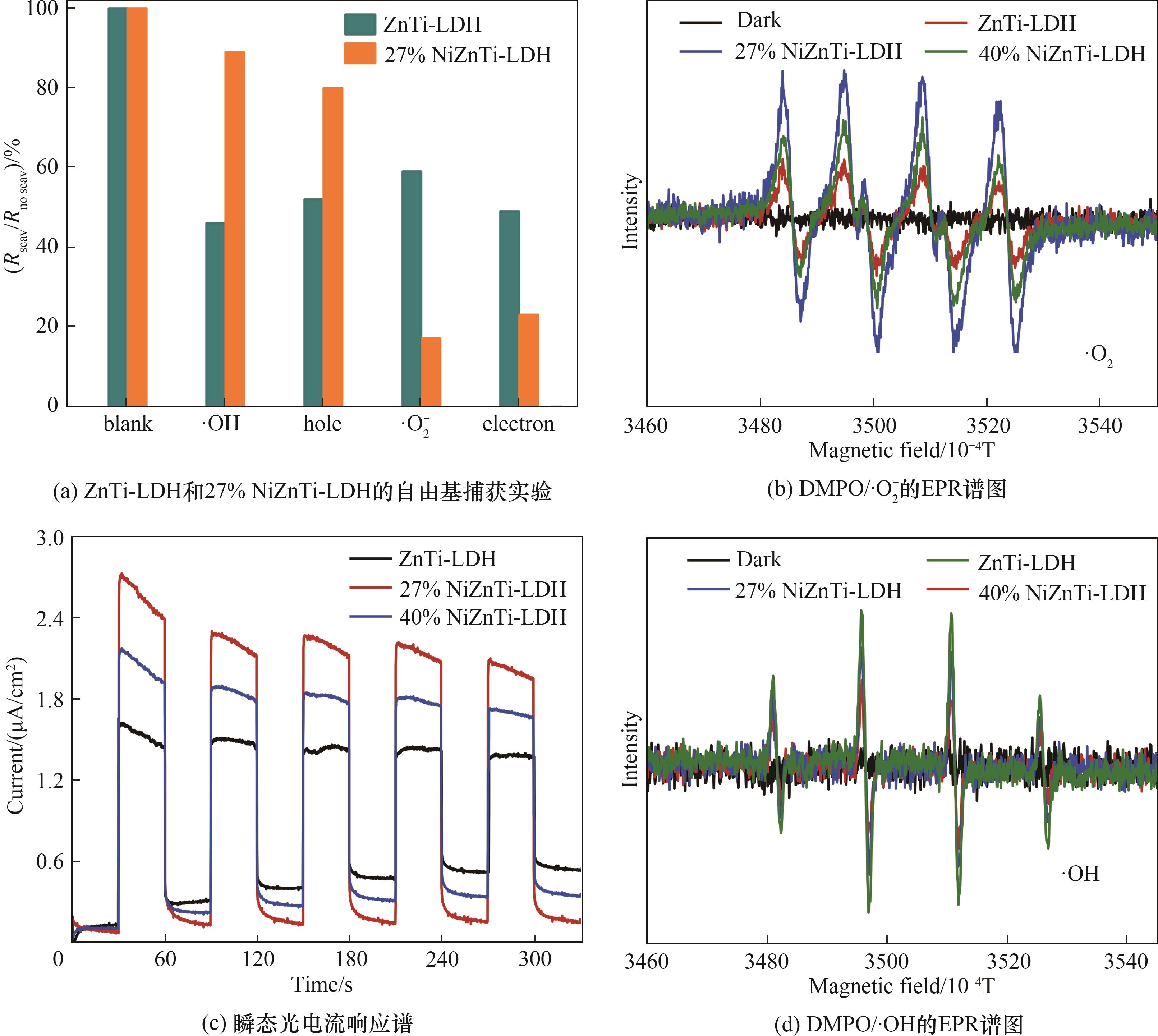
图11 光催化去除NO的自由基捕获实验;ZnTi-LDH、27% NiZnTi-LDH和40% NiZnTi-LDH悬浮液DMPO/∙O2-的EPR谱、瞬态光电流响应谱和DMPO/∙OH的EPR谱
Fig.11 Radical trapping experiments of photocatalytic removal of NO; EPR spectra of DMPO/∙O2-, transient photocurrent response and EPR spectra of DMPO/∙OH of ZnTi-LDH, 27% NiZnTi-LDH and 40% NiZnTi-LDH
| Sample | Catalyst amount/g | Light source | NO removal rate/% | NO x removal selectivity/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SrTiO3/SrCO3 | 0.05 | 300W Xe lamp (290—780 nm) | 47 | 86.17 | [ |
| TiO2/HAp | 0.1 | 300W Xe lamp (290—780 nm) | 44.6 | 92.0 | [ |
| ZnAlFe-LDHs | 0.05 | Xe lamp (≥510 nm) | 13 | 92 | [ |
| Bi2O3/CuBi2O4 | 0.1 | 300W Xe lamp (≥420 nm) | 30 | 93.3 | [ |
| Ni/Mg2Al-LDH | 0.4 | 8W UV lamp | 42 | 87 | [ |
| Ag/ZnTi-LDH | 0.1 | Xe lamp (290—780 nm) | 43 | 92 | [ |
| Pt-TiO2 | 0.05 | 500W tungsten lamp (≥420 nm) | 25.9 | 66 | [ |
| amorphous carbon nitride | 0.1 | 150W tungsten lamp (≥420 nm) | 57.1 | 86.3 | [ |
| Bi2O2CO3/Bi4O5Br2 | 0.1 | 300W Xe lamp (290—780 nm) | 53.2 | 89.3 | [ |
| 27% NiZnTi-LDH | 0.1 | Xe lamp (420—780 nm) | 52.1 | 97.4 | this work |
| Xe lamp (290—780 nm) | 64.8 | 96.9 |
表2 光催化去除NO各种催化剂的性能比较
Table 2 Comparison of photocatalytic NO removal performance over various catalysts
| Sample | Catalyst amount/g | Light source | NO removal rate/% | NO x removal selectivity/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SrTiO3/SrCO3 | 0.05 | 300W Xe lamp (290—780 nm) | 47 | 86.17 | [ |
| TiO2/HAp | 0.1 | 300W Xe lamp (290—780 nm) | 44.6 | 92.0 | [ |
| ZnAlFe-LDHs | 0.05 | Xe lamp (≥510 nm) | 13 | 92 | [ |
| Bi2O3/CuBi2O4 | 0.1 | 300W Xe lamp (≥420 nm) | 30 | 93.3 | [ |
| Ni/Mg2Al-LDH | 0.4 | 8W UV lamp | 42 | 87 | [ |
| Ag/ZnTi-LDH | 0.1 | Xe lamp (290—780 nm) | 43 | 92 | [ |
| Pt-TiO2 | 0.05 | 500W tungsten lamp (≥420 nm) | 25.9 | 66 | [ |
| amorphous carbon nitride | 0.1 | 150W tungsten lamp (≥420 nm) | 57.1 | 86.3 | [ |
| Bi2O2CO3/Bi4O5Br2 | 0.1 | 300W Xe lamp (290—780 nm) | 53.2 | 89.3 | [ |
| 27% NiZnTi-LDH | 0.1 | Xe lamp (420—780 nm) | 52.1 | 97.4 | this work |
| Xe lamp (290—780 nm) | 64.8 | 96.9 |
| 1 | Kreuzer L B, Patel C K. Nitric oxide air pollution: detection by optoacoustic spectroscopy[J]. Science, 1971, 173(3991): 45-47. |
| 2 | Tian H Z, Liu K Y, Hao J M, et al. Nitrogen oxides emissions from thermal power plants in China: current status and future predictions[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(19): 11350-11357. |
| 3 | Yu H S, Zhu Q Y, Tan Z C. Absorption of nitric oxide from simulated flue gas using different absorbents at room temperature and atmospheric pressure[J]. Applied Energy, 2012, 93: 53-58. |
| 4 | Casapu M, Kröcher O, Elsener M. Screening of doped MnO x -CeO2 catalysts for low-temperature NO-SCR[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2009, 88(3/4): 413-419. |
| 5 | Symalla M O, Drochner A, Vogel H, et al. IR-study of formation of nitrite and nitrate during NO x -adsorption on NSR-catalysts-compounds CeO2 and BaO/CeO2 [J]. Topics in Catalysis, 2007, 42/43(1/2/3/4): 199-202. |
