化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (12): 6536-6550.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250682
白阳1,2( ), 姚舒爽1, 徐梦旭1, 赵靖雨3, 于福顺1(
), 姚舒爽1, 徐梦旭1, 赵靖雨3, 于福顺1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-06-24
修回日期:2025-10-10
出版日期:2025-12-31
发布日期:2026-01-23
通讯作者:
于福顺
作者简介:白阳(1992—),男,博士,讲师,by9211@163.com
基金资助:
Yang BAI1,2( ), Shushuang YAO1, Mengxu XU1, Jingyu ZHAO3, Fushun YU1(
), Shushuang YAO1, Mengxu XU1, Jingyu ZHAO3, Fushun YU1( )
)
Received:2025-06-24
Revised:2025-10-10
Online:2025-12-31
Published:2026-01-23
Contact:
Fushun YU
摘要:
阴/阳离子Gemini表面活性剂复配体系在改善泡沫稳定性方面表现出显著协同效应,但其作用机制尚未完全阐明。通过表面张力与分子动力学模拟相结合的方法,系统研究了不同阴/阳离子Gemini表面活性剂复配体系在气/液界面的自组装行为及其界面性质。结果表明,胺基与阴离子极性基间的静电作用与几何构象适配效应,保证了极性基区域的紧凑构型;而尾链间的构象优化与长度相容性,则促进了尾链区域的有序堆积。这些分子间的协同作用共同主导了复配表面活性剂在气/液界面形成致密且高度有序的吸附层,并显著增强了极性基的水合作用。由此形成的强化水化层及界面结构延缓了泡沫液膜的排液速率,进而赋予泡沫优异的机械强度和抗扰动能力,从而显著提升其宏观稳定性。
中图分类号:
白阳, 姚舒爽, 徐梦旭, 赵靖雨, 于福顺. 阴/阳离子Gemini表面活性剂复配体系的泡沫稳定性调控及构效关系研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(12): 6536-6550.
Yang BAI, Shushuang YAO, Mengxu XU, Jingyu ZHAO, Fushun YU. Study on foam stability regulation and structure-activity relationship of mixed anionic/cationic Gemini surfactants[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(12): 6536-6550.
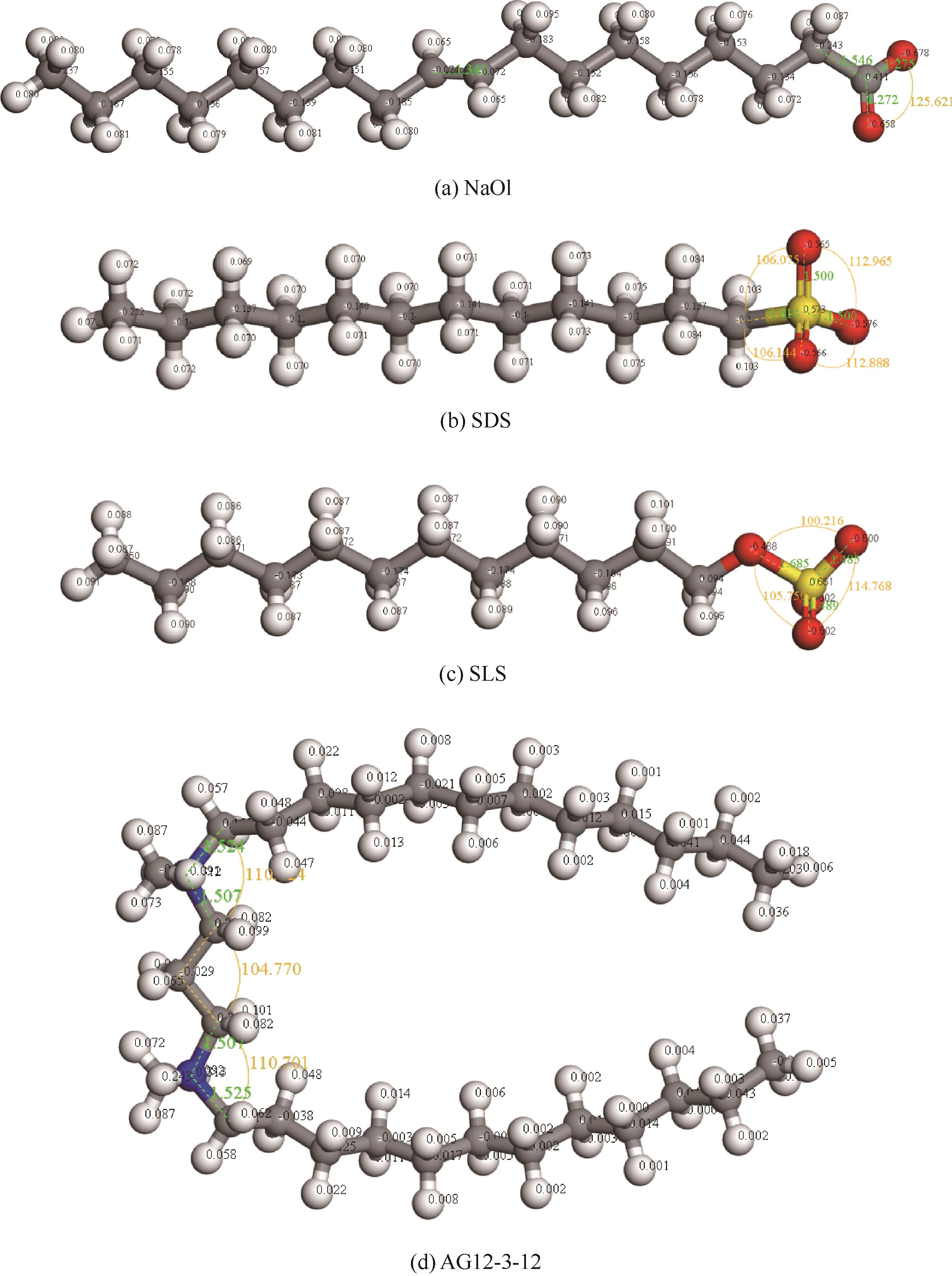
图1 几何优化后表面活性剂的离子结构模型及其原子电荷分布(白色、灰色、蓝色、红色、黄色球体分别代表氢、碳、氮、氧、硫原子,下同)
Fig.1 Ionic structure and atomic charge distribution of surfactants after geometry optimization (white, gray, blue, red, yellow and green spheres represent hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur corresponding atoms, respectively; same color scheme applies hereinafter)
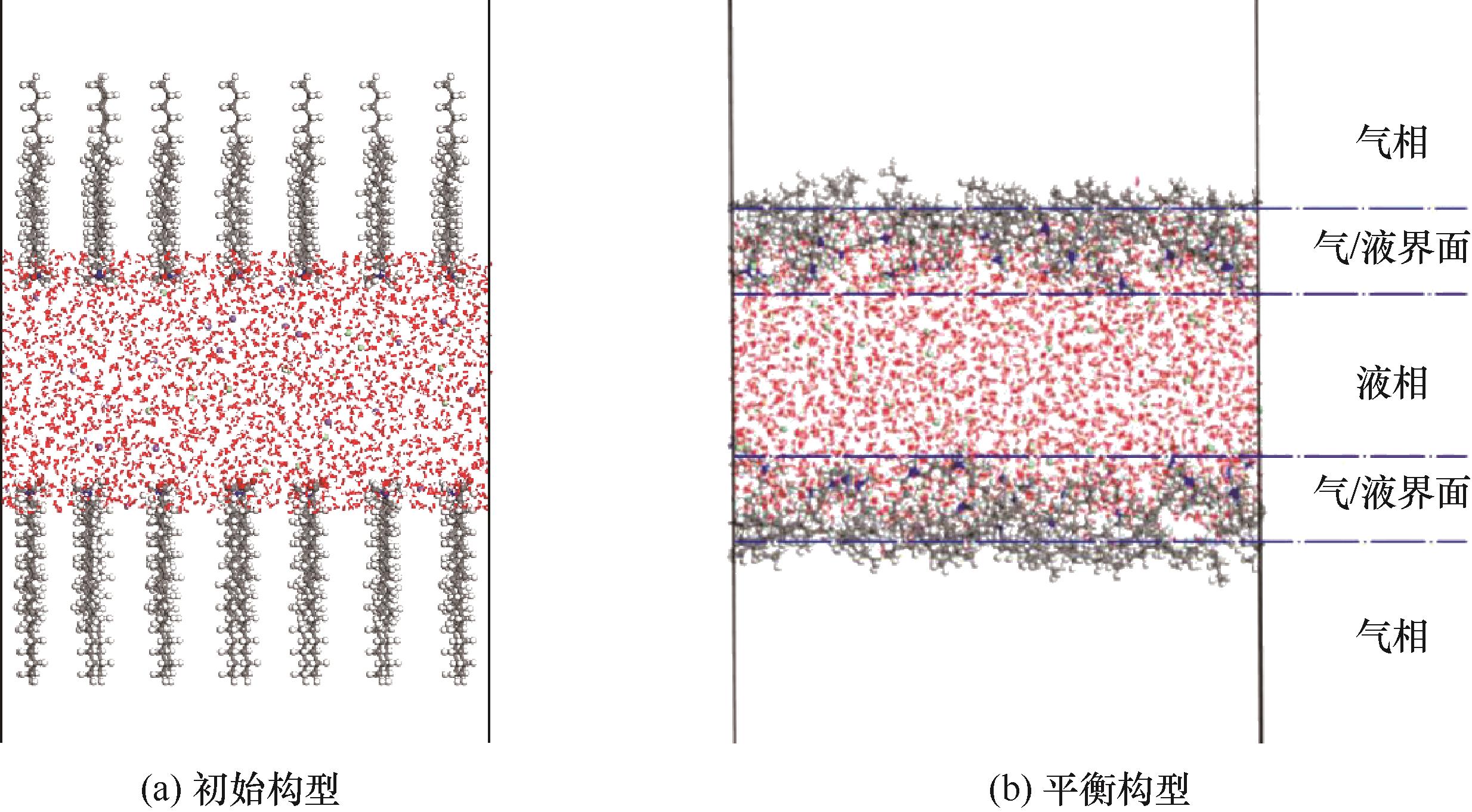
图2 表面活性剂在气/液界面的“三明治”结构模型(为方便观察,水分子以线条样式表示,下同)
Fig.2 The sandwich mode of surfactants at the air/water interface (for clarity, water molecules are shown as lines; the same applies hereinafter)
| 模拟体系 | AG12-3-12/个 | 阴离子表面活性剂/个 | 钠离子/个 | 氯离子/个 | 水分子/个 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AG12-3-12 | 28 | 0 | 0 | 56 | 3000 |
| NaOl | 0 | 56 | 56 | 0 | 3000 |
| SDS | 0 | 56 | 56 | 0 | 3000 |
| SLS | 0 | 56 | 56 | 0 | 3000 |
