• •
收稿日期:2025-10-26
修回日期:2025-12-02
出版日期:2025-12-17
通讯作者:
周池楼
作者简介:周池楼(1987—),男,博士,副教授,mezcl@scut.edu.cn
基金资助:
Chilou ZHOU1,2( ), Yawen SHEN1, Xianhui LIU1, Xiang LI2,3
), Yawen SHEN1, Xianhui LIU1, Xiang LI2,3
Received:2025-10-26
Revised:2025-12-02
Online:2025-12-17
Contact:
Chilou ZHOU
摘要:
氢能作为清洁能源,在未来的能源发展中具有关键地位。高压氢系统中,橡胶密封件在高压氢气环境下的动态密封性能退化是涉及气体扩散、溶胀变形与界面磨损等多物理场耦合的复杂物理过程。为阐明其内在机理,本研究建立了综合考虑高压氢气扩散-溶胀变形-摩擦磨损-密封性能退化的多物理场耦合模型,通过开发与ABAQUS结合的UMESHMOTION用户子程序,实现了橡胶O形密封圈氢扩散与机械磨损耦合仿真。系统探究了预压缩率、氢气压力、位移幅值和磨损循环次数等关键参数对接触应力、内部应力集中以及界面材料损失的影响规律。研究结果表明,吸氢膨胀效应在初期会通过增大接触应力来增强密封完整性,但同时也加剧了磨损积累,进而导致了接触应力的退化和应力集中程度加剧。较高的预压缩率和氢气压力虽可提升初始接触应力,但由于摩擦耗散和应力集中效应的增强,反而会削弱其长期服役性能。位移幅值和循环次数的增加则会显著加剧磨损程度,并改变最大磨损深度的分布位置。本研究揭示了高压氢环境中氢扩散与机械磨损耦合作用下橡胶O形密封圈的损伤退化机理,为氢系统用密封件的优化设计提供了重要理论依据。
中图分类号:
周池楼, 沈亚文, 刘先晖, 李翔. 氢-摩擦耦合作用下橡胶O形密封圈的损伤行为数值研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251193.
Chilou ZHOU, Yawen SHEN, Xianhui LIU, Xiang LI. Numerical study on damage behavior of rubber O-ring seals under hydrogen-friction coupling effects[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251193.
| The height difference between the deepest wear and the surrounding wear marks/μm | Relative error/% | |
|---|---|---|
| Simulation | Experiment | |
| 1007.7 | 1014.3 | 0.65 |
表1 模拟与实验中磨损最严重区域和周围磨痕的高度差结果对比[12]
Table 1 Comparison of the results of the height difference between the most worn area and the surrounding abrasion marks in the simulation and the experiment[12]
| The height difference between the deepest wear and the surrounding wear marks/μm | Relative error/% | |
|---|---|---|
| Simulation | Experiment | |
