CIESC Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 70 ›› Issue (9): 3483-3494.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20190169
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yiqun LI1( ),Chunhuan LUO1,2,Na LI1,3,Qingquan SU1,2(
),Chunhuan LUO1,2,Na LI1,3,Qingquan SU1,2( )
)
Received:2019-03-01
Revised:2019-05-09
Online:2019-09-05
Published:2019-09-05
Contact:
Qingquan SU
通讯作者:
苏庆泉
作者简介:李艺群(1990—),男,博士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Yiqun LI, Chunhuan LUO, Na LI, Qingquan SU. Study on CaCl2-LiCl/H2O as working pair of absorption refrigeration cycle[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(9): 3483-3494.
李艺群, 罗春欢, 李娜, 苏庆泉. 基于吸收式制冷循环的CaCl2-LiCl/H2O工质对研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(9): 3483-3494.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 成分 | 碳钢 | 紫铜 |
|---|---|---|
| C | 0.16 | — |
| Mn | 0.53 | — |
| Si | 0.3 | 0.006 |
| P | 0.035 | — |
| S | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| Zn | — | 0.005 |
| Pb | — | 0.05 |
| Sn | — | 0.05 |
| Fe | 余量 | 0.05 |
| Cu | — | 余量 |
Table 1 Composition of Q235 carbon steel and T6 copper
| 成分 | 碳钢 | 紫铜 |
|---|---|---|
| C | 0.16 | — |
| Mn | 0.53 | — |
| Si | 0.3 | 0.006 |
| P | 0.035 | — |
| S | 0.04 | 0.01 |
| Zn | — | 0.005 |
| Pb | — | 0.05 |
| Sn | — | 0.05 |
| Fe | 余量 | 0.05 |
| Cu | — | 余量 |
| w=40.0% | w=45.0% | w=50.0% | w=55.0% | w=60.0% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T/℃ | p/kPa | T/℃ | p/kPa | T/℃ | p/kPa | T/℃ | p/kPa | T/℃ | p/kPa |
| 25.1 | 1.255 | 25.0 | 0.898 | 25.0 | 0.667 | 25.2 | 0.388 | ||
| 30.0 | 1.980 | 29.7 | 1.313 | 29.8 | 0.914 | 30.1 | 0.491 | ||
| 34.8 | 2.801 | 35.2 | 1.827 | 35.1 | 1.248 | 35.0 | 0.691 | ||
| 40.2 | 3.835 | 40.0 | 2.440 | 40.1 | 1.711 | 40.2 | 0.990 | ||
| 45.3 | 5.172 | 45.0 | 3.222 | 45.5 | 2.240 | 44.8 | 1.342 | ||
| 50.0 | 6.735 | 49.9 | 4.191 | 49.7 | 2.895 | 49.6 | 1.915 | ||
| 55.2 | 8.418 | 54.8 | 5.379 | 55.1 | 3.755 | 55.3 | 2.602 | ||
| 60.5 | 10.736 | 59.6 | 6.855 | 60.0 | 4.804 | 60.1 | 3.351 | ||
| 65.0 | 13.016 | 65.1 | 8.746 | 65.3 | 6.060 | 65.0 | 4.392 | ||
| 69.9 | 16.262 | 70.0 | 10.840 | 69.7 | 7.640 | 70.4 | 5.525 | 70.1 | 4.529 |
| 74.6 | 19.902 | 75.3 | 13.457 | 74.8 | 9.578 | 74.9 | 7.008 | 75.0 | 5.660 |
| 80.0 | 24.473 | 80.2 | 16.629 | 79.9 | 11.942 | 79.6 | 8.794 | 80.3 | 7.173 |
| 85.1 | 29.233 | 84.8 | 20.408 | 85.1 | 14.799 | 85.0 | 10.985 | 85.3 | 8.735 |
| 89.7 | 35.130 | 89.9 | 24.920 | 90.1 | 18.241 | 90.1 | 13.647 | 89.9 | 10.847 |
| 95.0 | 42.020 | 95.0 | 30.250 | 95.2 | 22.364 | 95.3 | 16.832 | 95.2 | 13.227 |
| 100.2 | 49.987 | 100.0 | 36.798 | 100.3 | 27.363 | 99.9 | 20.640 | 100.1 | 16.154 |
Table 2 Saturated vapor pressures of CaCl2-LiCl(2∶1)/H2O
| w=40.0% | w=45.0% | w=50.0% | w=55.0% | w=60.0% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T/℃ | p/kPa | T/℃ | p/kPa | T/℃ | p/kPa | T/℃ | p/kPa | T/℃ | p/kPa |
| 25.1 | 1.255 | 25.0 | 0.898 | 25.0 | 0.667 | 25.2 | 0.388 | ||
| 30.0 | 1.980 | 29.7 | 1.313 | 29.8 | 0.914 | 30.1 | 0.491 | ||
| 34.8 | 2.801 | 35.2 | 1.827 | 35.1 | 1.248 | 35.0 | 0.691 | ||
| 40.2 | 3.835 | 40.0 | 2.440 | 40.1 | 1.711 | 40.2 | 0.990 | ||
| 45.3 | 5.172 | 45.0 | 3.222 | 45.5 | 2.240 | 44.8 | 1.342 | ||
| 50.0 | 6.735 | 49.9 | 4.191 | 49.7 | 2.895 | 49.6 | 1.915 | ||
| 55.2 | 8.418 | 54.8 | 5.379 | 55.1 | 3.755 | 55.3 | 2.602 | ||
| 60.5 | 10.736 | 59.6 | 6.855 | 60.0 | 4.804 | 60.1 | 3.351 | ||
| 65.0 | 13.016 | 65.1 | 8.746 | 65.3 | 6.060 | 65.0 | 4.392 | ||
| 69.9 | 16.262 | 70.0 | 10.840 | 69.7 | 7.640 | 70.4 | 5.525 | 70.1 | 4.529 |
| 74.6 | 19.902 | 75.3 | 13.457 | 74.8 | 9.578 | 74.9 | 7.008 | 75.0 | 5.660 |
