化工学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (7): 3768-3779.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20201818
杨瑞雄1( ),郑鑫1,陆涛1,赵誉泽1,杨庆华1,卢英华1,2,3,何宁1,2,凌雪萍1,2,3(
),郑鑫1,陆涛1,赵誉泽1,杨庆华1,卢英华1,2,3,何宁1,2,凌雪萍1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2020-12-15
修回日期:2021-02-27
出版日期:2021-07-05
发布日期:2021-07-05
通讯作者:
凌雪萍
作者简介:杨瑞雄(1996—),女,硕士研究生,基金资助:
YANG Ruixiong1( ),ZHENG Xin1,LU Tao1,ZHAO Yuze1,YANG Qinghua1,LU Yinghua1,2,3,HE Ning1,2,LING Xueping1,2,3(
),ZHENG Xin1,LU Tao1,ZHAO Yuze1,YANG Qinghua1,LU Yinghua1,2,3,HE Ning1,2,LING Xueping1,2,3( )
)
Received:2020-12-15
Revised:2021-02-27
Online:2021-07-05
Published:2021-07-05
Contact:
LING Xueping
摘要:
二十碳五烯酸(eicosapentaenoic acid,EPA)因具有调节血脂、降低纤维蛋白、预防心血管疾病以及抗炎抗过敏的生理功能,被广泛应用于食品、医疗、化妆品以及饲料添加等领域。目前,EPA的需求日益增加,但是富含多不饱和脂肪酸(polyunsaturated fatty acids,PUFAs)的鱼油等自然资源逐渐匮乏,利用改造的微生物菌种发酵生产EPA的方式成为主要趋势。本研究利用同源重组技术将Shewanella sp. SCRC2738的烯酰还原酶基因(enoyl-reductase,sh-ER)分别敲入Schizochytrium limacinum SR21的ORFB-ER和ORFC-ER基因中,调控多不饱和脂肪酸合成的偏好性以提高EPA的产量。研究表明,sh-ER替换ORFB-ER基因的重组菌株(B-sh-ER)中EPA含量提高了85.7%,聚酮合酶(polyketide synthases,PKS)途径相关基因转录水平明显上调。而sh-ER替换ORFC-ER基因的重组菌株(C-sh-ER)
中图分类号:
杨瑞雄, 郑鑫, 陆涛, 赵誉泽, 杨庆华, 卢英华, 何宁, 凌雪萍. 烯酰还原酶基因的替换对裂殖壶菌合成二十碳五烯酸的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(7): 3768-3779.
YANG Ruixiong, ZHENG Xin, LU Tao, ZHAO Yuze, YANG Qinghua, LU Yinghua, HE Ning, LING Xueping. Effects of substitution of ER domains on the synthesis of eicosapentaenoic acid in Schizochytrium limacinum SR21[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(7): 3768-3779.
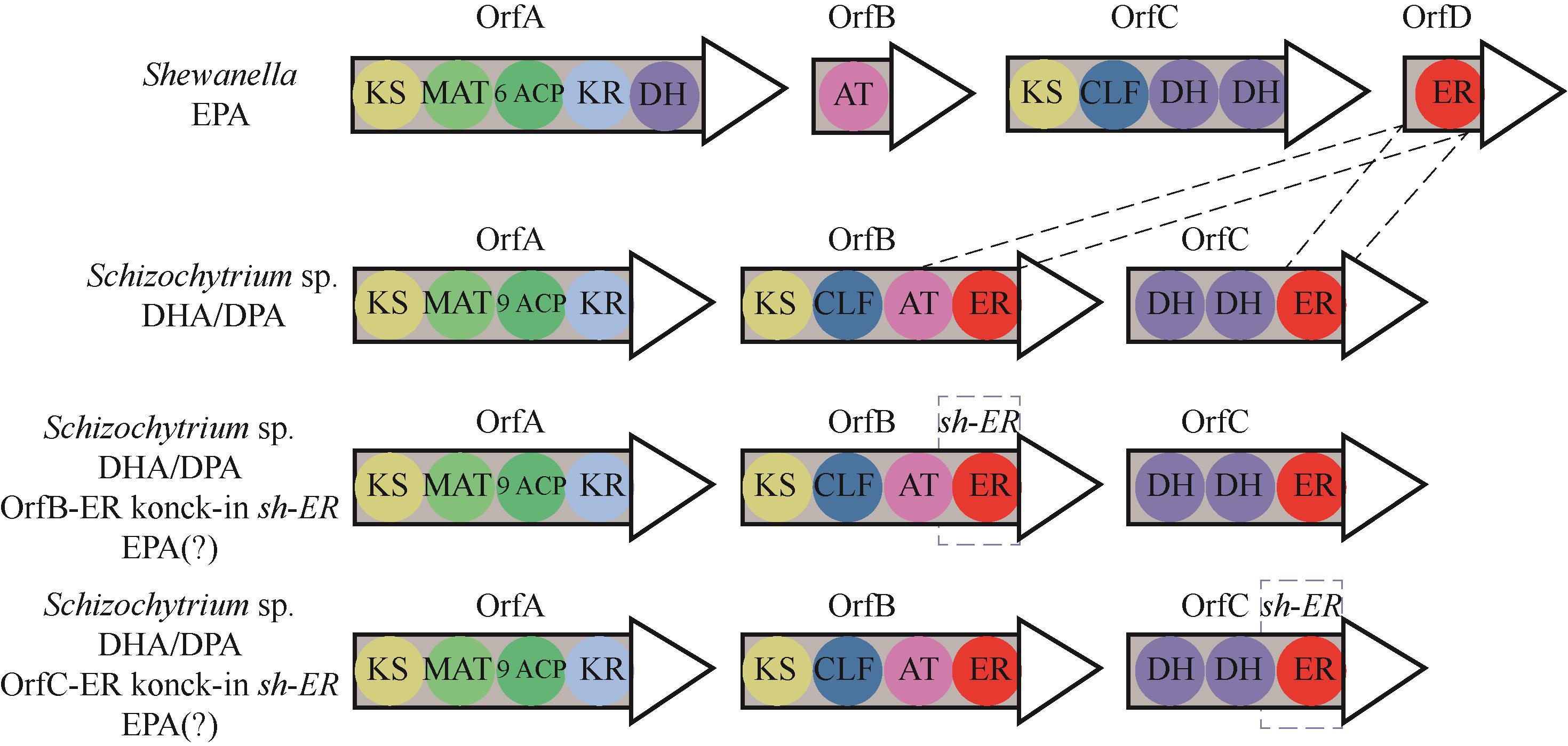
图1 希瓦氏菌、裂殖壶菌SR21、B-sh-ER菌株和C-sh-ER菌株中的PKS基因簇
Fig.1 PKS gene clusters of Shewanella sp. SCRC2738, Schizochytrium limacinum SR21, B-sh-ER strain and C-sh-ER strain

图3 含博来霉素抗性平板上生长的野生型菌株(a),B-sh-ER 菌株(b)和C-sh-ER菌株(c)
Fig.3 Wild strains(a), B-sh-ER strains (b) and C-sh-ER strains (c) grown on media containing zeocin
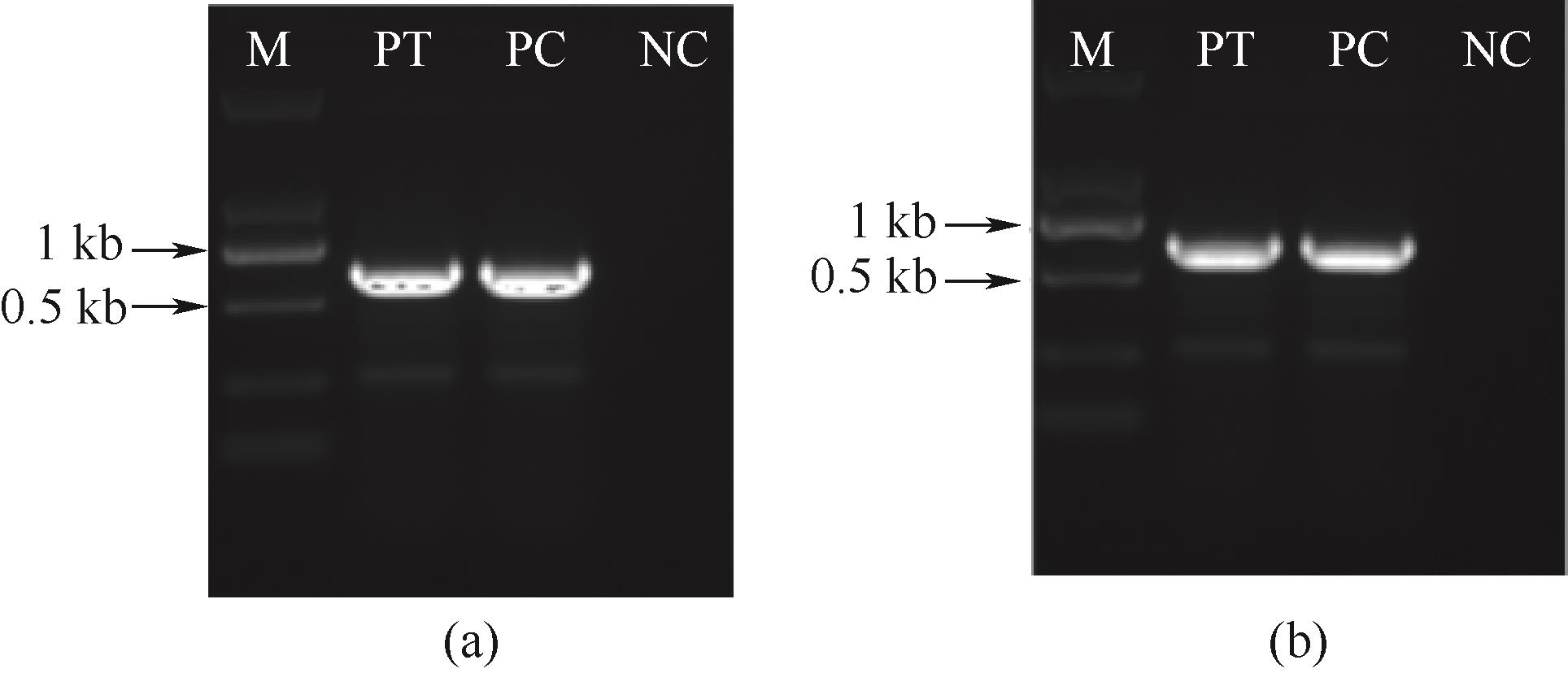
图4 B-sh-ER菌株中博来霉素表达框的基因组PCR (a); C-sh-ER菌株中博来霉素表达框的基因组PCR(b)
Fig.4 Genomic PCR of zeocin expression cassette in the B-sh-ER strains(a); Genomic PCR of zeocin expression cassette in the C-sh-ER strains (b)

图5 野生型菌株和B-sh-ER菌株中生物量(a),总油脂量(b)和油脂含量(c);野生型菌株和C-sh-ER菌株生物量(d)、总油脂量(e)和油脂含量(f)
Fig.5 Biomass (a), total lipids yield (b) and lipids content (c) in the wild strain and B-sh-ER strains; Biomass (d), total lipids yield (e) and lipids content (f) in the wild strain and C-sh-ER strains
