化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (10): 5322-5335.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250230
收稿日期:2025-03-10
修回日期:2025-03-27
出版日期:2025-10-25
发布日期:2025-11-25
通讯作者:
王世学
作者简介:王世学(1964—), 男, 博士, 教授, wangshixue_64@tju.edu.cn
基金资助:
Shixue WANG1,2( ), Zaihui YU1, Yu ZHU1,2, Jiting JIAN1
), Zaihui YU1, Yu ZHU1,2, Jiting JIAN1
Received:2025-03-10
Revised:2025-03-27
Online:2025-10-25
Published:2025-11-25
Contact:
Shixue WANG
摘要:
间接内重整固体氧化物燃料电池(IIR-SOFC)在紧邻电池片处增设重整多孔介质层,利用电池产生的热量对燃料气进行重整,为电池提供氢气。但受重整反应影响,电池内部温度分布不均匀,从而影响电池的发电性能和寿命。采用数值模拟方法得到板式间接内重整SOFC的燃料和空气的流动方向、运行温度、重整气流速对电池温度分布及发电特性的影响,并在重整流道内采用催化剂载量梯度分布方式改进温度分布。结果显示,阴、阳极流道内气体顺流情况下电池最大温差比逆流时小;随着工作温度的升高,电池内的最大温差逐渐增大;随着重整混合气入口流速的增加,温度梯度及功率密度先增大后减小。在改变重整流道内的催化剂载量分布后,电池内温度分布趋向均匀,温度梯度明显减小,最大温差减小约60%。
中图分类号:
王世学, 于在辉, 朱禹, 蹇季廷. 间接内重整板式固体氧化物燃料电池的温度分布特性及改进[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(10): 5322-5335.
Shixue WANG, Zaihui YU, Yu ZHU, Jiting JIAN. Temperature distribution characteristics and improvement of indirect internal reforming planar solid oxide fuel cells[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(10): 5322-5335.
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 阴/阳极流道宽度(w2)/mm | 2 |
| 阴/阳极流道高度(hcha,a/hcha,c) /mm | 1 |
| 流道长度(l) /mm | 100 |
| 重整流道宽度(w1) /mm | 4 |
| 重整流道高度(href) /mm | 4 |
| 阳极厚度(ha) /mm | 0.15 |
| 电解质厚度(hel) /mm | 0.1 |
| 阴极厚度(hc) /mm | 0.1 |
| 阳极/电解质/阴极宽度(w1) /mm | 4 |
| 连接体宽度(w1) /mm | 4 |
| 连接体高度(hcon,a/hcon,c)/mm | 2 |
表1 几何模型参数
Table 1 Geometric model parameters
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 阴/阳极流道宽度(w2)/mm | 2 |
| 阴/阳极流道高度(hcha,a/hcha,c) /mm | 1 |
| 流道长度(l) /mm | 100 |
| 重整流道宽度(w1) /mm | 4 |
| 重整流道高度(href) /mm | 4 |
| 阳极厚度(ha) /mm | 0.15 |
| 电解质厚度(hel) /mm | 0.1 |
| 阴极厚度(hc) /mm | 0.1 |
| 阳极/电解质/阴极宽度(w1) /mm | 4 |
| 连接体宽度(w1) /mm | 4 |
| 连接体高度(hcon,a/hcon,c)/mm | 2 |
| 边界条件 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 重整流道入口气体组分(xfuel,in)(N2∶CH4∶H2O∶H2) | 0.225∶0.25∶0.5∶0.025 |
