化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (7): 3172-3184.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241452
王佳丽1,2( ), 刘芳1,2, 陈伟1,3(
), 刘芳1,2, 陈伟1,3( ), 张晓英4, 李生廷4, 田甜2, 信翔宇2, 刘光2(
), 张晓英4, 李生廷4, 田甜2, 信翔宇2, 刘光2( ), 宋宇飞1,3(
), 宋宇飞1,3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-16
修回日期:2025-02-17
出版日期:2025-07-25
发布日期:2025-08-13
通讯作者:
陈伟,刘光,宋宇飞
作者简介:王佳丽(2001—),女,硕士研究生,wangjl0130@163.com
基金资助:
Jiali WANG1,2( ), Fang LIU1,2, Wei CHEN1,3(
), Fang LIU1,2, Wei CHEN1,3( ), Xiaoying ZHANG4, Shengting LI4, Tian TIAN2, Xiangyu XIN2, Guang LIU2(
), Xiaoying ZHANG4, Shengting LI4, Tian TIAN2, Xiangyu XIN2, Guang LIU2( ), Yufei SONG1,3(
), Yufei SONG1,3( )
)
Received:2024-12-16
Revised:2025-02-17
Online:2025-07-25
Published:2025-08-13
Contact:
Wei CHEN, Guang LIU, Yufei SONG
摘要:
MgH2作为一种具有高储氢容量[(7.6%(质量分数),110 kg·m-3]和低成本优势的固态储氢材料,其高热力学稳定性(脱氢焓值-74.7 kJ·mol-1)及缓慢的吸放氢动力学性能,严重制约了实际应用。研究表明,原位合成法通过自下而上的组装策略,成功实现了Mg/MgH2体系纳米化,有效调控其粒径从而改善储氢性能。本文综述了化学还原、热氢化、气相沉积等原位合成镁基储氢材料的原理,重点阐述了模板限制材料对Mg/MgH2体系粒径调节、吸放氢热/动力学性能与催化机理的影响,同时针对当前原位合成技术中存在的制备成本高、容量衰减大及空气稳定性差等挑战进行了探讨,展望了在纳米限域材料作用下原位制备高性能高储量镁基储氢材料的可行方向。
中图分类号:
王佳丽, 刘芳, 陈伟, 张晓英, 李生廷, 田甜, 信翔宇, 刘光, 宋宇飞. 模板限域原位制备镁基纳米复合材料进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3172-3184.
Jiali WANG, Fang LIU, Wei CHEN, Xiaoying ZHANG, Shengting LI, Tian TIAN, Xiangyu XIN, Guang LIU, Yufei SONG. Recent advances in magnesium-based nanocomposites via in-situ template-confined synthesis[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3172-3184.
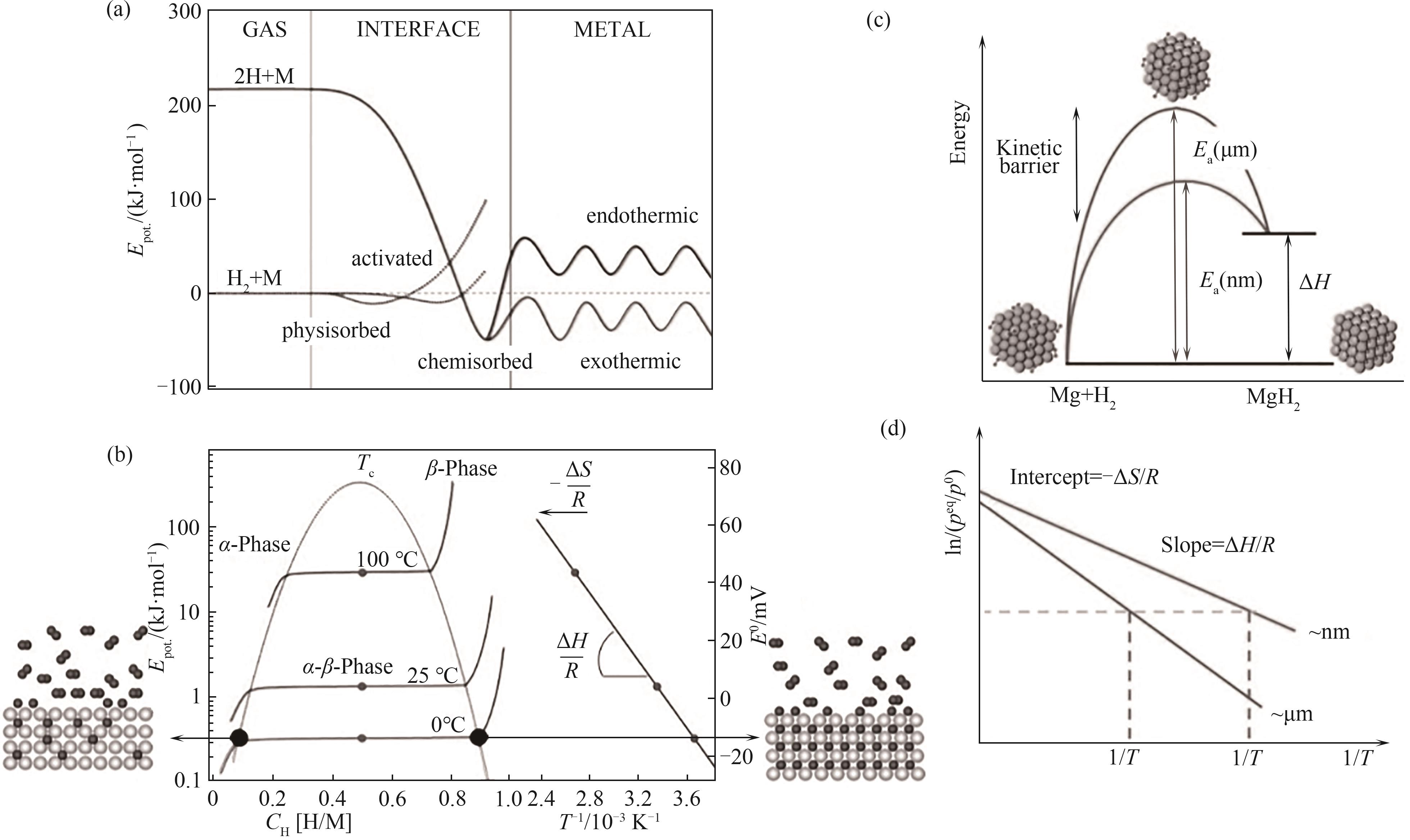
图1 氢化镁的动力学(a)与热力学(b)原理图[10];纳米化对氢化镁储氢过程中动力学(c)与热力学(d)的改善原理[11]
Fig. 1 Kinetic (a) and thermodynamic (b) schematics of magnesium hydride [10]; Improvement principle of kinetics (c) and thermodynamics (d) in hydrogen storage process of magnesium hydride by nanization[11]
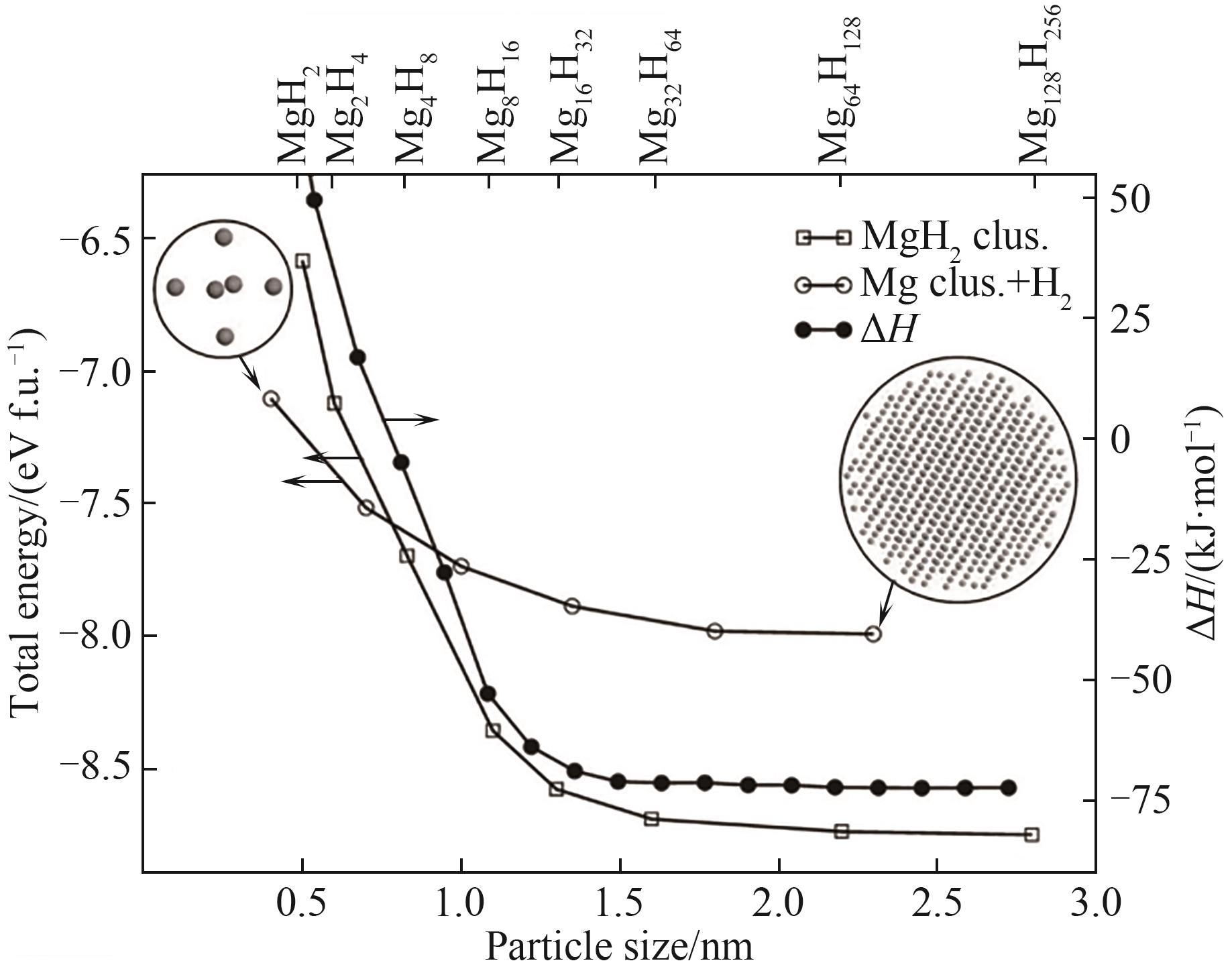
图2 MgH2纳米团簇的总能量、Mg纳米团簇与H2分子能量和形成能与粒径的关系[21]
Fig.2 Relationship between total energy of MgH2 nanoclusters, Mg nanoclusters and H2 molecular energy and formation energy and particle size[21]
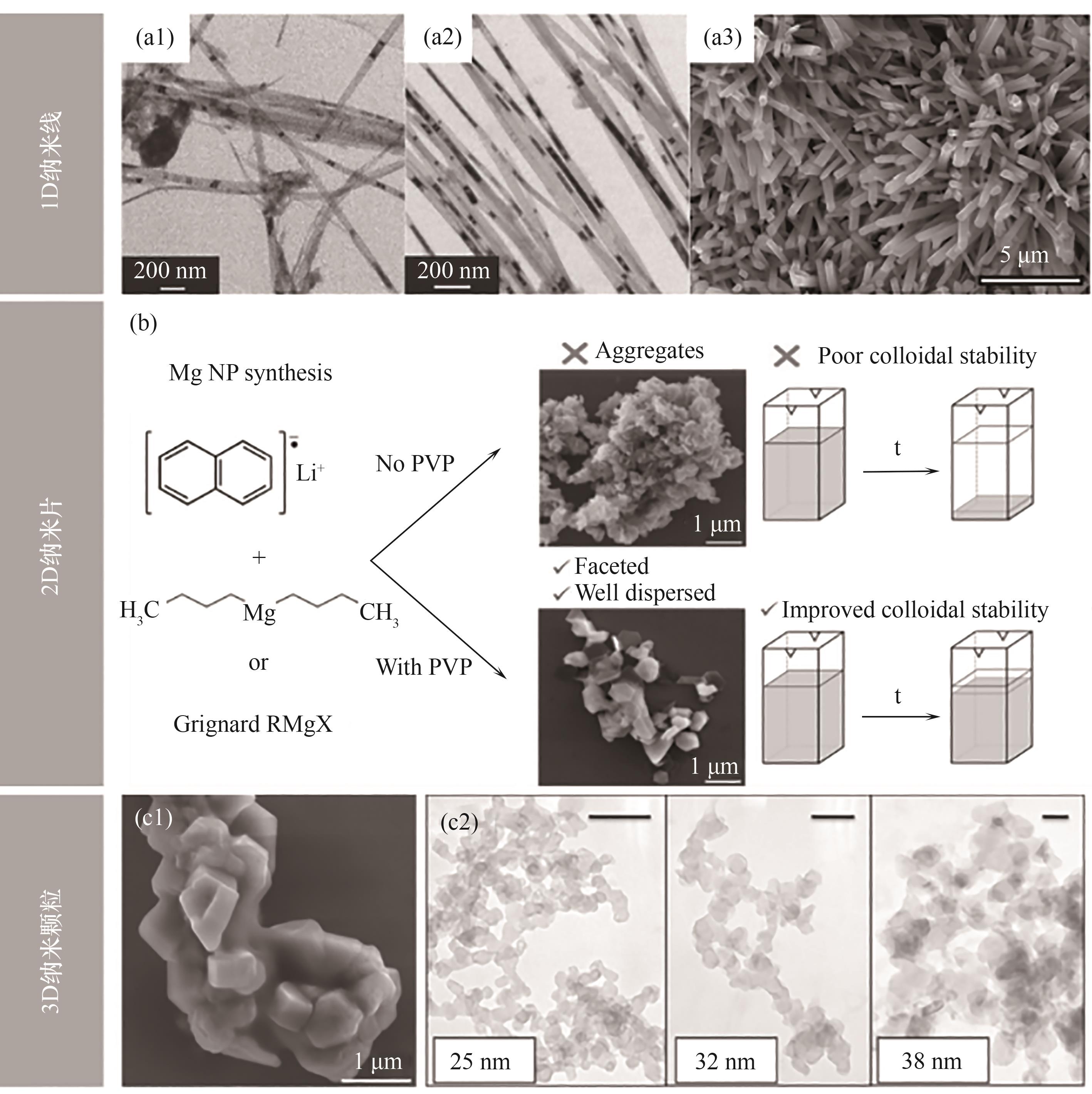
图4 (a1,a2) Mg纳米纤维的透射电镜(TEM)图[33];(a3) MeMgCl制备Mg纳米线的扫描电镜(SEM)图像[34];(b) 不同合成原料与封端剂制备不同形貌Mg的示意图[35];(c1) 在SDS存在下合成的Mg NPs的SEM图[35];(c2) 不同粒径Mg纳米晶体的TEM图[36]
Fig.4 (a1,a2) TEM images of Mg nanofibers[33]; (a3) SEM image of Mg nanowires prepared from MeMgCl[34]; (b) Diagram of Mg with different morphologies prepared by different synthetic raw materials and end-sealing agents[35]; (c1) SEM image of Mg NPs synthesized in the presence of SDS[35]; (c2) TEM images of Mg nanocrystals with different particle sizes[36]
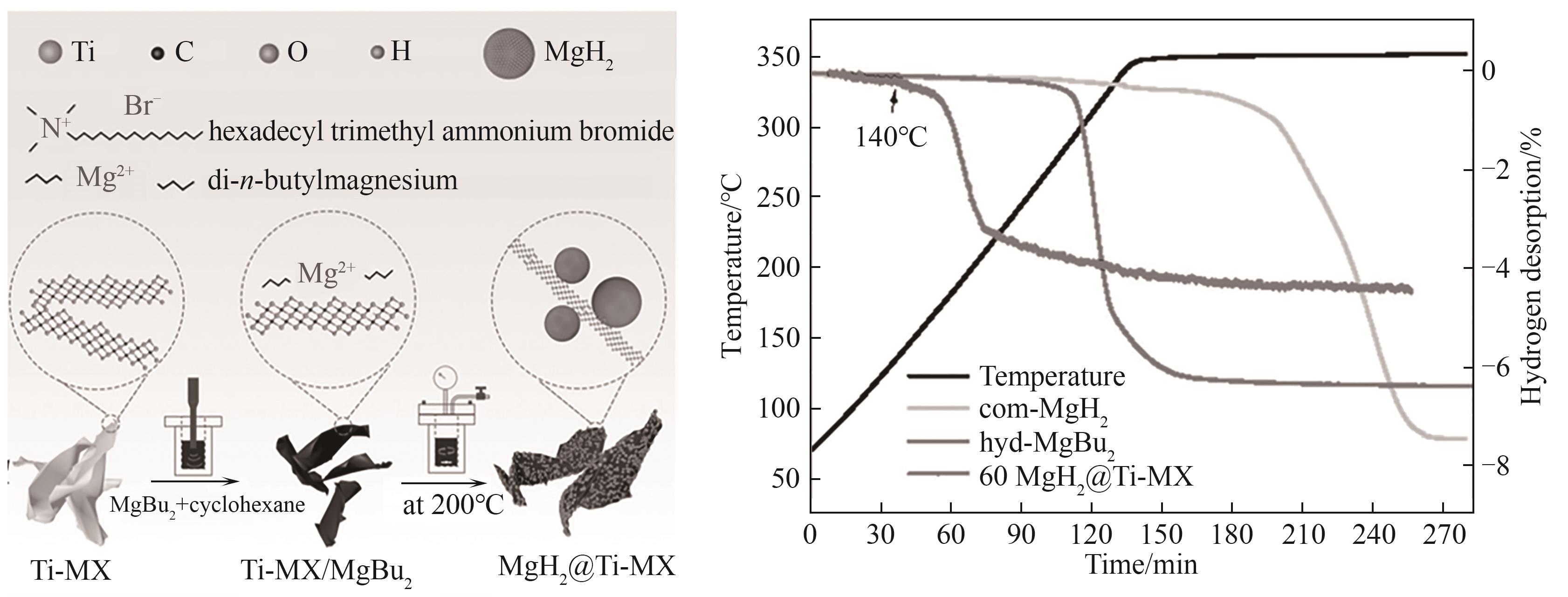
图8 MgH2@Ti-MX合成示意图及商用 MgH2、氢化MgBu2、60MgH2@Ti-MX的TPD曲线[76]
Fig.8 Schematic illustration of the fabrication of MgH2@Ti-MX and TPD curves of com-MgH2, hyd-MgBu2 and 60MgH2@Ti-MX[76]
| 材料 | 制备方法 | Mg/MgH2尺寸/nm | 起始脱氢温度/℃ | 吸放氢焓值ΔHabs/des/(kJ·mol-1) | 吸放氢活化能Eab/de/(kJ·mol-1) | 储氢量/%(质量) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCNs/Mg | 化学还原 | 5~15 | — | -65.86/76.73 Bulk:-74.7/74.06 | — | 4.35 | [ |
| Fe/Mg | 化学还原 | 3~10(5) | 约325(DSC) | ΔHdes = -59.9 ± 1.9 | Ede = 137 ± 6 | 约2.67 | [ |
| Mg-Ti | 化学还原 | 40~60(50) | 约300(DSC) | -73.0 ± 1.8/75.8 ± 4.7 | Ede = 50.2 | 6.2 | [ |
| Mg-Ni | 化学还原 | 10~20 | 约244(DSC) | -70.0/70.7 | 57.4/139.1 | 6.0 | [ |
