• •
何裕农1( ), 黄可儿1, 徐鹏宇1, 赵云鹏1, 石孝刚1, 蓝兴英1(
), 黄可儿1, 徐鹏宇1, 赵云鹏1, 石孝刚1, 蓝兴英1( ), 徐玉兵2, 高金森1, 徐春明1
), 徐玉兵2, 高金森1, 徐春明1
收稿日期:2025-08-28
修回日期:2025-12-15
出版日期:2025-12-17
通讯作者:
蓝兴英
作者简介:何裕农(1999—),男,博士研究生,2024310323@student.cup.edu.cn
基金资助:
Yunong HE1( ), Ke'er HUANG1, Pengyu XU1, Yunpeng ZHAO1, Xiaogang SHI1, Xingying LAN1(
), Ke'er HUANG1, Pengyu XU1, Yunpeng ZHAO1, Xiaogang SHI1, Xingying LAN1( ), Yubing XU2, Jinsen GAO1, Chunming XU1
), Yubing XU2, Jinsen GAO1, Chunming XU1
Received:2025-08-28
Revised:2025-12-15
Online:2025-12-17
Contact:
Xingying LAN
摘要:
为了实现FCC再生器CO2低成本捕集,提出了耦合绿电制氢的FCC再生器CO2原位富集工艺。基于流程模拟方法,以某炼油厂80万吨/年FCC装置为主体进行工艺流程再造,匹配相应规模电解水装置供氧,电解水副产氢气置换同等规模的天然气制氢装置产能。对新耦合工艺进行经济性分析,并与配备胺吸收CO2捕集的FCC空气再生及天然气制氢装置对比。结果表明,新耦合工艺CO2减排支出为109.9 元/tCO2,较胺吸收CO2捕集的支出降低了40.5%。进一步分析表明,新耦合工艺经济性受电网电价影响最敏感,未来可通过提高新能源供电比例等措施降低新耦合工艺操作成本。同时新耦合工艺经济性受碳利用收益影响不大,较胺吸收CO2捕集具有更好的抗CO2市场价格波动性能力。
中图分类号:
何裕农, 黄可儿, 徐鹏宇, 赵云鹏, 石孝刚, 蓝兴英, 徐玉兵, 高金森, 徐春明. 耦合绿电解水的FCC再生器CO2原位富集工艺经济性研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250960.
Yunong HE, Ke'er HUANG, Pengyu XU, Yunpeng ZHAO, Xiaogang SHI, Xingying LAN, Yubing XU, Jinsen GAO, Chunming XU. Economic study on the in-situ CO2 enrichment process in FCC regenerators coupled with green electrolysis[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250960.
| 项目 | FCC再生烟气 | 天然气重整炉膛烟道气 |
|---|---|---|
| 体积流量, Nm3/h | 80750.6 | 58494.8 |
| 质量流量, t/a | 910495.0 | 696991.6 |
| 组成① v.% | ||
| N2 | 0.751 | 0.673 |
| CO2 | 0.142 | 0.209 |
| H2O | 0.080 | 0.107 |
| O2 | 0.027 | 0.011 |
表1 FCC再生烟气与天然气重整炉膛烟道气组成及流量
Table 1 Composition and flow rate of FCC regenerator flue gas and natural gas reforming furnace flue gas
| 项目 | FCC再生烟气 | 天然气重整炉膛烟道气 |
|---|---|---|
| 体积流量, Nm3/h | 80750.6 | 58494.8 |
| 质量流量, t/a | 910495.0 | 696991.6 |
| 组成① v.% | ||
| N2 | 0.751 | 0.673 |
| CO2 | 0.142 | 0.209 |
| H2O | 0.080 | 0.107 |
| O2 | 0.027 | 0.011 |
| 模型设置 | 吸收塔 | 解吸塔 |
|---|---|---|
| 填料类型 | Mellapak 250Y | Mellapak 250Y |
| 流型 | Mixed | |
| 膜传质计算方法 | Liquid/discrxn;Gas/Consider film | |
| 传质系数 | Hanley-St10 | |
| 传热系数 | Chilton and Colburn | |
| 相界面积 | Hanley-St10 | |
| 持液量 | Brf-92 | |
| 修正方法 | ERRICO Massimiliano [ | AMIRKHOSROW Mahsa [ |
表2 吸收塔-解吸塔模型设置及模型修正方法
Table 2 Absorber-desorber model setup and model modification methods
| 模型设置 | 吸收塔 | 解吸塔 |
|---|---|---|
| 填料类型 | Mellapak 250Y | Mellapak 250Y |
| 流型 | Mixed | |
| 膜传质计算方法 | Liquid/discrxn;Gas/Consider film | |
| 传质系数 | Hanley-St10 | |
| 传热系数 | Chilton and Colburn | |
| 相界面积 | Hanley-St10 | |
| 持液量 | Brf-92 | |
