CIESC Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (3): 1194-1206.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20211439
• Separation engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xu WANG( ),Leyao ZHANG,Haoxuan ZHANG,Jiahui YAN,Yushuai WU,Dong WU,Huiyong CHEN(
),Leyao ZHANG,Haoxuan ZHANG,Jiahui YAN,Yushuai WU,Dong WU,Huiyong CHEN( ),Xiaoxun MA
),Xiaoxun MA
Received:2021-10-21
Revised:2021-12-03
Online:2022-03-14
Published:2022-03-15
Contact:
Huiyong CHEN
王旭( ),张乐瑶,张昊轩,演嘉辉,吴玉帅,吴冬,陈汇勇(
),张乐瑶,张昊轩,演嘉辉,吴玉帅,吴冬,陈汇勇( ),马晓迅
),马晓迅
通讯作者:
陈汇勇
作者简介:王旭(1995—),男,博士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Xu WANG, Leyao ZHANG, Haoxuan ZHANG, Jiahui YAN, Yushuai WU, Dong WU, Huiyong CHEN, Xiaoxun MA. Effect of hollow structure on the acetone adsorption property of tungsten-substituted MFI zeolite[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(3): 1194-1206.
王旭, 张乐瑶, 张昊轩, 演嘉辉, 吴玉帅, 吴冬, 陈汇勇, 马晓迅. 中空孔结构对W掺杂MFI分子筛丙酮吸附行为的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(3): 1194-1206.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 样品 | 金属含量/ %(质量) | 产率/% | 相对结晶度/% | 比表面积/(m2·g-1) | 外表面积/(m2·g-1) | S外表面积/S比表面积 | 微孔孔容/(cm3·g-1) | 总孔容/(cm3·g-1) | V微孔孔容/V总孔容 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-1 | — | 100 | 100 | 427 | 63 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.24 | 0.71 |
| WS-1 | 0.01 | 100 | 100 | 352 | 68 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.43 |
| HWS-1_S | 0.09 | 70 | 78 | 253 | 51 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.28 |
| HWS-1_W | 0.13 | 75 | 106 | 385 | 91 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 0.34 | 0.35 |
Table 1 Metal (W) contents, synthesis yields, crystallinities and textual properties of various zeolite samples
| 样品 | 金属含量/ %(质量) | 产率/% | 相对结晶度/% | 比表面积/(m2·g-1) | 外表面积/(m2·g-1) | S外表面积/S比表面积 | 微孔孔容/(cm3·g-1) | 总孔容/(cm3·g-1) | V微孔孔容/V总孔容 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-1 | — | 100 | 100 | 427 | 63 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.24 | 0.71 |
| WS-1 | 0.01 | 100 | 100 | 352 | 68 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.43 |
| HWS-1_S | 0.09 | 70 | 78 | 253 | 51 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.28 |
| HWS-1_W | 0.13 | 75 | 106 | 385 | 91 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 0.34 | 0.35 |
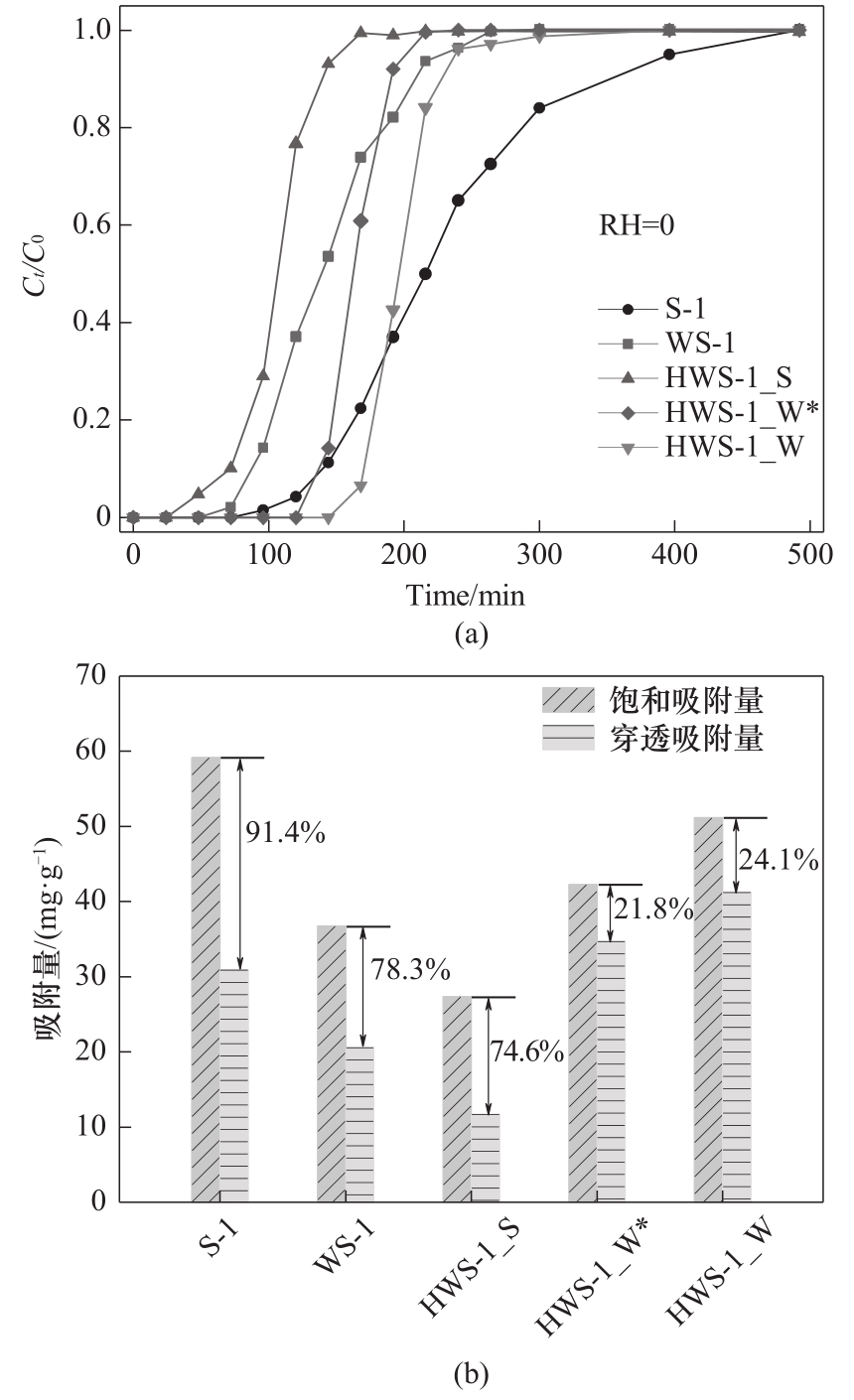
Fig.6 Breakthrough curves of acetone adsorption on parent and corresponding hollow zeolites (a), and differences between saturation capacities and breakthrough capacities on parent and corresponding hollow zeolite adsorbents (b)
| 样品 | Yoon-Nelson模型拟合值 | 实验值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | ||||
| S-1 | 218 | 0.024 | 0.995 | 216 |
| HWS-1_S | 106 | 0.076 | 0.996 | 102 |
| WS-1 | 140 | 0.036 | 0.998 | 141 |
| HWS-1_W*③ | 163 | 0.092 | 0.999 | 162 |
| HWS-1_W | 196 | 0.085 | 0.998 | 197 |
Table 2 Fitting of breakthrough curves by using Yoon-Nelson model
| 样品 | Yoon-Nelson模型拟合值 | 实验值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | ||||
| S-1 | 218 | 0.024 | 0.995 | 216 |
| HWS-1_S | 106 | 0.076 | 0.996 | 102 |
| WS-1 | 140 | 0.036 | 0.998 | 141 |