| 重整流道入口气体流速(ufuel,in) /(m/s) | ux =0.05,uy =uz =0 |
| 阴极入口气体组分(xair,in)(N2∶O2) | 79∶21 |
| 阴极入口流速(uair,in) /(m/s) | ux =1.5,uy =uz =0 |
| 阳/阴极出口压力(pout)/atm | 1 |
| 重整气体与阴极气体入口温度(T)/K | 1073 |
表2 模型边界条件
Table 2 Model boundary condition intent
| 边界条件 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 重整流道入口气体组分(xfuel,in)(N2∶CH4∶H2O∶H2) | 0.225∶0.25∶0.5∶0.025 |
| 重整流道入口气体流速(ufuel,in) /(m/s) | ux =0.05,uy =uz =0 |
| 阴极入口气体组分(xair,in)(N2∶O2) | 79∶21 |
| 阴极入口流速(uair,in) /(m/s) | ux =1.5,uy =uz =0 |
| 阳/阴极出口压力(pout)/atm | 1 |
| 重整气体与阴极气体入口温度(T)/K | 1073 |
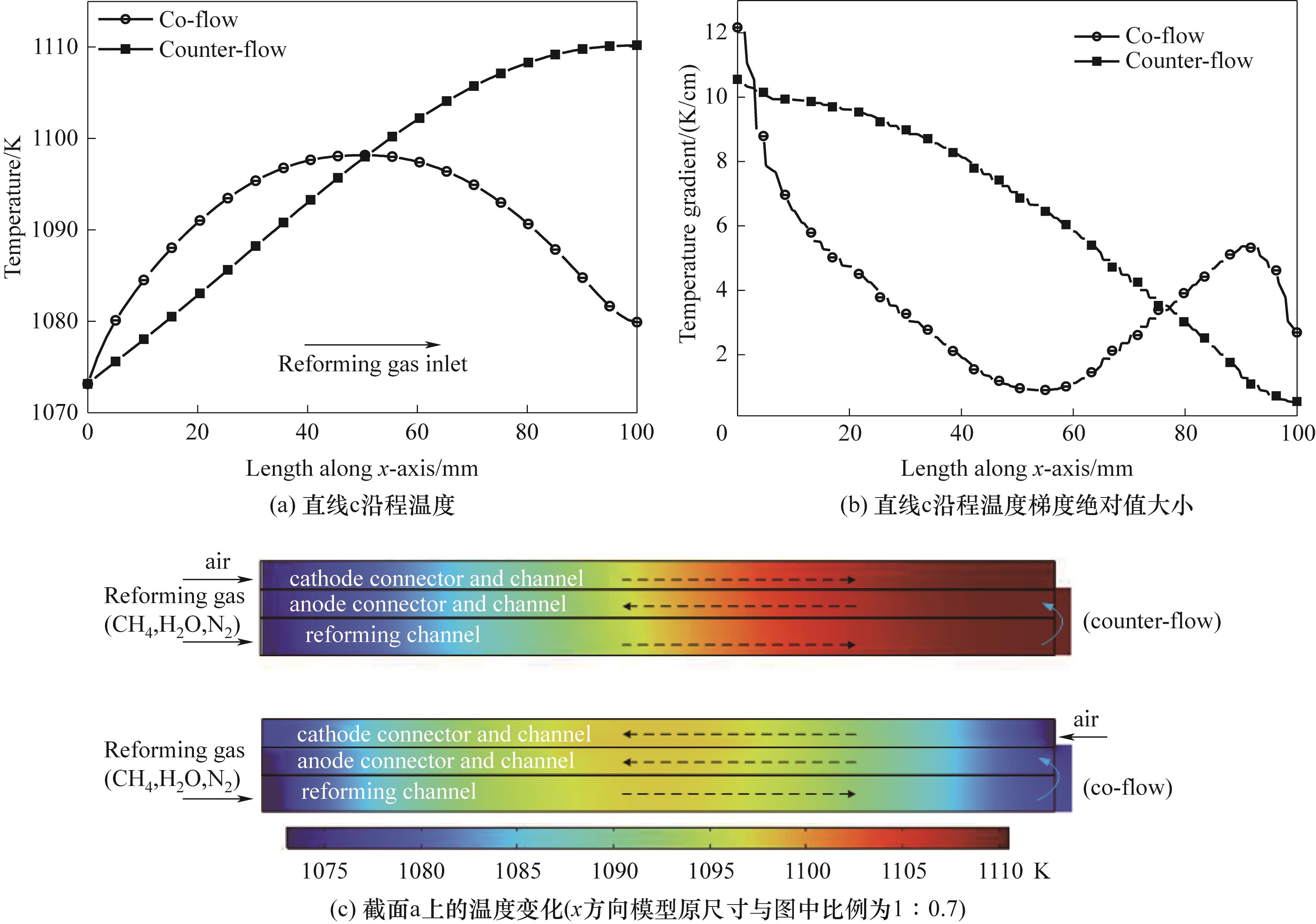
图6 不同流动方式下的电池内温度与温度梯度变化
Fig.6 Variations in temperature and temperature gradient within battery under different flow configurations (T=1073 K,ufuel=0.05 m/s, uair=1.5 m/s,VCell=0.7 V,p=1 atm)
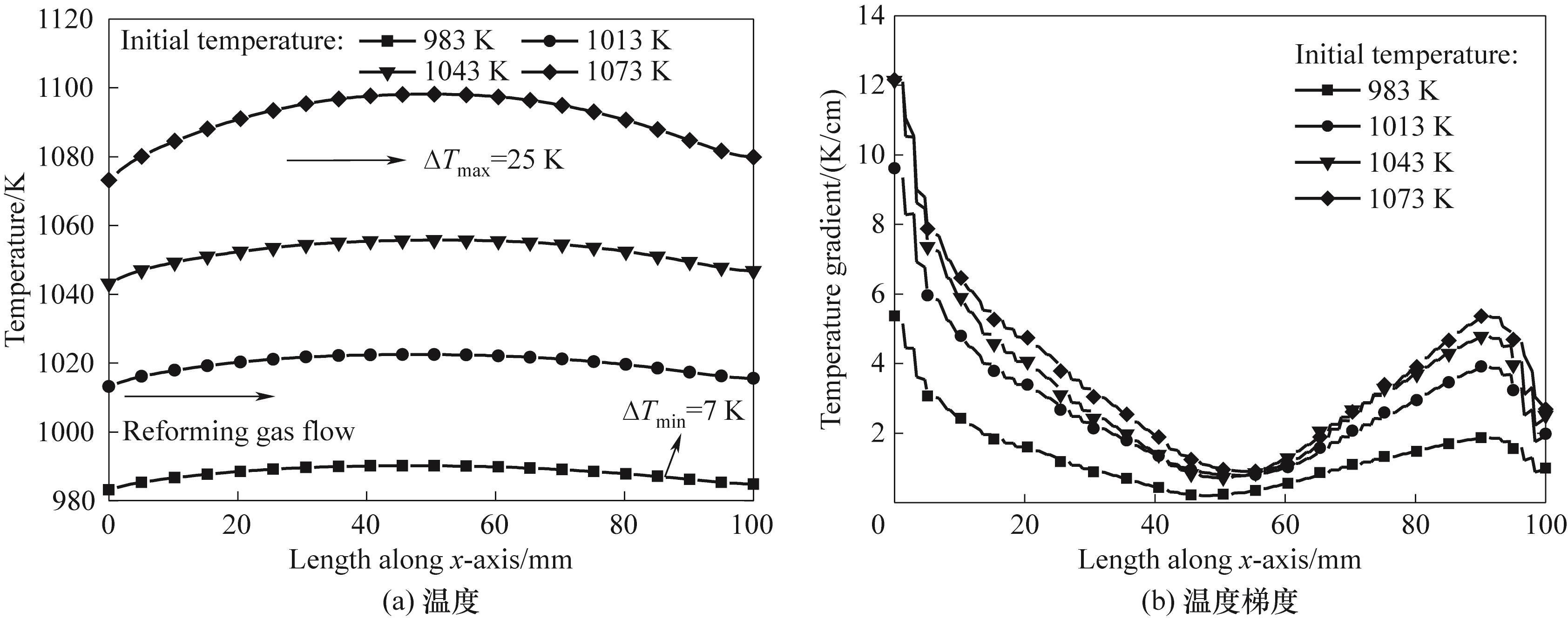
图8 不同初始运行温度下电池内温度和温度梯度沿直线c沿程变化(ufuel=0.05 m/s, uair=1.5 m/s,VCell=0.7 V, p=1 atm)
Fig.8 Variation of temperature and temperature gradient at different initial operating temperatures along Line c
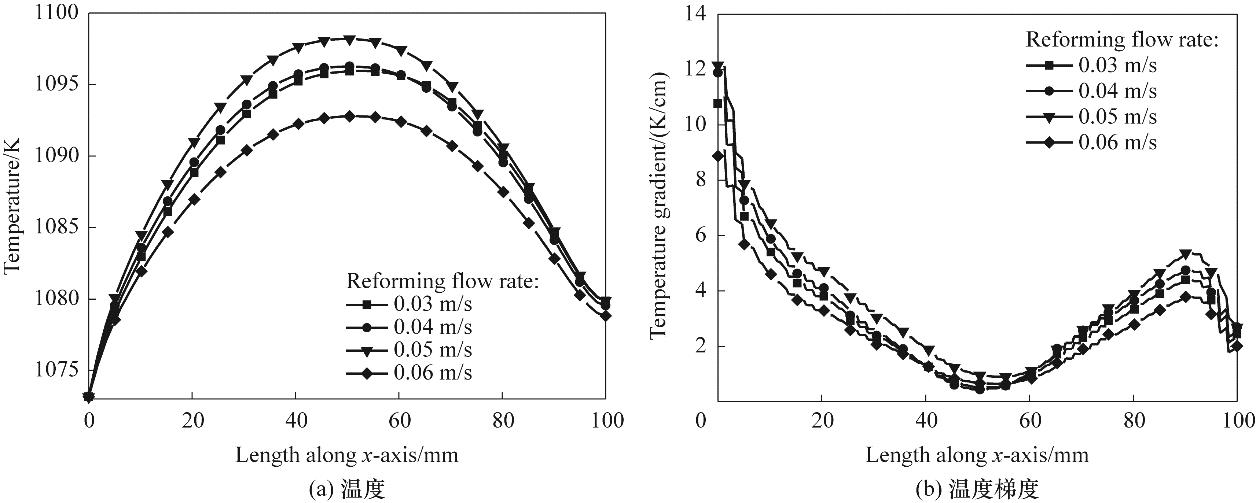
图10 不同流速下重整流道内温度、温度梯度沿直线c沿程变化(T=1073 K,uair=1.5 m/s,VCell=0.7 V, p=1 atm)
Fig.10 Evolution of temperature and temperature gradient in reforming channel under different flow rates along Line c
| 负载方式 | 最高温/K | 最低温/K | 最大温差/K | 最大温度梯度/(K/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均匀负载 | 1098.2 | 1073.15 | 25.0 | 12.16 |
| 两分区梯度负载 | 1091.1 | 1073.15 | 17.9 | 7.17 |
| 三分区梯度负载 | 1083.3 | 1073.15 | 10.1 | 5.12 |
表3 重整流道催化剂不同负载方式下IIR-SOFC内最高温、最低温、最大温差和最大温度梯度统计
Table 3 Statistics of maximum temperature, minimum temperature, maximum temperature difference, and temperature gradient within IIR-SOFC under different loading methods of reforming channel
| 负载方式 | 最高温/K | 最低温/K | 最大温差/K | 最大温度梯度/(K/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均匀负载 | 1098.2 | 1073.15 | 25.0 | 12.16 |
| 两分区梯度负载 | 1091.1 | 1073.15 | 17.9 | 7.17 |
| 三分区梯度负载 | 1083.3 | 1073.15 | 10.1 | 5.12 |
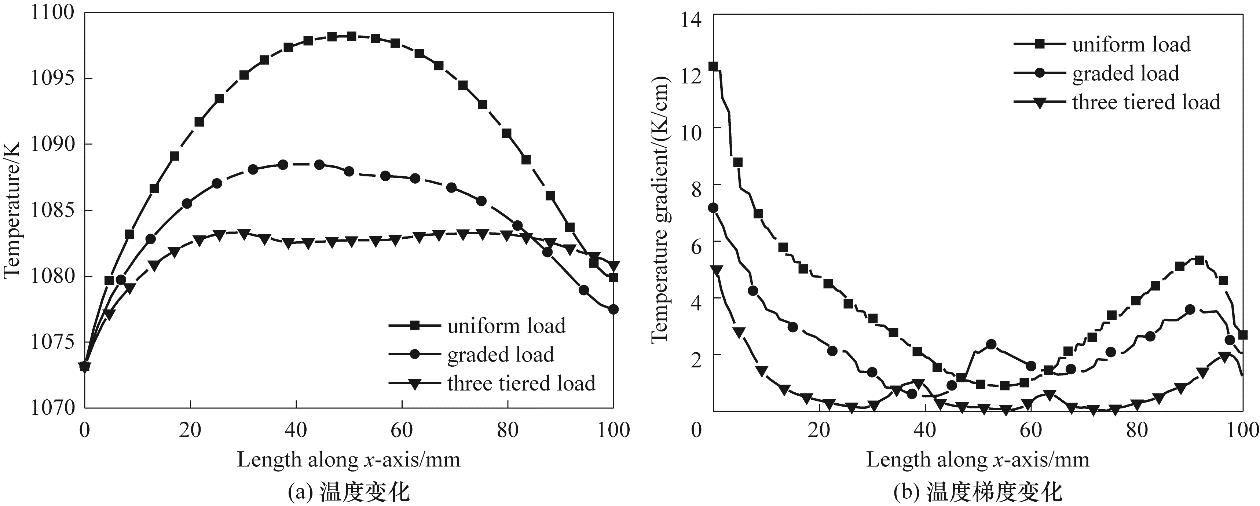