| 80.0 | 24.473 | 80.2 | 16.629 | 79.9 | 11.942 | 79.6 | 8.794 | 80.3 | 7.173 |
| 85.1 | 29.233 | 84.8 | 20.408 | 85.1 | 14.799 | 85.0 | 10.985 | 85.3 | 8.735 |
| 89.7 | 35.130 | 89.9 | 24.920 | 90.1 | 18.241 | 90.1 | 13.647 | 89.9 | 10.847 |
| 95.0 | 42.020 | 95.0 | 30.250 | 95.2 | 22.364 | 95.3 | 16.832 | 95.2 | 13.227 |
| 100.2 | 49.987 | 100.0 | 36.798 | 100.3 | 27.363 | 99.9 | 20.640 | 100.1 | 16.154 |
| i | Ai | Bi | Ci | AARD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -1.596×102 | -1.484×105 | 5.184×102 | 0.74% |
| 1 | 1.143×103 | 2.559×106 | 7.668×102 | |
| 2 | 1.362×104 | 2.625×103 | 4.173×102 | |
| 3 | 1.536×103 | -9.150×106 | -1.481×102 | |
| 4 | 8.118 | 2.110×106 | 8.453×10 |
Table 3 Regression parameters and AARD for saturated vapor pressures of CaCl2-LiCl(2∶1)/H2O
| i | Ai | Bi | Ci | AARD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -1.596×102 | -1.484×105 | 5.184×102 | 0.74% |
| 1 | 1.143×103 | 2.559×106 | 7.668×102 | |
| 2 | 1.362×104 | 2.625×103 | 4.173×102 | |
| 3 | 1.536×103 | -9.150×106 | -1.481×102 | |
| 4 | 8.118 | 2.110×106 | 8.453×10 |
| w=40.0% | w=45.0% | w=50.0% | w=55.0% | w=60.0% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T/℃ | ρ/(g·cm-3) | T/℃ | ρ/(g·cm-3) | T/℃ | ρ/(g·cm-3) | T/℃ | ρ/(g·cm-3) | T/℃ | ρ/(g·cm-3) |
| 30.0 | 1.8957 | 30.0 | 1.9434 | 30.1 | 1.9927 | 30.9 | 2.0393 | — | — |
| 39.8 | 1.8896 | 39.8 | 1.9374 | 39.9 | 1.9856 | 40.1 | 2.0331 | — | — |
| 50.0 | 1.8829 | 50.1 | 1.9309 | 50.0 | 1.9789 | 50.0 | 2.0267 | — | — |
| 60.0 | 1.8770 | 60.3 | 1.9241 | 60.0 | 1.9789 | 60.1 | 2.0203 | 60.0 | 2.0449 |
| 69.8 | 1.8708 | 69.9 | 1.9181 | 69.6 | 1.9672 | 69.9 | 2.0143 | 70.1 | 2.0371 |
| 79.9 | 1.8647 | 79.7 | 1.9125 | 79.6 | 1.9612 | 80.0 | 2.0085 | 80.0 | 2.0299 |
| 89.8 | 1.8590 | 89.7 | 1.9069 | 89.8 | 1.9550 | 89.9 | 2.0029 | 90.1 | 2.0248 |
| 99.9 | 1.8535 | 99.6 | 1.9012 | 99.6 | 1.9500 | 99.8 | 1.9978 | 99.9 | 2.0195 |
Table 4 Densities of CaCl2-LiCl(2∶1)/H2O
| w=40.0% | w=45.0% | w=50.0% | w=55.0% | w=60.0% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T/℃ | ρ/(g·cm-3) | T/℃ | ρ/(g·cm-3) | T/℃ | ρ/(g·cm-3) | T/℃ | ρ/(g·cm-3) | T/℃ | ρ/(g·cm-3) |
| 30.0 | 1.8957 | 30.0 | 1.9434 | 30.1 | 1.9927 | 30.9 | 2.0393 | — | — |
| 39.8 | 1.8896 | 39.8 | 1.9374 | 39.9 | 1.9856 | 40.1 | 2.0331 | — | — |
| 50.0 | 1.8829 | 50.1 | 1.9309 | 50.0 | 1.9789 | 50.0 | 2.0267 | — | — |
| 60.0 | 1.8770 | 60.3 | 1.9241 | 60.0 | 1.9789 | 60.1 | 2.0203 | 60.0 | 2.0449 |
| 69.8 | 1.8708 | 69.9 | 1.9181 | 69.6 | 1.9672 | 69.9 | 2.0143 | 70.1 | 2.0371 |
| 79.9 | 1.8647 | 79.7 | 1.9125 | 79.6 | 1.9612 | 80.0 | 2.0085 | 80.0 | 2.0299 |
| 89.8 | 1.8590 | 89.7 | 1.9069 | 89.8 | 1.9550 | 89.9 | 2.0029 | 90.1 | 2.0248 |
| 99.9 | 1.8535 | 99.6 | 1.9012 | 99.6 | 1.9500 | 99.8 | 1.9978 | 99.9 | 2.0195 |
| w=40.0% | w=45.0% | w=50.0% | w=55.0% | w=60.0% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T/℃ | η/(mPa·s) | T/℃ | η/(mPa·s) | T/℃ | η/(mPa·s) | T/℃ | η/(mPa·s) | T/℃ | η/(mPa·s) |
| 30.0 | 6.4417 | 30.0 | 10.0894 | 30.1 | 18.4371 | 30.9 | 33.5353 | — | — |
| 39.8 | 5.0810 | 39.8 | 7.9360 | 39.9 | 13.5747 | 40.1 | 23.8138 | — | — |
| 50.0 | 4.1293 | 50.1 | 6.2727 | 50.0 | 10.1141 | 50.0 | 17.5305 | — | — |
| 60.0 | 3.4514 | 60.3 | 5.0874 | 60.0 | 8.3263 | 60.1 | 13.6596 | 60.0 | 18.4415 |
| 69.8 | 2.9182 | 69.9 | 4.2625 | 69.6 | 6.6501 | 69.9 | 10.7005 | 70.1 | 14.0103 |
| 79.9 | 2.5188 | 79.7 | 3.5989 | 79.6 | 5.5813 | 80.0 | 8.7180 | 80.0 | 11.0275 |
| 89.8 | 2.1855 | 89.7 | 3.0674 | 89.8 | 4.7153 | 89.9 | 7.1871 | 90.1 | 9.0751 |
| 99.9 | 1.9162 | 99.6 | 2.6789 | 99.6 | 3.9853 | 99.8 | 6.0610 | 99.9 | 7.5790 |
Table 5 Viscosities of CaCl2-LiCl(2∶1)/H2O
