CIESC Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (1): 192-204.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20201161
• Reviews and monographs • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Yuqiong1( ),LI Yao1,JU Xiaojie1,2(
),LI Yao1,JU Xiaojie1,2( ),XIE Rui1,2,WANG Wei1,2,LIU Zhuang1,2,CHU Liangyin1,2
),XIE Rui1,2,WANG Wei1,2,LIU Zhuang1,2,CHU Liangyin1,2
Received:2020-08-14
Revised:2020-11-09
Online:2021-01-05
Published:2021-01-05
Contact:
JU Xiaojie
刘玉琼1( ),李瑶1,巨晓洁1,2(
),李瑶1,巨晓洁1,2( ),谢锐1,2,汪伟1,2,刘壮1,2,褚良银1,2
),谢锐1,2,汪伟1,2,刘壮1,2,褚良银1,2
通讯作者:
巨晓洁
作者简介:刘玉琼(1994—),女,博士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
LIU Yuqiong, LI Yao, JU Xiaojie, XIE Rui, WANG Wei, LIU Zhuang, CHU Liangyin. Progress in lead ion detection technologies based on 18-crown-6[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(1): 192-204.
刘玉琼, 李瑶, 巨晓洁, 谢锐, 汪伟, 刘壮, 褚良银. 基于18-冠-6的铅离子检测技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 192-204.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
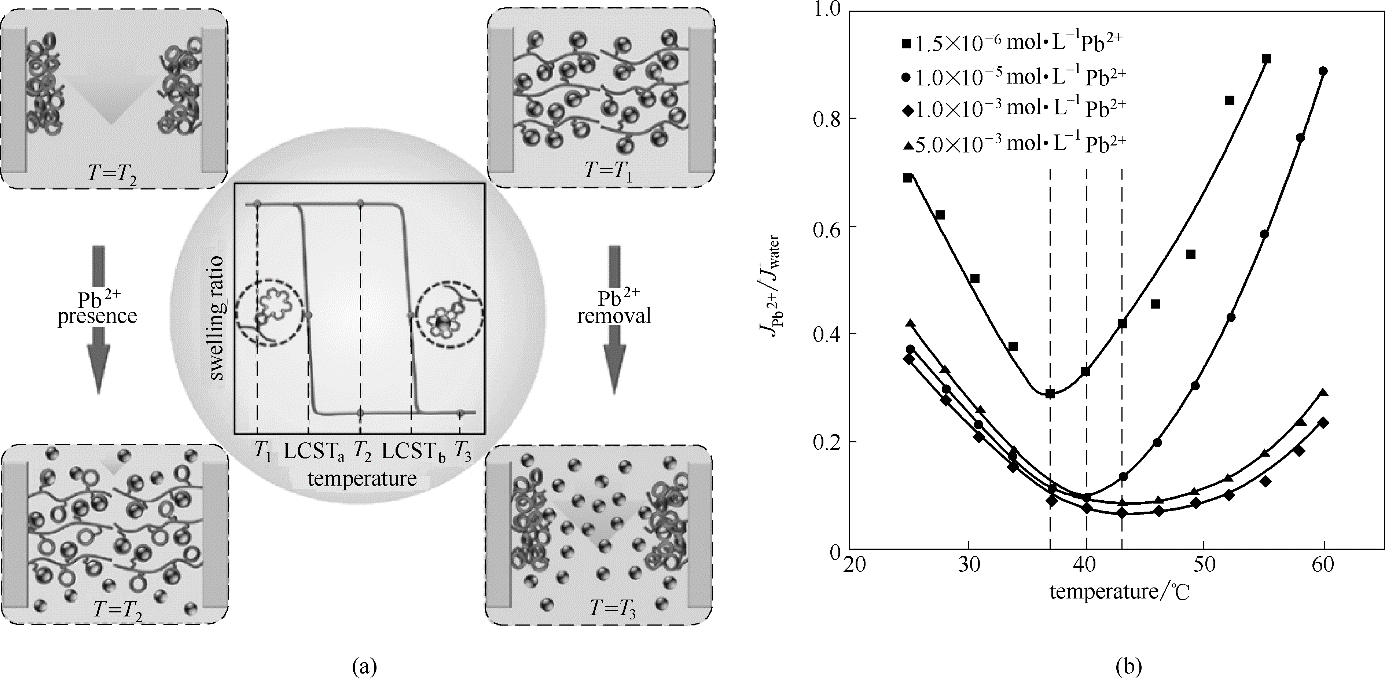
Fig.1 Schematic illustration of the linear polymer brush modified membrane responding to Pb2+ (a); The flux ratio (JPb2+/Jwater) changes responding to different Pb2+ concentrations at different temperature (b)[28]
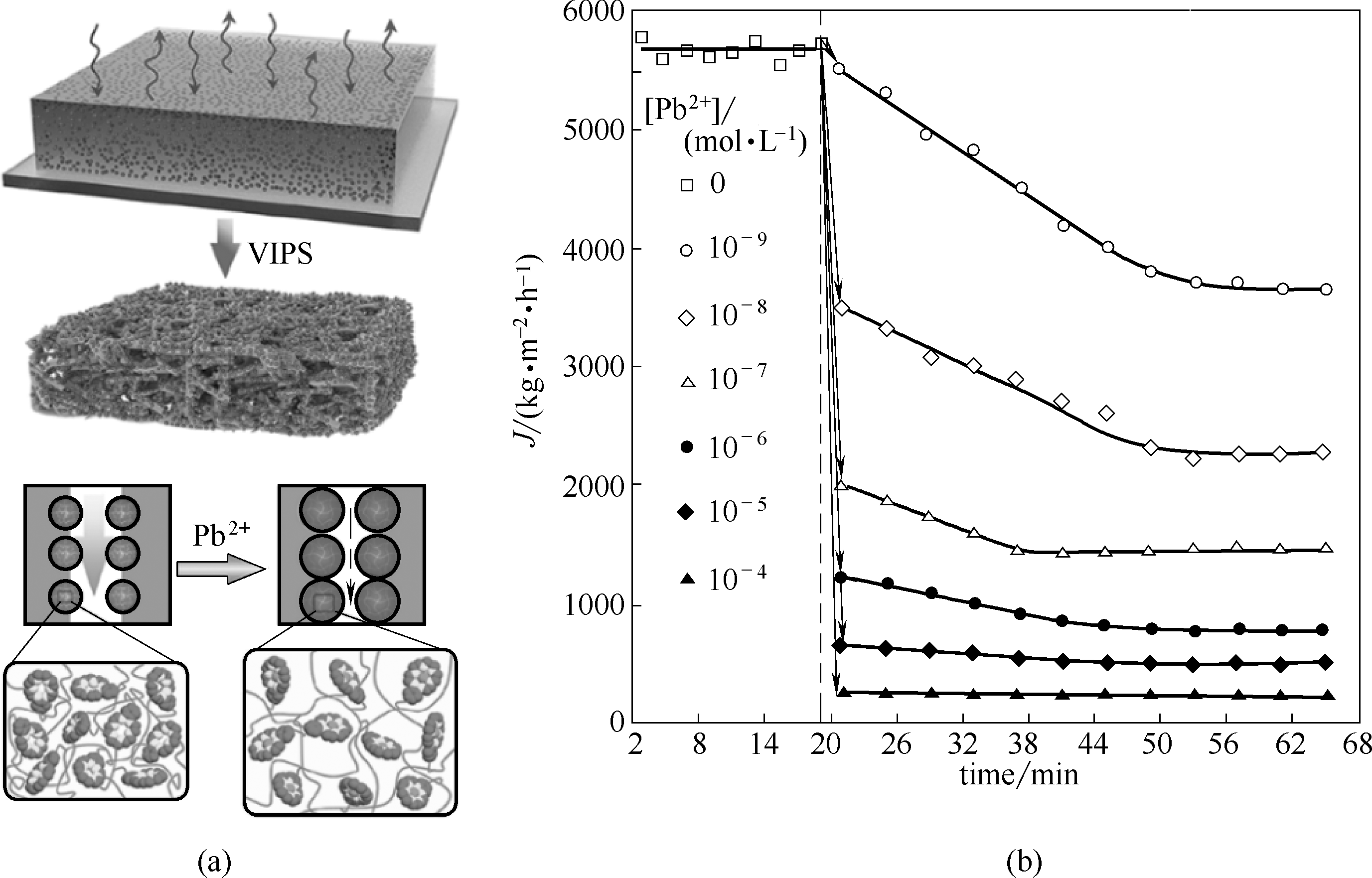
Fig.2 Schematic illustration of the fabrication and Pb2+-detection strategy of proposed novel smart membrane with smart nanogels as gates on membrane pores (a); The changes of fluxes across membrane switching the transmembrane solutions from deionized water to Pb2+ solution with different concentrations (b)[31]
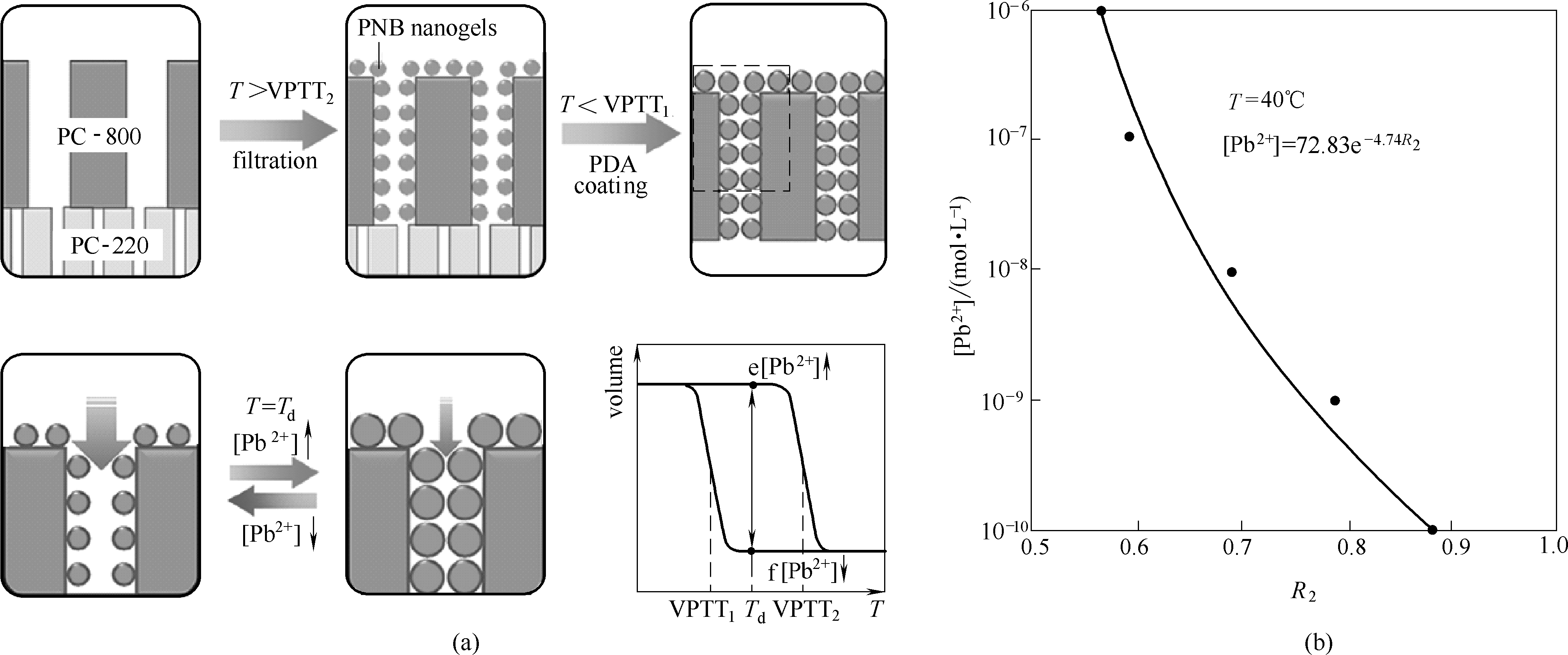
Fig.3 Schematic illustration of the fabrication of nanogel-immobilized membrane for Pb2+ detection (a); The relationship between the flux ratio (JPb2+/Jwater) and Pb2+ concentrations at 40℃ (b) [32]
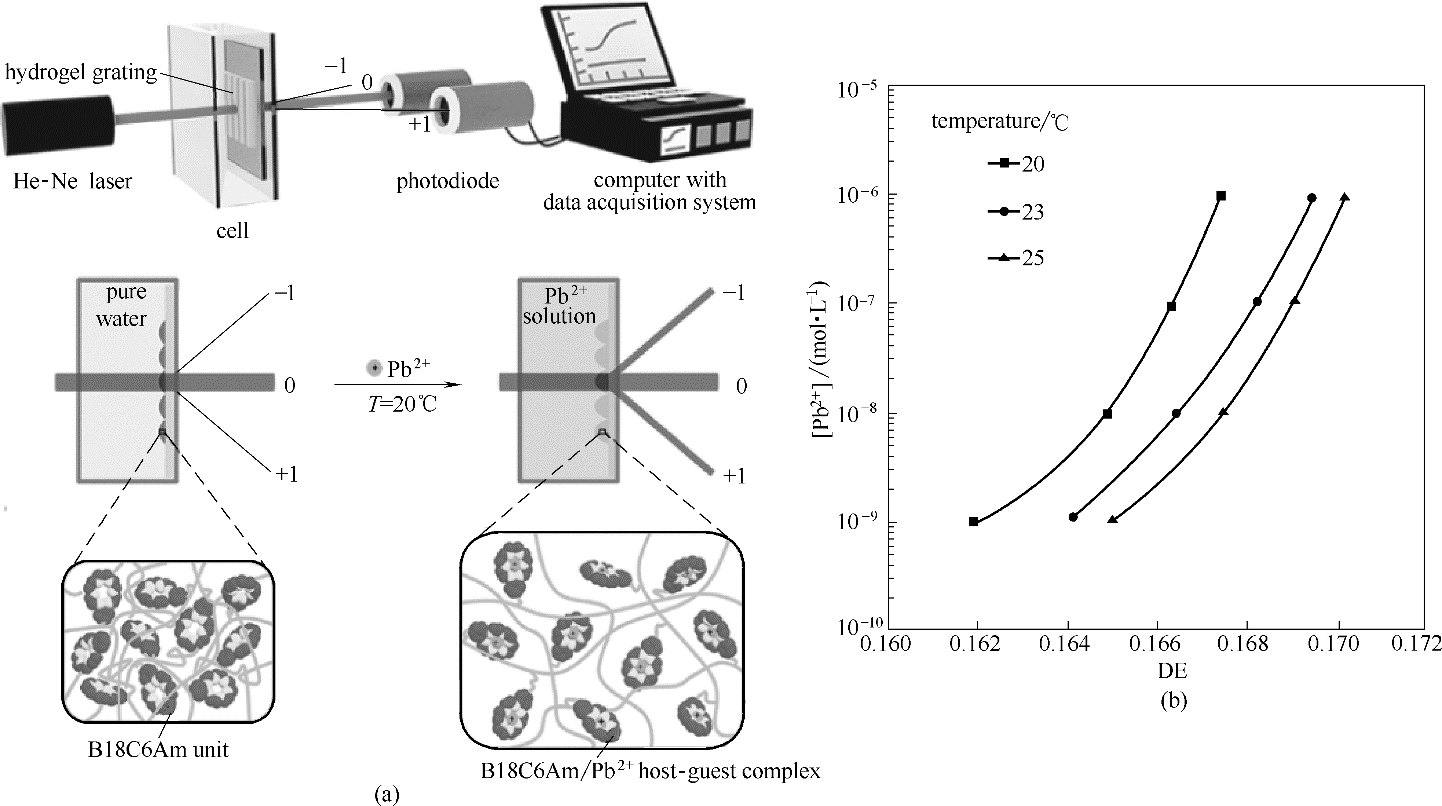
Fig.4 Schematic illustration of the smart hydrogel grating system for Pb2+ detection (a); Relationships between Pb2+ concentration and diffraction efficiency at different temperature (b)[42]

Fig.5 Schematic illustration of the preparation and ion-detection of photonic crystal polyelectrolyte gel (a); Reflection peak wavelength shift induced by the change in Pb2+ concentrations (b)[51]
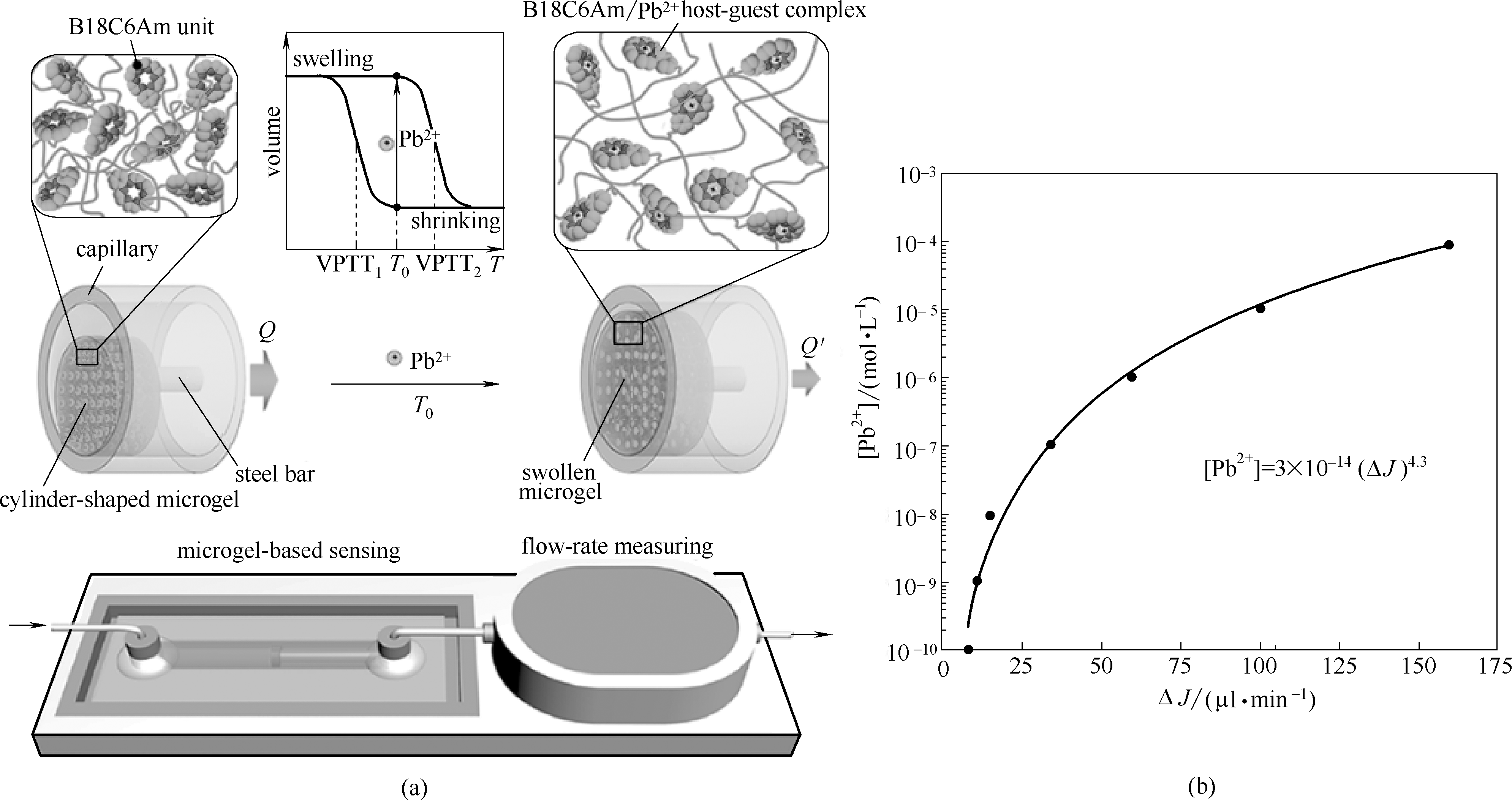
Fig.7 Schematic illustration of Pb2+-detection microchip equipped with smart microgel (a); The quantitative relationship between Pb2+ concentrations and the flow rate changes responding to Pb2+(b)[70]
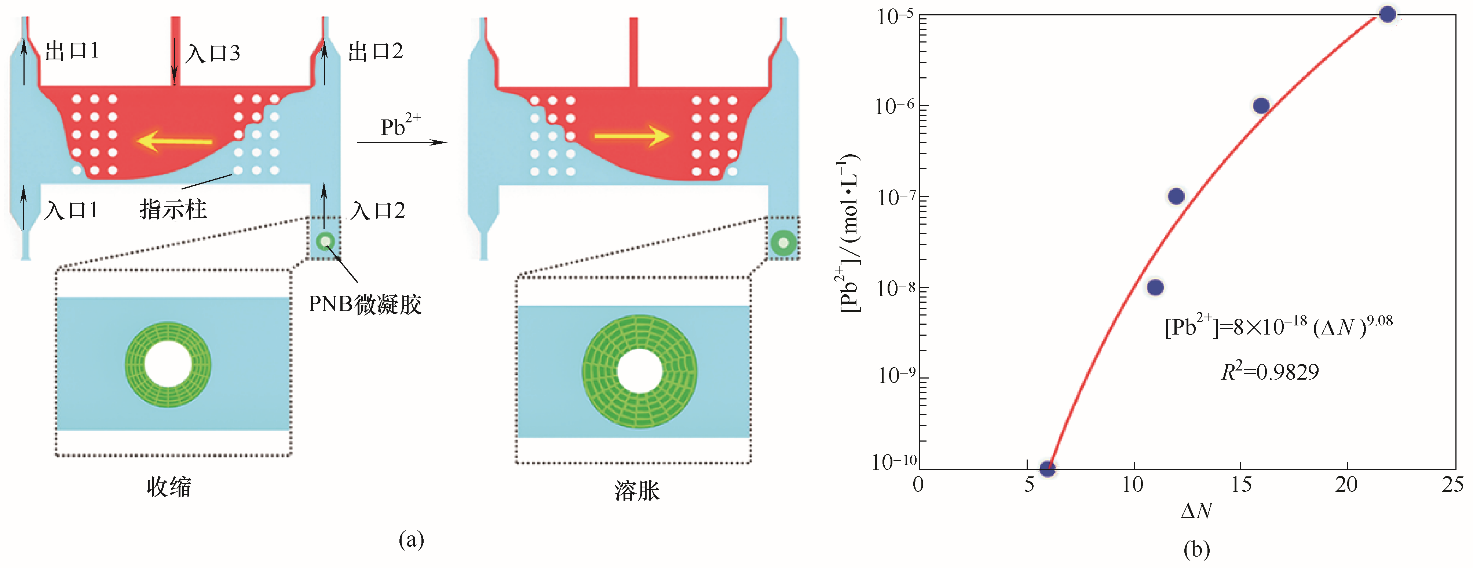
