化工学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (7): 3747-3756.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20201845
收稿日期:2020-12-16
修回日期:2021-03-16
出版日期:2021-07-05
发布日期:2021-07-05
通讯作者:
卢英华
作者简介:陈婷婷(1990—),女,博士研究生,基金资助:
CHEN Tingting( ),HAN Kaixin,CHEN Cuixue,LING Xueping,SHEN Liang,LU Yinghua(
),HAN Kaixin,CHEN Cuixue,LING Xueping,SHEN Liang,LU Yinghua( )
)
Received:2020-12-16
Revised:2021-03-16
Online:2021-07-05
Published:2021-07-05
Contact:
LU Yinghua
摘要:
以铁还原菌厦门希瓦氏菌Shewanella xiamenensis BC01(SXM)为研究对象,系统探究了SXM在不同有机溶剂胁迫下的行为变化。生长方面,SXM对有机溶剂的耐受性与其亲水性相关,甲醇、乙醇、丙酮及DMSO的耐受浓度可达5%,对异丙醇、丙醇及叔丁醇的耐受浓度为2%,对丁醇的耐受浓度仅为1%。形态方面,丙醇刺激下的SXM菌体被显著拉长为至少5 μm以上,而丁醇刺激下菌体则缩小至平均不足1 μm,且均为可逆变化;蛋白方面,在丙醇与丁醇刺激下,与铁代谢相关的TonB、IucA及含铁脱氢酶等蛋白表达量均下调,铁还原酶活性也被大幅抑制;基因层面,丙醇刺激下与电子传递相关的mtrC基因表达量提高147.6%。
中图分类号:
陈婷婷, 韩恺忻, 陈翠雪, 凌雪萍, 沈亮, 卢英华. 铁还原菌Shewanella xiamenensis BC01的有机溶剂应激研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(7): 3747-3756.
CHEN Tingting, HAN Kaixin, CHEN Cuixue, LING Xueping, SHEN Liang, LU Yinghua. Study of iron-reducing bacteria Shewanellaxiamenensis BC01 under organic solvents stress[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(7): 3747-3756.
| 外加溶剂 | 分子量 | lgP | 密度/(g/ml) | 溶解度/(g/100 H2O) | SGR① for 1%/(g/h) | SGR① for 2%/(g/h) | SGR① for 5%/ (g/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水(对照组) | 18.0 | — | 1.0 | 无穷大 | 0.2992② | ||
| 甲醇 | 32.0 | -0.5 | 0.792 | 无穷大 | 0.2336 | 0.2329 | 0.1836 |
| 乙醇 | 46.1 | -0.08 | 0.790 | 无穷大 | 0.2655 | 0.2328 | 0.0486 |
| 异丙醇 | 60.1 | 0.38 | 0.804 | 无穷大 | 0.3144 | 0.3550 | ND |
| 丙醇 | 60.1 | 0.59 | 0.785 | 无穷大 | 0.3035 | 0.1666 | ND |
| 叔丁醇 | 74.1 | 0.80 | 0.781 | 8.8 | 0.2484 | 0.1425 | ND |
| 丁醇 | 74.1 | 1.16 | 0.809 | 8.0 | 0.0244 | 0.0004 | ND |
| 丙酮 | 78.13 | -2.03 | 1.101 | 易溶 | 0.2432 | 0.2031 | 0.0115 |
| DMSO | 58.08 | -0.24 | 0.788 | 无穷大 | 0.2256 | 0.2047 | 0.1323 |
表1 有机溶剂的性质与SXM在不同溶剂培养下的比生长速率
Table 1 Physical properties of different organic solvents and specific growth rate for SXM cultured in different solvents
| 外加溶剂 | 分子量 | lgP | 密度/(g/ml) | 溶解度/(g/100 H2O) | SGR① for 1%/(g/h) | SGR① for 2%/(g/h) | SGR① for 5%/ (g/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水(对照组) | 18.0 | — | 1.0 | 无穷大 | 0.2992② | ||
| 甲醇 | 32.0 | -0.5 | 0.792 | 无穷大 | 0.2336 | 0.2329 | 0.1836 |
| 乙醇 | 46.1 | -0.08 | 0.790 | 无穷大 | 0.2655 | 0.2328 | 0.0486 |
| 异丙醇 | 60.1 | 0.38 | 0.804 | 无穷大 | 0.3144 | 0.3550 | ND |
| 丙醇 | 60.1 | 0.59 | 0.785 | 无穷大 | 0.3035 | 0.1666 | ND |
