• •
刚洁1( ), 唐竟耀1, 张成勇2, 陈彩霞2, 关云山1, 吕红梅1, 张卫东1(
), 唐竟耀1, 张成勇2, 陈彩霞2, 关云山1, 吕红梅1, 张卫东1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-11-11
修回日期:2025-12-15
出版日期:2026-01-19
通讯作者:
张卫东
作者简介:刚洁(1999—),女,硕士研究生,gangjie0251@163.com
基金资助:
Jie GANG1( ), Jingyao TANG1, Chengyong ZHANG2, Caixia CHEN2, Yunshan GUAN1, Hongmei LV1, Weidong ZHANG1(
), Jingyao TANG1, Chengyong ZHANG2, Caixia CHEN2, Yunshan GUAN1, Hongmei LV1, Weidong ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2025-11-11
Revised:2025-12-15
Online:2026-01-19
Contact:
Weidong ZHANG
摘要:
首先构建了硼物种分布三维图,系统阐明了不同初始浓度与pH协同作用下各硼形态的分布规律。在此基础上,成功合成一种磁性氢氧化铬基硼吸附材料。通过FT-IR和XPS等表征手段确认Cr–OH为关键活性位点。此外,结合Raman光谱技术,揭示了该材料对B(OH)₃和B(OH)
中图分类号:
刚洁, 唐竟耀, 张成勇, 陈彩霞, 关云山, 吕红梅, 张卫东. 磁性氢氧化铬硼吸附剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251251.
Jie GANG, Jingyao TANG, Chengyong ZHANG, Caixia CHEN, Yunshan GUAN, Hongmei LV, Weidong ZHANG. Preparation and Performance Study of Magnetic Chromium hydroxide Boron Adsorbent[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251251.