| 修正方法 | ERRICO Massimiliano [ | AMIRKHOSROW Mahsa [ |
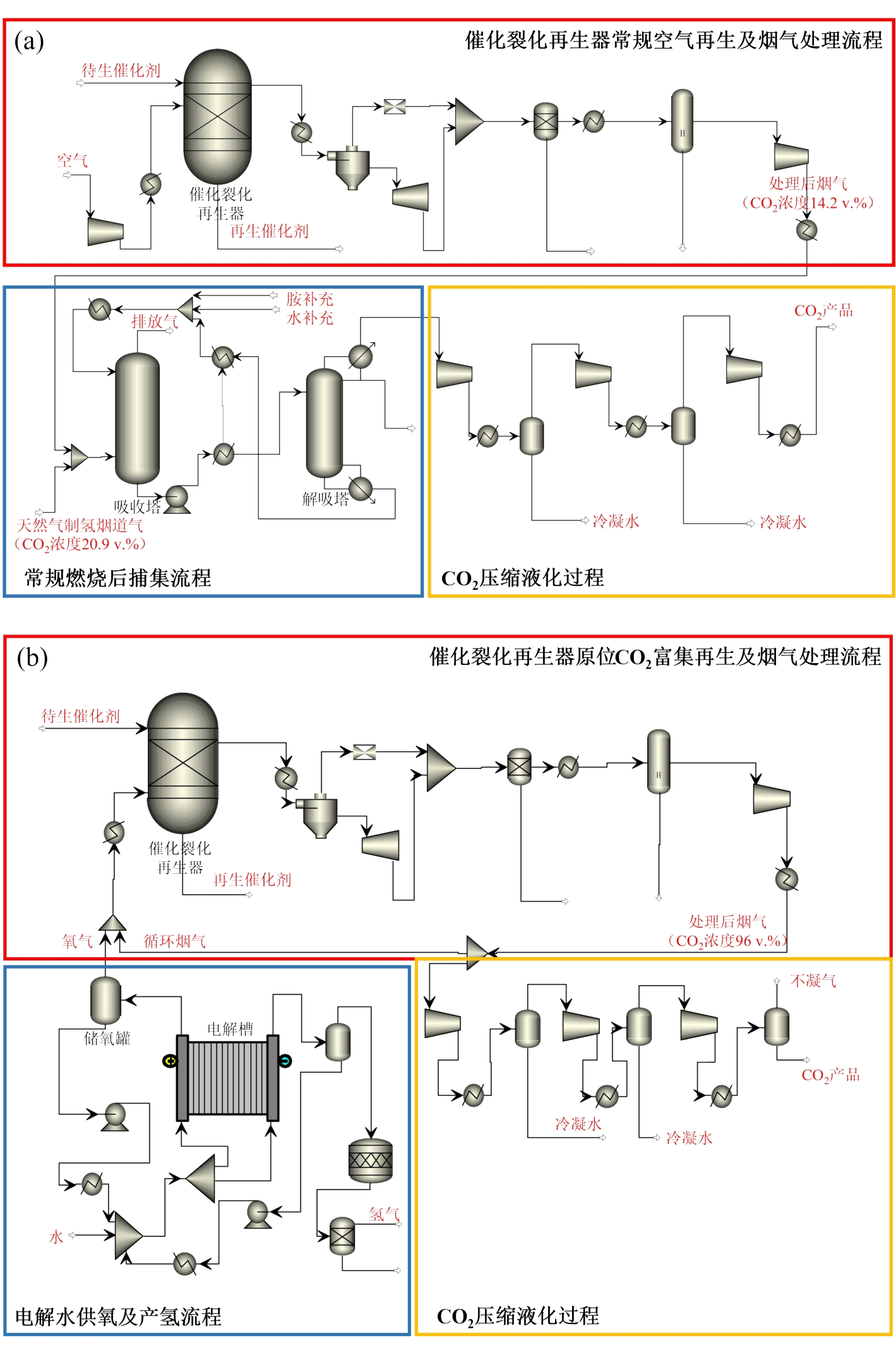
图4 Aspen模拟流程图:(a)常规FCC再生及天然气烟道气加装胺吸收CO2捕集;(b)耦合绿电制氢的FCC再生器CO2原位富集工艺
Fig.4 Aspen simulation flowsheets: (a) conventional FCC regeneration and amine-based CO2 capture installed for the natural-gas flue gas; (b) FCC regenerator in-situ CO2 enrichment process coupled with power-to-hydrogen production
| 单元 | 模型 | 温度, ℃ | 压力, kPa | 反应 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 方案一 | |||||
| 吸收塔 | RateSep | Top: 71.5 bottom: 46.5 | 101 | EQUIL: EQUIL: EQUIL: KINETIC: KINETIC: KINETIC: KINETIC: | |
| 解吸塔 | RateSep | Top: 100.5 bottom: 123.3 | 200 | ||
| 换热器 | Heater | Hot inlet:123.3 Cold outlet:108.2 | 700 | - | |
| 泵 | Pump | - | 700 | - | |
| 方案二 | |||||
| FCC再生器 | RStoic | 710 | 184 |
| |
| 主风机 | COMPR | - | 225 | - | |
| 碱性电解槽 | Electrolyzer | 90 | 1600 | Anode: Cathode: Overall: | |
| 泵 | Pump | - | 1600 | - | |
表3 流程模拟主要设备的模型选择及相关参数设置
Table 3 Model selection and parameter settings for main equipment in process simulation
| 单元 | 模型 | 温度, ℃ | 压力, kPa | 反应 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 方案一 | |||||
| 吸收塔 | RateSep | Top: 71.5 bottom: 46.5 | 101 | EQUIL: EQUIL: EQUIL: KINETIC: KINETIC: KINETIC: KINETIC: | |
| 解吸塔 | RateSep | Top: 100.5 bottom: 123.3 | 200 | ||
| 换热器 | Heater | Hot inlet:123.3 Cold outlet:108.2 | 700 | - | |
| 泵 | Pump | - | 700 | - | |
| 方案二 | |||||
| FCC再生器 | RStoic | 710 | 184 |
| |
| 主风机 | COMPR | - | 225 | - | |
| 碱性电解槽 | Electrolyzer | 90 | 1600 | Anode: Cathode: Overall: | |
| 泵 | Pump | - | 1600 | - | |
| 方案 | 装置 | 项目 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 方案一 | 胺吸收CO2捕集系统 | 吸收塔高, 塔径, m | 56, 6 |
| 解吸塔高, 塔径, m | 38, 4 | ||
| 贫液负载, mol CO2/mol amine | 0.146 | ||
| 富液负载, mol CO2/mol amine | 0.530 | ||
| 贫富液换热器温差, ℃ | 15 | ||
| 吨均CO2捕集能耗, GJ/tCO2 | 3.47 | ||
| CO2捕集量, t/a | 349953 | ||
| CO2减排率, % | 90 | ||
| 方案二 | 电解水系统 | O2总产量, t/a | 170651 |
| H2总产量, t/a | 21313 | ||
| 电解水系统耗电量, MWh/a | 1065462 | ||
| CO2原位富集再生 | 主风机负荷, kW | 1628 | |
| 外取热器负荷, kW | 6621 | ||
| 余热锅炉负荷, kW | 3760 | ||
| 烟机功率, kW | 1888 | ||
| 省煤器负荷, kW | 14445 | ||
| CO2捕集量, t/a | 176822 | ||
| CO2减排率, % | 99 |
表4 最优操作参数下流程模拟结果
Table 4 Process simulation results under optimal operating parameters
| 方案 | 装置 | 项目 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 方案一 | 胺吸收CO2捕集系统 | 吸收塔高, 塔径, m | 56, 6 |
| 解吸塔高, 塔径, m | 38, 4 | ||
| 贫液负载, mol CO2/mol amine | 0.146 | ||
| 富液负载, mol CO2/mol amine | 0.530 | ||
| 贫富液换热器温差, ℃ | 15 | ||
| 吨均CO2捕集能耗, GJ/tCO2 | 3.47 | ||
| CO2捕集量, t/a | 349953 | ||
