CIESC Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 70 ›› Issue (12): 4828-4834.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20190708
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Qi WANG( ),Ji ZHAO,Qiongpeng DAN,Xiyao LI,Qiong ZHANG,Yongzhen PENG(
),Ji ZHAO,Qiongpeng DAN,Xiyao LI,Qiong ZHANG,Yongzhen PENG( )
)
Received:2019-06-21
Revised:2019-09-09
Online:2019-12-05
Published:2019-12-05
Contact:
Yongzhen PENG
通讯作者:
彭永臻
作者简介:王琦(1995—),女,硕士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Qi WANG, Ji ZHAO, Qiongpeng DAN, Xiyao LI, Qiong ZHANG, Yongzhen PENG. Cultivation and enrichment of denitrifying phosphorus removal system for treating domestic sewage[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(12): 4828-4834.
王琦, 赵骥, 但琼鹏, 李夕耀, 张琼, 彭永臻. 反硝化聚磷菌的培养富集及处理生活污水的稳定运行[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(12): 4828-4834.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 阶段 | 运行模式 | 时间/h | 排水比 | 厌氧段进水量/L | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阶段Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ | A/O | 2/2 | 0.4 | 4 | — |
| 阶段Ⅳ | A/A/O | 2/2/1 | 0.4 | 3.5 | NaNO3配制 |
| 阶段Ⅴ | A/A/O | 2/2.5/0.5 | 0.4 | 3.5 | NaNO3配制 |
| 阶段Ⅵ | A/A/O | 2/2.5/0.5 | 0.6 | 3.5 | 全程硝化反应器 |
Table 1 Operation mode
| 阶段 | 运行模式 | 时间/h | 排水比 | 厌氧段进水量/L | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阶段Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ | A/O | 2/2 | 0.4 | 4 | — |
| 阶段Ⅳ | A/A/O | 2/2/1 | 0.4 | 3.5 | NaNO3配制 |
| 阶段Ⅴ | A/A/O | 2/2.5/0.5 | 0.4 | 3.5 | NaNO3配制 |
| 阶段Ⅵ | A/A/O | 2/2.5/0.5 | 0.6 | 3.5 | 全程硝化反应器 |
时间/ d | COD浓度/ (mg·L-1) | 平均 去除率/% | 反硝化除磷占总除磷的比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 93~103 | 200 | 93.83 | 85.71 |
| 136~146 | 250 | 96.72 | 87.10 |
| 124~135 | 300 | 95.33 | 59.01 |
| 112~123 | 320 | 91.05 | 58.02 |
| 104~111 | 350 | 87.89 | 70.52 |
Table 2 PO43- removal rate and denitrifying phosphorus removal ratio under different influent COD concentrations
时间/ d | COD浓度/ (mg·L-1) | 平均 去除率/% | 反硝化除磷占总除磷的比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 93~103 | 200 | 93.83 | 85.71 |
| 136~146 | 250 | 96.72 | 87.10 |
| 124~135 | 300 | 95.33 | 59.01 |
| 112~123 | 320 | 91.05 | 58.02 |
| 104~111 | 350 | 87.89 | 70.52 |
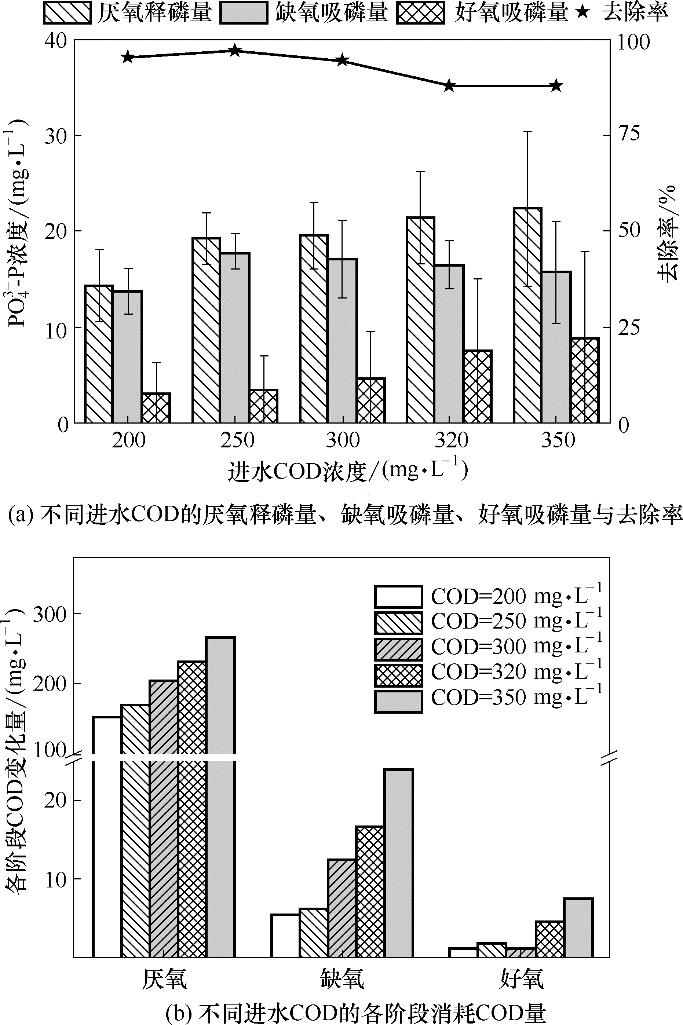
Fig.4 Anaerobic phosphorus release, anoxic phosphorus uptake, aerobic phosphorus uptake and COD change at various stages under different influent COD conditions
| 1 | Seviour R J, Mino T, Onuki M. The microbiology of biological phosphorus removal in activated sludge systems[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2010, 27(1): 99-127. |
| 2 | Barnard J L. Biological nutrient removal without addition of chemicals[J]. Water Research, 1975, 9(5): 485-490. |
| 3 | Kuba T, Smolders G, van Loosdrecht M C M, et al. Biological phosphorus removal from wastewater by anaerobic-anoxic sequencing batch reactor[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1993, 27(5/6 ): 241-252. |
| 4 | Saito T, Brdjanovic D, van Loosdrecht M C M. Effect of nitrite on phosphate uptake by phosphate accumulating organisms[J]. Water Research, 2004, 38(17): 3760-3768. |
| 5 | Vlekke G J F M, Comeau Y, Oldham W K. Biological phosphate removal from wastewater with oxygen or nitrate in sequencing batch reactors[J]. Environmental Technology Letters, 1988, 9(8): 791-796. |