| 叔丁醇 | 74.1 | 0.80 | 0.781 | 8.8 | 0.2484 | 0.1425 | ND |
| 丁醇 | 74.1 | 1.16 | 0.809 | 8.0 | 0.0244 | 0.0004 | ND |
| 丙酮 | 78.13 | -2.03 | 1.101 | 易溶 | 0.2432 | 0.2031 | 0.0115 |
| DMSO | 58.08 | -0.24 | 0.788 | 无穷大 | 0.2256 | 0.2047 | 0.1323 |
| 外加溶剂 | 测量粒径与原始粒径比值/% | PDI |
|---|---|---|
| LB (H2O) | 100.0 | 0.078 |
| 2% 甲醇 | 109.9 | 0.025 |
| 2% 乙醇 | 94.3 | 0.040 |
| 2% 丙醇 | 179.6 | 0.469 |
| 1% 丁醇 | 69.3 | 0.159 |
| 2% 叔丁醇 | 129.0 | 0.229 |
| 2% 丙酮 | 105.7 | 0.128 |
| 2% DMSO | 97.5 | 0.084 |
表2 有机溶剂应激下SXM的粒径变化
Table 2 Particle size distribution of SXM under cultured in different organic solvents
| 外加溶剂 | 测量粒径与原始粒径比值/% | PDI |
|---|---|---|
| LB (H2O) | 100.0 | 0.078 |
| 2% 甲醇 | 109.9 | 0.025 |
| 2% 乙醇 | 94.3 | 0.040 |
| 2% 丙醇 | 179.6 | 0.469 |
| 1% 丁醇 | 69.3 | 0.159 |
| 2% 叔丁醇 | 129.0 | 0.229 |
| 2% 丙酮 | 105.7 | 0.128 |
| 2% DMSO | 97.5 | 0.084 |

图3 不同应激条件下SXM的蛋白电泳分析(Ori:原始条件, P1、P2分别表示1%丙醇与2%丙醇, B1表示1%丁醇;箭头所示蛋白均经MALDI-TOF-TOF进行后续分析)
Fig.3 SDS-PAGE profiles of SXM cultured at normal condition (Ori), 1% n-propanol (P1), 2% n-propanol(P2) and 1% n-butanol (B1) for whole cell and periplasm, respectively(The proteins indicated by the arrows were followed by MALDI-TOF-TOF)
| 样品 | 蛋白及对应菌株 | 蛋白分数① | 蛋白编号 | 分子量 | 等电点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TonB | TonB-dependent receptor Shewanella sp. MR-4 | 657 | gi|499941499 | 82239 | 4.92 |
| IucA | IucA/IucC family protein Shewanella xiamenensis | 1079 | gi|659914351 | 72233 | 5.89 |
| P1 | phosphoglucomutase/phosph-omannomutase alpha/beta/subunit Shewanella xiamenensis | 543 | gi|659915240 | 63150 | 5.85 |
| P2 | iron-containing alcohol dehydrogenase Shewanella xiamenensis | 749 | gi|659915731 | 40394 | 5.34 |
| OmpA | OmpA family protein Shewanella xiamenensis | 328 | gi|659913939 | 40372 | 4.72 |
| porin | porin Shewanella xiamenensis | 1177 | gi|659913622 | 39016 | 4.60 |
| Hsp90 | heat shock protein 90 Shewanella oneidensis | 336 | gi|499384609 | 71779 | 5.25 |
| Ahd | aromatic hydrocarbon degradation membrane protein Shewanella xiamenensis | 845 | gi|659914295 | 45906 | 4.43 |
表3 醇类应激下SXM产生的差异蛋白
Table 3 Mascot protein identi?cation of differential proteins produced by SXM under cultured in different alcohols
| 样品 | 蛋白及对应菌株 | 蛋白分数① | 蛋白编号 | 分子量 | 等电点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TonB | TonB-dependent receptor Shewanella sp. MR-4 | 657 | gi|499941499 | 82239 | 4.92 |