Fig.8 Schematic illustration of Pb2+ -detection microchip based on smart microgel array (a); Relationship between the number changes of indicating pillars and the concentrations of Pb2+ (b)[71]
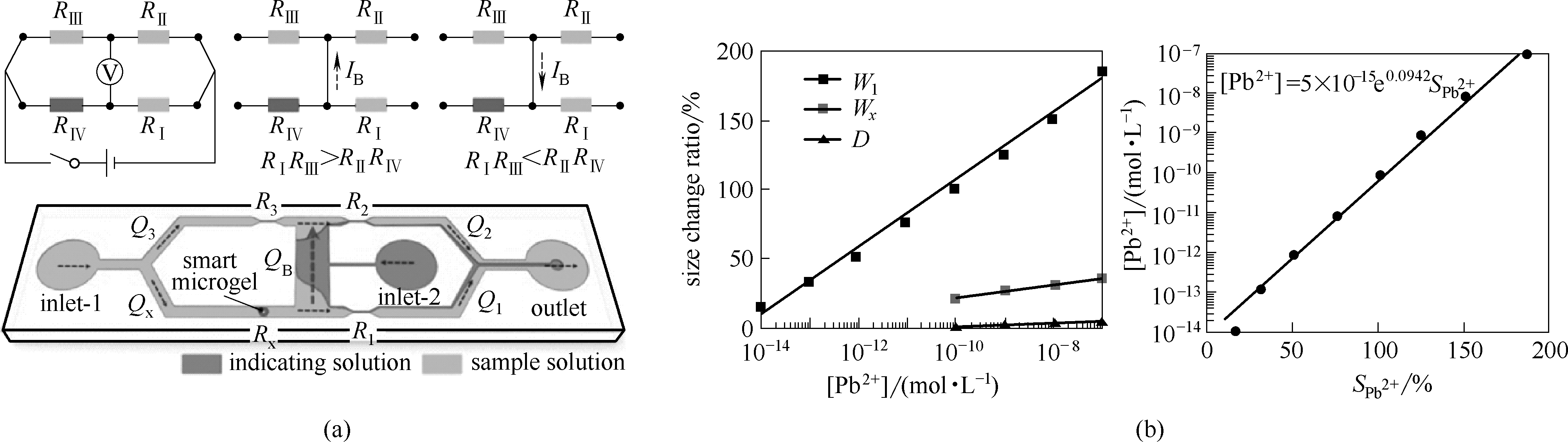
Fig.9 Schematic illustration of Pb2+ -detection Wheatstone-bridge microchip based on smart microgel (a); Relationship between the SPb2+ and the concentrations of Pb2+ (b)[72]
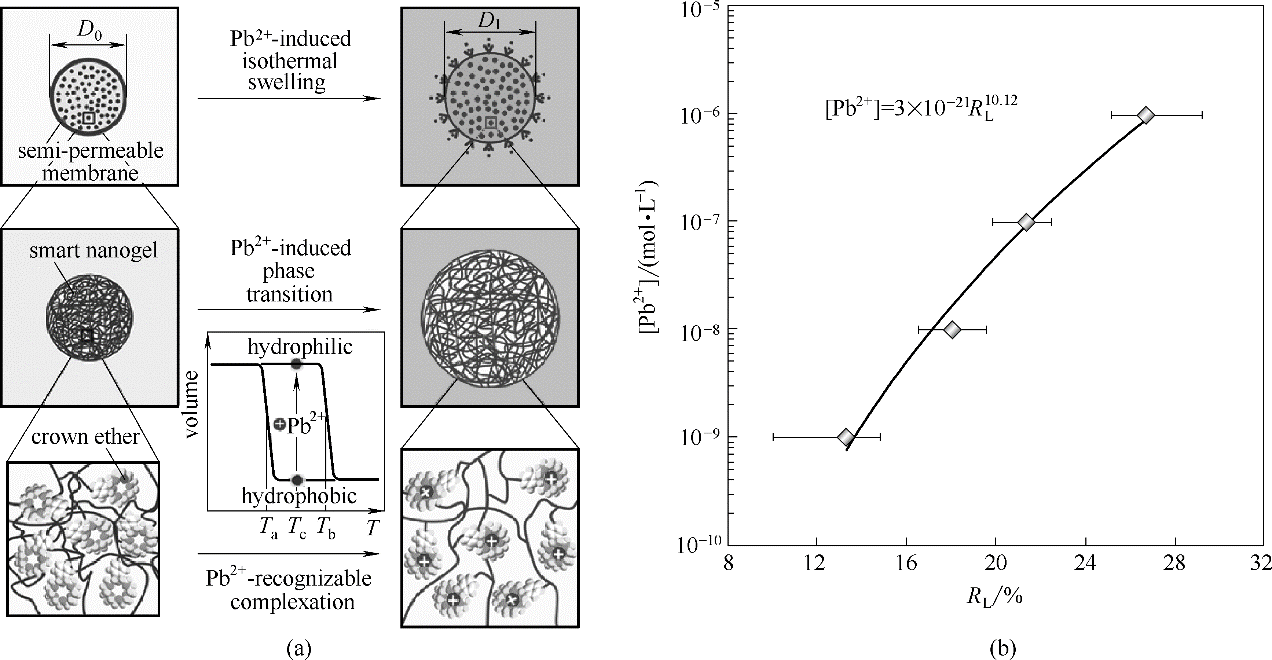
Fig.10 Schematic illustration of the smart microcapsule system for facilely detecting Pb2+ ions in water (a); The relationship between the length change ratio (RL) of the microcapsule membrane group and the Pb2+ concentrations (b) [76]

Fig.11 Schematic illustrations of the structure construction and the Pb2+ detection mechanism of the simple device equipped with smart hydrogel (a); Three-dimensional diagram of ΔLPb2+ as a function of both Pb2+ concentrations and temperature (b)[77]
| 智能高分子材料检测系统 | 最低检测限/(mol·L-1) | 测试仪器 | 优点 | 缺点 | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 智能膜 | 线性高分子修饰的智能膜 | 10-6 | 膜通量装置 | 测量装置简单,易储存 | 化学接枝方法复杂,可重复性差,膜结构难控制;蒸汽诱导相分离法制膜过程对温湿度要求严格,测试过程中样品消耗量大 | [ |
| 凝胶微球修饰的智能膜 | 10-10 | [ | ||||
| 智能光学元件 | 智能凝胶光栅 | 10-9 | 激光,光电二极管,数据处理软件 | 高精度,小型化,响应时间短 | 检测系统结构精细,易受干扰,对测试环境要求较高 | [ |
| 智能光子晶体 | 10-10 | 光纤光谱仪 | [ | |||
| 智能微悬臂梁 | 10-6 | 激光,位置敏感传感器 | [ | |||
| 智能微芯片 | 单通道智能微芯片 | 10-10 | 流量传感器 | 高精度,小型化,响应时间短 | 检测系统的构建较复杂 | [ |
| 惠斯通电桥智能微芯片 | 10-14 | 显微镜 | [ | |||
| 智能微胶囊 | 10-9 | 无 | 可视化检测 | 精度和可重复性较差 | [ | |
Table 1 Lead(Ⅱ) detection technologies based on 18-crown-6
| 智能高分子材料检测系统 | 最低检测限/(mol·L-1) | 测试仪器 | 优点 | 缺点 | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 智能膜 | 线性高分子修饰的智能膜 | 10-6 | 膜通量装置 | 测量装置简单,易储存 | 化学接枝方法复杂,可重复性差,膜结构难控制;蒸汽诱导相分离法制膜过程对温湿度要求严格,测试过程中样品消耗量大 | [ |
| 凝胶微球修饰的智能膜 | 10-10 | [ | ||||
| 智能光学元件 | 智能凝胶光栅 | 10-9 | 激光,光电二极管,数据处理软件 | 高精度,小型化,响应时间短 | 检测系统结构精细,易受干扰,对测试环境要求较高 | [ |
| 智能光子晶体 | 10-10 | 光纤光谱仪 | [ | |||
| 智能微悬臂梁 | 10-6 | 激光,位置敏感传感器 | [ | |||
| 智能微芯片 | 单通道智能微芯片 | 10-10 | 流量传感器 | 高精度,小型化,响应时间短 | 检测系统的构建较复杂 | [ |
| 惠斯通电桥智能微芯片 | 10-14 | 显微镜 | [ | |||
| 智能微胶囊 | 10-9 | 无 | 可视化检测 | 精度和可重复性较差 | [ | |
| 1 | Gidlow D. Lead toxicity[J]. Occup. Med., 2004, 65(5): 348-356. |
| 2 | Jang S H, Min B G, Jeong Y G, et al. Removal of lead ions in aqueous solution by hydroxyapatite/polyurethane composite foams[J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, 152(3): 1285-1292. |
| 3 | Nriagu J O, Pacyna J M. Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water and soils by trace metals[J]. Nature, 1988, 333(6169): 134-139. |
| 4 | Lidsky T I, Schneider J S. Lead neurotoxicity in children: basic mechanisms and clinical correlates[J]. Brain, 2003, 126: 5-19. |