| CO2减排率, % | 90 | ||
| 方案二 | 电解水系统 | O2总产量, t/a | 170651 |
| H2总产量, t/a | 21313 | ||
| 电解水系统耗电量, MWh/a | 1065462 | ||
| CO2原位富集再生 | 主风机负荷, kW | 1628 | |
| 外取热器负荷, kW | 6621 | ||
| 余热锅炉负荷, kW | 3760 | ||
| 烟机功率, kW | 1888 | ||
| 省煤器负荷, kW | 14445 | ||
| CO2捕集量, t/a | 176822 | ||
| CO2减排率, % | 99 |
| 新疆库车绿氢示范项目 | 方案二绿电解水及氧气储运系统设计结果 | |
|---|---|---|
| 建设规模 | ||
| 产H2规模, t/a | 20000 | 21313 |
| 产H2规模, Nm3/h | 26420 | 28154 |
| 产O2规模, t/a | 排空 | 170355 |
| 产O2规模, Nm3/h | 排空 | 17079.5 |
| 主要工程建设内容 | ||
| 光伏电站 | 光伏电站建设规模为355.47 MWp | 光伏电站建设规模为355.47 MWp |
| 制氢系统 | 52套1000Nm3/h制氢规模电解水设备 | 60套1000Nm3/h制氢规模电解水设备 |
| 储运系统 | 储氢:10台2000m3球罐 储氧:氧气直接排空 | 储氢:10台2000m3球罐 储氧:2台2000m3储罐 |
| 能源消耗 | ||
| 光伏用电(电解系统), 万kWh/a | 57552.07 | 63412.7 |
| 外购电(电解系统), 万kWh/a | 39147.09 | 43133.5 |
| 光伏用电(氧气液化), 万kWh/a | - | 4570.5 |
| 外购电(氧气液化), 万kWh/a | - | 3108.8 |
表5 示范项目与方案二绿电解水及氧气储运系统对比
Table 5 Comparison of demonstration project and green electrolysis coupled with oxygen storage and transportation system in the second scheme
| 新疆库车绿氢示范项目 | 方案二绿电解水及氧气储运系统设计结果 | |
|---|---|---|
| 建设规模 | ||
| 产H2规模, t/a | 20000 | 21313 |
| 产H2规模, Nm3/h | 26420 | 28154 |
| 产O2规模, t/a | 排空 | 170355 |
| 产O2规模, Nm3/h | 排空 | 17079.5 |
| 主要工程建设内容 | ||
| 光伏电站 | 光伏电站建设规模为355.47 MWp | 光伏电站建设规模为355.47 MWp |
| 制氢系统 | 52套1000Nm3/h制氢规模电解水设备 | 60套1000Nm3/h制氢规模电解水设备 |
| 储运系统 | 储氢:10台2000m3球罐 储氧:氧气直接排空 | 储氢:10台2000m3球罐 储氧:2台2000m3储罐 |
| 能源消耗 | ||
| 光伏用电(电解系统), 万kWh/a | 57552.07 | 63412.7 |
| 外购电(电解系统), 万kWh/a | 39147.09 | 43133.5 |
| 光伏用电(氧气液化), 万kWh/a | - | 4570.5 |
| 外购电(氧气液化), 万kWh/a | - | 3108.8 |
| 公用工程 | 原装置 | 方案一 | 方案二 |
|---|---|---|---|
天然气制氢 催化裂化常规空气再生 | 加装胺吸收CO2捕集 | 电解水 催化裂化CO2原位富集再生 | |
| 循环冷却水 | 基准 | +119.49% | -11.16% |
| 除盐水 | 基准 | 0.00% | -33.32% |
| 电 | 基准 | +185.36% | +5292.94% |
| 3.5 MPa蒸汽(243℃) | 基准 | 0.00% | +100.00% |
| 1.0 MPa蒸汽(180℃) | 基准 | 0.00% | -268.83% |
| 0.3 MPa蒸汽(134℃) | 基准 | +3283.00% | -100.00% |
| 天然气 | 基准 | 0.00% | -96.27% |
表6 各低碳转型方案主要公用工程消耗对比
Table 6 Comparison of major utility consumption for each low-carbon transition scheme
| 公用工程 | 原装置 | 方案一 | 方案二 |
|---|---|---|---|
天然气制氢 催化裂化常规空气再生 | 加装胺吸收CO2捕集 | 电解水 催化裂化CO2原位富集再生 | |
| 循环冷却水 | 基准 | +119.49% | -11.16% |
| 除盐水 | 基准 | 0.00% | -33.32% |
| 电 | 基准 | +185.36% | +5292.94% |
| 3.5 MPa蒸汽(243℃) | 基准 | 0.00% | +100.00% |
| 1.0 MPa蒸汽(180℃) | 基准 | 0.00% | -268.83% |
| 0.3 MPa蒸汽(134℃) | 基准 | +3283.00% | -100.00% |
| 天然气 | 基准 | 0.00% | -96.27% |
| 项目 | 估算方法及价格假设 |
|---|---|
| 固定成本 | |
| 税① | 根据盈利情况计算 |
| 保险 | 根据固定资产投资计算 |
| 直接生产成本 | |
| 循环冷却水 | 0.5元/吨 |
| 除盐水 | 10元/吨 |