| HWS-1_W*③ | 163 | 0.092 | 0.999 | 162 |
| HWS-1_W | 196 | 0.085 | 0.998 | 197 |
| 理论模型 | 参数 | S-1 | WS-1 | HWS-1_S | HWS-1_W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 准一级模型 | k1/min-1 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.01 | 0.003 |
| qe/(mg·g-1) | 64.73 | 45.64 | 34.91 | 110.99 | |
| R2 | 0.983 | 0.991 | 0.988 | 0.992 | |
| 准二级模型 | k2/min-1 | 5.79×10-5 | 7.91×10-5 | 1.28×10-4 | 7.75×10-6 |
| qe/(mg·g-1) | 87.22 | 68.93 | 53.63 | 198.83 | |
| R2 | 0.968 | 0.987 | 0.985 | 0.992 | |
| 班厄姆模型 | k3/min-z | 9.80×10-4 | 1.95×10-3 | 2.20×10-3 | 1.14×10-3 |
| qe/(mg·g-1) | 59.77 | 38.33 | 28.26 | 62.25 | |
| z | 1.388 | 1.371 | 1.445 | 1.346 | |
| R2 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.997 | |
| 表观扩散系数 | (D/r02) | 5.10 | 8.63 | 12.9 | 7.56 |
| R2 | 0.993 | 0.995 | 0.996 | 0.988 |
Table 3 Fitting parameters of acetone adsorption kinetics of parent and corresponding hollow zeolite adsorbents
| 理论模型 | 参数 | S-1 | WS-1 | HWS-1_S | HWS-1_W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 准一级模型 | k1/min-1 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.01 | 0.003 |
| qe/(mg·g-1) | 64.73 | 45.64 | 34.91 | 110.99 | |
| R2 | 0.983 | 0.991 | 0.988 | 0.992 | |
| 准二级模型 | k2/min-1 | 5.79×10-5 | 7.91×10-5 | 1.28×10-4 | 7.75×10-6 |
| qe/(mg·g-1) | 87.22 | 68.93 | 53.63 | 198.83 | |
| R2 | 0.968 | 0.987 | 0.985 | 0.992 | |
| 班厄姆模型 | k3/min-z | 9.80×10-4 | 1.95×10-3 | 2.20×10-3 | 1.14×10-3 |
| qe/(mg·g-1) | 59.77 | 38.33 | 28.26 | 62.25 | |
| z | 1.388 | 1.371 | 1.445 | 1.346 | |
| R2 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 0.997 | |
| 表观扩散系数 | (D/r02) | 5.10 | 8.63 | 12.9 | 7.56 |
| R2 | 0.993 | 0.995 | 0.996 | 0.988 |
| 样品 | 穿透时间 | 饱和吸附量 | (Qwet/Qdry)/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RH=0 | RH=10% | RH=0 | RH=10% | ||
| S-1 | 120 | 96 | 59.2 | 49.7 | 83.9 |
| HWS-1_S | 48 | 36 | 27.4 | 21.5 | 78.5 |
| WS-1 | 80 | 60 | 36.8 | 32.1 | 87.2 |
| HWS-1_W*② | 135 | 100 | 42.3 | 36.4 | 86.0 |
| HWS-1_W | 160 | 120 | 51.2 | 40.4 | 78.9 |
| HWS-1_W_R③ | 156 | 110 | 50.1 | 38.8 | 77.4 |
Table 4 Acetone adsorption breakthrough times and saturation adsorption capacities of parent and corresponding hollow zeolite adsorbents at RH = 0 and RH = 10%
| 样品 | 穿透时间 | 饱和吸附量 | (Qwet/Qdry)/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RH=0 | RH=10% | RH=0 | RH=10% | ||
| S-1 | 120 | 96 | 59.2 | 49.7 | 83.9 |
| HWS-1_S | 48 | 36 | 27.4 | 21.5 | 78.5 |
| WS-1 | 80 | 60 | 36.8 | 32.1 | 87.2 |
| HWS-1_W*② | 135 | 100 | 42.3 | 36.4 | 86.0 |
| HWS-1_W | 160 | 120 | 51.2 | 40.4 | 78.9 |
| HWS-1_W_R③ | 156 | 110 | 50.1 | 38.8 | 77.4 |
| 1 | He C, Cheng J, Zhang X, et al. Recent advances in the catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds: a review based on pollutant sorts and sources[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(7): 4471-4568. |
| 2 | Maudhuit A, Raillard C, Héquet V, et al. Adsorption phenomena in photocatalytic reactions: the case of toluene, acetone and heptane[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 170(2/3): 464-470. |
| 3 | 孙静, 董一霖, 李法齐, 等. Co3O4改性USY分子筛吸附和催化氧化甲苯特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(6): 3306-3315. |
