CIESC Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (4): 1598-1606.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230091
• Separation engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yangguang LYU( ), Peipei ZUO, Zhengjin YANG(
), Peipei ZUO, Zhengjin YANG( ), Tongwen XU(
), Tongwen XU( )
)
Received:2023-02-20
Revised:2023-03-20
Online:2023-06-02
Published:2023-04-05
Contact:
Zhengjin YANG, Tongwen XU
通讯作者:
杨正金,徐铜文
作者简介:吕阳光(1996—),男,硕士研究生,yglv@mail.ustc.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yangguang LYU, Peipei ZUO, Zhengjin YANG, Tongwen XU. Triazine framework polymer membranes for methanol/n-hexane separation via organic solvent nanofiltration[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1598-1606.
吕阳光, 左培培, 杨正金, 徐铜文. 三嗪框架聚合物膜用于有机纳滤甲醇/正己烷分离[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1598-1606.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
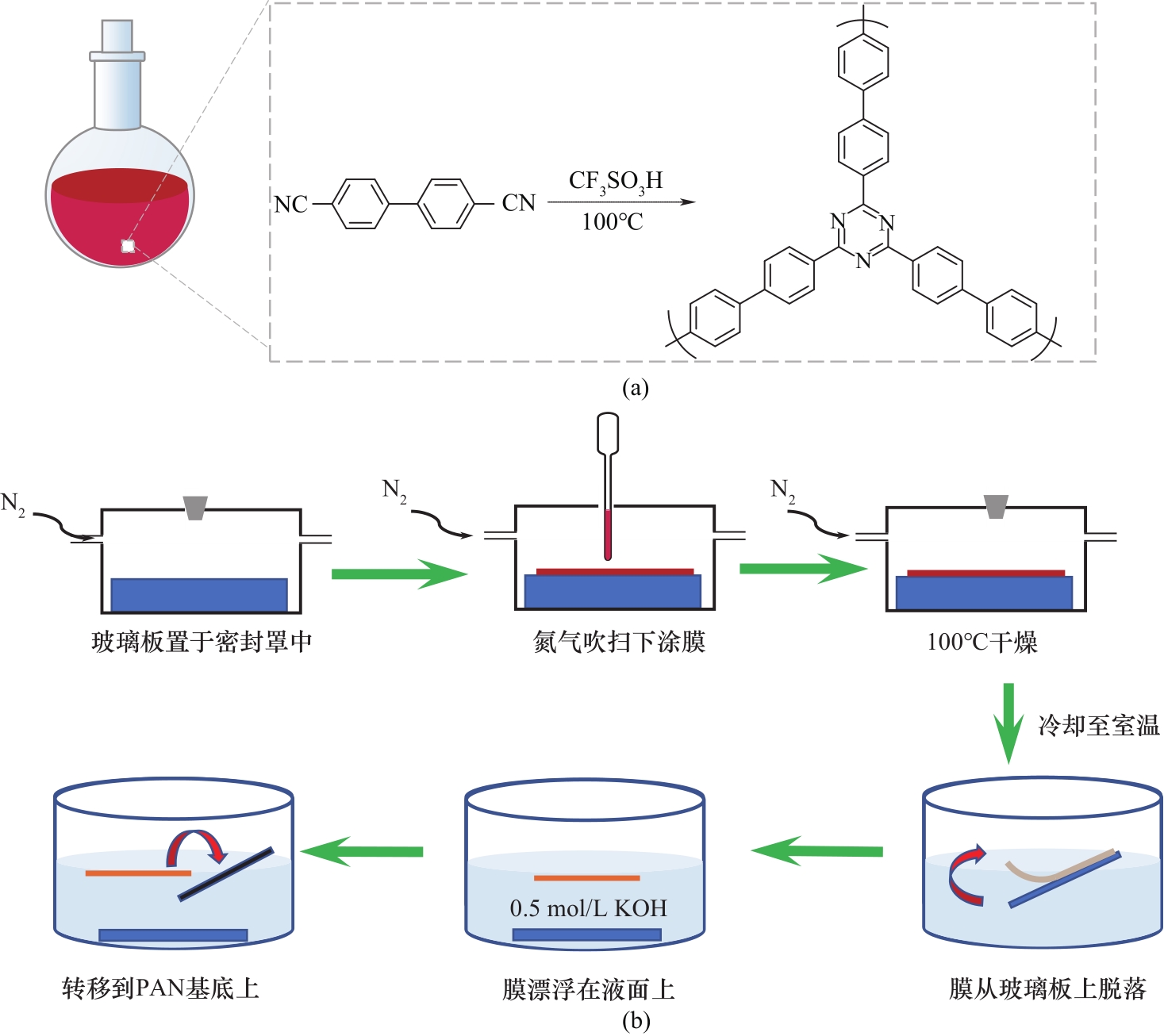
Fig.1 Covalent triazine framework synthesized by the superacid catalytic polymerization of 4,4′-biphenyldicarbonitrile (a) and schematic diagram of the preparation of CTF-BP membranes (b)
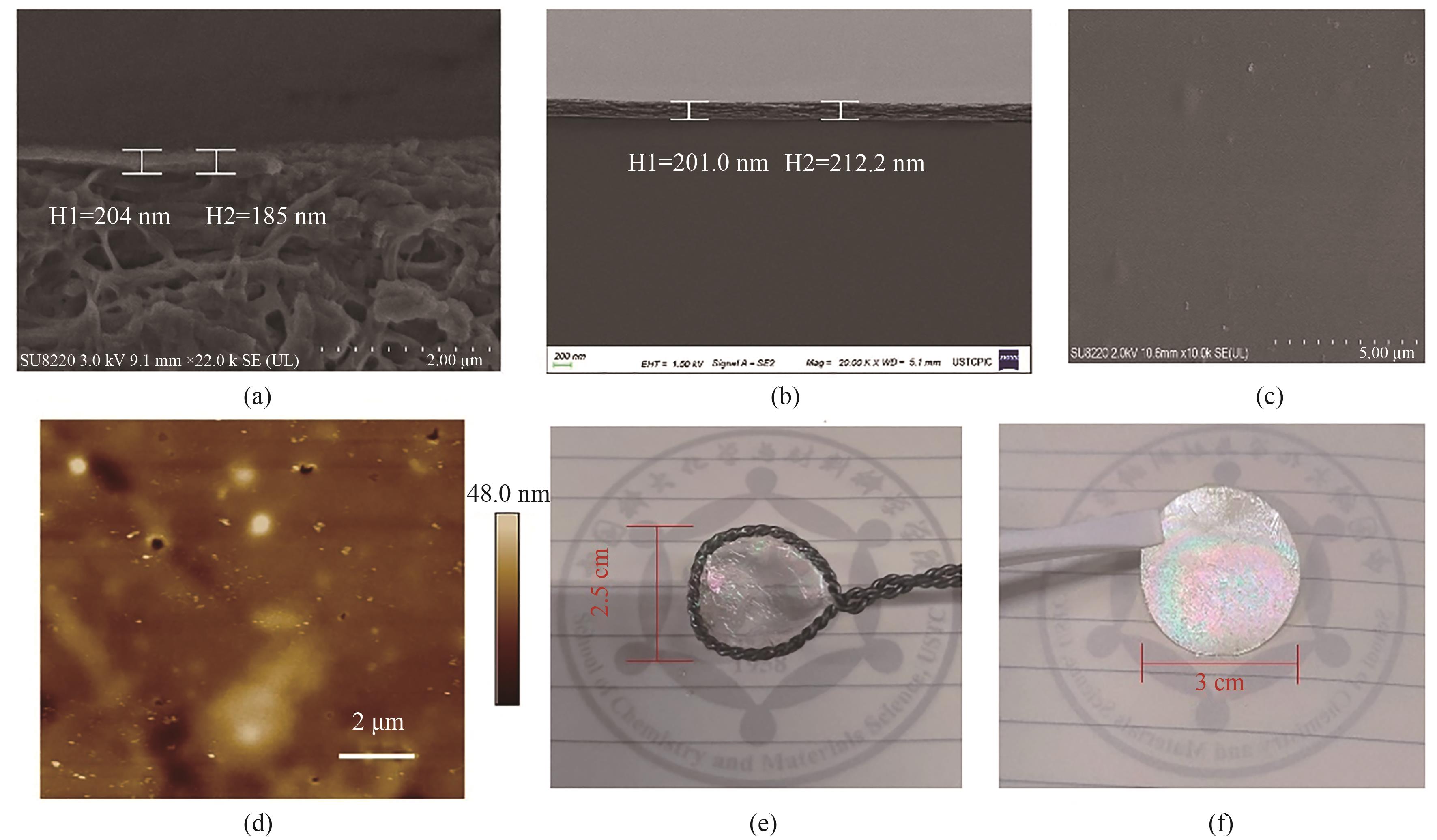
Fig.4 Cross-sectional SEM images of the CTF-BP membrane supported on porous HPAN (a) and glass plate (b), SEM (c) and AFM (d) images of the surface morphology of CTF-BP, photos of a free-standing CTF-BP membrane on an iron loop (e) and on an HPAN substrate (f)
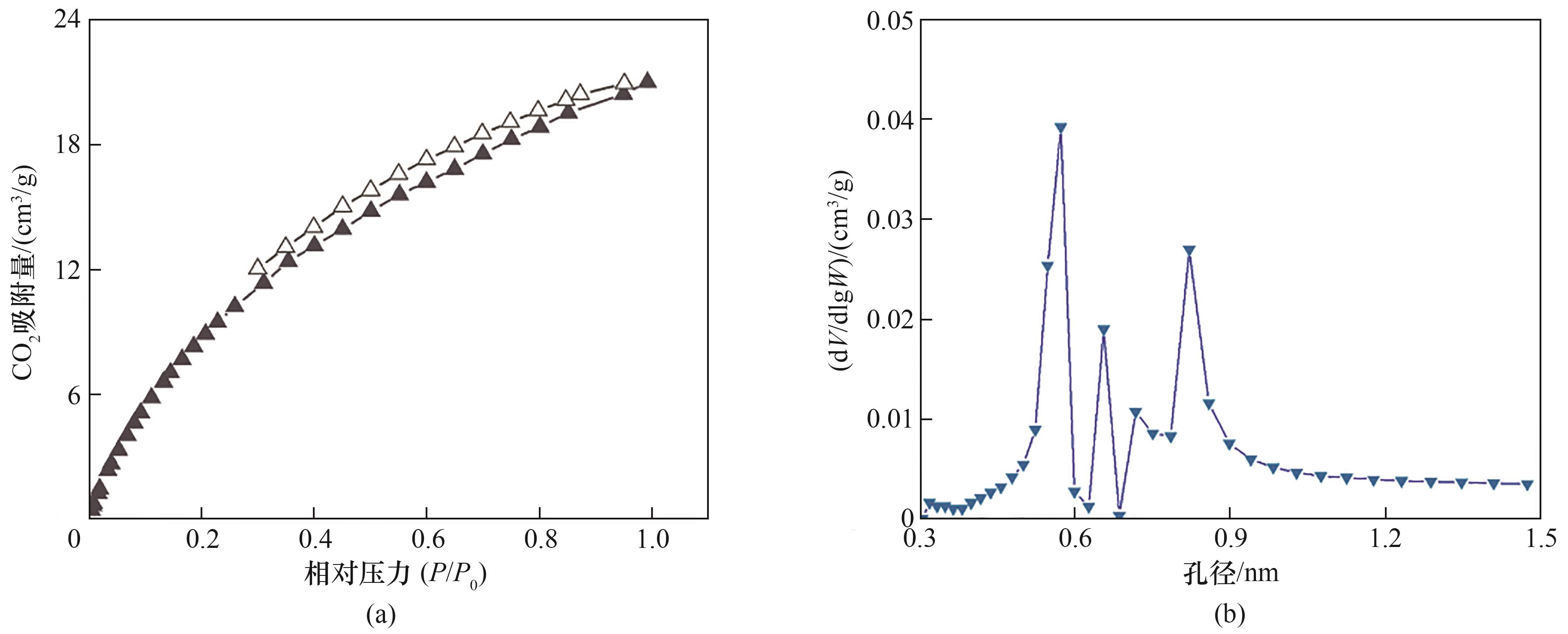
Fig.5 CO2 sorption isotherms of CTF-BP membrane (273 K) (a), the pore size distribution of CTF-BP calculated according to density functional theory (DFT) based on the CO2 sorption isotherms (b)
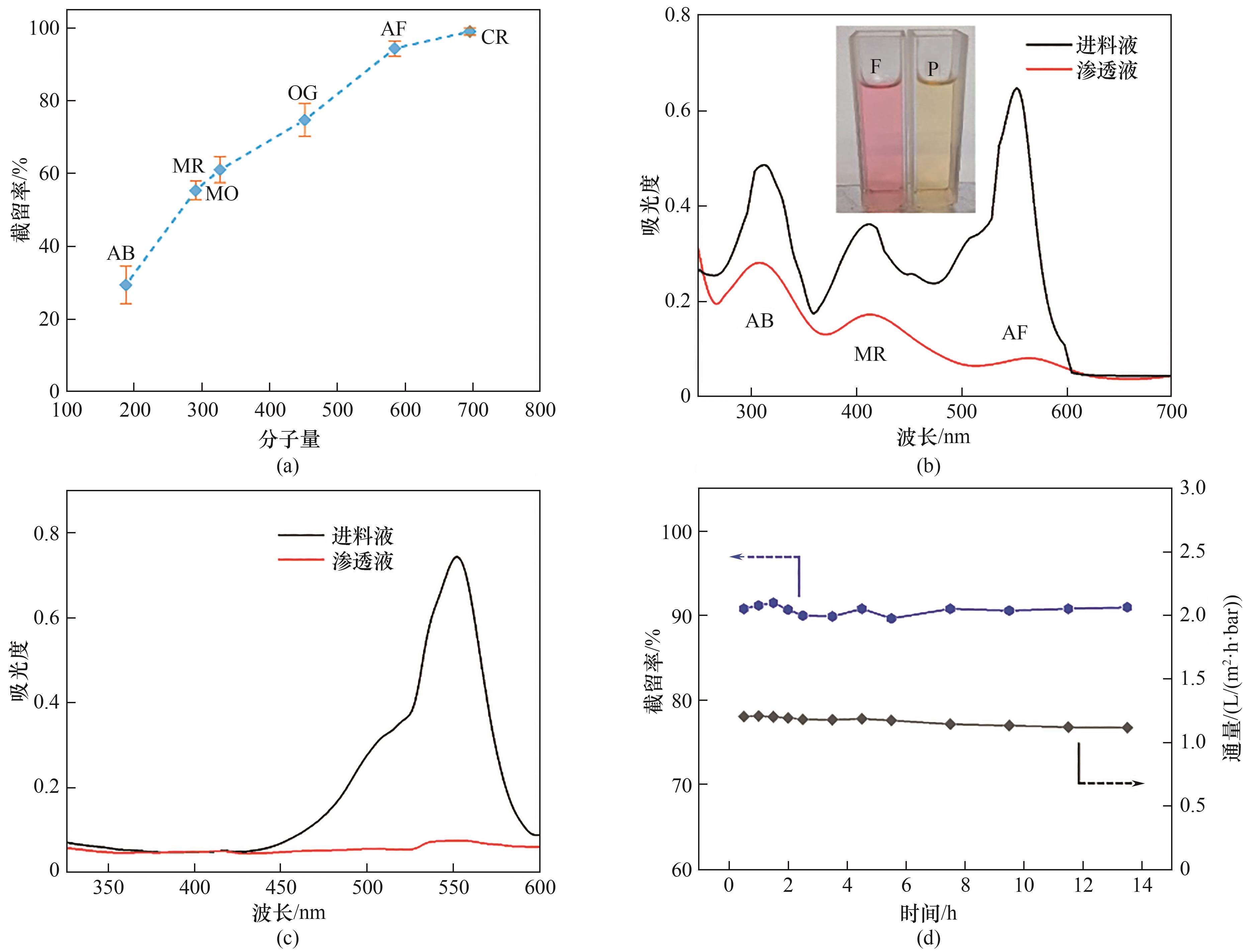