| 1007.7 | 1014.3 | 0.65 |
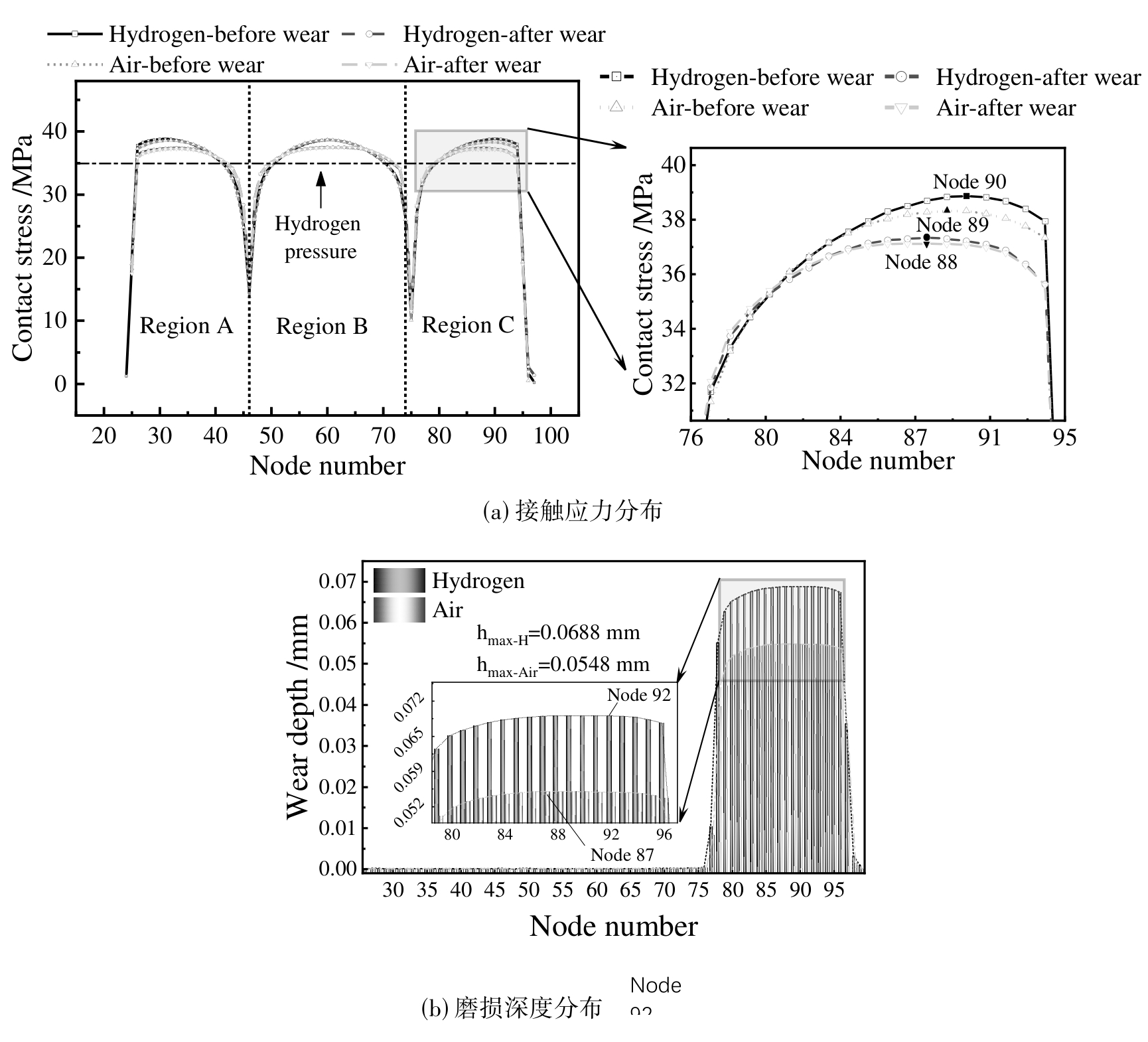
图6 氢环境与空气环境下O形圈的接触应力分布,磨损深度分布和接触界面节点布局图
Fig. 6 Distribution of contact stress, wear depth under hydrogen and air environments, and the nodal layout of the rubber O-ring contact interface
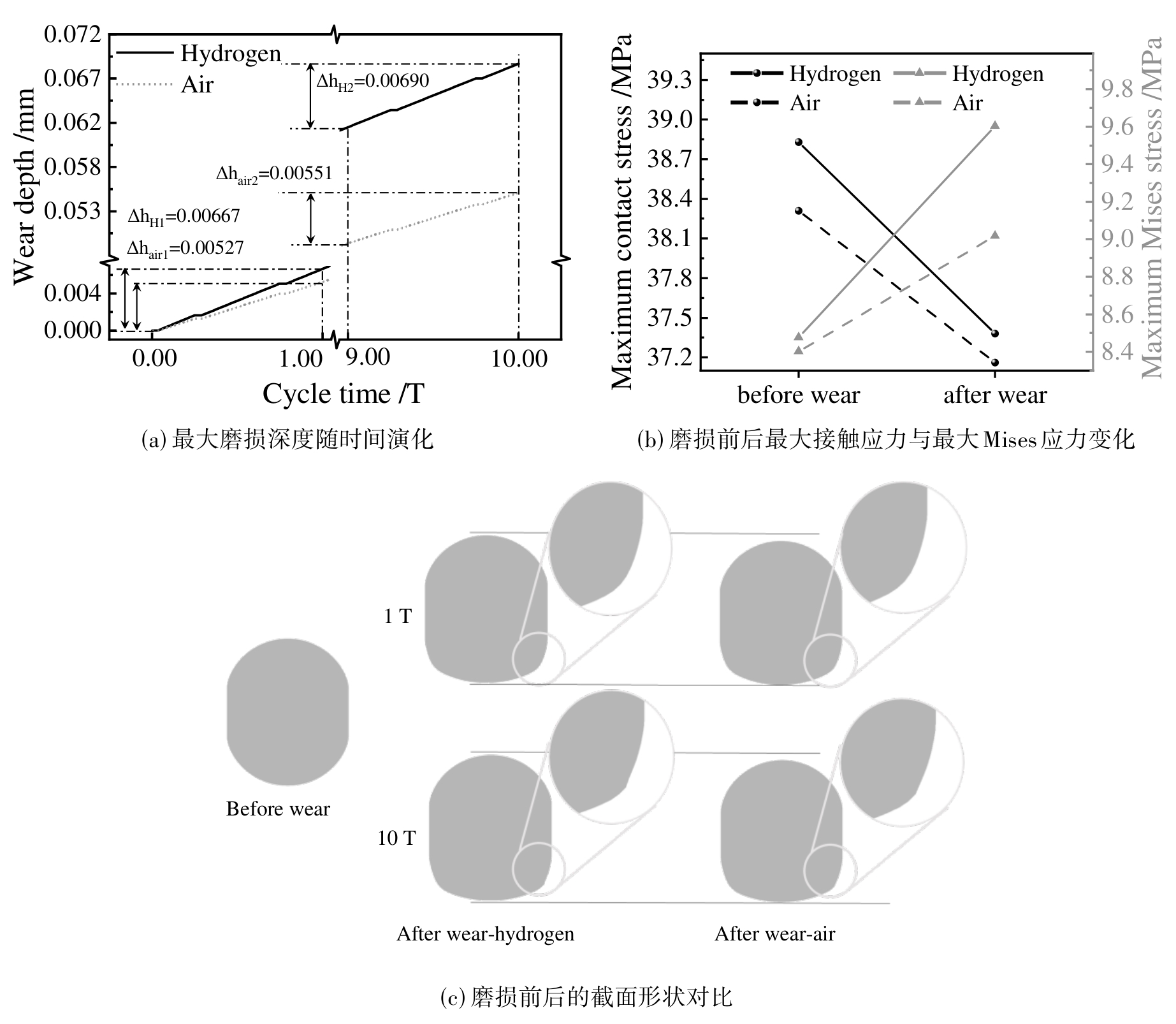
图7 氢环境与空气环境下O形圈的最大磨损深度随时间演化,磨损前后最大接触应力与最大Mises应力变化和磨损前后的截面形状对比
Fig. 7 Temporal evolution of the maximum wear depth, variations in maximum contact stress and maximum Mises stress before and after wear, and cross-sectional profiles of the rubber O-ring before and after wear under hydrogen and air environments
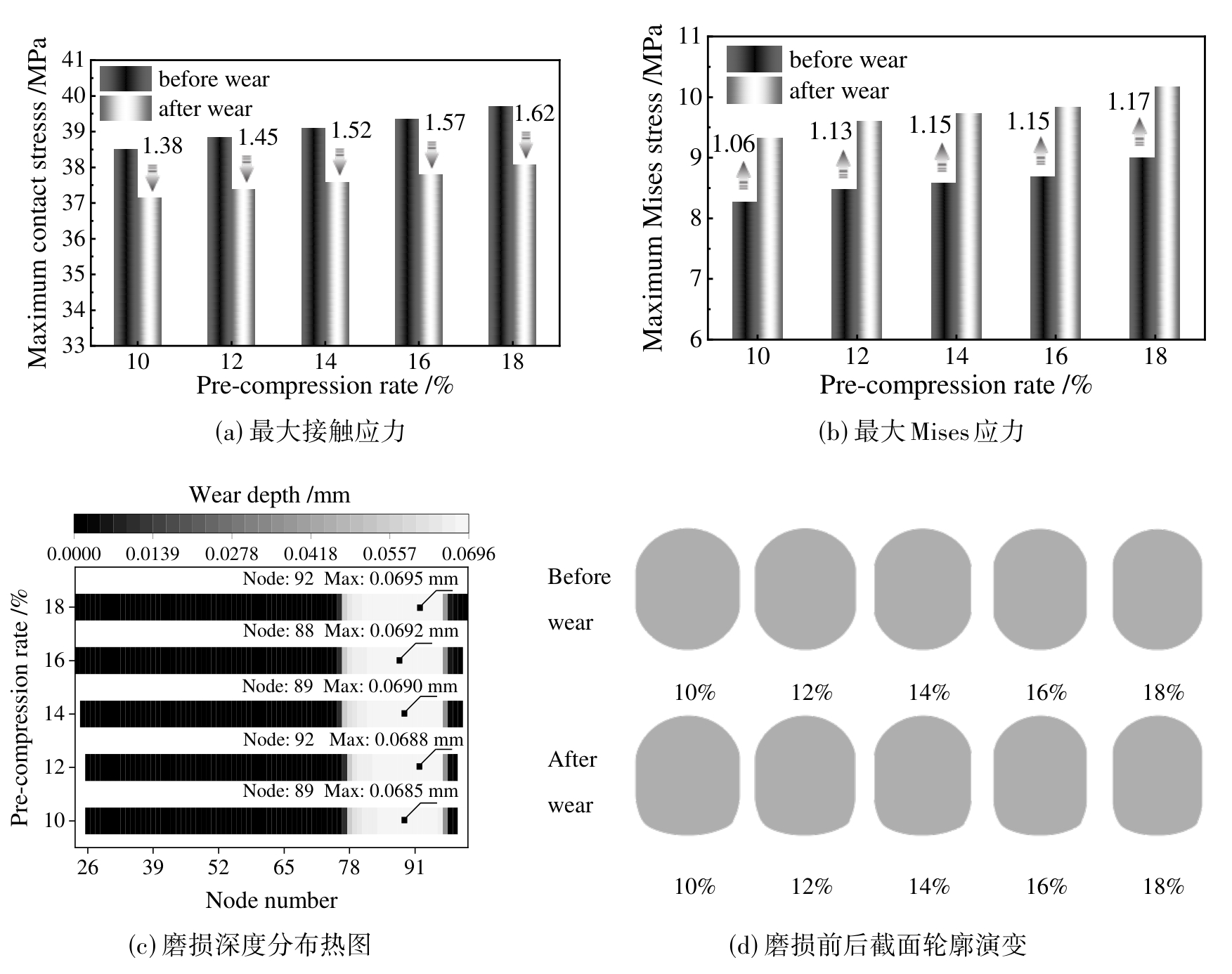
图8 不同预压缩率下橡胶O形圈的最大接触应力,最大Mises应力,磨损深度分布热图和磨损前后截面轮廓演变
Fig. 8 Maximum contact stress, maximum Mises stress, heat map of wear depth distribution and evolution of cross-section profile before and after wear of rubber O-rings with different pre-compression rates
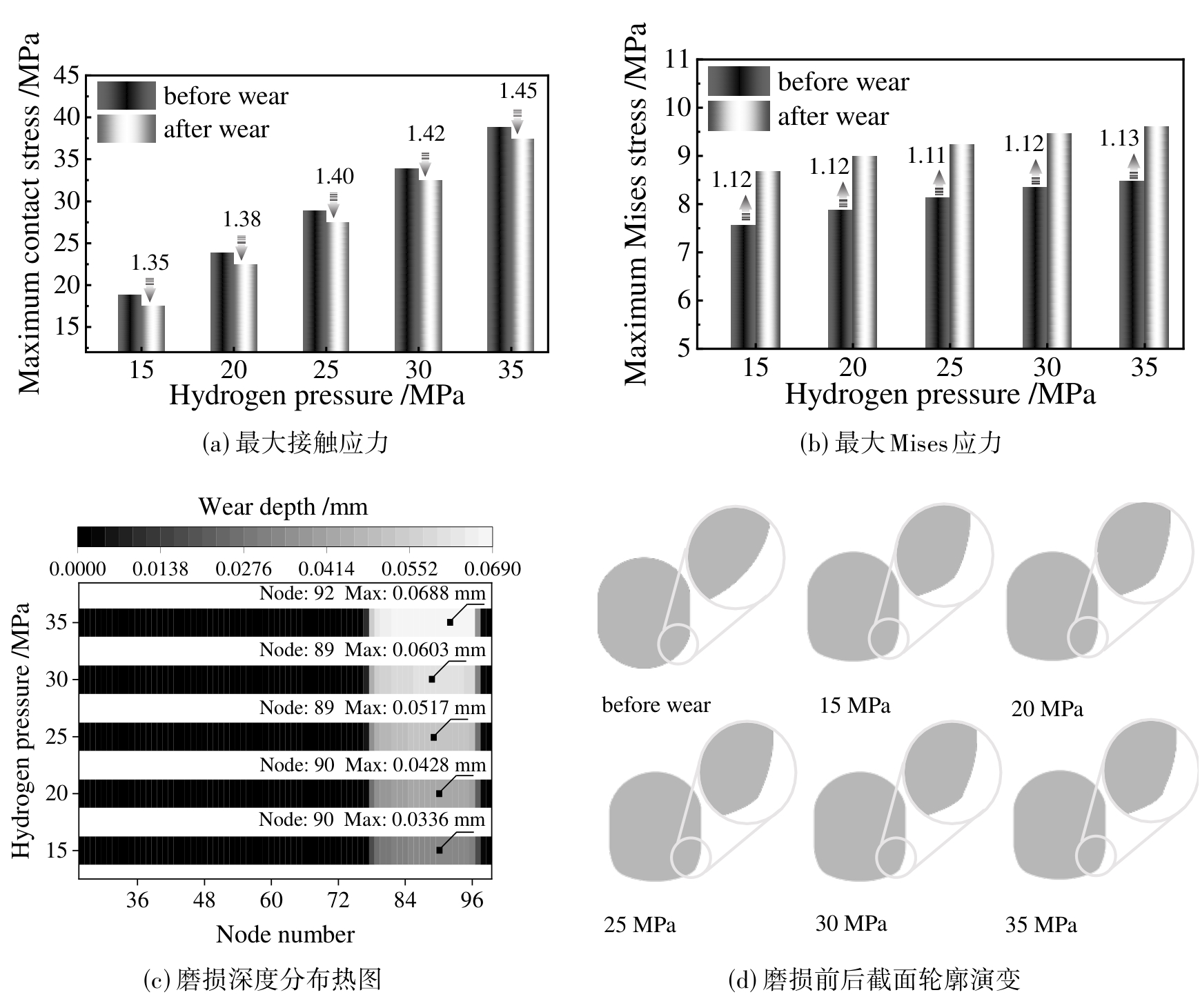
图9 不同氢气压力下橡胶O形圈的最大接触应力,最大Mises应力,磨损深度分布热图和磨损前后截面轮廓演变
Fig. 9 Maximum contact stress, maximum Mises stress, heat map of wear depth distribution and evolution of cross-section profile before and after wear of rubber O-rings with different hydrogen pressures
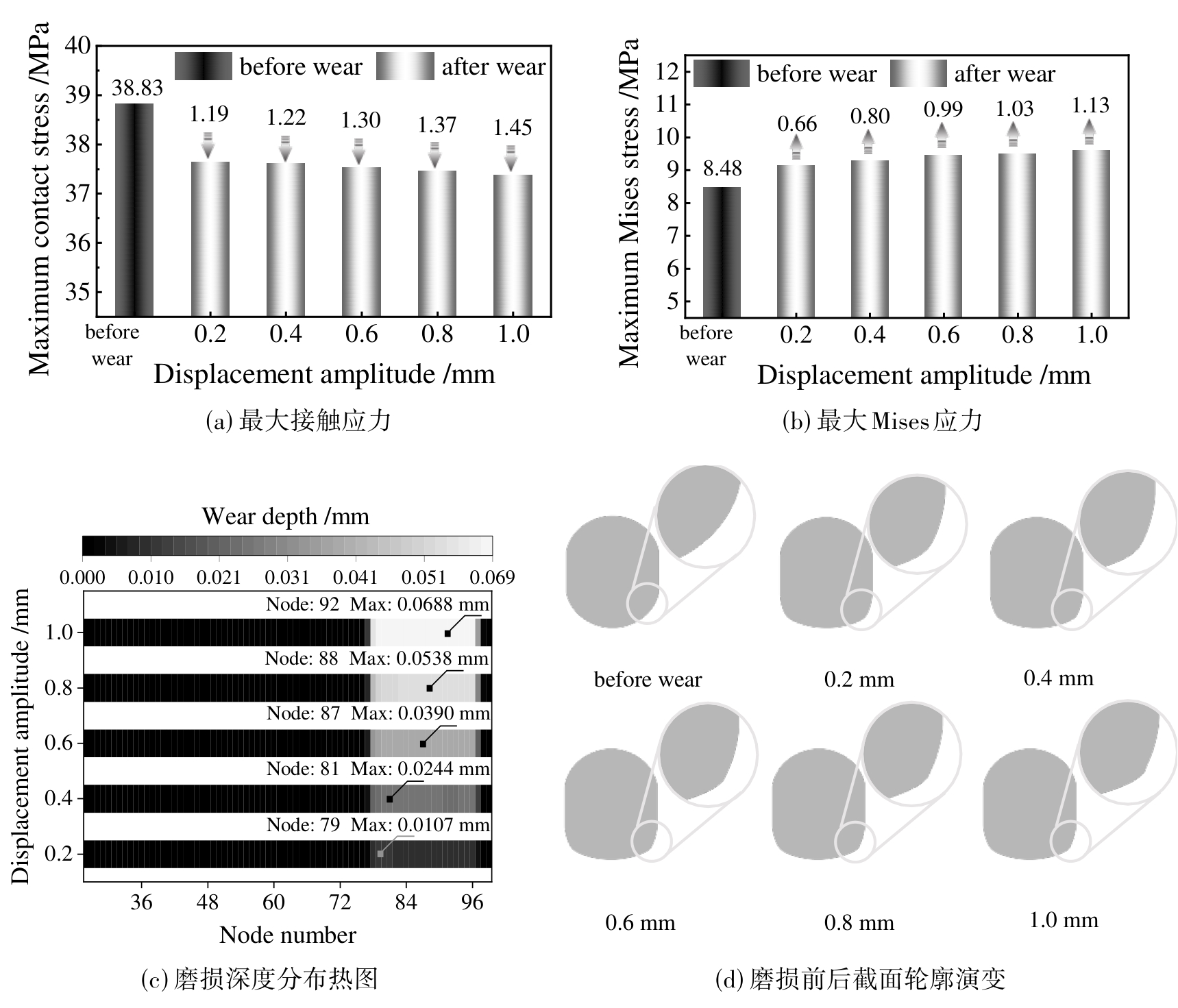
图10 不同位移幅值下橡胶O形圈的最大接触应力,最大Mises应力,磨损深度分布热图和磨损前后截面轮廓演变
Fig. 10 Maximum contact stress, maximum Mises stress, heat map of wear depth distribution and evolution of cross-section profile before and after wear of rubber O-rings with different displacement amplitudes
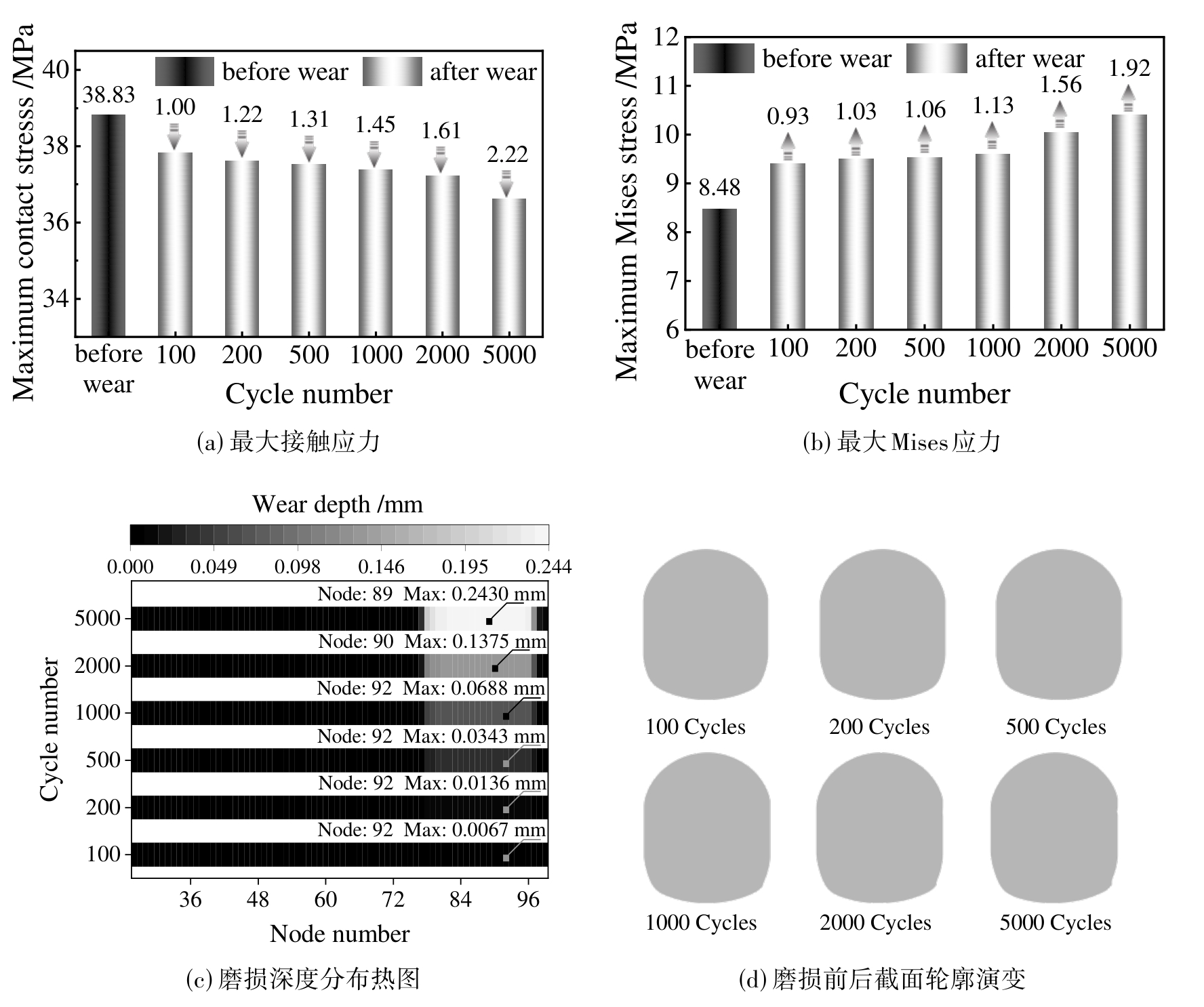
图11 不同磨损循环周期下橡胶O形圈的最大接触应力,最大Mises应力,磨损深度分布热图和磨损前后截面轮廓演变
