化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (7): 3498-3508.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241392
吴天灏1,2( ), 叶霆威2, 林延1,2, 黄振1,2(
), 叶霆威2, 林延1,2, 黄振1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-02
修回日期:2024-12-27
出版日期:2025-07-25
发布日期:2025-08-13
通讯作者:
黄振
作者简介:吴天灏(2000—),男,硕士研究生,wuth@ms.giec.ac.cn
基金资助:
Tianhao WU1,2( ), Tingwei YE2, Yan LIN1,2, Zhen HUANG1,2(
), Tingwei YE2, Yan LIN1,2, Zhen HUANG1,2( )
)
Received:2024-12-02
Revised:2024-12-27
Online:2025-07-25
Published:2025-08-13
Contact:
Zhen HUANG
摘要:
提出一种通过生物质化学链气化(biomass chemical looping gasification,BCLG)耦合水蒸气化学链重整制氢(chemical looping reforming hydrogen production,CLRHP)制备H2/CO可控合成气的生物质化学链气化原位补氢(BCLG-CLRHP)的新型技术。以NiFe2O4(ZrO2)为载氧体,在反应温度为900℃,晶格氧(OC)和生物质(B)的质量比为0.5时,合成气产率最高,为0.61 L/g(生物质)。在BCLG过程中,蒸汽(S)和生物质(B)的质量比为0.24时,生物质碳转化率为92%,载氧体还原程度较高且BCLG过程产生的合成气中H2/CO达1.0,表明水蒸气的添加显著提高了生物质碳转化率和合成气中的H2/CO。在CLRHP过程中调控水蒸气含量,可以制备高浓度H2,同时整合BCLG与CLRHP过程产生的气体,可获得H2/CO达2.2,CO2/CO为0.67的清洁合成气。在15次循环实验后,BCLG-CLRHP过程制备的合成气中H2/CO为1.8,CO2/CO为0.71。所提出的方法可以潜在地应用于提供具有H2/CO为1.0~2.2的清洁合成气,用于各种合成过程,例如费托合成、乙酸和羰基合成。
中图分类号:
吴天灏, 叶霆威, 林延, 黄振. 生物质化学链气化原位补氢制H2/CO可控合成气[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3498-3508.
Tianhao WU, Tingwei YE, Yan LIN, Zhen HUANG. In-situ hydrogen supplementation of biomass chemical looping gasification to produce syngas with controllable H2/CO[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3498-3508.
| 元素分析/% | 工业分析/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | N | S | 灰分 | 挥发分 | 固定碳 |
| 49.69 | 6.51 | 43.75 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.61 | 85.7 | 13.69 |
表1 松木的元素分析和工业分析(干基)
Table 1 Proximate analysis and ultimate analysis of pine wood (dried basis)
| 元素分析/% | 工业分析/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | N | S | 灰分 | 挥发分 | 固定碳 |
| 49.69 | 6.51 | 43.75 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.61 | 85.7 | 13.69 |