| Mg@Pt | 化学还原 | 3(Pt) | 287.5 | — | 82.4/152.8 | 6.5 | [ |
| Mg@Ti@Ni | 化学还原 | 50~600 | 340(DSC) | -67.12/69.84 | Ede = 63.7 | 6.27 | [ |
| Mg-Ni-TiS2 | 化学还原 | 70(Mg-Ni) | — | -71.13/72.25 | Eab = 79.4 ± 0.9 | 约4.7 | [ |
| Mg/ZIF-67 | 化学还原 | — | 约289 | -67.5/77.8 | Ede = 161.73 | 5.1 | [ |
| 0.6 MgH2@CMK-3 | 浸渍加氢 | 1~2 | 50 | ΔHdes = 55.4 | — | 5.5 | [ |
| MgH2@BCNTs | 浸渍加氢 | 15~20 | 220 | ΔHdes = 68.92 | Ede = 97.97 | 5.79 | [ |
| MgH2@CoS-NBs | 浸渍加氢 | 5~10 | 约282(DSC) | -65.6/68.1 | 57.4/120.8 | 3.23 | [ |
| Mg@Ni-MOF | 浸渍加氢 | 3 | 约305(DSC) | -65.7/69.7 | 41.5/144.7 | 2.7 | [ |
| MgH2/TiO2 | 溶剂热法 | — | 180 | — | — | 3.4 | [ |
| MHCH-5 | 溶剂热法 | 约5.5 | 约140 | -46.9/49.1 | 31/43 | 6.63 | [ |
| Mg75(TiC0.6)12@C | 气相沉积 | <50 | — | — | 54.7/56.5 | 5.2 | [ |
表1 不同材料限制后MgH2的储氢性能(未特殊标明情况下,起始脱氢温度均通过TPD测试所得)
Table 1 Hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 limited by different materials (Unless otherwise stated, the initial dehydrogenation temperatures are determined through TPD tests)
| 材料 | 制备方法 | Mg/MgH2尺寸/nm | 起始脱氢温度/℃ | 吸放氢焓值ΔHabs/des/(kJ·mol-1) | 吸放氢活化能Eab/de/(kJ·mol-1) | 储氢量/%(质量) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCNs/Mg | 化学还原 | 5~15 | — | -65.86/76.73 Bulk:-74.7/74.06 | — | 4.35 | [ |
| Fe/Mg | 化学还原 | 3~10(5) | 约325(DSC) | ΔHdes = -59.9 ± 1.9 | Ede = 137 ± 6 | 约2.67 | [ |
| Mg-Ti | 化学还原 | 40~60(50) | 约300(DSC) | -73.0 ± 1.8/75.8 ± 4.7 | Ede = 50.2 | 6.2 | [ |
| Mg-Ni | 化学还原 | 10~20 | 约244(DSC) | -70.0/70.7 | 57.4/139.1 | 6.0 | [ |
| Mg@Pt | 化学还原 | 3(Pt) | 287.5 | — | 82.4/152.8 | 6.5 | [ |
| Mg@Ti@Ni | 化学还原 | 50~600 | 340(DSC) | -67.12/69.84 | Ede = 63.7 | 6.27 | [ |
| Mg-Ni-TiS2 | 化学还原 | 70(Mg-Ni) | — | -71.13/72.25 | Eab = 79.4 ± 0.9 | 约4.7 | [ |
| Mg/ZIF-67 | 化学还原 | — | 约289 | -67.5/77.8 | Ede = 161.73 | 5.1 | [ |
| 0.6 MgH2@CMK-3 | 浸渍加氢 | 1~2 | 50 | ΔHdes = 55.4 | — | 5.5 | [ |
| MgH2@BCNTs | 浸渍加氢 | 15~20 | 220 | ΔHdes = 68.92 | Ede = 97.97 | 5.79 | [ |
| MgH2@CoS-NBs | 浸渍加氢 | 5~10 | 约282(DSC) | -65.6/68.1 | 57.4/120.8 | 3.23 | [ |
| Mg@Ni-MOF | 浸渍加氢 | 3 | 约305(DSC) | -65.7/69.7 | 41.5/144.7 | 2.7 | [ |
| MgH2/TiO2 | 溶剂热法 | — | 180 | — | — | 3.4 | [ |
| MHCH-5 | 溶剂热法 | 约5.5 | 约140 | -46.9/49.1 | 31/43 | 6.63 | [ |
| Mg75(TiC0.6)12@C | 气相沉积 | <50 | — | — | 54.7/56.5 | 5.2 | [ |
| [1] | Hussain S A, Razi F, Hewage K, et al. The perspective of energy poverty and 1st energy crisis of green transition[J]. Energy, 2023, 275: 127487. |
| [2] | Zhao X, Ma X, Chen B, et al. Challenges toward carbon neutrality in China: strategies and countermeasures[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2022, 176: 105959. |
| [3] | 李灿. 绿色氢能在"双碳"战略中的作用[J]. 科技导报, 2024, 42(15): 1-2. |
| Li C. The role of green hydrogen energy in dual carbon strategy[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2024, 42(15): 1-2. | |
| [4] | 徐立军, 苏昕, 朱迪, 等. "双碳"目标下氢能产业技术发展分析[J]. 新疆大学学报(自然科学版中英文), 2024, 41(4): 385-407. |
| Xu L J, Su X, Zhu D, et al. Analysis of the technological development of the hydrogen energy industry in the context of dual-carbon targets[J]. Journal of Xinjiang University (Natural Science Edition in Chinese and English), 2024, 41(4): 385-407. | |
| [5] | Osman A I, Mehta N, Elgarahy A M, et al. Hydrogen production, storage, utilisation and environmental impacts: a review[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2022, 20(1): 153-188. |