| 6 | Meinhold J, Arnold E, Isaacs S. Effect of nitrite on anoxic phosphate uptake in biological phosphorus removal activated sludge[J]. Water Research, 1999, 33(8): 1871-1883. |
| 7 | Hu J Y, Ong S L, Ng W J, et al. A new method for characterizing denitrifying phosphorus removal bacteria by using three different types of electron acceptors[J]. Water Research, 2003, 37(14): 3463-3471. |
| 8 | 李军, 彭永臻, 杨秀山, 等. 序批式生物膜法反硝化除磷特性及其机理[J]. 中国环境科学, 2004, 24(2): 219-223. |
| Li J, Peng Y Z, Yang X S, et al. Characteristics and mechanism of the phosphorus removal by denitrification with sequencing batch biofilm technique[J]. China Environmental Science, 2004, 24(2): 219-223. | |
| 9 | Kuba T, van Loosdrecht M C M, Heijnen J J. Phosphorus and nitrogen removal with minimal COD requirement by integration of denitrifying dephosphatation and nitrification in a two-sludge system[J]. Water Research, 1996, 30(7): 1702-1710. |
| 10 | Kuba T, van Loosdrecht M C M, Brandse F A, et al. Occurrence of denitrifying phosphorus removing bacteria in modified UCT-type wastewater treatment plants[J]. Water Research, 2016, 31(4): 777-786. |
| 11 | Bortone G, Libelli S M, Tilche A, et al. Anoxic phosphate uptake in the dephanox process[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1999, 40(4/5): 177-185. |
| 12 | Whang L M, Park J K. Competition between polyphosphate and glycogen-accumulating organisms in enhanced-biological-phosphorus-removal systems: effect of temperature and sludge age[J]. Water Environment Research, 2006, 78(1): 4-11. |
| 13 | Wang Y Y, Peng Y Z, Li T W, et al. Phosphorus removal under anoxic conditions in a continuous-flow A2N two-sludge process[J]. Water Science & Technology A Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research, 2004, 50(6): 37-44. |
| 14 | Carvalho G, Lemos P C, Oehmen A, et al. Denitrifying phosphorus removal: linking the process performance with the microbial community structure [J]. Water Research, 2007, 41(19): 4383-4396. |
| 15 | Ma Y, Peng Y Z, Wang X L. Improving nutrient removal of the AAO process by an influent bypass flow by denitrifying phosphorus removal[J]. Desalination, 2009, 246(1/2/3): 534-544. |
| 16 | 国家环境保护局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. |
| The State Environmental Protection Administration. Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Method[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2002. | |
| 17 | 张勇, 王淑莹, 赵伟华, 等. 中试规模AAO曝气生物滤池双污泥系统的启动运行[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(10): 4228-4235. |
| Zhang Y, Wang S Y, Zhao W H, et al. Start-up of pilot-scale AAO-BAF two-sludge system[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(10): 4228-4235. | |
| 18 | Randall C W, Bamard J L, Stensel H D. Design and Retrofit of Wastewater Treatment Plants for Biological Nutrient Removal: Volume V[M]. CRC Press, 1998. |
| 19 | 王晓莲, 王淑莹, 彭永臻. 进水C/P比对A2/O工艺性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2005, 56(9): 1765-1770. |
| Wang X L, Wang S Y, Peng Y Z. Effects of feed water C/P ratio on performance of anaerobic-anoxic-oxic process[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering(China), 2005, 56(9): 1765-1770. | |