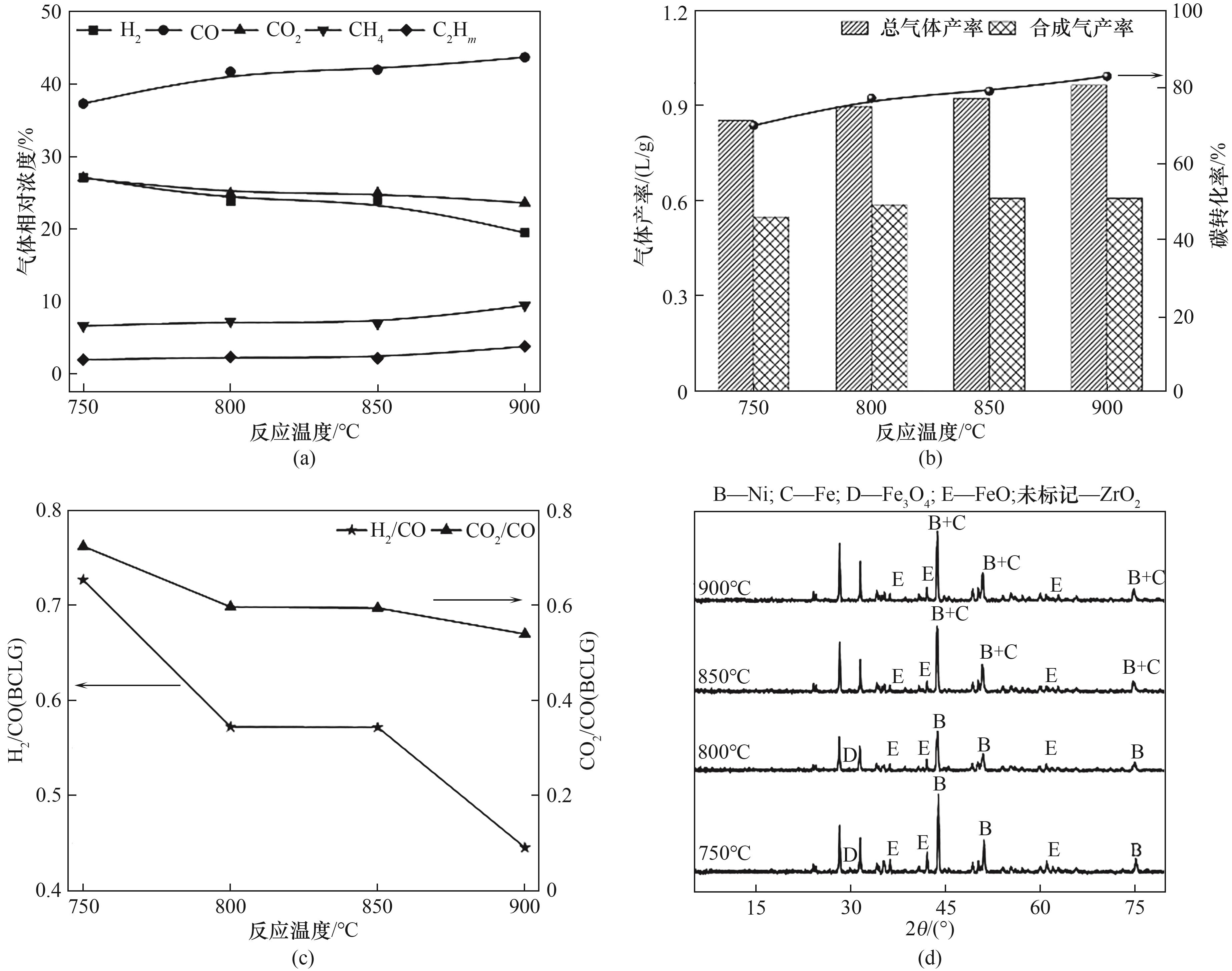
图3 (a)反应温度对BCLG过程气体产物的影响;(b)反应温度对BCLG过程碳转化率以及气体产率的影响;(c)反应温度对BCLG产生合成气中H2/CO以及CO2/CO的影响;(d)不同反应温度反应后载氧体的XRD谱图
Fig.3 (a) Effect of reaction temperature on the gas products of the BCLG process; (b) Effect of reaction temperature on the carbon conversion and gas yield of the BCLG process; (c) Effect of reaction temperature on the H2/CO and CO2/CO in the syngas produced by BCLG; (d) XRD patterns of the OCs after the reaction at different reaction temperatures
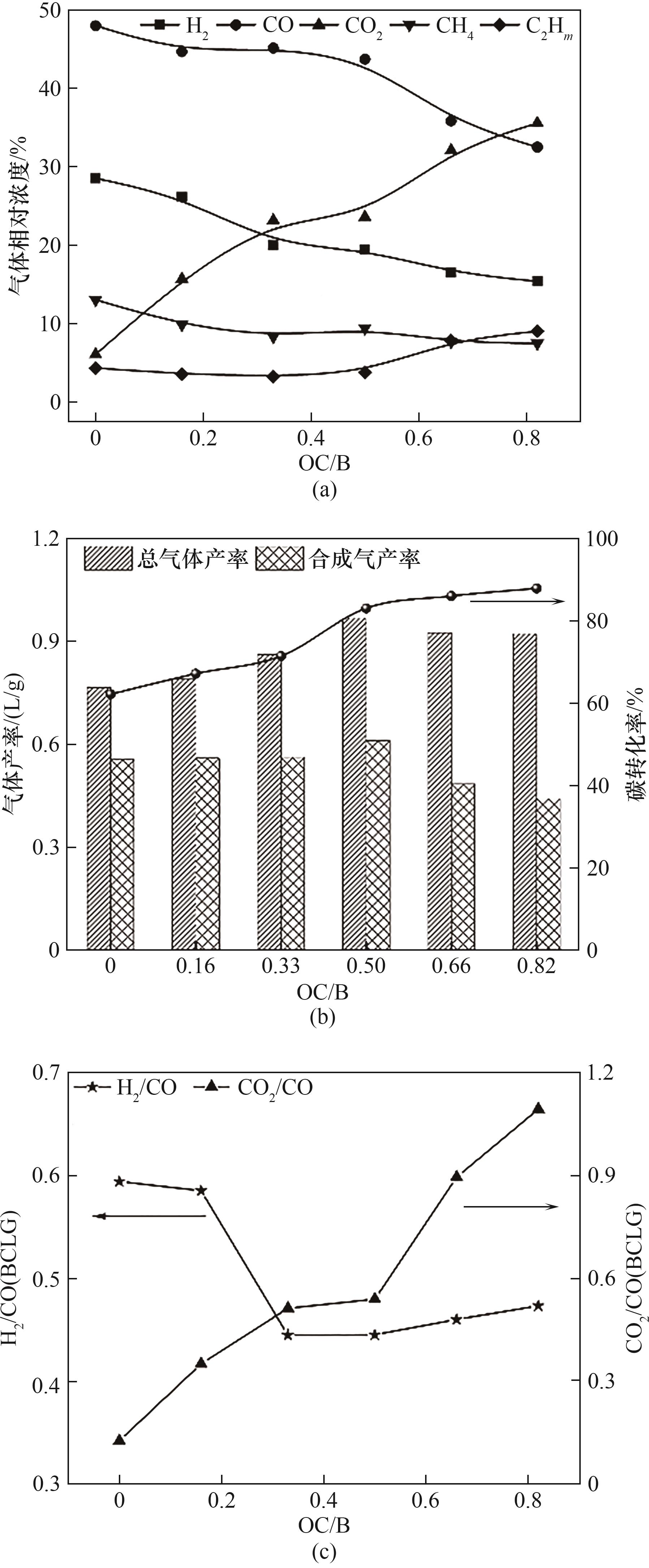
图4 (a)OC/B对BCLG过程气体产物的影响;(b)OC/B对BCLG过程碳转化率以及气体产率的影响;(c)OC/B对BCLG产生合成气中H2/CO以及CO2/CO的影响
Fig.4 (a) Effect of OC/B on gas products of BCLG process; (b) Effect of OC/B on carbon conversion and gas yield of BCLG process; (c) Effect of OC/B on H2/CO and CO2/CO in syngas produced by BCLG
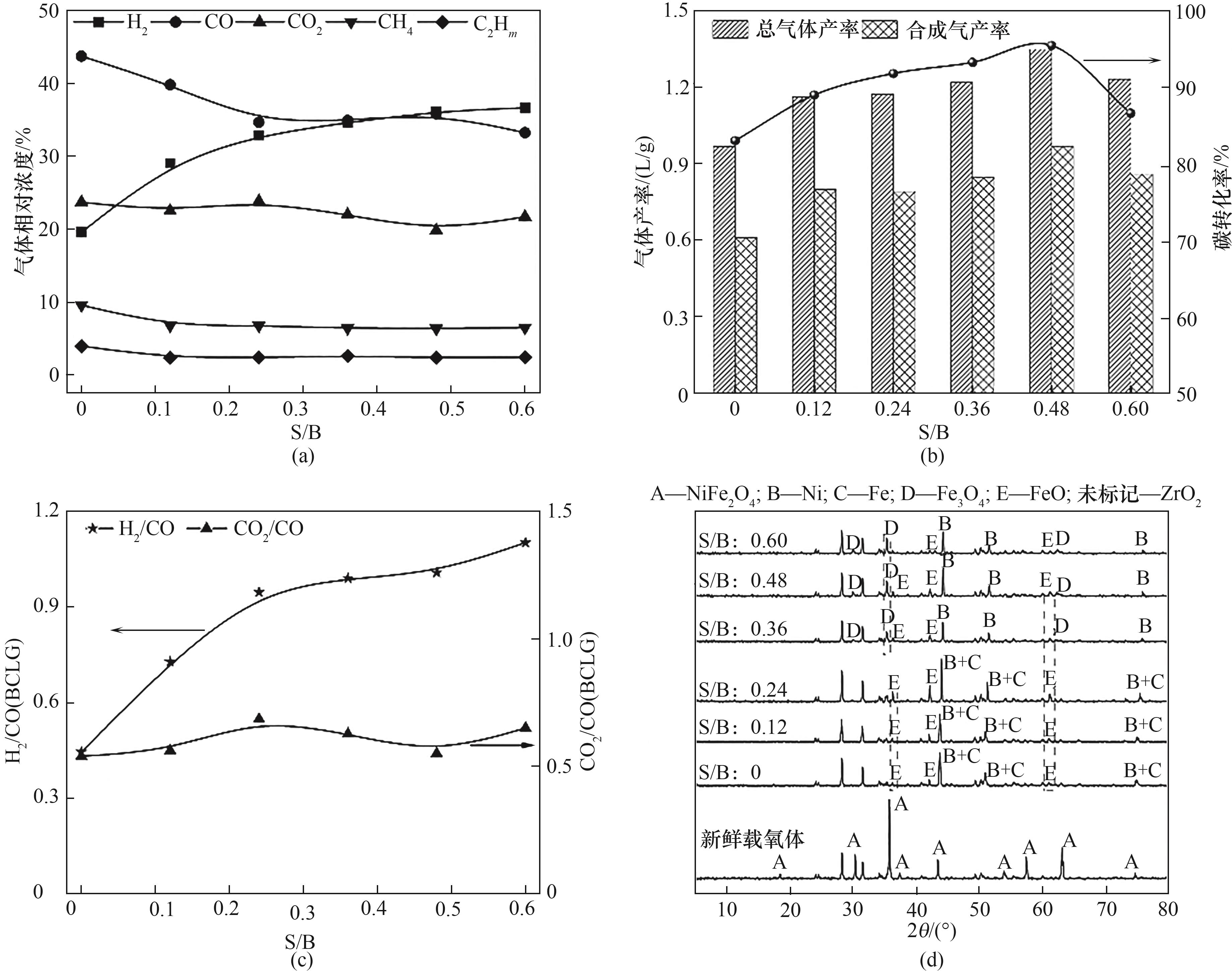
图5 (a)S/B对BCLG过程气体产物的影响;(b)S/B对BCLG过程碳转化率以及气体产率的影响;(c)S/B对BCLG产生合成气中H2/CO以及CO2/CO的影响;(d)不同S/B反应后载氧体的XRD谱图
Fig.5 (a) Effect of S/B on the gas products of BCLG process; (b) Effect of S/B on the carbon conversion as well as the gas yield of BCLG process; (c) Effect of S/B on the H2/CO as well as the CO2/CO in the syngas produced by BCLG; (d) XRD profiles of the OCs after the reaction with different S/B
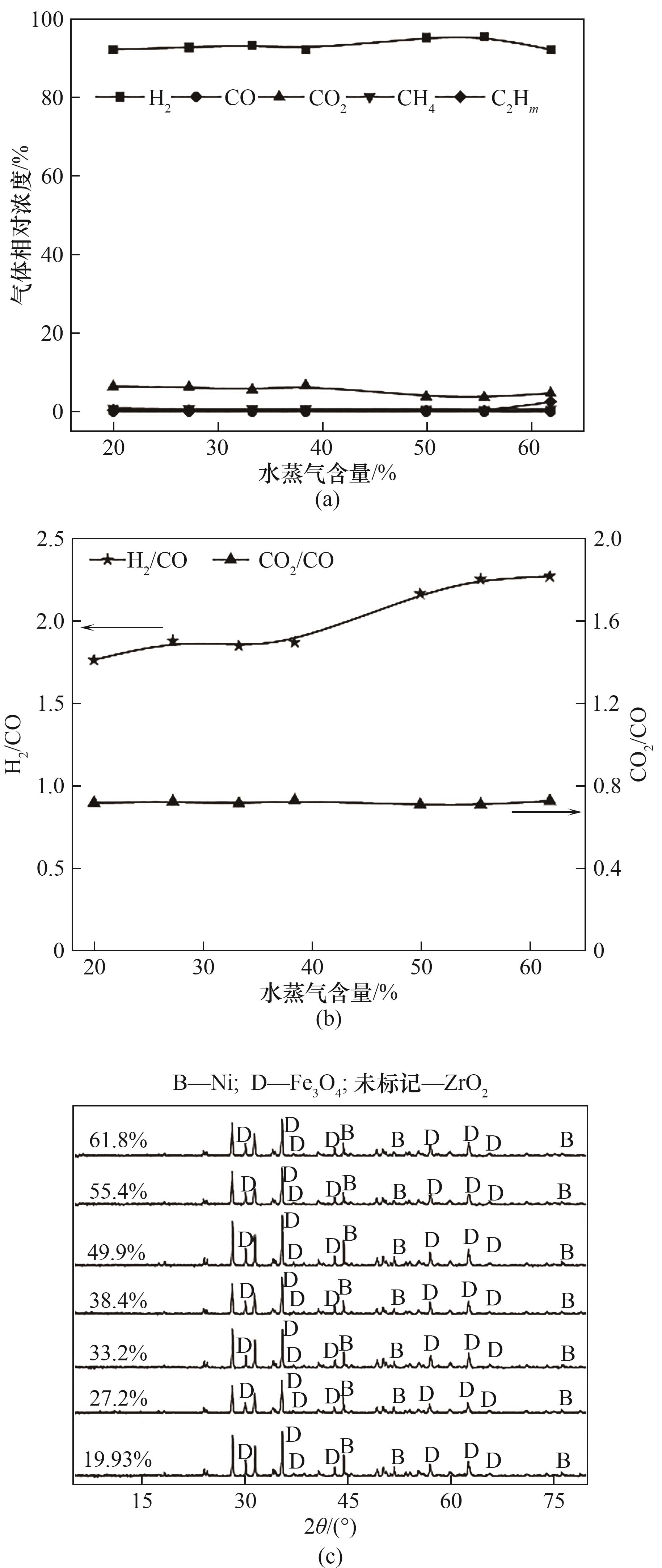
图6 (a)水蒸气浓度对CLRHP气体产物相对浓度的影响;(b)S/B对总合成气中H2/CO以及CO2/CO的影响;(c)不同蒸汽浓度反应后载氧体的XRD谱图
Fig.6 (a) Effect of steam concentration on the relative concentration of CLRHP gas products; (b) Effect of S/B on the H2/CO as well as the CO2/CO in the total syngas; (c) XRD patterns of the OCs after the reaction with different vapor concentrations
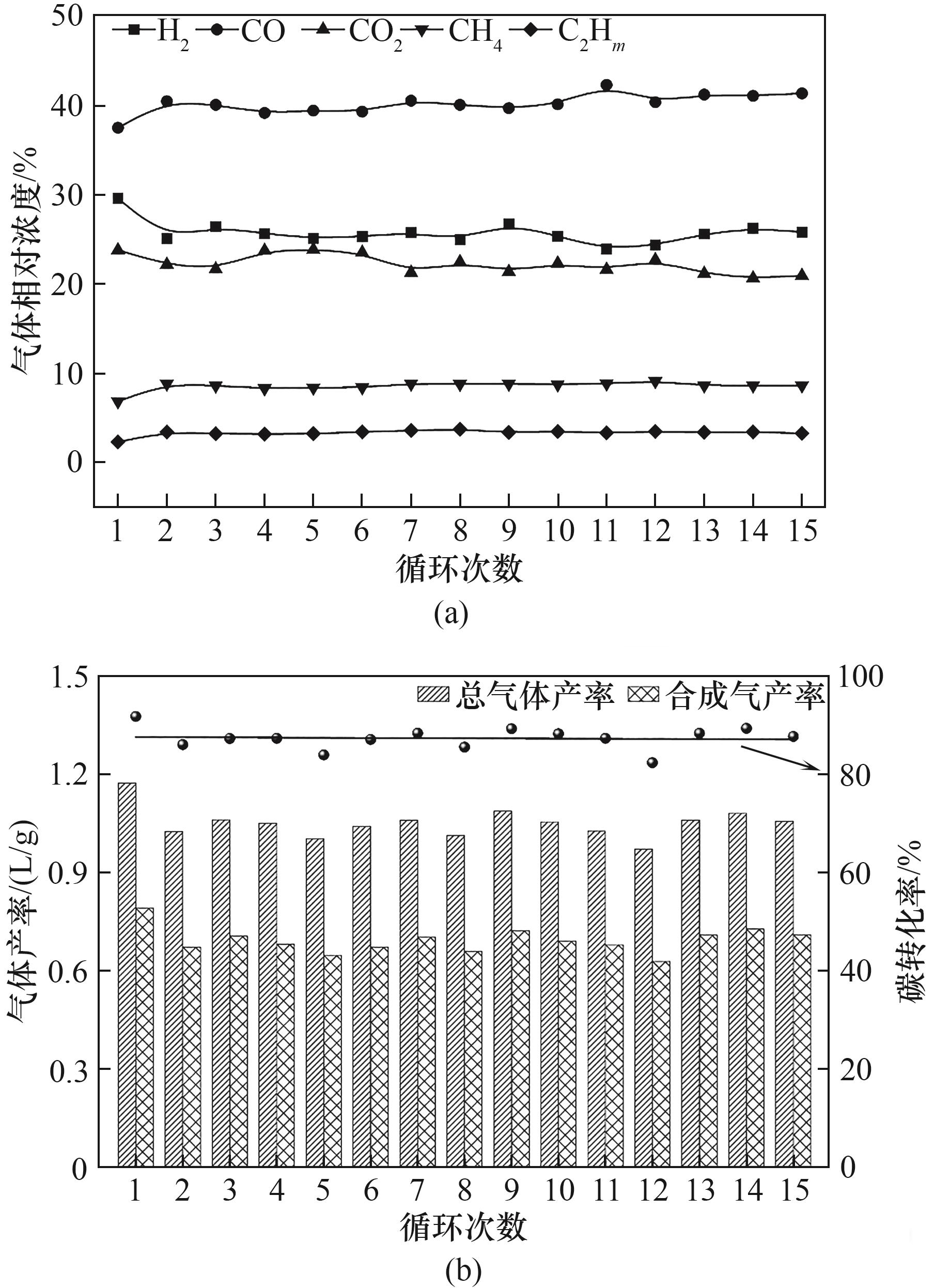
图7 (a)循环次数对BCLG过程气体产物的影响;(b)循环次数对BCLG过程碳转化率以及气体产率的影响