| AG12-3-12/NaOl复配体系 | 14 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 3000 |
| AG12-3-12/SDS复配体系 | 14 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 3000 |
| AG12-3-12/SLS复配体系 | 14 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 3000 |
表1 不同模拟体系中各表面活性剂的数量
Table 1 The quantity of each surfactant in different simulation systems
| 模拟体系 | AG12-3-12/个 | 阴离子表面活性剂/个 | 钠离子/个 | 氯离子/个 | 水分子/个 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AG12-3-12 | 28 | 0 | 0 | 56 | 3000 |
| NaOl | 0 | 56 | 56 | 0 | 3000 |
| SDS | 0 | 56 | 56 | 0 | 3000 |
| SLS | 0 | 56 | 56 | 0 | 3000 |
| AG12-3-12/NaOl复配体系 | 14 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 3000 |
| AG12-3-12/SDS复配体系 | 14 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 3000 |
| AG12-3-12/SLS复配体系 | 14 | 28 | 28 | 28 | 3000 |
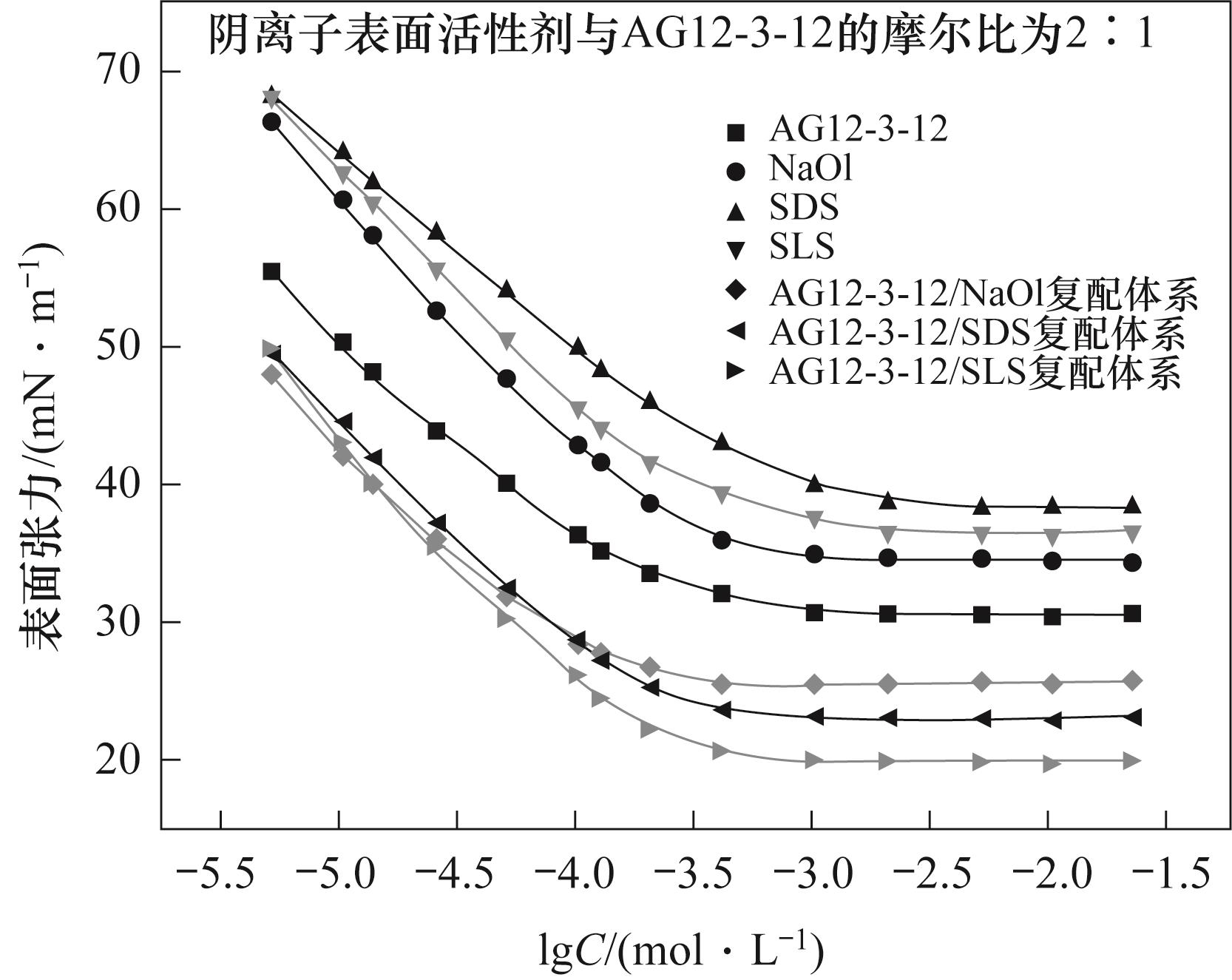
图3 单一及复配表面表面活性剂体系的溶液表面张力与浓度对数图
Fig.3 The plot of solution surface tension versus the logarithm of concentration for single and mixed surfactant systems
| 表面活性剂种类 | CMC/(mol·L-1) | 界面张力CMC/(mN·m-1) | Γmax/(mol·m-2) | Amin/nm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AG12-3-12 | 7.93×10-4 | 30.56 | 0.74×10-6 | 2.23 |
| NaOl | 1.26×10-3 | 34.62 | 1.57×10-6 | 1.06 |
| SDS | 2.51×10-3 | 38.33 | 1.51×10-6 | 1.10 |
| SLS | 2.45×10-3 | 36.63 | 1.63×10-6 | 1.02 |
| AG12-3-12/NaOl复配体系 | 3.16×10-4 | 25.55 | 2.77×10-6 | 0.60 |
| AG12-3-12/SDS复配体系 | 4.02×10-4 | 23.11 | 3.06×10-6 | 0.54 |
| AG12-3-12/SLS复配体系 | 4.41×10-4 | 20.06 | 3.13×10-6 | 0.53 |
表2 单一及复配表面活性剂体系的临界胶束浓度与界面吸附参数
Table 2 CMC and interfacial adsorption parameters of single and mixed surfactant systems
| 表面活性剂种类 | CMC/(mol·L-1) | 界面张力CMC/(mN·m-1) | Γmax/(mol·m-2) | Amin/nm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AG12-3-12 | 7.93×10-4 | 30.56 | 0.74×10-6 | 2.23 |
| NaOl | 1.26×10-3 | 34.62 | 1.57×10-6 | 1.06 |
| SDS | 2.51×10-3 | 38.33 | 1.51×10-6 | 1.10 |
| SLS | 2.45×10-3 | 36.63 | 1.63×10-6 | 1.02 |
| AG12-3-12/NaOl复配体系 | 3.16×10-4 | 25.55 | 2.77×10-6 | 0.60 |
| AG12-3-12/SDS复配体系 | 4.02×10-4 | 23.11 | 3.06×10-6 | 0.54 |
| AG12-3-12/SLS复配体系 | 4.41×10-4 | 20.06 | 3.13×10-6 | 0.53 |
| 表面活性剂种类 | 泡沫半衰期/s |
|---|---|
| AG12-3-12 | 334 |
| NaOl | 266 |
| SDS | 285 |