| 5 | Olympio K P K, Goncalves C, Günther W M R, et al. Neurotoxicity and aggressiveness triggered by low-level lead in children: a review[J]. Pan. Am. J. Public. Health, 2009, 26(3): 266-275. |
| 6 | Mahmoud M E, Kenawy I M M, Hafez M A H, et al. Removal, preconcentration and determination of trace heavy metal ions in water samples by AAS via chemically modified silica gel N-(1-carboxy-6-hydroxy) benzylidenepropylamine ion exchanger[J]. Desalination, 2010, 250(1): 62-70. |
| 7 | Jurado J M, Martín M J, Pablos F, et al. Direct determination of copper, lead and cadmium in aniseed spirits by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry[J]. Food Chem., 2007, 101(3): 1296-1304. |
| 8 | İ Narin, Soylak M, Elçi L, et al. Determination of trace metal ions by AAS in natural water samples after preconcentration of pyrocatechol violet complexes on an activated carbon column [J]. Talanta, 2000, 52(6): 1041-1046. |
| 9 | Zhou Q, Zhao N, Xie G. Determination of lead in environmental waters with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction prior to atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 189(1/2): 48-53. |
| 10 | Chen Y, Li M, Fu L, et al. Simultaneous determination of trace cadmium and lead in single human hair by tungsten electrothermal vaporization-flame atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J]. Microchem. J., 2014, 114: 182-186. |
| 11 | Karadjova I B, Lampugnani L, D'ulivo A, et al. Determination of lead in wine by hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry in the presence of hexacyanoferrate(Ⅲ)[J]. Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2007, 388(4): 801-807. |
| 12 | Aydin F A, Soylak M. Separation, preconcentration and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometric (ICP-MS) determination of thorium(Ⅳ), titanium(Ⅳ), iron(Ⅲ), lead(Ⅱ) and chromium(Ⅲ) on 2-nitroso-1-naphthol impregnated MCI GEL CHP20P resin[J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2010, 173(1/2/3): 669-674. |
| 13 | Lin M L, Jiang S J. Determination of As, Cd, Hg and Pb in herbs using slurry sampling electrothermal vaporisation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Food Chem., 2013, 141(3): 2158-2162. |
| 14 | Otero-Romaní J, Moreda-Pineiro A, Bermejo-Barrera P, et al. Inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectrometry/mass spectrometry for the determination of Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in seawater after ionic imprinted polymer based solid phase extraction[J]. Talanta, 2009, 79(3): 723-729. |
| 15 | Pedersen C J. The discovery of crown ethers[J]. Science, 1988, 241(4865): 536-540. |