| 0.3 MPa低压蒸汽 | 214元/吨 |
| 1.0 MPa低压蒸汽 | 258元/吨 |
| 3.5 MPa中压蒸汽 | 279元/吨 |
| 电价②(光伏) | 0.103元/kWh |
| 电价②(电网) | 0.350元/kWh |
| 天然气③ | 2.5元/Nm3 |
| 维护费用及辅助材料成本(含胺损失成本) | 根据固定资产投资、运行过程计算 |
| 运营劳动成本及实验室成本 | 根据项目定员计算 |
| 销售、一般和管理费用 | |
| 行政成本、分销与市场营销费用、研发成本 | 根据总运营成本计算 |
表7 总运营成本的成本估算内容及价格假设
Table 7 Cost estimation contents and price assumptions for total operating costs
| 项目 | 估算方法及价格假设 |
|---|---|
| 固定成本 | |
| 税① | 根据盈利情况计算 |
| 保险 | 根据固定资产投资计算 |
| 直接生产成本 | |
| 循环冷却水 | 0.5元/吨 |
| 除盐水 | 10元/吨 |
| 0.3 MPa低压蒸汽 | 214元/吨 |
| 1.0 MPa低压蒸汽 | 258元/吨 |
| 3.5 MPa中压蒸汽 | 279元/吨 |
| 电价②(光伏) | 0.103元/kWh |
| 电价②(电网) | 0.350元/kWh |
| 天然气③ | 2.5元/Nm3 |
| 维护费用及辅助材料成本(含胺损失成本) | 根据固定资产投资、运行过程计算 |
| 运营劳动成本及实验室成本 | 根据项目定员计算 |
| 销售、一般和管理费用 | |
| 行政成本、分销与市场营销费用、研发成本 | 根据总运营成本计算 |
| 项目 | 原装置 | 方案一 | 方案二 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 总资本支出,万元 | |||
| 固定资产投资 | 0 | +29252.2 | +101694.6 |
| 其他支出 | 0 | +7313.1 | +25423.7 |
| 总运营成本,万元/年 | |||
| 固定成本 | 基准 | +196.5 | -250.0 |
| 直接生产成本 | 基准 | +16869.8 | +4696.0 |
| 销售、一般和管理费用 | 基准 | +1196.8 | +297.1 |
| 总年均成本,万元/年 | 基准 | +20457.5 | +13453.6 |
| 收益,万元/年 | |||
| CO2产品收益 | 0 | +10498.6 | +5304.7 |
| 碳排放配额收益 | 0 | +3499.5 | +3882.5 |
| 总净利润,万元/年 | 基准 | -6459.4 | -4266.4 |
表8 各转型方案成本、收益计算结果
Table 8 Cost and revenue calculation results for each transformation scheme
| 项目 | 原装置 | 方案一 | 方案二 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 总资本支出,万元 | |||
| 固定资产投资 | 0 | +29252.2 | +101694.6 |
| 其他支出 | 0 | +7313.1 | +25423.7 |
| 总运营成本,万元/年 | |||
| 固定成本 | 基准 | +196.5 | -250.0 |
| 直接生产成本 | 基准 | +16869.8 | +4696.0 |
| 销售、一般和管理费用 | 基准 | +1196.8 | +297.1 |
| 总年均成本,万元/年 | 基准 | +20457.5 | +13453.6 |
| 收益,万元/年 | |||
| CO2产品收益 | 0 | +10498.6 | +5304.7 |
| 碳排放配额收益 | 0 | +3499.5 | +3882.5 |
| 总净利润,万元/年 | 基准 | -6459.4 | -4266.4 |
| 方案一 | 方案二 | |
|---|---|---|
| 吨均CO2减排成本, 元/tCO2 | 584.6 | 346.5 |
| 吨均CO2减排收益, 元/tCO2 | 400.0 | 236.6 |
| 净利润, 元/tCO2 | 184.6 | 109.9 |
表9 方案吨均CO2减排成本、收益及净利润对比
Table 9 Comparison of CO2 emission reduction cost, revenue, and net profit per ton for each scheme
| 方案一 | 方案二 | |
|---|---|---|
| 吨均CO2减排成本, 元/tCO2 | 584.6 | 346.5 |
| 吨均CO2减排收益, 元/tCO2 | 400.0 | 236.6 |
| 净利润, 元/tCO2 | 184.6 | 109.9 |
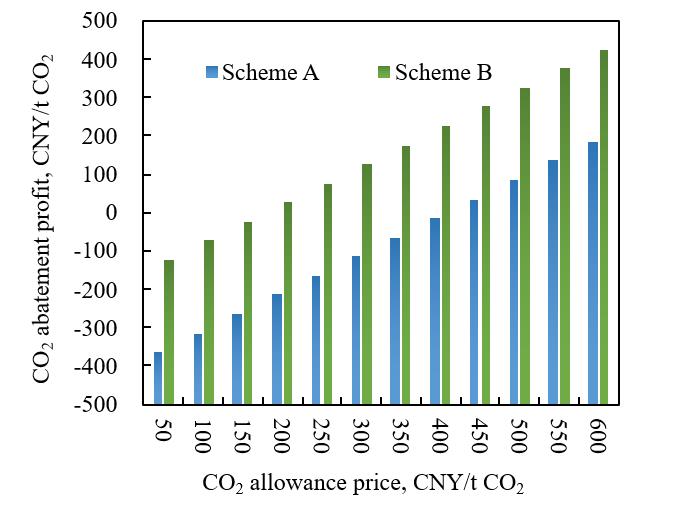
图7 碳排放配额价格对低碳转型单位CO2减排净利润影响
Fig. 7 Impact of carbon emission quota prices on net profit per unit of CO2 emission reduction in low-carbon transformation
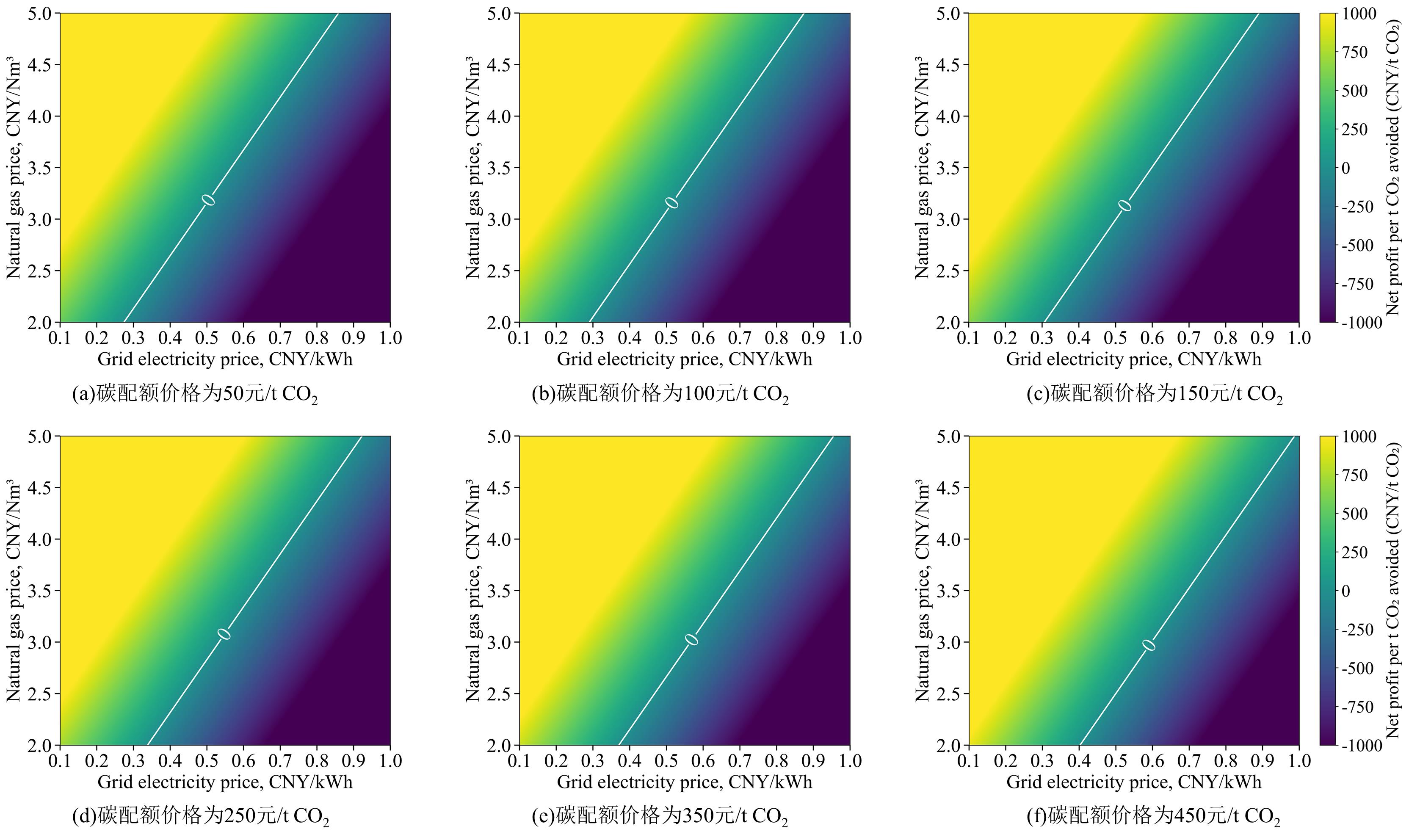
图9 不同条件下新耦合工艺保持盈亏平衡所需碳利用收益分布
Fig. 9 Distribution of carbon utilization revenue required to maintain breakeven under different conditions for the new coupled process