| SLS | 292 |
| AG12-3-12/NaOl复配体系 | 352 |
| AG12-3-12/SDS复配体系 | 366 |
| AG12-3-12/SLS复配体系 | 381 |
表3 单一及复配表面活性剂体系的泡沫半衰期
Table 3 Half-life of foam for single and mixed surfactant systems
| 表面活性剂种类 | 泡沫半衰期/s |
|---|---|
| AG12-3-12 | 334 |
| NaOl | 266 |
| SDS | 285 |
| SLS | 292 |
| AG12-3-12/NaOl复配体系 | 352 |
| AG12-3-12/SDS复配体系 | 366 |
| AG12-3-12/SLS复配体系 | 381 |
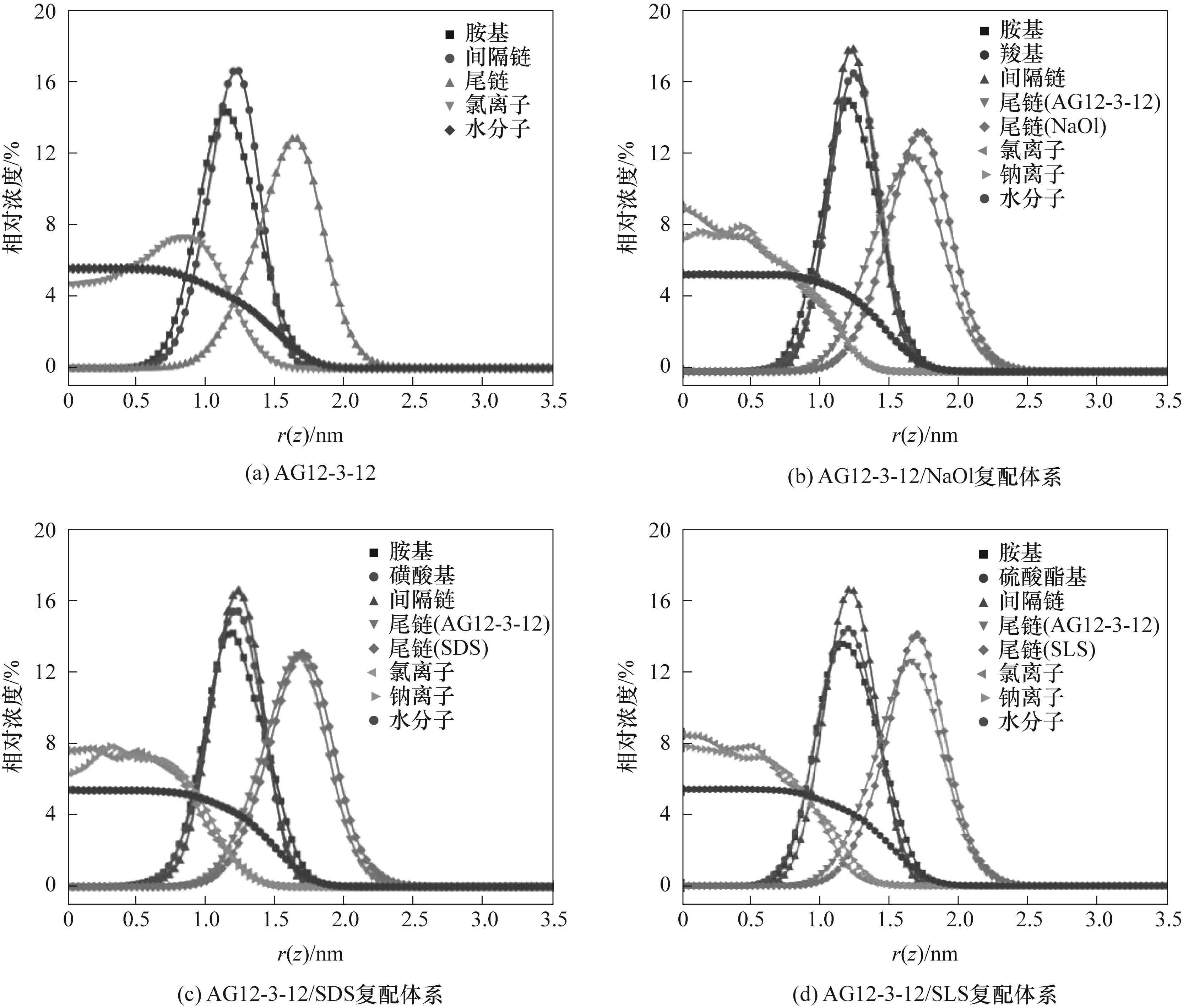
图6 单一及复配表面活性剂体系中各组分在气/液界面的浓度分布
Fig.6 Concentration distribution of individual components in single and mixed surfactant systems at the air/water interface
| 体系 | 水分子配位数/个 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 胺基 | 阴离子极性基 | 合计 | |
| AG12-3-12 | 281.92 | — | 281.92 |
| AG12-3-12/NaOl复配体系 | 143.14 | 236.98 | 380.12 |
| AG12-3-12/SDS复配体系 | 150.84 | 233.78 | 384.62 |
| AG12-3-12/SLS复配体系 | 146.56 | 242.54 | 389.10 |
表4 不同模拟体系的水分子配位数
Table 4 Coordination number of water molecules in different simulation systems
| 体系 | 水分子配位数/个 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 胺基 | 阴离子极性基 | 合计 | |
| AG12-3-12 | 281.92 | — | 281.92 |
| AG12-3-12/NaOl复配体系 | 143.14 | 236.98 | 380.12 |
| AG12-3-12/SDS复配体系 | 150.84 | 233.78 | 384.62 |
| AG12-3-12/SLS复配体系 | 146.56 | 242.54 | 389.10 |
| 体系 | 扩散系数/(nm2·ps-1) | |
|---|---|---|
| 表面活性剂分子 | 水分子 | |
| AG12-3-12 | 4.67×10-4 | 3.70×10-3 |
| AG12-3-12/NaOl复配体系 | 6.83×10-4 | 3.30×10-3 |
| AG12-3-12/SDS复配体系 | 7.67×10-4 | 3.18×10-3 |
| AG12-3-12/SLS复配体系 | 8.33×10-4 | 2.97×10-3 |
表5 不同模拟体系中表面活性剂分子及水分子的扩散系数
Table 5 Diffusion coefficients of surfactant molecules and water molecules in different simulation systems
| 体系 | 扩散系数/(nm2·ps-1) | |
|---|---|---|
| 表面活性剂分子 | 水分子 | |
| AG12-3-12 | 4.67×10-4 | 3.70×10-3 |
| AG12-3-12/NaOl复配体系 | 6.83×10-4 | 3.30×10-3 |
| AG12-3-12/SDS复配体系 | 7.67×10-4 | 3.18×10-3 |
| AG12-3-12/SLS复配体系 | 8.33×10-4 | 2.97×10-3 |
| 模拟体系 | IFE/(kJ·mol-1) | Esynergism/(kJ·mol-1) | 界面厚度/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| AG12-3-12/NaOl | -1221.39 | -206.94 | 0.672 |
| AG12-3-12/SDS | -1276.06 | -264.18 | 0.730 |
| AG12-3-12/SLS | -1305.23 | -296.53 | 0.768 |
表6 不同模拟体系的IFE、Esynergism及界面厚度
Table 6 IFE, Esynergism and interfacial thickness for different simulation systems