Fig.7 (a) Effect of the number of cycles on the gas product of the BCLG process; (b) Effect of the number of cycles on the carbon conversion rate as well as the gas yield of the BCLG process
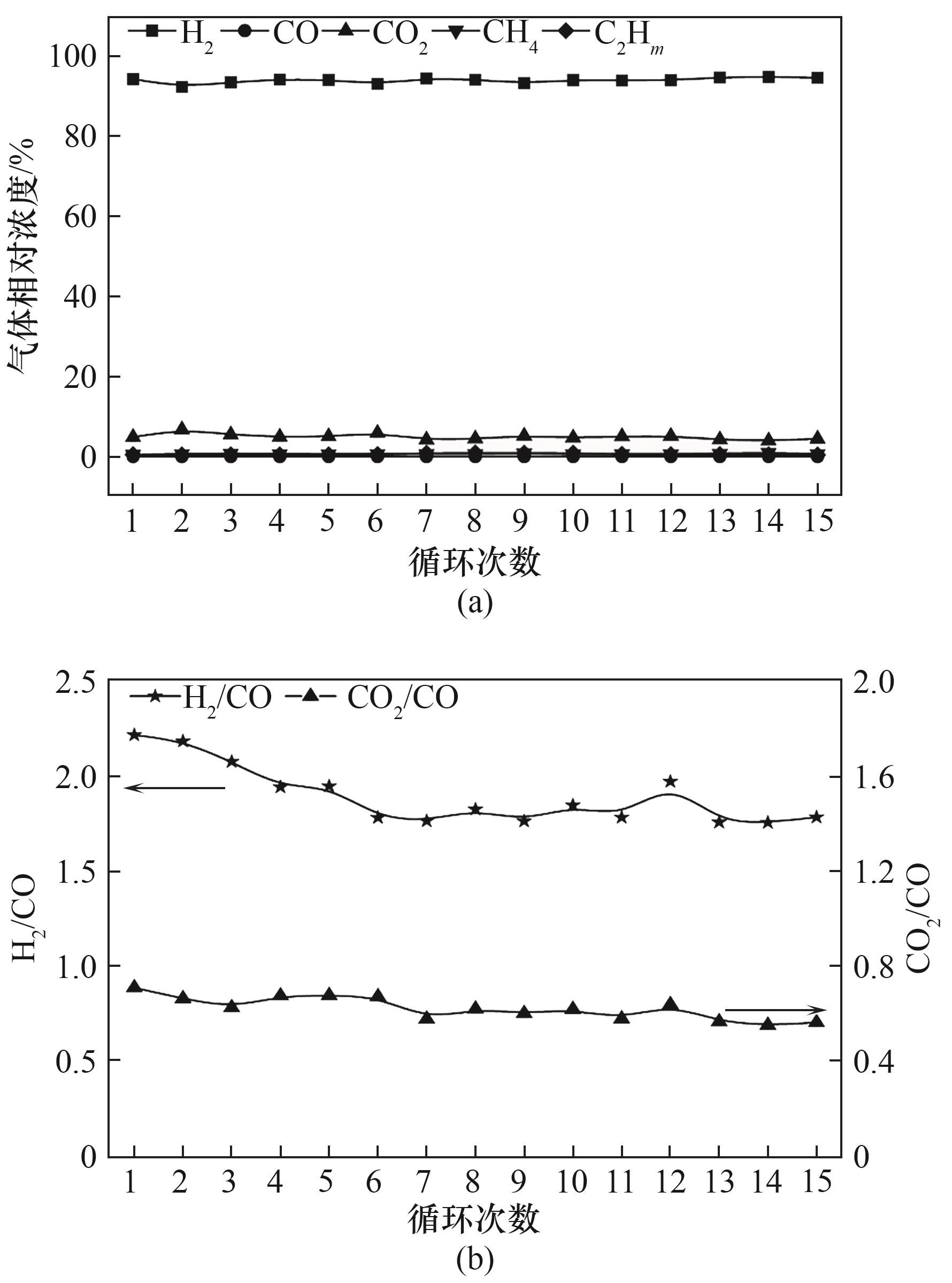
图8 (a)循环次数对CLRHP过程气体产物的影响;(b)循环次数对BCLG-CLRHP总合成气中H2/CO以及CO2/CO的影响
Fig.8 (a) Effect of the number of cycles on the gas products of the CLRHP process; (b) Effect of the number of cycles on the H2/CO as well as the CO2/CO in the total synthesis gas of BCLG-CLRHP
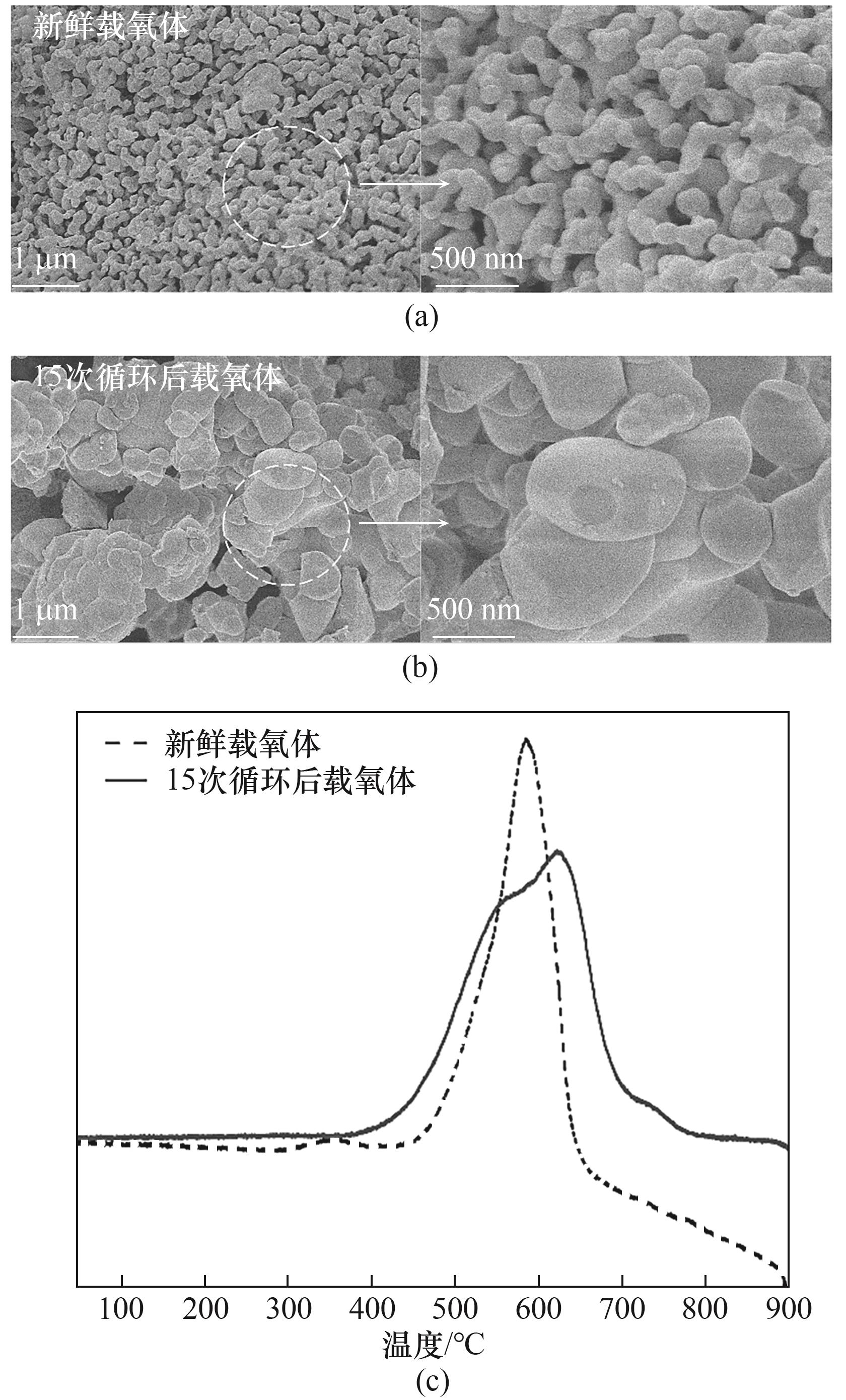
图10 (a)新鲜载氧体的SEM分析;(b)循环15次后载氧体的SEM分析;(c)新鲜和循环后的载氧体的H2-TPR曲线
Fig.10 (a) SEM analysis of fresh OCs; (b) SEM analysis of OCs after 15 cycles; (c) H2-TPR curves of fresh and cycled OCs
| [1] | Zhu X, Zhang M Y, Li K Z, et al. Chemical-looping water splitting over ceria-modified iron oxide: performance evolution and element migration during redox cycling[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 179: 92-103. |
| [2] | 李攀, 马腾杰, 林钰程, 等. 生物质热化学转化制氢技术研究进展[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45(10): 645-654. |
| Li P, Ma T J, Lin Y C, et al. Advancements in hydrogen production from biomass thermochemical conversion[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2024, 45(10): 645-654. | |
| [3] | 姚彬, 张文存, 朱瑞龙. 生物质能源制备合成气的技术探讨及研究现状[J]. 现代化工, 2021, 41(5): 54-58. |
| Yao B, Zhang W C, Zhu R L. Technical discussion and research status of syngas from biomass energy[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2021, 41(5): 54-58. | |
| [4] | Tong A, Bayham S, Kathe M V, et al. Iron-based syngas chemical looping process and coal-direct chemical looping process development at Ohio State University[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 113: 1836-1845. |
| [5] | Wang S, Wu F, Wang X D. Experimental and kinetics analysis on biomass chemical looping gasification using lean iron ore as oxygen carrier[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 474: 145855. |