图14 重整流道催化剂不同负载方式下温度和温度梯度沿直线c变化(T=1073 K, ufuel=0.05 m/s, uair=1.5 m/s, VCell=0.7 V, p=1 atm)
Fig.14 Variations in temperature and temperature gradient along Line c under different loading methods of reforming channel
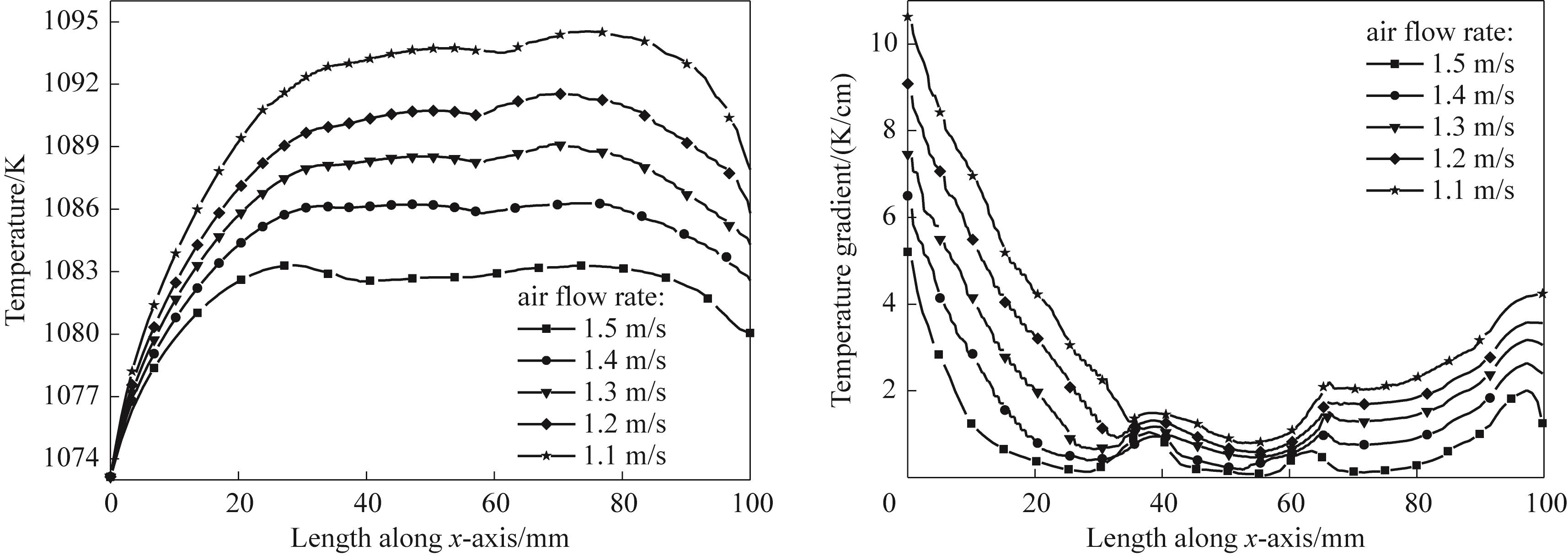
图16 三分区梯度负载方式下不同空气流速下电池内沿直线c的沿程温度和温度梯度分布
Fig.16 Temperature and temperature gradient distribution along Line c under different air flow velocities in three tiered loading configuration(T=1073 K,ufuel=0.05 m/s,VCell=0.7 V, p=1 atm)
| 空气流速/(m/s) | 最高温/K | 最低温/K | 最大温差/K | 最大温度梯度/(K/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | 1094.5 | 1073.15 | 21.35 | 10.63 |
| 1.2 | 1091.6 | 1073.15 | 18.45 | 9.08 |
| 1.3 | 1089.1 | 1073.15 | 15.9 | 7.48 |
| 1.4 | 1086.3 | 1073.15 | 13.15 | 6.50 |
| 1.5 | 1083.3 | 1073.15 | 10.1 | 5.12 |
表4 三分区梯度负载方式IIR-SOFC模型不同空气流速下电池内最高温、最低温、最大温差和温度梯度统计
Table 4 Statistics of maximum temperature, minimum temperature, maximum temperature difference and temperature gradient within battery under different air flow velocities in three tiered gradient loading configuration
| 空气流速/(m/s) | 最高温/K | 最低温/K | 最大温差/K | 最大温度梯度/(K/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | 1094.5 | 1073.15 | 21.35 | 10.63 |
| 1.2 | 1091.6 | 1073.15 | 18.45 | 9.08 |
| 1.3 | 1089.1 | 1073.15 | 15.9 | 7.48 |
| 1.4 | 1086.3 | 1073.15 | 13.15 | 6.50 |
| 1.5 | 1083.3 | 1073.15 | 10.1 | 5.12 |
| [1] | Bilal Hanif M, Motola M, Qayyum S, et al. Recent advancements, doping strategies and the future perspective of perovskite-based solid oxide fuel cells for energy conversion[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 428: 132603. |
| [2] | de Arespacochaga N, Valderrama C, Mesa C, et al. Biogas deep clean-up based on adsorption technologies for solid oxide fuel cell applications[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 255: 593-603. |
| [3] | Arteaga-Perez L E, Casas Y, Peralta L M, et al. An auto-sustainable solid oxide fuel cell system fueled by bio-ethanol. Process simulation and heat exchanger network synthesis[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2009, 150(1): 242-251. |