| w=40.0% | w=45.0% | w=50.0% | w=55.0% | w=60.0% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T/℃ | η/(mPa·s) | T/℃ | η/(mPa·s) | T/℃ | η/(mPa·s) | T/℃ | η/(mPa·s) | T/℃ | η/(mPa·s) |
| 30.0 | 6.4417 | 30.0 | 10.0894 | 30.1 | 18.4371 | 30.9 | 33.5353 | — | — |
| 39.8 | 5.0810 | 39.8 | 7.9360 | 39.9 | 13.5747 | 40.1 | 23.8138 | — | — |
| 50.0 | 4.1293 | 50.1 | 6.2727 | 50.0 | 10.1141 | 50.0 | 17.5305 | — | — |
| 60.0 | 3.4514 | 60.3 | 5.0874 | 60.0 | 8.3263 | 60.1 | 13.6596 | 60.0 | 18.4415 |
| 69.8 | 2.9182 | 69.9 | 4.2625 | 69.6 | 6.6501 | 69.9 | 10.7005 | 70.1 | 14.0103 |
| 79.9 | 2.5188 | 79.7 | 3.5989 | 79.6 | 5.5813 | 80.0 | 8.7180 | 80.0 | 11.0275 |
| 89.8 | 2.1855 | 89.7 | 3.0674 | 89.8 | 4.7153 | 89.9 | 7.1871 | 90.1 | 9.0751 |
| 99.9 | 1.9162 | 99.6 | 2.6789 | 99.6 | 3.9853 | 99.8 | 6.0610 | 99.9 | 7.5790 |
| w=40.0% | w=45.0% | w=50.0% | w=55.0% | w=60.0% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T/℃ | cp /(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | T/℃ | cp /(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | T/℃ | cp /(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | T/℃ | cp /(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | T/℃ | cp /(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) |
| 30.0 | 2.68 | 30.0 | 2.56 | 30.0 | 2.43 | 30.0 | 2.28 | — | — |
| 40.0 | 2.69 | 40.0 | 2.57 | 40.0 | 2.45 | 40.0 | 2.30 | — | — |
| 50.0 | 2.70 | 50.0 | 2.59 | 50.0 | 2.46 | 50.0 | 2.31 | — | — |
| 60.0 | 2.71 | 60.0 | 2.60 | 60.0 | 2.48 | 60.0 | 2.34 | 60.0 | 2.21 |
| 70.0 | 2.74 | 70.0 | 2.63 | 70.0 | 2.50 | 70.0 | 2.35 | 70.0 | 2.23 |
| 80.0 | 2.76 | 80.0 | 2.65 | 80.0 | 2.52 | 80.0 | 2.38 | 80.0 | 2.26 |
| 90.0 | 2.78 | 90.0 | 2.68 | 90.0 | 2.55 | 90.0 | 2.40 | 90.0 | 2.28 |
| 100.0 | 2.80 | 100.0 | 2.70 | 100.0 | 2.57 | 100.0 | 2.42 | 100.0 | 2..29 |
Table 6 Specific heat capacity of CaCl2-LiCl(2∶1)/H2O
| w=40.0% | w=45.0% | w=50.0% | w=55.0% | w=60.0% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T/℃ | cp /(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | T/℃ | cp /(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | T/℃ | cp /(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | T/℃ | cp /(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | T/℃ | cp /(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) |
| 30.0 | 2.68 | 30.0 | 2.56 | 30.0 | 2.43 | 30.0 | 2.28 | — | — |
| 40.0 | 2.69 | 40.0 | 2.57 | 40.0 | 2.45 | 40.0 | 2.30 | — | — |
| 50.0 | 2.70 | 50.0 | 2.59 | 50.0 | 2.46 | 50.0 | 2.31 | — | — |
| 60.0 | 2.71 | 60.0 | 2.60 | 60.0 | 2.48 | 60.0 | 2.34 | 60.0 | 2.21 |
| 70.0 | 2.74 | 70.0 | 2.63 | 70.0 | 2.50 | 70.0 | 2.35 | 70.0 | 2.23 |
| 80.0 | 2.76 | 80.0 | 2.65 | 80.0 | 2.52 | 80.0 | 2.38 | 80.0 | 2.26 |
| 90.0 | 2.78 | 90.0 | 2.68 | 90.0 | 2.55 | 90.0 | 2.40 | 90.0 | 2.28 |
| 100.0 | 2.80 | 100.0 | 2.70 | 100.0 | 2.57 | 100.0 | 2.42 | 100.0 | 2..29 |
| i | Ai | Bi | Ci | AARD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2.2760×10 | 2.9488×10-2 | 1.8683×10-4 | 0.19% |
| 1 | 3.6877×10 | -1.2945×10-1 | 8.6798×10-4 | |
| 2 | -6.9317×102 | 1.4542×10-1 | -9.6057×10-4 |
Table 7 Regression parameters and AARD for specific heat capacities of CaCl2-LiCl(2∶1)/H2O
| i | Ai | Bi | Ci | AARD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2.2760×10 | 2.9488×10-2 | 1.8683×10-4 | 0.19% |
| 1 | 3.6877×10 | -1.2945×10-1 | 8.6798×10-4 | |
| 2 | -6.9317×102 | 1.4542×10-1 | -9.6057×10-4 |
| w=40.0% | w=45.0% | w=50.0% | w=55.0% | w=60.0% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T/℃ | h/(kJ·kg-1) | T/℃ | h/(kJ·kg-1) | T/℃ | h/(kJ·kg-1) | T/℃ | h/(kJ·kg-1) | T/℃ | h/(kJ·kg-1) |
| 30.0 | 321.29 | 30.0 | 310.46 | 30.0 | 304.27 | 30.0 | 298.49 | — | — |