| 模拟体系 | IFE/(kJ·mol-1) | Esynergism/(kJ·mol-1) | 界面厚度/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| AG12-3-12/NaOl | -1221.39 | -206.94 | 0.672 |
| AG12-3-12/SDS | -1276.06 | -264.18 | 0.730 |
| AG12-3-12/SLS | -1305.23 | -296.53 | 0.768 |
| [1] | Yekeen N, Manan M A, Idris A K, et al. Influence of surfactant and electrolyte concentrations on surfactant adsorption and foaming characteristics[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2017, 149: 612-622. |
| [2] | Shibata Y, Hyde A, Asakuma Y, et al. Thermal response of a non-ionic surfactant layer at the water/oil interface during microwave heating[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2018, 556: 127-133. |
| [3] | Govender S, Swart P. Surfactant formulations for multi-functional surface modification[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2008, 331(1/2): 97-102. |
| [4] | Liu D T, Yang X, Liu P, et al. Synthesis and characterization of gemini ester surfactant and its application in efficient fabric softening[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2020, 299: 112236. |
| [5] | Huang Z Q, Cheng C, Zhong H, et al. Flotation of sylvite from potash ore by using the Gemini surfactant as a novel flotation collector[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 132: 22-26. |
| [6] | Liu W G, Zhao L, Liu W B, et al. Synthesis and utilization of a gemini surfactant as a collector for the flotation of hemimorphite from quartz[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 134: 394-401. |
| [7] | Tyagi P, Tyagi R. Synthesis, structural properties and applications of gemini surfactants: a review[J]. Tenside Surfactants Detergents, 2009, 46(6): 373-382. |
| [8] | Sun Z, Yan X X, Xiao Y, et al. Pickering emulsions stabilized by colloidal surfactants: role of solid particles[J]. Particuology, 2022, 64: 153-163. |
| [9] | Pu X Q, Liu R R, Xie Y T, et al. One-step preparation of biocompatible amphiphilic dimer nanoparticles with tunable particle morphology and surface property for interface stabilization and drug delivery[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2025, 36(3): 109820. |