| 6 | 张顾平, 王贝贝, 周舟, 等. 半导体材料在光催化低浓度氮氧化物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 259-275. |
| Zhang G P, Wang B B, Zhou Z, et al. Research progress of semiconductor materials for photocatalytic low concentration nitrogen oxides[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(1): 259-275. | |
| 7 | Pastor A, Rodriguez-Rivas F, de Miguel G, et al. Effects of Fe3+ substitution on Zn-Al layered double hydroxides for enhanced NO photochemical abatement[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 387: 124110. |
| 8 | Chen Q, Long H M, Chen M J, et al. In situ construction of biocompatible Z-scheme α-Bi2O3/CuBi2O4 heterojunction for NO removal under visible light[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 272: 119008. |
| 9 | Hu Y, Song X, Jiang S M, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Pt-doped TiO2 for NO x oxidation both under UV and visible light irradiation: a synergistic effect of lattice Pt4+ and surface PtO[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 274: 102-112. |
| 10 | Zhu Y P, Zhu R L, Zhu G Q, et al. Plasmonic Ag coated Zn/Ti-LDH with excellent photocatalytic activity[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 433: 458-467. |
| 11 | Lv X S, Zhang J Y, Dong X G, et al. Layered double hydroxide nanosheets as efficient photocatalysts for NO removal: band structure engineering and surface hydroxyl ions activation[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 277: 119200. |
| 12 | Xu M X, Wang Y H, Geng J F, et al. Photodecomposition of NO x on Ag/TiO2 composite catalysts in a gas phase reactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 307: 181-188. |
| 13 | Shang H, Huang S, Li H, et al. Dual-site activation enhanced photocatalytic removal of NO with Au/CeO2 [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 386: 124047. |
| 14 | Ma J Z, Wang C X, He H. Enhanced photocatalytic oxidation of NO over g-C3N4-TiO2 under UV and visible light[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 184: 28-34. |
| 15 | Li Y H, Ho W, Lv K L, et al. Carbon vacancy-induced enhancement of the visible light-driven photocatalytic oxidation of NO over g-C3N4 nanosheets[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 430: 380-389. |
| 16 | Fauzi A A, Jalil A A, Hassan N S, et al. A critical review on relationship of CeO2-based photocatalyst towards mechanistic degradation of organic pollutant[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 286: 131651. |
| 17 | Kallawar G A, Barai D P, Bhanvase B A. Bismuth titanate based photocatalysts for degradation of persistent organic compounds in wastewater: a comprehensive review on synthesis methods, performance as photocatalyst and challenges[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 318: 128563. |
| 18 | Anantharaj S, Karthick K, Kundu S. Evolution of layered double hydroxides (LDH) as high performance water oxidation electrocatalysts: a review with insights on structure, activity and mechanism[J]. Materials Today Energy, 2017, 6: 1-26. |
