化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (7): 3742-3751.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241507
• 过程安全 • 上一篇
范振宁1( ), 梁海宁1, 房茂立1, 赫一凡2, 于帅2, 闫兴清2, 安佳然2, 乔帆帆2, 喻健良2(
), 梁海宁1, 房茂立1, 赫一凡2, 于帅2, 闫兴清2, 安佳然2, 乔帆帆2, 喻健良2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-25
修回日期:2025-03-17
出版日期:2025-07-25
发布日期:2025-08-13
通讯作者:
喻健良
作者简介:范振宁(1985—),男,硕士,高级工程师,jh05-128@163.com
Zhenning FAN1( ), Haining LIANG1, Maoli FANG1, Yifan HE2, Shuai YU2, Xingqing YAN2, Jiaran AN2, Fanfan QIAO2, Jianliang YU2(
), Haining LIANG1, Maoli FANG1, Yifan HE2, Shuai YU2, Xingqing YAN2, Jiaran AN2, Fanfan QIAO2, Jianliang YU2( )
)
Received:2024-12-25
Revised:2025-03-17
Online:2025-07-25
Published:2025-08-13
Contact:
Jianliang YU
摘要:
基于工业规模CO2管道放空实验平台,开展了密相和超临界相CO2节流放空实验。通过对放空实验的结果进行分析和对比,揭示了不同初始相态CO2放空过程中,放空管管内CO2的压力、温度和相态的演变规律和差异,为实际工业CO2管道放空操作提供直接的数据支持和参考建议。结果表明,密相和超临界相CO2放空过程阀门上游截面和下游截面压力会分别经历快速降压阶段和充压阶段。各截面温度演变过程均会经历两段温降和温升过程。相较密相CO2放空,超临界相CO2放空阀门前后截面的压差更大,这可能会对阀门造成更为强烈的冲击。然而,尽管可能存在上述问题,超临界相CO2放空相较密相CO2放空管内CO2可以更早脱离气液饱和相。因此,超临界CO2放空时管内发生干冰冻堵的风险也相对较低。
中图分类号:
范振宁, 梁海宁, 房茂立, 赫一凡, 于帅, 闫兴清, 安佳然, 乔帆帆, 喻健良. CO2管道不同相态节流放空特性研究与对比[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3742-3751.
Zhenning FAN, Haining LIANG, Maoli FANG, Yifan HE, Shuai YU, Xingqing YAN, Jiaran AN, Fanfan QIAO, Jianliang YU. Research and comparison of throttling and venting characteristics of CO2 pipelines in different phase states[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3742-3751.
表1 实验条件
Table 1 Experimental conditions
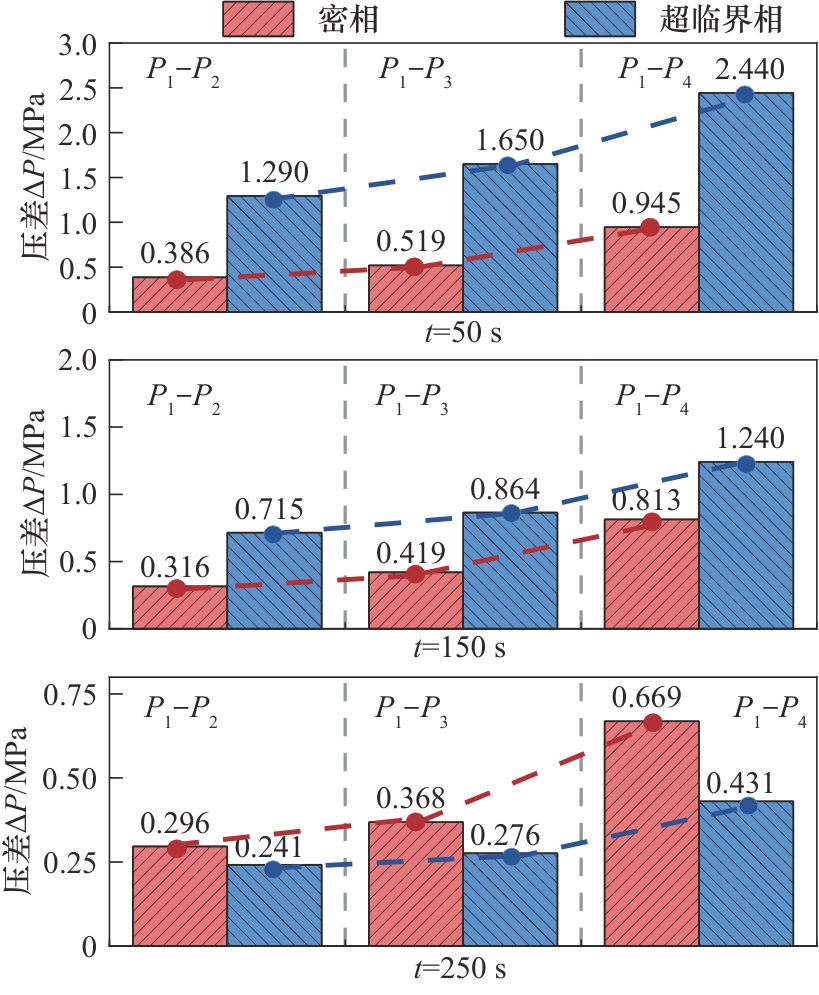
图7 密相(Test 1)和超临界相(Test 2)CO2放空不同时刻各截面压差
Fig.7 Pressure difference at different sections at different time points for dense-phase (Test 1) and supercritical (Test 2) CO2 venting
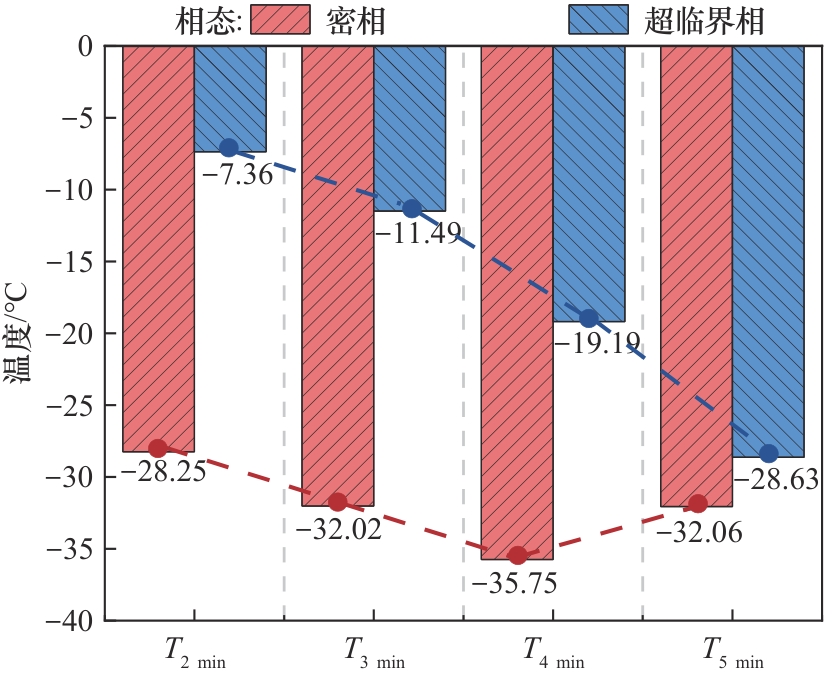
图10 密相(Test 1)和超临界相(Test 2)CO2放空管内截面最低温度对比
Fig.10 Comparison of the minimum temperature at the pipeline sections for dense-phase (Test 1) and supercritical (Test 2) CO2 venting
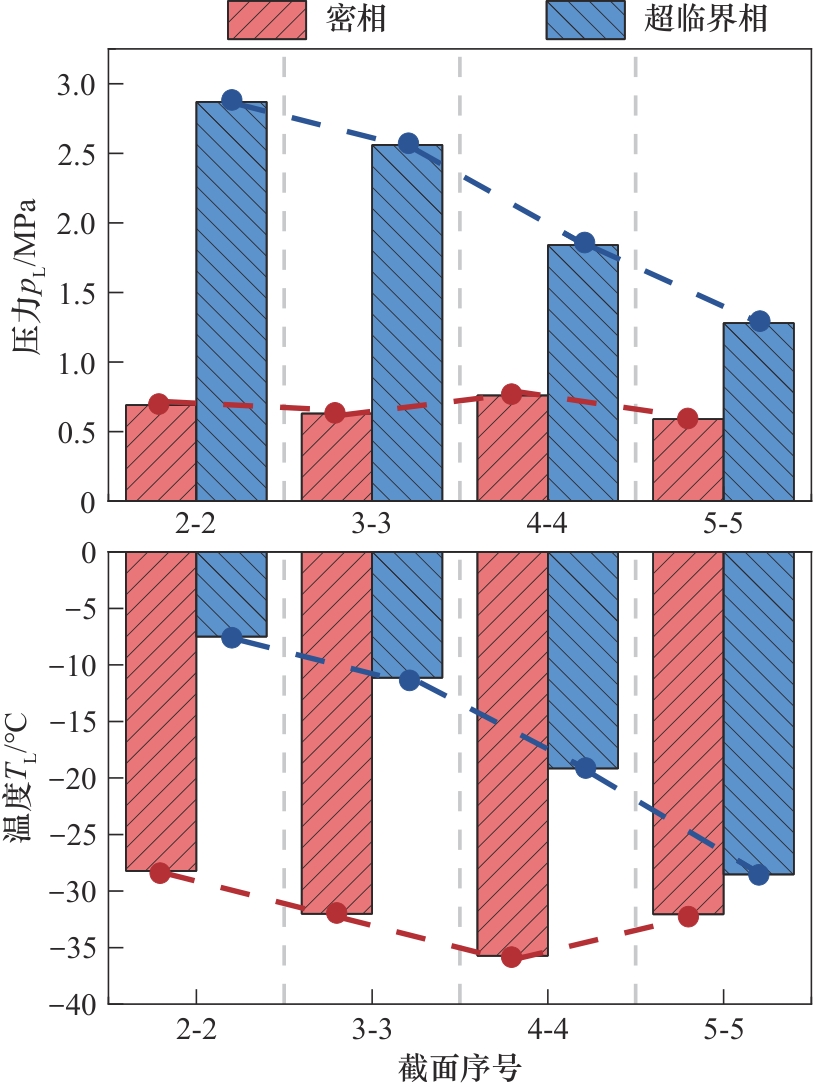
图14 密相(Test 1)和超临界相(Test 2)CO2放空介质脱离气液饱和相时的压力和温度
Fig.14 Pressure and temperature at the point of departure from the gas-liquid saturation region in dense-phase (Test 1) and supercritical (Test 2) CO2
