CIESC Journal ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (3): 1315-1323.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20211479
• Surface and interface engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Rui WANG1,2( ),Ying REN1,2,Wei CHEN1,2(
),Ying REN1,2,Wei CHEN1,2( ),Yongsheng HAN1,2,3(
),Yongsheng HAN1,2,3( )
)
Received:2021-10-15
Revised:2021-12-27
Online:2022-03-14
Published:2022-03-15
Contact:
Wei CHEN,Yongsheng HAN
王瑞1,2( ),任瑛1,2,陈卫1,2(
),任瑛1,2,陈卫1,2( ),韩永生1,2,3(
),韩永生1,2,3( )
)
通讯作者:
陈卫,韩永生
作者简介:王瑞(1994—),女,硕士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Rui WANG, Ying REN, Wei CHEN, Yongsheng HAN. Molecular dynamics simulation on the dynamic structure of icing interface[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(3): 1315-1323.
王瑞, 任瑛, 陈卫, 韩永生. 冰水界面动态结构的分子动力学模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(3): 1315-1323.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX

Fig.1 The complex dynamic process of the interface microstructure in the process of ice crystal growth in liquid water characterized by order parameters (a); The structure of liquid water, ice-water and ice crystal with probability distribution curve (PDC) of order parameters for water molecules (b)
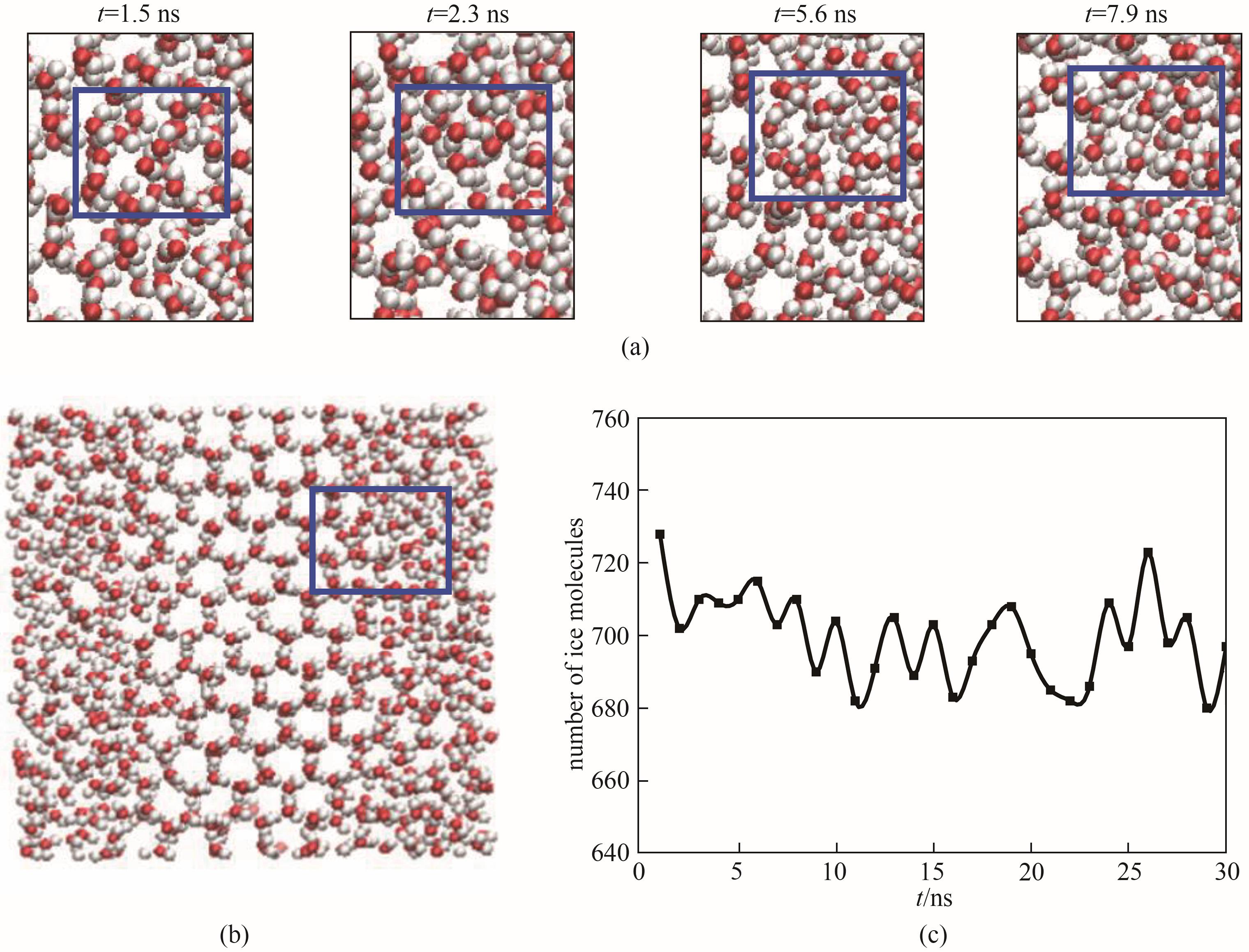
Fig.3 The structures of the ice-water interface at different time (a); Schematic diagram of the ice-water interface (b); The number of ice-like water molecules changes with times at the two-phase equilibrium condition (c)

Fig.6 Probability distribution curve (PDC) of the order parameters in ice-water system formed by three different crystal planes, and the figures in the histogram represent the number of water molecules at liquid (left) and solid phases (right), respectively
| 1 | Mukhopadhyay A, Basu S, Singha S, et al. Inner-view of nanomaterial incited protein conformational changes: insights into designable interaction[J]. Research, 2018, 2018: 1-15. |
| 2 | Libbrecht K G. Physical dynamics of ice crystal growth[J]. Annual Review of Materials Research, 2017, 47(1): 271-295. |
| 3 | Brumberg A, Hammonds K, Baker I, et al. Single-crystal Ih ice surfaces unveil connection between macroscopic and molecular structure[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(21): 5349-5354. |
| 4 | Tsai J W. Studies in molecular dynamics[D]. San Francisco: Stanford University.1997. |
| 5 | Rahman A, Stillinger F H. Molecular dynamics study of liquid water[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1971, 55(7): 3336-3359. |
| 6 | Gao Q W, Zhang Y M, Xu S T, et al. Physicochemical properties and structure of fluid at nano-/micro-interface: progress in simulation and experimental study[J]. Green Energy & Environment, 2020, 5(3): 274-285. |
| 7 | Joselevich E. Self-organized growth of complex nanotube patterns on crystal surfaces[J]. Nano Research, 2009, 2(10): 743-754. |
| 8 | Libbrecht K. Growth rates of the principal facets of ice between -10℃ and -40℃[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2003, 247(3/4): 530-540. |
| 9 | Karim O A, Haymet A D J. The ice/water interface[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 1987, 138(6): 531-534. |
| 10 | Báez L A, Clancy P. Existence of a density maximum in extended simple point charge water[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1994, 101(11): 9837-9840. |
| 11 | Hayward J A, Haymet A D J. The ice/water interface: orientational order parameters for the basal, prism, { 20 2 ¯ 1 } , and { 2 1 ¯ 1 ¯ 0 } interfaces of ice Ih[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2002, 4(15): 3712-3719. |
| 12 | Jorgensen W L, Madura J D. Temperature and size dependence for Monte Carlo simulations of TIP4P water[J]. Molecular Physics, 1985, 56(6): 1381-1392. |