Fig. 11 Maximum contact stress, maximum Mises stress, heat map of wear depth distribution and evolution of cross-section profile before and after wear of rubber O-rings with different wear cycle numbers
| [1] | Le T T, Sharma P, Bora B J, et al. Fueling the future: a comprehensive review of hydrogen energy systems and their challenges[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 54: 791-816. |
| [2] | 李怡, 王纪元, 潘旭海, 等. 碱性电解水制氢安全研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(10): 4961-4975. |
| Li Y, Wang J Y, Pan X H, et al. Research progress on safety of hydrogen production by alkaline electrolysis of water[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(10): 4961-4975. | |
| [3] | 周池楼, 刘先晖, 张永君, 等. 钢中夹杂物对氢扩散行为的影响规律[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(9): 135-144. |
| Zhou C L, Liu X H, Zhang Y J, et al. Influence of inclusions in steel on hydrogen diffusion behavior[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(9): 135-144. | |
| [4] | Theiler G, Cano Murillo N, Halder K, et al. Effect of high-pressure hydrogen environment on the physical and mechanical properties of elastomers[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 58: 389-399. |
| [5] | Zhou C L, Liu X H, Zheng Y R, et al. A comprehensive review of hydrogen-induced swelling in rubber composites[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2024, 275: 111342. |
| [6] | Lei X Z, Zheng B, Xue D X. Study on the expansion of nitrile rubber in high-pressure hydrogen gas atmospheres: Calculations and experiments[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science, 2024, 64(8): 3847-3853. |