| [6] | 何笑, 刘晶晶, 李文瑶, 等. 玉米秸秆化学链热解过程铁基复合载氧体的载氧-催化性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(10): 4153-4163. |
| He X, Liu J J, Li W Y, et al. Oxygen-carrying and catalytic properties of iron-based composite oxygen carrier for chemical looping pyrolysis of corn stalk[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(10): 4153-4163. | |
| [7] | 仉利, 姚宗路, 赵立欣, 等. 生物质热化学转化提质及其催化剂研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(8): 3416-3427. |
| Zhang L, Yao Z L, Zhao L X, et al. Research progress on thermochemical conversion of biomass to enhance quality and catalyst[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(8): 3416-3427. | |
| [8] | Abdalla A, Farooqui A, Mohamedali M, et al. Copper-based chemical looping air separation process: thermodynamics, kinetic modeling, and simulation of the fluidized beds[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024, 335: 126149. |
| [9] | Chen J, Zhao K, Zhao Z L, et al. Reaction schemes of barium ferrite in biomass chemical looping gasification for hydrogen-enriched syngas generation via an outer-inner looping redox reaction mechanism[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2019, 189: 81-90. |
| [10] | Ren S J, Wu S L, Weng Q H. Physics-informed machine learning methods for biomass gasification modeling by considering monotonic relationships[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 369: 128472. |
| [11] | Wu S L, Kang D, Zhang H Y, et al. The oxidation characteristics of furan derivatives and binary TPGME blends under engine relevant conditions[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2019, 37(4): 4635-4643. |
| [12] | 沈天绪, 沈来宏. 基于3kW塔式串行流化床差异燃料的化学链燃烧解析[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(1): 138-147. |
| Shen T X, Shen L H. Investigation of multi-fuel chemical looping combustion in a 3kW interconnected fluidized bed reactors[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(1): 138-147. | |
