CIESC Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (6): 2705-2712.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20200081
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jia JU1( ),Wenxu QI1,2,Pengfei KONG1,Jiayu TANG1,Feixue LIANG1,Xiaoxin ZHANG1,Gaohong HE2(
),Wenxu QI1,2,Pengfei KONG1,Jiayu TANG1,Feixue LIANG1,Xiaoxin ZHANG1,Gaohong HE2( ),Lei YANG1
),Lei YANG1
Received:2020-01-19
Revised:2020-03-25
Online:2020-06-05
Published:2020-06-05
Contact:
Gaohong HE
鞠佳1( ),祁文旭1,2,孔鹏飞1,汤佳玉1,梁飞雪1,张晓欣1,贺高红2(
),祁文旭1,2,孔鹏飞1,汤佳玉1,梁飞雪1,张晓欣1,贺高红2( ),杨磊1
),杨磊1
通讯作者:
贺高红
作者简介:鞠佳(1978—),女,博士,讲师,基金资助:CLC Number:
Jia JU, Wenxu QI, Pengfei KONG, Jiayu TANG, Feixue LIANG, Xiaoxin ZHANG, Gaohong HE, Lei YANG. Preparation of TiO2/PVDF blend microfiltration membrane and its adsorption of bilirubin[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(6): 2705-2712.
鞠佳, 祁文旭, 孔鹏飞, 汤佳玉, 梁飞雪, 张晓欣, 贺高红, 杨磊. TiO2/PVDF共混微滤膜的制备及其吸附胆红素的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(6): 2705-2712.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
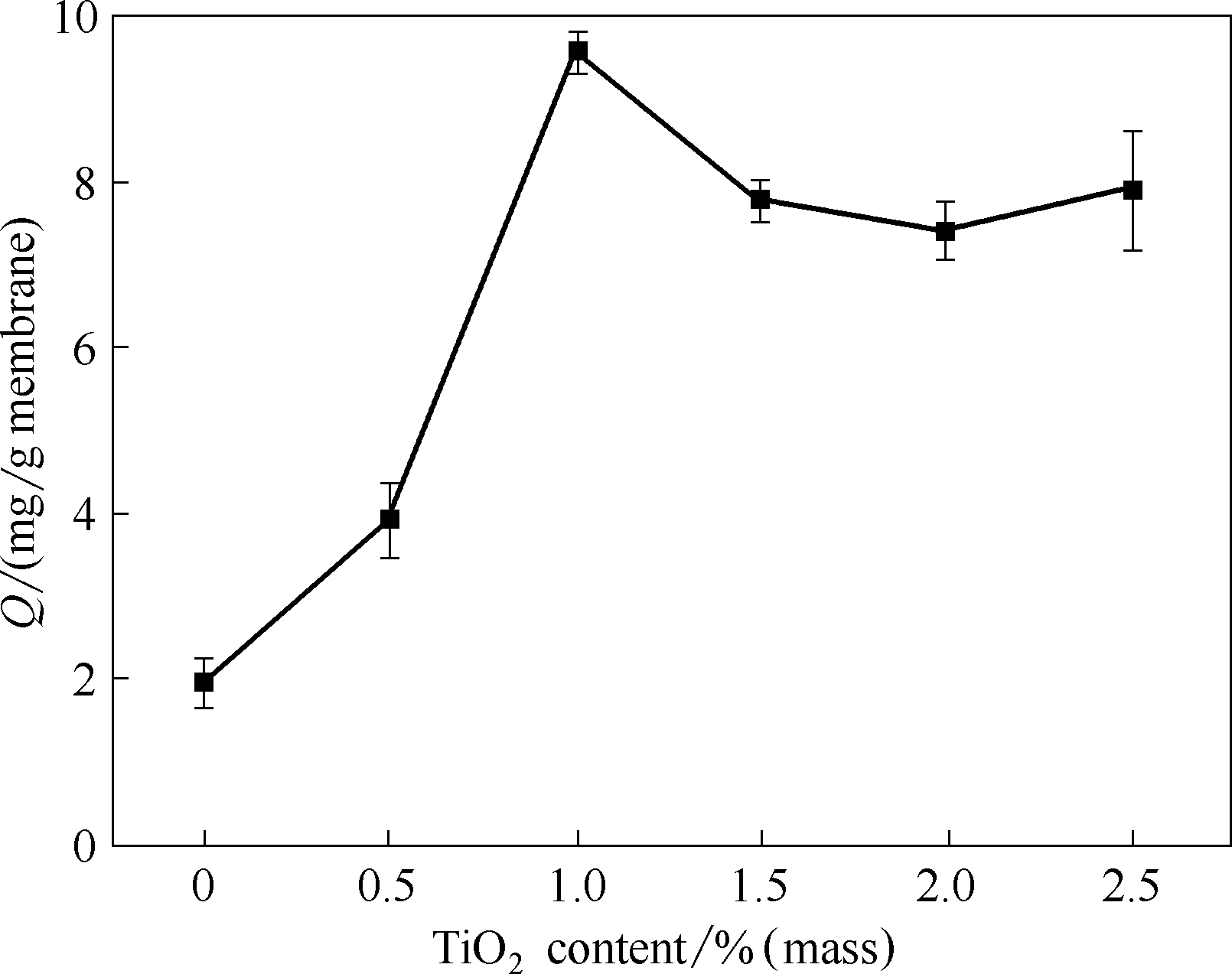
Fig.3 Effect of TiO2 content on bilirubin adsorption capacity of TiO2/PVDF blend microfiltration membrane(bilirubin concentration 2.5 mg/ml, pH 10.9, 25℃, adsorption time 2 h)
| 膜 | J / (ml/(cm2·min)) | θ/ (°) | W1 / g | W2 / g | VM / cm2 | ε / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF-10-0膜 | 18.6 | 71 | 0.0149 | 0.0513 | 0.052 | 70.0 |
| PVDF-10-1膜 | 32.8 | 58 | 0.0175 | 0.0559 | 0.056 | 68.5 |
Table 1 Comparison of properties of microfiltration membranes
| 膜 | J / (ml/(cm2·min)) | θ/ (°) | W1 / g | W2 / g | VM / cm2 | ε / % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF-10-0膜 | 18.6 | 71 | 0.0149 | 0.0513 | 0.052 | 70.0 |
| PVDF-10-1膜 | 32.8 | 58 | 0.0175 | 0.0559 | 0.056 | 68.5 |
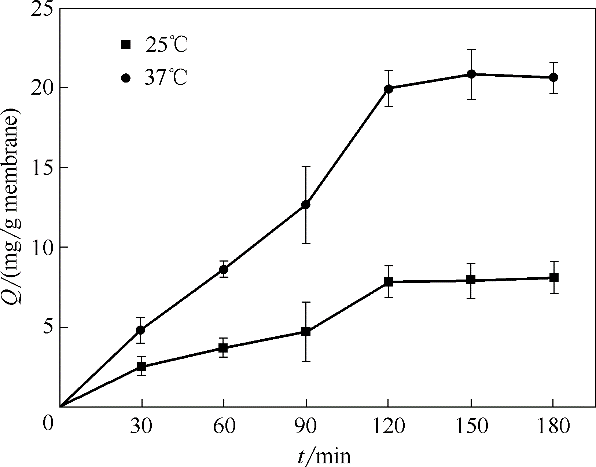
Fig.6 Effects of adsorption temperature and time on bilirubin adsorption capacity of TiO2/PVDF blend microfiltration membrane(bilirubin concentration 2.5 mg/ml, pH 10.9)
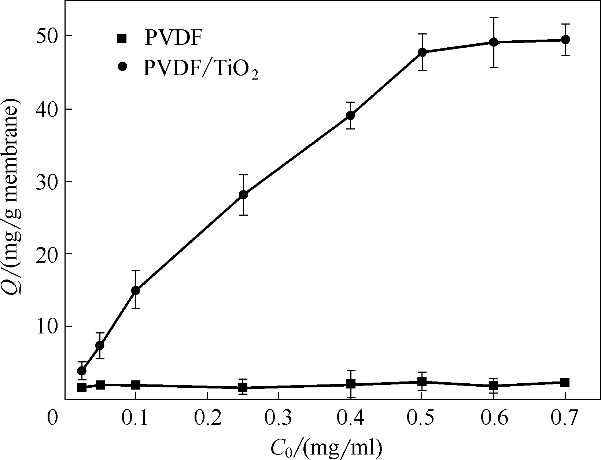
Fig.7 Effect of initial bilirubin concentration on bilirubin adsorption capacity of TiO2/PVDF blend microfiltration membrane(pH 10.9, 37℃, adsorption time 2 h)
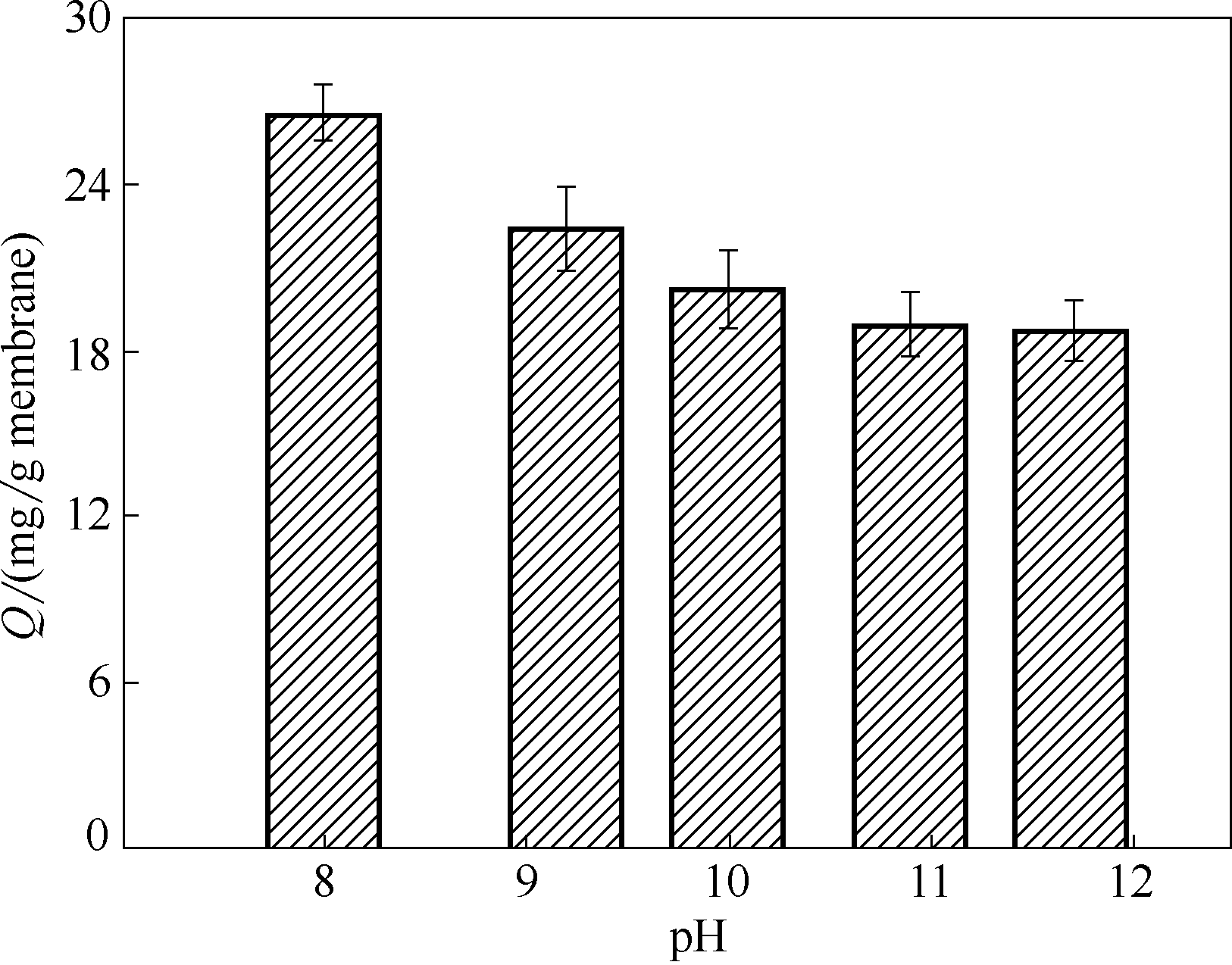