| [7] | Jeon S K, Jung J K, Chung N K, et al. Investigation of physical and mechanical characteristics of rubber materials exposed to high-pressure hydrogen[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(11): 2233. |
| [8] | Rajesh J J, Bijwe J. Influence of fillers on the low amplitude oscillating wear behaviour of polyamide 11[J]. Wear, 2004, 256(1/2): 1-8. |
| [9] | 汤洁, 张丽慧, 周春宇, 等. 橡胶减摩抗磨改性研究进展[J]. 摩擦学学报(中英文), 2024, 44(3): 379-395. |
| Tang J, Zhang L H, Zhou C Y, et al. Research progress on antifriction and anti-wear modification of rubber[J]. Tribology, 2024, 44(3): 379-395. | |
| [10] | 左雯雯, 李锦春, 尤秀兰, 等. 芳纶浆粕增强丁腈橡胶复合材料的摩擦磨损性能[J]. 化工学报, 2010, 61(5): 1331-1336. |
| Zuo W W, Li J C, You X L, et al. Tribological properties of PPTA-pulp reinforced NBR composites[J]. CIESC Journal, 2010, 61(5): 1331-1336. | |
| [11] | Sawae Y, Morita T, Takeda K, et al. Friction and wear of PTFE composites with different filler in high purity hydrogen gas[J]. Tribology International, 2021, 157: 106884. |
| [12] | Duranty A, Roosendaal P, Simmons B. Preliminary test methodology for linear reciprocating ball-on-flat in situ friction and wear studies of polymers in high pressure hydrogen[R]. Richland: Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, 2016. |
| [13] | Duranty E R, Roosendaal T J, Pitman S G, et al. An in situ tribometer for measuring friction and wear of polymers in a high pressure hydrogen environment[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2017, 88(9): 095114. |