| 吸附剂 | pH | Qe/(mmol·g-1) | c0/(mol·L-1) | 脱附再生条件 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氧化镁 | 9 | 4.23 | 0.019 | 350 ℃煅烧 | [ |
| 8 | 3.98 | ||||
| 5 | 3.7 | ||||
| 氢氧化镍 | 9 | 2.04 | 0.019 | 0.05 mol·L-1 NaOH | [ |
| 8 | 1.85 | ||||
| 5 | 1.67 | ||||
| E-氢氧化镍 | 9 | 2.92 | 0.019 | 0.05 mol·L-1 NaOH | [ |
| 氢氧化锆 | 9 | 1.79 | 0.019 | 0.5 mol·L-1 NaOH | [ |
| 8 | 0.93 | ||||
| 5 | 0.60 | ||||
| 氢氧化铬 | 8 | 1.94 | 0.08 | pH=12 水溶液 | 本文 |
| 5 | 0.7 | 0.08 | pH=12 水溶液 | ||
| 8 | 0.65 | 0.019 | pH=12 水溶液 |
表1 金属氧化物和氢氧化物吸附硼的性能比较
Table 1 Comparison of the performance of metal oxides and hydroxides in adsorbing boron
| 吸附剂 | pH | Qe/(mmol·g-1) | c0/(mol·L-1) | 脱附再生条件 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氧化镁 | 9 | 4.23 | 0.019 | 350 ℃煅烧 | [ |
| 8 | 3.98 | ||||
| 5 | 3.7 | ||||
| 氢氧化镍 | 9 | 2.04 | 0.019 | 0.05 mol·L-1 NaOH | [ |
| 8 | 1.85 | ||||
| 5 | 1.67 | ||||
| E-氢氧化镍 | 9 | 2.92 | 0.019 | 0.05 mol·L-1 NaOH | [ |
| 氢氧化锆 | 9 | 1.79 | 0.019 | 0.5 mol·L-1 NaOH | [ |
| 8 | 0.93 | ||||
| 5 | 0.60 | ||||
| 氢氧化铬 | 8 | 1.94 | 0.08 | pH=12 水溶液 | 本文 |
| 5 | 0.7 | 0.08 | pH=12 水溶液 | ||
| 8 | 0.65 | 0.019 | pH=12 水溶液 |