| IucA | IucA/IucC family protein Shewanella xiamenensis | 1079 | gi|659914351 | 72233 | 5.89 |
| P1 | phosphoglucomutase/phosph-omannomutase alpha/beta/subunit Shewanella xiamenensis | 543 | gi|659915240 | 63150 | 5.85 |
| P2 | iron-containing alcohol dehydrogenase Shewanella xiamenensis | 749 | gi|659915731 | 40394 | 5.34 |
| OmpA | OmpA family protein Shewanella xiamenensis | 328 | gi|659913939 | 40372 | 4.72 |
| porin | porin Shewanella xiamenensis | 1177 | gi|659913622 | 39016 | 4.60 |
| Hsp90 | heat shock protein 90 Shewanella oneidensis | 336 | gi|499384609 | 71779 | 5.25 |
| Ahd | aromatic hydrocarbon degradation membrane protein Shewanella xiamenensis | 845 | gi|659914295 | 45906 | 4.43 |
| 外加溶剂 | 全细胞酶活/(U/L) | |
|---|---|---|
| 以铁酸盐为底物 | 以FeCl3为底物 | |
| LB (H2O) | 286.1±12.0 | 9.5±0.6 |
| 丙醇 | 74.0±4.1 | 3.3±0.23 |
| 丁醇 | 72.2±3.2 | 3.0±0.05 |
表4 不同溶剂应激时SXM的铁还原酶酶活
Table 4 Fe reductase activities of SXM bearing different solvents
| 外加溶剂 | 全细胞酶活/(U/L) | |
|---|---|---|
| 以铁酸盐为底物 | 以FeCl3为底物 | |
| LB (H2O) | 286.1±12.0 | 9.5±0.6 |
| 丙醇 | 74.0±4.1 | 3.3±0.23 |
| 丁醇 | 72.2±3.2 | 3.0±0.05 |
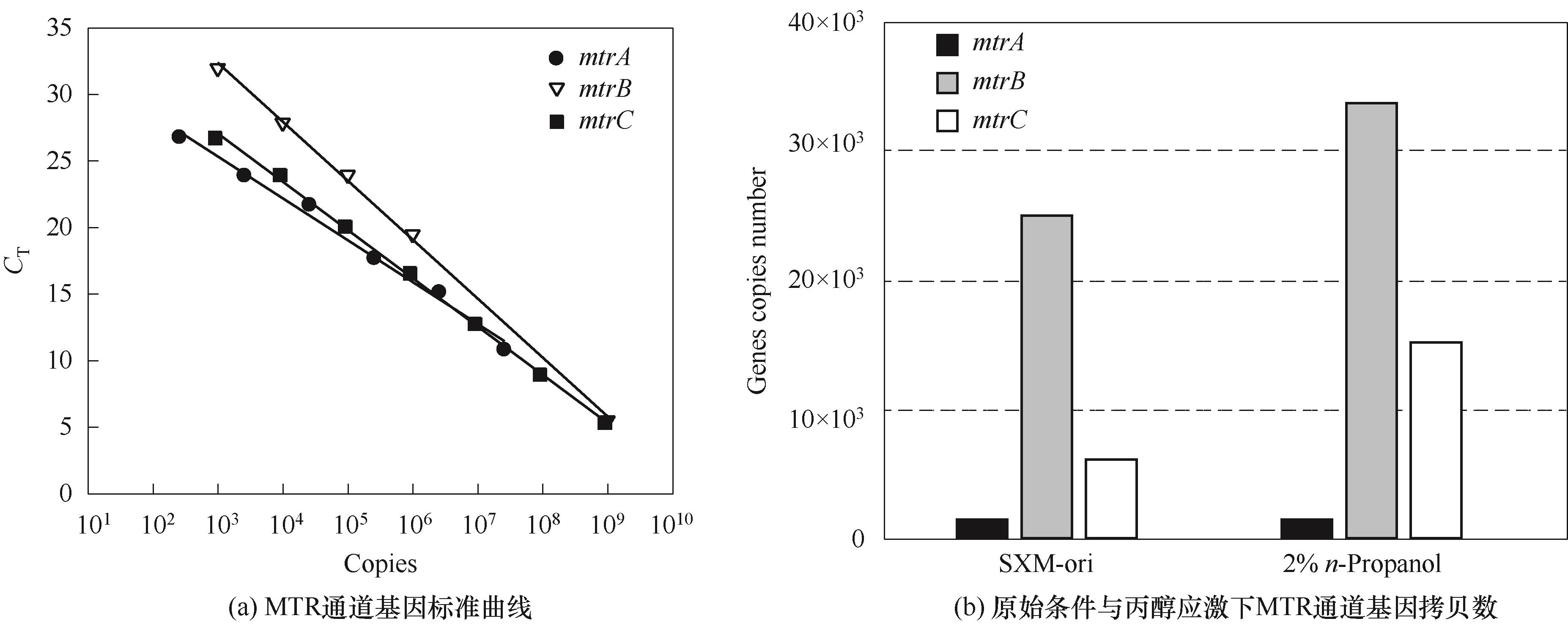
图4 MTR通道基因的标准曲线与不同溶剂应激下基因的表达量
Fig.4 The quantification real time PCR (qRT-PCR) standard curves of genes of MTR pathway (mtrA, mtrB and mrtC) and gene expression level under solvent stress
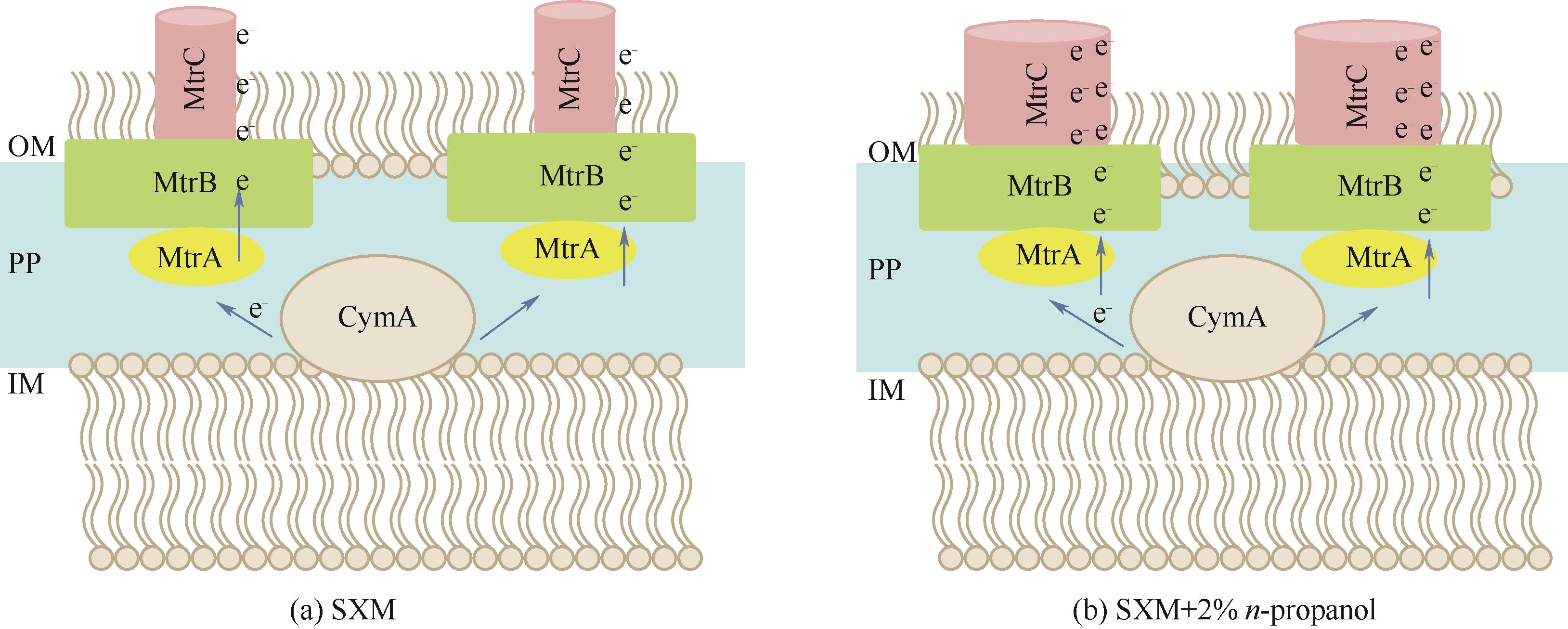
图5 不同培养条件下MTR通道变化的推测示意图
Fig.5 Proposed mechanism of electrons transfer through the outer membrane associated proteins (MtrA, MtrB and MtrC) under LB medium and 2% n-propanol in LB respectively
| 1 | Oram J, Jeuken L J C. Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 electron acceptor taxis and the perception of electrodes poised at oxidative potentials[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2017, 5(1): 99-105. |
| 2 | Hau H H, Gralnick J A. Ecology and biotechnology of the genus Shewanella[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 2007, 61: 237-258. |
| 3 | Hofle M G, Brettar I. Genotyping of heterotrophic bacteria from the central Baltic sea by use of low-molecular-weight RNA profiles[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1996, 62(4): 1383-1390. |
| 4 | Fredrickson J K, Romine M F, Beliaev A S, et al. Towards environmental systems biology of Shewanella[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2008, 6(8): 592-603. |
| 5 | Shi L, Rosso K M, Clarke T A, et al. Molecular underpinnings of Fe(Ⅲ) oxide reduction by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2012, 3: 50. |