| [14] | Kuang W B, Bennett W D, Roosendaal T J, et al. In situ friction and wear behavior of rubber materials incorporating various fillers and/or a plasticizer in high-pressure hydrogen[J]. Tribology International, 2021, 153: 106627. |
| [15] | 王可胜, 刘全坤, 张德元. D2钢系列涂层磨损性能的数值模拟[J]. 物理学报, 2009, 58(F06): 89-93. |
| Wang K S, Liu Q K, Zhang D Y. Numerical simulation of the tribological behaviour of the serial coatings of D2 steel[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2009, 58(F06): 89-93. | |
| [16] | Kaufmann A. Wear of dry-running piston rod sealing rings: modelling and experiments[D]. Leoben: Technical University of Leoben, 2019. |
| [17] | Huang T C, Lin C Y, Liao K C. Experimental and numerical investigations of the wear behavior and sealing performance of PTFE rotary lip seals based on the elasto-hydrodynamic analysis with considerations of the asperity contact[J]. Tribology International, 2023, 187: 108747. |
| [18] | Li X, Peng G L, Li Z. Prediction of seal wear with thermal–structural coupled finite element method[J]. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design, 2014, 83: 10-21. |
| [19] | Zhao Y, Feng Z M, Li Y C, et al. Analysis of Contact Surface Wear Performance of O-Ring Dynamic Seal Based on Archard Model[J]. Tehnički Vjesnik - Technical Gazette, 2022, 29(5): 1441-1453. |
| [20] | Zhang Y, Lou Z C, Wei F, et al. Hybrid lubrication model study of slip ring combination seal under the influence of frictional heat[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2024, 238(4): 426-449. |