Fig.9 Effect of bilirubin solution pH on bilirubin adsorption capacity of TiO2/PVDF blend microfiltration membrane(bilirubin concentration 2.4 mg/ml, 37℃, adsorption time 2 h)
| 吸附剂 | 胆红素饱和吸附量/ (mg/g membrane) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|
| TiO2纳米晶体膜 | 17.1 | [ |
| Procion Blue H-5R担载纤维素膜 | 26.0 | [ |
| 聚(吡咯-3-羧酸)氧化铝复合膜 | 40.7 | [ |
| β-环糊精改性聚醚砜中空纤维膜 | 51.0 | [ |
| TiO2颗粒 | 2.4 | 本文 |
| TiO2/PVDF复合膜 | 49.5 | 本文 |
Table 2 Comparison of adsorption performance of TiO2/PVDF composite membrane with other adsorption materials
| 吸附剂 | 胆红素饱和吸附量/ (mg/g membrane) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|
| TiO2纳米晶体膜 | 17.1 | [ |
| Procion Blue H-5R担载纤维素膜 | 26.0 | [ |
| 聚(吡咯-3-羧酸)氧化铝复合膜 | 40.7 | [ |
| β-环糊精改性聚醚砜中空纤维膜 | 51.0 | [ |
| TiO2颗粒 | 2.4 | 本文 |
| TiO2/PVDF复合膜 | 49.5 | 本文 |
| 1 | Houlihan D D, Armstrong M J, Newsome P N. Investigation of Jaundice[J]. Medicine, 2011, 39(9): 518-522. |
| 2 | 赖芳芳, 张丙宏. 胆红素对新生儿神经系统影响的研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2018, 24(9): 1704-1708. |
| Lai F F, Zhang B H. Research progress of the effect of bilirubin on neonatal nervous system[J]. Medical Recapitulate, 2018, 24(9): 1704-1708. | |
| 3 | 麻开旺, 陈俊平, 李光大. 胆红素医用吸附剂研究进展[J]. 离子交换与吸附, 2014, (3): 278-288. |
| Ma K W, Chen J P, Li G D. Research progress in medical bilirubin adsorbent[J]. Ion Exchange and Adsorption, 2014, (3): 278-288. | |
| 4 | Shi W, Zhang F, Zhang G. Adsorption of bilirubin with polylysine carrying chitosan-coated nylon affinity membranes[J]. Journal of Chromatography B, 2005, 819(2): 301-306. |
| 5 | Timin A, Rumyantsev E, Solomonov A. Synthesis and application of amino-modified silicas containing albumin as hemoadsorbents for bilirubin adsorption[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2014, 385: 81-88. |
| 6 | Piemonte V, Turchetti L, Annesini M C. Bilirubin removal from albumin-containing solutions: dynamic adsorption on anionic resin[J]. Asia-Pacific Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2010, 5(5): 708-713. |
| 7 | 倪非非, 舒桂明, 李可, 等. 用于胆红素吸附的β-环糊精改性PVDF血浆分离膜的制备[J]. 膜科学与技术, 2018, 38(3): 17-24. |
| Ni F F, Shu G M, Li K, et al. Preparation of PVDF plasma separation adsorption membrane by modified β-cyclodextrin for bilirubin removal[J]. Membrane Science and Technology, 2018, 38(3): 17-24. | |
| 8 | Chen J, Ma Y, Wang L, et al. Preparation of chitosan/SiO2-loaded graphene composite beads for efficient removal of bilirubin[J]. Carbon, 2018, 143: 352-361. |
