CIESC Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 70 ›› Issue (8): 3177-3187.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20190001
Previous Articles Next Articles
Jiapei ZHAO1( ),Chin Eng LOO2,Hao ZHOU3,Mingxi ZHOU3,Fu WANG1,Jinliang YUAN1(
),Chin Eng LOO2,Hao ZHOU3,Mingxi ZHOU3,Fu WANG1,Jinliang YUAN1( )
)
Received:2019-01-02
Revised:2019-07-07
Online:2019-08-05
Published:2019-08-05
Contact:
Jinliang YUAN
通讯作者:
袁金良
作者简介:赵加佩(1985—),男,博士,讲师,<email>jiapeizhao@126.com</email>
基金资助:CLC Number:
Jiapei ZHAO, Chin Eng LOO, Hao ZHOU, Mingxi ZHOU, Fu WANG, Jinliang YUAN. Effect of sinter mix properties on the flame front properties and iron ore sintering performance[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(8): 3177-3187.
赵加佩, 周昊, 周明煕, 王甫, 袁金良. 铁矿石烧结中混合料特性对火焰烽面与烧结性能的影响机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(8): 3177-3187.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 成分 | 质量分数/% | |
|---|---|---|
| 基础碱度(碱度值1.8) | 高碱度(碱度值2.2) | |
| Fe2O3 | 83.36 | 81.40 |
| CaO | 8.78 | 10.74 |
| SiO2 | 4.88 | 4.88 |
| Al2O3 | 1.48 | 1.48 |
| MgO | 1.50 | 1.50 |
Table 1 Sinter mix chemistry for BASE and HB cases
| 成分 | 质量分数/% | |
|---|---|---|
| 基础碱度(碱度值1.8) | 高碱度(碱度值2.2) | |
| Fe2O3 | 83.36 | 81.40 |
| CaO | 8.78 | 10.74 |
| SiO2 | 4.88 | 4.88 |
| Al2O3 | 1.48 | 1.48 |
| MgO | 1.50 | 1.50 |
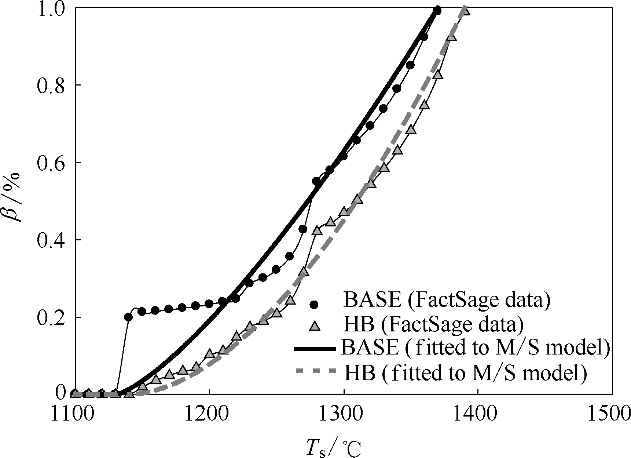
Fig.1 Variation of melt fraction β with temperature T s for the examples of two basicity levels (BASE and HB) predicted by thermochemical modelling with FactSage(The two lines indicate the results fitted to the melting and solidification model according to Eq. (3))
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 床高(含铺底料层)/mm | 550 |
| 铺底料层厚度/mm | 30 |
| 烧结杯截面积/m2 | 0.09 |
| 床点火温度/℃ | 1200 |
| 点火时间/s | 90 |
| 点火负压/kPa | 6 |
| 烧结负压/kPa | 16 |
| 落下强度试验(2m高)/次 | 4 |
| 焦炭添加量/%(dob②) | 6.00, 6.25①, 6.50 |
| 碱度(CaO/SiO2) | 1.5, 1.8①, 2.1 |
| 混合料水分含量/%(tmb③) | 6.7, 7.2①, 7.6 |
Table 2 Summary of conditions for return fines balanced sinter pot tests[10,11]
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 床高(含铺底料层)/mm | 550 |
| 铺底料层厚度/mm | 30 |
| 烧结杯截面积/m2 | 0.09 |
| 床点火温度/℃ | 1200 |
| 点火时间/s | 90 |
| 点火负压/kPa | 6 |
| 烧结负压/kPa | 16 |
| 落下强度试验(2m高)/次 | 4 |
| 焦炭添加量/%(dob②) | 6.00, 6.25①, 6.50 |
| 碱度(CaO/SiO2) | 1.5, 1.8①, 2.1 |
| 混合料水分含量/%(tmb③) | 6.7, 7.2①, 7.6 |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 床高(含铺底料层)/mm | 600 |
| 铺底料层厚度/mm | 30 |
| 烧结杯截面积/m2 | 0.088 |
| 床点火温度/℃ | 1200 |
| 点火时间/s | 90 |
| 点火负压/kPa | 6 |
| 烧结负压/kPa | 16 |
| 落下强度试验(2m高)/次 | 4 |
| 返矿用量/%(dob②) | 32.4 |
| 焦炭添加量/%(dob②) | 5.9, 6.15, 6.4①, 6.65, 6.9 |
| 碱度(CaO/SiO2) | 0.8, 1.4, 2.0①, 2.6, 3.2 |
| 混合料水分含量/%(tmb③) | 6.5, 6.8, 7.1①, 7.4, 7.7 |