| 6 | Xu W H, Jin Z H, Pang X, et al. Interaction between biocompatible graphene oxide and live Shewanella in the self-assembled hydrogel: the role of physicochemical properties[J]. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 2020, 3(7): 4263-4272. |
| 7 | Ng I S, Chen T T, Lin R, et al. Decolorization of textile azo dye and Congo red by an isolated strain of the dissimilatory manganese-reducing bacterium Shewanella xiamenensis BC01[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 98(5): 2297-2308. |
| 8 | Xu F C, Mou Z Y, Geng J Y, et al. Azo dye decolorization by a halotolerant exoelectrogenic decolorizer isolated from marine sediment[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 158: 30-36. |
| 9 | Shen L, Jin Z H, Xu W H, et al. Enhanced treatment of anionic and cationic dyes in wastewater through live bacteria encapsulation using graphene hydrogel[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(19): 7817-7824. |
| 10 | Li Y X, Chen Z, Shi Y Y, et al. Function of c-type cytochromes of Shewanella xiamenensis in enhanced anaerobic bioreduction of Cr(Ⅵ) by graphene oxide and graphene oxide/polyvinyl alcohol films[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 387: 122018. |
| 11 | Shen L, Jin Z H, Wang D, et al. Enhance wastewater biological treatment through the bacteria induced graphene oxide hydrogel[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 190: 201-210. |
| 12 | Wang H F, Zhao H P, Zhu L Z. Structures of nitroaromatic compounds induce Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 to adopt different electron transport pathways to reduce the contaminants[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 384: 121495. |
| 13 | Zou L, Huang Y H, Long Z E, et al. On-going applications of Shewanella species in microbial electrochemical system for bioenergy, bioremediation and biosensing[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 35(1): 1-9. |
| 14 | Watson V J, Logan B E. Power production in MFCs inoculated with Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 or mixed cultures[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2010, 105(3): 489-498. |
| 15 | Wu D, Xing D F, Lu L, et al. Ferric iron enhances electricity generation by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 in MFCs[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 135: 630-634. |