| [6] | Yan X R, Zheng W G, Wei Y J, et al. Current status and economic analysis of green hydrogen energy industry chain[J]. Processes, 2024, 12(2): 315. |
| [7] | Xu Y H, Zhou Y, Li Y T, et al. Research progress and application prospects of solid-state hydrogen storage technology[J]. Molecules, 2024, 29(8): 1767. |
| [8] | 毕秋艳, 党力, 曹海莲, 等. 青海盐湖镁资源开发与利用研究进展[J]. 盐湖研究, 2022, 30(1): 101-109. |
| Bi Q Y, Dang L, Cao H L, et al. Development and utilization of magnesium resources in Qinghai salt lakes[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2022, 30(1): 101-109. | |
| [9] | Ding Z, Li Y T, Yang H, et al. Tailoring MgH2 for hydrogen storage through nanoengineering and catalysis[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2022, 10(11): 2946-2967. |
| [10] | Züttel A. Materials for hydrogen storage[J]. Materials Today, 2003, 6(9): 24-33. |
| [11] | Ren L, Li Y H, Zhang N, et al. Nanostructuring of Mg-based hydrogen storage materials: recent advances for promoting key applications[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2023, 15(1): 93. |
| [12] | Duan C W, Su Z H, Tian Y T, et al. Mechanochemical assisted hydrogenation of Mg-CNTs-Ni: kinetics modeling and reaction mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 441: 136059. |
| [13] | Zhang Q Y, Huang Y K, Xu L, et al. Highly dispersed MgH2 nanoparticle-graphene nanosheet composites for hydrogen storage[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2019, 2(6): 3828-3835. |
| [14] | Guo F H, Zhang T B, Shi L M, et al. Hydrogen absorption/desorption cycling performance of Mg-based alloys with in-situ formed Mg2Ni and LaH x (x = 2, 3) nanocrystallines[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2023, 11(4): 1180-1192. |
| [15] | Gao H, Shao Y, Shi R, et al. Effect of few-layer Ti3C2T x supported nano-Ni via self-assembly reduction on hydrogen storage performance of MgH2 [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(42): 47684-47694. |
| [16] | Lan Z Q, Hong F F, Shi W T, et al. Effect of MOF-derived carbon-nitrogen nanosheets co-doped with nickel and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on hydrogen storage performance of MgH2 [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 468: 143692. |
| [17] | Meng Y, Zhang J, Ju S L, et al. Understanding and unlocking the role of V in boosting the reversible hydrogen storage performance of MgH2 [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11(18): 9762-9771. |
| [18] | Wan L F, Liu Y S, Cho E S, et al. Atomically thin interfacial suboxide key to hydrogen storage performance enhancements of magnesium nanoparticles encapsulated in reduced graphene oxide[J]. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(9): 5540-5545. |
| [19] | Zhang L T, Tian G B, Wu F Y, et al. The influence of grain size and catalytic doping on magnesium hydride nanocrystals for hydrogen storage[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2023, 178: 111335. |
| [20] | Cheung S, Deng W Q, Van Duin A C T, et al. ReaxFF(MgH) reactive force field for magnesium hydride systems[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2005, 109(5): 851-859. |
| [21] | Vajeeston P, Sartori S, Ravindran P, et al. MgH2 in carbon scaffolds: a combined experimental and theoretical investigation[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(40): 21139-21147. |