| 20 | Panswad T, Tongkhammak N, Anotai J. Estimation of intracellular phosphorus content of phosphorus-accumulating organisms at different P: COD feeding ratios[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2007, 84(2): 141-145. |
| 21 | 郝王娟, 薛涛, 黄霞. 进水磷碳比对聚磷菌与聚糖菌竞争生长的影响[J]. 中国给水排水, 2007, 23(17): 95-98. |
| Hao W J, Xue T, Huang X. Effect of influent P/C ratio on competition between phosphate and glycogen accumulating organisms[J]. China Water and Wastewater, 2007, 23(17): 95-98. | |
| 22 | 李志勇, 彭永臻, 张艳萍, 等. 硝酸盐浓度及投加方式对反硝化除磷的影响[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2003, 25(6): 323-325. |
| Li Z Y, Peng Y Z, Zhang Y P, et al. Effect of nitrate on denitrifying dephosphatation[J]. Environmental Pollution and Control, 2003, 25(6): 323-325. | |
| 23 | Kerrn J P, Henze M. Biological phosphorus uptake under anoxic and aerobic conditions[J]. Water Research, 1993, 27(4): 617-624. |
| 24 | Kerrn-Jespersen J P, Henze M, Strube R. Biological phosphorus release and uptake under alternating anaerobic and anoxic conditions in a fixed-film reactor[J]. Water Research, 1994, 28(5): 1253-1255. |
| 25 | Wachtmeister A, Kuba T, van Loosdrecht M C M, et al. A sludge characterization assay for aerobic and denitrifying phosphorus removing sludge[J]. Water Research, 1997, 31(3): 471-478. |
| 26 | 王亚宜, 王淑莹, 彭永臻, 等. 污水有机碳源特征及温度对反硝化聚磷的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2006, 26(2): 186-192. |
| Wang Y Y, Wang S Y, Peng Y Z, et al. The influence of carbon source and temperature on the denitrifying dephosphorus removal in wastewater treatment process[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2006, 26(2): 186-192. | |
| 27 | Kerrn-Jespersen J P, Henze M. Biological phosphorus uptake under anoxic and aerobic conditions[J]. Water Research, 1993, 27(4): 617-624. |
| 28 | 王亚宜, 杜红, 彭永臻, 等. A2N反硝化除磷脱氮工艺及其影响因素[J]. 中国给水排水, 2003, 19(9): 8-11. |
| Wang Y Y, Du H, Peng Y Z, et al. A2N process for denitrifying phosphorus and nitrogen removal and its affecting factors[J]. China Water and Wastewater, 2003, 19(9): 8-11. | |
| 29 | 侯红勋, 彭永臻, 殷芳芳, 等. NO2-作为电子受体对反硝化吸磷影响动力学研究[J]. 环境科学, 2008, 2(7): 1874-1879. |
| Hou H X, Peng Y Z, Yin F F, et al. Inhibitory effect kinetics of nitrite acting as electron acceptor on anoxic phosphorus uptake and denitrification[J]. Environmental Science, 2008, 2(7): 1874-1879. | |
| 30 | 马娟, 彭永臻, 王丽, 等. 反硝化除磷技术及其影响因素分析[J]. 工业水处理, 2009, 29(4): 4-8. |
| Ma J, Peng Y Z, Wang L, et al. Analysis of denitrification-dephosphorization technology and its influential factors[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2009, 29(4): 4-8. | |
| 31 | 任南琪, 陈鸣歧. pH值对反硝化除磷的影响[J]. 黑龙江科技学院学报, 2004, 14(5): 284-286. |
| Ren N Q, Chen M Q. Effect of pH on denitrification and phosphorus removal[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang University of Science and Technology, 2004, 14(5): 284-286. |
| [1] | Longyi LYU, Wenbo JI, Muda HAN, Weiguang LI, Wenfang GAO, Xiaoyang LIU, Li SUN, Pengfei WANG, Zhijun REN, Guangming ZHANG. Enhanced anaerobic removal of halogenated organic pollutants by iron-based conductive materials: research progress and future perspectives [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3193-3202. |