| [13] | 汪德成, 金保昇, 金朝阳, 等. 松木屑与废橡胶化学链共气化特性试验[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(3): 956-965. |
| Wang D C, Jin B S, Jin Z Y, et al. High hydrogen syngas production from chemical looping co-gasification of sawdust and waste tires[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2020, 39(3): 956-965. | |
| [14] | Liu G, Sun Z S, Zhao H R, et al. Chemical looping reforming of toluene as bio-oil model compound via NiFe2O4@SBA-15 for hydrogen-rich syngas production[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2023, 174: 106851. |
| [15] | Liu S, He F, Huang Z, et al. Screening of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles as oxygen carrier in chemical looping hydrogen production[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2016, 30(5): 4251-4262. |
| [16] | Sun G Z, Liang W Z, Wang K, et al. Investigation on hydrogen-rich syngas preparation from high wet sludge mixed with sawdust based on iron oxygen carrier[J]. Fuel, 2023, 343: 127853. |
| [17] | 颜蓓蓓, 李志宇, 李健, 等. 生物质化学链气化氧载体的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(10): 3956-3965. |
| Yan B B, Li Z Y, Li J, et al. Research progress of oxygen carrier in biomass chemical looping gasification[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2020, 39(10): 3956-3965. | |
| [18] | Zhao H B, Guo L, Zou X X. Chemical-looping auto-thermal reforming of biomass using Cu-based oxygen carrier[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 157: 408-415. |
| [19] | Dou B L, Zhang H, Cui G M, et al. Hydrogen production and reduction of Ni-based oxygen carriers during chemical looping steam reforming of ethanol in a fixed-bed reactor[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(42): 26217-26230. |