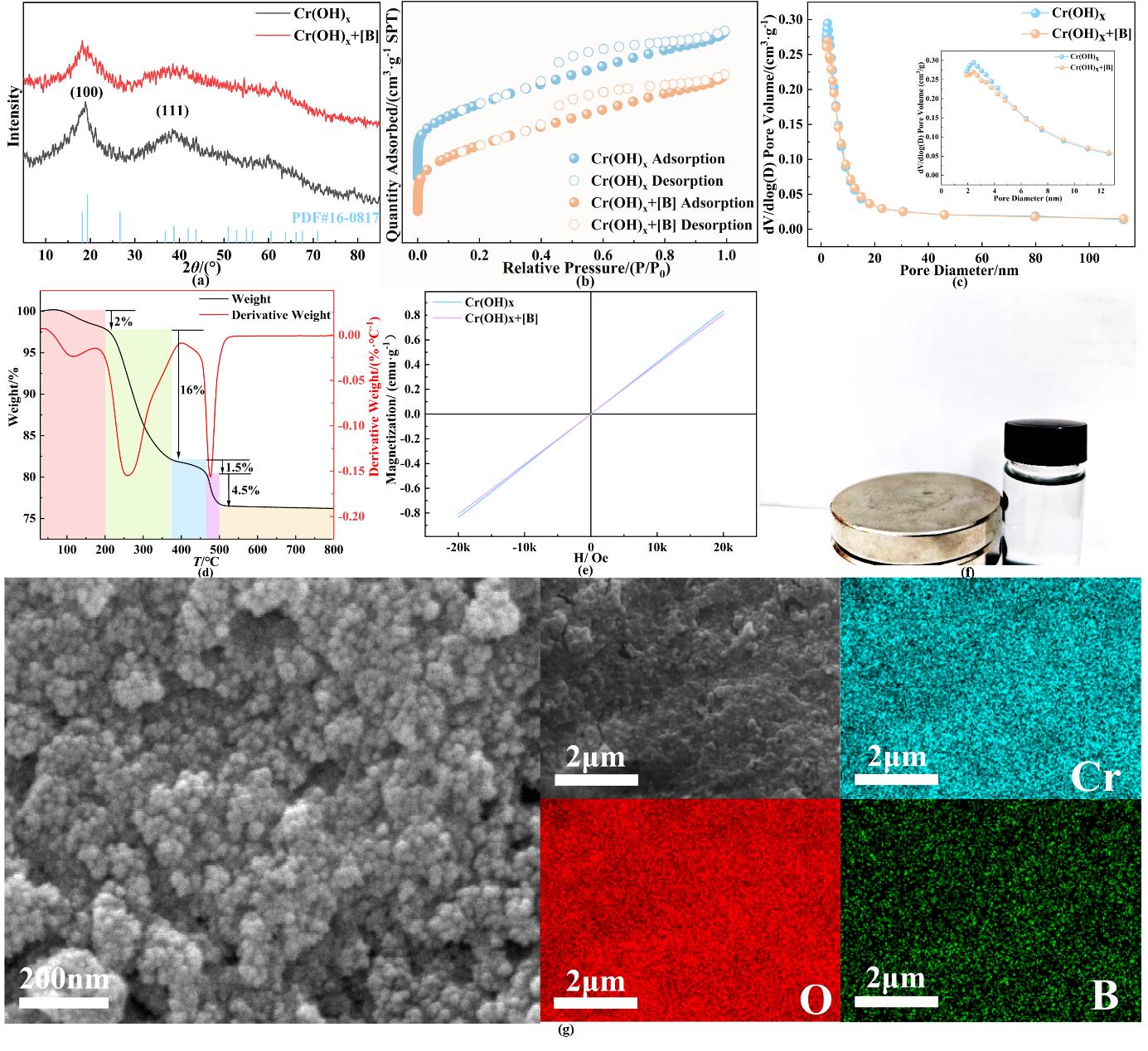
图1 Cr(OH)x吸附剂的(a)PXRD;(b)氮气吸附-脱附等温线;(c)孔径分布图;(d)TGA;(e)磁滞回线;(f)磁性吸附体系实物图;(g)扫描电镜图片及其元素组成注:Cr (OH)x adsorbents
Fig. 1 (a) PXRD; (b) Nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms; (c) Pore size distribution diagram; (d) TGA; (e) Hysteresis loop; (f) Physical diagram of the magnetic adsorption system; and (g) SEM images and EDS-mapping of as-prepared
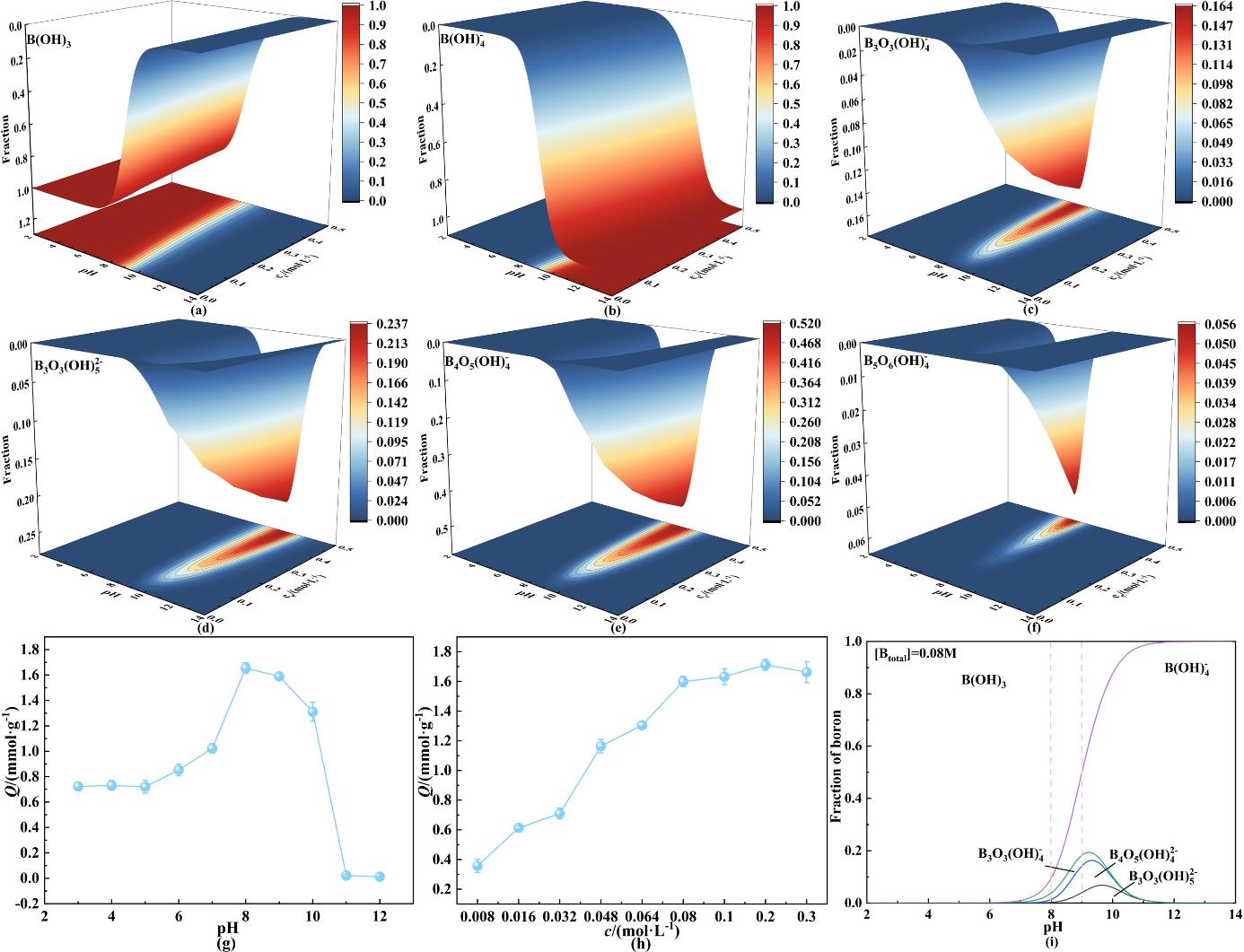
图2 (a-f) B(OH)₃、B(OH)4-、B₃O₃(OH)4-、B₃O₃(OH)52-、B₄O₅(OH)42-和B₅O₆(OH)4-分布含量图;(g) pH对吸附性能的影响;(h)浓度对吸附性能的影响;(i) 0.08 mol·L-1硼酸溶液中硼物种的含量积分
Fig. 2 (a-f) Distribution of B(OH)₃, B(OH)4-, B₃O₃(OH)4-, B₃O₃(OH)52-, B₄O₅(OH)42-, and B₅O₆(OH)4-; (g) pH effect on adsorption; (h) Concentration effect on adsorption; (i) integral of boron content in 0.08 mol·L-1 boric acid solution
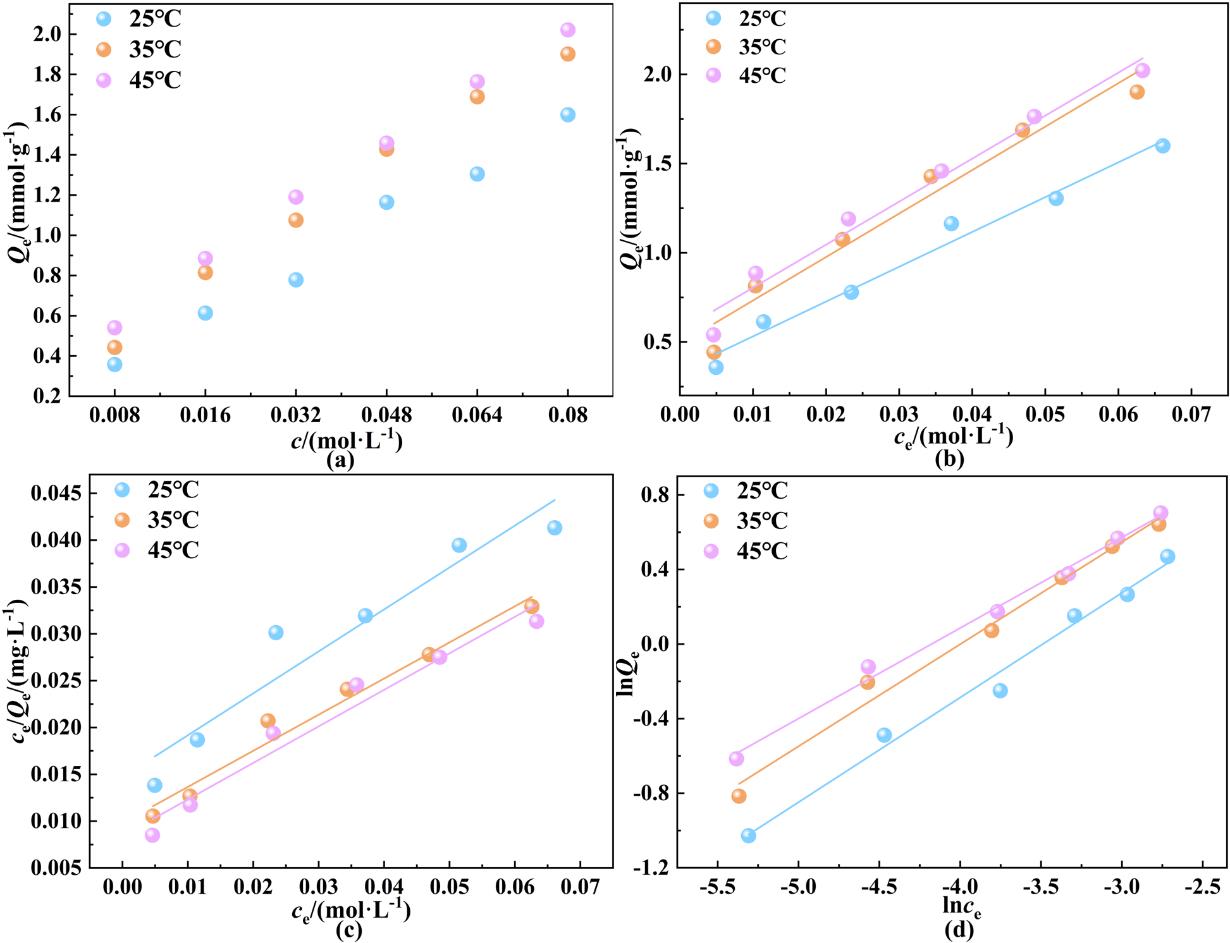
图3 (a)温度与浓度对吸附性能的影响;(b) Henry模型;(c) Langmuir模型及(d) Freundlich模型对吸附等温线拟合结果
Fig. 3 (a) Effect of temperature and concentration on adsorption performance; (b) Henry; (c) Langmuir; and (d) Freundlich model fitting results for adsorption isotherms.