| [10] | Bai Y, Cui W S, Gao Y J, et al. Synergistic mechanism of mixed cationic/anionic collectors on lepidolite flotation from the perspective of improving the performance of flotation foam[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2023, 656: 130354. |
| [11] | Bai Y, Xu M X, Liu G Q, et al. The effect of spacer chain length on foam stability of mixed amine gemini surfactant/NaOl by molecular dynamic simulations[J]. Langmuir, 2025, 41(10): 6553-6564. |
| [12] | 郑延成, 连响, 谢谦, 等. 阳离子Gemini表面活性剂与脂肪醇醚磺酸盐的相互作用研究[J]. 精细石油化工, 2015, 32(6): 19-23. |
| Zheng Y C, Lian X, Xie Q, et al. Study on the interaction of cationic gemini surfactant and alkyl ethoxypropane sulfonate[J]. Speciality Petrochemicals, 2015, 32(6): 19-23. | |
| [13] | 王帅, 宋宝旭, 马芳源, 等. 不同药剂体系下载金黄铁矿的浮选泡沫性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2024, 34(11): 3832-3842. |
| Wang S, Song B X, Ma F Y, et al. Flotation foam performance of gold-bearing pyrite from different reagent systems[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2024, 34(11): 3832-3842. | |
| [14] | Bai Y, Xu M X, Wen W X, et al. Synergistic mechanism of dodecylamine/octanol mixtures enhancing lepidolite flotation from the self-aggregation behaviors at the air/liquid interface[J]. Physicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing, 2023, 59(6): 176510. |
| [15] | 廖艺, 牛亚宾, 潘艳秋, 等. 复配表面活性剂对油水界面行为和性质影响的模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4003-4014. |
| Liao Y, Niu Y B, Pan Y Q, et al. Modeling the effects of mixed surfactants on the behaviors and properties of the oil-water interface with molecular dynamics[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 4003-4014. | |
| [16] | Heinz H, Lin T J, Kishore Mishra R, et al. Thermodynamically consistent force fields for the assembly of inorganic, organic, and biological nanostructures: the INTERFACE force field[J]. Langmuir, 2013, 29(6): 1754-1765. |
| [17] | Lin T J, Heinz H. Accurate force field parameters and pH resolved surface models for hydroxyapatite to understand structure, mechanics, hydration, and biological interfaces[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(9): 4975-4992. |
| [18] | 刘佳霖, 任瑛, 陈卫, 等. 油水界面上阴/阳离子型复配表面活性剂体系的分子动力学模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2019, 19(3): 533-543. |