| [22] | 欧阳柳章, 叶素云, 朱敏. MmM5/Mg复合薄膜的显微结构与储氢性能的关系[J]. 电子显微学报, 2009, 28(4): 356-360. |
| Ouyang L Z, Ye S Y, Zhu M. Microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of MmNi3.5(CoAlMn)1.5/Mg multi-layers[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2009, 28(4): 356-360. | |
| [23] | Huang L J, Shi S T, Cui J, et al. Thermally-assisted milling and hydrogenolysis for synthesizing ultrafine MgH2 with destabilized thermodynamics[J]. Nanotechnology, 2021, 32(28): 285402. |
| [24] | Wang Y Q, Lan Z Q, Huang X, et al. Study on catalytic effect and mechanism of MOF (MOF = ZIF-8, ZIF-67, MOF-74) on hydrogen storage properties of magnesium[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(54): 28863-28873. |
| [25] | Tan D Z, Peng C, Zhang Q G. Microstructural characteristics and hydrogen storage properties of the Mg-Ni-TiS2 nanocomposite prepared by a solution-based method[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(44): 16756-16768. |
| [26] | Lu C, Ma Y L, Li F, et al. Visualization of fast "hydrogen pump" in core-shell nanostructured Mg@Pt through hydrogen-stabilized Mg3Pt[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(24): 14629-14637. |
| [27] | Cho Y, Kang S, Wood B C, et al. Heteroatom-doped graphenes as actively interacting 2D encapsulation media for Mg-based hydrogen storage[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(18): 20823-20834. |
| [28] | Wang Y R, Chen X W, Zhang H Y, et al. Heterostructures built in metal hydrides for advanced hydrogen storage reversibility[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(31): 2002647. |
| [29] | Hu M M, Xie X B, Chen M, et al. TiCX-decorated Mg nanoparticles confined in carbon shell: preparation and catalytic mechanism for hydrogen storage[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 817: 152813. |
| [30] | Rieke R D, Hudnall P M. Activated metals. Ⅰ. Preparation of highly reactive magnesium metal[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1972, 94(20): 7178-7179. |
| [31] | Rieke R D, Bales S E. Activated metals. Ⅳ. Preparation and reactions of highly reactive magnesium metal[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1974, 96(6): 1775-1781. |
| [32] | Aguey-Zinsou K F, Ares-Fernández J R. Synthesis of colloidal magnesium: a near room temperature store for hydrogen[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2008, 20(2): 376-378. |
| [33] | Sun Y H, Aguey-Zinsou K F. Synthesis of magnesium nanofibers by electroless reduction and their hydrogen interaction properties[J]. Particle & Particle Systems Characterization, 2017, 34(4): 1600276. |
| [34] | Viyannalage L, Lee V, Dennis R V, et al. From Grignard's reagents to well-defined Mg nanostructures: distinctive electrochemical and solution reduction routes[J]. Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(42): 5169-5171. |
| [35] | Wayman T M R, Lomonosov V, Ringe E. Capping agents enable well-dispersed and colloidally stable metallic magnesium nanoparticles[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Nanomaterials and Interfaces, 2024, 128(11): 4666-4676. |
| [36] | Norberg N S, Arthur T S, Fredrick S J, et al. Size-dependent hydrogen storage properties of Mg nanocrystals prepared from solution[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(28): 10679-10681. |