| 19 | Yang Z Z, Wei J J, Zeng G M, et al. A review on strategies to LDH-based materials to improve adsorption capacity and photoreduction efficiency for CO2 [J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2019, 386: 154-182. |
| 20 | Boumeriame H, da Silva E S, Cherevan A S, et al. Layered double hydroxide (LDH)-based materials: a mini-review on strategies to improve the performance for photocatalytic water splitting[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022, 64: 406-431. |
| 21 | Zhang J W, Shen B X, Hu Z Z, et al. Uncovering the synergy between Mn substitution and O vacancy in ZnAl-LDH photocatalyst for efficient toluene removal[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 296: 120376. |
| 22 | 任静, 谭玲, 赵宇飞, 等. 超薄二维材料光/电催化CO2还原的最新进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 398-424. |
| Ren J, Tan L, Zhao Y F, et al. Latest development of ultrathin two-dimensional materials for photocatalytic and electrocatalytic CO2 reduction[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(1): 398-424. | |
| 23 | Wang J K, Xu Y Q, Li J X, et al. Highly selective photo-hydroxylation of phenol using ultrathin NiFe-layered double hydroxide nanosheets under visible-light up to 550 nm[J]. Green Chemistry, 2020, 22(24): 8604-8613. |
| 24 | Huo W C, Cao T, Liu X Y, et al. Anion intercalated layered-double-hydroxide structure for efficient photocatalytic NO remove[J]. Green Energy & Environment, 2019, 4(3): 270-277. |
| 25 | Rodriguez-Rivas F, Pastor A, de Miguel G, et al. Cr3+ substituted Zn-Al layered double hydroxides as UV-Vis light photocatalysts for NO gas removal from the urban environment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 706: 136009. |
| 26 | Cheng G, Liu X, Song X J, et al. Visible-light-driven deep oxidation of NO over Fe doped TiO2 catalyst: synergic effect of Fe and oxygen vacancies[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 277: 119196. |
| 27 | Lu Y F, Huang Y, Zhang Y F, et al. Effects of H2O2 generation over visible light-responsive Bi/Bi2O2- x CO3 nanosheets on their photocatalytic NO x removal performance[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 363: 374-382. |
| 28 | Gu Z Y, Cui Z T, Wang Z J, et al. Carbon vacancies and hydroxyls in graphitic carbon nitride: promoted photocatalytic NO removal activity and mechanism[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 279: 119376. |
| 29 | Li J X, Xu Y Q, Ding Z Z, et al. Photocatalytic selective oxidation of benzene to phenol in water over layered double hydroxide: a thermodynamic and kinetic perspective[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 388: 124248. |
| 30 | Zou J H, Wang Z T, Guo W, et al. Photocatalytic selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol over ZnTi-LDH: the effect of surface OH groups[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 260: 118185. |
| 31 | Lei B, Cui W, Sheng J P, et al. Synergistic effects of crystal structure and oxygen vacancy on Bi2O3 polymorphs: intermediates activation, photocatalytic reaction efficiency, and conversion pathway[J]. Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(6): 467-476. |