| [21] | Zhou C L, Zheng J Y, Gu C H, et al. Sealing performance analysis of rubber O-ring in high-pressure gaseous hydrogen based on finite element method[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(16): 11996-12004. |
| [22] | Zhou C L, Zheng Y R, Liu X H. Fretting characteristics of rubber X-ring exposed to high-pressure gaseous hydrogen[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(19): 7112. |
| [23] | Rivlin R S. Large elastic deformations of isotropic materials. IV. further developments of the general theory[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1948, 241(835): 379-397. |
| [24] | Yamabe J, Koga A, Nishimura S. Failure behavior of rubber O-ring under cyclic exposure to high-pressure hydrogen gas[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2013, 35: 193-205. |
| [25] | Yamabe J, Nishimura S. Influence of fillers on hydrogen penetration properties and blister fracture of rubber composites for O-ring exposed to high-pressure hydrogen gas[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(4): 1977-1989. |
| [26] | Castagnet S, Grandidier J C, Comyn M, et al. Mechanical testing of polymers in pressurized hydrogen: tension, creep and ductile fracture[J]. Experimental Mechanics, 2012, 52(3): 229-239. |
| [27] | Menon, Kruizenga, Mills B E, et al. Polymer behavior in high pressure hydrogen, helium, and argon environments as applicable to the hydrogen infrastructure[R]. Albuquerque: Sandia National Laboratories, 2017. |
| [28] | Archard J F. Contact and rubbing of flat surfaces[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1953, 24(8): 981-988. |