| Model and parameter | Henry | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T(℃) | KH/(mL·g-1) | R2 | KL/(L·mol-1) | Qm/(mmol·g-1) | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 |
| 25 | 19.5 | 0.976 | 30.5 | 2.23 | 0.903 | 7.10 | 0.561 | 0.985 |
| 35 | 24.4 | 0.951 | 39.3 | 2.59 | 0.967 | 8.94 | 0.548 | 0.984 |
| 45 | 24.1 | 0.972 | 46.3 | 2.56 | 0.953 | 7.61 | 0.486 | 0.992 |
表2 Henry、Langmuir和Freundlich模型对吸附等温线的拟合参数
Table 2 Fitting parameters of Henry, Langmuir, and Freundlich adsorption isotherm models
| Model and parameter | Henry | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T(℃) | KH/(mL·g-1) | R2 | KL/(L·mol-1) | Qm/(mmol·g-1) | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 |
| 25 | 19.5 | 0.976 | 30.5 | 2.23 | 0.903 | 7.10 | 0.561 | 0.985 |
| 35 | 24.4 | 0.951 | 39.3 | 2.59 | 0.967 | 8.94 | 0.548 | 0.984 |
| 45 | 24.1 | 0.972 | 46.3 | 2.56 | 0.953 | 7.61 | 0.486 | 0.992 |
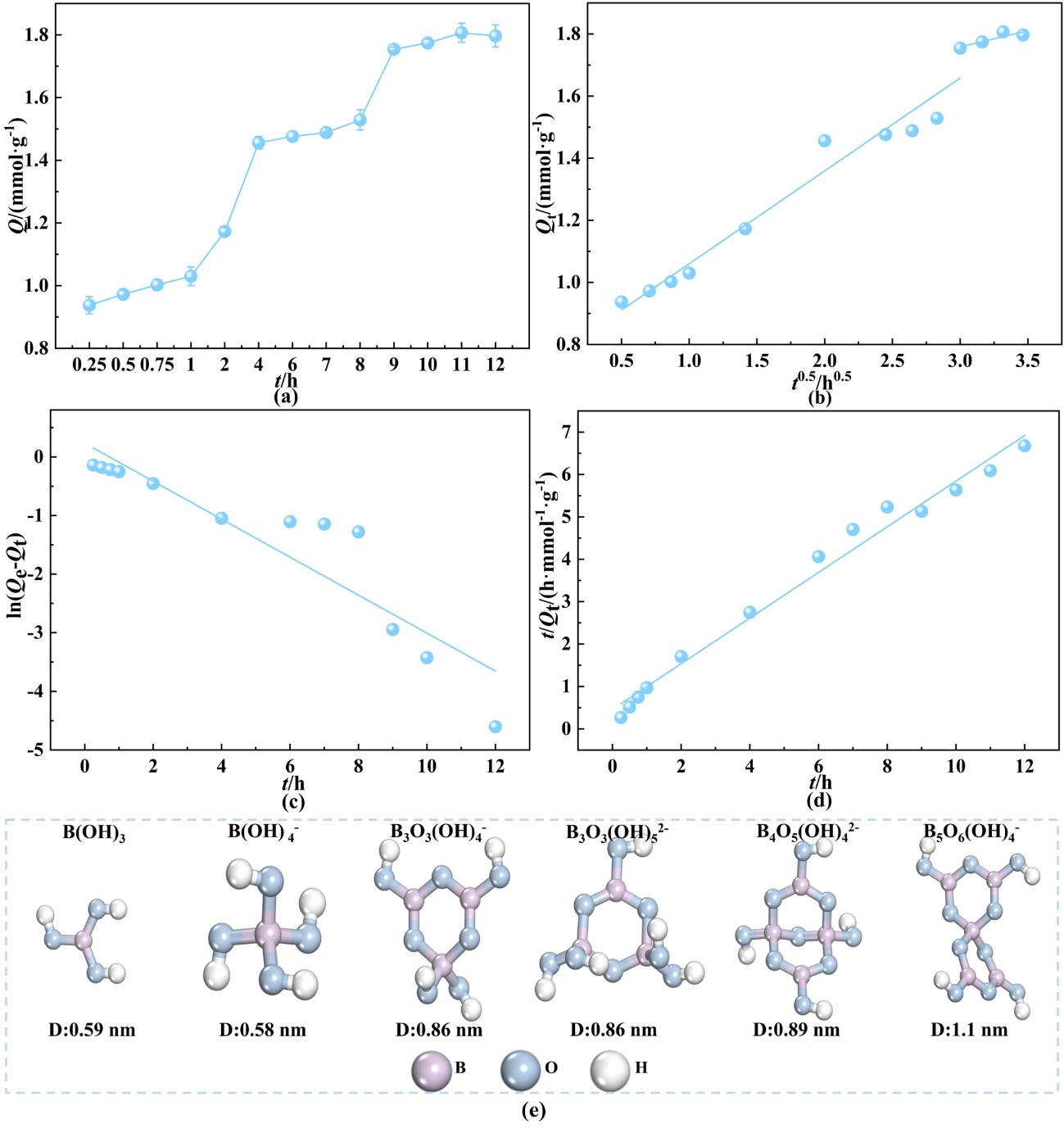
图4 (a)吸附时间对吸附性能的影响;(b)氢氧化铬对硼的颗粒内扩散模型拟合;(c)准一级吸附动力学模型拟合;(d) 准二级吸附动力学模型拟合;(e) B(OH)₃、B(OH)4-、B₃O₃(OH)4-、B₃O₃(OH)52-、B₄O₅(OH)42-和B₅O₆(OH)4-的水合直径
Fig. 4 (a) Effect of adsorption time on performance; (b) Intraparticle diffusion model fitting for boron adsorption by chromium hydroxide; (c) Pseudo-first-order kinetic model fitting; (d) Pseudo-second-order kinetic model fitting; (e) The hydrated diameters of B(OH)₃, B(OH)4-, B₃O₃(OH)4-, B₃O₃(OH)52-, B₄O₅(OH)42-, and B₅O₆(OH)4-
| Model and parameter | Intraparticle diffusion model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ki/(mmol·g-1·h-0.5) | Q1/(mmol·g-1) | R2 | ki/(mmol·g-1·h-0.5) | Q2/(mmol·g-1) | R2 | |
| Value | 0.299 | 0.761 | 0.954 | 0.105 | 1.445 | 0.679 |
| Model and parameter | Quasi-first-order kinetic model | Quasi-second-order kinetic model | ||||
| k1/h-1 | Qe/(mmol·g-1) | R2 | k2/(g·mmol-1·h-1) | Qe/(mmol·g-1) | R2 | |
| Value | 0.324 | 1.263 | 0.829 | 0.629 | 1.857 | 0.983 |
表3 吸附动力学模型拟合参数
Table 3 Kinetic model parameters for boron adsorption
| Model and parameter | Intraparticle diffusion model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ki/(mmol·g-1·h-0.5) | Q1/(mmol·g-1) | R2 | ki/(mmol·g-1·h-0.5) | Q2/(mmol·g-1) | R2 | |
| Value | 0.299 | 0.761 | 0.954 | 0.105 | 1.445 | 0.679 |
| Model and parameter | Quasi-first-order kinetic model | Quasi-second-order kinetic model | ||||
| k1/h-1 | Qe/(mmol·g-1) | R2 | k2/(g·mmol-1·h-1) | Qe/(mmol·g-1) | R2 | |
| Value | 0.324 | 1.263 | 0.829 | 0.629 | 1.857 | 0.983 |
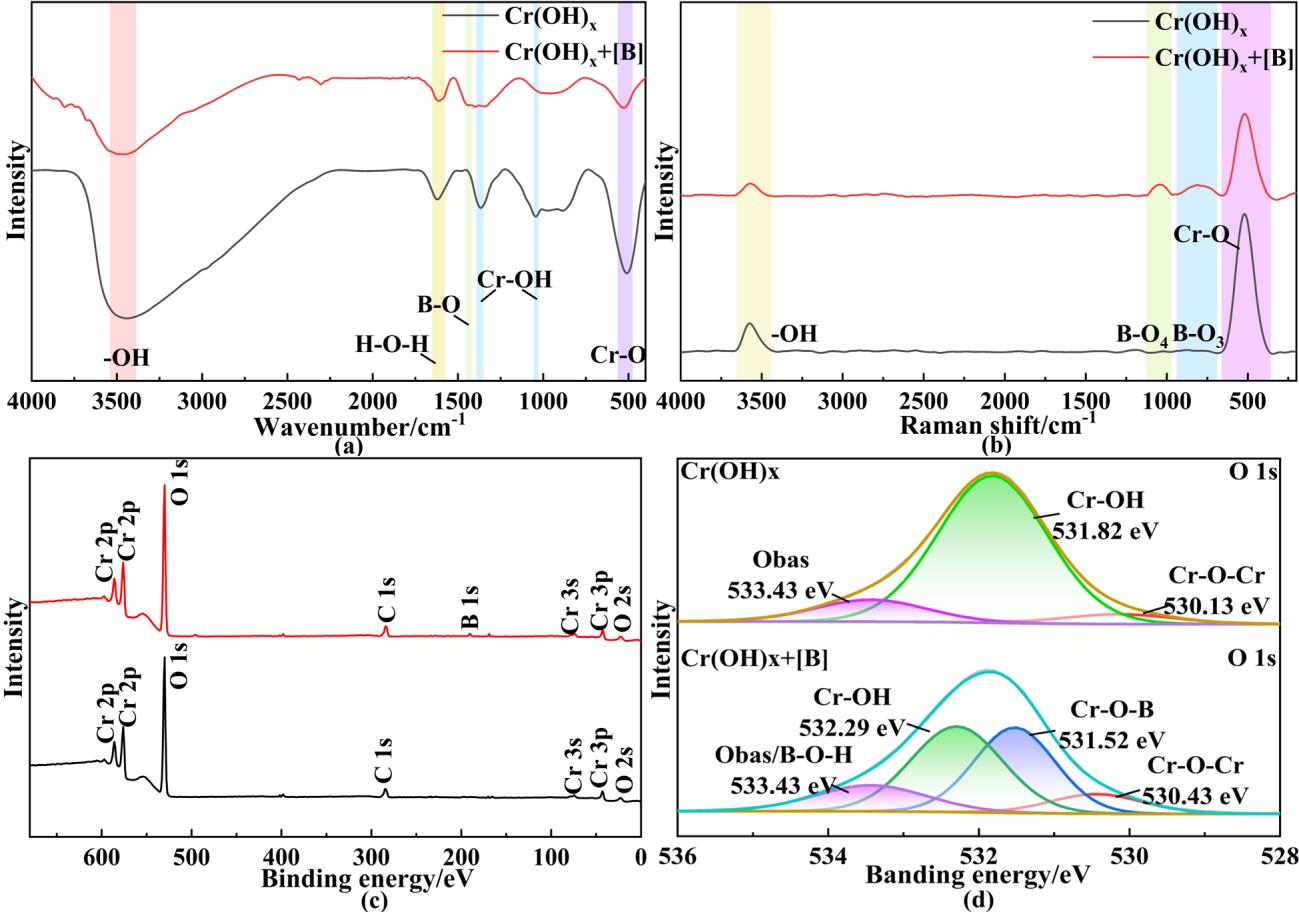
图5 吸附剂吸附前后(a)红外光谱的对比图;(b)拉曼光谱的对比图;(c) XPS总谱图;(d) O 1s分峰拟合谱图
Fig. 5 Comparison of (a) infrared spectra; (b) Raman spectra; (c) XPS survey spectrum; and (d) O 1s peak-fitting spectrum of the adsorbent before and after adsorption
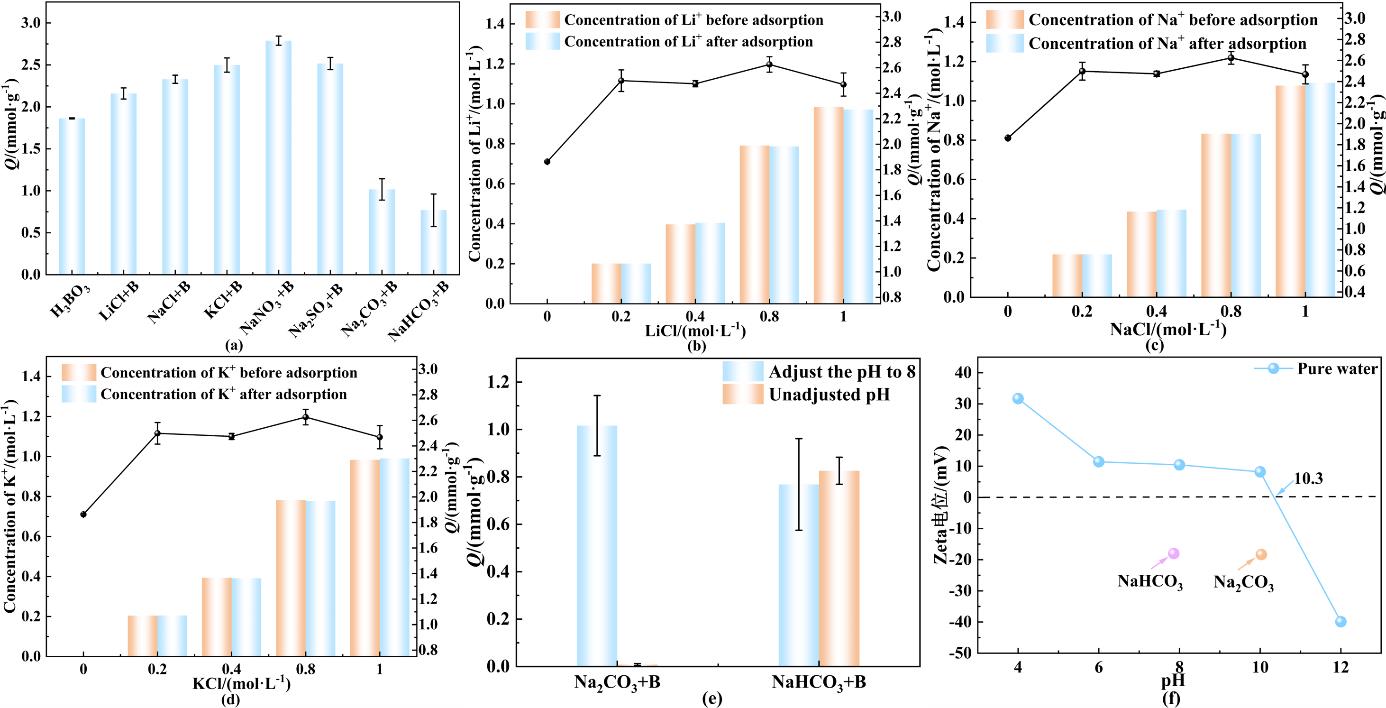
图6 (a)共存盐对吸附性能的影响;不同浓度(b) LiCl;(c) NaCl;(d) KCl对吸附性能的影响;(e)体系pH对吸附性能的影响;(f) zeta电位