Fig.6 Rejection rate as a function of the molecular weight of varied dyes (a), the UV-Vis spectra of the feed mixture consisting of AB, MR, AF and permeant (b), ultraviolet visible absorption spectra of AF before and after filtration through CTF-BP membranes (c), long-term OSN test of CTF-BP membrane in separating a solution mixture of acid fuchsine and methanol (20 mg/L) (d)
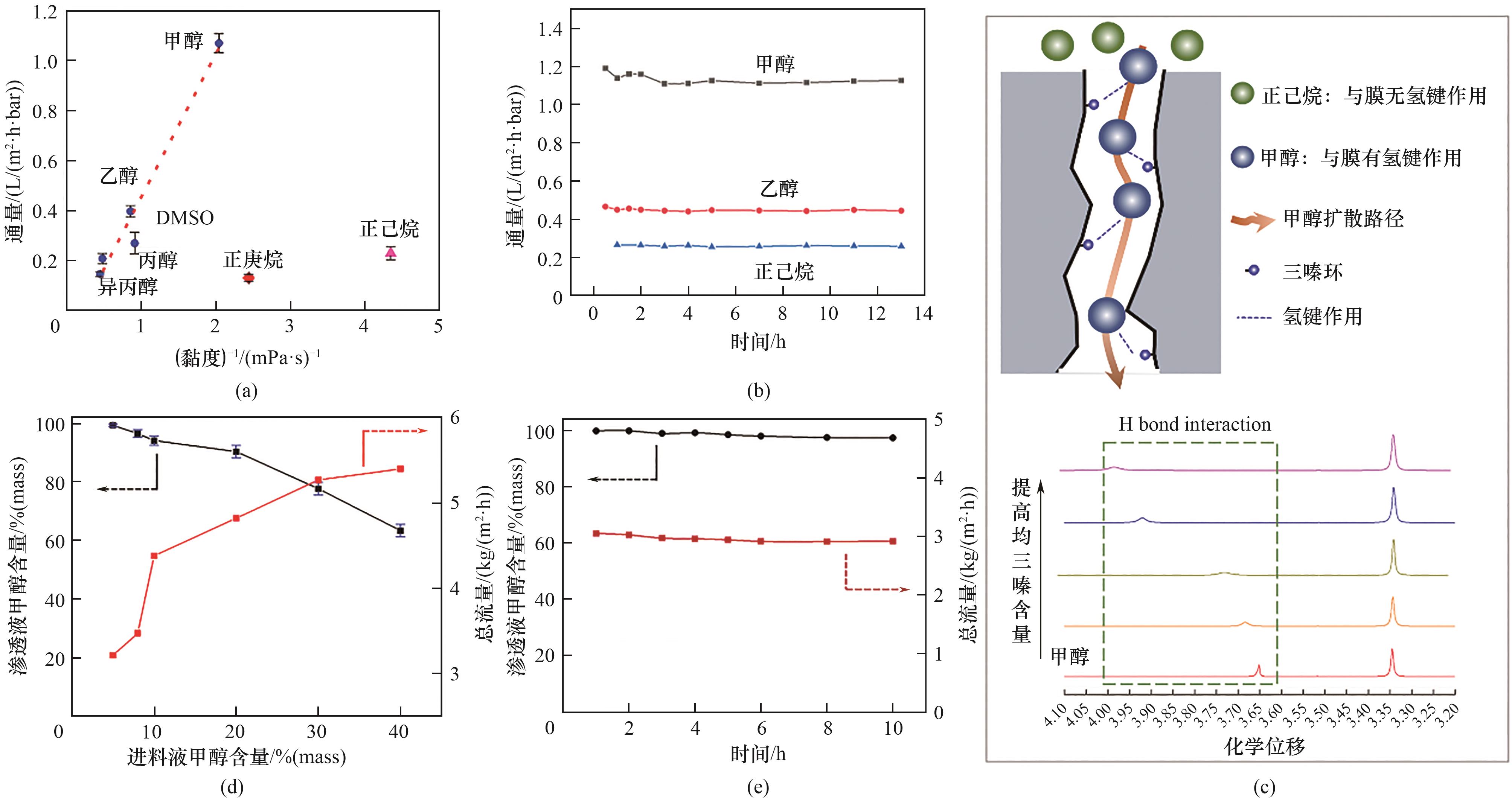
Fig.7 Solvents permeance through the CTF-BP membrane versus the solvent viscosity for the membrane (a), plot of methanol, ethanol and n-hexane permeances with time for CTF-BP membranes (b), schematic diagram of the separation mechanism of methanol/n-hexane mixture (the upper panel) and 1H NMR spectra of 100 μl methanol with varied mass of 1,3,5-triazine from 0.05 g to 0.20 g (c), dependence of methanol concentration in permeate and total flux on methanol concentration in feed for membranes of methanol/n-hexane mixture (d), long time separation performance of methanol/n-hexane with the 8% (mass) methanol in feed solution (e)
| 1 | Paul M, Jons S D. Chemistry and fabrication of polymeric nanofiltration membranes: a review[J]. Polymer, 2016, 103: 417-456. |
| 2 | Bhosle B M, Subramanian R. New approaches in deacidification of edible oils—a review[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2005, 69(4): 481-494. |
| 3 | Abels C, Carstensen F, Wessling M. Membrane processes in biorefinery applications[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 444: 285-317. |
| 4 | Gould R M, White L S, Wildemuth C R. Membrane separation in solvent lube dewaxing[J]. Environmental Progress, 2001, 20(1): 12-16. |
| 5 | Székely G, Bandarra J, Heggie W, et al. Organic solvent nanofiltration: a platform for removal of genotoxins from active pharmaceutical ingredients[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 381(1/2): 21-33. |