| [20] | Niu Y H, Chi Z Y, Li M. Advancements in biomass gasification research utilizing iron-based oxygen carriers in chemical looping: a review[J]. Materials Reports: Energy, 2024, 4(3): 100282. |
| [21] | Ji J Q, Shen L H. Rational design of enhanced oxygen deficiency-enriched NiFe2O4 embedded in silica matrix as oxygen carriers for high-quality syngas production via biomass chemical looping gasification (BCLG)[J]. Energy, 2024, 310: 133199. |
| [22] | Ge H J, Guo W J, Shen L H, et al. Biomass gasification using chemical looping in a 25kWth reactor with natural hematite as oxygen carrier[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 286: 174-183. |
| [23] | He F, Huang Z, Wei G Q, et al. Biomass chemical-looping gasification coupled with water/CO2-splitting using NiFe2O4 as an oxygen carrier[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2019, 201: 112157. |
| [24] | Huang Z, He F, Feng Y P, et al. Synthesis gas production through biomass direct chemical looping conversion with natural hematite as an oxygen carrier[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 140: 138-145. |
| [25] | Huang Z, Zheng A Q, Deng Z B, et al. In-situ removal of toluene as a biomass tar model compound using NiFe2O4 for application in chemical looping gasification oxygen carrier[J]. Energy, 2020, 190: 116360. |
| [26] | Hsieh T L, Zhang Y T, Xu D K, et al. Chemical looping gasification for producing high purity, H2-rich syngas in a cocurrent moving bed reducer with coal and methane cofeeds[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(7): 2461-2475. |
| [27] | Liu G C, Liao Y F, Wu Y T, et al. Synthesis gas production from microalgae gasification in the presence of Fe2O3 oxygen carrier and CaO additive[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 212: 955-965. |
| [28] | Liu G C, Liao Y F, Wu Y T, et al. Characteristics of microalgae gasification through chemical looping in the presence of steam[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(36): 22730-22742. |