| [4] | Xie Y Y, Ding H P, Xue X J. Direct methane fueled solid oxide fuel cell model with detailed reforming reactions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 228: 917-924. |
| [5] | Zhang J G, Zhang D, Liu T, et al. An efficient and durable solid oxide fuel cell integrated with coal gasification system[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(100): 40029-40036. |
| [6] | Wang J, Zhang D, Liu T, et al. Self-assembled FeRu bimetallic nanocatalysts for efficient and durable mutual CO-CO2 conversion in a reversible solid oxide electrochemical cell[J]. Science China Materials, 2024, 67(5): 1471-1480. |
| [7] | Janardhanan V M, Heuveline V, Deutschmann O. Performance analysis of a SOFC under direct internal reforming conditions[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 172(1): 296-307. |
| [8] | Sciazko A, Komatsu Y, Nakamura A, et al. 3D microstructures of solid oxide fuel cell Ni-YSZ anodes with carbon deposition[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 460: 141680. |
| [9] | Tran D L, Tran Q T, Sakamoto M, et al. Modelling of CH4 multiple-reforming within the Ni-YSZ anode of a solid oxide fuel cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 359: 507-519. |
| [10] | Fu Q R, Li Z Y, Liu Z J, et al. Performance study of solid oxide fuel cell with Ni-foam indirect internal reformer: intrinsic reforming kinetics and temperature uniformity[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 457: 141170. |
| [11] | Kim-Lohsoontorn P, Priyakorn F, Wetwatana U, et al. Modelling of a tubular solid oxide fuel cell with different designs of indirect internal reformer[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2014, 23(2): 251-263. |
| [12] | Dokmaingam P, Irvine J T S, Assabumrungrat S, et al. Modeling of IT-SOFC with indirect internal reforming operation fueled by methane: effect of oxygen adding as autothermal reforming[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(24): 13271-13279. |