| 6 | Siew W E, Livingston A G, Ates C, et al. Continuous solute fractionation with membrane cascades—a high productivity alternative to diafiltration[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2013, 102: 1-14. |
| 7 | Khan N A, Zhang R N, Wu H, et al. Solid-vapor interface engineered covalent organic framework membranes for molecular separation[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(31): 13450-13458. |
| 8 | Cheng X Q, Wang Z X, Jiang X, et al. Towards sustainable ultrafast molecular-separation membranes: from conventional polymers to emerging materials[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2018, 92: 258-283. |
| 9 | Vandezande P, Gevers L E M, Vankelecom I F J. Solvent resistant nanofiltration: separating on a molecular level[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2008, 37(2): 365-405. |
| 10 | Cheng C, Iyengar S A, Karnik R. Molecular size-dependent subcontinuum solvent permeation and ultrafast nanofiltration across nanoporous graphene membranes[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2021, 16(9): 989-995. |
| 11 | Jung B, Ma S C, Miang Khor C, et al. Impact of polarity reversal on inorganic scaling on carbon nanotube-based electrically-conducting nanofiltration membranes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 452: 139216. |
| 12 | See Toh Y H, Lim F W, Livingston A G. Polymeric membranes for nanofiltration in polar aprotic solvents[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2007, 301(1/2): 3-10. |
| 13 | Chung T S. A critical review of polybenzimidazoles[J]. Polymer Reviews, 1997, 37(2): 277-301. |