Fig. 6 (a) Influence of coexisting salts on adsorption performance; Influence of different concentrations of (b) LiCl; (c) NaCl; and (d) KCl on adsorption performance; (e) The influence of system pH on adsorption performance; and (f) zeta potential
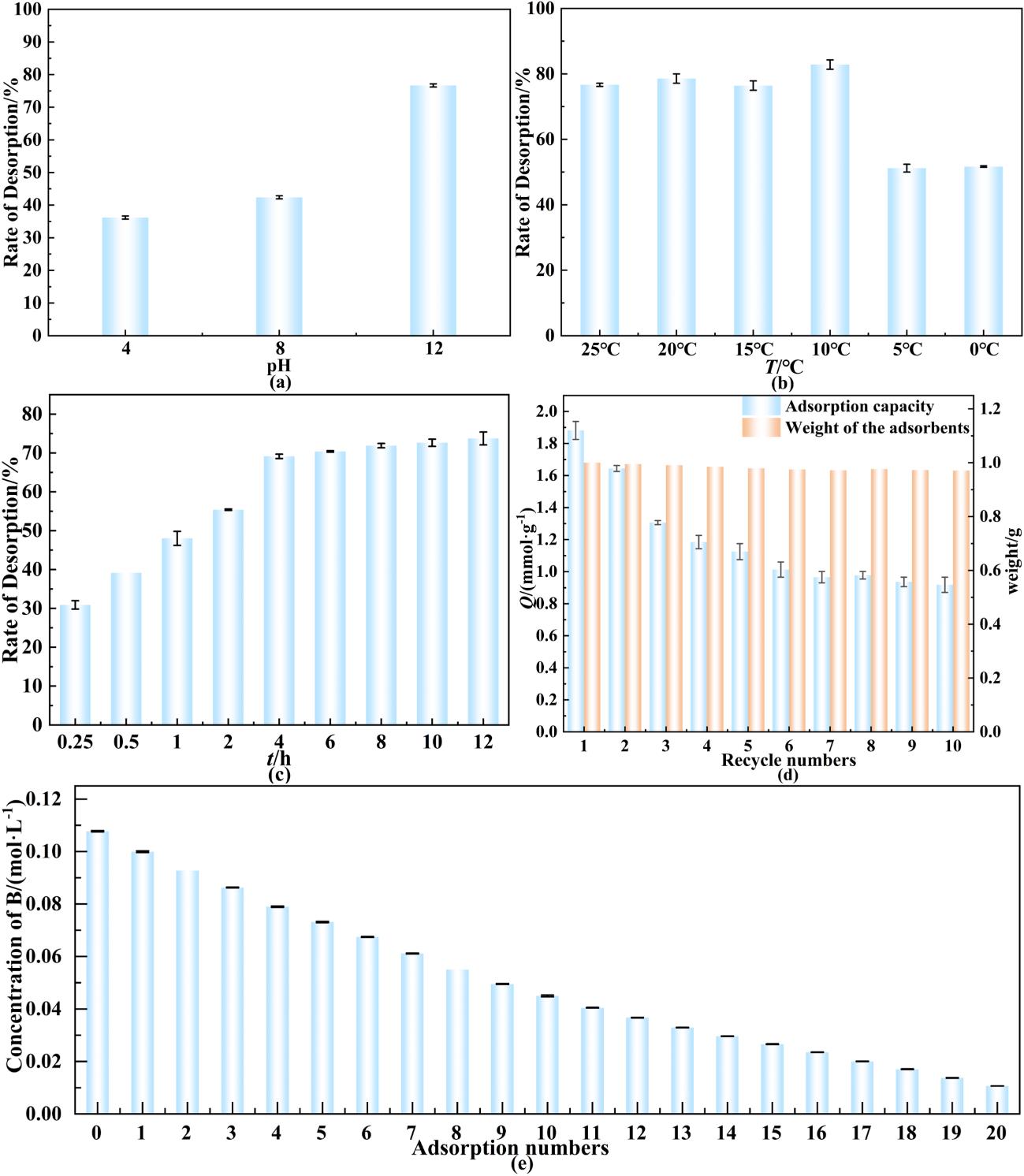
图7 吸附剂的再生性能:(a)洗脱液pH值对洗脱率的影响;(b洗脱液温度对洗脱率的影响;(c)洗脱时间对洗脱率的影响;(d)连续10次循环的吸附性能;(e)真实卤水20次循环吸附
Fig. 7 Regeneration performance of the adsorbent: (a) Influence of the pH value; (b) temperature of the eluent; (c) elution time on the elution rate; (d) Adsorption performance over 10 consecutive cycles; (e) 20 cycles of adsorption in real brine
| 样品 | Cl-(mol·L-1) | Na+ (mol·L-1) | B (mol·L-1) | Li+ (mol·L-1) | Ca2+ (mol·L-1) | Mg2+ (mol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 吸附前 | 4.46 | 1.9 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.0002 | ND |
| 吸附后 | 4.38 | 2.4 | 0.01 | 0.8 | 0.00008 | ND |
表4 XX锂业有限公司高锂合格液经硼吸附剂处理前后的组成分析
Table 4 Compositional analysis of high lithium solution from XX Lithium Industry Co., Ltd. Before and after boron adsorbent treatment
| 样品 | Cl-(mol·L-1) | Na+ (mol·L-1) | B (mol·L-1) | Li+ (mol·L-1) | Ca2+ (mol·L-1) | Mg2+ (mol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 吸附前 | 4.46 | 1.9 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.0002 | ND |
| 吸附后 | 4.38 | 2.4 | 0.01 | 0.8 | 0.00008 | ND |
| [1] | Nasef M M, Nallappan M, Ujang Z. Polymer-based chelating adsorbents for the selective removal of boron from water and wastewater: a review[J]. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 2014, 85: 54-68. |
| [2] | Goren A Y, Okten H E. Energy production from treatment of industrial wastewater and boron removal in aqueous solutions using microbial desalination cell[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 285: 131370. |
| [3] | Guan Z M, Lv J F, Bai P, et al. Boron removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption: a review[J]. Desalination, 2016, 383: 29-37. |
| [4] | 李韵浩, 李艾艾, 杨斌斌, 等. 溶胀嵌入脂肪酸分子制备高脱硼反渗透膜[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(3): 1343-1351. |
| Li Y H, Li A A, Yang B B, et al. Preparation of high boron removal reverse osmosis membrane by embedding fatty acid molecules after swelling[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(3): 1343-1351. | |
| [5] | de Azevedo J C V, de Urzedo A P F M, da Luz Mesquita P, et al. Recent advances in boron removal in aqueous media. An approach to the adsorption process and process optimization[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2024, 31(8): 12207-12228. |
| [6] | Bai S Q, Han J, Du C, et al. Removal of boron and silicon by a modified resin and their competitive adsorption mechanisms[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(24): 30275-30284. |