| Sun J, Dong Y L, Li F Q, et al. Study on adsorption and catalytic oxidation characteristics of toluene on Co3O4 modified USY molecular sieve[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(6): 3306-3315. | |
| 4 | 高君安, 王伟, 张傑, 等. 用于高湿度废气中甲苯吸附净化的疏水型ZSM-5分子筛的合成及其吸附性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(1): 337-343. |
| Gao J A, Wang W, Zhang J, et al. Study on synthesis and adsorption performance of hydrophobic ZSM-5 zeolites for removal of toluene in high-humidity exhaust gas[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(1): 337-343. | |
| 5 | Sui H, Liu J J, He L, et al. Adsorption and desorption of binary mixture of acetone and ethyl acetate on silica gel[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 197: 185-194. |
| 6 | Baek S W, Kim J R, Ihm S K. Design of dual functional adsorbent/catalyst system for the control of VOC’s by using metal-loaded hydrophobic Y-zeolites[J]. Catalysis Today, 2004, 93/94/95: 575-581. |
| 7 | Ouzzine M, Romero-Anaya A J, Lillo-Ródenas M A, et al. Spherical activated carbons for the adsorption of a real multicomponent VOC mixture[J]. Carbon, 2019, 148: 214-223. |
| 8 | Yang C T, Miao G, Pi Y H, et al. Abatement of various types of VOCs by adsorption/catalytic oxidation: a review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 370: 1128-1153. |
| 9 | Zhang X Y, Gao B, Creamer A E, et al. Adsorption of VOCs onto engineered carbon materials: a review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 338: 102-123. |
| 10 | Zhang L, Peng Y X, Zhang J, et al. Adsorptive and catalytic properties in the removal of volatile organic compounds over zeolite-based materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2016, 37(6): 800-809. |
| 11 | Shah I K, Pre P, Alappat B J. Effect of thermal regeneration of spent activated carbon on volatile organic compound adsorption performances[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2014, 45(4): 1733-1738. |
| 12 | Veerapandian S K P, de Geyter N, Giraudon J M, et al. The use of zeolites for VOCs abatement by combining non-thermal plasma, adsorption, and/or catalysis: a review[J]. Catalysts, 2019, 9(1): 98. |
| 13 | Song W, Justice R E, Jones C A, et al. Size-dependent properties of nanocrystalline silicalite synthesized with systematically varied crystal sizes[J]. Langmuir, 2004, 20(11): 4696-4702. |
| 14 | Li X Q, Zhang L, Yang Z Q, et al. Adsorption materials for volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and the key factors for VOCs adsorption process: a review[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 235: 116213. |
| 15 | Lou F J, Zhang G H, Ren L M, et al. Impacts of nano-scale pore structure and organic amine assembly in porous silica on the kinetics of CO2 adsorptive separation[J]. Nano Research, 2021, 14(9): 3294-3302. |
| 16 | Chen L H, Sun M H, Wang Z, et al. Hierarchically structured zeolites: from design to application[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(20): 11194-11294. |
| 17 | Li Y, Li L, Yu J H. Applications of zeolites in sustainable chemistry[J]. Chem, 2017, 3(6): 928-949. |