| 9 | Li Z, Song X, Cui S, et al. Fabrication of macroporous reduced graphene oxide composite aerogels reinforced with chitosan for high bilirubin adsorption[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(15): 8338-8348. |
| 10 | Wu K, Yang W, Jiao Y, et al. A Surface molecularly imprinted electrospun polyethersulfone (PES) fiber mat for selective removal of bilirubin[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2017, 5(29): 5763-5773. |
| 11 | Yang Z, Zhang C. Molecularly imprinted hydroxyapatite thin film for bilirubin recognition[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2011, 29(1): 167-171. |
| 12 | Yola M L, Gode C, Atar N. Molecular imprinting polymer with polyoxometalate/carbon nitride nanotubes for electrochemical recognition of bilirubin[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 246: 135-140. |
| 13 | Ma C, Gao Q, Xia K, et al. Three-dimensionally porous graphene: a high-performance adsorbent for removal of albumin-bonded bilirubin[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B, 2017, 149: 146-153. |
| 14 | Muller B R. Effect of particle size and surface area on the adsorption of albumin-bonded bilirubin on activated carbon[J]. Carbon, 2010, 48(12): 3607-3615. |
| 15 | Zong W, Chen J, Han W, et al. Preparation of chitosan/amino multiwalled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite beads for bilirubin adsorption in hemoperfusion[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B, 2018, 106(1): 96-103. |
| 16 | Ou Y, Gong Q, Liang J. Carbon nanotube-chitosan composite beads with radially aligned channels and nanotube-exposed walls for bilirubin adsorption[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2015, 17(4): 460-466. |
| 17 | Ju J, Liang F, Zhang X, et al. Advancement in separation materials for blood purification therapy[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2019, 27(6): 1383-1390. |
| 18 | 张晖, 刘国聪. N掺杂TiO2纳米膜吸附胆红素分子的石英晶体微天平研究[J]. 分析科学学报, 2011, 27(6): 24-29. |
| Zhang H, Liu G C. Studies on the adsorption behavior of bilirubin on N-doped TiO2 nanofilm by quartz crystal microbalance[J]. Journal of Analytical Science, 2011, 27(6): 24-29. | |