| Fatty acid | Composition/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wild strain | B-sh-ER strain | C-sh-ER strain | |
| C14:0 | 3.39 ± 0.05 | 3.59 ± 0.13 | 4.09 ± 0.30 |
| C14:1 | 1.20 ± 0.02 | 1.81 ± 0.11a | 1.69 ± 0.14a |
| C16:0 | 53.02 ± 0.60 | 53.88 ± 0.71 | 55.38 ± 0.10 |
| C18:0 | 1.75 ± 0.01 | 2.61 ± 0.15a | 2.04 ± 0.16 |
| ARA | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 0.37 ± 0.01a | 0.53 ± 0.08a |
| EPA | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 0.78 ± 0.01b | 0.37 ± 0.02 |
| DPA | 6.51 ± 0.03 | 6.08 ± 0.10 | 4.45 ± 0.18a |
| DHA | 29.76 ± 0.25 | 27.63 ± 0.77 | 29.52 ± 0.62 |
| EPA×100/DHA | 1.61 ± 0.03 | 2.82 ± 0.03b | 1.25 ± 0.07a |
| SFAs | 58.15 ± 0.65 | 60.08 ± 0.69 | 61.51 ± 0.57a |
| PUFAs | 37.45 ± 0.27 | 34.71 ± 0.70a | 34.87 ± 0.32a |
表1 野生型菌株、B-sh-ER菌株和C-sh-ER菌株脂肪酸组成
Table 1 Fatty acid composition of wild strains, C-sh-ER strains and B-sh-ER strains
| Fatty acid | Composition/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wild strain | B-sh-ER strain | C-sh-ER strain | |
| C14:0 | 3.39 ± 0.05 | 3.59 ± 0.13 | 4.09 ± 0.30 |
| C14:1 | 1.20 ± 0.02 | 1.81 ± 0.11a | 1.69 ± 0.14a |
| C16:0 | 53.02 ± 0.60 | 53.88 ± 0.71 | 55.38 ± 0.10 |
| C18:0 | 1.75 ± 0.01 | 2.61 ± 0.15a | 2.04 ± 0.16 |
| ARA | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 0.37 ± 0.01a | 0.53 ± 0.08a |
| EPA | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 0.78 ± 0.01b | 0.37 ± 0.02 |
| DPA | 6.51 ± 0.03 | 6.08 ± 0.10 | 4.45 ± 0.18a |
| DHA | 29.76 ± 0.25 | 27.63 ± 0.77 | 29.52 ± 0.62 |
| EPA×100/DHA | 1.61 ± 0.03 | 2.82 ± 0.03b | 1.25 ± 0.07a |
| SFAs | 58.15 ± 0.65 | 60.08 ± 0.69 | 61.51 ± 0.57a |
| PUFAs | 37.45 ± 0.27 | 34.71 ± 0.70a | 34.87 ± 0.32a |
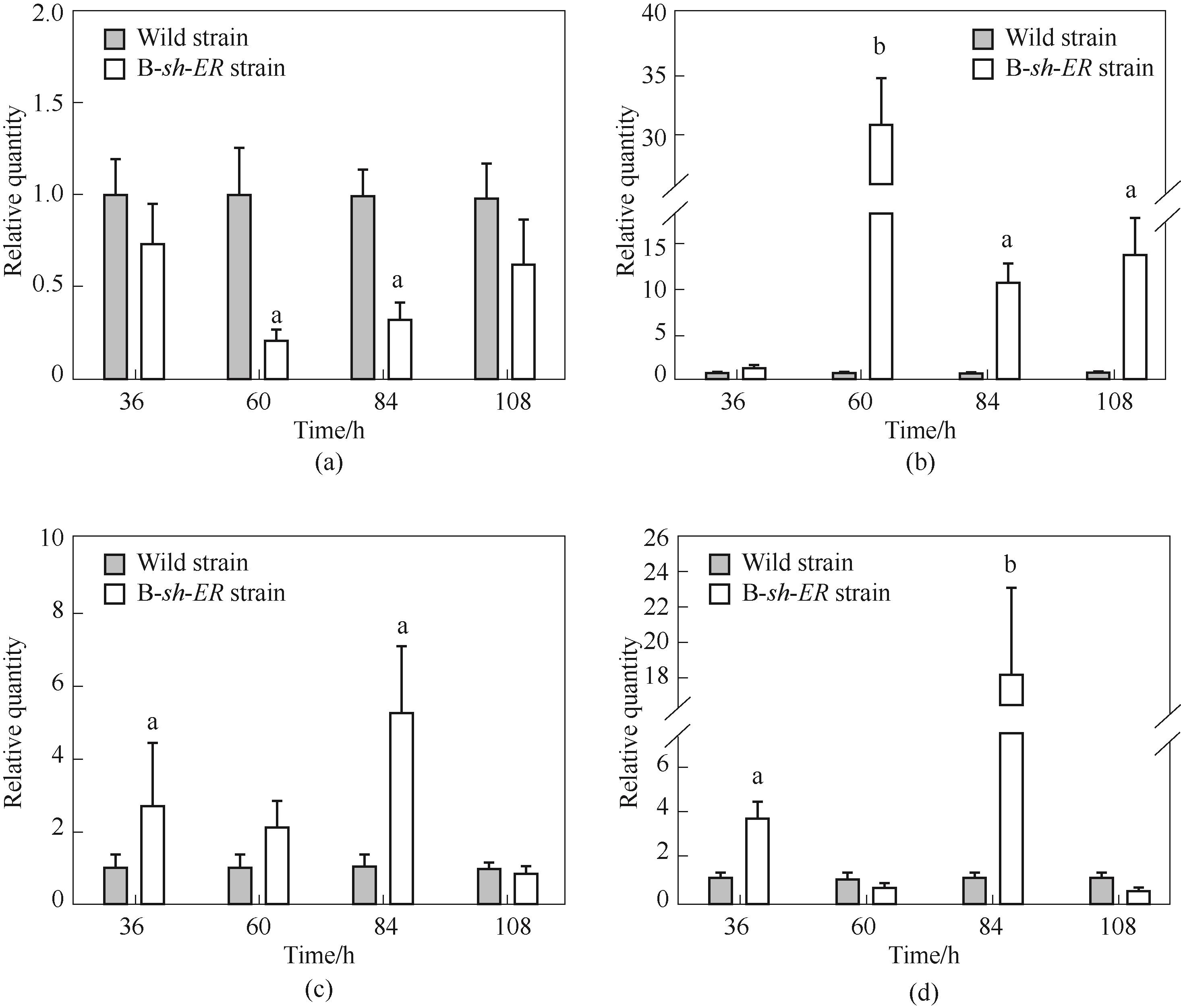
图6 B-sh-ER菌株相关基因转录水平分析(a) 裂殖壶菌烯酰还原酶基因ORFB-ER;(b) 希瓦氏菌烯酰还原酶基因sh-ER;(c) 裂殖壶菌烯酰还原酶基因ORFC-ER;(d)酰基转移酶(AT)基因
Fig.6 The transcription level of related gene in B-sh-ER strain(a) Schizochytrium limacinum SR21 enoyl-reductase gene ORFB-ER; (b) Shewanella sp. SCRC2738 enoyl-reductase gene sh-ER; (c) Schizochytrium limacinum SR21 enoyl-reductase gene ORFC-ER; (d) acyl transferase (AT) gene

图8 野生菌株和B-sh-ER菌株的补料分批发酵参数(a) 生物量;(b) 总油脂量;(c) EPA产量;(d) DHA产量;(e) EPA×100/DHA
Fig.8 Fed-batch fermentation parameters of wild strain and B-sh-ER strain
| Lipid profile | Wild strain | B-sh-ER strain |
|---|---|---|
| total lipid/(g/L) | 56.90 ± 1.36 | 73.24 ± 1.09b |
| PUFAs/% | 42.34 ± 0.76 | 32.02 ± 1.21a |