| 14 | Sani N A A, Lau W J, Ismail A F. Polyphenylsulfone-based solvent resistant nanofiltration (SRNF) membrane incorporated with copper-1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylate (Cu-BTC) nanoparticles for methanol separation[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(17): 13000-13010. |
| 15 | Zhu L F, Yu H W, Zhang H J, et al. Mixed matrix membranes containing MIL-53(Al) for potential application in organic solvent nanofiltration[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(89): 73068-73076. |
| 16 | Lim S K, Goh K, Bae T H, et al. Polymer-based membranes for solvent-resistant nanofiltration: a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2017, 25(11): 1653-1675. |
| 17 | Geens J, van der Bruggen B, Vandecasteele C. Characterisation of the solvent stability of polymeric nanofiltration membranes by measurement of contact angles and swelling[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2004, 59(5): 1161-1164. |
| 18 | Yushkin A A, Anokhina T S, Bazhenov S D, et al. Sorption and nanofiltration characteristics of PIM-1 material in polar and non-polar solvents[J]. Petroleum Chemistry, 2018, 58(13): 1154-1158. |
| 19 | Wang C X, Li C X, Rutledge E R C, et al. Aromatic porous polymer network membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration under extreme conditions[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(31): 15891-15899. |
| 20 | Agarwal P, Hefner R E, Ge S R, et al. Nanofiltration membranes from crosslinked Troger’s base polymers of intrinsic microporosity (PIMs)[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020, 595: 117501. |
| 21 | Abdulhamid M A, Szekely G. Organic solvent nanofiltration membranes based on polymers of intrinsic microporosity[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2022, 36: 100804. |