| [7] | Wang B Y, Guo X H, Bai P. Removal technology of boron dissolved in aqueous solutions: a review[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2014, 444: 338-344. |
| [8] | Shao Y F, Hu C, Liu R R, et al. Selective and efficient adsorption of H3BO3 from Salt Lake brine solution by ZIF-67-derived hollow cobalt sulfide[J]. Desalination, 2025, 613: 119019. |
| [9] | Wu B, Jiang X, Yu S N, et al. Unveiling the nature of boric acid adsorption by metal-organic frameworks with hexanuclear clusters[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 433: 133543. |
| [10] | Öcal Z B, Öncel M S, Keskinler B, et al. Sustainable treatment of boron industry wastewater with precipitation-adsorption hybrid process and recovery of boron species[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2024, 182: 719-726. |
| [11] | Kluczka J, Pudło W, Krukiewicz K. Boron adsorption removal by commercial and modified activated carbons[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2019, 147: 30-42. |
| [12] | Kluczka J, Gnus M, Kazek-Kęsik A, et al. Zirconium-chitosan hydrogel beads for removal of boron from aqueous solutions[J]. Polymer, 2018, 150: 109-118. |
| [13] | Kurashina M, Li H Y, Shiba K, et al. Syntheses of D-glucamine and N-methyl-D-glucamine modified chitosan for boron adsorption[J]. Modern Physics Letters B, 2022, 36(16): 2242001. |
| [14] | Li P, Liu C, Zhang L, et al. Enhanced boron adsorption onto synthesized MgO nanosheets by ultrasonic method[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2017, 34: 938-946. |
| [15] | Bouguerra W, Mnif A, Hamrouni B, et al. Boron removal by adsorption onto activated alumina and by reverse osmosis[J]. Desalination, 2008, 223(1/2/3): 31-37. |
| [16] | Seki Y, Seyhan S, Yurdakoc M. Removal of boron from aqueous solution by adsorption on Al2O3 based materials using full factorial design[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 138(1): 60-66. |
| [17] | Chen T, Wang Q F, Lyu J F, et al. Boron removal and reclamation by magnetic magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticle: an adsorption and isotopic separation study[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 231: 115930. |
| [18] | Fukuda H, Tsuchiya K, Toba Y, et al. Rapid boron removal from wastewater using low-crystalline magnesium oxide[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(5): 104171. |
| [19] | del Mar de la Fuente García-Soto M, Camacho E M. Boron removal by means of adsorption with magnesium oxide[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2006, 48(1): 36-44. |
| [20] | de la Fuente García-Soto M M, Muñoz Camacho E. Boron removal by means of adsorption processes with magnesium oxide: Modelization and mechanism[J]. Desalination, 2009, 249(2): 626-634. |
| [21] | Jiang Y M, Yang A N, Ju H Q, et al. Mechanism of metal doping in regulating the boron adsorption performance of Fe3O4 nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Communications, 2025, 61(57): 10530-10533. |