| DHA/% | 33.22 ± 0.38 | 25.10 ± 0.68a |
| DPA/% | 8.37 ± 0.46 | 5.92 ± 0.49a |
| EPA/% | 0.75 ± 0.02 | 1.00 ± 0.02a |
| C16:0/% | 49.54 ± 0.89 | 57.40 ± 0.72a |
表2 补料分批发酵野生型菌株和B-sh-ER菌株的脂肪酸组成
Table 2 Fatty acid composition of the wild strain and B-sh-ER strain in fed-batch fermentation
| Lipid profile | Wild strain | B-sh-ER strain |
|---|---|---|
| total lipid/(g/L) | 56.90 ± 1.36 | 73.24 ± 1.09b |
| PUFAs/% | 42.34 ± 0.76 | 32.02 ± 1.21a |
| DHA/% | 33.22 ± 0.38 | 25.10 ± 0.68a |
| DPA/% | 8.37 ± 0.46 | 5.92 ± 0.49a |
| EPA/% | 0.75 ± 0.02 | 1.00 ± 0.02a |
| C16:0/% | 49.54 ± 0.89 | 57.40 ± 0.72a |
| Strains | DCW/(g/L) | EPA yield/(mg/L) | EPA proportion/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Schizochytrium limacinum SR21 | 159.7 | 732.4 | 1.0 |
| Thraustochytrid Aurantiochytrium[ | 144.4 | 2700.0 | 3.1 |
| Schizochytrium sp. MYA1381[ | 182 | 1650.0 | 1.45 |
| Nitzschia laevis[ | 22.1 | 695.2 | 3.3 |
| Nitzschia laevis[ | — | 1112.0 | 2.4 |
| Phaeodactylum tricornutum[ | 16.2 | 356.4 | 2.2 |
| Mortierella alpine ATCC 32222[ | 20.1 | 588.5 | — |
| Mortierella alpina ST1358[ | 10 | 1800.0 | 26.4 |
表3 相关菌株EPA产量及占比
Table 3 EPA yield and proportion of related strains
| Strains | DCW/(g/L) | EPA yield/(mg/L) | EPA proportion/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Schizochytrium limacinum SR21 | 159.7 | 732.4 | 1.0 |
| Thraustochytrid Aurantiochytrium[ | 144.4 | 2700.0 | 3.1 |
| Schizochytrium sp. MYA1381[ | 182 | 1650.0 | 1.45 |
| Nitzschia laevis[ | 22.1 | 695.2 | 3.3 |
| Nitzschia laevis[ | — | 1112.0 | 2.4 |
| Phaeodactylum tricornutum[ | 16.2 | 356.4 | 2.2 |
| Mortierella alpine ATCC 32222[ | 20.1 | 588.5 | — |
| Mortierella alpina ST1358[ | 10 | 1800.0 | 26.4 |
| 引物名称 | 引物序列 |
|---|---|
| ORFB-ER-F | GTTGAAGCCTCCGCCTTTATG |
| ORFB-ER-R | CCTGCTCTTGGGTGATCTCGC |
| ORFC-ER-F | CAGCCTGCTCCTTGGTAATCT |
| ORFC-ER-R | CATCAAGAACCGCATCATCG |
| AT-F | TGCTACACGGTGCTGCTCTCTGATG |
| AT-R | ACGTACATTAGCGCTAGGCTGGGC |
| sh-ER-F | TCGCTCAAACCGCTGACATCGTA |
| sh-ER-R | CGGCGTAGTAGGCGTACTTCACG |
表A1
Table A1 Primers for RT-qPCR
| 引物名称 | 引物序列 |
|---|---|
| ORFB-ER-F | GTTGAAGCCTCCGCCTTTATG |
| ORFB-ER-R | CCTGCTCTTGGGTGATCTCGC |
| ORFC-ER-F | CAGCCTGCTCCTTGGTAATCT |
| ORFC-ER-R | CATCAAGAACCGCATCATCG |
| AT-F | TGCTACACGGTGCTGCTCTCTGATG |
| AT-R | ACGTACATTAGCGCTAGGCTGGGC |
| sh-ER-F | TCGCTCAAACCGCTGACATCGTA |
| sh-ER-R | CGGCGTAGTAGGCGTACTTCACG |