| [37] | Liu W, Aguey-Zinsou K F. Size effects and hydrogen storage properties of Mg nanoparticles synthesised by an electroless reduction method[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(25): 9718-9726. |
| [38] | Jia Y, Yao X D. Carbon scaffold modified by metal (Ni) or non-metal (N) to enhance hydrogen storage of MgH2 through nanoconfinement[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(36): 22933-22941. |
| [39] | Mao J F, Zou J X, Lu C, et al. Hydrogen storage and hydrolysis properties of core-shell structured Mg-MF x (M=V, Ni, La and Ce) nano-composites prepared by arc plasma method[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 366: 131-142. |
| [40] | Xia G L, Zhang L J, Chen X W, et al. Carbon hollow nanobubbles on porous carbon nanofibers: an ideal host for high-performance sodium-sulfur batteries and hydrogen storage[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2018, 14: 314-323. |
| [41] | Zhang J G, Zhu Y F, Lin H J, et al. Metal hydride nanoparticles with ultrahigh structural stability and hydrogen storage activity derived from microencapsulated nanoconfinement[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(24): 1700760. |
| [42] | Jangid M K, Sharma S S, Ray J, et al. Structural, optical and electrical characterizations of Mg/Ti/Ni multilayer thin films deposited by DC magnetron sputtering for hydrogen storage[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(96): 37921-37929. |
| [43] | Reddy G L N, Kumar S. Hydrogen storage studies in Pd/Ti/Mg films[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(5): 2840-2849. |
| [44] | Abdul Majid N A, Watanabe J, Notomi M. Improved desorption temperature of magnesium hydride via multi-layering Mg/Fe thin film[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(5): 4181-4187. |
| [45] | Setijadi E J, Boyer C, Aguey-Zinsou K F. Switching the thermodynamics of MgH2 nanoparticles through polystyrene stabilisation and oxidation[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(75): 39934-39940. |
| [46] | Song M Y, Choi E, Kwak Y J. Synthesis of a Mg-based alloy with a hydrogen-storage capacity of over 7wt% by adding a polymer CMC via transformation-involving milling[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2018, 108: 23-31. |
| [47] | Song M Y, Choi E, Kwak Y J. Preparation of a Mg-based alloy with a high hydrogen-storage capacity by adding a polymer CMC via milling in a hydrogen atmosphere[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(7): 3779-3789. |
| [48] | Song M Y, Kwak Y J. Hydrogen storage properties of Mg alloy prepared by incorporating polyvinylidene fluoride via reactive milling[J]. Korean Journal of Metals and Materials, 2018, 56(12): 878-884. |
| [49] | Cao H J, Georgopanos P, Capurso G, et al. Air-stable metal hydride-polymer composites of Mg(NH2)2-LiH and TPX™[J]. Materials Today Energy, 2018, 10: 98-107. |
| [50] | Makridis S S, Gkanas E I, Panagakos G, et al. Polymer-stable magnesium nanocomposites prepared by laser ablation for efficient hydrogen storage[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(26): 11530-11535. |
| [51] | Rafatnejad M, Raygan S, Sefidmooy Azar M. Investigation of dehydrogenation performance and air stability of MgH2-PMMA nanostructured composite prepared by direct high-energy ball-milling[J]. Materials for Renewable and Sustainable Energy, 2020, 9(2): 14. |