| [1] | 吴达, 蒋淑娇, 魏强, 等. 能源转型中渣油高效利用技术的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2024, 43(5): 2343-2353. |
| Wu D, Jiang S J, Wei Q, et al. Research progress on efficient utilization technology of residue in energy transition[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2024, 43(5): 2343-2353. | |
| [2] | 邵志才. 沸腾床渣油加氢工艺及其在炼油结构转型中的作用[J]. 石油炼制与化工, 2023, 54(6): 133-138. |
| Shao Z C. Ebullated-bed residue hydrocracking process and its role in the structural transformation for refinary[J]. Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals, 2023, 54(6): 133-138. | |
| [3] | 彭特, 龚剑洪, 朱金泉. "双碳" 政策下重油催化裂解技术研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2024, 53(1): 200-205, 217. |
| Peng T, Gong J H, Zhu J Q. Research progress of heavy oil deep catalytic cracking under "Double Carbon" policy[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2024, 53(1): 200-205, 217. | |
| [4] | 魏志强, 曹建军, 孙丽丽, 等. 中国炼化产业实现碳达峰与碳中和路径及支撑技术[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2024, 40(1): 1-11. |
| Wei Z Q, Cao J J, Sun L L, et al. The path and supporting technology of carbon peak and carbon neutrality in China's refining and chemical industry[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 2024, 40(1): 1-11. | |
| [5] | 蓝兴英, 赵云鹏, 吕明珠, 等. 一种二氧化碳零排放催化裂化非完全再生方法: 113877397B [P]. 2023-04-25. |
| Lan X Y, Zhao Y P, Lv M Z, et al. A method for non-complete regeneration of catalytic cracking with zero carbon dioxide emission: 113877397B[P]. 2023-04-25. | |
| [6] | 蓝兴英, 赵云鹏, 吕明珠, 等.一种二氧化碳零排放的催化裂化再生方法: 113877371B [P]. 2023-04-25. |
| Lan X Y, Zhao Y P, Lv M Z, et al. A method for catalytic regeneration with zero carbon dioxide emission: 113877371B[P]. 2023-04-25. | |
| [7] | Zhao Y P, Li C L, Shi X G, et al. Simulation analysis of CO2 in situ enrichment technology of fluidized catalytic cracking regenerator[J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 434: 119386. |
| [8] | 黎春霖, 赵云鹏, 石孝刚, 等. 催化裂化再生器二氧化碳原位富集工艺研究[J]. 石油炼制与化工, 2024, 55(1): 208-217. |
| Li C L, Zhao Y P, Shi X G, et al. Study on in situ enrichment process of carbon dioxide in fluid catalytic cracking regenerator[J]. Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals, 2024, 55(1): 208-217. | |
| [9] | 周璇, 闫鸿飞, 李秋芝, 等. 氧燃烧-二氧化碳捕集催化裂化技术研究[J]. 现代化工, 2013, 33(10): 96-98, 100. |
| Zhou X, Yan H F, Li Q Z, et al. Investigation on oxycombustion-carbon dioxide capture catalytic cracking technology[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2013, 33(10): 96-98, 100. | |
