CIESC Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (1): 213-221.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20210863
• Fluid dynamics and transport phenomena • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yingjie FEI1( ),Chunying ZHU1(
),Chunying ZHU1( ),Taotao FU1,Xiqun GAO2,Youguang MA1
),Taotao FU1,Xiqun GAO2,Youguang MA1
Received:2021-06-28
Revised:2021-09-03
Online:2022-01-18
Published:2022-01-05
Contact:
Chunying ZHU
通讯作者:
朱春英
作者简介:费滢洁(1998—),女,硕士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Yingjie FEI, Chunying ZHU, Taotao FU, Xiqun GAO, Youguang MA. Breakup dynamics of bubbles stabilized by nanoparticles with permanent obstruction in a microfluidic Y-junction[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(1): 213-221.
费滢洁, 朱春英, 付涛涛, 高习群, 马友光. Y型微通道内纳米颗粒稳定气泡的完全阻塞破裂动力学[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 213-221.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
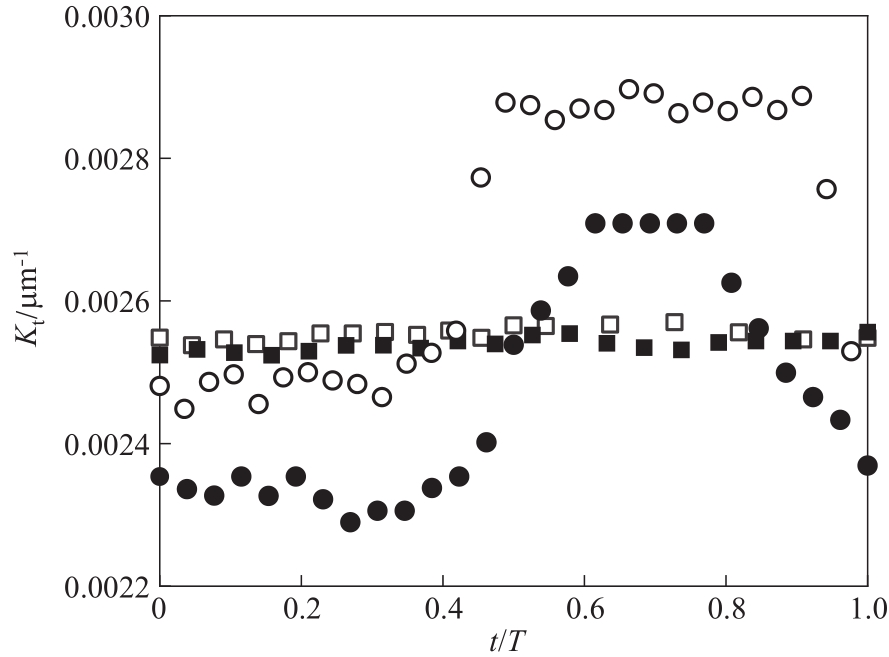
Fig.6 The evaluation of bubble tip curvature (Qd = 0.8 ml·min-1)■,□ Qc = 2.5 ml·min-1, breakup with permanent obstruction; ●,○ Qc = 3 ml·min-1, breakup with partial obstruction; hollow symbols for original bubbles, solid symbols for hardening bubbles
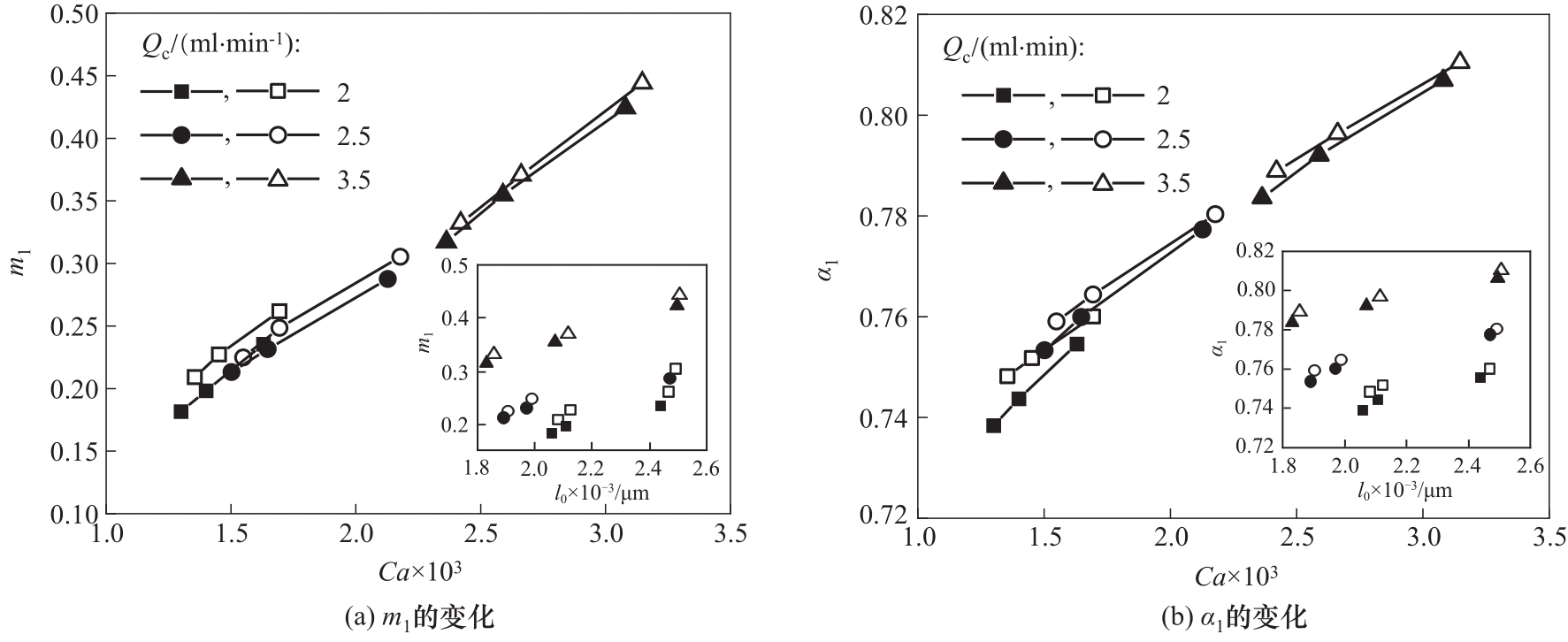
Fig.8 The variation of pre-exponential factor m1 and power-law exponent α1 with Ca and l0 in squeezing stage (hollow symbols for original bubbles, solid symbols for hardening bubbles)

Fig.9 The variation of pre-exponential factor m2 and power-law exponent α2 with Ca and l0 in pinch-off stage (hollow symbols for original bubbles, solid symbols for hardening bubbles)
| 1 | 陈光文, 袁权. 微化工技术[J]. 化工学报, 2003, 54(4): 427-439. |
| Chen G W, Yuan Q. Micro-chemical technology[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2003, 54(4): 427-439. | |
| 2 | Kashid M, Renken A, Kiwi-Minsker L. Mixing efficiency and energy consumption for five generic microchannel designs[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 167(2/3): 436-443. |
| 3 | 程曜峰, 张丽娟, 张炜, 等. 微萃取器在多粘菌素B萃取工艺中的应用[J]. 化学工业与工程, 2021, 38(2): 55-60. |
| Cheng Y F, Zhang L J, Zhang W, et al. Application of microextractor in polymyxin B extraction process[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2021, 38(2): 55-60. | |
| 4 | 王彦, 王靖涛. 微流控技术制备聚酰胺微胶囊的工艺研究[J]. 化学工业与工程, 2018, 35(6): 20-25. |
| Wang Y, Wang J T. Preparation of polyamide microcapsules based on microfluidics[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2018, 35(6): 20-25. | |
| 5 | Günther A, Jensen K F. Multiphase microfluidics: from flow characteristics to chemical and materials synthesis[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2006, 6(12): 1487-1503. |
| 6 | du Toit H, MacDonald T J, Huang H, et al. Continuous flow synthesis of citrate capped gold nanoparticles using UV induced nucleation[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(16): 9632-9638. |