| 19 | Yamazaki K, Shinke K, Ogino T. Selective adsorption of bilirubin against albumin to oxidized single-wall carbon nanohorns[J]. Colloids & Surfaces B Biointerfaces, 2013, 112(12): 103-107. |
| 20 | Yang Z, Si S, Fung Y. Bilirubin adsorption on nanocrystalline titania films[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2007, 515(7/8): 3344-3351. |
| 21 | 谢亚林, 司士辉, 杨政鹏, 等. 胆红素在纳米TiO2膜上的吸附行为研究[J]. 化学通报, 2006, 69(12): 931-936. |
| Xie Y L, Si S H, Yang Z P, et al. Study of adsorption behavior of bilirubin on nanocrystalline titania films[J]. Chemistry Bulletin, 2006, 69(12): 931-936. | |
| 22 | 李孟岩, 鞠佳, 谢磊, 等. PVDF微滤膜的制备、改性及其血液净化应用初探[J]. 辽宁石油化工大学学报, 2019, 39(4): 8-10. |
| Li M Y, Ju J, Xie L, et al. Preliminary study on preparation, modification and blood purification of PVDF microfiltration membrane[J]. Journal of Liaoning Shihua University, 2019, 39(4): 8-10. | |
| 23 | 阮雪华, 徐燕, 周子渊, 等. 聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)改性多孔膜动态吸附废水中的Co2+[J]. 化工进展, 2017, 36(12): 4658-4663. |
| Ruan X H, Xu Y, Zhou Z Y, et al. Dynamic adsorption of Co2+ from wastewater by polyethyleneimine (PEI) -grafted porous membranes[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2017, 36(12): 4658-4663. | |
| 24 | 聂飞, 贺高红, 赵薇, 等. 疏水SiO2/PTFPMS杂化复合膜的制备及其气体分离性能[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(8): 3019-3025. |
| Nie F, He G H, Zhao W, et al. Preparation and gas separation performance of hydrophobic SiO2/PTFPMS hybrid composite membrane[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(8): 3019-3025. | |
| 25 | Chen Z, Deng M, Chen Y, et al. Preparation and performance of cellulose acetate/polyethyleneimine blend microfiltration membranes and their applications[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2004, 235(1/2): 73-86. |
| 26 | Ju J, He G, Duan Z, et al. Improvement of bilirubin adsorption capacity of cellulose acetate/polyethyleneimine membrane using sodium deoxycholate[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 79: 144-152. |
| 27 | 鞠佳, 聂飞, 段志军, 等. 亲和膜配基的结构和密度对胆红素吸附的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(1): 303-310. |
| Ju J, Nie F, Duan Z J, et al. Effect of ligand composition and ligand density of affinity membrane on bilirubin removal[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(1): 303-310. | |
| 28 | 郭春刚, 张召才, 李雪梅, 等. 纳米TiO2复配添加剂对PVDF中空纤维膜结构和性能的影响[J]. 净水技术, 2013, 32(4): 67-71. |