| 22 | Zhou S Y, Zhao Y L, Zheng J F, et al. High-performance functionalized polymer of intrinsic microporosity (PIM) composite membranes with thin and stable interconnected layer for organic solvent nanofiltration[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 591: 117347. |
| 23 | Dong G X, Lee Y M. Microporous polymeric membranes inspired by adsorbent for gas separation[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(26): 13294-13319. |
| 24 | Ma C H, Urban J J. Hydrogen-bonded polyimide/metal-organic framework hybrid membranes for ultrafast separations of multiple gas pairs[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(32): 1903243. |
| 25 | Genduso G, Amelio A, Luis P, et al. Separation of methanol-tetrahydrofuran mixtures by heteroazeotropic distillation and pervaporation[J]. AIChE Journal, 2014, 60(7): 2584-2595. |
| 26 | Jiang L Y, Wang Y, Chung T S, et al. Polyimides membranes for pervaporation and biofuels separation[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2009, 34(11): 1135-1160. |
| 27 | Cabasso I. Organic liquid mixtures separation by permselective polymer membranes (Ⅰ): Selection and characteristics of dense isotropic membranes employed in the pervaporation process[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Product Research and Development, 1983, 22(2): 313-319. |
| 28 | Sheng F M, Hou L X, Wang X X, et al. Electro-nanofiltration membranes with positively charged polyamide layer for cations separation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020, 594: 117453. |
| 29 | He X, Sin H, Liang B, et al. Controlling the selectivity of conjugated microporous polymer membrane for efficient organic solvent nanofiltration[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(32): 1900134. |