| 18 | Feng A H, Yu Y, Mi L, et al. Structural, textural and toluene adsorption properties of NH4HF2 and alkali modified USY zeolite[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2019, 290: 109646. |
| 19 | Feng A H, Mi L, Yu Y, et al. Development of intracrystalline mesoporosity in NH4HF2-etched NaY zeolites by surfactant-templating and its effect on toluene adsorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 390: 124529. |
| 20 | Cosseron A F, Daou T J, Tzanis L, et al. Adsorption of volatile organic compounds in pure silica CHA, BEA, MFI and STT-type zeolites[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2013, 173: 147-154. |
| 21 | Zhu L L, Shen D K, Luo K H. A critical review on VOCs adsorption by different porous materials: species, mechanisms and modification methods[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 389: 122102. |
| 22 | Dai C Y, Zhang A F, Li L L, et al. Synthesis of hollow nanocubes and macroporous monoliths of silicalite-1 by alkaline treatment[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2013, 25(21): 4197-4205. |
| 23 | Medeiros-Costa I C, Dib E, Nesterenko N, et al. Silanol defect engineering and healing in zeolites: opportunities to fine-tune their properties and performances[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2021, 50(19): 11156-11179. |
| 24 | Grand J, Talapaneni S N, Vicente A, et al. One-pot synthesis of silanol-free nanosized MFI zeolite[J]. Nature Materials, 2017, 16(10): 1010-1015. |
| 25 | Grand J, Talapaneni S N, Aleksandrov H A, et al. Hydrophobic tungsten-containing MFI-type zeolite films for exhaust gas detection[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(13): 12914-12919. |
| 26 | Dubray F, Moldovan S, Kouvatas C, et al. Direct evidence for single molybdenum atoms incorporated in the framework of MFI zeolite nanocrystals[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(22): 8689-8693. |
| 27 | Guo Y, Quan X, Lu N, et al. High photocatalytic capability of self-assembled nanoporous WO3 with preferential orientation of (002) planes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(12): 4422-4427. |
| 28 | Zhang H Y, Yang X T, Song X J, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of tungsten-tin bimetallic MFI type zeolites and their catalytic properties for cyclohexene epoxidation[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020, 303: 110277. |
| 29 | Wang X, You Q, Wu Y S, et al. Tungsten-substituted Silicalite-1 with an interconnected hollow structure for catalytic epoxidation of cyclohexene[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2021, 317: 111028. |
| 30 | Dai C Y, Zhang S H, Zhang A F, et al. Hollow zeolite encapsulated Ni–Pt bimetals for sintering and coking resistant dry reforming of methane[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(32): 16461-16468. |
| 31 | Wang Y S, Jia H, Fang X, et al. CO2 and water vapor adsorption properties of framework hybrid W-ZSM-5/silicalite-1 prepared from RHA[J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(41): 24642-24652. |