| Guo C G, Zhang Z C, Li X M, et al. Influence on structure and performance for PVDF hollow fiber membrane with combined additives of nanoscale TiO2[J]. Water Purification Technology, 2013, 32(4): 67-71. | |
| 29 | Davies C R, Malchesky P S, Saidel G M. Temperature and albumin effects on adsorption of bilirubin from standard solution using anion-exchange resin[J]. Artificial Organs, 1990, 14(1): 14-19. |
| 30 | Xie M, Sun J, Chen L. Procion Blue H-5R functionalized cellulose membrane with specific removal of bilirubin[J]. Cellulose, 2019, 26(13/14): 8073-8085. |
| 31 | Shi W, Cao H, Song C, et al. Poly(pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid)-alumina composite membrane for affinity adsorption of bilirubin[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 353(1/2): 151-158. |
| 32 | Salimi E, Ghaee A, Ismail A F. β-Cyclodextrin modified PES hollow fiber membrane, a new strategy for bilirubin separation[J]. Materials Letters, 2018, 215: 276-279. |
| [1] | Yan GAO, Peng WU, Chao SHANG, Zejun HU, Xiaodong CHEN. Preparation of magnetic agarose microspheres based on a two-fluid nozzle and their protein adsorption properties [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3457-3471. |
| [2] | Rubin ZENG, Zhongjie SHEN, Qinfeng LIANG, Jianliang XU, Zhenghua DAI, Haifeng LIU. Study of the sintering mechanism of Fe2O3 nanoparticles based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365. |
| [3] | Bingchun SHENG, Jianguo YU, Sen LIN. Study on lithium resource separation from underground brine with high concentration of sodium by aluminum-based lithium adsorbent [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3375-3385. |
| [4] | Ruihang ZHANG, Pan CAO, Feng YANG, Kun LI, Peng XIAO, Chun DENG, Bei LIU, Changyu SUN, Guangjin CHEN. Analysis of key parameters affecting product purity of natural gas ethane recovery process via ZIF-8 nanofluid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3386-3393. |
| [5] | Jie WANG, Xiaolin QIU, Ye ZHAO, Xinyang LIU, Zhongqiang HAN, Yong XU, Wenhan JIANG. Preparation and properties of polyelectrolyte electrostatic deposition modified PHBV antioxidant films [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3068-3078. |
| [6] | Jie LIU, Lisheng WU, Jinjin LI, Zhenghong LUO, Yinning ZHOU. Preparation and properties of polyether-based vinylogous urethane reversible crosslinked polymers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3051-3057. |