| Liu J L, Ren Y, Chen W, et al. Molecular dynamics simulations of binary mixtures of anionic/cationic surfactants at oil-water interface[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2019, 19(3): 533-543. | |
| [19] | 李亚娉, 吕韦钦, 曹绪龙, 等. 十二烷基硫酸钠与甜菜碱在气液和油水界面的复配协同作用研究[J]. 化学学报, 2014, 72(5): 615-623. |
| Li Y P, Lyu W Q, Cao X L, et al. Study of the synergistic effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate and betaine at the air/water and oil/water interfaces[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2014, 72(5): 615-623. | |
| [20] | Wang L, Liu R Q, Hu Y H, et al. Adsorption of mixed DDA/NaOL surfactants at the air/water interface by molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 155: 167-174. |
| [21] | 曹绪龙, 赵海娜, 马骋, 等. 阴阳离子表面活性剂混合体系对原油的乳化及增粘行为[J]. 物理化学学报, 2014, 30(7): 1297-1302. |
| Cao X L, Zhao H N, Ma C, et al. Behavior of emulsification and thickening of crude oil in mixed cationic and anionic surfactant systems[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2014, 30(7): 1297-1302. | |
| [22] | Wiberg K B, Rablen P R. Why does thioformamide have a larger rotational barrier than formamide [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1995, 117(8): 2201-2209. |
| [23] | 白阳. 组合捕收剂在白云母浮选中的协同作用及其机理研究[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2020. |
| Bai Y. Study on synergistic effect and mechanism of mixed collector on muscovite flotation[D]. Fuxin: Liaoning Technical University, 2020. | |
| [24] | Tah B, Pal P, Mahato M, et al. Aggregation behavior of SDS/CTAB catanionic surfactant mixture in aqueous solution and at the air/water interface[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2011, 115(26): 8493-8499. |
| [25] | Wen Y P, Zeng P H, Xu L, et al. Impacts of hydrophobic chain length on foam stability and CO2 geo-sequestration capacity of sugar-based nonionic surfactants: molecular dynamics simulation and laboratory experiments[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2024, 12(6): 114643. |
| [26] | Liu H J, Liu Y, Shang Y Z, et al. Molecular simulation and experimental studies on the interfacial properties of a mixed surfactant SDS/C4mimBr[J]. Molecular Simulation, 2019, 45(3): 223-229. |