| 32 | Wu H Y, Zhang X L, Yang C Y, et al. Alkali-hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of W-MCM-41 mesoporous materials with various Si/W molar ratios[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2013, 270: 590-595. |
| 33 | Watmanee S, Suriye K, Praserthdam P, et al. Formation of isolated tungstate sites on hierarchical structured SiO2- and HY zeolite-supported WO x catalysts for propene metathesis[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2019, 376: 150-160. |
| 34 | Hu Q, Li J J, Hao Z P, et al. Dynamic adsorption of volatile organic compounds on organofunctionalized SBA-15 materials[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2009, 149(1/2/3): 281-288. |
| 35 | Li X F, Wang J, Guo Y Y, et al. Adsorption and desorption characteristics of hydrophobic hierarchical zeolites for the removal of volatile organic compounds[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 411: 128558. |
| 36 | Chandak M V, Lin Y S. Hydrophobic zeolites as adsorbents for removal of volatile organic compounds from air[J]. Environmental Technology, 1998, 19(9): 941-948. |
| 37 | Mi Z R, Li J, Lu T T, et al. Reducing the dosage of the organic structure-directing agent in the crystallization of pure silica zeolite MFI (silicalite-1) for volatile organic compounds (VOCs) adsorption[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2021, 8(13): 3354-3362. |
| 38 | Guo M, Liu Q, Lu S, et al. Synthesis of silanol-rich MCM-48 with mixed surfactants and their application in acetone adsorption: equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies[J]. Langmuir, 2020, 36(39): 11528-11537. |
| 39 | Fang H J, Zheng A M, Chu Y Y, et al. 13C chemical shift of adsorbed acetone for measuring the acid strength of solid acids: a theoretical calculation study[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(29): 12711-12718. |
| 40 | Huang S S, Deng W, Zhang L, et al. Adsorptive properties in toluene removal over hierarchical zeolites[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020, 302: 110204. |
| 41 | Zhou J, Fan W, Wang Y D, et al. The essential mass transfer step in hierarchical/nano zeolite: surface diffusion[J]. National Science Review, 2020, 7(11): 1630-1632. |
| 42 | Zhu Z G, Xu H, Jiang J G, et al. Hydrophobic nanosized all-silica beta zeolite: efficient synthesis and adsorption application[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(32): 27273-27283. |
| 43 | Bal'Zhinimaev B S, Paukshtis E A, Toktarev A V, et al. Effect of water on toluene adsorption over high silica zeolites[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2019, 277: 70-77. |
| 44 | Iyoki K, Kikumasa K, Onishi T, et al. Extremely stable zeolites developed via designed liquid-mediated treatment[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(8): 3931-3938. |
| [1] | Bingchun SHENG, Jianguo YU, Sen LIN. Study on lithium resource separation from underground brine with high concentration of sodium by aluminum-based lithium adsorbent [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3375-3385. |
| [2] | Ruihang ZHANG, Pan CAO, Feng YANG, Kun LI, Peng XIAO, Chun DENG, Bei LIU, Changyu SUN, Guangjin CHEN. Analysis of key parameters affecting product purity of natural gas ethane recovery process via ZIF-8 nanofluid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3386-3393. |