| 16 | Heipieper H J, Neumann G, Cornelissen S, et al. Solvent-tolerant bacteria for biotransformations in two-phase fermentation systems[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2007, 74(5): 961-973. |
| 17 | 王鑫昕, 王少华, 李维,等. 细菌的有机溶剂耐受机制[J]. 生物工程学报, 2009, 25(5): 641-649. |
| Wang X X, Wang S H, Li W, et al. Tolerant mechanisms of bacteria to organic solvents[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2009, 25(5): 641-649. | |
| 18 | Isken S, Derks A, Wolffs P F, et al. Effect of organic solvents on the yield of solvent-tolerant Pseudomonas putida S12[J]. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1999, 65(6): 2631-2635. |
| 19 | Li X Z, Poole K. Organic solvent-tolerant mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa display multiple antibiotic resistance[J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 1999, 45(1): 18-22. |
| 20 | Matsumoto M, de Bont J A M, Isken S. Isolation and characterization of the solvent-tolerant Bacillus cereus strain R1[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2002, 94(1): 45-51. |
| 21 | Zahir Z, Seed K D, Dennis J J. Isolation and characterization of novel organic solvent-tolerant bacteria[J]. Extremophiles, 2006, 10(2): 129-138. |
| 22 | Na K S, Kuroda A, Takiguchi N, et al. Isolation and characterization of benzene-tolerant Rhodococcus opacus strains[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2005, 99(4): 378-382. |
| 23 | Kato C, Inoue A, Horikoshi K. Isolating and characterizing deep-sea marine microorganisms[J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 1996, 14(1): 6-12. |
| 24 | Sardessai Y, Bhosle S. Tolerance of bacteria to organic solvents[J]. Research in Microbiology, 2002, 153(5): 263-268. |
| 25 | Stancu M M. Solvent tolerance mechanisms in Shewanella putrefaciens IBB_Po6[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2015, 226(3): 1-16. |
| 26 | Kieboom J, Dennis J J, Zylstra G J, et al. Active efflux of organic solvents by Pseudomonas putida S12 is induced by solvents[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1998, 180(24): 6769-6772. |
| 27 | Nemecek-Marshall M, Wojciechowski C, Wagner W P, et al. Acetone formation in the Vibrio family: a new pathway for bacterial leucine catabolism[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1999, 181(24): 7493-7499. |