| 16 | Izatt R M, Pawlak K, Bradshaw J S, et al. Thermodynamic and kinetic data for macrocycle interactions with cations and anions[J]. Cheminform, 1991, 23(7): 322. |
| 17 | 巨晓洁,谢锐,汪伟,等. 基于冠醚的离子识别响应型智能材料研究新进展[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(1): 261-267. |
| Ju X J, Xie R, Wang W, et al. Development of ion-recognition-responsive smart materials based on crown ethers[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(1): 261-267. | |
| 18 | 刘壮, 巨晓洁, 谢锐, 等. Pb2+识别响应型智能高分子功能材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(5): 1571-1576. |
| Liu Z, Ju X J, Xie R, et al. Progress of Pb2+-recognition-responsive smart polymeric functional materials[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(5): 1571-1576. | |
| 19 | Liu Z, Wang W, Xie R, et al. Stimuli-responsive smart gating membranes[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45(3): 460-475. |
| 20 | Hara N, Ohashi H, Ito T, et al. Reverse response of an ion-recognition polyampholyte to specific ion signals at different pHs[J]. Macromolecules, 2009, 42(4): 980-986. |
| 21 | Jie Z, Chu L Y, Li Y K, et al. Dual thermo- and pH-sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels with rapid response behaviors[J]. Polymer, 2007, 48(6): 1718-1728. |
| 22 | Chae I, Khan M F, Song J, et al. Standoff mechanical resonance spectroscopy based on infrared-sensitive hydrogel microcantilevers[J]. Anal. Chem., 2016, 88(19): 9678-9684. |
| 23 | Shiraki Y, Tsuruta K, Morimoto J, et al. Preparation of molecule-responsive microsized hydrogels via photopolymerization for smart microchannel microvalves[J]. Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2015, 36(6): 515-519. |
| 24 | Li J, Yim D, Jang W D, et al. Recent progress in the design and applications of fluorescence probes containing crown ethers[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46(9): 2367-2650. |
| 25 | 谢锐, 巨晓洁, 汪伟, 等. 智能膜对传质和反应与分离过程的调控[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(9): 3279-3286. |
| Xie R, Ju X J, Wang W, et al. Regulation on rates of mass transfer, reaction and separation via smart membranes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(9): 3279-3286. | |
| 26 | Chen Z H, Liu Z, Hu J Q, et al. β-Cyclodextrin-modified graphene oxide membranes with large adsorption capacity and high flux for efficient removal of bisphenol A from water[J]. J. Membr. Sci., 2020, 595: 117510. |
| 27 | Chu L Y, Li Y, Zhu J H, et al. Control of pore size and permeability of a glucose-responsive gating membrane for insulin delivery[J]. J. Control Release, 2004, 97(1): 43-53. |