| 1 | Gong Y M, Wan X, Jiang M L, et al. Metabolic engineering of microorganisms to produce omega-3 very long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids[J]. Progress in Lipid Research, 2014, 56: 19-35. |
| 2 | Peet M. Nutrition and schizophrenia: beyond omega-3 fatty acids[J]. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids, 2004, 70(4): 417-422. |
| 3 | Oppedisano F, Macrì R, Gliozzi M, et al. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of n-3 PUFAs: their role in cardiovascular protection[J]. Biomedicines, 2020, 8(9): 306. |
| 4 | Amigó N, Akinkuolie A O, Chiuve S E, et al. Habitual fish consumption, n-3 fatty acids, and nuclear magnetic resonance lipoprotein subfractions in women[J]. Journal of the American Heart Association, 2020, 9(5): e014963. |
| 5 | 夏尧干, 王宇, 邹雯燕, 等. 鱼油脂肪酸EPA和DHA的分离影响研究[J]. 淮阴工学院学报, 2020, 29(5): 49-52. |
| Xia Y G, Wang Y, Zou W Y, et al. Study on the separation effect of EPA and DHA from fish oil fatty acids[J]. Journal of Huaiyin Institute of Technology, 2020, 29(5): 49-52. | |
| 6 | Yazawa K. Production of eicosapentaenoic acid from marine bacteria[J]. Lipids, 1996, 31(1): S297-S300. |
| 7 | El Razak A A, Ward A C, Glassey J. Screening of marine bacterial producers of polyunsaturated fatty acids and optimisation of production[J]. Microbial Ecology, 2014, 67(2): 454-464. |
| 8 | Zhang J W, Burgess J G. Enhanced eicosapentaenoic acid production by a new deep-sea marine bacterium Shewanella electrodiphila MAR441T[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(11): e0188081. |
| 9 | Wen Z Y, Chen F. Heterotrophic production of eicosapentaenoic acid by microalgae[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2003, 21(4): 273-294. |
| 10 | Wang S, Lan C Z, Wang Z J, et al. Optimizing eicosapentaenoic acid production by grafting a heterologous polyketide synthase pathway in the Thraustochytrid aurantiochytrium[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2020, 68(40): 11253-11260. |
| 11 | Sayanova O, Napier J A. Metabolic engineering of microalgae for sustainable production of omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2016, 5(3): 198-212. |
| 12 | Hayashi S, Satoh Y, Ogasawara Y, et al. Control mechanism for cis double-bond formation by polyunsaturated fatty-acid synthases[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(8): 2326-2330. |
| 13 | Ren L J, Chen S L, Geng L J, et al. Exploring the function of acyltransferase and domain replacement in order to change the polyunsaturated fatty acid profile of Schizochytrium sp[J]. Algal Research, 2018, 29: 193-201. |