| [29] | Choi B L, Jung J K, Baek U B, et al. Effect of functional fillers on tribological characteristics of acrylonitrile butadiene rubber after high-pressure hydrogen exposures[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(5): 861. |
| [30] | Eayal Awwad K Y, Fallahnezhad K, Yousif B F, et al. Finite element analysis and experimental validation of polymer–metal contacts in block-on-ring configuration[J]. Friction, 2024, 12(3): 554-568. |
| [31] | Mukras S, Kim N H, Sawyer W G, et al. Numerical integration schemes and parallel computation for wear prediction using finite element method[J]. Wear, 2009, 266(7/8): 822-831. |
| [32] | Põdra P, Andersson S. Simulating sliding wear with finite element method[J]. Tribology International, 1999, 32(2): 71-81. |
| [33] | Martínez-Londoño J C, Martínez-Trinidad J, Hernández-Fernández A, et al. Finite element analysis on AISI 316L stainless steel exposed to ball-on-flat dry sliding wear test[J]. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2023, 76(1): 97-106. |
| [34] | Bose K K, Ramkumar P. Finite element method based sliding wear prediction of steel-on-steel contacts using extrapolation techniques[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2019, 233(10): 1446-1463. |
| [35] | Zhou C L, Shen Y W, Wang H X, et al. Numerical analysis of hydrogen-induced blister crack effect on rubber O-ring dynamic sealing performance[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science, 2025, 65(6): 2851-2870. |
| [36] | Zhang L, Wei X H. A novel structure of rubber ring for hydraulic buffer seal based on numerical simulation[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(5): 2036. |