| [3] | Yan GAO, Peng WU, Chao SHANG, Zejun HU, Xiaodong CHEN. Preparation of magnetic agarose microspheres based on a two-fluid nozzle and their protein adsorption properties [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3457-3471. |
| [4] | Ji CHEN, Ze HONG, Zhao LEI, Qiang LING, Zhigang ZHAO, Chenhui PENG, Ping CUI. Study on coke dissolution loss reaction and its mechanism based on molecular dynamics simulations [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2935-2946. |
| [5] | Jie WANG, Xiaolin QIU, Ye ZHAO, Xinyang LIU, Zhongqiang HAN, Yong XU, Wenhan JIANG. Preparation and properties of polyelectrolyte electrostatic deposition modified PHBV antioxidant films [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3068-3078. |
| [6] | Shaoyun CHEN, Dong XU, Long CHEN, Yu ZHANG, Yuanfang ZHANG, Qingliang YOU, Chenglong HU, Jian CHEN. Preparation and adsorption properties of monolayer polyaniline microsphere arrays [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2228-2238. |
| [7] | Caihong LIN, Li WANG, Yu WU, Peng LIU, Jiangfeng YANG, Jinping LI. Effect of alkali cations in zeolites on adsorption and separation of CO2/N2O [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2013-2021. |
| [8] | Chenxin LI, Yanqiu PAN, Liu HE, Yabin NIU, Lu YU. Carbon membrane model based on carbon microcrystal structure and its gas separation simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2057-2066. |
| [9] | Yu PAN, Zihang WANG, Jiayun WANG, Ruzhu WANG, Hua ZHANG. Heat and moisture performance study of Cur-LiCl coated heat exchanger [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1352-1359. |
| [10] | Xuanjun WU, Chao WANG, Zijian CAO, Weiquan CAI. Deep learning model of fixed bed adsorption breakthrough curve hybrid-driven by data and physical information [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1145-1160. |
| [11] | Xiaowan PENG, Xiaonan GUO, Chun DENG, Bei LIU, Changyu SUN, Guangjin CHEN. Modeling and simulation of CH4/N2 separation process with two absorption-adsorption columns using ZIF-8 slurry [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 784-795. |
| [12] | Jinlin MENG, Yu WANG, Qunfeng ZHANG, Guanghua YE, Xinggui ZHOU. Pore network model of low-temperature nitrogen adsorption-desorption in mesoporous materials [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 893-903. |
| [13] |
Wan XU, Zhenbin CHEN, Huijuan ZHANG, Fangfang NIU, Ting HUO, Xingsheng LIU.
Study on synthesis, adsorption and desorption performance of linear temperature-sensitive segment polymer regulated intelligent |
| [14] | Jiahao JIANG, Xiaole HUANG, Jiyun REN, Zhengrong ZHU, Lei DENG, Defu CHE. Qualitative and quantitative study on Pb2+ adsorption by biochar in solution [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 830-842. |
| [15] | Yingxi DANG, Peng TAN, Xiaoqin LIU, Linbing SUN. Temperature swing for CO2 capture driven by radiative cooling and solar heating [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 469-478. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||