| [52] | Ruminski A M, Bardhan R, Brand A, et al. Synergistic enhancement of hydrogen storage and air stability via Mg nanocrystal-polymer interfacial interactions[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(11): 3267-3271. |
| [53] | Jeon K J, Moon H R, Ruminski A M, et al. Air-stable magnesium nanocomposites provide rapid and high-capacity hydrogen storage without using heavy-metal catalysts[J]. Nature Materials, 2011, 10(4): 286-290. |
| [54] | Liang H, Chen D D, Chen M F, et al. Study of the synthesis of PMMA-Mg nanocomposite for hydrogen storage application[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(7): 4743-4753. |
| [55] | Shinde S S, Kim D H, Yu J Y, et al. Self-assembled air-stable magnesium hydride embedded in 3-D activated carbon for reversible hydrogen storage[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(21): 7094-7103. |
| [56] | Jia Y, Sun C H, Cheng L N, et al. Destabilization of Mg-H bonding through nano-interfacial confinement by unsaturated carbon for hydrogen desorption from MgH2 [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2013, 15(16): 5814-5820. |
| [57] | Liu M J, Zhao S C, Xiao X Z, et al. Novel 1D carbon nanotubes uniformly wrapped nanoscale MgH2 for efficient hydrogen storage cycling performances with extreme high gravimetric and volumetric capacities[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 61: 540-549. |
| [58] | Liu Y N, Zou J X, Zeng X Q, et al. Study on hydrogen storage properties of Mg nanoparticles confined in carbon aerogels[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(13): 5302-5308. |
| [59] | Huang Y Q, Xia G L, Chen J, et al. One-step uniform growth of magnesium hydride nanoparticles on graphene[J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2017, 27(1): 81-87. |
| [60] | Ali W, Qin Y Y, Khan N A, et al. Highly air-stable magnesium hydrides encapsulated by nitrogen-doped graphene nanospheres with favorable hydrogen storage kinetics[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 480: 148163. |
| [61] | Xia G L, Tan Y B, Chen X W, et al. Monodisperse magnesium hydride nanoparticles uniformly self-assembled on graphene[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(39): 5981-5988. |
| [62] | Cho E S, Ruminski A M, Aloni S, et al. Graphene oxide/metal nanocrystal multilaminates as the atomic limit for safe and selective hydrogen storage[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7(1): 10804. |
| [63] | Cho E S, Ruminski A M, Liu Y S, et al. Hierarchically controlled inside-out doping of Mg nanocomposites for moderate temperature hydrogen storage[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 27(47): 1704316. |
| [64] | Lyu J Z, Kudiiarov V, Svyatkin L, et al. On the catalytic mechanism of 3D and 4D transition-metal-based materials on the hydrogen sorption properties of Mg/MgH2 [J]. Catalysts, 2023, 13(3): 519. |
| [65] | Liu H, Wang Z Z, Zhang J Z, et al. Recent advances in hydrogen storage of MgH2 doped by Ni[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2019, 267(2): 022042. |
| [66] | Ding S J, Qiao Y Q, Cai X C, et al. Catalytic mechanisms of nickel nanoparticles for the improved dehydriding kinetics of magnesium hydride[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2024, 12(10): 4278-4288. |