| 7 | 崔永晋, 李严凯, 王凯, 等. 微分散设备数量放大方式研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(10): 4350-4364. |
| Cui Y J, Li Y K, Wang K, et al. Recent advances of numbering-up technology of micro-dispersion devices[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(10): 4350-4364. | |
| 8 | Tetradis-Meris G, Rossetti D, Pulido de Torres C, et al. Novel parallel integration of microfluidic device network for emulsion formation[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(19): 8881-8889. |
| 9 | Link D R, Anna S L, Weitz D A, et al. Geometrically mediated breakup of drops in microfluidic devices[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2004, 92(5): 054503. |
| 10 | Fu T T, Ma Y G, Funfschilling D, et al. Dynamics of bubble breakup in a microfluidic T-junction divergence[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2011, 66(18): 4184-4195. |
| 11 | Wang X D, Zhu C Y, Fu T T, et al. Critical lengths for the transition of bubble breakup in microfluidic T-junctions[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2014, 111: 244-254. |
| 12 | Leshansky A M, Afkhami S, Jullien M C, et al. Obstructed breakup of slender drops in a microfluidic T junction[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2012, 108(26): 264502. |
| 13 | Hoang D A, Portela L M, Kleijn C R, et al. Dynamics of droplet breakup in a T-junction[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2013, 717: R4. |
| 14 | Yamada M, Doi S, Maenaka H, et al. Hydrodynamic control of droplet division in bifurcating microchannel and its application to particle synthesis[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2008, 321(2): 401-407. |
| 15 | Liang D, Ma R, Fu T T, et al. Dynamics and formation of alternating droplets under magnetic field at a T-junction[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 200: 248-256. |
| 16 | Dubash N, Mestel A J. Breakup behavior of a conducting drop suspended in a viscous fluid subject to an electric field[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2007, 19(7): 072101. |
| 17 | Lang L Y, Li H B, Wang X, et al. Experimental study and field demonstration of air-foam flooding for heavy oil EOR[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 185: 106659. |
| 18 | Andersons J, Kirpluks M, Cabulis P, et al. Bio-based rigid high-density polyurethane foams as a structural thermal break material[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 260: 120471. |
| 19 | Godefroidt T, Ooms N, Pareyt B, et al. Ingredient functionality during foam-type cake making: a review[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 2019, 18(5): 1550-1562. |
| 20 | Aichele J, Giammarinaro B, Reinwald M, et al. Capturing the shear and secondary compression waves: high-frame-rate ultrasound imaging in saturated foams[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2019, 123(14): 148001. |
| 21 | Zhao Y J, Jones S A, Brown M B. Dynamic foams in topical drug delivery[J]. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 2010, 62(6): 678-684. |