| 13 | Jorgensen W L, Chandrasekhar J, Madura J D, et al. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1983, 79(2): 926-935. |
| 14 | Svishchev I M, Kusalik P G. Crystallization of liquid water in a molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1994, 73(7): 975-978. |
| 15 | Wang J, Tang Y W, Zeng X C. Solid-liquid interfacial free energy of water: a molecular dynamics simulation study[J]. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 2007, 3(4): 1494-1498. |
| 16 | Chung Y J, Rick S W. The effects of charge transfer interactions on the properties of ice I h [J]. Journal of Statistical Physics, 2011, 145(2): 355-364. |
| 17 | Louden P B, Gezelter J D. Friction at ice-I h /water interfaces is governed by solid/liquid hydrogen-bonding[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121(48): 26764-26776. |
| 18 | Ramírez B V, Benito R M, Torres-Arenas J, et al. Water phase transitions from the perspective of hydrogen-bond network analysis[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2018, 20(44): 28308-28318. |
| 19 | Bryk T, Haymet A D J. Ice 1h/water interface of the SPC/E model: molecular dynamics simulations of the equilibrium basal and prism interfaces[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2002, 117(22): 10258-10268. |
| 20 | Tadmor E B, Miller R E. Modeling Materials[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2009. |
| 21 | Xu J, Wang X W, He X F, et al. Application of the Mole-8.5 supercomputer: probing the whole influenza virion at the atomic level[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(20): 2114-2118. |
| 22 | Ayubian S, Alawneh S, Richard M, et al. Implementation and performance of a GPU-based Monte-Carlo framework for determining design ice load[C]//2017 International Conference on High Performance Computing & Simulation (HPCS). Genoa, Italy:IEEE, 2017: 109-116. |
| 23 | Berendsen H J C, Grigera J R, Straatsma T P. The missing term in effective pair potentials[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1987, 91(24): 6269-6271. |
| 24 | Vega C, Sanz E, Abascal J L F. The melting temperature of the most common models of water[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2005, 122(11): 114507. |
| 25 | Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K. VMD: visual molecular dynamics[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics, 1996, 14(1): 33-38. |
| 26 | Steinhardt P J, Nelson D R, Ronchetti M. Bond-orientational order in liquids and glasses[J]. Physical Review B, 1983, 28(2): 784-805. |
| 27 | Arunan E, Desiraju G R, Klein R A, et al. Defining the hydrogen bond: an account (IUPAC Technical Report)[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 2011, 83(8): 1619-1636. |
| 28 | Cuthbertson M J, Poole P H. Mixturelike behavior near a liquid-liquid phase transition in simulations of supercooled water[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2011, 106(11): 115706. |
| 29 | Sanz E, Vega C, Espinosa J R, et al. Homogeneous ice nucleation at moderate supercooling from molecular simulation[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(40): 15008-15017. |
| 30 | Errington J R, Debenedetti P G. Relationship between structural order and the anomalies of liquid water[J]. Nature, 2001, 409(6818): 318-321. |
| 31 | Tang F J, Ohto T, Sun S M, et al. Molecular structure and modeling of water-air and ice-air interfaces monitored by sum-frequency generation[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(8): 3633-3667. |
| 32 | Vega C, McBride C, Sanz E, et al. Radial distribution functions and densities for the SPC/E, TIP4P and TIP5P models for liquid water and ices I h, I c, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX, XI and XII[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2005, 7(7): 1450-1456. |