| [1] | 梁鼎成, 谢珠璨, 葛君函, 等. 高碳资源利用演化及低碳化实现的途径研究[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2025, 31(2): 51-62. |
| Liang D C, Xie Z C, Ge J H, et al. Study on the evolution of high carbon resource and the ways to realize low carbonization[J]. China Industrial Economics, 2025, 31(2): 51-62. | |
| [2] | 夏婷, 苏鑫, 李少彦, 等. 典型发达国家能源消费和温室气体排放演变特性研究[J]. 水力发电, 2025, 51(2): 12-18, 92. |
| Xia T, Su X, Li S Y, et al. Evolution characteristics of energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions in typical developed countries[J]. Water Power, 2025, 51(2): 12-18, 92. | |
| [3] | Zheng Y N, Ren D M, Hu Z G, et al. Research on the development trend of fossil energy power generation and non-fossil energy power generation in China[C]//2016 IEEE PES Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC). Xi'an: IEEE, 2016: 1742-1748. |
| [4] | 赵宗慈, 罗勇, 黄建斌. 全球变暖与中国变暖[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(6): 808-812. |
| Zhao Z C, Luo Y, Huang J B. Global warming and China warming[J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(6): 808-812. | |
| [5] | 陈莎, 麦兴宇, 刘影影, 等. 甘肃省碳中和路径下二氧化碳减排与环境健康效益协同分析[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2024, 24(2): 796-808. |
| Chen S, Mai X Y, Liu Y Y, et al. Analysis of carbon dioxide emission reduction and environmental health co-benefits under the path way of carbon neutral in Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2024, 24(2): 796-808. | |
| [6] | 龙丹, 曾雪玲, 赵峰, 等. CCUS环境下温度影响G级油井水泥碳化过程的试验研究[J]. 水泥, 2024(12): 1-4. |
| Long D, Zeng X L, Zhao F, et al. Experimental study on effect of temperature on carbonization process of G-class oil well cement under CCUS environment[J]. Cement, 2024(12): 1-4. | |
| [7] | Lu T, Li Z M, Du L P. Enhancing foam stability and addressing asphaltene deposition for improved oil recovery in CCUS applications using aerogel nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 481: 148290. |
| [8] | 郭克星, 闫光龙, 张阿昱, 等. CO2捕集、利用与封存技术及CO2管道研究现状与发展[J]. 天然气与石油, 2023, 41(1): 28-40. |