| [13] | Najafi Maharluie H, Rahmani M. Mathematical modeling of solid oxide fuel cell performance with indirect internal reforming and thermal interaction analysis[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2024, 316: 118842. |
| [14] | Nagata S, Momma A, Kato T, et al. Numerical analysis of output characteristics of tubular SOFC with internal reformer[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2001, 101(1): 60-71. |
| [15] | Nishino T, Szmyd J S. Numerical analysis of a cell-based indirect internal reforming tubular SOFC operating with biogas[J]. Journal of Fuel Cell Science and Technology, 2010, 7(5): 051004. |
| [16] | Xu J G, Froment G F. Methane steam reforming, methanation and water-gas shift(Ⅰ): Intrinsic kinetics[J]. AIChE Journal, 1989, 35(1): 88-96. |
| [17] | Akkaya A V. Electrochemical model for performance analysis of a tubular SOFC[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2007, 31(1): 79-98. |
| [18] | Wang J S, Wang S X, Zhu Y, et al. Numerical investigation of parameter distributions in high-temperature PEMFCs under various cooling surface temperature gradients[J]. Fuel, 2024, 367: 131554. |
| [19] | Yuan J L, Huang Y, Sundén B, et al. Analysis of parameter effects on chemical reaction coupled transport phenomena in SOFC anodes[J]. Heat and Mass Transfer, 2009, 45(4): 471-484. |
| [20] | Le Bars M, Worster M G. Interfacial conditions between a pure fluid and a porous medium: implications for binary alloy solidification[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2006, 550: 149. |
| [21] | Krishna R, Wesselingh J A. The Maxwell-Stefan approach to mass transfer[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1997, 52(6): 861-911. |
| [22] | Butcher H, Quenzel C J E, Breziner L, et al. Design of an annular microchannel reactor (AMR) for hydrogen and/or syngas production via methane steam reforming[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(31): 18046-18057. |