| 28 | Liu Z, Luo F, Ju X J, et al. Gating membranes for water treatment: detection and removal of trace Pb2+ ions based on molecular recognition and polymer phase transition[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(34): 9659-9671. |
| 29 | Misumi Y, Tanaka T. Stimuli-responsive polymers: chemical induced reversible phase separation of an aqueous solution of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) with pendent crown ether groups[J]. Polymer, 1993, 34(21): 4531-4535. |
| 30 | Zhang B, Ju X J, Xie R, et al. Comprehensive effects of metal ions on responsive characteristics of P(NIPAM-co-B18C6Am)[J]. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2012, 116(18): 5527-5536. |
| 31 | Wang Y, Liu Z, Luo F, et al. A novel smart membrane with ion-recognizable nanogels as gates on interconnected pores for simple and rapid detection of trace lead(Ⅱ) ions in water[J]. J. Membr. Sci., 2019, 575: 28-37. |
| 32 | Yan P J, He F, Wang W, et al. Novel membrane detector based on smart nanogels for ultrasensitive detection of trace threat substances[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10(42): 36425-36434. |
| 33 | Gaylord T K, Moharam M G. Analysis and applications of optical diffraction by gratings[J]. P. IEEE, 1985, 73(5): 894-937. |
| 34 | Fayer M. Dynamics of molecules in condensed phases: picosecond holographic grating experiments[J]. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 1982, 33(1): 63-87. |
| 35 | Nelson K A. Laser-induced excited state and ultrasonic wave gratings: amplitude and phase grating contributions to diffraction [J]. J. Chem. Phys., 1982, 77(3): 1144-1152. |
| 36 | Bailey R C, Hupp J T. Large-scale resonance amplification of optical sensing of volatile compounds with chemoresponsive visible-region diffraction gratings[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124(23): 6767-6774. |
| 37 | Dang X, Stevenson K J, Hupp J T. Monitoring molecular adsorption on high-area titanium dioxide via modulated diffraction of visible light [J]. Langmuir, 2016, 17(11): 3109-3112. |
| 38 | Henne W A, Doorneweerd D D, Lee J, et al. Detection of folate binding protein with enhanced sensitivity using a functionalized quartz crystal microbalance sensor[J]. Anal. Chem., 2006, 78(14): 4880-4884. |
| 39 | Sendroiu I E, Corn R M. Nanoparticle diffraction gratings for DNA detection on photopatterned glass substrates[J]. Biointerphases, 2008, 3(3): FD23-FD29. |
| 40 | Morhard F, Pipper J, Dahint R, et al. Immobilization of antibodies in micropatterns for cell detection by optical diffraction[J]. Sensors Actuat. B Chem., 2000, 70(1/2/3): 232-242. |