| [7] | Ji CHEN, Ze HONG, Zhao LEI, Qiang LING, Zhigang ZHAO, Chenhui PENG, Ping CUI. Study on coke dissolution loss reaction and its mechanism based on molecular dynamics simulations [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2935-2946. |
| [8] | Yong LI, Jiaqi GAO, Chao DU, Yali ZHAO, Boqiong LI, Qianqian SHEN, Husheng JIA, Jinbo XUE. Construction of Ni@C@TiO2 core-shell dual-heterojunctions for advanced photo-thermal catalytic hydrogen generation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2458-2467. |
| [9] | Juhui CHEN, Qian ZHANG, Lingfeng SHU, Dan LI, Xin XU, Xiaogang LIU, Chenxi ZHAO, Xifeng CAO. Study on flow characteristics of nanoparticles in a rotating fluidized bed based on DEM method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2374-2381. |
| [10] | Caihong LIN, Li WANG, Yu WU, Peng LIU, Jiangfeng YANG, Jinping LI. Effect of alkali cations in zeolites on adsorption and separation of CO2/N2O [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2013-2021. |
| [11] | Chenxin LI, Yanqiu PAN, Liu HE, Yabin NIU, Lu YU. Carbon membrane model based on carbon microcrystal structure and its gas separation simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2057-2066. |
| [12] | Shaoyun CHEN, Dong XU, Long CHEN, Yu ZHANG, Yuanfang ZHANG, Qingliang YOU, Chenglong HU, Jian CHEN. Preparation and adsorption properties of monolayer polyaniline microsphere arrays [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2228-2238. |
| [13] | Xuehong WU, Linlin LUAN, Yanan CHEN, Min ZHAO, Cai LYU, Yong LIU. Preparation and thermal properties of degradable flexible phase change films [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1818-1826. |
| [14] | Yu PAN, Zihang WANG, Jiayun WANG, Ruzhu WANG, Hua ZHANG. Heat and moisture performance study of Cur-LiCl coated heat exchanger [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1352-1359. |
| [15] | Haiqin LIU, Bowen LI, Zhe LING, Liang LIU, Juan YU, Yimin FAN, Qiang YONG. Facile preparation and properties of chemically modified galactomannan films via mild hydroxy-alkyne click reaction [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1370-1378. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||