| Guo K X, Yan G L, Zhang A Y, et al. Status quo and development of the research on CO2 capture, utilization and storage technology and CO2 pipeline[J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2023, 41(1): 28-40. | |
| [9] | 陆诗建, 张娟娟, 杨菲, 等. CO2管道输送技术进展与未来发展浅析[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 2022, 58(6): 944-952. |
| Lu S J, Zhang J J, Yang F, et al. Progress and future development trend of CO2 pipeline transportation technology[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Science), 2022, 58(6): 944-952. | |
| [10] | 陈俊文, 关沛丰, 汤晓勇, 等. 超临界CO2管道输送流动保障分析要点探讨[J]. 天然气与石油, 2024, 42(2): 8-15. |
| Chen J W, Guan P F, Tang X Y, et al. Discussion on flow assurance issues in supercritical CO2 pipeline transmission[J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2024, 42(2): 8-15. | |
| [11] | 欧阳欣, 李玉星, 路建鑫, 等. 超临界/密相CO2管道流量波动瞬态仿真计算模型[J]. 油气储运, 2024, 43(11): 1231-1238. |
| Ouyang X, Li Y X, Lu J X, et al. Transient simulation model for flow fluctuation in supercritical/dense CO2 pipeline[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2024, 43(11): 1231-1238. | |
| [12] | Liu C C, Wu P Z, Song F Z, et al. Flow resistance characteristics of two-phase CO2 with a large pressure gradient: theoretical and experimental research[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2022, 114: 103566. |
| [13] | Yan X Q, Guo X L, Yu J L, et al. Flow characteristics and dispersion during the vertical anthropogenic venting of supercritical CO2 from an industrial scale pipeline[J]. Energy Procedia, 2018, 154: 66-72. |
| [14] | Cosham A, Jones D G, Armstrong K, et al. The decompression behaviour of carbon dioxide in the dense phase[C]//2012 9th International Pipeline Conference. Calgary, Alberta, Canada, 2013: 447-464. |
| [15] | de Koeijer G, Borch J H, Jakobsenb J, et al. Experiments and modeling of two-phase transient flow during CO2 pipeline depressurization[J]. Energy Procedia, 2009, 1(1): 1683-1689. |
| [16] | Gu S W, Li Y X, Teng L, et al. A new model for predicting the decompression behavior of CO2 mixtures in various phases[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2018, 120: 237-247. |