| 14 | Matsuda T, Sakaguchi K, Hamaguchi R, et al. Analysis of Δ12-fatty acid desaturase function revealed that two distinct pathways are active for the synthesis of PUFAs in T. aureum ATCC 34304[J]. Journal of Lipid Research, 2012, 53(6): 1210-1222. |
| 15 | Aasen I M, Ertesvåg H, Heggeset T M B, et al. Thraustochytrids as production organisms for docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), squalene, and carotenoids[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2016, 100(10): 4309-4321. |
| 16 | Yaguchi T, Tanaka S, Yokochi T, et al. Production of high yields of docosahexaenoic acid by Schizochytrium sp. strain SR21[J]. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society, 1997, 74(11): 1431-1434. |
| 17 | Wallis J G, Watts J L, Browse J. Polyunsaturated fatty acid synthesis: what will they think of next?[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2002, 27(9): 467-473. |
| 18 | Marrakchi H, Dewolf W E, Quinn C, et al. Characterization of Streptococcuspneumoniae enoyl-(acyl-carrier protein) reductase (FabK)[J]. The Biochemical Journal, 2003, 370(Pt 3): 1055-1062. |
| 19 | Heath R J, Rock C O. Enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase (fabI) plays a determinant role in completing cycles of fatty acid elongation in Escherichia coli[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1995, 270(44): 26538-26542. |
| 20 | Ling X P, Zhou H, Yang Q H, et al. Functions of enyolreductase (ER) domains of PKS cluster in lipid synthesis and enhancement of PUFAs accumulation in Schizochytrium limacinum SR21 using triclosan as a regulator of ER[J]. Microorganisms, 2020, 8(2): 300. |
| 21 | Lee S J, Seo P S, Kim C H, et al. Isolation and characterization of the eicosapentaenoic acid biosynthesis gene cluster from Shewanella sp. BR-2[J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2009, 19(9): 881-887. |
| 22 | Metz J G, Roessler P, Facciotti D, et al. Production of polyunsaturated fatty acids by polyketide synthases in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes[J]. Science, 2001, 293(5528): 290-293. |
| 23 | Peng Y F, Chen W C, Xiao K, et al. DHA production in Escherichia coli by expressing reconstituted key genes of polyketide synthase pathway from marine bacteria[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(9): e0162861. |