| 28 | Gralnick J A, Vali H, Lies D P, et al. Extracellular respiration of dimethyl sulfoxide by Shewanella oneidensis strain MR-1[J]. PNAS, 2006, 103(12): 4669-4674. |
| 29 | Aono R, Tsukagoshi N, Yamamoto M. Involvement of outer membrane protein TolC, a possible member of the mar-sox regulon, in maintenance and improvement of organic solvent tolerance of Escherichia coli K-12[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1998, 180(4): 938-944. |
| 30 | Salas E C, Sun Z, Lüttge A, et al. Reduction of graphene oxide via bacterial respiration[J]. ACS Nano, 2010, 4(8): 4852-4856. |
| [1] | 陈雅鑫, 袁航, 刘冠章, 毛磊, 杨纯, 张瑞芳, 张光亚. 蛋白质纳米笼介导的酶自固定化研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2773-2782. |
| [2] | 侯文起, 孙彦, 董晓燕. 碱化修饰甲状腺素运载蛋白显著增强对淀粉样β蛋白聚集的抑制作用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2100-2110. |
| [3] | 吕阳光, 左培培, 杨正金, 徐铜文. 三嗪框架聚合物膜用于有机纳滤甲醇/正己烷分离[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1598-1606. |
| [4] | 郑少杰, 王建斌, 胡激江, 李伯耿, 袁文博, 王宗, 姚臻. 单体组成切换法调控聚丙烯/丁烯合金的结构与性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 904-915. |
| [5] | 王靖楠, 庞建, 秦磊, 郭超, 吕波, 李春, 王超. 丁烯基多杀菌素高产菌株的选育和改造策略[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 566-576. |
| [6] | 王之豪, 宋欣, 殷亚然, 张先明. 微流控纺丝中凝胶速率对螺旋纤维形貌的调控机制[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5158-5166. |
| [7] | 成珊, 罗睿, 田红, 王振琦, 黄经春, 乔瑜. 水热碳化温度对污泥有机氮固液相迁移转化路径影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5220-5229. |
| [8] | 李南星, 张麟. 靶向于Galectin-10蛋白的哮喘抑制剂设计[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4847-4853. |
| [9] | 于筱溪, 闫真真, 蒋其辉, 吴霞, 张余晓, 王晓娟, 黄方. 溴化1-辛基-3-甲基咪唑聚集状态对蛋白质结晶的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4854-4860. |
| [10] | 段凌暄, 姚光晓, 江亮, 王世珍. 耐有机溶剂氨基酸脱氢酶基因挖掘与非天然氨基酸的非水相合成[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(7): 3757-3767. |
| [11] | 杨瑞雄, 郑鑫, 陆涛, 赵誉泽, 杨庆华, 卢英华, 何宁, 凌雪萍. 烯酰还原酶基因的替换对裂殖壶菌合成二十碳五烯酸的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(7): 3768-3779. |
| [12] | 苏楠, 吴亦楠, 陈韵亿, 金丽华, 张翀, Aikawa Shimpei, Hasunuma Tomohisa, Kondo Akihiko, 邢新会. ARTP诱变钝顶螺旋藻突变体比较组学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(12): 6298-6310. |
| [13] | 秦磊, 俞杰, 宁小钰, 孙文涛, 李春. 合成生物系统构建与绿色生物“智”造[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(9): 3979-3994. |
| [14] | 宋易航, 王楚浩, 方柏山. 胶原酶研究进展与应用[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(9): 3213-3227. |
| [15] | 徐超, 薛誉, 陈虹月, 胡燚. 手性脯氨酸类离子液体化学修饰猪胰脂肪酶催化性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(6): 2221-2228. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号