| 41 | Wang X Q, Ye G, Wang X G. Hydrogel diffraction gratings functionalized with crown ether for heavy metal ion detection[J]. Sensors Actuat. B Chem., 2014, 193: 413-419. |
| 42 | Peng H Y, Wang W, Gao F, et al. Ultrasensitive diffraction gratings based on smart hydrogels for highly selective and rapid detection of trace heavy metal ions[J]. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2018, 6(42): 11356-11367. |
| 43 | 邓开发, 是度芳, 蒋美萍, 等. 光子晶体研究进展[J]. 量子电子学报, 2004, 21(5): 555-564. |
| Deng K F, Shi D F, Jiang M P, et al. Progress in the study of photonic crystal[J]. Chinese Journal of Quantume Electronics, 2004, 21(5): 555-564. | |
| 44 | Weissman J M, Sunkara H B, Tse A S, et al. Thermally switchable periodicities and diffraction from mesoscopically ordered materials[J]. Science, 1996, 274(5289): 959-963. |
| 45 | Goponenko A V, Asher S A. Modeling of stimulated hydrogel volume changes in photonic crystal Pb2+ sensing materials[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127(30): 10753-10759. |
| 46 | Holtz J H, Asher S A. Polymerized colloidal crystal hydrogel films as intelligent chemical sensing materials[J]. Nature, 1997, 389: 829-832. |
| 47 | Asher S A, Sharma A C, Goponenko A V, et al. Photonic crystal aqueous metal cation sensing materials [J]. Anal. Chem., 2003, 75(7): 1676-1683. |
| 48 | Asher S A, Alexeev V L, Goponenko A V, et al. Photonic crystal carbohydrate sensors: low ionic strength sugar sensing[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125(11): 3322-3329. |
| 49 | Sharma A C, Jana T, Kesavamoorthy R, et al. A general photonic crystal sensing motif: creatinine in bodily fluids[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(9): 2971-2977. |
| 50 | Lee Y J, Braun P V. Tunable inverse opal hydrogel pH sensors[J]. Adv. Mater., 2003, 15(7/8): 563-566. |
| 51 | Hong W, Li W, Hu X, et al. Highly sensitive colorimetric sensing for heavy metal ions by strong polyelectrolyte photonic hydrogels[J]. J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21(43): 17193-17201. |
| 52 | Fritz J, Baller M K, Lang H P, et al. Translating biomolecular recognition into nanomechanics[J]. Science, 2000, 288(5464): 316-318. |
| 53 | Ji H F, Thundat T, Dabestani R, et al. Ultrasensitive detection of CrO42- using a microcantilever sensor[J]. Anal. Chem., 2001, 73(7): 1572-1576. |
| 54 | Hwang K S, Lee M H, Lee J, et al. Peptide receptor-based selective dinitrotoluene detection using a microcantilever sensor[J]. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2011, 30(1): 249-254. |