| 40.0 | 348.13 | 40.0 | 336.07 | 40.0 | 328.64 | 40.0 | 321.34 | — | — |
| 50.0 | 375.14 | 50.0 | 361.88 | 50.0 | 353.22 | 50.0 | 344.40 | — | — |
| 60.0 | 402.33 | 60.0 | 387.89 | 60.0 | 378.01 | 60.0 | 367.66 | 60.0 | 353.23 |
| 70.0 | 429.71 | 70.0 | 414.10 | 70.0 | 403.00 | 70.0 | 391.14 | 70.0 | 375.46 |
| 80.0 | 457.26 | 80.0 | 440.51 | 80.0 | 428.21 | 80.0 | 414.82 | 80.0 | 397.92 |
| 90.0 | 484.99 | 90.0 | 467.12 | 90.0 | 453.63 | 90.0 | 438.72 | 90.0 | 420.60 |
| 100.0 | 512.91 | 100.0 | 493.93 | 100.0 | 479.26 | 100.0 | 462.83 | 100.0 | 443.52 |
Table 8 Specific enthalpies of CaCl2-LiCl(2∶1)/H2O
| w=40.0% | w=45.0% | w=50.0% | w=55.0% | w=60.0% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T/℃ | h/(kJ·kg-1) | T/℃ | h/(kJ·kg-1) | T/℃ | h/(kJ·kg-1) | T/℃ | h/(kJ·kg-1) | T/℃ | h/(kJ·kg-1) |
| 30.0 | 321.29 | 30.0 | 310.46 | 30.0 | 304.27 | 30.0 | 298.49 | — | — |
| 40.0 | 348.13 | 40.0 | 336.07 | 40.0 | 328.64 | 40.0 | 321.34 | — | — |
| 50.0 | 375.14 | 50.0 | 361.88 | 50.0 | 353.22 | 50.0 | 344.40 | — | — |
| 60.0 | 402.33 | 60.0 | 387.89 | 60.0 | 378.01 | 60.0 | 367.66 | 60.0 | 353.23 |
| 70.0 | 429.71 | 70.0 | 414.10 | 70.0 | 403.00 | 70.0 | 391.14 | 70.0 | 375.46 |
| 80.0 | 457.26 | 80.0 | 440.51 | 80.0 | 428.21 | 80.0 | 414.82 | 80.0 | 397.92 |
| 90.0 | 484.99 | 90.0 | 467.12 | 90.0 | 453.63 | 90.0 | 438.72 | 90.0 | 420.60 |
| 100.0 | 512.91 | 100.0 | 493.93 | 100.0 | 479.26 | 100.0 | 462.83 | 100.0 | 443.52 |
| i | Ai | Bi | Ci | Di | AARD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -1.4508×103 | 5.7582×103 | -1.1136×104 | 8.1644×103 | 0.02% |
| 1 | 1.4530×101 | -7.3293×101 | 1.4604×102 | -1.0071×10-2 | |
| 2 | -1.9842×10-2 | 1.2769×10-1 | -2.6044×10-1 | 1.7708×10-1 |
Table 9 Regression parameters and AARD for specific enthalpies of CaCl2-LiCl(2∶1)/H2O
| i | Ai | Bi | Ci | Di | AARD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -1.4508×103 | 5.7582×103 | -1.1136×104 | 8.1644×103 | 0.02% |
| 1 | 1.4530×101 | -7.3293×101 | 1.4604×102 | -1.0071×10-2 | |
| 2 | -1.9842×10-2 | 1.2769×10-1 | -2.6044×10-1 | 1.7708×10-1 |
| w=40.0% | w=45.0% | w=50.0% | w=55.0% | w=60.0% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T/℃ | s/(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | T/℃ | s/(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | T/℃ | s/(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | T/℃ | s/(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | T/℃ | s/(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) |
| 30.0 | 1.6839 | 30.0 | 1.6936 | 30.0 | 1.7027 | 30.0 | 1.7132 | — | — |
| 40.0 | 1.7710 | 40.0 | 1.7768 | 40.0 | 1.7819 | 40.0 | 1.7875 | — | — |
| 50.0 | 1.8558 | 50.0 | 1.8578 | 50.0 | 1.8595 | 50.0 | 1.8592 | — | — |
| 60.0 | 1.9387 | 60.0 | 1.9371 | 60.0 | 1.9353 | 60.0 | 1.9298 | 60.0 | 1.9398 |
| 70..0 | 2.0210 | 70..0 | 2.0152 | 70..0 | 2.0088 | 70..0 | 1.9995 | 70..0 | 2.0054 |
| 80.0 | 2.0991 | 80.0 | 2.0921 | 80.0 | 2.0813 | 80.0 | 2.0689 | 80.0 | 2.0701 |
| 90.0 | 2.1769 | 90.0 | 2.1667 | 90.0 | 2.1524 | 90.0 | 2.1358 | 90.0 | 2.1338 |
| 100.0 | 2.2531 | 100.0 | 2.2400 | 100.0 | 2.2221 | 100.0 | 2.2014 | 100.0 | 2.1949 |
Table 10 Specific entropies of CaCl2-LiCl(2∶1)/H2O
| w=40.0% | w=45.0% | w=50.0% | w=55.0% | w=60.0% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T/℃ | s/(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | T/℃ | s/(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | T/℃ | s/(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | T/℃ | s/(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | T/℃ | s/(kJ·kg-1·℃-1) |
| 30.0 | 1.6839 | 30.0 | 1.6936 | 30.0 | 1.7027 | 30.0 | 1.7132 | — | — |
| 40.0 | 1.7710 | 40.0 | 1.7768 | 40.0 | 1.7819 | 40.0 | 1.7875 | — | — |