| [67] | Li F, Huang Z N, Wang Y Q, et al. Effect of MOF-derived nanoparticle-cumulated flower-like CoFe@C coated composites on hydrogenation/dehydrogenation performance of MgH2 [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 485: 150008. |
| [68] | Cui J, Liu J W, Wang H, et al. Mg-TM (TM: Ti, Nb, V, Co, Mo or Ni) core-shell like nanostructures: synthesis, hydrogen storage performance and catalytic mechanism[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(25): 9645-9655. |
| [69] | Bu F Q, Wajid A, Yang N, et al. Fabrication of amorphous TiO2 hydrogen channels and graphene wrappers to enhance the hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 with extremely high cycle stability[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2024, 12(20): 12190-12197. |
| [70] | Ren L, Zhu W, Li Y H, et al. Oxygen vacancy-rich 2D TiO2 nanosheets: a bridge toward high stability and rapid hydrogen storage kinetics of nano-confined MgH2 [J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2022, 14(1): 144. |
| [71] | Zhu L, Liao Y X, Zhong Y J, et al. Improved reversible dehydrogenation performance of MgH2 by the synergistic effects of porous boron nitride and NbF5 [J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2020, 29: 101418. |
| [72] | Bolarin J A, Zou R, Li Z, et al. MXenes for magnesium-based hydrides: a review[J]. Applied Materials Today, 2022, 29: 101570. |
| [73] | Zhou D S, Zhao D L, Sun H F, et al. Two-dimensional material MXene and its derivatives enhance the hydrogen storage properties of MgH2: a review and summary[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 71: 279-297. |
| [74] | Liu H Z, Duan X Q, Wu Z Y, et al. Exfoliation of compact layered Ti2VAlC2 MAX to open layered Ti2VC2 MXene towards enhancing the hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 468: 143688. |
| [75] | Lan Z Q, Fu H, Zhao R L, et al. Roles of in situ-formed NbN and Nb2O5 from N-doped Nb2C MXene in regulating the re/hydrogenation and cycling performance of magnesium hydride[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 431: 133985. |
| [76] | Zhu W, Ren L, Lu C, et al. Nanoconfined and in situ catalyzed MgH2 self-assembled on 3D Ti3C2 MXene folded nanosheets with enhanced hydrogen sorption performances[J]. Acs Nano, 2021, 15(11): 18494-18504. |
| [77] | Zhou D S, Sun H F, Guo S H, et al. Hydrogen storage properties of Mg-based alloys modified with metal-organic frameworks and carbon-based porous materials: a review and summary[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 57: 1373-1388. |
| [78] | Ma Z W, Zhang Q Y, Panda S, et al. In situ catalyzed and nanoconfined magnesium hydride nanocrystals in a Ni-MOF scaffold for hydrogen storage[J]. Sustainable Energy & Fuels, 2020, 4(9): 4694-4703. |
| [79] | Xing X F, Zhang X J, Wei M X, et al. Nanoencapsulated MgBu2@ZIF-67 to construct high loading Mg-Co@C nanocomposites: breaking through the barrier of room temperature onset dehydrogenation[J]. Small, 2024, 20(44): 2402982. |
| [80] | Xing X F, Wang Y X, Zhang Z, et al. MgBu2 nanosheets encapsulated in ZIF-8 for producing carbon scaffold in situ nanoconfined Mg hydrogen storage materials: record-high loading and decreased dehydrogenation enthalpy[J]. Nano Energy, 2024, 127: 109740. |