| [17] | 叶晓. 超临界二氧化碳输送管道内节流与放空特性研究[D]. 东营: 中国石油大学(华东), 2018. |
| Ye X. Study on throttling and venting characteristics in supercritical carbon dioxide pipeline[D]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum (Huadong), 2018. | |
| [18] | Yamasaki H, Yamaguchi H, Hattori K, et al. Experimental observation of CO2 dry-ice behavior in an evaporator/sublimator[J]. Energy Procedia, 2017, 143: 375-380. |
| [19] | Cao Q, Yan X Q, Yu S, et al. Experimental investigation of the characteristics of supercritical CO2 during the venting process[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2021, 110: 103424. |
| [20] | 郭晓璐. CO2管道泄漏中介质压力响应、相态变化和扩散特性研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2017. |
| Guo X L. Study on pressure response, phase change and diffusion characteristics of medium in CO2 pipeline leakage[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2017. | |
| [21] | Martynov S, Mac Dowell N, Brown S, et al. Assessment of integral thermo-hydraulic models for pipeline transportation of dense-phase and supercritical CO2 [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015, 54(34): 8587-8599. |
| [22] | 李家强, 梁海宁, 刘建武. 国内二氧化碳长输管道建设安全性分析[J]. 油气田地面工程, 2014, 33(4): 30-31. |
| Li J Q, Liang H N, Liu J W. Safety analysis of domestic long-distance carbon dioxide pipeline construction[J]. Oil-Gas Field Surface Engineering, 2014, 33(4): 30-31. | |
| [23] | 大连理工大学. 化工原理-上册[M]. 3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2015. |
| Dalian University of Technology. Principles of Chemical Engineering-Volume Ⅰ[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2015. | |
| [24] | 李顺丽. 二氧化碳节流特性与安全泄放控制方案研究[D]. 东营: 中国石油大学(华东), 2016. |
| Li S L. Study on throttling characteristics of carbon dioxide and safety discharge control scheme[D]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum (Huadong), 2016. | |
| [25] | Cao Z G, Hu Y W, Chen L, et al. Experimental study of leakage characteristics and risk prediction of N2-containing dense-phase CO2 pipelines in real transportation conditions[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2024, 187: 1112-1125. |