| 22 | Binks B P, Horozov T S. Aqueous foams stabilized solely by silica nanoparticles[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2005, 44(24): 3722-3725. |
| 23 | Ravera F, Santini E, Loglio G, et al. Effect of nanoparticles on the interfacial properties of liquid/liquid and liquid/air surface layers[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 2006, 110(39): 19543-19551. |
| 24 | Binks B P, Kirkland M, Rodrigues J A. Origin of stabilisation of aqueous foams in nanoparticle-surfactant mixtures[J]. Soft Matter, 2008, 4(12): 2373. |
| 25 | van Steijn V, Kleijn C R, Kreutzer M T. Flows around confined bubbles and their importance in triggering pinch-off[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103(21): 214501. |
| 26 | Jullien M C, Tsang Mui Ching M J, Cohen C, et al. Droplet breakup in microfluidic T-junctions at small capillary numbers[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2009, 21(7): 072001. |
| 27 | Garstecki P, Fuerstman M J, Stone H A, et al. Formation of droplets and bubbles in a microfluidic T-junction-scaling and mechanism of break-up[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2006, 6(3): 437-446. |
| 28 | Fei W J, Gu Y, Bishop K J M. Active colloidal particles at fluid-fluid interfaces[J]. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 2017, 32: 57-68. |
| 29 | Fei Y J, Zhu C Y, Fu T T, et al. The breakup dynamics of bubbles stabilized by nanoparticles in a microfluidic Y-junction[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 245: 116867. |
| 30 | Wu Y N, Wang R Y, Dai C L, et al. Precisely tailoring bubble morphology in microchannel by nanoparticles self-assembly[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(9): 3707-3713. |
| 31 | Burton J C, Waldrep R, Taborek P. Scaling and instabilities in bubble pinch-off[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2005, 94(18): 184502. |
| 32 | Eggers J, Fontelos M A, Leppinen D, et al. Theory of the collapsing axisymmetric cavity[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 98(9): 094502. |
| 33 | Du W, Fu T T, Zhang Q D, et al. Self-similar breakup of viscoelastic thread for droplet formation in flow-focusing devices[J]. AIChE Journal, 2017, 63(11): 5196-5206. |
| [1] | Rubin ZENG, Zhongjie SHEN, Qinfeng LIANG, Jianliang XU, Zhenghua DAI, Haifeng LIU. Study of the sintering mechanism of Fe2O3 nanoparticles based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365. |
| [2] | Xuanzhi HE, Yongqing HE, Guiye WEN, Feng JIAO. Ferrofluid droplet neck self-similar breakup behavior [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2889-2897. |
| [3] | Yong LI, Jiaqi GAO, Chao DU, Yali ZHAO, Boqiong LI, Qianqian SHEN, Husheng JIA, Jinbo XUE. Construction of Ni@C@TiO2 core-shell dual-heterojunctions for advanced photo-thermal catalytic hydrogen generation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2458-2467. |