Table 3 Summary of conditions for simulation cases with constant return fines level
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 床高(含铺底料层)/mm | 600 |
| 铺底料层厚度/mm | 30 |
| 烧结杯截面积/m2 | 0.088 |
| 床点火温度/℃ | 1200 |
| 点火时间/s | 90 |
| 点火负压/kPa | 6 |
| 烧结负压/kPa | 16 |
| 落下强度试验(2m高)/次 | 4 |
| 返矿用量/%(dob②) | 32.4 |
| 焦炭添加量/%(dob②) | 5.9, 6.15, 6.4①, 6.65, 6.9 |
| 碱度(CaO/SiO2) | 0.8, 1.4, 2.0①, 2.6, 3.2 |
| 混合料水分含量/%(tmb③) | 6.5, 6.8, 7.1①, 7.4, 7.7 |

Fig.2 Sinter pot test results of return fines level, yield, FFS, productivity and coke rate at increasing basicity levels(MT, β mean, yield, FFS, productivity and coke rate predicted by the model are also shown)

Fig.3 Sinter pot test results of return fines level, yield, FFS, productivity and coke rate at increasing coke addition levels(MT, β mean, yield, FFS, productivity and coke rate predicted by the model are also shown)
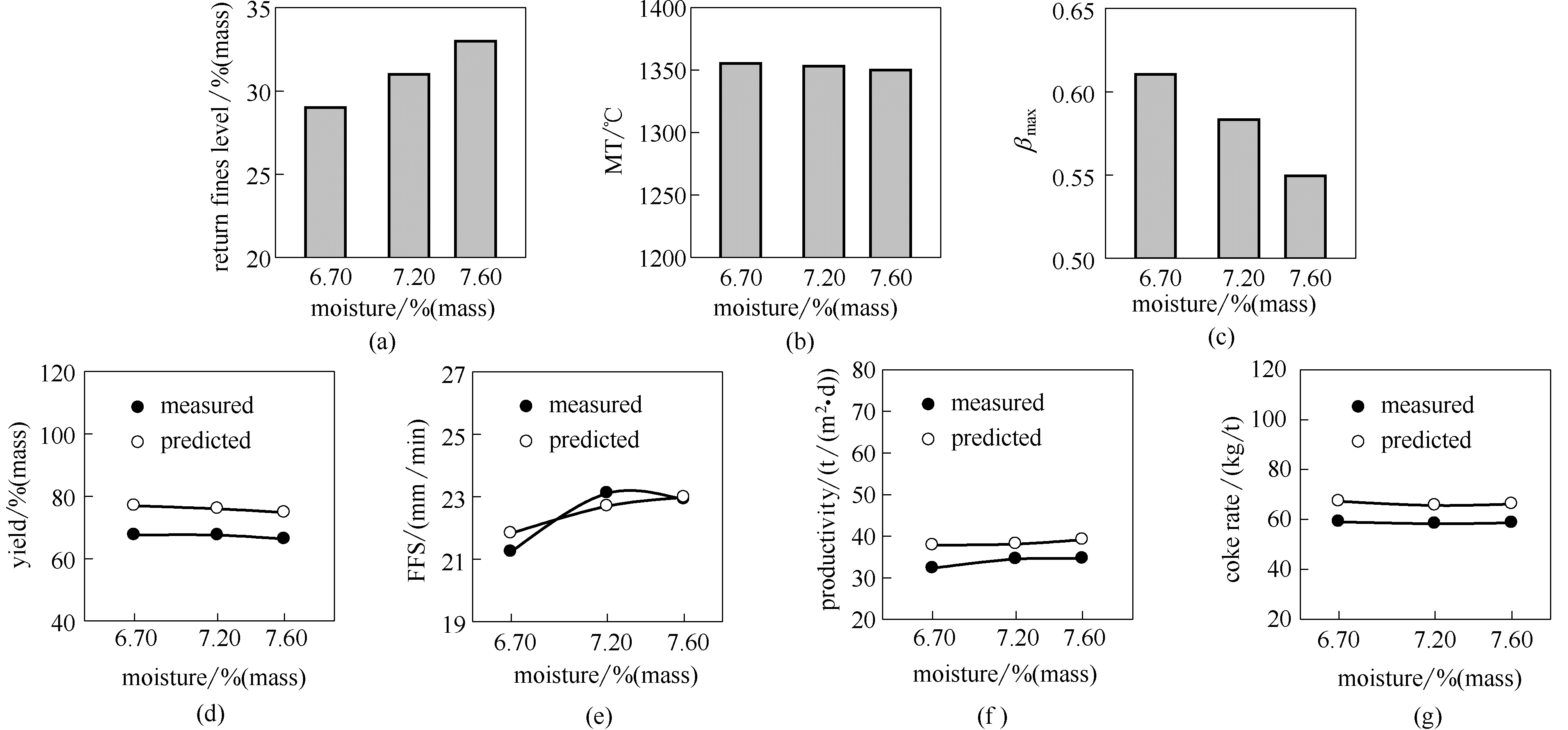
Fig.4 Sinter pot test results of return fines level, yield, FFS, productivity and coke rate at increasing mix moisture levels(MT, β mean, yield, FFS, productivity and coke rate predicted by the model are also shown)
| 1 | Zhao J , Loo C E , Ellis B G . Improving energy efficiency in iron ore sintering through segregation: a theoretical investigation [J]. ISIJ Int., 2016, 56(7): 1148-1156. |
| 2 | Zhou H , Zhao J P , Loo C E , et al . Model predictions of important bed and gas properties during iron ore sintering [J]. ISIJ Int., 2012, 52(12): 2168-2176. |
| 3 | Zhao J , Loo C E , Zhou H , et al . Modelling and analysis of the combustion behaviour of granulated fuel particles in iron ore sintering [J]. Combust. Flame, 2018, 189: 257-274. |
| 4 | Loo C E , Hutchens M F . Quantifying the resistance to airflow during iron ore sintering [J]. ISIJ Int., 2003, 43(5): 630-636. |
| 5 | Loo C E , Matthews L T . Assimilation of large ore and flux particles in iron ore sintering [J]. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall.(Sect. C: Miner Process. Extr. Metall),1992,101: C105-C117. |
| 6 | Lu L , Adam M , Kilburn M , et al . Substitution of charcoal for coke breeze in iron ore sintering [J]. ISIJ Int., 2013, 53(9): 1607-1616. |
| 7 | Zhao J , Loo C E . Dependence of flame front speed on iron ore sintering conditions [J]. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. (TIMM C), 2016, 125(3): 165-171. |
| 8 | Bhagat R P . Factors affecting return sinter fines regimed and strand productivity in iron ore sintering [J]. ISIJ Int., 1999, 39(9): 889-895. |
| 9 | Umadevi T , Sah R , Mahapatra P C . Influence of sinter basicity (CaO/SiO2) on low and high alumina iron ore sinter quality [J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy, 2014, 123(2): 75-85. |