| [27] | Wang L, Sun N, Wang Z, et al. Self-assembly of mixed dodecylamine–dodecanol molecules at the air/water interface based on large-scale molecular dynamics[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019, 276: 867-874. |
| [28] | Zhao T T, Xu G Y, Yuan S L, et al. Molecular dynamics study of alkyl benzene sulfonate at air/water interface: effect of inorganic salts[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2010, 114(15): 5025-5033. |
| [29] | 李宏恩, 赵会军, 于鹏飞, 等. 阴/两性离子表面活性剂复配体系界面性能探究[J]. 石油化工, 2021, 50(3): 236-241. |
| Li H E, Zhao H J, Yu P F, et al. Research on interface performance of anionic/zwitterionic surfactant compound system[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 2021, 50(3): 236-241. | |
| [30] | Afrin T, Karobi S N, Rahman M M, et al. Water structure modification by sugars and its consequence on micellization behavior of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide in aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Solution Chemistry, 2013, 42(7): 1488-1499. |
| [31] | Sarangi D, Samantaray A C, Sahu R, et al. Interactions of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide with 1, 3-dioxolanein water: a study of viscosity and volumetric properties[J]. Asian Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 32(1): 53-58. |
| [32] | Xu Y F, Wang Z H, Han X, et al. Impact of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate concentration on the stability of the crude oil–mineral water interfacial film: a molecular dynamics simulation study[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2022, 36(8): 4358-4369. |
| [33] | 李杰训, 许云飞, 王志华. 剪切流场中油-水界面成膜的影响因素及微观机制[J]. 石油学报, 2024, 45(8): 1244-1256. |
| Li J X, Xu Y F, Wang Z H. Influencing factors and micromechanisms of film formation at oil-water interface in shear flow field[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2024, 45(8): 1244-1256. | |
| [34] | Rivera J L, McCabe C, Cummings P T. Molecular simulations of liquid-liquid interfacial properties: water-n-alkane and water-methanol-n-alkane systems[J]. Physical Review. E, 2003, 67: 011603. |