| [81] | Ren L, Zhu W, Zhang Q Y, et al. MgH2 confinement in MOF-derived N-doped porous carbon nanofibers for enhanced hydrogen storage[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 434: 134701. |
| [82] | Ma Z W, Panda S, Zhang Q Y, et al. Improving hydrogen sorption performances of MgH2 through nanoconfinement in a mesoporous CoS nano-boxes scaffold[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 406: 126790. |
| [83] | Han D J, Kwon C, Cho Y, et al. Tailoring hierarchical pore structures in carbon scaffolds for hydrogen storage of nanoconfined magnesium[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 481: 148451. |
| [84] | Liu W, Setijadi E J, Aguey-Zinsou K F. Tuning the thermodynamic properties of MgH2 at the nanoscale via a catalyst or destabilizing element coating strategy[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(48): 27781-27792. |
| [85] | Liu Y N, Zou J X, Zeng X Q, et al. A co-precipitated Mg-Ti nano-composite with high capacity and rapid hydrogen absorption kinetics at room temperature[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(81): 42764-42771. |
| [86] | Liu Y N, Zou J X, Zeng X Q, et al. Hydrogen storage properties of a Mg-Ni nanocomposite coprecipitated from solution[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(32): 18401-18411. |
| [87] | Lu C, Zou J X, Shi X Y, et al. Synthesis and hydrogen storage properties of core-shell structured binary Mg@Ti and ternary Mg@Ti@Ni composites[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(4): 2239-2247. |
| [1] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [2] | 郭松源, 周晓庆, 缪五兵, 汪彬, 耑锐, 曹庆泰, 陈成成, 杨光, 吴静怡. 火箭上升段含多孔板液氧贮箱增压输运数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 62-74. |
| [3] | 臧子晴, 李修真, 谈莹莹, 刘晓庆. 分凝器对两级分离自复叠制冷循环特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 17-25. |
| [4] | 李银龙, 刘国强, 晏刚. 分馏与闪蒸分离耦合自复叠制冷循环性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 26-35. |
| [5] | 朱腾飞, 刘晔. 低GWP制冷剂在新能源汽车空调应用性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 343-350. |
| [6] | 吴迪, 胡斌, 姜佳彤. R1233zd(E)高温热泵实验研究与应用分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 377-383. |
| [7] | 苏伟, 赵大海, 金旭, 刘忠彦, 李静, 张小松. 吸湿液滴与混合润湿性表面协同抑霜特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 140-151. |
| [8] | 龚宇, 王胜利, 孙金菊, 海阔, 黄文. 微型多级压缩机充气系统的热力学模型及规律探究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3626-3638. |
| [9] | 董泽明, 娄聚伟, 王楠, 陈良奇, 王江峰, 赵攀. 含余热回收的超临界压缩二氧化碳储能系统热力学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3477-3486. |
| [10] | 郭梁, 陈烨, 贾启明, 谢秀娟. 液氦贮罐的自增压理论模拟及实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3561-3571. |
| [11] | 高照, 吴熙, 夏丹, 张霖宙. 石油加工分子管理平台热力学及分离单元模块开发[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3212-3225. |
| [12] | 李琳, 王明媚, 宋二伟, 王雯雯, 张耀昌, 王二强. 异戊二烯-正戊烷分离工艺的热力学分析及优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2549-2558. |
| [13] | 江锦波, 陈竹鑫, 肖洋溢, 彭新, 陈源, 于辰, 孟祥铠, 彭旭东. 运行工况对超临界CO2干气密封端面热力学过程及稳态性能影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2913-2928. |
| [14] | 韩光泽, 张佩璇. 静电场作用下液体凝固点变化的热力学机理[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2544-2548. |
| [15] | 刘淑丽, 周文豪, 张少良, 沈永亮. 太阳能直接吸收相变集-蓄热器的放热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1722-1730. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号