| 30 | Yasuda T, Shimizu T, Liu F, et al. Electro-functional octupolar π-conjugated columnar liquid crystals[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(34): 13437-13444. |
| 31 | Zhu X, Tian C C, Mahurin S M, et al. A superacid-catalyzed synthesis of porous membranes based on triazine frameworks for CO2 separation[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(25): 10478-10484. |
| 32 | Li J Q, Zhang M X, Feng W L, et al. PIM-1 pore-filled thin film composite membranes for tunable organic solvent nanofiltration[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020, 601: 117951. |
| 33 | Cook M, Gaffney P R J, Peeva L G, et al. Roll-to-roll dip coating of three different PIMs for organic solvent nanofiltration[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 558: 52-63. |
| 34 | Marchetti P, Jimenez Solomon M F, Szekely G, et al. Molecular separation with organic solvent nanofiltration: a critical review[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(21): 10735-10806. |
| 35 | Huang T F, Moosa B A, Hoang P, et al. Molecularly-porous ultrathin membranes for highly selective organic solvent nanofiltration[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1-10. |
| 36 | He P P, Zhao S, Mao C Y, et al. In-situ growth of double-layered polyaniline composite membrane for organic solvent nanofiltration[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 420: 129338. |
| 37 | Polotskaya G, Pulyalina A, Goikhman M, et al. Novel polyheteroarylene membranes for separation of methanol‒hexane mixture by pervaporation[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 1-12. |