| 55 | Thundat T, Wachter E A, Sharp S L, et al. Detection of mercury vapor using resonating microcantilevers[J]. Appl. Phys. Lett., 1995, 66(13): 1695-1697. |
| 56 | Persson H H J, Caseri W R, Suter U W. Versatile method for chemical reactions with self-assembled monolayers of alkanethiols on gold[J]. Langmuir, 2001, 17(12): 3643-3650. |
| 57 | Kadam A R, Nordin G P, George M A. Comparison of microcantilever Hg sensing behavior with thermal higher order modes for as-deposited sputtered and thermally evaporated Au films[J]. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. Microelectron., 2006, 24(5): 2271-2275. |
| 58 | Ji H F, Zhang Y, Purushotham V V, et al. 1,6-Hexanedithiol monolayer as a receptor for specific recognition of alkylmercury[J]. Analyst, 2005, 130(12): 1577-1579. |
| 59 | Maraldo D, Mutharasan R. Optimization of antibody immobilization for sensing using piezoelectrically excited-millimeter-sized cantilever (PEMC) sensors[J]. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem., 2007, 123(1): 474-479. |
| 60 | Lemieux M C, McConney M E, Lin Y H, et al. Polymeric nanolayers as actuators for ultrasensitive thermal bimorphs[J]. Nano Lett., 2006, 6(4): 730-734. |
| 61 | Li M, Tang H X, Roukes M L. Ultra-sensitive NEMS-based cantilevers for sensing, scanned probe and very high-frequency applications[J]. Nat. Nanotechnol., 2007, 2: 114-120. |
| 62 | Meyer G, Amer N M. Novel optical approach to atomic force microscopy[J]. Appl. Phys. Lett., 1998, 53(12): 1045-1047. |
| 63 | Lavrik N V, Sepaniak M J, Datskos P G. Cantilever transducers as a platform for chemical and biological sensors[J]. Rev. Sci. Instrum., 2004, 75(7): 2229-2253. |
| 64 | Liu K, Ji H F. Detection of Pb2+ using a hydrogel swelling microcantilever sensor[J]. Anal. Sci., 2004, 20(1): 9-11. |
| 65 | Whitesides G M. The origins and the future of microfluidics[J]. Nature, 2006, 442(7101): 368-373. |
| 66 | Mark D, Haeberle S, Roth G, et al. Microfluidic lab-on-a-chip platforms: requirements, characteristics and applications[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39: 1153–1182. |
| 67 | Wang F, Zhang Z, Zhong Q X, et al. Design of polarization imaging detection system for lung cancer cells based on microfluidic chip[J]. J. Med. Syst., 2019, 43(4):85-92. |
| 68 | Yang C H, Hsieh Y L, Tsou P H, et al. Thermopneumatic suction integrated microfluidic blood analysis system[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(3): e0208676. |
| 69 | Zhao Z T, Al-Ameen M A, Duan K, et al. On-chip porous microgel generation for microfluidic enhanced VEGF detection[J]. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 74: 305-312. |