| 50.0 | 1.8558 | 50.0 | 1.8578 | 50.0 | 1.8595 | 50.0 | 1.8592 | — | — |
| 60.0 | 1.9387 | 60.0 | 1.9371 | 60.0 | 1.9353 | 60.0 | 1.9298 | 60.0 | 1.9398 |
| 70..0 | 2.0210 | 70..0 | 2.0152 | 70..0 | 2.0088 | 70..0 | 1.9995 | 70..0 | 2.0054 |
| 80.0 | 2.0991 | 80.0 | 2.0921 | 80.0 | 2.0813 | 80.0 | 2.0689 | 80.0 | 2.0701 |
| 90.0 | 2.1769 | 90.0 | 2.1667 | 90.0 | 2.1524 | 90.0 | 2.1358 | 90.0 | 2.1338 |
| 100.0 | 2.2531 | 100.0 | 2.2400 | 100.0 | 2.2221 | 100.0 | 2.2014 | 100.0 | 2.1949 |
| i | Ai | Bi | Ci | Di | AARD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.5469×102 | -1.0106×103 | 2.1465×103 | -1.5011×103 | 0.98% |
| 1 | -1.2590×100 | 8.1964×100 | -1.7371×101 | 1.2146×101 | |
| 2 | 3.4252×10-3 | -2.2055×10-2 | 4.6621×10-2 | -3.2573×10-2 | |
| 3 | -3.0971×10-6 | 1.9836×10-5 | -4.1854×10-5 | 2.9198×10-5 |
Table 11 Regression parameters and AARD for specific entropies of CaCl2-LiCl(2∶1)/H2O
| i | Ai | Bi | Ci | Di | AARD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.5469×102 | -1.0106×103 | 2.1465×103 | -1.5011×103 | 0.98% |
| 1 | -1.2590×100 | 8.1964×100 | -1.7371×101 | 1.2146×101 | |
| 2 | 3.4252×10-3 | -2.2055×10-2 | 4.6621×10-2 | -3.2573×10-2 | |
| 3 | -3.0971×10-6 | 1.9836×10-5 | -4.1854×10-5 | 2.9198×10-5 |
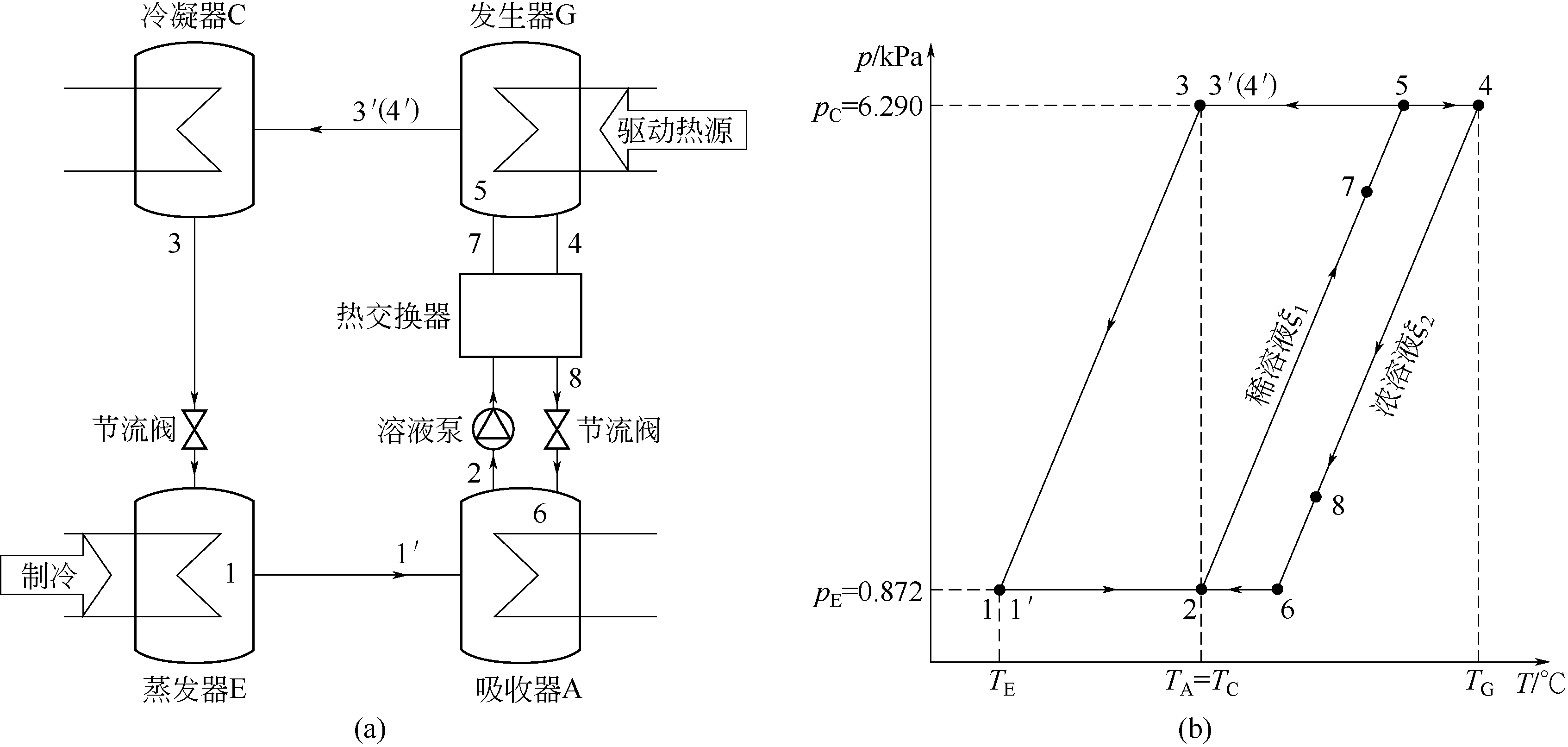
Fig.10 Schematic diagramforabsorption refrigeration system (a) and p-T diagramfor anabsorption refrigeration system under standard operating conditions (b)
| 工质对 | 稀溶液 | 浓溶液 |
|---|---|---|
| ① CaCl2-LiCl (2∶1)/H2O | 54.20% | 57.20% |
| ② LiBr/H2O | 56.40% | 59.40% |
| ③ CaCl2-LiBr-LiNO3-KNO3(16.2∶2∶2∶1)/H2O | 58.50% | 61.50% |
| ④ CaCl2-LiNO3-LiBr (8.72∶1∶1)/H2O | 57.30% | 60.30% |
| ⑤ CaCl2-LiBr (1.35∶1)/H2O | 55.80% | 58.80% |
Table 12 Concentrations of various working pairs under the same refrigeration conditions
| 工质对 | 稀溶液 | 浓溶液 |
|---|---|---|
| ① CaCl2-LiCl (2∶1)/H2O | 54.20% | 57.20% |
| ② LiBr/H2O | 56.40% | 59.40% |
| ③ CaCl2-LiBr-LiNO3-KNO3(16.2∶2∶2∶1)/H2O | 58.50% | 61.50% |
| ④ CaCl2-LiNO3-LiBr (8.72∶1∶1)/H2O | 57.30% | 60.30% |
| ⑤ CaCl2-LiBr (1.35∶1)/H2O | 55.80% | 58.80% |
| 点 | 物质 | p/k Pa | T/℃ | w/% | h/ (kJ·kg-1) | s/ (kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | D/ (kg·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 冷凝水 | 0.872 | 5.0 | 0 | 439.6 | 1.6082 | 1 |
| 1′ | 水蒸气 | 0.872 | 5.0 | 0 | 2927.9 | 10.5598 | 1 |
| 2 | 稀溶液 | 0.872 | 37.0 | 54.2 | 314.7 | 1.7639 | 19.1 |
| 3 | 冷凝水 | 6.290 | 37.0 | 0 | 573.5 | 2.0639 | 1 |
| 4 | 浓溶液 | 6.290 | 75.2 | 57.2 | 397.1 | 2.0360 | 18.1 |
| 4′ | 水蒸气 | 6.290 | 75.2 | 0 | 3058.5 | 10.0539 | 1 |
| 5 | 稀溶液 | 6.290 | 72.2 | 54.2 | 398.5 | 2.0168 | 19.1 |
| 6 | 浓溶液 | 6.290 | 39.9 | 57.2 | 316.8 | 1.7908 | 18.1 |
| 7 | 稀溶液 | — | 64.8 | 54.2 | 380.8 | 1.9654 | 19.1 |
| 8 | 浓溶液 | — | 44.6 | 57.2 | 327.3 | 1.8274 | 18.1 |
Table 13 Typical points’ state parameters in absorption refrigeration cycle using CaCl2-LiCl(2∶1)/H2O as
| 点 | 物质 | p/k Pa | T/℃ | w/% | h/ (kJ·kg-1) | s/ (kJ·kg-1·℃-1) | D/ (kg·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 冷凝水 | 0.872 | 5.0 | 0 | 439.6 | 1.6082 | 1 |
| 1′ | 水蒸气 | 0.872 | 5.0 | 0 | 2927.9 | 10.5598 | 1 |
| 2 | 稀溶液 | 0.872 | 37.0 | 54.2 | 314.7 | 1.7639 | 19.1 |
| 3 | 冷凝水 | 6.290 | 37.0 | 0 | 573.5 | 2.0639 | 1 |
| 4 | 浓溶液 | 6.290 | 75.2 | 57.2 | 397.1 | 2.0360 | 18.1 |
| 4′ | 水蒸气 | 6.290 | 75.2 | 0 | 3058.5 | 10.0539 | 1 |
| 5 | 稀溶液 | 6.290 | 72.2 | 54.2 | 398.5 | 2.0168 | 19.1 |
| 6 | 浓溶液 | 6.290 | 39.9 | 57.2 | 316.8 | 1.7908 | 18.1 |
| 7 | 稀溶液 | — | 64.8 | 54.2 | 380.8 | 1.9654 | 19.1 |
| 8 | 浓溶液 | — | 44.6 | 57.2 | 327.3 | 1.8274 | 18.1 |