| 24 | Lee S J, Kim C H, Seo P S, et al. Enhancement of heterologous production of eicosapentaenoic acid in Escherichia coli by substitution of promoter sequences within the biosynthesis gene cluster[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2008, 30(12): 2139-2142. |
| 25 | Gemperlein K, Dietrich D, Kohlstedt M, et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acid production by Yarrowia lipolytica employing designed myxobacterial PUFA synthases[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 4055. |
| 26 | Xue Z X, Sharpe P L, Hong S P, et al. Production of omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid by metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2013, 31(8): 734-740. |
| 27 | Takeyama H, Takeda D, Yazawa K, et al. Expression of the eicosapentaenoic acid synthesis gene cluster from Shewanella sp. in a transgenic marine cyanobacterium, Synechococcus sp[J]. Microbiology, 1997, 143 ( Pt 8): 2725-2731. |
| 28 | Ling X P, Guo J, Liu X T, et al. Impact of carbon and nitrogen feeding strategy on high production of biomass and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) by Schizochytrium sp. LU310[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2015, 184: 139-147. |
| 29 | Li Z P, Meng T, Ling X P, et al. Overexpression of malonyl-CoA: ACP transacylase in Schizochytrium sp. to improve polyunsaturated fatty acid production[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2018, 66(21): 5382-5391. |
| 30 | Li Z, Ling X, Zhou H, et al. Screening chemical modulators of benzoic acid derivatives to improve lipid accumulation in Schizochytrium limacinum SR21 with metabolomics analysis[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels, 2019, 12: 209. |
| 31 | Pan X S, Wang B B, Duan R, et al. Enhancing astaxanthin accumulation in Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous by a phytohormone: metabolomic and gene expression profiles[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 2020, 13(5): 1446-1460. |
| 32 | Li J P, Wei Y X, Li J C, et al. A novel duplex SYBR Green real-time PCR with melting curve analysis method for beef adulteration detection[J]. Food Chemistry, 2021, 338: 127932. |
| 33 | Ren L J, Zhuang X Y, Chen S L, et al. Introduction of ω-3 desaturase obviously changed the fatty acid profile and sterol content of Schizochytrium sp[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2015, 63(44): 9770-9776. |