| [26] | Pakravesh A, Zarei H. Prediction of Joule-Thomson coefficients and inversion curves of natural gas by various equations of state[J]. Cryogenics, 2021, 118: 103350. |
| [27] | Botros K K, Geerligs J, Rothwell B, et al. Measurements of decompression wave speed in binary mixtures of carbon dioxide and impurities[J]. Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 2017, 139(2): 021301. |
| [1] | 密晓光, 孙国刚, 程昊, 张晓慧. 印刷电路板式天然气冷却器性能仿真模型和验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 426-434. |
| [2] | 任现超, 谷雅秀, 段少斌, 贾文竹, 李汉林. 翅片式椭圆套管蒸发式冷凝器传热传质性能实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 75-83. |
| [3] | 沙鑫权, 胡然, 丁磊, 蒋珍华, 吴亦农. 空间用单机两级有阀线性压缩机研制及测试[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 114-122. |
| [4] | 孙浩然, 吴成云, 王艳蒙, 孙静楠, 胡仞与, 段钟弟. 热对流影响下液滴蒸发特性模型与实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 123-132. |
| [5] | 燕子腾, 詹飞龙, 丁国良. 空调用套管式分流器结构设计及分流效果验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 152-159. |
| [6] | 袁琳慧, 王瑜. 单服务器浸没射流式液冷系统散热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 160-169. |
| [7] | 孙云龙, 徐肖肖, 黄永方, 郭纪超, 陈卫卫. 水平光滑管内CO2流动沸腾的非绝热可视化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 230-236. |
| [8] | 郭纪超, 徐肖肖, 孙云龙. 基于植物工厂中的CO2浓度气流模拟及优化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 237-245. |
| [9] | 孔繁臣, 张硕, 唐明生, 邹慧明, 胡舟航, 田长青. 二氧化碳直线压缩机气体轴承模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 281-288. |
| [10] | 吴迪, 胡斌, 姜佳彤. R1233zd(E)高温热泵实验研究与应用分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 377-383. |
| [11] | 黄国瑞, 赵耀, 谢明熹, 陈尔健, 代彦军. 一种新型数据中心余热回收系统实验与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 409-417. |
| [12] | 何婷, 张开, 林文胜, 陈利琼, 陈家富. 沼气超临界压力低温脱碳-液化耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 418-425. |
| [13] | 丁宏鑫, 干文翔, 赵雍洋, 贾润泽, 康子祺, 赵玉隆, 向勇. X65钢焊接接头在超临界CO2相及富H2O相中的腐蚀机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3426-3435. |
| [14] | 刘沁雯, 叶恒冰, 张逸伟, 朱法华, 钟文琪. 煤与禽类粪便混合燃料的加压富氧燃烧特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3487-3497. |
| [15] | 黄荣廷, 陶奕淳, 陈江林, 李世航, 杨子系, 王仕远, 罗祥轩. 矿井除湿溶液再生速率预测研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3572-3584. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号