| CaCl2-LiCl(2∶1)/H2O | LiBr/H2O | CaCl2-LiBr-LiNO3-KNO3 (16.2∶2∶2∶1) /H2O | CaCl2-LiNO3-LiBr (8.72∶1∶1)/H2O | CaCl2-LiBr(1.35∶1)/H2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.803 | 0.762 | 0.793 | 0.805 | 0.788 |
Table 14 COP of absorption refrigeration cycles using different working pairs
| CaCl2-LiCl(2∶1)/H2O | LiBr/H2O | CaCl2-LiBr-LiNO3-KNO3 (16.2∶2∶2∶1) /H2O | CaCl2-LiNO3-LiBr (8.72∶1∶1)/H2O | CaCl2-LiBr(1.35∶1)/H2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.803 | 0.762 | 0.793 | 0.805 | 0.788 |
| 过程 | ?损失/kW | |
|---|---|---|
| CaCl2-LiCl(2∶1)/H2O | LiBr/H2O | |
| 蒸发过程 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 冷凝过程 | 0.3 | 0.8 |
| 吸收过程 | 49.2 | 55.3 |
| 发生过程 | 310.9 | 332.7 |
| 热交换过程 | 25.7 | 31.4 |
Table 15 Exergy destruction in each part of absorption refrigeration cycle using CaCl2-LiCl(2∶1)/H2O or
| 过程 | ?损失/kW | |
|---|---|---|
| CaCl2-LiCl(2∶1)/H2O | LiBr/H2O | |
| 蒸发过程 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 冷凝过程 | 0.3 | 0.8 |
| 吸收过程 | 49.2 | 55.3 |
| 发生过程 | 310.9 | 332.7 |
| 热交换过程 | 25.7 | 31.4 |
| 1 | 国家发展改革委, 科技部, 工业和信息化部, 等 . “十三五”节能环保产业发展规划[J]. 有色冶金节能, 2017, 33(1): 1-7+13. |
| National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Science and Technology, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, et al . The 13th five-year plan for energy conservation and environmental protection industries[J]. Energy Saving of Non-Ferrous Metallurgy, 2017, 33(1): 1-7+13. | |
| 2 | 王长庆 . 吸收式制冷技术的应用与发展[J]. 能源技术, 2000, 21(1): 31-35. |
| Wang C Q . Application and development of absorption refrigeration technology[J]. Power & Energy, 2000, 21(1): 31-35. | |
| 3 | Inoue N , Irie K , Fukusumi Y . Absorption heat pump: US 7464562[P]. 2008-12-16. |
| 4 | Srikhirin P , Aphornratana S , Chungpaibulpatana S . A review of absorption refrigeration technologies[J]. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev., 2001, 5(4): 343-372. |
| 5 | Bellos E , Tzivanidis C , Antonopoulos K A . Exergetic, energetic and financial evaluation of a solar driven absorption cooling system with various collector types[J]. Appl. Therm. Eng., 2016, 102: 749-759. |
| 6 | Leonzio G . Solar systems integrated with absorption heat pumps and thermal energy storages: state of art[J]. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev., 2017, 70: 492-505. |
| 7 | Alobaid M , Hughes B , Calautit J K , et al . A review of solar driven absorption cooling with photovoltaic thermal systems[J]. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev., 2017, 76: 728-742. |
| 8 | Misra R D , Sahoo P K , Sahoo S , et al . Thermoeconomic optimization of a single effect water/LiBr vapour absorption refrigeration system[J]. Int. J. Refrig., 2003, 26(2): 158-169. |
| 9 | Kaynakli O , Kilic M . Theoretical study on the effect of operating conditions on performance of absorption refrigeration system[J]. Energ. Convers. Manage., 2007, 48(2): 599-607. |
| 10 | 车德勇, 孙佰仲, 国文学, 等 . 溴化锂吸收式制冷技术的应用与发展[J]. 东北电力大学学报, 2003, 23(6): 36-40. |
| Che D Y , Sun B Z , Guo W X , et al . Application and development of lithium bromide absorption refrigeration technology[J].J. Northeast. Dianli Uiniv., 2003, 23(6): 36-40. | |
| 11 | Lin P , Wang R Z , Xia Z Z . Numerical investigation of a two-stage air-cooled absorption refrigeration system for solar cooling: cycle analysis and absorption cooling performances[J]. Renew. Energ., 2011, 36(5): 1401-1412. |
| 12 | Malinina O S , Baranenko A V , Zaitsev A V . Influence of the average daily outdoor air parameters on the efficiency of solar lithium bromide-water absorption refrigeration machine[C]//AIP Conference Proceedings. AIP Publishing, 2018, 2007(1): 030040. |