| [4] | Juhui CHEN, Qian ZHANG, Lingfeng SHU, Dan LI, Xin XU, Xiaogang LIU, Chenxi ZHAO, Xifeng CAO. Study on flow characteristics of nanoparticles in a rotating fluidized bed based on DEM method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2374-2381. |
| [5] | Lu DENG, Xiaojie JU, Wenjie ZHANG, Rui XIE, Wei WANG, Zhuang LIU, Dawei PAN, Liangyin CHU. Controllable preparation of radioactive chitosan embolic microspheres by microfluidic method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1781-1794. |
| [6] | Xintong HUANG, Yuhao GENG, Hengyuan LIU, Zhuo CHEN, Jianhong XU. Research progress on new functional nanoparticles prepared by microfluidic technology [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 355-364. |
| [7] | Guojuan QU, Tao JIANG, Tao LIU, Xiang MA. Modulating luminescent behaviors of Au nanoclusters via supramolecular strategies [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 397-407. |
| [8] | Wei ZHANG, Haoyang LI, Chungang XU, Xiaosen LI. Research progress on the microscopic mechanism and analytical methods of gas hydrate formation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 3815-3827. |
| [9] | Xin ZHANG, Rui XU, Xinyu LU, Yong'an NIU. Synthesis and photocatalysis of SiO2@BiOCl-Bi24O31Cl10 core-shell microspheres [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3636-3646. |
| [10] | Chengyi AI, Jinshuo QIAO, Zhenhuan WANG, Wang SUN, Kening SUN. Investigation on PrBaFe2O6-δ anode material with in-situ FeNi nanoparticle in direct carbon solid oxide fuel cell [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3708-3719. |
| [11] | Jing WAN, Lin ZHANG, Yachao FAN, Xiemin LIU, Peicheng LUO, Feng ZHANG, Zhibing ZHANG. Bioreactor scale-up simulation and experimental study based on mesoscale PBM model [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2698-2707. |
| [12] | Dawei PAN, Wei WANG, Rui XIE, Xiaojie JU, Zhuang LIU, Liangyin CHU. Progress on regulation of meso-scale structures for microfluidic emulsion-template synthesis of functional microparticles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2306-2317. |
| [13] | Haihang TONG, Dezhi SHI, Jiayu LIU, Huayi CAI, Dan LUO, Fei CHEN. Research progress on dark fermentative bio-hydrogen production from lignocellulose assisted by metal nanoparticles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(4): 1417-1435. |
| [14] | Miao ZHANG, Honghai YANG, Yong YIN, Yue XU, Junjie SHEN, Xincheng LU, Weigang SHI, Jun WANG. Start-up and heat transfer characteristics of a pulsating heat pipe with graphene oxide nanofluids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(3): 1136-1146. |
| [15] | Zhihao WANG, Xin SONG, Yaran YIN, Xianming ZHANG. Regulation of gelation rate on the morphology of helical fibers during microfluidic spinning [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(11): 5158-5166. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||