| 32 | Liu Y Y, Chen S, Li K L, et al. Promote the activation and ring opening of intermediates for stable photocatalytic toluene degradation over Zn-Ti-LDH[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 606: 1435-1444. |
| 33 | Zhao Y F, Chen G B, Bian T, et al. Defect-rich ultrathin ZnAl-layered double hydroxide nanosheets for efficient photoreduction of CO2 to CO with water[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(47): 7824-7831. |
| 34 | Tan L, Xu S M, Wang Z L, et al. Highly selective photoreduction of CO2 with suppressing H2 evolution over monolayer layered double hydroxide under irradiation above 600 nm[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2019, 131(34): 11986-11993. |
| 35 | Liu C, Guo W, Chen J S, et al. Ultrathin ZnTi-LDH nanosheets for photocatalytic aerobic oxidation of aniline based on coordination activation[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2021, 11(1): 162-170. |
| 36 | 徐振和, 李泓江, 高雨, 等. In2O3/Ag:ZnIn2S4 “Type Ⅱ”型异质结构材料的制备及可见光催化性能[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3625-3635. |
| Xu Z H, Li H J, G Y, et al. Preparation of In2O3/Ag:ZnIn2S4 “Type Ⅱ” heterogeneous structure materials for visible light catalysis[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3625-3635. | |
| 37 | Luna A L, Novoseltceva E, Louarn E, et al. Synergetic effect of Ni and Au nanoparticles synthesized on titania particles for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 191: 18-28. |
| 38 | Hao X J, Tan L, Xu Y Q, et al. Engineering active Ni sites in ternary layered double hydroxide nanosheets for a highly selective photoreduction of CO2 to CH4 under irradiation above 500 nm[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59: 3008-3015. |
| 39 | Yang J, Chen P Y, Dai J, et al. Solar-energy-driven conversion of oxygen-bearing low-concentration coal mine methane into methanol on full-spectrum-responsive WO3- x catalysts[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 247: 114767. |
| 40 | Huang Y, Gao Y X, Zhang Q, et al. Biocompatible FeOOH-carbon quantum dots nanocomposites for gaseous NO x removal under visible light: improved charge separation and high selectivity[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 354: 54-62. |
| 41 | Rodriguez-Rivas F, Pastor A, Barriga C, et al. Zn-Al layered double hydroxides as efficient photocatalysts for NO x abatement[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 346: 151-158. |
| 42 | Shang H, Li M Q, Li H, et al. Oxygen vacancies promoted the selective photocatalytic removal of NO with blue TiO2 via simultaneous molecular oxygen activation and photogenerated hole annihilation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(11): 6444-6453. |
| 43 | Jin S, Dong G H, Luo J M, et al. Improved photocatalytic NO removal activity of SrTiO3 by using SrCO3 as a new co-catalyst[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 227: 24-34. |