| 70 | Lin S, Wang W, Ju X J, et al. Ultrasensitive microchip based on smart microgel for real-time online detection of trace threat analytes[J]. Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA, 2016, 113(8): 2023-2028. |
| 71 | 汪伟, 彭减, 林硕, 等. 智能微流控检测芯片的构建及其Pb2+检测性能[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(1): 42-48. |
| Wang W, Peng J, Lin S, et al. Fabrication of smart microfluidic chip and its Pb2+-detection performance[J]. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog., 2020, 39(1): 42-48. | |
| 72 | Peng J, Zhao N, Lin S, et al. Smart microfluidic analogue of Wheatstone-bridge for real-time continuous detection with ultrasensitivity and wide dynamic range[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 407: 127138. |
| 73 | Mu X T, Ju X J, Zhang L, et al. Chitosan microcapsule membranes with nanoscale thickness for controlled release of drugs[J]. J. Membr. Sci., 2019, 590:117275. |
| 74 | 刘文英, 巨晓洁, 谢锐, 等. 共挤出流体法制备功能化胶囊膜的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(10): 4365-4378. |
| Liu W Y, Ju X J, Xie R, et al. Recent progress in preparation of functional capsule membranes based on co-extrusion minifluidic technique[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(10): 4365-4378. | |
| 75 | 温霜, 巨晓洁, 谢锐, 等. 肠靶向海藻酸钙基微胶囊的制备及控释性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(8): 3797-3806. |
| Wen S, Ju X J, Xie R, et al. Fabrication and controlled-release properties of intestinal-targeted Ca-alginate-based capsules[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(8): 3797-3806. | |
| 76 | Liu W Y, Ju X J, Faraj Y, et al. Capsule membranes encapsulated with smart nanogels for facile detection of trace lead(II) ions in water[J]. J. Membr. Sci., 2020, 613: 118523. |
| 77 | Chen A L, Yu H R, Ju X J, et al. Visual detection of lead(Ⅱ) using a simple device based on P(NIPAM-co-B18C6Am) hydrogel[J]. RSC Adv., 2014, 4(50): 26030-26037. |
| [1] | Shanshan YANG, Yuyang YAO, Yundi DONG, Zhipeng XU, Shangshang GAO, Huimin RUAN, Jiangnan SHEN. Preparation and performance of ion exchange membrane with K+ selectivity based on dibenzo-18-crown-6 modification [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(4): 1781-1793. |
| [2] | JU Xiaojie, XIE Rui, WANG Wei, CHU Liangyin. Development of ion-recognition-responsive smart materials based on crown ethers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(1): 261-267. |
| [3] | GUO Xiaojing, ZHU Yudan, WEI Mingjie, WU Ximing, LÜ Linghong, LU Xiaohua. Theoretical Study of Hydration Effects on the Selectivity of 18-Crown-6 Between K+ and Na+ [J]. , 2011, 19(2): 212-216. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||