| [10] | Tang Y N, Li S Y, Liu C, et al. Process simulation and techno-economic analysis on novel CO2 capture technologies for fluid catalytic cracking units[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2023, 249: 107855. |
| [11] | Re M, Li S Z, Laukkanen T, et al. Profitability analysis of H2 production by water electrolysis in an integrated oxy-fuel combustion thermal power plant[J]. Fuel, 2025, 398: 135544. |
| [12] | de Mello L F, Pimenta R D M, Moure G T, et al. A technical and economical evaluation of CO2 capture from FCC units[J]. Energy Procedia, 2009, 1(1): 117-124. |
| [13] | de Mello L F, Gobbo R, Moure G T, et al. Oxy-combustion technology development for fluid catalytic crackers (FCC)–large pilot scale demonstration[J]. Energy Procedia, 2013, 37: 7815-7824. |
| [14] | Fu C, Anantharaman R. Modelling of the oxy-combustion fluid catalytic cracking units[M]//27th European Symposium on Computer Aided Process Engineering. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2017: 331-336. |
| [15] | Huang J B, Balcombe P, Feng Z X. Technical and economic analysis of different colours of producing hydrogen in China[J]. Fuel, 2023, 337: 127227. |
| [16] | Jang D, Kim J, Kim D, et al. Techno-economic analysis and Monte Carlo simulation of green hydrogen production technology through various water electrolysis technologies[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 258: 115499. |
| [17] | Li Q S, Khosravi A, Farsaei A, et al. Thermodynamics, economic and carbon emission analysis of power-to-methanol process through alkaline electrolysis and monoethanolamine (MEA) carbon capture[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2024, 293: 120029. |
| [18] | Shin H, Jang D, Lee S, et al. Techno-economic evaluation of green hydrogen production with low-temperature water electrolysis technologies directly coupled with renewable power sources[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2023, 286: 117083. |
| [19] | 朱兵, 陈定江, 蒋萌, 等. 化学工程在低碳发展转型中的关键作用探讨: 从物质资源利用与碳排放关联的视角[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(12): 5893-5903. |
| Zhu B, Chen D J, Jiang M, et al. Key role of chemical engineering in transition to low-carbon development in perspective of the linkage between resource utilization and carbon emissions[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(12): 5893-5903. | |
| [20] | Roussanaly S, Anantharaman R, Jordal K, et al. Understanding the cost of retrofitting CO2 capture in an integrated oil refinery: cost estimation and economic evaluation of CO2 capture options for refineries [R]. Trondheim: SINTEF Energi AS (SINTEF Energy Research), 2017. |