| [1] | Guoli ZHOU, Xiangke HAN, Wenjia WU, Jingtao WANG, Maowa ZHANG, Fengli LI. Construction heterostructure g-C3N4@AM lamellar membrane and its performance of organic solvent nanofiltation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(2): 941-950. |
| [2] | Houhu ZHANG, Xiaoli WU, Chongchong CHEN, Jingjing CHEN, Jingtao WANG. Preparation of 2D lamellar CD-MOF membranes for accurate separation of mixed solvents [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(10): 4539-4550. |
| [3] | LIU Jiawei, HAO Yufeng, SU Yanlei. Biomimetic modification and stability of graphene quantum dots nanofiltration membranes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(6): 3390-3398. |
| [4] | LI Yan, WANG Min, ZHAO Youjing, WANG Huaiyou, YANG Hongjun, ZHU Zenghu. Study on separation of magnesium and lithium from salt lake brine with high magnesium-to-lithium mass ratio by nanofiltration membrane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(6): 3130-3139. |
| [5] | RAN Jin,HUANG Qiang,AI Xinyu,WU Yuying,ZHANG Pengpeng,DOU Yan. Construction of Zn-BTC/MoS2 composite two dimensional membranes and performance of organic solvent nanofiltation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(4): 2148-2155. |
| [6] | LU Zhibin, XIE Xing, LU Sida, HE Chang, ZHANG Bingjian, CHEN Qinglin. Surrogate model-based optimal design of multi-stage nanofiltration separation system for saline wastewater [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(3): 1400-1408. |
| [7] | HE Pengpeng, ZHAO Song, MAO Chenyue, WANG Zhi, WANG Jixiao. Research progress of solvent-resistant composite nanofiltration membrane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(2): 727-747. |
| [8] | YANG Fengrui, WANG Zhi, YAN Fangzheng, HAN Xianglei, WANG Jixiao. Progress in separation of monovalent/divalent inorganic salt solutions by nanofiltration [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(2): 799-813. |