| 10 | Loo C E , Wong D J . Fundamental insights into the sintering behaviour of goethitic ore blends [J]. ISIJ Int., 2005, 45(4): 459-468. |
| 11 | Loo C E , Wong D J . Fundamental factors determining laboratory sintering results [J]. ISIJ Int., 2005, 45(4): 449-458. |
| 12 | Zhao J P , Loo C E , Dukino R D . Modelling fuel combustion in iron ore sintering [J]. Combust. Flame, 2015, 162(4): 1019-1034. |
| 13 | Litster J , Waters A . Influence of the material properties of iron ore sinter feed on granulation effectiveness [J]. Powder Technol., 1988, 55(2): 141-151. |
| 14 | Litster J , Waters A , Nicol S . A model for predicting the size distribution of product from a granulating drum [J]. Trans. ISIJ, 1986, 26(12): 1036-1044. |
| 15 | Hinkley J , Waters A G , Litster J D . An investigation of pre-ignition air flow in ferrous sintering [J]. Int. J. Miner. Process, 1994, 42(1/2): 37-52. |
| 16 | Zhou H , Zhao J P , Loo C E , et al . Numerical modeling of the iron ore sintering process [J]. ISIJ Int., 2012, 52(9): 1550–1558. |
| 17 | Zhao J , Loo C E , Yuan J , et al . A fundamental study of the cocombustion of coke and charcoal during iron ore sintering [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(8): 8743-8759. |
| 18 | Ni M , Xiao H , Chi Y , et al . Combustion and inorganic bromine emission of waste printed circuit boards in a high temperature furnace [J]. Waste Management, 2012, 32(3): 568-574. |
| 19 | Xiao H , Zhou Z , Zhou H , et al . Conversion of HBr to Br2 in the flue gas from the combustion of waste printed circuit boards in post-combustion area [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 161: 239-244. |
| 20 | Xiao H , Chi Y , Buekens A . Combustion characteristics of waste printed circuit boards in thermogravimetric analyzers [J]. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 2015, 33(4): 1105-1110. |
| 21 | Kawaguchi T , Sato S , Takata K . Development and application of an integrated simulation model for iron ore sintering[C]// Ironmaking Conf. Proc. ISS, 1987: 99-106. |
| 22 | Nakano M , Okazaki J . Ideal behavior of sinter block densification and relation thereof to yield and strength in iron ore sintering [J]. ISIJ Int., 2011, 51(9): 1418-1424. |
| 23 | Yang W , Choi A , Choi E S , et al . Combustion characteristics in an iron ore sintering bed — evaluation of fuel substitution [J]. Combust. Flame, 2006, 145(3): 447-463. |
| 24 | Cheng Z , Yang J , Zhou L , et al . Sinter strength evaluation using process parameters under different conditions in iron ore sintering process [J]. Appl. Therm. Eng., 2016, 105: 894-904. |
| 25 | Zhao J , Loo C E . Dependence of flame front speed on iron ore sintering conditions[C]// Iron Ore Conference 2015. 2015: 83-90. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||