| 44 | Yao J, Zhang Y F, Wang Y W, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic removal of NO over titania/hydroxyapatite (TiO2/HAp) composites with improved adsorption and charge mobility ability[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(40): 24683-24689. |
| 45 | Duan Y Y, Wang Y, Gan L Y, et al. Amorphous carbon nitride with three coordinate nitrogen (N3C) vacancies for exceptional NO x abatement in visible light[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(19): 2004001. |
| 46 | Zhu G Q, Li S P, Gao J Z, et al. Constructing a 2D/2D Bi2O2CO3/Bi4O5Br2 heterostructure as a direct Z-scheme photocatalyst with enhanced photocatalytic activity for NO x removal[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 493: 913-925. |
| 47 | 胡小龙, 公文学, 彭艺, 等. 配体诱导制备NM88(D)/COF-OMe复合材料及可见光芬顿联合降解抗生素磺胺甲嘧啶研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4730-4739. |
| Hu X L, Gong W X, Peng Y, et al. Construction of NM88(D)/COF-OMe composite via ligand-induced interfacial growth strategy for highly efficient photo-Fenton degradation of antibiotic sulfamerazine under visible light[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(9): 4730-4739. |
| [1] | 杨菲菲, 赵世熙, 周维, 倪中海. Sn掺杂的In2O3催化CO2选择性加氢制甲醇[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3366-3374. |
| [2] | 陈宇豪, 陈晓平, 马吉亮, 梁财. 市政污泥回转窑焚烧气态污染物排放特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2170-2178. |
| [3] | 王永倩, 王平, 程康, 毛晨林, 刘文锋, 尹智成, Ferrante Antonio. 氨气/甲烷贫预混旋转湍流火焰稳定性及NO生成[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4087-4094. |
| [4] | 孙晓明, 沙琪昊, 王陈伟, 周道金. 用于甲醇重整制氢的铜基催化剂研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(12): 5975-6001. |
| [5] | 毛晨林,王平,Shrotriya Prashant,何宏凯,Ferrante Antonio. 含氨燃料预混火焰的层流火焰速度及NO排放特性[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(10): 5330-5343. |
| [6] | 孙敬方, 葛成艳, 安冬琦, 仝庆, 高飞, 董林. 稀土铈基催化材料氧空位的表征方法综述[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(8): 3403-3415. |
| [7] | 张吕鸿, 马号朋, 澹台晓伟, 杨娜. 苯甲酸型低共熔溶剂吸收一氧化氮的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(8): 3644-3651. |
| [8] | 邹雷, 刘国强, 江苗苗, 杨则恒, 张卫新. ZIF-67衍生Co/NC多孔碳材料的改性及其电催化水氧化性能[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(6): 2821-2829. |
| [9] | 刘帅, 李学雷, 王烁天, 李旭贺, 王彦娟, 苑兴洲, 张健, 封瑞江. CeO2改性WO3/g-C3N4光催化氧化脱硫性能[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(4): 1618-1626. |
| [10] | 刘晓刚, 魏波, 史芸菲, 孙巾茹, 田雨, 赵玉, 迟姚玲, 王虹, 李翠清, 宋永吉. La1-xLixMnO3钙钛矿催化剂同时消除NO和碳烟催化性能[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(3): 1053-1059. |
| [11] | 原荷峰,马自在,王淑敏,李晋平,王孝广. 富氧空位Co3O4纳米线的制备及其电解水性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(12): 5831-5841. |
| [12] | 赵海谦, 高继慧, 周伟, 王忠华, 吴少华. 抗坏血酸对Fe2+/H2O2体系氧化NO的促进作用[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(7): 2636-2642. |
| [13] | 张雷, 张力, 闫云飞, 杨仲卿, 郭名女. 掺杂Ce、Zr对CO2钙基吸附剂循环特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(2): 612-617. |
| [14] | 曹蕃, 苏胜, 向军, 王鹏鹰, 胡松, 孙路石, 张安超. SCR反应过程中NO/NH3在γ-Al2O3表面吸附特性[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(10): 4056-4062. |
| [15] | 刘杨先, 潘剑锋, 刘勇. UV/H2O2氧化联合CaO吸收脱除NO的传质-反应动力学[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(3): 1062-1068. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号