| [2] | Nan HU, Demin TAO, Zhaolan YANG, Xuebing WANG, Xiangxu ZHANG, Yulong LIU, Dexin DING. Remediation of percolate water from uranium tailings reservoir by coupling iron-carbon micro-electrolysis and sulfate reducing bacteria [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2655-2667. |
| [3] | Yanshan WANG, Xiaochao ZHU, Yingjin SONG, Yihang LI. Study on anaerobic digestion pretreatment coupled with hydrothermal carbonization of grass [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(2): 904-913. |
| [4] | Yiran WANG, Chaoyang GUAN, Xiang GAO, Hongxia CHEN. Experimental study on boiling dynamics modulation by porous foam deaeration board [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(11): 4948-4956. |
| [5] | Xinjie GAO, Zaizhou XU, Yongzhen PENG, Yuwei HUANG, Jing DING, Zeming AN, Chuanxin WANG. Enhance nitrogen removal via endogenous denitrification in a sludge double recirculation-anaerobic/aerobic/anoxic process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(11): 5098-5105. |
| [6] | Haibo LIU, Nan WANG, Hongzhou LIU, Tiezhu CHEN, Jianchang LI. Effects of voltage perturbation on the activities of microorganisms and key enzymes in EAD metabolic flux [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(10): 4603-4612. |
| [7] | MA Zhibin, ZHANG Sen, SHAN Xueyuan, GUO Yanxia, CHENG Fangqin. Migration of lithium, gallium and rare earth elements in coal, coal slime, and coal gangue during combustion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(6): 3349-3358. |
| [8] | WEI Wei, CAI Xinyu, LIU Zaiwen, ZUO Min. Disturbance rejection control for wastewater treatment processes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(3): 1567-1574. |
| [9] | Junpeng TIAN, Yuanhui SHEN, Donghui ZHANG, Zhongli TANG. Simulation and analysis of CH4/N2 separation by vacuum pressure swing adsorption with structured composite adsorption media [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(11): 5675-5685. |
| [10] | Xiaojing ZHANG,Bingbing MA,Han ZHANG,Denghui WEI,Hongli ZHANG,Hao HU,Zirui ZHAO. Comparison of the performance of Anammox process in the treatment of wastewater from different antibiotics [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(11): 5810-5819. |
| [11] | Hong CHEN,Jing XIE,Yuying CHENG,Xin YU,Shanping CHEN,Gang XUE,Meilin WANG,Yi LUO,Xiangyu HE. Study on performance and mechanism of enhanced biological nitrification by zero-valent iron [J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(10): 5372-5383. |
| [12] | Guoyu WEN, Wei WANG, Rui XIE, Xiaojie JU, Zhuang LIU, Liangyin CHU. Recent progress of hydrogel materials in the field of enrichment and separation of metal ions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(9): 3866-3875. |
| [13] | Zongyue LIU, Hong YANG, Shaolun WANG, Jiawei WANG. Rapid industrial enrichment of nitrifying bacteria [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(8): 3722-3729. |
| [14] | Yuexi WU, Wei ZENG, Hong LIU, Jianmin LI, Yongzhen PENG. Exploration of nitrogen transformation pathway in Feammox [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(5): 2265-2272. |
| [15] | Yu ZHANG, Rong HUA, Xiaokang KOU, Fuping LIU, Jie KONG, Feng ZHANG, Feifan HE, Yu FENG. Preparation of amino modified styrene-divinylbenzene resin and its adsorption of rhenium [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(5): 2109-2117. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||