| [21] | Collodi G, Azzaro G, Ferrari N, et al. Techno-economic evaluation of deploying CCS in SMR based merchant H2 production with NG as feedstock and fuel[J]. Energy Procedia, 2017, 114: 2690-2712. |
| [22] | Notz R, Mangalapally H P, Hasse H. Post combustion CO2 capture by reactive absorption: Pilot plant description and results of systematic studies with MEA[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2012, 6: 84-112. |
| [23] | Zhang Y, Chen H, Chen C C, et al. Rate-based process modeling study of CO2 capture with aqueous monoethanolamine solution[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(20): 9233-9246. |
| [24] | Errico M, Madeddu C, Pinna D, et al. Model calibration for the carbon dioxide-amine absorption system[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 183: 958-968. |
| [25] | Amirkhosrow M, Nemati Lay E. Simulation model evaluation of desorber column in CO2 capture process by MEA scrubbing: a rigorous rate-based model for kinetic model and mass transfer correlations analysis[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2020, 203: 106390. |
| [26] | Madeddu C, Errico M, Baratti R. Process analysis for the carbon dioxide chemical absorption–regeneration system[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 215: 532-542. |
| [27] | Oh H T, Kum J, Park J, et al. Pre-combustion CO2 capture using amine-based absorption process for blue H2 production from steam methane reformer[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 262: 115632. |
| [28] | Kvamsdal H M, Rochelle G T. Effects of the temperature bulge in CO2 absorption from flue gas by aqueous monoethanolamine[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008, 47(3): 867-875. |
| [29] | Abdin Z, Webb C J, Gray E M. Modelling and simulation of an alkaline electrolyser cell[J]. Energy, 2017, 138: 316-331. |
| [30] | Sánchez M, Amores E, Abad D, et al. Aspen Plus model of an alkaline electrolysis system for hydrogen production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(7): 3916-3929. |
| [31] | Assunção R, Eckl F, Ramos C P, et al. Oxygen liquefaction economical value in the development of the hydrogen economy[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 62: 109-118. |
| [32] | Peters M S, Timmerhaus K D. Plant Design and Economics for Chemical Engineers[M]. 4th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1992: 137-294. |