| 34 | Ren L J, Huang H, Xiao A H, et al. Enhanced docosahexaenoic acid production by reinforcing acetyl-CoA and NADPH supply in Schizochytrium sp. HX-308[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2009, 32(6): 837-843. |
| 35 | Snoep J L, Yomano L P, Westerhoff H V, et al. Protein burden in Zymomonas mobilis: negative flux and growth control due to overproduction of glycolytic enzymes[J]. Microbiology, 1995, 141(9): 2329-2337. |
| 36 | Nishida I, Murata N. CHILLING SENSITIVITY IN PLANTS AND CYANOBACTERIA: the crucial contribution of membrane lipids[J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 1996, 47: 541-568. |
| 37 | Venkateswaran K, Moser D P, Dollhopf M E, et al. Polyphasic taxonomy of the genus Shewanella and description of Shewanella oneidensis sp. nov[J]. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, 1999, 49Pt 2: 705-724. |
| 38 | Lippmeier J C, Crawford K S, Owen C B, et al. Characterization of both polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthetic pathways in Schizochytrium sp. [J]. Lipids, 2009, 44(7): 621-630. |
| 39 | Hauvermale A, Kuner J, Rosenzweig B, et al. Fatty acid production in Schizochytrium sp.: involvement of a polyunsaturated fatty acid synthase and a type I fatty acid synthase[J]. Lipids, 2006, 41(8): 739-747. |
| 40 | Cerón Garcí M C, Fernández Sevilla J M, Acién Fernández F G, et al. Mixotrophic growth of Phaeodactylum tricornutum on glycerol: growth rate and fatty acid profile[J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2000, 12(3/4/5): 239-248. |
| 41 | Shi H S, Chen H Q, Gu Z N, et al. Application of a delta-6 desaturase with α-linolenic acid preference on eicosapentaenoic acid production in Mortierella alpina[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15(1): 117. |
| 42 | Okuda T, Ando A, Negoro H, et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) production by an oleaginous fungus Mortierella alpina expressing heterologous the Δ17-desaturase gene under ordinary temperature[J]. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, 2015, 117(12): 1919-1927. |
| 43 | Cui G Z, Ma Z X, Liu Y J, et al. Overexpression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enhanced the polyunsaturated fatty acid composition of Aurantiochytrium sp. SD116[J]. Algal Research, 2016, 19: 138-145. |
| 44 | Khozin-Goldberg I, Yu H Z, Adlerstein D, et al. Triacylglycerols of the red microalga Porphyridium cruentum can contribute to the biosynthesis of eukaryotic galactolipids[J]. Lipids, 2000, 35(8): 881-889. |