| [9] | LIU Ning, CHU Changhui, WANG Qian, SUN Shipeng. Preparation of nanofiltration membrane for separation of mixed monovalent salts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(1): 578-588. |
| [10] | Ju WANG, Shufeng NIU, Ying FEI, Hong QI. Fabrication and stability of GO/Al2O3 composite nanofiltration membranes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(6): 2795-2803. |
| [11] | Yanqing XU, Wenfei LI, Mengyao WU, Jiangnan SHEN. Preparation of self-assembled graphene oxide / nano TiO2 composite nanofiltration membrane for inkjet printing dye [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(3): 1352-1361. |
| [12] | Lixue LIU, Shaofeng ZHANG, Changwei ZHAO, Erhu BAOLE, Ling YU, Jun WANG. Preparation of composite nanofiltration membrane with β-cyclodextrin as aqueous monomer and dye rejection properties [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(2): 889-898. |
| [13] | Yanjun XU, Zehai XU, Qin MENG, Chong SHEN, Rui HOU, Guoliang ZHANG. Preparation and performance of novel rGO/uCN composite nanofiltration membrane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(9): 3565-3572. |
| [14] | Yuanhui TANG, Yang HU, Zhiqin YAN, Chunyu LI. Experimental study on nanofiltration separation of high concentrated saline glyphosate solution [J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(7): 2574-2583. |
| [15] | XU Zhonghuang, LEI Pingping, HONG Yubin, DING Matai, HE Xumin, LAN Weiguang. Preparation and performance of graphene oxide/basic aluminum sulfate doped polyethersulfone/polyamide composite nanofiltration membrane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(9): 4066-4074. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||