| [37] | Dragoni E, Strozzi A. Theoretical analysis of an unpressurized elastomeric O-ring seal inserted into a rectangular groove[J]. Wear, 1989, 130(1): 41-51. |
| [1] | 彭建斌, 李明, 谢军龙, 陈建业. 液氢接收终端液氢泄漏扩散及爆炸超压研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 453-461. |
| [2] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [3] | 丁昊, 王林, 刘豪. R290/R245fa汽液相平衡混合规则对比研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 9-16. |
| [4] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [5] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [6] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [7] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [8] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [9] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [10] | 何婷, 黄舒阳, 黄坤, 陈利琼. 基于余热利用的天然气化学吸收脱碳-高温热泵耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [11] | 贾志勇, 沈宪琨, 蓝晓程, 王铁峰. 气体密度对高压流态化影响的CFD-DEM模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4383-4397. |
| [12] | 王一飞, 李玉星, 欧阳欣, 赵雪峰, 孟岚, 胡其会, 殷布泽, 郭雅琦. 基于裂尖减压特性的CO2管道断裂扩展数值计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4683-4693. |
| [13] | 杨开源, 陈锡忠. 颗粒破碎的离散元及有限离散元模拟方法比较[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4398-4411. |
| [14] | 段炼, 周星睿, 袁文君, 陈飞. 连续相速度脉动对微通道内聚合物液滴生成和形貌的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4578-4585. |
| [15] | 陈昇, 李子争, 苗超, 白学刚, 李飞, 刘家璇, 李天天, 杨爽, 吕蓉蓉, 王江云. 大尺度密集场景高危氯气非均匀湍流扩散特性三维CFD模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4630-4643. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号