| [23] | Wilhite B A, Breziner L, Mettes J, et al. Radial microchannel reactors (RMRs) for efficient and compact steam reforming of methane: experimental demonstration and design simulations[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2013, 27(8): 4403-4410. |
| [24] | Haberman B A, Young J B. Three-dimensional simulation of chemically reacting gas flows in the porous support structure of an integrated-planar solid oxide fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2004, 47(17/18): 3617-3629. |
| [25] | Ferguson J R, Fiard J M, Herbin R. Three-dimensional numerical simulation for various geometries of solid oxide fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 1996, 58(2): 109-122. |
| [26] | Ahmad Hajimolana S, Hussain M A, Daud W M A W, et al. Mathematical modeling of solid oxide fuel cells: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2011, 15(4): 1893-1917. |
| [27] | Khazaee I, Rava A. Numerical simulation of the performance of solid oxide fuel cell with different flow channel geometries[J]. Energy, 2017, 119: 235-244. |
| [28] | Newman J S, Balsara N P. Electrochemical Systems[M]. 4th ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2021. |
| [29] | Bove R, Ubertini S. Modeling Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: Methods, Procedures and Techniques[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2008. |
| [30] | Patcharavorachot Y, Arpornwichanop A, Chuachuensuk A. Electrochemical study of a planar solid oxide fuel cell: role of support structures[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 177(2): 254-261. |
| [31] | Milewski J. Advanced Methods of Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Modeling[M]. London: Springer, 2011. |
| [32] | Todd B, Young J B. Thermodynamic and transport properties of gases for use in solid oxide fuel cell modelling[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2002, 110(1): 186-200. |