| [33] | Kum J, Oh H T, Park J, et al. Techno-economic analysis and optimization of a CO2 absorption process with a solvent looping system at the absorber using an MDEA/PZ blended solvent for steam methane reforming[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 455: 140685. |
| [34] | 王驰中, 高鑫, 陈衡, 等. 中国各地区光伏发电平价上网成本效益综合分析[J]. 可再生能源, 2024, 42(10): 1295-1301. |
| Wang C Z, Gao X, Chen H, et al. Comprehensive cost-benefit analysis of photovoltaic power grid parity in various regions of China[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2024, 42(10): 1295-1301. |
| [1] | 吴成云, 孙浩然. 民用飞机空调系统性能仿真与燃油代偿损失研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 351-359. |
| [2] | 周怀荣, 伊嘉伟, 曹阿波, 郭奥雪, 王东亮, 杨勇, 杨思宇. 共电解耦合CO2间接加氢制甲醇工艺集成设计与性能评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4586-4600. |
| [3] | 田鹏, 张忠林, 任超, 孟国超, 郝晓刚, 刘叶刚, 侯起旺, ABUDULA Abuliti, 官国清. 基于自热再生的一种低温甲醇洗工艺建模与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4601-4612. |
| [4] | 邹家庆, 张肇钰, 张建国, 张博宇, 刘定胜, 毛庆, 王挺, 李建军. 碱水制氢电解槽极板通道中气泡的生成及演化性质[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4786-4799. |
| [5] | 周奕彤, 周明熙, 刘若晨, 叶爽, 黄伟光. 光伏与电网协同驱动氢基直接还原铁炼钢的技术经济分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4318-4330. |
| [6] | 范夏雨, 孙建辰, 李可莹, 姚馨雅, 商辉. 机器学习驱动液态有机储氢技术的系统优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [7] | 杨宁, 李皓男, LIN Xiao, GEORGIADOU Stella, LIN Wen-Feng. 从塑料废弃物到能源催化剂:塑料衍生碳@CoMoO4复合材料在电解水析氢反应中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4081-4094. |
| [8] | 王御风, 罗小雪, 范鸿亮, 吴白婧, 李存璞, 魏子栋. 耦合电解水制氢的绿色有机电合成——电极界面调控策略综述[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3753-3771. |
| [9] | 刘沁雯, 叶恒冰, 张逸伟, 朱法华, 钟文琪. 煤与禽类粪便混合燃料的加压富氧燃烧特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3487-3497. |
| [10] | 高照, 吴熙, 夏丹, 张霖宙. 石油加工分子管理平台热力学及分离单元模块开发[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3212-3225. |
| [11] | 陈佳祥, 周伟, 张学伟, 王丽杰, 黄玉明, 于洋, 孙苗婷, 李宛静, 袁骏舒, 张宏博, 孟晓晓, 高继慧, 赵广播. 脉冲电压下二维PEMWE模型的制氢特性仿真研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3521-3530. |
| [12] | 吴天灏, 叶霆威, 林延, 黄振. 生物质化学链气化原位补氢制H2/CO可控合成气[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3498-3508. |
| [13] | 廖鹏伟, 刘庆辉, 潘安, 王嘉岳, 符小贵, 杨思宇, 余皓. 考虑不确定性的风电制氢系统:多时间尺度运行策略[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2743-2754. |
| [14] | 张涵川, 尚超, 吕文祥, 黄德先, 张亚宁. 基于无监督时序聚类的催化裂化装置工况划分识别与产率预测方法[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2781-2790. |
| [15] | 宋粉红, 王文光, 郭亮, 范晶. C元素修饰g-C3N4对TiO2的调控及复合材料光催化产氢性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2983-2994. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号