| 13 | Mortazavi M , Schmid M , Moghaddam S . Compact and efficient generator for low grade solar and waste heat driven absorption systems[J]. Appl. Energ., 2017, 198: 173-179. |
| 14 | Wang M , Ferreira C A I . Absorption heat pump cycles with NH3–ionic liquid working pairs[J]. Appl. Energ., 2017, 204: 819-830. |
| 15 | Luo C H , Chen K , Li Y Q , et al . Crystallization temperature, vapor pressure, density, viscosity, and specific heat capacity of the LiNO3/[BMIM] Cl/H2O ternary system[J]. J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2017, 62(10): 3043-3052. |
| 16 | Luo C H , Li Y Q , Chen K , et al . Thermodynamic properties and corrosivity of a new absorption heat pump working pair: lithium nitrate+ 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide+ water[J]. Fluid Phase Equilib., 2017, 451: 25-39. |
| 17 | Luo C H , Li Y Q , Li N , et al . Thermophysical properties of lithium nitrate+ 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium diethylphosphate+ water system[J]. J. Chem. Thermodyn., 2018, 126: 160-170. |
| 18 | 李娜, 罗春欢, 苏庆泉 . CaCl2-LiBr-LiNO3-KNO3/H2O工质对的热物性和腐蚀性[J]. 过程工程学报, 2018, 18(4): 764-768. |
| Li N , Luo C H , Su Q Q . Thermophysical properties and corrosivity of CaCl2-LiBr-LiNO3-KNO3/H2O working pair[J]. Chin. J. Proc. Eng., 2018, 18(4): 764-768. | |
| 19 | Li N , Luo C H , Su Q Q . A working pair of CaCl2–LiBr–LiNO3/H2O and its application in a single-stage solar-driven absorption refrigeration cycle[J]. Int. J. Refrig., 2018, 86: 1-13. |
| 20 | 李娜, 罗春欢, 苏庆泉 . CaCl2-LiBr (1.35: 1)/H2O工质对的热物性及应用[J]. 工程科学学报, 2018, 40(2): 167-176. |
| Li N , Luo C H , Su Q Q . Thermophysical properties and applications of CaCl2-LiBr(1.35:1)/ H2O as a working pair[J]. Chin. J. Eng., 2018, 40(2): 167-176. | |
| 21 | Safarov J T . Vapor pressure of heat transfer fluids of absorption refrigeration machines and heat pumps: binary solutions of lithium nitrate with methanol[J]. J. Chem. Thermodyn., 2005, 37(12): 1261-1267. |
| 22 | Kim J S , Lee H . Solubilities, vapor pressures, densities, and viscosities of the LiBr+ LiI+ HO (CH2)3OH+ H2O system[J]. J.Chem. Eng. Data, 2001, 46(1): 79-83. |
| 23 | Park Y , Kim J S , Lee H , et al . Density, vapor pressure, solubility, and viscosity for water+ lithium bromide+ lithium nitrate+ 1, 3-propanediol[J]. J.Chem. Eng. Data, 1997, 42(1): 145-148. |
| 24 | He Z , Zhao Z , Zhang X , et al . Thermodynamic properties of new heat pump working pairs: 1,3-dimethylimidazolium dimethylphosphate and water, ethanol and methanol[J]. Fluid Phase Equilib., 2010, 298(1): 83-91. |
| 25 | 陈东, 谢继红 . 热泵技术及其应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008: 206-220. |
| Chen D , Xie J H . Technology and Application of Heat Pump[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008: 206-220. | |
| 26 | Yang D T , Zhu Y J , Liu S C , et al . Thermodynamic properties of a ternary AHP working pair: lithium bromide + 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride+ H2O[J]. J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2019, 64(2): 574-583. |
| 27 | Aprhornratana S , Eames I W . Thermodynamic analysis of absorption refrigeration cycles using the second law of thermodynamics method[J]. Int. J. Refrig., 1995, 18(4): 244-252. |
| 28 | Şencan A , Yakut K A , Kalogirou S A . Exergy analysis of lithium bromide/water absorption systems[J]. Renew. Energ., 2005, 30(5): 645-657. |
| 29 | Patel H A , Patel L N , Jani D , et al . Energetic analysis of single stage lithium bromide water absorption refrigeration system[J]. Procedia Technology, 2016, 23: 488-495. |
| 30 | 戴永庆 . 溴化锂吸收式制冷技术及应用[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2001: 49-67. |
| Dai Y Q . LiBr Absorption Refrigeration Technology and Application[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2001: 49-67. | |