| [33] | Oliveira E L G, Grande C A, Rodrigues A E. Steam methane reforming in a Ni/Al2O3 catalyst: kinetics and diffusional limitations in extrudates[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2009, 87(6): 945-956. |
| [34] | Singhal Subhash, Kendall Kevin. High Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: Fundamentals, Design, and Applicatons[M]. Oxford, UK: Elsevier, 2003. |
| [35] | Liese E A, Gemmen R S. Performance comparison of internal reforming against external reforming in a solid oxide fuel cell, gas turbine hybrid system[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2005, 127(1): 86-90. |
| [1] | 苏伟, 赵大海, 金旭, 刘忠彦, 李静, 张小松. 吸湿液滴与混合润湿性表面协同抑霜特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 140-151. |
| [2] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [3] | 郭松源, 周晓庆, 缪五兵, 汪彬, 耑锐, 曹庆泰, 陈成成, 杨光, 吴静怡. 火箭上升段含多孔板液氧贮箱增压输运数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 62-74. |
| [4] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [5] | 臧子晴, 李修真, 谈莹莹, 刘晓庆. 分凝器对两级分离自复叠制冷循环特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 17-25. |
| [6] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [7] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [8] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [9] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [10] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [11] | 李银龙, 刘国强, 晏刚. 分馏与闪蒸分离耦合自复叠制冷循环性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 26-35. |
| [12] | 何婷, 黄舒阳, 黄坤, 陈利琼. 基于余热利用的天然气化学吸收脱碳-高温热泵耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [13] | 朱腾飞, 刘晔. 低GWP制冷剂在新能源汽车空调应用性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 343-350. |
| [14] | 吴迪, 胡斌, 姜佳彤. R1233zd(E)高温热泵实验研究与应用分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 377-383. |
| [15] | 杨开源, 陈锡忠. 颗粒破碎的离散元及有限离散元模拟方法比较[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4398-4411. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号