| 33 | Sánchez M A, Kling T, Ishiyama T, et al. Experimental and theoretical evidence for bilayer-by-bilayer surface melting of crystalline ice[J]. PNAS, 2017, 114(2): 227-232. |
| [1] | Jiajia ZHAO, Shixiang TIAN, Peng LI, Honggao XIE. Microscopic mechanism of SiO2-H2O nanofluids to enhance the wettability of coal dust [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3931-3945. |
| [2] | Jianbo HU, Hongchao LIU, Qi HU, Meiying HUANG, Xianyu SONG, Shuangliang ZHAO. Molecular dynamics simulation insight into translocation behavior of organic cage across the cellular membrane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3756-3765. |
| [3] | Minghao SONG, Fei ZHAO, Shuqing LIU, Guoxuan LI, Sheng YANG, Zhigang LEI. Multi-scale simulation and study of volatile phenols removal from simulated oil by ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3654-3664. |
| [4] | Linzheng WANG, Yubing LU, Ruizhi ZHANG, Yonghao LUO. Analysis on thermal oxidation characteristics of VOCs based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [5] | Ji CHEN, Ze HONG, Zhao LEI, Qiang LING, Zhigang ZHAO, Chenhui PENG, Ping CUI. Study on coke dissolution loss reaction and its mechanism based on molecular dynamics simulations [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2935-2946. |
| [6] | Ming DONG, Jinliang XU, Guanglin LIU. Molecular dynamics study on heterogeneous characteristics of supercritical water [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2836-2847. |
| [7] | Yuanchao LIU, Xuhao JIANG, Ke SHAO, Yifan XU, Jianbin ZHONG, Zhuan LI. Influence of geometrical dimensions and defects on the thermal transport properties of graphyne nanoribbons [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2708-2716. |
| [8] | Hao GU, Fujian ZHANG, Zhen LIU, Wenxuan ZHOU, Peng ZHANG, Zhongqiang ZHANG. Desalination performance and mechanism of porous graphene membrane in temporal dimension under mechanical-electrical coupling [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2067-2074. |
| [9] | Chenxin LI, Yanqiu PAN, Liu HE, Yabin NIU, Lu YU. Carbon membrane model based on carbon microcrystal structure and its gas separation simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2057-2066. |
| [10] | Yi LIAO, Yabin NIU, Yanqiu PAN, Lu YU. Modeling the effects of mixed surfactants on the behaviors and properties of the oil-water interface with molecular dynamics [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 4003-4014. |
| [11] | Songtao YANG, Dongyang LI, Yuqing NIU, Xingang LI, Shaohui KANG, Hong LI, Kaikai YE, Zhiquan ZHOU, Xin GAO. Molecular simulation progress in studying thermodynamic properties and potential functions of fluorides [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 3828-3840. |
| [12] | Mo ZHENG, Xiaoxia LI. Revealing reaction compromise in competition for volatile radicals during coal pryolysis via ReaxFF MD simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2732-2741. |
| [13] | Chunhui LI, Hui HE, Mingjian HE, Meng ZHANG, Yang GAO, Caishan JIAO. Extraction kinetics of Ce(Ⅳ) from nitric acid solutions using ionic liquid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(4): 1606-1614. |
| [14] | Jinyuan ZHANG, Na XU, Wenyun HE, Yaodong LYU, Zilu LIU, Xingfang ZHANG. Analysis on applicability of PEO/OTAC/NaSal mixture as the drag-reduction additives for firefighting system by mesoscopic molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(3): 1157-1165. |
| [15] | Wenhao CAI, Xiongwen XU. Influence of wall charge on ice adhesion on copper surface [J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(12): 5517-5525. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||