| [29] | Cheng D Y, Yong Q R, Zhao Y C, et al. Study on the interaction of the Fe-based oxygen carrier with ashes[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2020, 34(8): 9796-9809. |
| [30] | Gao Z X, Zeng D W, Wu S L, et al. High-purity hydrogen production from real biomass pyrolysis vapors via a chemical looping process[J]. Sustainable Energy & Fuels, 2023, 7(9): 2200-2208. |
| [31] | Zhen H, Wang Y H, Fang S W, et al. Chemical looping gasification of benzene as a biomass tar model compound using hematite modified by Ni as an oxygen carrier[J]. Applications in Energy and Combustion Science, 2023, 15: 100172. |
| [32] | Zheng Z M, Luo L X, Feng A W, et al. CaO-assisted alkaline liquid waste drives corn stalk chemical looping gasification for hydrogen production[J]. ACS Omega, 2020, 5(38): 24403-24411. |
| [33] | Hu Q, Shen Y, Chew J W, et al. Chemical looping gasification of biomass with Fe2O3/CaO as the oxygen carrier for hydrogen-enriched syngas production[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 379: 122346. |
| [34] | Wei G Q, Zhao W N, Meng J G, et al. Hydrogen production from vegetable oil via a chemical looping process with hematite oxygen carriers[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 200: 588-597. |
| [35] | Huang Z, Deng Z B, He F, et al. Reactivity investigation on chemical looping gasification of biomass char using nickel ferrite oxygen carrier[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(21): 14458-14470. |
| [36] | Huang Z, Zhang Y, Fu J J, et al. Chemical looping gasification of biomass char using iron ore as an oxygen carrier[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(40): 17871-17883. |