| [22] | Mahdavi S, Salehi Z, Zarabi M. Isotherm and kinetic studies for adsorption of boron on nano-copper oxide (CuO) in non-competitive and competitive solutions[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2020, 192: 259-270. |
| [23] | Song T, Gao F F, Du X, et al. Removal of boron in aqueous solution by magnesium oxide with the hydration process[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2023, 665: 131211. |
| [24] | Tsai H C, Lo S L. Boron recovery from high boron containing wastewater using modified sub-micron Ca(OH)2 particle[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2015, 12(1): 161-172. |
| [25] | Lin J Y, Shih Y J, Chen P Y, et al. Precipitation recovery of boron from aqueous solution by chemical oxo-precipitation at room temperature[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 164: 1052-1058. |
| [26] | Song T, Luo Q L, Gao F F, et al. Adsorption and electro-assisted method removal of boron in aqueous solution by nickel hydroxide[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2023, 118: 372-382. |
| [27] | 许丹丹. 锆基无机非金属材料对水溶液中硼吸附分离的研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2023. |
| Xu D D. Study of zirconium-based inorganic non-metallic materials for boron adsorption and separation in aqueous solutions[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2023. | |
| [28] | Al-Ghouti M A, Khan M, Malik A, et al. Development of novel nano-γ-Al2O3 adsorbent from waste aluminum foil for the removal of boron and bromide from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2022, 50: 103312. |
| [29] | Huang Z L, Chen C G, Xie J Y, et al. The evolution of dehydration and thermal decomposition of nanocrystalline and amorphous chromium hydroxide[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2016, 118: 225-230. |
| [30] | Lu T, Chen F W. Multiwfn: a multifunctional wavefunction analyzer[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2012, 33(5): 580-592. |
| [31] | Lu T. A comprehensive electron wavefunction analysis toolbox for chemists, Multiwfn[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2024, 161(8). DOI:10.1063/5.0216272 . |
| [32] | Lu T, Chen F W. Quantitative analysis of molecular surface based on improved Marching Tetrahedra algorithm[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling, 2012, 38: 314-323. |
| [33] | Gautam C, Yadav A K, Singh A K. A review on infrared spectroscopy of borate glasses with effects of different additives[J]. International Scholarly Research Notices, 2012, 2012(1): 428497. |
| [34] | 张爱芸, 姚燕. 硼酸盐水溶液中硼物种的存在形式及影响因素[J]. 盐湖研究, 2007, 15(2): 50-56. |
| Zhang A Y, Yao Y. The polyborate Present in aqueous solutions containing boron and the affection factors[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2007, 15(2): 50-56. | |