| 45 | Fernández F G A, Pérez J A S, Sevilla J M F, et al. Modeling of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) production from Phaeodactylum tricornutum cultures in tubular photobioreactors. Effects of dilution rate, tube diameter, and solar irradiance[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2000, 68(2): 173-183. |
| 46 | Huerlimann R, de Nys R, Growth Heimann K., content lipid, productivity, and fatty acid composition of tropical microalgae for scale-up production[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2010, 107(2): 245-257. |
| [1] | 高学金, 姚玉卓, 韩华云, 齐咏生. 基于注意力动态卷积自编码器的发酵过程故障监测[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2503-2521. |
| [2] | 赵春雷, 郭亮, 高聪, 宋伟, 吴静, 刘佳, 刘立明, 陈修来. 代谢工程改造大肠杆菌生产软骨素[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2111-2122. |
| [3] | 毕浩然, 张洋, 王凯, 徐晨晨, 霍奕影, 陈必强, 谭天伟. 微生物制造绿色化学品研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 1-13. |
| [4] | 刘雪, 张莉娟, 赵广荣. 大肠杆菌偏利共培养系统合成大豆苷元[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4015-4024. |
| [5] | 王悦琳, 晁伟, 蓝晓程, 莫志朋, 佟淑环, 王铁峰. 合成气生物发酵法制乙醇的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3448-3460. |
| [6] | 童海航, 石德智, 刘嘉宇, 蔡桦伊, 罗丹, 陈飞. 金属纳米颗粒辅助木质纤维素暗发酵生物制氢的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(4): 1417-1435. |
| [7] | 高学金, 何紫鹤, 高慧慧, 齐咏生. 基于联合典型变量矩阵的多阶段发酵过程质量相关故障监测[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(3): 1300-1314. |
| [8] | 王靖楠, 庞建, 秦磊, 郭超, 吕波, 李春, 王超. 丁烯基多杀菌素高产菌株的选育和改造策略[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 566-576. |
| [9] | 刘海波, 王楠, 刘洪周, 陈铁柱, 李建昌. 电压扰动对EAD代谢通量中微生物与关键酶活性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4603-4612. |
| [10] | 王欣慧, 王颖, 姚明东, 肖文海. 维生素A生物合成的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4311-4323. |
| [11] | 周武林, 高惠芳, 吴玉玲, 张显, 徐美娟, 杨套伟, 邵明龙, 饶志明. 重组酿酒酵母生物合成菜油甾醇[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(8): 4314-4324. |
| [12] | 陈婷婷, 韩恺忻, 陈翠雪, 凌雪萍, 沈亮, 卢英华. 铁还原菌Shewanella xiamenensis BC01的有机溶剂应激研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(7): 3747-3756. |
| [13] | 高子熹, 郭树奇, 费强. 生物转化温室气体生产单细胞蛋白的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(6): 3202-3214. |
| [14] | 刘聪, 谢莉, 杨慧中. 基于改进DPC的青霉素发酵过程多模型软测量建模[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(3): 1606-1615. |
| [15] | 孙晶晶, 贾丽娜, 林波, 王艳, 龚俊波. 药物-药物共晶的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 828-840. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号