| [35] | Alejandre J, Tildesley D J, Chapela G A. Molecular dynamics simulation of the orthobaric densities and surface tension of water[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1995, 102(11): 4574-4583. |
| [1] | 胡国祥, 朱忆魁, 龙华, 刘晓雯, 熊勤钢. 组分配比影响氯化胆碱-乳酸低共熔溶剂碱木质素溶解度的底层机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4449-4461. |
| [2] | 李相海, 赖德林, 孔纲, 周健. 双仿生表面水下疏油协同机制的分子动力学模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4551-4562. |
| [3] | 高正, 汪辉, 屈治国. 数据驱动辅助高通量筛选阴离子柱撑金属有机框架储氢[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4259-4272. |
| [4] | 叶鑫煌, 薛嘉豪, 赵玉来. 可聚型Gemini表面活性剂的制备、表征及其稳定高内相乳液的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4331-4340. |
| [5] | 林嘉豪, 付芳忠, 叶昊辉, 胡金, 姚明灿, 范鹤林, 王旭, 王瑞祥, 徐志峰. NdF3含量对NdF3-LiF熔盐局域结构和输运性质的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3834-3841. |
| [6] | 王小令, 王绍清, 赵云刚, 常方哲, 穆瑞峰. 基于ReaxFF MD模拟的煤加氢热解有机Ca转化机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4297-4309. |
| [7] | 彭梦圆, 李家明, 沙敏, 张丁. 季铵盐氟碳表面活性剂复配体系的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4177-4184. |
| [8] | 李姿睿, 齐凯, 王军, 夏国栋. 基于Janus纳米通道的脱盐过程分子动力学模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3531-3538. |
| [9] | 乔亮, 李尚, 刘新亮, 王明, 张沛, 侯影飞. 三元共聚物稠油降黏剂的合成及分子模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3686-3695. |
| [10] | 刘峰, 韩春硕, 张益, 刘彦成, 郁林军, 申家伟, 高晓泉, 杨凯. 高温高盐环境下单烃链和双烃链表面活性剂对油水界面性质影响的微观机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2939-2957. |
| [11] | 胡嘉朗, 姜明源, 金律铭, 张永刚, 胡鹏, 纪红兵. 机器学习辅助MOFs高通量计算筛选及气体分离研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 1973-1996. |
| [12] | 李紫鹃, 谭晓艳, 吴永盛, 杨陈怡, 陈红, 毕小刚, 刘捷, 喻发全. 分子模拟研究三维扭曲催化芳烃-降冰片烯环化聚合物膜的CO2/N2分离机理[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2348-2357. |
| [13] | 齐昊, 王玉杰, 李申辉, 邹琦, 刘轶群, 赵之平. 双金属Co/Zn-ZIFs中C3H6和C3H8吸附和扩散行为分子模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2313-2326. |
| [14] | 陈建兵, 常昊, 高明, 邢兵, 张磊, 刘奇磊. 基于反应模板与分子动力学的胺基相变吸收剂分相预测方法[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2387-2396. |
| [15] | 朱峰, 赵跃, 马凤翔, 刘伟. 改性UIO-66对SF6/N2混合气体及其分解产物的吸附特性[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1604-1616. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号