| [35] | Papassiopi N, Vaxevanidou K, Christou C, et al. Synthesis, characterization and stability of Cr(III) and Fe(III) hydroxides[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 264: 490-497. |
| [36] | Jiang L Y, Xin S, Wu X L, et al. Non-sacrificial template synthesis of Cr2O3–C hierarchical core/shell nanospheres and their application as anode materials in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2010, 20(35): 7565-7569. |
| [37] | 彭姣玉, 杨克利, 边绍菊, 等. 盐水溶液中单硼酸盐物种(B(OH)3和B(OH) 4 - )的拉曼光谱定量分析[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2022, 42(8): 2456-2462. |
| Peng J Y, Yang K L, Bian S J, et al. Quantitative analysis of monoborates (H3BO3 and B(OH) 4 - ) in aqueous solution by Raman spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2022, 42(8): 2456-2462. | |
| [38] | Li Y B, Wang T, Liu X, et al. Construction and properties of UiO-66-based bulk high-efficiency boron adsorbents[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2025, 313: 121720. |
| [1] | 臧子晴, 李修真, 谈莹莹, 刘晓庆. 分凝器对两级分离自复叠制冷循环特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 17-25. |
| [2] | 裴星亮, 叶翠平, 裴赢丽, 李文英. 碱改性MIL-53(Cr)选择性吸附分离二甲苯异构体[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 258-267. |
| [3] | 李银龙, 刘国强, 晏刚. 分馏与闪蒸分离耦合自复叠制冷循环性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 26-35. |
| [4] | 吴梓航, 徐震原, 游锦方, 潘权稳, 王如竹. 基于吸附式储冷技术的深井钻探设备冷却系统[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 309-317. |
| [5] | 李文龙, 常程, 吴小林, 姬忠礼. 油水聚结过滤材料中的液体分布特性及过程压降演化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4850-4861. |
| [6] | 张建民, 何美贵, 贾万鑫, 赵静, 金万勤. 聚氧化乙烯/冠醚共混膜及其二氧化碳分离性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4862-4871. |
| [7] | 郭旭, 贾继宁, 姚克俭. 基于优化CNN-BiLSTM神经网络的间歇精馏过程建模[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4613-4629. |
| [8] | 王杰, 林渠成, 张先明. 基于分解算法的混合气体多级膜分离系统全局优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4670-4682. |
| [9] | 田宇红, 杜壮壮, 徐慧芳, 祝自强, 王宇聪. ZIF-8基多孔液体制备及其SO2吸附性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4284-4296. |
| [10] | 陈治宏, 吴佳伟, 楼小玲, 贠军贤. 化学品生物制造过程机器学习的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3789-3804. |
| [11] | 张荟钦, 赵泓竣, 付正军, 庄力, 董凯, 贾添智, 曹雪丽, 孙世鹏. 纳滤膜在离子型稀土浸出液提浓中的应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4095-4107. |
| [12] | 史松伟, 赵诚, 刘帅, 应雨轩, 严密. 富铁飞灰耦合Fe-Zn/Al2O3脱除沼气H2S研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4239-4247. |
| [13] | 蒋明虎, 汪帆, 邢雷, 赵立新, 李新亚, 陈丁玮. 井下含气对油水分离管柱流场特性及性能影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3361-3372. |
| [14] | 王佳丽, 刘芳, 陈伟, 张晓英, 李生廷, 田甜, 信翔宇, 刘光, 宋宇飞. 模板限域原位制备镁基纳米复合材料进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3172-3184. |
| [15] | 高照, 吴熙, 夏丹, 张霖宙. 石油加工分子管理平台热力学及分离单元模块开发[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3212-3225. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号