| [1] | 陈佳祥, 周伟, 张学伟, 王丽杰, 黄玉明, 于洋, 孙苗婷, 李宛静, 袁骏舒, 张宏博, 孟晓晓, 高继慧, 赵广播. 脉冲电压下二维PEMWE模型的制氢特性仿真研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3521-3530. |
| [2] | 刘沁雯, 叶恒冰, 张逸伟, 朱法华, 钟文琪. 煤与禽类粪便混合燃料的加压富氧燃烧特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3487-3497. |
| [3] | 陆昕晟, 郭晓镭, 王世丞, 陆海峰, 刘海峰. 秸秆类生物质的粉碎特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3539-3551. |
| [4] | 廖鹏伟, 刘庆辉, 潘安, 王嘉岳, 符小贵, 杨思宇, 余皓. 考虑不确定性的风电制氢系统:多时间尺度运行策略[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2743-2754. |
| [5] | 张畅, 解强, 沙雨桐, 王炳杰, 梁鼎成, 刘金昌. 低灰低硅竹炭的制备及衍生硬炭的电化学性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 3073-3083. |
| [6] | 宋粉红, 王文光, 郭亮, 范晶. C元素修饰g-C3N4对TiO2的调控及复合材料光催化产氢性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2983-2994. |
| [7] | 姬海燕, 刘家印, 吴海军, 何璟琳, 靳紫恒, 魏钿航, 江霞. 低温等离子体在生物质气化制氢中的应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2419-2433. |
| [8] | 赵鹏飞, 戚若玫, 郭新锋, 方虎, 徐庐飞, 李潇, 林今. 千标方级碱性水电解制氢系统氧中氢杂质分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1765-1778. |
| [9] | 陶智能, 邱彤, 王保国. 阴离子交换膜电解水制氢稳态建模[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1711-1721. |
| [10] | 戴文智, 沈雄健, 宋晓博, 杨新乐. 生物质双级蒸发双回热有机朗肯循环系统环境分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1230-1242. |
| [11] | 万俊, 宋佳芮, 范春煌, 魏乐乐, 聂依娜, 刘琳. 高效空穴转移助力光催化碱性甲醇-水溶液制氢[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1064-1075. |
| [12] | 李京润, 杨思宇, 刘庆辉, 潘安, 王嘉岳, 符小贵, 余皓. 大规模风电耦合火电制氢多情景下不同运行策略分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1191-1206. |
| [13] | 白谨豪, 管小平, 杨宁. 压滤式水电解槽乳突板内的流动特性分析与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 584-595. |
| [14] | 张珂, 任维杰, 王梦娜, 范凯锋, 常丽萍, 李佳斌, 马涛, 田晋平. Bunsen反应产物在微通道中的液-液两相混合特性[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 623-636. |
| [15] | 殷梦凡, 王倩, 郑涛, 姬奎, 王绍贵, 郭辉, 林志强, 张睿, 孙晖, 刘海燕, 刘植昌, 徐春明, 孟祥海, 王月平. 可再生能源电解水制氢-低温低压合成氨万吨级工业示范流程设计[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 825-834. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号