| 31 | 王林 . 小型吸收式制冷机原理与应用[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2011: 93-109. |
| Wang L . Principle and Application of Small-sized Absorption Refrigerator[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2011: 93-109. |
| [1] | Hongxin YU, Shuangquan SHAO. Simulation analysis of water crystallization process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 250-258. |
| [2] | Fei KANG, Weiguang LYU, Feng JU, Zhi SUN. Research on discharge path and evaluation of spent lithium-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3903-3911. |
| [3] | Jiaqi CHEN, Wanyu ZHAO, Ruichong YAO, Daolin HOU, Sheying DONG. Synthesis of pistachio shell-based carbon dots and their corrosion inhibition behavior on Q235 carbon steel [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3446-3456. |
| [4] | Shuang LIU, Linzhou ZHANG, Zhiming XU, Suoqi ZHAO. Study on molecular level composition correlation of viscosity of residual oil and its components [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3226-3241. |
| [5] | Yu FU, Xingchong LIU, Hanyu WANG, Haimin LI, Yafei NI, Wenjing ZOU, Yue LEI, Yongshan PENG. Research on F3EACl modification layer for improving performance of perovskite solar cells [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3554-3563. |
| [6] | Jing ZHAO, Chengwen GU, Xigao JIAN, Zhihuan WENG. Preparation and performance evaluation of magnolol-based epoxy resin anti-corrosion coatings [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3010-3017. |
| [7] | Yanhui LI, Shaoming DING, Zhouyang BAI, Yinan ZHANG, Zhihong YU, Limei XING, Pengfei GAO, Yongzhen WANG. Corrosion micro-nano scale kinetics model development and application in non-conventional supercritical boilers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2436-2446. |
| [8] | Bowen LEI, Jianhua WU, Qihang WU. Research on high injection superheat cycle for R290 low pressure ratio heat pump [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1875-1883. |
| [9] | Bimao ZHOU, Shisen XU, Xiaoxiao WANG, Gang LIU, Xiaoyu LI, Yongqiang REN, Houzhang TAN. Effect of burner bias angle on distribution characteristics of gasifier slag layer [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1939-1949. |
| [10] | Yongquan ZHANG, Weiwei XUAN. Mechanism of alkali metal/(FeO+CaO+MgO) influence on the structure and viscosity of silicate ash slag [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1764-1771. |
| [11] | Xiaodan SU, Ganyu ZHU, Huiquan LI, Guangming ZHENG, Ziheng MENG, Fang LI, Yunrui YANG, Benjun XI, Yu CUI. Optimization of wet process phosphoric acid hemihydrate process and crystallization of gypsum [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1805-1817. |
| [12] | Yuming CHEN, Wei LI, Xiang YAN, Jingdai WANG, Yongrong YANG. Research progress on regulation of aggregation structure for nascent polyethylene [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 487-499. |
| [13] | Weiyi SU, Jiahui DING, Chunli LI, Honghai WANG, Yanjun JIANG. Research progress of enzymatic reactive crystallization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 617-629. |
| [14] | Xuan ZHOU, Mengya LI, Jie SUN, Zhenkai CEN, Qiangsan LYU, Lishan ZHOU, Haitao WANG, Dandan HAN, Junbo GONG. The regulation mechanism of additives on the amino acid crystal growth [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 500-510. |
| [15] | Zhiyuan JIN, Guorong SHAN, Pengju PAN. Preparation and heat and salt resistance of AM/AMPS/SSS terpolymer [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 916-923. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||